Native Wound-Repair Proteins Retained in Multilayer Placental CAMPs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
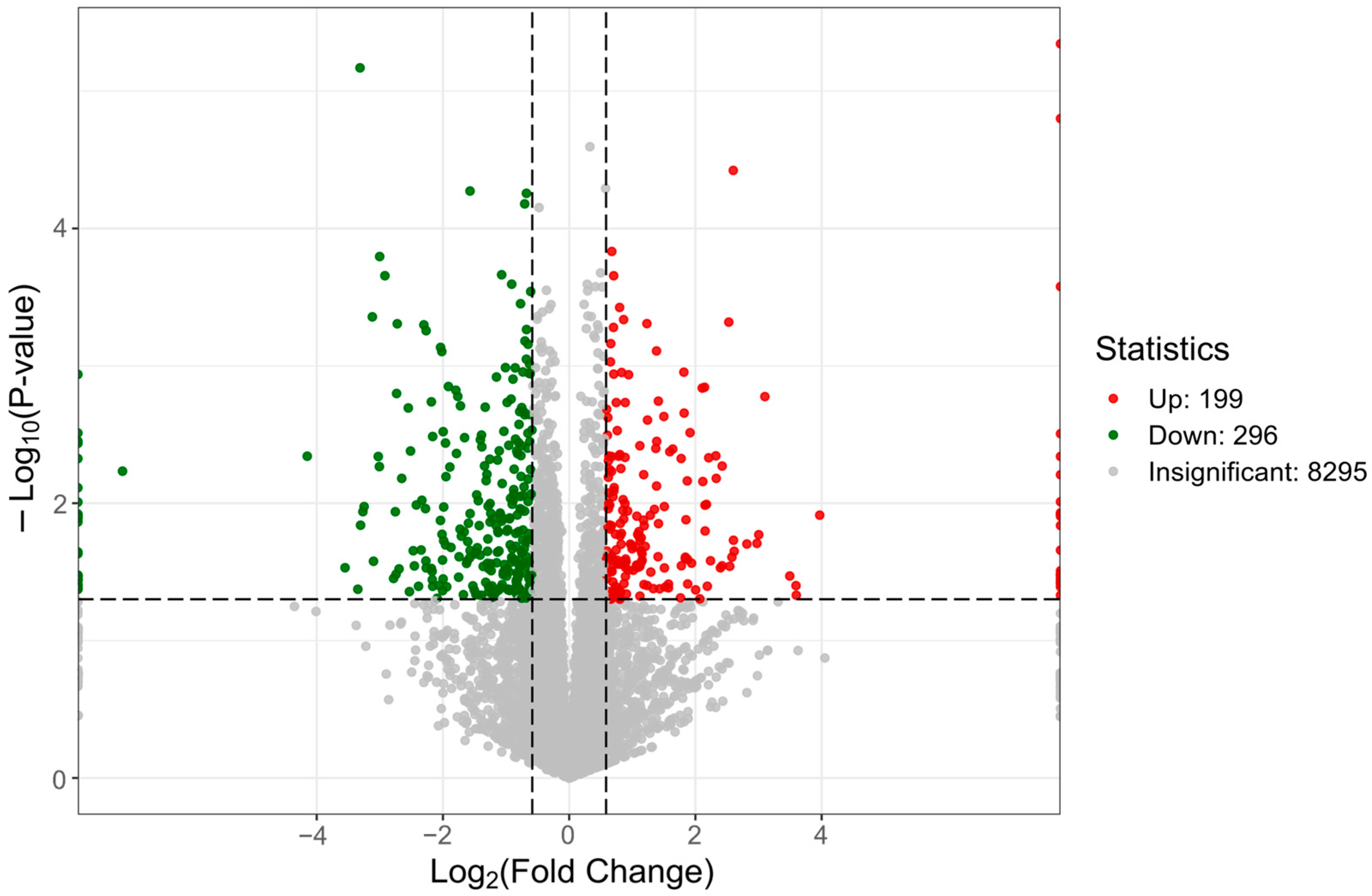
2.1. Proteomic Composition of Multilayer Placental Technologies
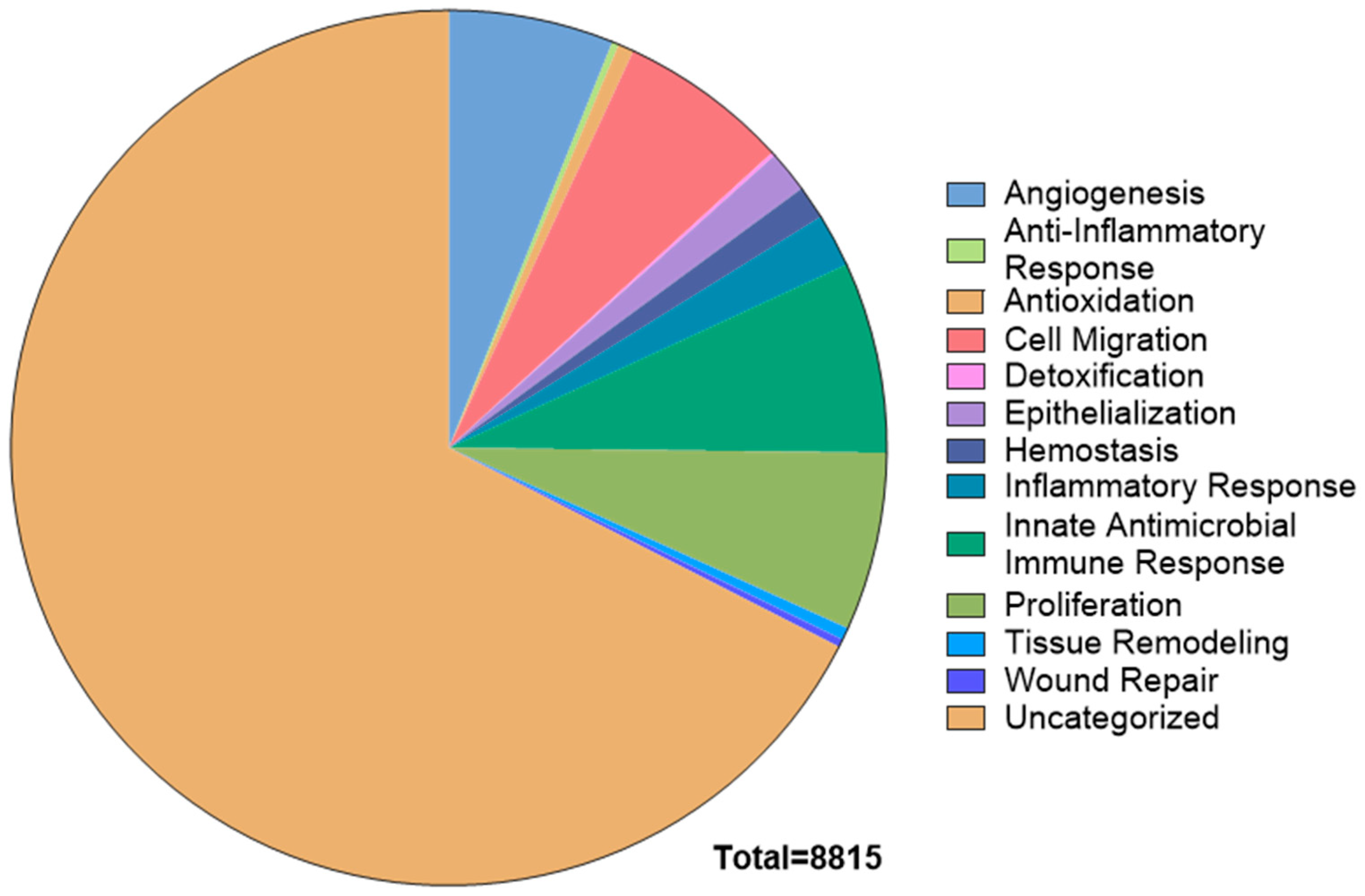
2.2. Pathway Enrichment Analysis of the CAMP Proteome
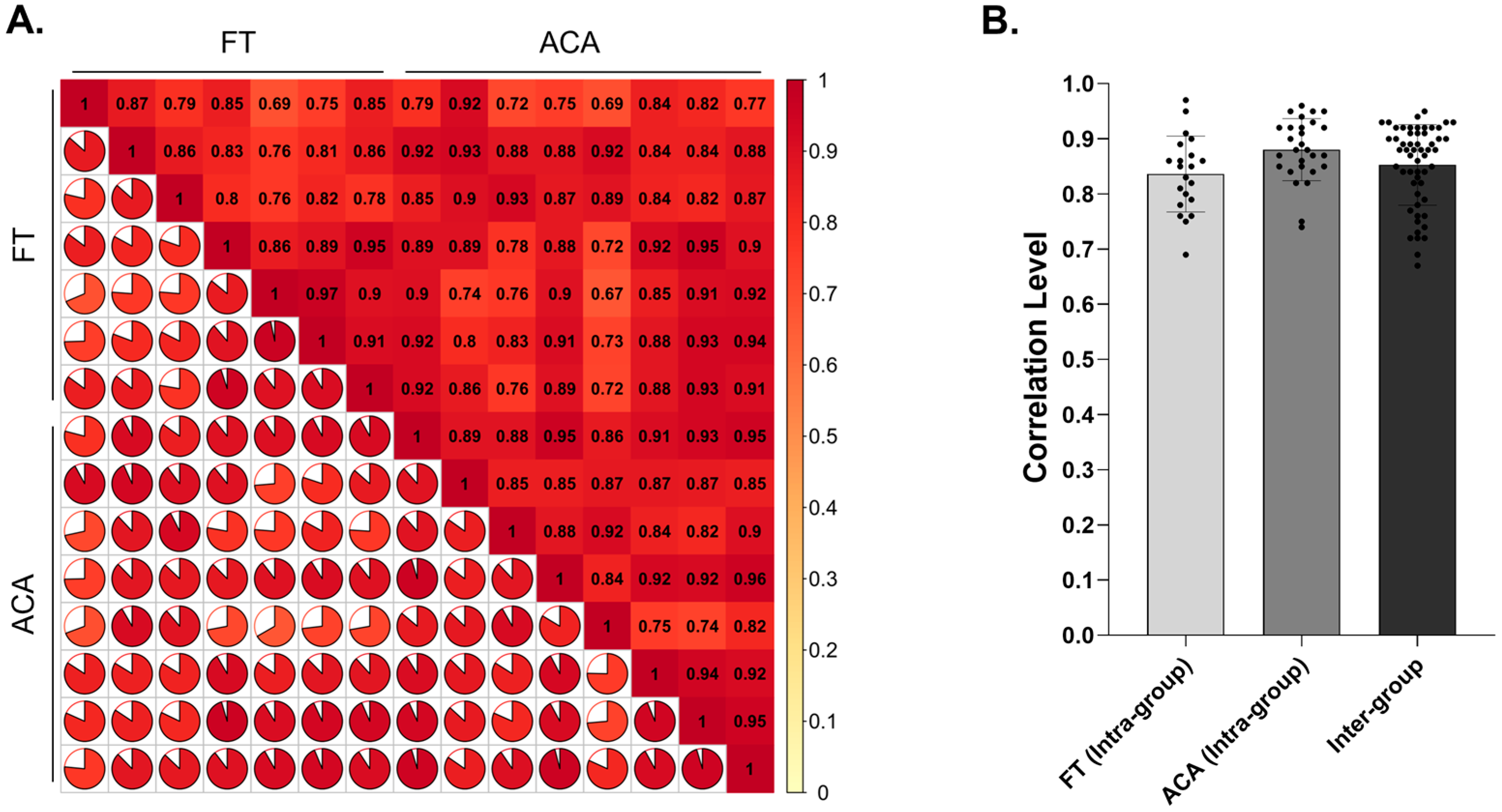
2.3. Evaluation of Soluble Proteins Under Physiological Conditions
2.4. In Vitro Angiogenesis Assessment of Soluble Proteins
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Placental Membrane-Derived CAMP Technologies
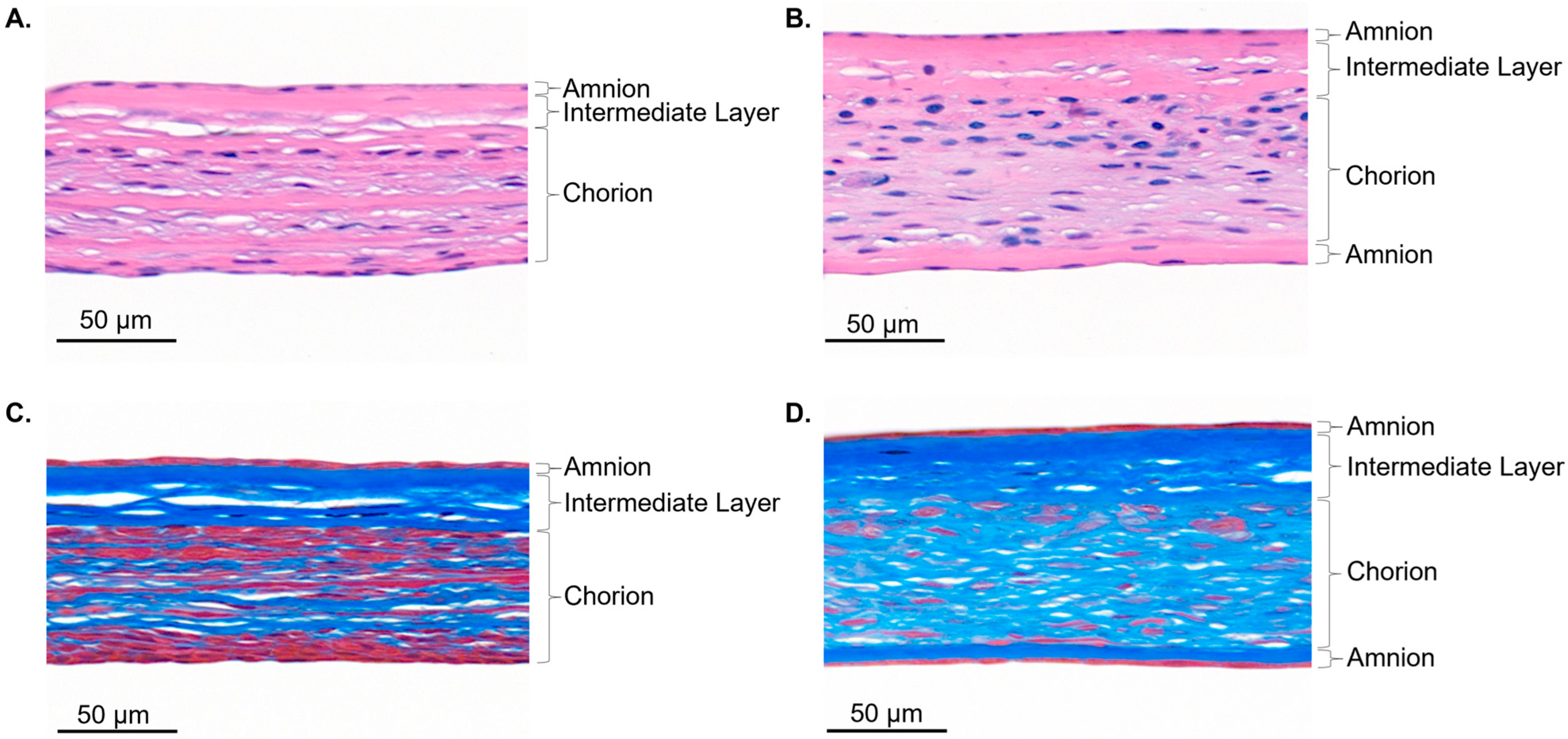
3.2. Histological Assessment
3.3. Global Proteomic Profiling
3.3.1. Proteomic Analysis
3.3.2. Bioinformatics and Functional Category Analysis
3.4. L-Series Human Antibody Array for Soluble Protein Profiling
3.5. In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay
Quantitative Analysis of Angiogenic Activity
3.6. Data Analysis and Handling
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AATB | American Association of Tissue Banks |
| ACA | Amnion–Intermediate–Chorion–Amnion |
| ANG-2 | Angiopoietin-2 |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| BCA | Bicinchoninic Acid |
| BH | Benjamini–Hochberg |
| CAMPs | Cellular, Acellular, Matrix-like Products |
| Da | Dalton |
| ddaPASEF | Data-Dependent Acquisition–Parallel Accumulation-Serial Fragmentation |
| DPBS | Dulbecco’s Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| EGF | Epidermal Growth Factor |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| FC | Fold Change |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| FT | Full-Thickness |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| GOA | Gene Ontology Annotation |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| HUVEC | Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| KOG | EuKaryotic Orthologous Groups |
| L/min | Liter per Minutes |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| LVES | Large Vessel Endothelial Supplement |
| M | Molar |
| m/z | mass-to-charge ratio |
| mM | microMolar |
| ms | Milliseconds |
| MTS | Masson’s Trichrome |
| ns | Not Significant |
| PDGF | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-AA |
| PMSF | phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride |
| RFU | Relative Fluorescence Unit |
| RPM | Rotations Per Minute |
| timsTOF | Trapped Ion Mobility Spectrometry-Time of Flight |
| µg/mL | Micrograms per Milliliter |
| µL | microLiter |
| µm | micrometer |
| V | Volts |
| Vs/cm2 | Volts-seconds per square centimeter |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| UHPLC | Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
Appendix A
| Mechanisms | Proteins Detected |
|---|---|
