Graphene Nanoplatelet-Embedded Urinary Catheters for Enhanced Photothermal Sterilization Against Bacterial Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
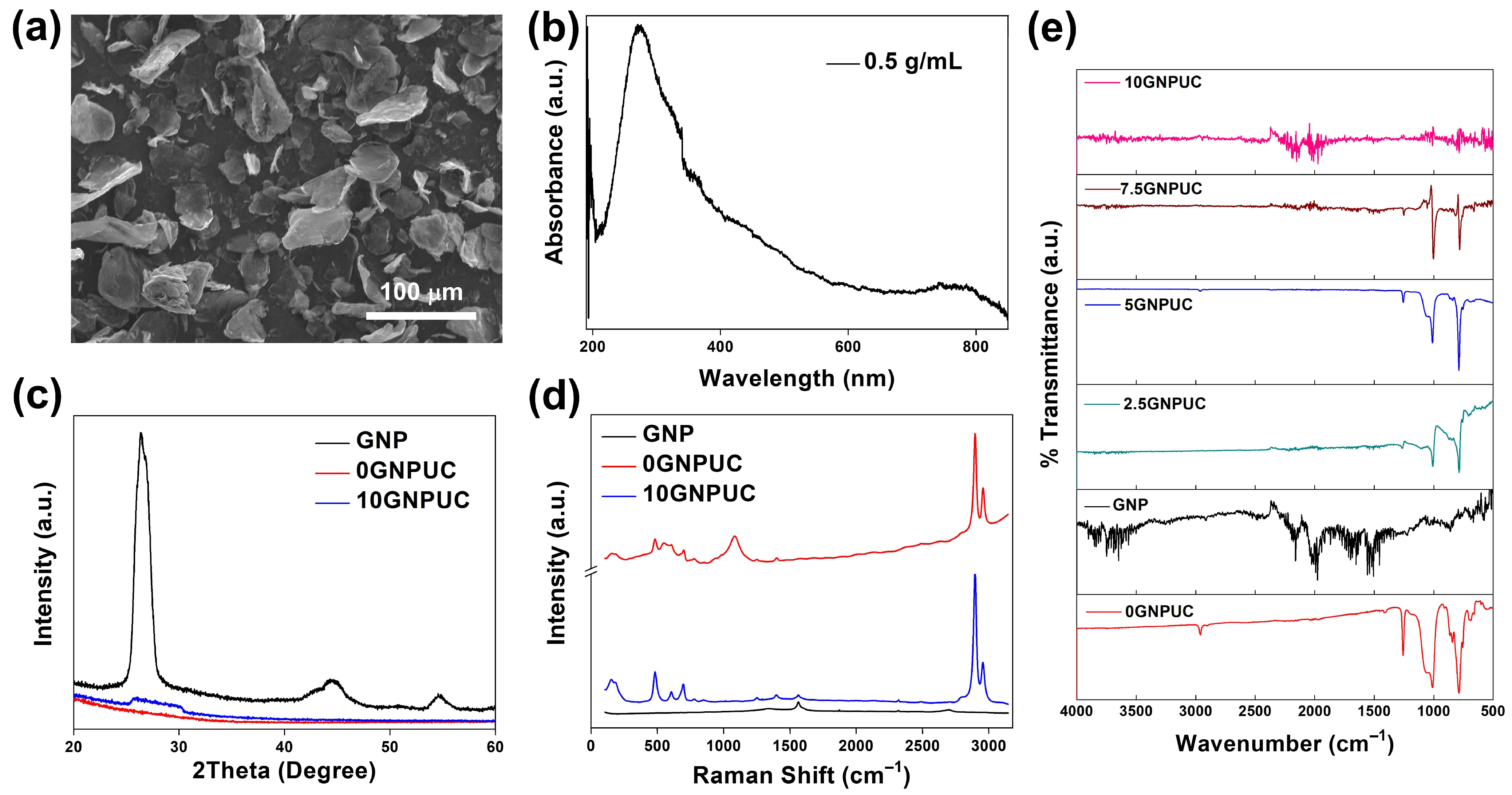
2.1. Optical and Structural Characterization (SEM, UV–Vis–NIR, XRD, Raman, and FTIR)
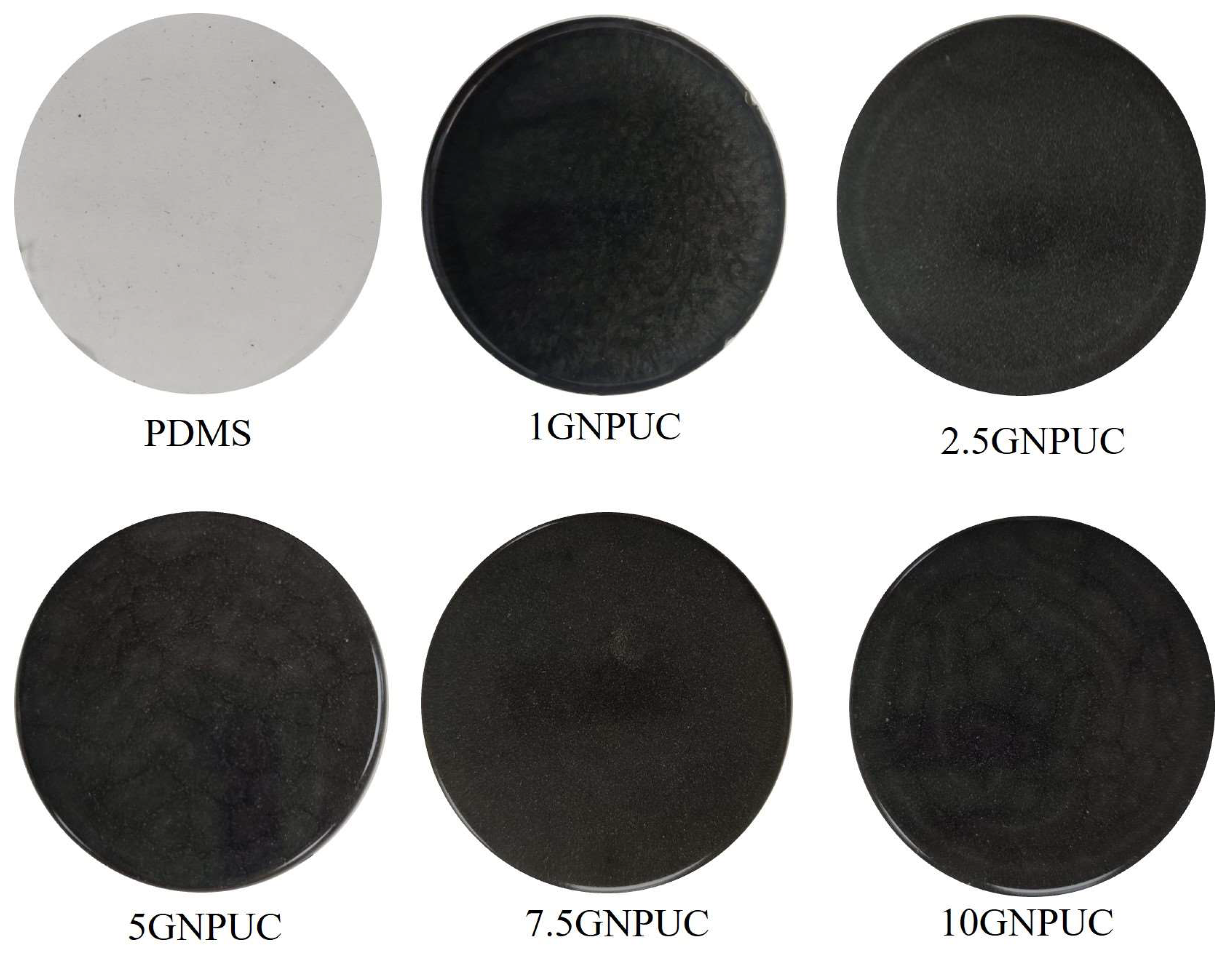
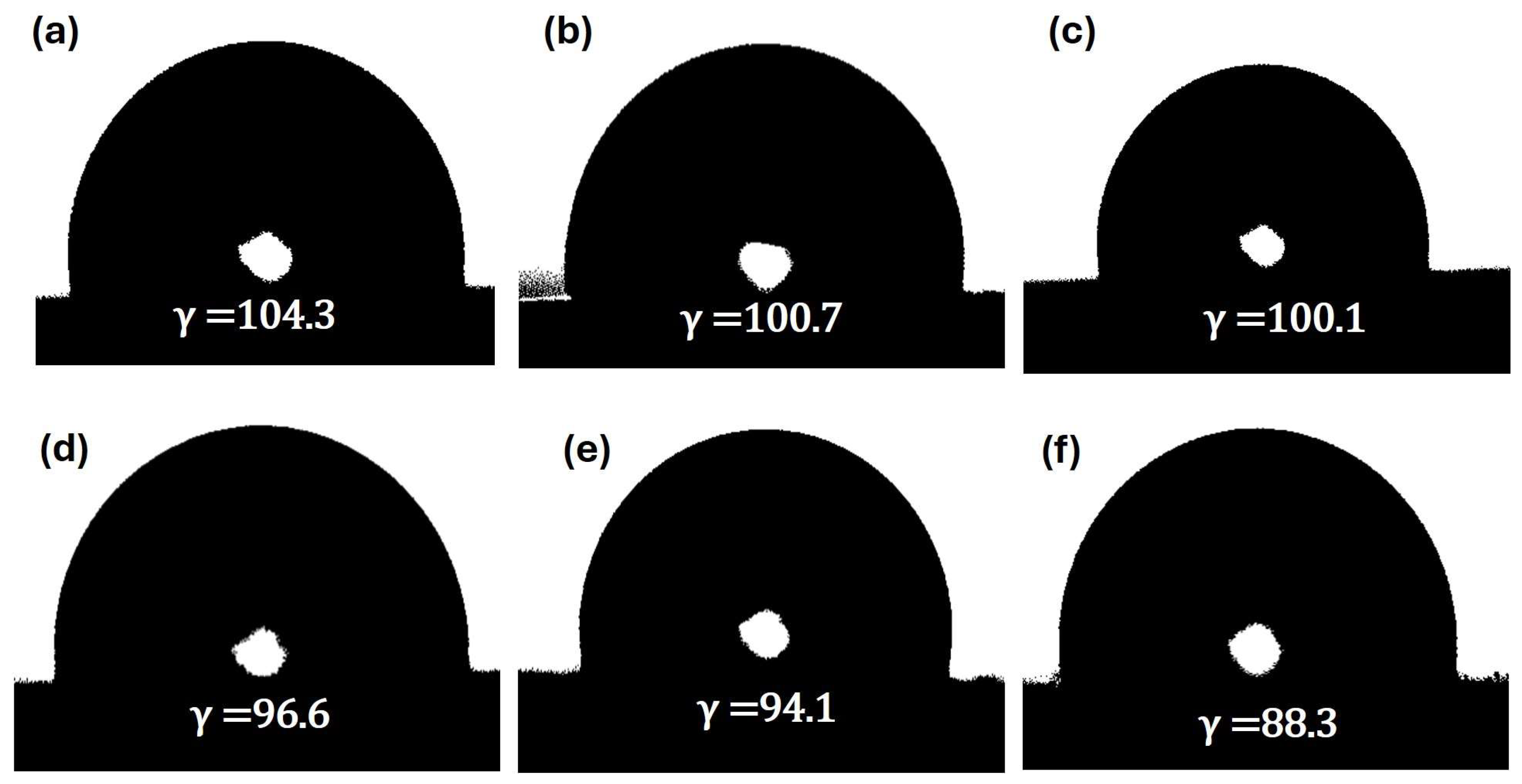
2.2. Morphology and Surface Wettability of GNPUCs
2.3. Photothermal Conversion Performance
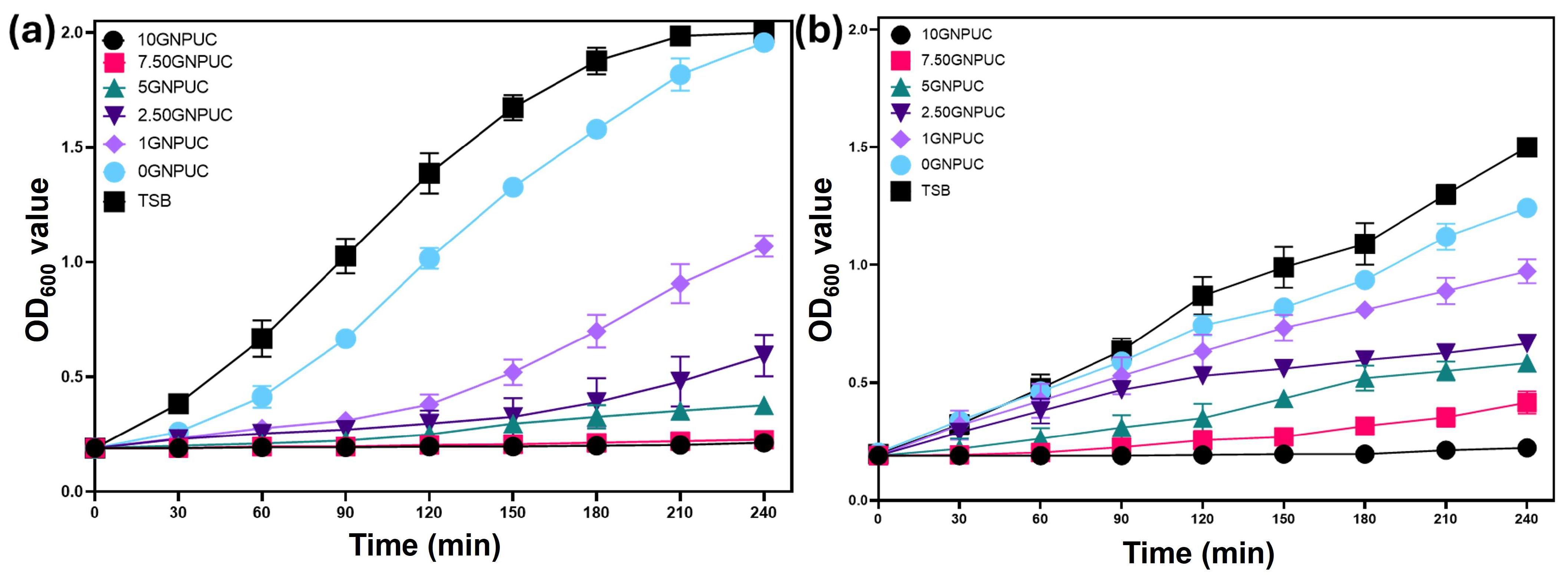
2.4. Bacterial Growth Curve Analysis
2.5. Evaluation of Photothermal Antibacterial Activity by an Agar Plate Test (CFU Counts)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of GNP-Embedded Urinary Catheters (GNPUCs)
4.3. Material Characterization
4.4. Photothermal Properties of GNPUCs
4.5. Photothermal Antibacterial Assay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PPT | Photothermal therapy |
| GNPs | Graphene nanoplatelets |
| UC | Urinary catheter |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| GNPUC | Urinary catheter embedded with graphene nanoplatelets |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| S. aureus | Staphylococcus aureus |
| CAIs | Catheter-associated infections |
| HAIs | Healthcare-associated infections |
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| APTT | Antibacterial photothermal therapy |
References
- Rubi, H.; Mudey, G.; Kunjalwar, R. Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI). Cureus 2022, 14, e30385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werneburg, G.T. Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections: Current Challenges and Future Prospects. Res. Rep. Urol. 2022, 14, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singha, P.; Locklin, J.; Handa, H. A review of the recent advances in antimicrobial coatings for urinary catheters. Acta Biomater. 2017, 50, 20–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Mireles, A.L.; Walker, J.N.; Caparon, M.; Hultgren, S.J. Urinary tract infections: Epidemiology, mechanisms of infection and treatment options. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamm, W.E.; Norrby, S.R. Urinary tract infections: Disease panorama and challenges. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183 (Suppl. S1), S1–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleziak, J.; Błażejewska, M.; Duszyńska, W. Catheter-associated urinary tract infections in the intensive care unit during and after the COVID- 19 pandemic. BMC Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655, Correction in: Lancet 2022, 400, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köves, B.; Magyar, A.; Tenke, P. Spectrum and antibiotic resistance of catheter-associated urinary tract infections. GMS Infect. Dis. 2017, 5, Doc06. [Google Scholar]
