Genome-Wide Identification and Biotic Stress Responses of TLP Gene Family in Citrus sinensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Physicochemical Property Analysis of CsTLP Gene Family
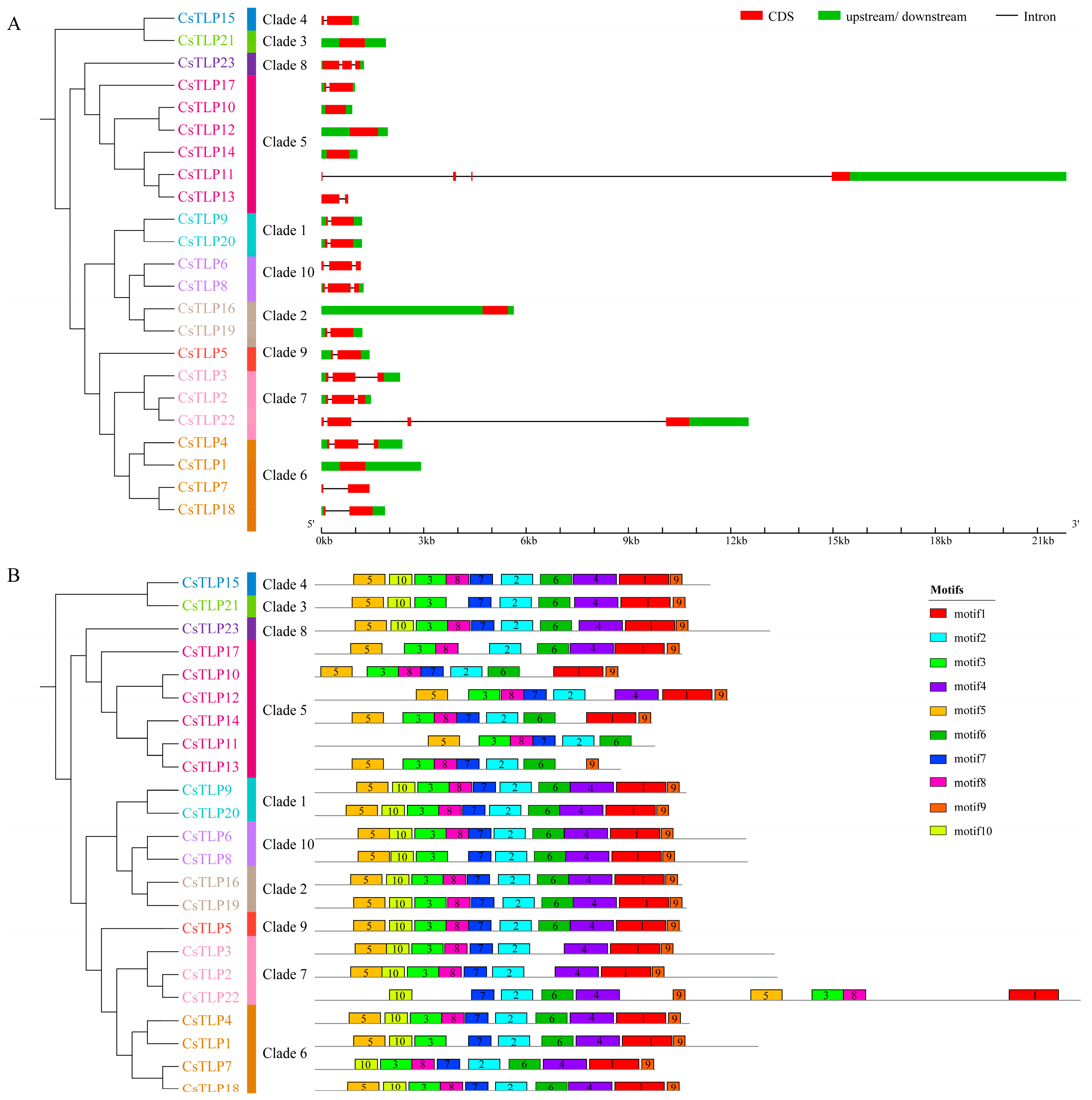
2.2. Chromosome Distribution, Gene Structure and Conserved Motif Analysis of the CsTLP Gene Family
2.3. Secondary and Tertiary Structure Analysis of CsTLP Proteins
2.4. The Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Analysis of the CsTLP Gene Family
2.5. Collinearity Analysis of the CsTLP Gene Family
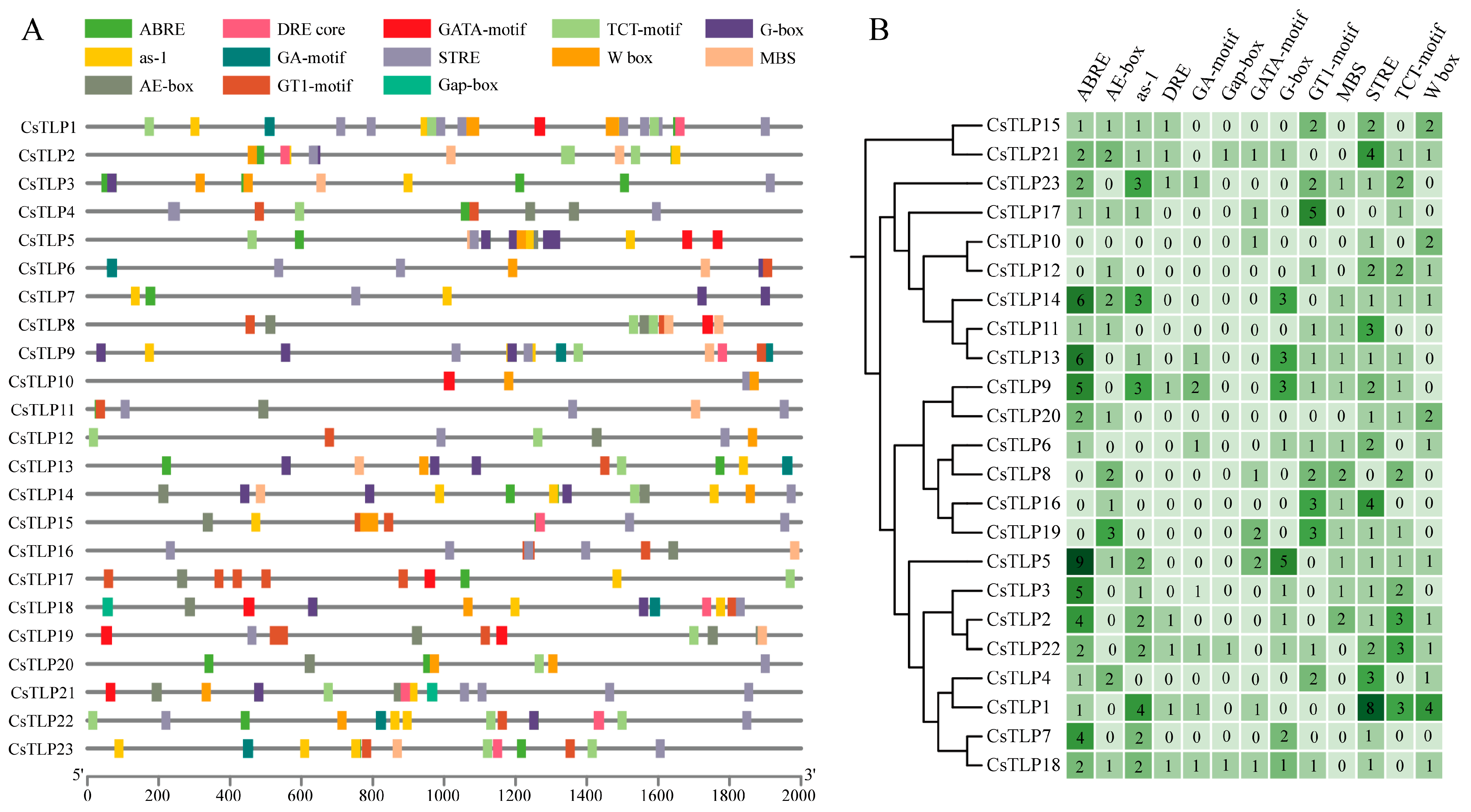
2.6. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements in the CsTLP Gene Family
2.7. Analysis of Tissue-Specific Expression of the CsTLP Gene Family
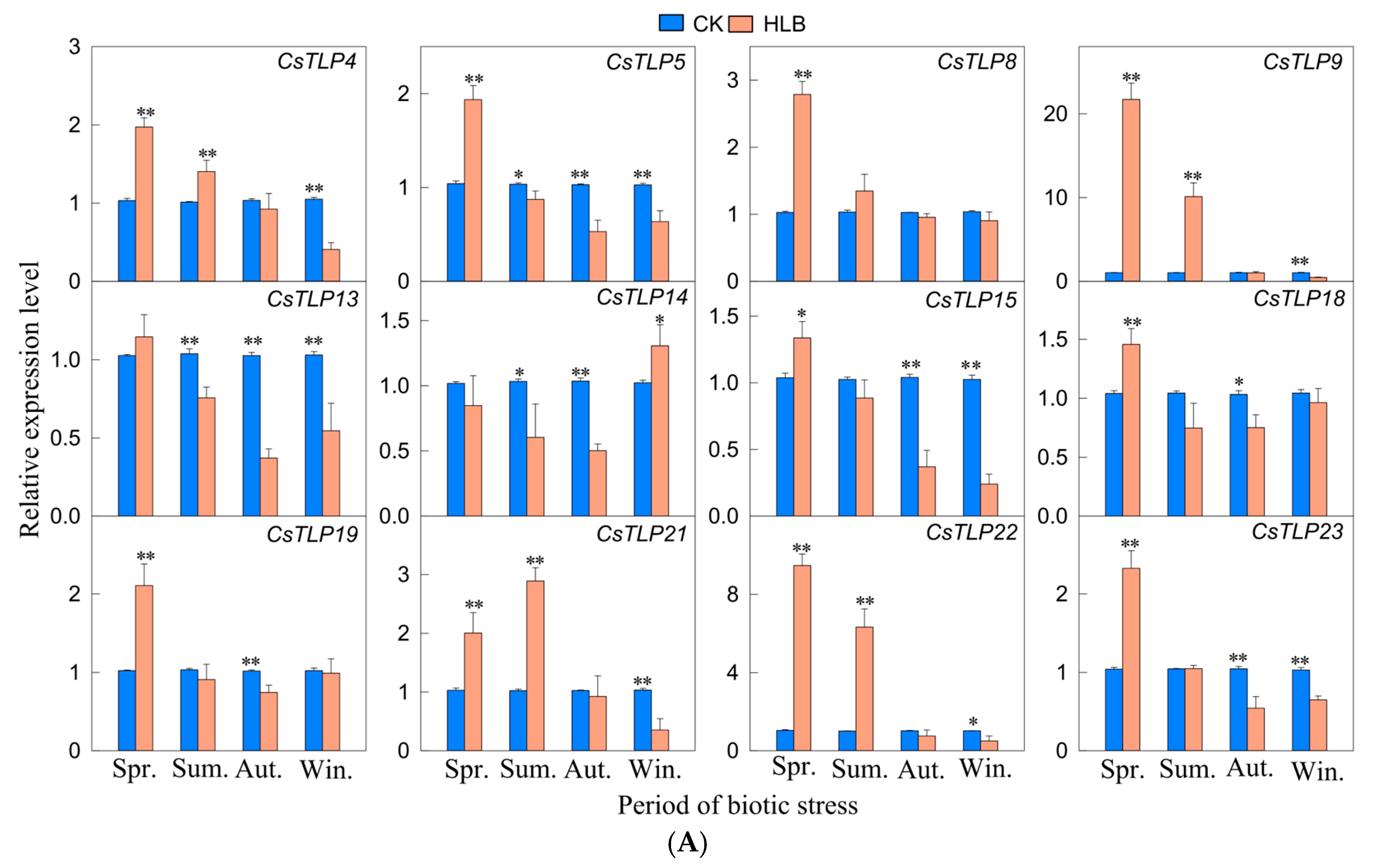
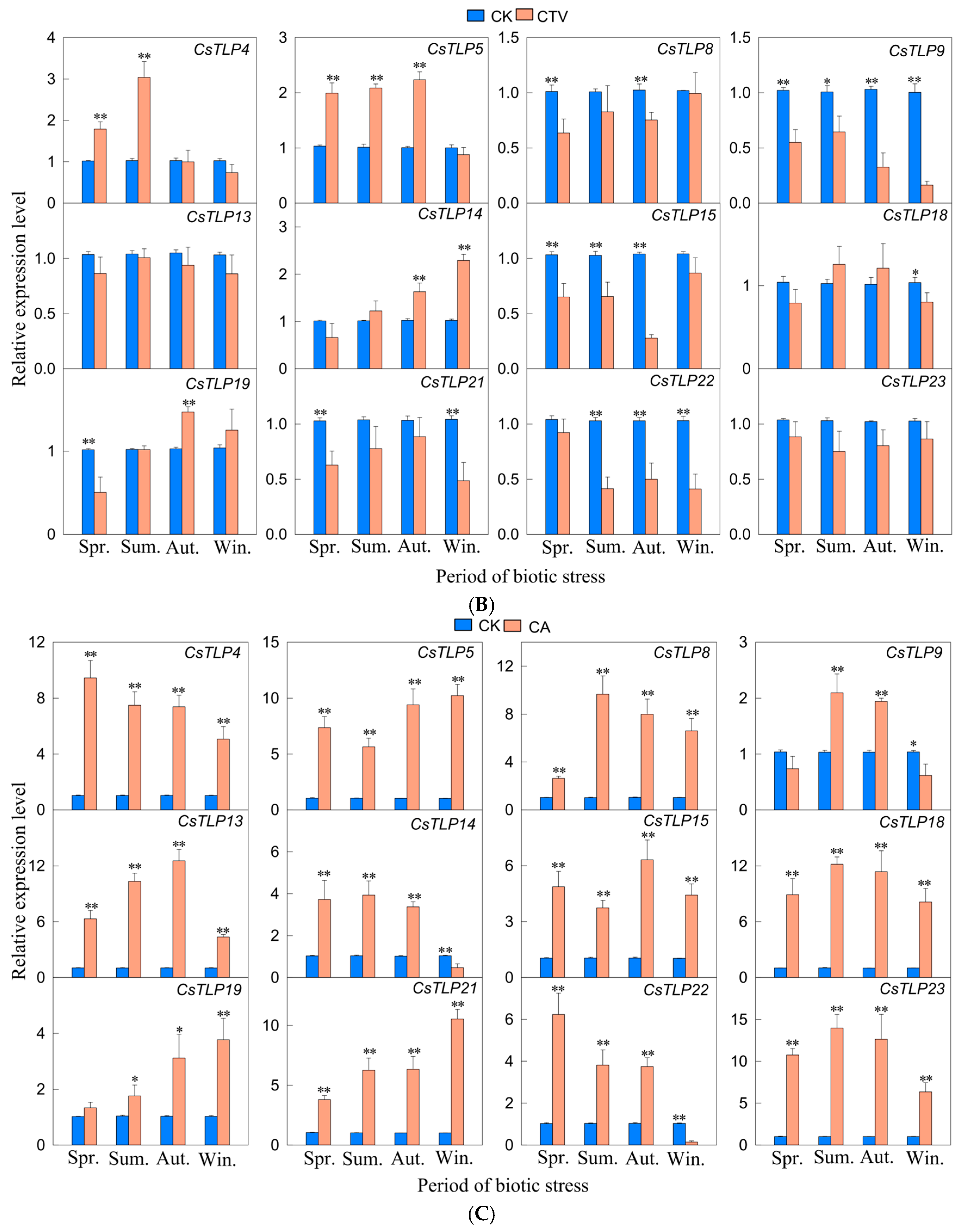
2.8. Real-Time qPCR Analysis of the CsTLP Gene Family Under Biotic Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Treatment
4.2. Identification of the CsTLP Gene Family
4.3. Chromosomal Localization, Gene Structure, and Conserved Motifs of the CsTLP Gene Family
4.4. Prediction of Secondary and Tertiary Structures of CsTLP Proteins
4.5. Multiple Sequence Alignment, Phylogenetic Tree, and Collinearity Analysis of the CsTLP Gene Family
4.6. Cis-Acting Elements and Tissue Specificity Analysis of the CsTLP Gene Family
4.7. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TLPs | Thaumatin-like proteins |
| PR | Pathogenesis-related |
| CDS | Coding sequence |
| GA | Gibberellic acid |
| aa | Amino acid |
| MW | Molecular weight |
| pI | Isoelectric point |
| NLS | N-terminal nuclear localization signal |
| ORF | Open reading frame |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| ZF | Zinc finger |
| SAR | Systemic acquired resistance |
| HR | Hypersensitive response |
| HLB | Citrus huanglongbing |
| CTV | Citrus tristeza virus |
| CA | Citrus Anthracnose |
| IDRs | Intrinsically disordered regions |
| TMH | Transmembrane helix |
| AREB | Abscisic acid response elements |
| HIPPs | Heavy metal-associated isoprenylated plant proteins |
| UTR | Untranslated region |
| REDDD | Arginine, glutamic acid, and three aspartic acid residues |
References
- Li, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Bao, J.; Lin, F. Research on the molecular interaction mechanism between plants and pathogenic fungi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.L.; Scala, F.; Ruocco, M.; Lorito, M. The Molecular biology of the interactions between trichoderma spp., phytopathogenic fungi, and plants. Phytopathology 2006, 96, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sels, J.; Mathys, J.; De Coninck, B.M.A.; Cammue, B.P.A.; De Bolle, M.F.C. Plant pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins: A focus on PR peptides. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, E.; Nanda, S.; Joshi, R.K. Molecular characterization and heterologous expression of a pathogen induced PR5 gene from garlic (Allium sativum L.) conferring enhanced resistance to necrotrophic fungi. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 144, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Pandey, S.; Pati, P.K. Interaction between pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins and phytohormone signaling pathways in conferring disease tolerance in plants. Physiol. Plant. 2025, 177, e70174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Lv, Y.; Hou, Z.; Li, X.; Ding, L. Expansion and evolution of thaumatin-like protein (TLP) gene family in six plants. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 79, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Guo, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Characterization of rice and maize CONSTITUTIVE EXPRESSER OF PATHOGENESIS-RELATED GENES5 in plant immunity. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2023, 165, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, I.; Tripathi, R.K.; Wilkins, O.; Singh, J. Thaumatin-Like Protein (TLP) Gene family in barley: Genome-wide exploration and expression analysis during germination. Genes 2020, 11, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xu, Y.; Wang, K.; Guo, W.; Gu, Y.; Lyu, S.; Huang, J.; Lin, H.; Huang, C.; Xu, Z.; et al. Genome-wide identification of TLP gene family and their roles in Carya cathayensis Sarg in response to Botryosphaeria dothidea. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 849043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Sui, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, F. Genome-Wide Analyses of Thaumatin-like protein family genes reveal the involvement in the response to low-temperature stress in Ammopiptanthus nanus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yu, H.; He, S.; Zhang, P.; Ma, X. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the TLP gene family in Phyllostachys edulis and association with witches’ broom disease resistance in bamboo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Shumayla; Tyagi, S.; Alok, A.; Singh, K.; Upadhyay, S.K. Thaumatin-like protein kinases: Molecular characterization and transcriptional profiling in five cereal crops. Plant Sci. 2020, 290, 110317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, R.C.; Sandeep; Kamthan, M.; Kumar, S.; Ghosh, S. A thaumatin-like protein of Ocimum basilicum confers tolerance to fungal pathogen and abiotic stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, C.; Danish, S.; Kesawat, M.S.; Panwar, B.S.; Verma, M.; Arya, L.; Yadav, S.; Sharma, V. Genome-wide comprehensive characterization and expression analysis of TLP gene family revealed its responses to hormonal and abiotic stresses in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus). Gene 2022, 844, 146818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faillace, G.R.; Turchetto-Zolet, A.C.; Guzman, F.L.; de Oliveira-Busatto, L.A.; Bodanese-Zanettini, M.H. Genome-wide analysis and evolution of plant thaumatin-like proteins: A focus on the origin and diversification of osmotins. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2019, 294, 1137–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Miao, L.; Yang, X.; Jiang, G. Genome-wide characterization and expression of the TLP gene family associated with Colletotrichum gloeosporioides inoculation in Fragaria x ananassa. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Sang, X.; Wang, T.; Gong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, P.; Wang, H. Genome-wide identification of the thaumatin-like protein family genes in Gossypium barbadense and analysis of their responses to Verticillium dahliae infection. Plants 2021, 10, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guan, H.; Wei, F.; Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Huang, J. Genome-wide identification of thaumatin-like protein family genes in Panax notoginseng and analysis of their responses to Fusarium solani infection. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2024, 71, 2267–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Sun, M.; Shao, C.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, X. Genome-wide analysis and characterization of the TaTLP gene family in wheat and functional characterization of the TaTLP44 in response to Rhizoctonia cerealis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 207, 108323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, B.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Deng, M.; Lv, J.; Zhao, K. Tomato-Thaumatin-like Protein Genes Solyc08g080660 and Solyc08g080670 Confer Resistance to Five Soil-Borne Diseases by Enhancing β-1,3-Glucanase Activity. Genes 2023, 14, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; He, Y. Genome-wide identification and characterization of thaumatin-like protein family genes in wheat and analysis of their responses to Fusarium head blight infection. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2022, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimova, O.K.; Kochieva, E.Z.; Shchennikova, A.V.; Filyushin, M.A. Thaumatin-like Protein (TLP) Genes in Garlic (Allium sativum L.): Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression in response to Fusarium proliferatum infection. Plants 2022, 11, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, D.; Ye, X.; Liu, D.; Cheng, H. The potential of different ripeness of blood oranges (Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck) for sale in advance after low-temperature storage: Anthocyanin