| Wound Repair | Angiopoietin-1, Angiopoietin-2, Angiopoietin-4, ANGPTL1, ANGPTL2, ANGPTL7, Axl, WISP-1, CD40, Fractalkine, Endothelin, Endoglin, ErbB2, ErbB3, Epiregulin, FACX, F3, FGF-10, FGF Basic, Hepassocin, Frizzled-6, Frizzled-7, HB-EGF, IGF-I, IL-1 alpha, IL-6, Insulin, VEGF R2, Kininostatin, Lck, MMP-12, HRG-alpha, PDGF-AA, PDGF-BB, PDGF R alpha, PECAM-1, PF4, uPA, uPAR, Angiostatin, SAA, Shh-N, TFPI, TGF-beta 1, TGF-beta 2, TGF-beta RI, Thrombospondin-1, TIMP-1, TLR4, TMEFF2, Dtk, VEGF, VEGF-B |
| Angiogenesis | Activin RIA, Angiogenin, Angiopoietin-1, Angiopoietin-2, Angiopoietin-4, Amphiregulin, Bax, BMP-2, BMP-4, BMP-5, BMP-7, CV-2, BMPR-IA, BMPR-II, Eotaxin, MCP-1, Eotaxin-2, CTGF, NOV, CCR2, CCR3, CD40, VE-Cadherin, Cerberus 1, Cryptic, Endostatin, Cripto-1, M-CSF, M-CSF R, G-CSF R, beta-Catenin, Fractalkine, IP-10, BLC, IL-8, CXCR3, Decorin, Dkk-1, EDA-A2, EDAR, Endothelin, EGF, EGF R, Endoglin, ErbB2, Epiregulin, Endocan, EYA2, F3, Fas Ligand, DANCE, FGF-10, FGF-16, FGF-18, FGF Basic, FGF-6, FGF-7, FGF-8, FGF-9, VEGF R3, Frizzled-3, Frizzled-4, Frizzled-5, Frizzled-6, GDF11, GDF3, GDNF, Glypican 3, Osteoactivin, Grb2, GREMLIN, Progranulin, IGF-I, IGFBP-rp1, IL-10, IL-17F, IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, sgp130, Activin A, Activin B, VEGF R2, Leptin, Leptin R, LIF, LRP-1, LRP-6, HGFR, MFG-E8, MMP-12, MMP-14, MMP-15, MMP-19, MMP-2, MMP-20, MMP-8, MMP-9, NGF R, NrCam, NRG3, Neuropilin-2, NT-4, PDGF-AA, PDGF-BB, PDGF-C, PDGF R alpha, PDGF R beta, PECAM-1, PF4, PlGF, Angiostatin, Prolactin, EG-VEGF, RELT, ROBO4, EDG-1, sFRP-1, Shh-N, Smad 1, Smad 4, Smad 5, Smad 7, SPARC, TGF-alpha, TGF-beta 1, TGF-beta 2, TGF-beta 3, TGF-beta RI, TGF-beta RII, TGF-beta RIII, Thrombospondin-1, Thrombospondin-2, Thrombospondin-4, Tie-1, TLR3, TWEAK R, TWEAK, PD-ECGF, VEGF, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D |
| Inflammatory Response | D6, Activin RIA, Angiopoietin-1, Angiopoietin-2, Angiopoietin-4, ANGPTL1, ANGPTL2, ANGPTL7, Axl, Bax, BMP-2, BMP-6, BMPR-IB, I-309, Eotaxin, MCP-4, CCL14, MIP-1d, HCC-4, Tarc, PARC, MIP-3 beta, MCP-1, MIP-3 alpha, MDC, Eotaxin-2, TECK, Eotaxin-3, CTACK, CCL28, MIP-1a, MIP-1b, RANTES, MCP-3, MCP-2, CTGF, WISP-1, CCR1, CCR2, CCR3, CCR4, CCR5, CCR6, CCR7, HCR, CD14, CD 163, CD40, CNTF, M-CSF, M-CSF R, Fractalkine, GRO-a, IP-10, I-TAC, BLC, MIP 2, GRO, ENA-78, GCP-2, IL-8, MIG, CXCR2, CXCR3, CXCR4, CXCR6, Endothelin, Endoglin, Erythropoietin, ErbB2, ErbB3, Epiregulin, FACX, F3, FGF-10, FGF Basic, FGF-4, FGF-7, Hepassocin, Frizzled-6, Frizzled-7, Progranulin, Granzyme A, HB-EGF, IFN-gamma, IFN-gamma R1, IGF-I, IL-10, IL-10 R beta, IL-13, IL-17, IL-17B, IL-17C, IL-17D, IL-17F, IL-17R, IL-17RC, IL-18 R alpha, IL-18 R beta, IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-1 F10, IL-1 RI, IL-1 R3, IL-1 R4, IL-1 R6, IL-1 ra, IL-20 R beta, IL-22, IL-23, IL-23 