Magnesium Preserves Calcium Homeostasis and Contributes to Protect Myotubes from Inflammation-Induced Damage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
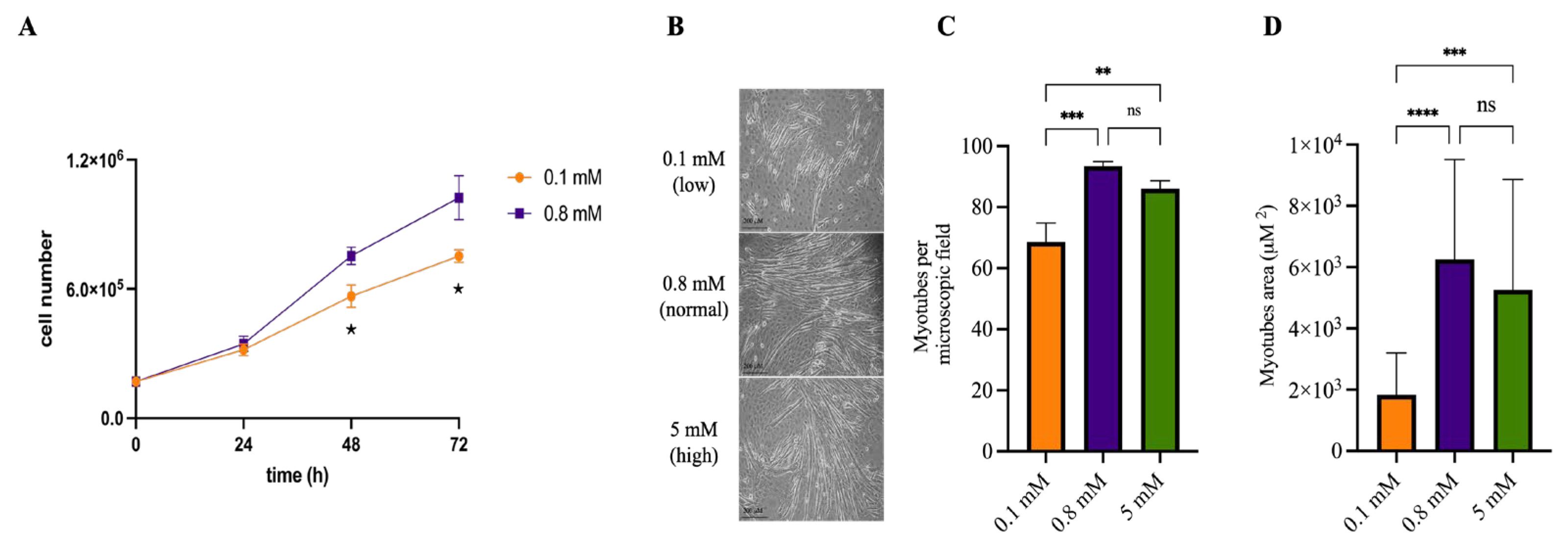
2.1. Mg2+ Availability Affects Myotube Differentiation
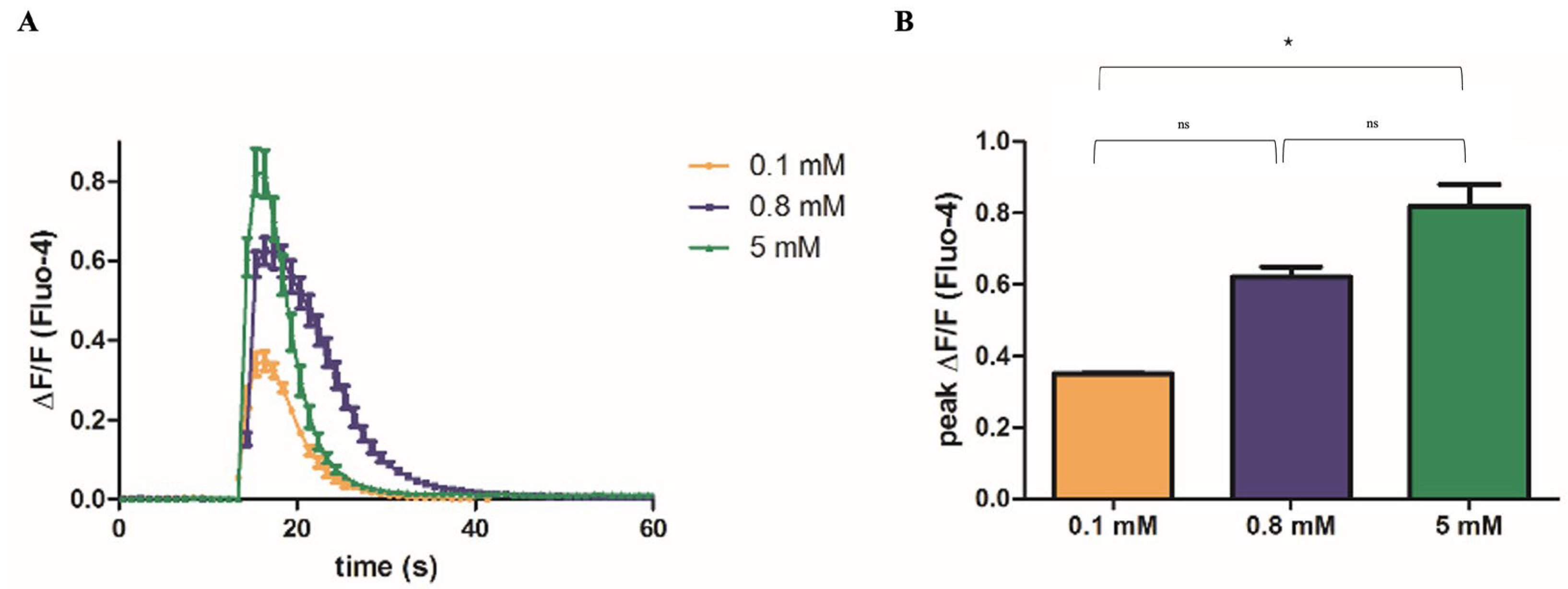
2.2. Mg2+ Availability Affects Ca2+ Release from the SR
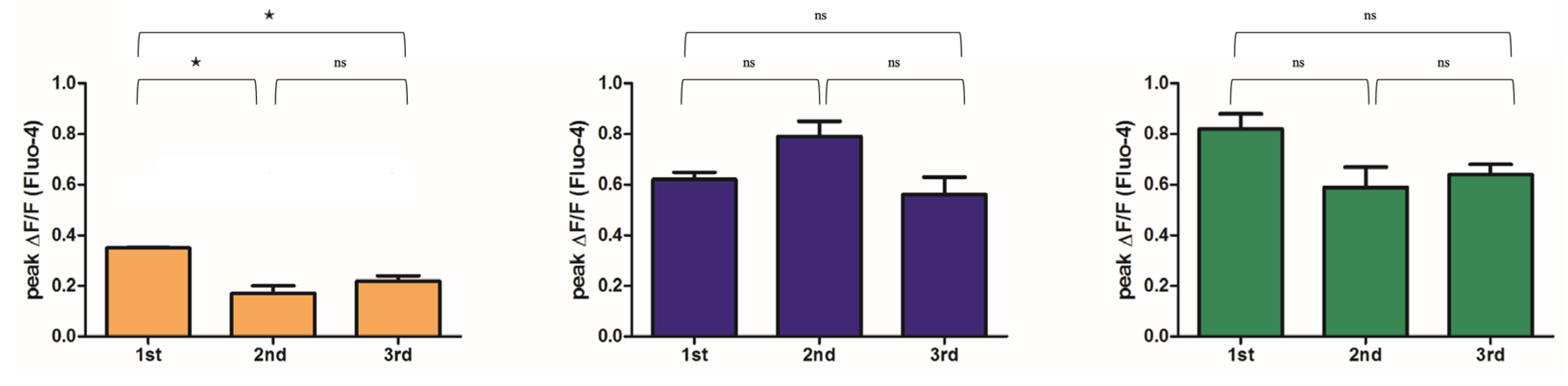
2.3. Mg2+ Availability Impairs Intracellular Ca2+ Store Refilling
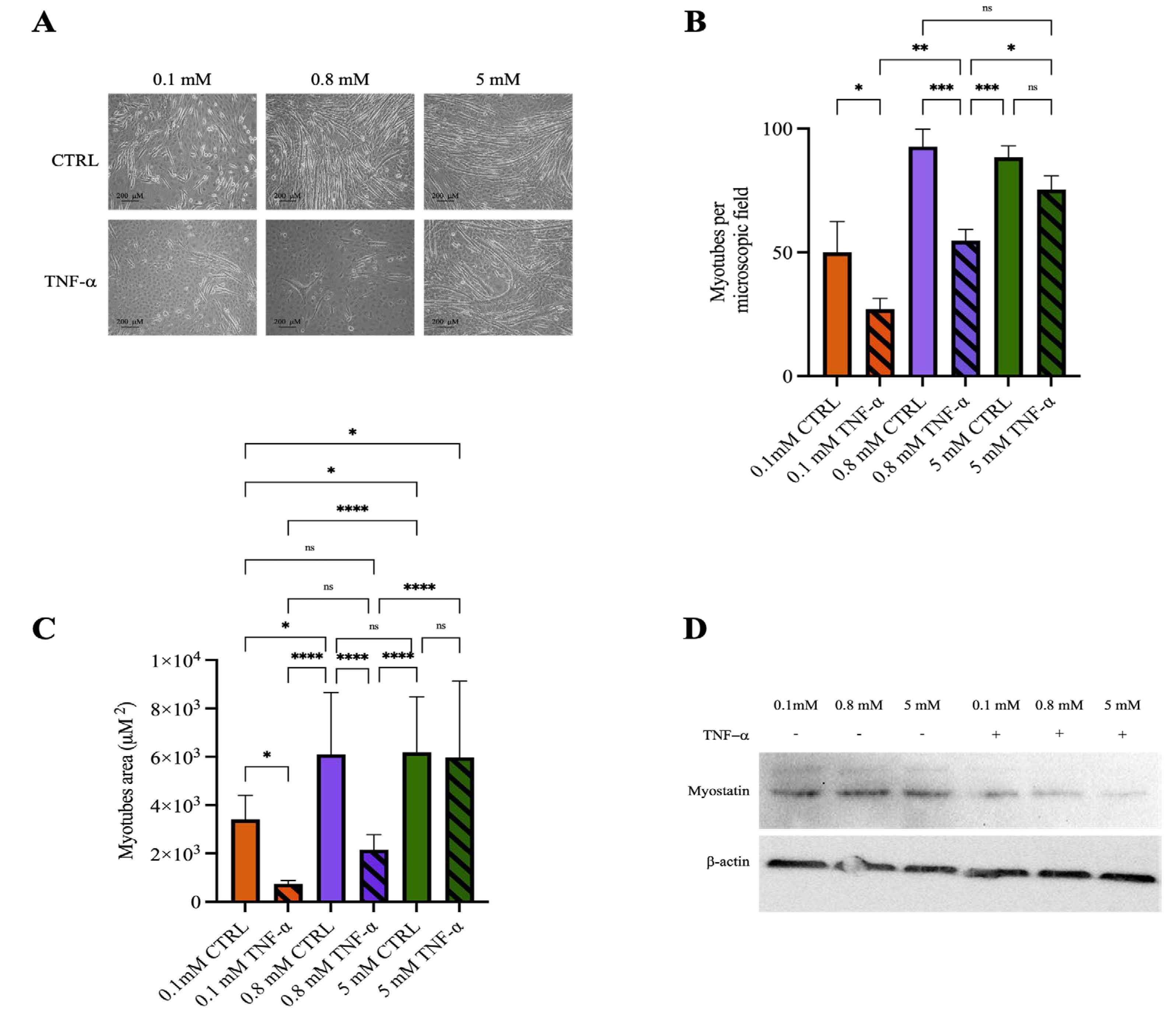
2.4. Mg2+ Availability Affects Myotube Resistance to Inflammatory Stimuli
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Differentiation
4.2. Western Blot
4.3. Calcium Measurements
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Baaij, J.H.F.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J. Magnesium in Man: Implications for Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M.; de Baaij, J.H.F.; Hoenderop, J.G.J. Magnesium Disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1998–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlingmann, K.P.; Waldegger, S.; Konrad, M.; Chubanov, V.; Gudermann, T. TRPM6 and TRPM7—Gatekeepers of human magnesium metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2007, 1772, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luongo, F.; Pietropaolo, G.; Gautier, M.; Dhennin-Duthille, I.; Ouadid-Ahidouch, H.; Wolf, F.I.; Trapani, V. TRPM6 is Essential for Magnesium Uptake and Epithelial Cell Function in the Colon. Nutrients 2018, 10, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Castiglioni, S.; Locatelli, L.; Zocchi, M.; Mazur, A. Magnesium and inflammation: Advances and perspectives. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 115, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapani, V.; Petito, V.; Di Agostini, A.; Arduini, D.; Hamersma, W.; Pietropaolo, G.; Luongo, F.; Arena, V.; Stigliano, E.; Lopetuso, L.R.; et al. Dietary Magnesium Alleviates Experimental Murine Colitis Through Upregulation of the Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 6 Channel. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 2198–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashique, S.; Kumar, S.; Hussain, A.; Mishra, N.; Garg, A.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Farid, A.; Gupta, G.; Dua, K.