enhancements, volatile compounds, and taste attributes. Food Chem. 2023, 417, 135934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.; Lazaro, E.; Duarte, B.; Magalhaes, T.; Duarte, A.; Benhadi-Marin, J.; Pereira, J.A.; Vicent, A.; Parnell, S.; Cunniffe, N.J. Developing epidemiological preparedness for a plant disease invasion: Modelling citrus huanglongbing in the European Union. Plants People Planet 2025, 7, 1403–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, M.F.; Panebianco, S.; Azzaro, A.; Catara, V.; Cirvilleri, G. Assessing copper-alternative products for the control of pre- and postharvest citrus anthracnose. Plants 2023, 12, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, P.; Xu, L.; Cheng, T. Serological and molecular detection of citrus tristeza virus: A review. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yokomi, R.K.; Folimonova, S.Y. Citrus tristeza virus: A century-long challenge for the world’s citrus industries. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2024, 185, 304–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Long, Y.; Deng, G.; Men, Y.; Lu, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Han, H. Manganese-based nanozyme enabled efficient mitigation of Huanglongbing-induced oxidative damage in Citrus. Environ. Sci. Nano 2025, 12, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Tang, C.; Qian, M.; Zhang, M.; Xie, Z.; Wu, M.; Khan, W.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; et al. Genome-wide identification of thaumatin-like protein family in pear and functional analysis their roles in pollen growth. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 104, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Ma, X.; Xu, S.; Cheng, J.; Xu, W.; Elsheery, N.I.; Cheng, Y. Genome-wide identification of TLP gene family in Populus trichocarpa and functional characterization of PtTLP6, preferentially expressed in phloem. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, X.; Guo, C.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Analysis of the grape (Vitis vinifera L.) thaumatin-like protein (TLP) gene family and demonstration that TLP29 contributes to disease resistance. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Cui, Y.; Qiao, K.; Zhu, L.; Fan, S.; Ma, Q. Comprehensive genome-wide analysis of thaumatin-like gene family in four cotton species and functional identification of GhTLP19 involved in regulating tolerance to Verticillium dahlia and drought. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 575015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zeng, W.; Qi, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, F. The module consisting of transcription factor WRKY14 and thaumatin-like protein TLP25 is involved in winter adaptation in Ammopiptanthus mongolicus. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e14560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muoki, R.C.; Paul, A.; Kaachra, A.; Kumar, S. Membrane localized thaumatin-like protein from tea (CsTLP) enhanced seed yield and the plant survival under drought stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 163, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, H.; Rajput, R.; Pandey, A.; Upadhyay, S.K. Molecular Characterization Revealed the Role of Thaumatin-Like Proteins of Bread Wheat in Stress Response. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 807448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Xu, H.; Xiao, S.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Y. The large soybean (Glycine max) WRKY TF family expanded by segmental duplication events and subsequent divergent selection among subgroups. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leister, D. Tandem and segmental gene duplication and recombination in the evolution of plant disease resistance genes. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhou, X.; Luan, Y.; Luan, F. Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression analysis of the TLP gene family in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Genomics 2020, 112, 2499–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; González, J.M.; Ramachandran, S. Comparative genomic and transcriptomic analysis of tandemly and segmentally duplicated genes in rice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clauss, M.J.; Mitchell-Olds, T. Functional divergence in tandemly duplicated Arabidopsis thaliana trypsin inhibitor genes. Genetics 2004, 166, 1419–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, S.I.R.; Kaewwongwal, A.; Laosatit, K.; Yimram, T.; Lin, Y.; Chen, X.; Nakazono, M.; Somta, P. Tandemly duplicated genes encoding polygalacturonase inhibitors are associated with bruchid (Callosobruchus chinensis) resistance in moth bean (Vigna aconitifolia). Plant Sci. 2022, 323, 111402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despons, L.; Baret, P.V.; Frangeul, L.; Louis, V.L.; Durrens, P.; Souciet, J. Genome-wide computational prediction of tandem gene arrays: Application in yeasts. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kunze, S.; Ni, X.; Feussner, I.; Kolomiets, M.V. Comparative molecular and biochemical characterization of segmentally duplicated 9-lipoxygenase genes ZmLOX4 and ZmLOX5 of maize. Planta 2010, 231, 1425–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lü, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, J.; Qi, K.