R, IL-17E, IL-27, IL-2 R alpha, IL-31 RA, IL-1 F6, IL-1 F8, IL-1 F9, IL-1 F7, IL-4, IL-4 R, IL-5, IL-5 R alpha, IL-6, IL-6 R, IL-9, Activin A, Activin B, Insulin, LFA-1 alpha, MAC-1, VEGF R2, Kininostatin, Kremen-1, LBP, Lck, Lipocalin-2, LRP-1, MIF, MMP-12, MMP-2, MMP-25, HRG-alpha, PDGF-AA, PDGF-BB, PDGF R alpha, PECAM-1, PF4, uPA, uPAR, Angiostatin, Pentraxin3, EN-RAGE, SAA, E-Selectin, P-selectin, Shh-N, SIGIRR, Smad 1, TFPI, TGF-beta 1, TGF-beta 2, TGF-beta RI, Thrombospondin-1, TIMP-1, TLR1, TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TMEFF2, TSG-6, TWEAK R, TNF RI, TNF RII, OX40 Ligand, Dtk, VCAM-1, VEGF, VEGF-B, Lymphotactin |
| Proliferation | Activin RIIA, Adiponectin, Angiogenin, Angiopoietin-1, Angiopoietin-4, Amphiregulin, Artemin, Bax, BMP-2, BMP-4, BMP-5, BMP-6, BMP-7, CV-2, BMPR-IA, BMPR-IB, BMPR-II, BTC, Eotaxin, CCL14, MIP-3 beta, MCP-1, Eotaxin-2, Eotaxin-3, RANTES, MCP-2, CTGF, NOV, WISP-1, CCR2, CCR3, CD40, B7-1, VE-Cadherin, Cerberus 1, CLC, CNTF, CNTF R alpha, Endostatin, Cripto-1, TSLP R, M-CSF, M-CSF R, GM-CSF, GM-CSF R alpha, GCSF, G-CSF R, Csk, Cardiotrophin-1, CTLA-4, beta-Catenin, Fractalkine, GRO-a, IP-10, I-TAC, SDF-1, ENA-78, IL-8, MIG, CXCR2, CXCR3, Endothelin, EGF, EGF R, Endoglin, Erythropoietin, ErbB2, ErbB3, ErbB4, Epiregulin, Endocan, F3, FADD, Fas Ligand, DANCE, FGF-10, FGF-13 1B, FGF-16, FGF-17, FGF-18, FGF-19, FGF Basic, FGF-20, FGF-21, FGF-23, FGF-4, FGF-5, FGF-6, FGF-7, FGF-8, FGF-9, FGF-BP, FGF R3, FGF R4, FGF R5, Hepassocin, VEGF R3, Follistatin, Frizzled-3, Frizzled-4, Frizzled-5, Frizzled-6, Frizzled-7, GDF11, GDF5, GDF9, GDNF, GHR, Glypican 3, Osteoactivin, GREMLIN, Progranulin, HB-EGF, HGF, IFN-beta, IFN-gamma, IGF-I, IGF-I R, IGF-II, IGFBP-2, IGFBP-3, IGFBP-4, IGFBP-6, IGFBP-rp1, IL-10, IL-11, IL-12 p70, IL-12 p40, IL-12 R beta 1, IL-12 R beta 2, IL-13, IL-13 R alpha 2, IL-15, IL-17, IL-18 R beta, IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-2, IL-20 R beta, IL-21, IL-23, IL-23 R, IL-24, IL-26, IL-27, IL-2 R alpha, IL-3, IL-31 RA, IL-3 R alpha, IL-4, IL-5, IL-5 R alpha, IL-6, IL-6 R, sgp130, IL-7, IL-7 R alpha, IL-9, Activin A, Insulin, Insulin R, VEGF R2, SCF, Leptin, Leptin R, Galectin-3, LIF, LIF R alpha, MIF, MMP-12, MMP-14, MMP-16, MMP-2, MMP-7, MMP-9, beta-NGF, NGF R, HRG-alpha, Neuropilin-2, NT-3, OSM, Osteocrin, PDGF-AA, PDGF-BB, PDGF-C, PDGF-D, PDGF R alpha, PDGF R beta, PF4, PlGF, uPA, Angiostatin, Prolactin, EG-VEGF, RELM beta, EDG-1, sFRP-1, sFRP-4, Shh-N, SLPI, Smad 1, Smad 4, Smad 7, SPARC, TGF-alpha, TGF-beta 1, TGF-beta 2, TGF-beta 3, TGF-beta RI, TGF-beta RII, TGF-beta RIII, Thrombospondin-1, Thrombospondin-4, Thrombopoietin, Tie-1, TIMP-1, TLR4, HVEM, TNF RII, DR6, TRANCE, TWEAK, OX40 Ligand, VCAM-1, VEGF, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, Lymphotactin |