- Musco, S.; Giammò, A.; Savoca, F.; Gemma, L.; Geretto, P.; Soligo, M.; Sacco, E.; Del Popolo, G.; Li Marzi, V. How to Prevent Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections: A Reappraisal of Vico’s Theory-Is History Repeating Itself? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.K.; Advani, S.D.; Kofman, A.D.; Lo, E.; Maragakis, L.L.; Pegues, D.A.; Pettis, A.M.; Saint, S.; Trautner, B.; Yokoe, D.S.; et al. Strategies to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infections in acute-care hospitals: 2022 Update. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2023, 44, 1209–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquier, A.; Erkilic, B.; Babinet, M.; Pulcini, C.; Agrinier, N.; on behalf of the ORANEAT Study Group. Resident-, prescriber-, and facility-level factors associated with antibiotic use in long-term care facilities: A systematic review of quantitative studies. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2024, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranjec, C.; Mathew, J.P.; Ovchinnikov, K.; Fadayomi, I.; Yang, Y.; Kjos, M.; Li, W.-W. A bacteriocin-based coating strategy to prevent vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium biofilm formation on materials of interest for indwelling medical devices. Biofilm 2024, 8, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nye, T.M.; Zou, Z.; Obernuefemann, C.L.P.; Pinkner, J.S.; Lowry, E.; Kleinschmidt, K.; Bergeron, K.; Klim, A.; Dodson, K.W.; Flores-Mireles, A.L.; et al. Microbial co-occurrences on catheters from long-term catheterized patients. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trautner, B.W.; Darouiche, R.O. Role of biofilm in catheter-associated urinary tract infection. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2004, 32, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Chen, H. Photothermal bactericidal surfaces: Killing bacteria using light instead of biocides. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, F.; Hou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Luo, X. Injectable self-healing CuS nanoparticle complex hydrogels with antibacterial, anti-cancer, and wound healing properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, P.; Balasubramanian, C.; Hans, S.; Patil, C.; Nema, S. Oxygen Plasma for Prevention of Biofilm Formation on Silicone Catheter Surfaces: Influence of Plasma Exposure Time. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process 2022, 42, 815–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khantamat, O.; Li, C.-H.; Yu, F.; Jamison, A.C.; Shih, W.-C.; Cai, C.; Lee, T.R. Gold nanoshell-decorated silicone surfaces for the near-infrared (NIR) photothermal destruction of the pathogenic bacterium E. faecalis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2015, 7, 3981–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Bharti, A.; Agarwal, V.; Kumar, N.; Saxena, K. ZnO coating on silicon rubber urinary catheter to reduce the biofilm infections. Adv. Mater. Process. 2022, 8, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Gao, X.; Chen, Z.; Feng, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Super-lubricating hybrid elastomer with rapid photothermal sterilization and strong anti-cell adhesion. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 134763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saukani, M.; Lai, C.-H.; Mutalik, C.; Krisnawati, D.I.; Chu, H.-Y.; Kuo, T.-R. Copper Sulfide Nanorod-Embedded Urinary Catheter with Hydrophobicity and Photothermal Sterilization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelshtein, I.; Shoshani, S.; Jacobi, G.; Natan, M.; Dudchenko, N.; Perkas, N.; Tkachev, M.; Bengalli, R.; Fiandra, L.; Mantecca, P.; et al. Protecting the Antibacterial Coating of Urinal Catheters for Improving Safety. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Li, J.; Gu, R.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Qu, D.; Wang, R.; Wang, D. Preparation of Antibacterial and Antiadhesive Urinary Catheters with Robust Double-Network Gelatin-Polyacrylamide-Ag Nanoparticle Hydrogel Coatings. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2025, 7, 1084–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lv, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, C. Platinum Nanoparticles Regulated V2C MXene Nanoplatforms with NIR-II Enhanced Nanozyme Effect for Photothermal and Chemodynamic Anti-Infective Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2400366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Wei, W.; Dai, H. A Multifunctional Hydrogel with Photothermal Antibacterial and AntiOxidant Activity for Smart Monitoring and Promotion of Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2402531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yougbaré, S.; Mutalik, C.; Krisnawati, D.I.; Kristanto, H.; Jazidie, A.; Nuh, M.; Cheng, T.-M.; Kuo, T.