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Genome-wide identification, evolution, and expression analysis of the KT/HAK/KUP family in pear. Genome 2018, 61, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.A.; Terol, J.; Ibanez, V.; López-García, A.; Pérez-Román, E.; Borredá, C.; Domingo, C.; Tadeo, F.R.; Carbonell-Caballero, J.; Alonso, R.; et al. Genomics of the origin and evolution of Citrus. Nature 2018, 554, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffares, D.C.; Penkett, C.J.; Bähler, J. Rapidly regulated genes are intron poor. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyson, H.J.; Wright, P.E. Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2005, 6, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aknadibossian, V.; Huguet-Tapia, J.C.; Golyaev, V.; Pooggin, M.M.; Folimonova, S.Y. Transcriptomic alterations in the sweet orange vasculature correlate with growth repression induced by a variant of citrus tristeza virus. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1162613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Pei, T.; Wan, H.; Wei, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C.; Fu, S. Identification and analysis of bZIP family genes in Citrus sinensis and the role of CsbZIP24 in response to Huanglongbing. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 336, 113436. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Hu, Y.; Li, F.; Zuo, X.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Li, R. Genome-wide characterization of heavy metal-associated isoprenylated plant protein gene family from Citrus sinensis in response to huanglongbing. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1369883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesús-Pires, C.; Ferreira-Neto, J.R.C.; Pacifico Bezerra-Neto, J.; Kido, E.A.; de Oliveira Silva, R.L.; Pandolfi, V.; Wanderley-Nogueira, A.C.; Binneck, E.; da Costa, A.F.; Pio-Ribeiro, G.; et al. Plant thaumatin-like proteins: Function, evolution and biotechnological applications. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2020, 21, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Nadeem, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, N.; Zhu, H.; Tang, C. GhTLP1, a thaumatin-like protein 1, improves Verticillium wilt resistance in cotton via JA, ABA and MAPK signaling pathway-plant pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, J.; Liu, G.; Yang, X. Antifungal properties of a thaumatin-like protein from watermelon. Acta Physiol. Plant 2018, 40, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeny, O.P.; Nyaboga, E.N.; Njiru, P.N.; Orinda, G. Overexpression of rice thaumatin-like protein (Ostlp) gene in transgenic cassava results in enhanced tolerance to Colletotrichum gloeosporioides f. sp. manihotis. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Liang, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, D.; Wang, H. Transgenic expression of TaTLP1, a thaumatin-like protein gene, reduces susceptibility to common root rot and leaf rust in wheat. Crop J. 2021, 9, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Huang, G. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the ascorbate peroxidase gene family in Citrus sinensis in response to Huanglongbing. Trop. Plant Biol. 2024, 17, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Hedo, M.; Hoddle, M.S.; Alferez, F.; Tena, A.; Wade, T.; Chakravarty, S.; Wang, N.; Stelinski, L.L.; Urbaneja, A. Huanglongbing (HLB) and its vectors: Recent research advances and future challenges. Entomol. Gen. 2025, 45, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, A.; Kurt, S.; Guarnaccia, V. Distribution and characterization of Colletotrichum species associated with Citrus anthracnose in eastern Mediterranean region of Turkey. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 163, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.C.D.; Pinto, P.I.S.; Guerra, R.; Duarte, A.; Power, D.M.; Marques, N.T. Gene transcripts responsive to drought stress identified in Citrus macrophylla bark tissue transcriptome have a modified response in plants infected by Citrus tristeza virus. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 307, 111526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cao, L.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wu, G.; Tian, S.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; et al. Genomic analyses of primitive, wild and cultivated citrus provide insights into asexual reproduction. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An improvement of the 2^(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat. Bioinforma. Biomath. 2013, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, T.; Qureshi, H.; Fatima, A.; Sattar, K.; Albasher, G.; Kamal, A.; Ayaz, A.; Zaman, W. Citrus sinensis Peel Oil Extraction and Evaluation as an Antibacterial and Antifungal Agent. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Name | Gene ID | AA | MW (kDa) | pI | II | AI | GRAVY | Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CsTLP1 | Cs_ont_1g028250.1 | 296 | 30.67 | 4.66 | 44.14 | 71.01 | 0.145 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP2 | Cs_ont_1g028270.1 | 309 | 32.22 | 4.50 | 51.85 | 59.77 | −0.072 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP3 | Cs_ont_3g002150.1 | 307 | 32.62 | 4.69 | 47.53 | 61.99 | −0.066 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP4 | Cs_ont_3g002160.1 | 250 | 26.20 | 4.93 | 41.26 | 59.76 | −0.089 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP5 | Cs_ont_3g004110.1 | 245 | 25.11 | 4.50 | 33.53 | 67.71 | 0.178 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP6 | Cs_ont_3g009770.1 | 288 | 30.83 | 8.59 | 37.51 | 73.09 | 0.085 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP7 | Cs_ont_3g021910.1 | 227 | 23.34 | 4.60 | 42.39 | 65.86 | 0.004 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP8 | Cs_ont_3g026270.1 | 289 | 