| Cell Migration | D6, Activin RIA, Activin RIB, Angiogenin, Angiopoietin-1, Angiopoietin-2, Angiopoietin-4, Artemin, Axl, Bax, BMP-2, BMP-4, BMP-5, BMP-7, CV-2, BMPR-II, I-309, Eotaxin, MCP-4, CCL14, MIP-1d, HCC-4, Tarc, PARC, MIP-3 beta, MCP-1, MIP-3 alpha, MDC, Eotaxin-2, TECK, Eotaxin-3, CTACK, CCL28, MIP-1a, MIP-1b, RANTES, MCP-3, MCP-2, CTGF, NOV, WISP-1, CCR1, CCR2, CCR3, CCR4, CCR5, CCR6, CCR7, CCR8, CCR9, HCR, CD40, VE-Cadherin, Cerberus 1, Cripto-1, M-CSF, M-CSF R, GM-CSF, G-CSF R, beta-Catenin, Fractalkine, GRO-a, IP-10, I-TAC, SDF-1, BLC, CXCL14, CXCL16, MIP 2, GRO, ENA-78, GCP-2, IL-8, MIG, CXCR1, CXCR2, CXCR3, CXCR4, CXCR5, CXCR6, Decorin, Endothelin, EGF, EGF R, Endoglin, ErbB4, FACX, F3, FADD, FGF-10, FGF-13 1B, FGF-16, FGF-18, FGF-19, FGF Basic, FGF-4, FGF-7, FGF-8, FGF-9, FGF-BP, FGF R4, VEGF R3, Follistatin-like 1, Frizzled-3, Frizzled-4, GDF-15, GDNF, GFR alpha-1, GFR alpha-3, Glypican 3, Glypican 5, Osteoactivin, GREMLIN, Progranulin, HB-EGF, HGF, ICAM-1, IFN-gamma, IGF-I, IGF-I R, IGFBP-6, IL-10, IL-12 p70, IL-12 p40, IL-16, IL-17, IL-17R, IL-17RC, IL-1 beta, IL-1 RI, IL-23, TCCR, IL-4, IL-6, IL-6 R, Insulin, Insulin R, LFA-1 alpha, VEGF R2, SCF, LBP, Lck, Lipocalin-2, Leptin, Galectin-3, HGFR, MIF, MMP-12, MMP-14, MMP-2, MMP-7, MMP-9, DAN, NrCam, NRG3, Neuropilin-2, Neurturin, NT-3, PDGF-AA, PDGF-BB, PDGF-C, PDGF-D, PDGF R alpha, PDGF R beta, PECAM-1, PF4, PlGF, uPA, Angiostatin, ROBO4, EN-RAGE, EDG-1, SAA, E-Selectin, L-Selectin, P-selectin, Shh-N, Smad 4, SPARC, TGF-beta 1, TGF-beta 2, TGF-beta RI, TGF-beta RII, TGF-beta RIII, Thrombospondin-1, Thrombospondin-4, TLR4, TMEFF2, TSG-6, TWEAK R, HVEM, TRANCE, TWEAK, TRADD, TREM-1, Dtk, VCAM-1, VEGF, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, Lymphotactin |
| Tissue Remodeling | Axl, Bax, BMPR-II, CCR2, M-CSF R, Csk, beta-Catenin, FGF-10, FGF-8, VEGF R3, GDF5, Osteoactivin, GREMLIN, IGF-I, IL-12 p40, IL-15, IL-1 alpha, IL-2, IL-20 R alpha, IL-21, IL-23, IL-6, IL-7, Leptin, Leptin R, LIF, MMP-14, MMP-2, Angiostatin, EDG-1, sFRP-1, TGF-beta 1, TGF-beta 2, Thrombospondin-4, Tie-1, TIMP-1, TRANCE |
| Epithelialization | sFRP-1, GDF5, MMP-12, Eotaxin-2, SPARC, MCP-1, IL-12 p40, ErbB4, Tie-1, Endoglin, Thrombospondin-1, TGF-beta RIII, Frizzled-7, Eotaxin-3, VEGF-C, VEGF-B, IL-10, CXCR3, IL-26, TGF-beta 2, SDF-1, Angiogenin, F3, Thrombospondin-4, IL-12 p70, Prolactin, PDGF-BB, NGF R, ErbB3, IGF-II, Neuropilin-2, FGF-18, FGF-16, VEGF R3, TWEAK, BMP-6, BMP-5, FGF-BP, Angiopoietin-1, ErbB2, CCR3, Eotaxin, Leptin, BMPR-IA, RANTES, RELM beta, HGF, EGF R, Glypican 3, TGF-beta 1, EGF, Progranulin, VEGF R2, Shh-N, Epiregulin, IGFBP-3, TRANCE, TGF-beta RI, Hepassocin, IGFBP-4, FGF Basic, EG-VEGF, FGF-10, FGF-7, Angiopoietin-4, Activin RIIA, IL-17, IGF-I, CV-2, MMP-14, beta-Catenin, BMP-4, Bax, Follistatin, TGF-alpha, NOV, Amphiregulin, VEGF, IL-6, FGF-9, BMPR-II |