-R. Nanomaterials for the Photothermal Killing of Bacteria. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Bharate, P.; Lai, C.H.; Ziem, B.; Böttcher, C.; Schulz, A.; Beckert, F.; Hatting, B.; Mülhaupt, R.; Seeberger, P.H.; et al. Multivalency at Interfaces: Supramolecular Carbohydrate-Functionalized Graphene Derivatives for Bacterial Capture, Release, and Disinfection. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6051–6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Sun, L.; Li, X.; Ji, J.; Yu, Q.; Shen, L.; et al. Construction of nanomaterials with targeting phototherapy properties to inhibit resistant bacteria and biofilm infections. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-W.; Yao, K.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanomaterials with a photothermal effect for antibacterial activities: An overview. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 8680–8691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Ye, Z.; Lei, W.; Jia, F.; Jin, Q.; Ren, K.F.; Ji, J. Surface-Adaptive Gold Nanoparticles with Effective Adherence and Enhanced Photothermal Ablation of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9330–9339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y. A Polydopamine Nanoparticle-Knotted Poly(ethylene glycol) Hydrogel for On-Demand Drug Delivery and Chemo-photothermal Therapy. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Li, J.; Tan, L.; Cui, Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Liu, X. Ag2S decorated nanocubes with enhanced near-infrared photothermal and photodynamic properties for rapid sterilization. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2019, 33, 100201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draviana, H.T.; Fitriannisa, I.; Khafid, M.; Krisnawati, D.I.; Widodo; Lai, C.-H.; Fan, Y.-J.; Kuo, T.-R. Size and charge effects of metal nanoclusters on antibacterial mechanisms. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Yin, Q.; Liu, M. Nanomaterials as carriers to improve the photodynamic antibacterial therapy. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1044627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Liping, L.; Muyue, Z.; Wei, L.; Rongguang, L. Antibacterial functionalized carbon dots and their application in bacterial infections and inflammation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 9386–9403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.; Lahiri, I.; Seelaboyina, R.; Kang, Y.S. Synthesis of graphene and its applications: A review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2010, 35, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, J.R.; Dreyer, D.R.