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. A narrative review on the role of magnesium in immune regulation, inflammation, infectious diseases, and cancer. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2023, 42, 74, Erratum in J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2023, 42, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazidi, M.; Rezaie, P.; Banach, M. Effect of magnesium supplements on serum C-reactive protein: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, S.; Mazur, A.; Maier, J.A. The central role of magnesium in skeletal muscle: From myogenesis to performance. Magnes. Res. 2024, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocchi, M.; Locatelli, L.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Mazur, A.; Béchet, D.; Maier, J.A.; Castiglioni, S. Magnesium Homeostasis in Myogenic Differentiation—A Focus on the Regulation of TRPM7, MagT1 and SLC41A1 Transporters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, M. Cytoplasmic Free Concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in Skeletal Muscle Fibers at Rest and during Contraction. Jpn. J. Physiol. 1998, 48, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.M.; Szegedi, C.; Jóna, I.; Vogel, P.D. Insights into the Regulation of the Ryanodine Receptor: Differential Effects of Mg2+ and Ca2+ on ATP Binding. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 9408–9415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furutani, Y.; Funaba, M.; Matsui, T. Magnesium deficiency up-regulates Myod expression in rat skeletal muscle and C2C12 myogenic cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2011, 29, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocchi, M.; Béchet, D.; Mazur, A.; Maier, J.A.; Castiglioni, S. Magnesium Influences Membrane Fusion during Myogenesis by Modulating Oxidative Stress in C2C12 Myoblasts. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukaski, H.C. Magnesium, zinc, and chromium nutriture and physical activity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 585S–593S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-W.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chen, W.-L. Association between oral intake magnesium and sarcopenia: A cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L. Magnesium and Aging. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Berton, L.; Carraro, S.; Bolzetta, F.; De Rui, M.; Perissinotto, E.; Toffanello, E.D.; Bano, G.; Pizzato, S.; Miotto, F.; et al. Effect of oral magnesium supplementation on physical performance in healthy elderly women involved in a weekly exercise program: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayle, D.; Coudy-Gandilhon, C.; Gueugneau, M.; Castiglioni, S.; Zocchi, M.; Maj-Zurawska, M.; Palinska-Saadi, A.; Mazur, A.; Béchet, D.; Maier, J.A. Magnesium Deficiency Alters Expression of Genes Critical for Muscle Magnesium Homeostasis and Physiology in Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Van Remmen, H. The SarcoEndoplasmic Reticulum Calcium ATPase (SERCA) Pump: A Potential Target for Intervention in Aging and Skeletal Muscle Pathologies. Skelet. Muscle 2021, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, F.H.; Lukaski, H.C. Update on the relationship between magnesium and exercise. Magnes. Res. 2006, 19, 180–189. [Google Scholar]
- Astier, C.; Rock, E.; Lab, C.; Gueux, E.; Mazur, A.; Rayssiguier, Y. Functional alterations in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes of magnesium-deficient rat skeletal muscle as consequences of free radical-mediated process. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.N.; Blackmore, D.G.; Gilbert, D.F.; Murphy, R.M.; Launikonis, B.S. Store-operated calcium entry remains fully functional in aged mouse skeletal muscle despite a decline in STIM1 protein expression. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, A.M.; Zhao, X.; Weisleder, N.; Brotto, L.S.; Bougoin, S.; Nosek, T.M.; Reid, M.; Hardin, B.; Pan, Z.; Ma, J.; et al. Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry (SOCE) Contributes to Normal Skeletal Muscle Contractility in young but not in aged skeletal muscle. Aging 2011, 3, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, E.; Astier, C.; Lab, C.; Vignon, X.; Gueux, E.; Motta, C.; Rayssiguier, Y. Dietary Magnesium Deficiency in Rats Enhances Free Radical Production in Skeletal Muscle. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepeda, V.; Ródenas-Munar, M.; García, S.; Bouzas, C.; Tur, J.A. Unlocking the Power of Magnesium: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Regarding Its Role in Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, A.A.; Kelaiditi, E.; Jennings, A.; Steves, C.J.; Spector, T.D.; MacGregor, A. Dietary Magnesium Is Positively Associated With Skeletal Muscle Power and Indices of Muscle Mass and May Attenuate the Association Between Circulating C-Reactive Protein and Muscle Mass in Women. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 31, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Bellosta, R. Dietary magnesium supplementation improves lifespan in a mouse model of progeria. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.C.; Liu, J.-P.; Iqbal, J.; Hussain, M.; Jiang, X.-C.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zheng, T.; Li, W.; Sica, A.C.; et al. Mg deficiency results in modulation of serum lipids, glutathione, and NO synthase isozyme activation in cardiovascular tissues: Relevance to de novo synthesis of ceramide, serum Mg and atherogenesis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2011, 4, 103–118. [Google Scholar]
- De Larichaudy, J.; Zufferli, A.; Serra, F.; Isidori, A.M.; Naro, F.; Dessalle, K.; Desgeorges, M.; Piraud, M.; Cheillan, D.; Vidal, H.; et al. TNF-α- and tumor-induced skeletal muscle atrophy involves sphingolipid metabolism. Skelet. Muscle 2012, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Gupta, P.; Dutt, V.; Sharma, O.; Gupta, S.; Dua, A.; Injeti, E.; Mittal, A. Cinnamaldehyde attenuates TNF-α induced skeletal muscle loss in C2C12 myotubes regulation of protein synthesis, proteolysis, oxidative stress and inflammation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 753, 109922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-K.; Choi, Y.H.; Nam, T.-J. Pyropia yezoensis protein protects against TNF-α-induced myotube atrophy in C2C12 myotubes via the NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Xing, S.; Shen, C.; Wang, X.; Yue, Y.; Song, J.; Chen, M.; et al. TNF alpha inhibits myogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells through NF-κB activation and impairment of IGF-1 signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powrózek, T.; Pigoń-Zając, D.; Mazurek, M.; Otieno, M.O.; Rahnama-Hezavah, M.; Małecka-Massalska, T. TNF-α Induced Myotube Atrophy in C2C12 Cell Line Uncovers Putative Inflammatory-Related lncRNAs Mediating Muscle Wasting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lin, S.; Chen, W.; Lian, G.; Wu, W.; Chen, A.; Sagor, M.I.H.; Luo, L.; Wang, H.; Xie, L. TNF-α contributes to sarcopenia through caspase-8/caspase-3/GSDME-mediated pyroptosis. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogra, C.; Changotra, H.; Mohan, S.; Kumar, A. Tumor Necrosis Factor-like Weak Inducer of Apoptosis Inhibits Skeletal Myogenesis through Sustained Activation of Nuclear Factor-κB and Degradation of MyoD Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 10327–10336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geromella, M.S.; Braun, J.L.; Fajardo, V.A. Measuring SERCA-mediated calcium uptake in mouse muscle homogenates. STAR Protoc. 2023, 4, 101987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Barbagallo, M.; Lauretani, F.; Bandinelli, S.; Bos, A.; Corsi, A.M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L. Magnesium and muscle performance in older persons: The InCHIANTI study1–3. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, F.H. Magnesium deficiency and increased inflammation: Current perspectives. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, A.R.S.; Cruz, K.J.C.; Severo, J.S.; Morais, J.B.S.; De Freitas, T.E.C.; Araújo, R.S.; Marreiro, D.D.N. Hypomagnesemia and its relation with chronic low-grade inflammation in obesity. Front. Public Health 2017, 63, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pietropaolo, G.; Castiglioni, S.; Maier, J.A.; Wolf, F.I.; Trapani, V. Magnesium Preserves Calcium Homeostasis and Contributes to Protect Myotubes from Inflammation-Induced Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209912
Pietropaolo G, Castiglioni S, Maier JA, Wolf FI, Trapani V. Magnesium Preserves Calcium Homeostasis and Contributes to Protect Myotubes from Inflammation-Induced Damage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209912
Chicago/Turabian StylePietropaolo, Giuseppe, Sara Castiglioni, Jeanette A. Maier, Federica I. Wolf, and Valentina Trapani. 2025. "Magnesium Preserves Calcium Homeostasis and Contributes to Protect Myotubes from Inflammation-Induced Damage" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209912
APA StylePietropaolo, G., Castiglioni, S., Maier, J. A., Wolf, F. I., & Trapani, V. (2025). Magnesium Preserves Calcium Homeostasis and Contributes to Protect Myotubes from Inflammation-Induced Damage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209912