| Innate Immune Response | B7-1, MMP-12, GCSF, MMP-8, Adiponectin, IL-24, IL-10 R alpha, FGF-10, Frizzled-5, GM-CSF, IL-18 BPa, FGF-19, Glypican 3, Bax, VEGF-D, IL-12 R beta 2, MMP-9, G-CSF R, Activin A, Activin B, IL-17B R, MCP-3, MCP-2, TMEFF1, CNTF, Smad 1, CCR5, CCR6, MDC, IL-1 F10, D6, CXCR6, E-Selectin, TRAIL R2, GRO-a, IL-1 R4, IL-10 R beta, M-CSF, GRO, MIP 2, Tarc, Pentraxin3, Eotaxin-2, PF4, IL-17C, RANTES, MCP-1, IL-4 R, VCAM-1, IL-5 R alpha, TLR1, MMP-3, Fractalkine, CXCR4, HCC-4, TECK, IL-18 R alpha, MIF, IL-22, MIP-1b, FADD, IP-10, CCL28, Galectin-3, TSG-6, MMP-25, Thrombospondin-1, HCR, Insulin, IL-1 F9, IL-1 F8, IL-1 F7, IL-27, CXCL14, IL-18 R beta, Eotaxin-3, TNF RII, Axl, IFN-alpha/beta R2, CTACK, CCR2, I-309, ENA-78, CXCR3, CXCL16, SAA, IL-17B, IL-31 RA, Lymphotactin, IL-1 F6, IL-8, LFA-1 alpha, IFN-alpha/beta R1, MIP-1d, CCL14, IL-1 R3, SDF-1, Fas Ligand, IFN-gamma R1, IL-9,Cripto-1, OX40 Ligand, I-TAC, M-CSF R, F3, IL-13, LRP-1, TIMP-1, BMP-2, IL-17D, IL-17E, Granzyme A, CXCR2, PARC, CD14, MIG, IL-1 ra, MAC-1, BMPR-IB, Kininostatin, IL-2 R alpha, Erythropoietin, IL-1 alpha, IFN-gamma, IFN-beta, IL-5, IL-4, SIGIRR, MIP-1a, CD40, Activin RIA, Grb2, Endothelin, BMP-6, CCR7, CCR1, IL-12 R beta 1, MCP-4, MIP-3 beta, IL-20 R beta, CCR9, CCR4, CCR3, Eotaxin, IL-1 RI, IL-21, CD 163, IL-1 R6, TNF RI, TLR3, IL-10, BLC, MICA, MIP-3 alpha, Lipocalin-2, SLPI, EN-RAGE, IL-17R, IL-17RC, TGF-beta 1, GCP-2, IL-7 R alpha, TCCR, Angiogenin, TLR2, IL-12 p70, IL-1 beta, IL-22 R, TLR4, HVEM, MMP-7, DEFA5, P-selectin, IL-12 p40, BD-1, IL-23, IL-17F, IL-17, IL-6 R, LBP, IL-23 R, IL-6, TREM-1, Progranulin |
References
- Silini, A.R.; Cargnoni, A.; Magatti, M.; Pianta, S.; Parolini, O. The Long Path of Human Placenta, and Its Derivatives, in Regenerative Medicine. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protzman, N.M.; Mao, Y.; Long, D.; Sivalenka, R.; Gosiewska, A.; Hariri, R.J.; Brigido, S.A. Placental-Derived Biomaterials and Their Application to Wound Healing: A Review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Rajasekaran, R.; Saha, B.; Dixit, K.; Vaidya, P.V.; Ojha, A.K.; Dhara, S. Human placenta/umbilical cord derivatives in regenerative medicine-Prospects and challenges. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 4789–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.C.; Van De Walle, A.; Chang, J.; Juran, C.; McFetridge, P.S. Human Perinatal-Derived Biomaterials. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, O.B.; Rakosi, A.; Macquhae, F.; Herskovitz, I.; Fox, J.D.; Kirsner, R.S. A Review of Cellular and Acellular Matrix Products: Indications, Techniques, and Outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 138, 138S–147S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Carter, M.; Cole, W.; Crombie, R.; Kapp, D.L.; Kim, P.; Milne, C.; Molnar, J.; Niezgoda, J.; Woo, K.; et al. Best practice for wound repair and regeneration use of cellular, acellular and matrix-like products (CAMPs). J. Wound Care 2023, 32, S1–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Mantay, M.; Brannan, C.; Griffiths, S. Placental Tissues as Biomaterials in Regenerative Medicine. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 6751456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyen, M.L.; Ferguson, V.L.; Calvin, S.E. Fracture Resistance of Human Amnion. Am. Soceity Mech. Eng. 2007, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Griffiths, S. Intermediate layer contribution in placental membrane allografts. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2020, 14, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, A.K.; Dalvi, Y.B.; Balram, B.; Kj, N.; Anil, S. Amnion and Chorion Membranes for Root Coverage Procedures: An In Vitro Evaluation of its Physical Characteristics. Periodontics Prosthodont. 2018, 4, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, J.F., 3rd. Extracellular matrix dynamics and fetal membrane rupture. Reprod. Sci. 2013, 20, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, T.J.; Rennert, R.; Zabek, N.; Massee, M.; Lim, J.J.; Temenoff, J.S.; Li, W.W.; Gurtner, G. Biological properties of dehydrated human amnion/chorion composite graft: Implications for chronic wound healing. Int. Wound J. 2013, 10, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonvallet, P.P.; Damaraju, S.M.; Modi, H.N.; Stefanelli, V.L.; Lin, Q.; Saini, S.; Gandhi, A. Biophysical Characterization of a Novel Tri-Layer Placental Allograft Membrane. Adv. Wound Care 2022, 11, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Easley, A.; Menchaca, K.T.; Fanniel, V.; Gomez, R.; Marquez, J.; Hill, S. Comparative Study of Placental Allografts with Distinct Layer Composition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzell, B.; Ork, B.; Softic, D.; Morse, J.; Hutchens, W.; Meng, F.; McLean, J.B.; Moore, M.A.; Qin, X. Characterization of a full-thickness decellularized and lyophilized human placental membrane for clinical applications. Int. Wound J. 2024, 21, e14888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamede, A.C.; Carvalho, M.J.; Abrantes, A.M.; Laranjo, M.; Maia, C.J.; Botelho, M.F. Amniotic membrane: From structure and functions to clinical applications. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 349, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riau, A.K.; Beuerman, R.W.; Lim, L.S.; Mehta, J.S. Preservation, sterilization and de-epithelialization of human amniotic membrane for use in ocular surface reconstruction. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, S.; Scheel, J.; Noone, A.; McElwain, C.J.; Scaife, C.; Gupta, S.; English, J.; McCarthy, C.; McCarthy, F.P. A proteomic profile of the healthy human placenta. Clin. Proteomics 2023, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkhenany, H.; El-Derby, A.; Abd Elkodous, M.; Salah, R.A.; Lotfy, A.; El-Badri, N. Applications of the amniotic membrane in tissue engineering and regeneration: The hundred-year challenge. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.P.; Kirsner, R.S. Angiogenesis in wound repair: Angiogenic growth factors and the extracellular matrix. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 60, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosique, R.G.; Rosique, M.J.; Farina Junior, J.A. Curbing Inflammation in Skin Wound Healing: A Review. Int. J. Inflam. 2015, 2015, 316235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukaegbu, K.; Allen, E.; Svoboda, K.K.H. Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidants in Wound Healing: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Int. Wound J. 2025, 22, e70330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grada, A.; Otero-Vinas, M.; Prieto-Castrillo, F.; Obagi, Z.; Falanga, V. Research Techniques Made Simple: Analysis of Collective Cell Migration Using the Wound Healing Assay. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, e11–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- auf dem Keller, U.; Kumin, A.; Braun, S.; Werner, S. Reactive oxygen species and their detoxification in healing skin wounds. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2006, 11, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eming, S.A.; Krieg, T.; Davidson, J.M. Inflammation in wound repair: Molecular and cellular mechanisms. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, A.S.; Mansbridge, J.N. The Innate Immune System in Acute and Chronic Wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2016, 5, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landen, N.X.; Li, D.; Stahle, M. Transition from inflammation to proliferation: A critical step during wound healing. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakyari, M.; Farrokhi, A.; Maharlooei, M.K.; Ghahary, A. Critical Role of Transforming Growth Factor Beta in Different Phases of Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2013, 2, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousselle, P.; Braye, F.; Dayan, G. Re-epithelialization of adult skin wounds: Cellular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 146, 344–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhajj, M.; Goyal, A. Physiology, Granulation Tissue. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- McQuilling, J.P.; Vines, J.B.; Kimmerling, K.A.; Mowry, K.C. Proteomic Comparison of Amnion and Chorion and Evaluation of the Effects of Processing on Placental Membranes. Wounds 2017, 29, E36–E40. [Google Scholar]