31.00 | 7.37 | 44.15 | 70.90 | −0.121 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP9 | Cs_ont_4g012400.1 | 248 | 26.75 | 9.38 | 54.46 | 76.41 | 0.036 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP10 | Cs_ont_5g040270.1 | 203 | 21.88 | 5.73 | 28.24 | 64.43 | −0.186 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP11 | Cs_ont_5g040300.1 | 227 | 24.88 | 6.58 | 34.60 | 61.06 | −0.365 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP12 | Cs_ont_5g040310.1 | 276 | 30.02 | 5.92 | 28.84 | 60.07 | −0.167 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP13 | Cs_ont_5g040320.1 | 204 | 21.98 | 8.24 | 34.43 | 78.48 | −0.072 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP14 | Cs_ont_5g040330.1 | 225 | 24.54 | 8.13 | 24.13 | 63.29 | −0.193 | Vacuole |
| CsTLP15 | Cs_ont_6g002020.1 | 264 | 29.07 | 6.09 | 57.99 | 71.70 | −0.025 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP16 | Cs_ont_6g017000.1 | 245 | 25.70 | 7.82 | 40.96 | 75.22 | 0.079 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP17 | Cs_ont_6g022360.1 | 245 | 26.51 | 4.92 | 46.79 | 72.04 | −0.213 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP18 | Cs_ont_6g022370.1 | 244 | 25.69 | 5.81 | 34.85 | 55.74 | −0.145 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP19 | Cs_ont_7g000750.1 | 248 | 26.53 | 8.16 | 38.46 | 71.61 | 0.094 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP20 | Cs_ont_7g028380.1 | 236 | 25.11 | 4.94 | 41.34 | 65.34 | −0.143 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP21 | Cs_ont_8g002970.1 | 248 | 26.73 | 8.16 | 55.84 | 70.04 | −0.037 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP22 | Cs_ont_8g027660.1 | 512 | 53.75 | 6.44 | 44.91 | 60.66 | −0.107 | Extracellular |
| CsTLP23 | Cs_ont_9g005100.1 | 304 | 32.36 | 5.05 | 41.12 | 68.36 | 0.036 | Extracellular |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Fan, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Tong, X. Genome-Wide Identification and Biotic Stress Responses of TLP Gene Family in Citrus sinensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010133
Li X, Fan L, Liu C, Wang X, Zhang X, Tong X. Genome-Wide Identification and Biotic Stress Responses of TLP Gene Family in Citrus sinensis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010133
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xingtao, Lizhen Fan, Chang Liu, Xinrui Wang, Xiaoyuan Zhang, and Xiaonan Tong. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Biotic Stress Responses of TLP Gene Family in Citrus sinensis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010133
APA StyleLi, X., Fan, L., Liu, C., Wang, X., Zhang, X., & Tong, X. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Biotic Stress Responses of TLP Gene Family in Citrus sinensis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010133