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 2011, 52, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.T. Graphene-based nano composites and their applications. A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navasingh, R.J.H.; Kumar, R.; Marimuthu, K.; Planichamy, S.; Khan, A.; Asiri, A.M.; Asad, M. Graphene-based nano metal matrix composites: A review. Nanocarbon Its Compos. 2019, 153–170. [Google Scholar]
- Parveen, K.; Peipei, H.; Rongzhao, Z.; Bo, L. Antibacterial Properties of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Esfandiar, A. Wrapping Bacteria by Graphene Nanosheets for Isolation from Environment, Reactivation by Sonication, and Inactivation by Near-Infrared Irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 6279–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Kim, J.; Choi, M.; Jeon, S. Advancing solar energy applications with graphene: The potential of minimally oxidized graphene. Nano Converg. 2025, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renteria, J.D.; Nika, D.L.; Balandin, A.A. Graphene Thermal Properties: Applications in Thermal Management and Energy Storage. Appl. Sci. 2014, 4, 525–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanizza, C.; Stefanelli, M.; Risuglia, A.; Bruni, E.; Ietto, F.; Incoronato, F.; Marra, F.; Preziosi, A.; Mancini, P.; Sarto, M.S.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Biocompatibility Studies on Engineered Fabric with Graphene Nanoplatelets. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Sun, H.; Qu, X. Antibacterial applications of graphene-based nanomaterials: Recent achievements and challenges. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2016, 105, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kim, J.H. Synthesis, toxicity, biocompatibility, and biomedical applications of graphene and graphene-related materials. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1927–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQurashi, D.M.; AlQurashi, T.F.; Alam, R.I.; Shaikh, S.; Tarkistani, M.A.M. Advanced Nanoparticles in Combating Antibiotic Resistance: Current Innovations and Future Directions. J. Nanotheranostics 2025, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Kim, J.; Huang, Z.; Lee, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, P.; Sessler, J.L.; Kim, J.S. Dual-laser “808 and 1064 nm” strategy that circumvents the Achilles’ heel of photothermal therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2503574122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; He, Q.; Zhang, H.; Meng, X.; Min, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, P.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, Y. Enhancing near-infrared photothermal activity through precise in-plane interface engineering in CuS–Au and CuS@Au ultrathin nanoplates for combating multidrug-resistant bacteria. J. Mater. Chem. C 2025, 13, 5370–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Su, Y.-L.; Hu, S.-H.; Chen, S.-Y. Functionalized graphene nanocomposites for enhancing photothermal therapy in tumor treatment. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2016, 105, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Piner, R.D.; Kohlhaas, K.A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 2007, 45, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.C. Raman spectroscopy of graphene and graphite: Disorder, electron–phonon coupling, doping and nonadiabatic effects. Solid State Commun. 2007, 143, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malard, L.M.; Pimenta, M.A.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Raman spectroscopy in graphene. Phys. Rep. 2009, 473, 51–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.S.; Tabish, T.A.; Thorat, N.D.; Swati, G.; Sahu, N.K. Photothermal therapy using graphene quantum dots. APL Bioeng. 2023, 7, 031502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, N.K.; Parida, R.; Parida, B.N.; Nayak, N.C. Investigating the structural, thermal, and electrical properties of PVDF/PMMA blends reinforced with GNP, MXene, and GNP-MXene hybrids. Discov. Appl. Sci 2025, 7, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusko, V.; Khannanov, A.; Rakhmatullin, A.; Dimiev, A.M. Unraveling the infrared spectrum of graphene oxide. Carbon 2024, 229, 119507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markad, G.B.; Padma, N.; Chadha, R.; Gupta, K.C.; Rajarajan, A.K.; Deb, P.; Kapoor, S. Mutual influence on aggregation and magnetic properties of graphene oxide and copper phthalocyanine through non-covalent, charge transfer interaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 505, 144624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrousseaux, C.; Sautou, V.; Descamps, S.; Traoré, O. Modification of the surfaces of medical devices to prevent microbial adhesion and biofilm formation. J. Hosp. Infect. 2013, 85, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lei, H.; Kan, A.; Xie, H.; Yu, W. Photothermal applications based on graphene and its derivatives: A state-of-the-art review. Energy 2021, 216, 119262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamie, S.; Shih, P.-J.; Soufi Zomorod, M.; Heravi, P.; Ahadian, M.M.; Hatami, N. Hyperthermia response of PEGylated magnetic graphene nanocomposites for heating applications and accelerate antibacterial activity using magnetic fluid hyperthermia. Appl. Phys. A. 2020, 126, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doveri, L.; Diaz Fernandez, Y.A.; Dacarro, G. Nanomaterials for Photothermal Antimicrobial Surfaces. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 25575–25590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birhanu Hayilesilassie, R.; Gemta, A.B.; Maremi, F.T.; Getahun Kumela, A.; Gudishe, K.; Dana, B.D. Detection and photothermal inactivation of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bloodstream bacteria using photonic crystal biosensor and plasmonic core–shell. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 11594–11603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, J.; Sarkhel, S.; Mukherjee, N.; Jaiswal, A. Nanomaterial-Based Antimicrobial Coating for Biomedical Implants: New Age Solution for Biofilm-Associated Infections. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 45962–45980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhuang, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Yan, W.; Zhang, J. Differences in cellular damage induced by dielectric barrier discharge plasma between Salmonella Typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 132, 107445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, J.; Prakash, H. Photo-disinfection processes for bacterial inactivation and underlying principles for water constituents’ impact: A review. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 14, 100482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Song, Z.; Du, T.; Du, X. Antimicrobial materials based on photothermal action and their application in wound treatment. Burn. Trauma 2024, 12, tkae046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, M.J.; Savard, T.; Brassard, J. Interactions Between Infectious Foodborne Viruses and Bacterial Biofilms Formed on Different Food Contact Surfaces. Food Environ. Virol. 2022, 14, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKintosh, E.E.; Patel, J.D.; Marchant, R.E.; Anderson, J.M. Effects of biomaterial surface chemistry on the adhesion and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis in vitro. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2006, 78, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, M.D.; Bongiovanni Abel, S.; Barbero, C.A.; Paulucci, N.S.; Yslas, E.I. Low-Power NIR-Triggered Photothermal Inactivation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with Polypyrrole Nanoparticles. Polymers 2025, 17, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, S.; Han, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, M.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, G.; Dong, L.; Wen, H.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; et al. Recent Advancements on Photothermal Conversion and Antibacterial Applications over MXenes-Based Materials. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Islam, K.S.; Dip, T.M.; Chowdhury, M.F.M.; Debnath, S.R.; Hasan, S.M.M.; Sakib, M.S.; Saha, T.; Padhye, R.; Houshyar, S. A review on nanomaterial-based additive manufacturing: Dynamics in properties, prospects, and challenges. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 9, 1197–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas-Segura, A.; Ivanova, K.; Ivanova, A.; Ivanov, I.; Todorova, K.; Dimitrov, P.; Ciardelli, G.; Tzanov, T. Mussel-Inspired Sonochemical Nanocomposite Coating on Catheters for Prevention of Urinary Infections. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2024, 16, 34656–34668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

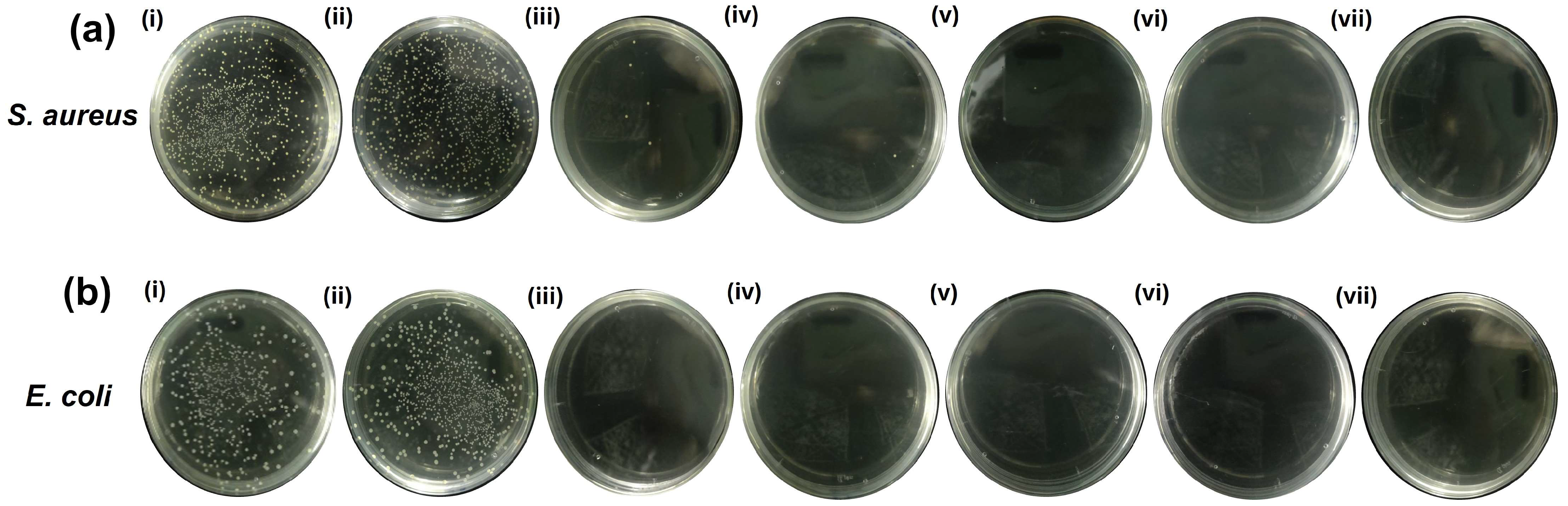
| Bacteria | Control | 0GNPUC | 1GNPUC | 2.5GNPUC | 5GNPUC | 7.5GNPUC | 10GNPUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | 100 | 95 | 0.86 | 0.56 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| E. coli | 100 | 93 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nivedita; Tzou, K.-Y.; Saukani, M.; Kuo, T.-R. Graphene Nanoplatelet-Embedded Urinary Catheters for Enhanced Photothermal Sterilization Against Bacterial Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209922
Nivedita, Tzou K-Y, Saukani M, Kuo T-R. Graphene Nanoplatelet-Embedded Urinary Catheters for Enhanced Photothermal Sterilization Against Bacterial Infections. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209922
Chicago/Turabian StyleNivedita, Kai-Yi Tzou, Muhammad Saukani, and Tsung-Rong Kuo. 2025. "Graphene Nanoplatelet-Embedded Urinary Catheters for Enhanced Photothermal Sterilization Against Bacterial Infections" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209922
APA StyleNivedita, Tzou, K.-Y., Saukani, M., & Kuo, T.-R. (2025). Graphene Nanoplatelet-Embedded Urinary Catheters for Enhanced Photothermal Sterilization Against Bacterial Infections. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209922