- Nazari Hashemi, P.; Chaventre, F.; Bisson, A.; Gueudry, J.; Boyer, O.; Muraine, M. Mapping of proteomic profile and effect of the spongy layer in the human amniotic membrane. Cell Tissue Bank. 2020, 21, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, T.J.; Lim, J.J.; Zabek, N.; Massee, M. Cytokines in single layer amnion allografts compared to multilayer amnion/chorion allografts for wound healing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuilling, J.P.; Burnette, M.; Kimmerling, K.A.; Kammer, M.; Mowry, K.C. A mechanistic evaluation of the angiogenic properties of a dehydrated amnion chorion membrane in vitro and in vivo. Wound Repair. Regen. 2019, 27, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, T.J.; Lim, J.J.; Massee, M.; Zabek, N.; Rennert, R.; Gurtner, G.; Li, W.W. Angiogenic properties of dehydrated human amnion/chorion allografts: Therapeutic potential for soft tissue repair and regeneration. Vasc. Cell 2014, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQuilling, J.P.; Vines, J.B.; Mowry, K.C. In vitro assessment of a novel, hypothermically stored amniotic membrane for use in a chronic wound environment. Int. Wound J. 2017, 14, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Jiang, S.; Du, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Lu, X.; Ma, L.; Zhu, H.; Wei, J.; Yu, Y. Conditioned medium from primary cytotrophoblasts, primary placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells, or sub-cultured placental tissue promoted HUVEC angiogenesis in vitro. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, D.; Son, H.; Gsponer, J. Categorizer: A tool to categorize genes into user-defined biological groups based on semantic similarity. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute, E.B. QuickGO: Gene Ontology Browser. Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/QuickGO/ (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Consortium, G.O. Downloads-Gene Ontology Consortium. Available online: https://current.geneontology.org/products/pages/downloads.html (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Carpentier, G.; Berndt, S.; Ferratge, S.; Rasband, W.; Cuendet, M.; Uzan, G.; Albanese, P. Angiogenesis Analyzer for ImageJ-A comparative morphometric analysis of “Endothelial Tube Formation Assay” and “Fibrin Bead Assay”. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Association of Tissue Banks. Standards for Tissue Banking, 14th ed.; American Association of Tissue Banks: Arlington, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
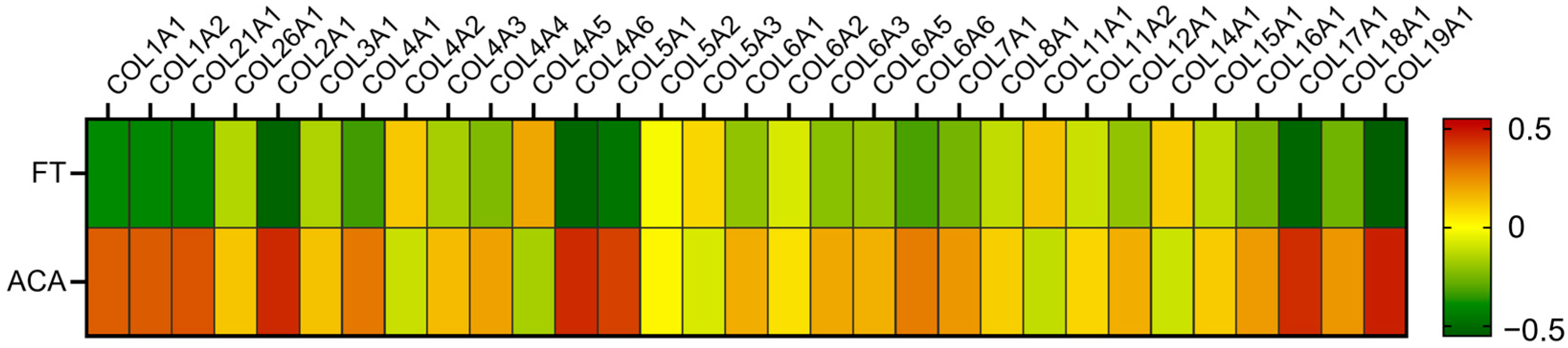

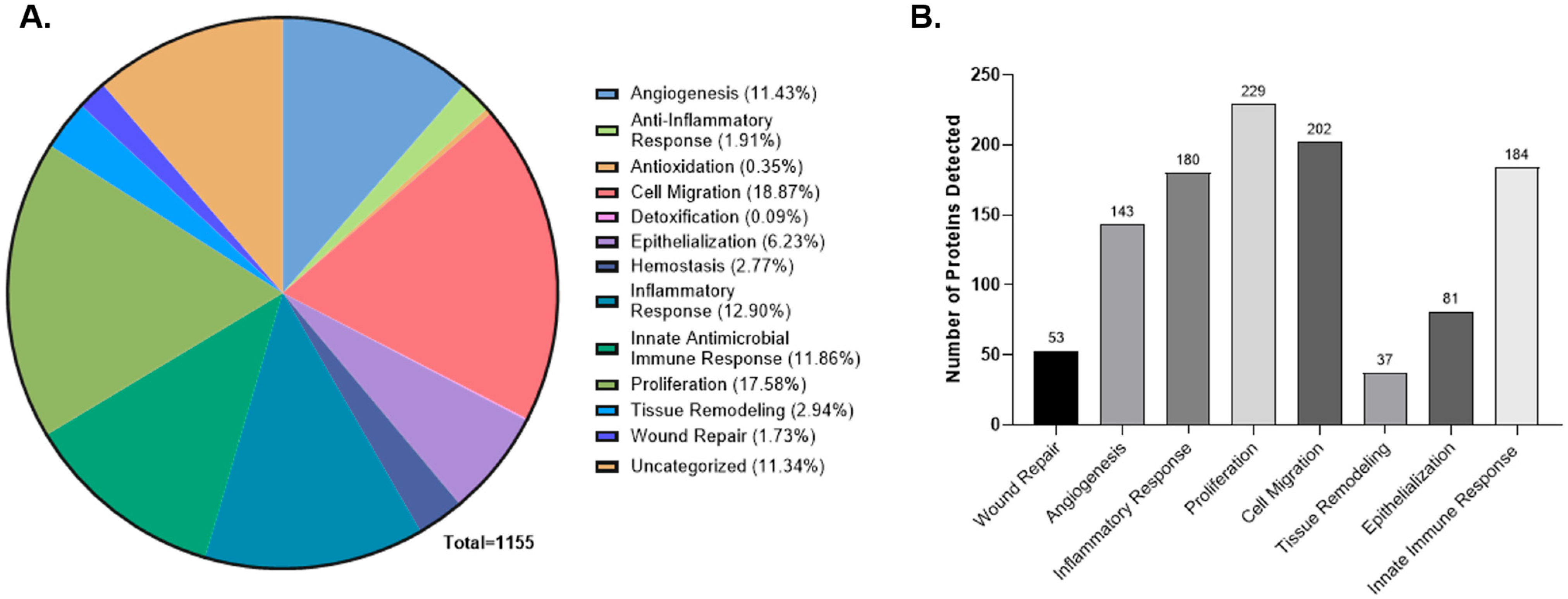
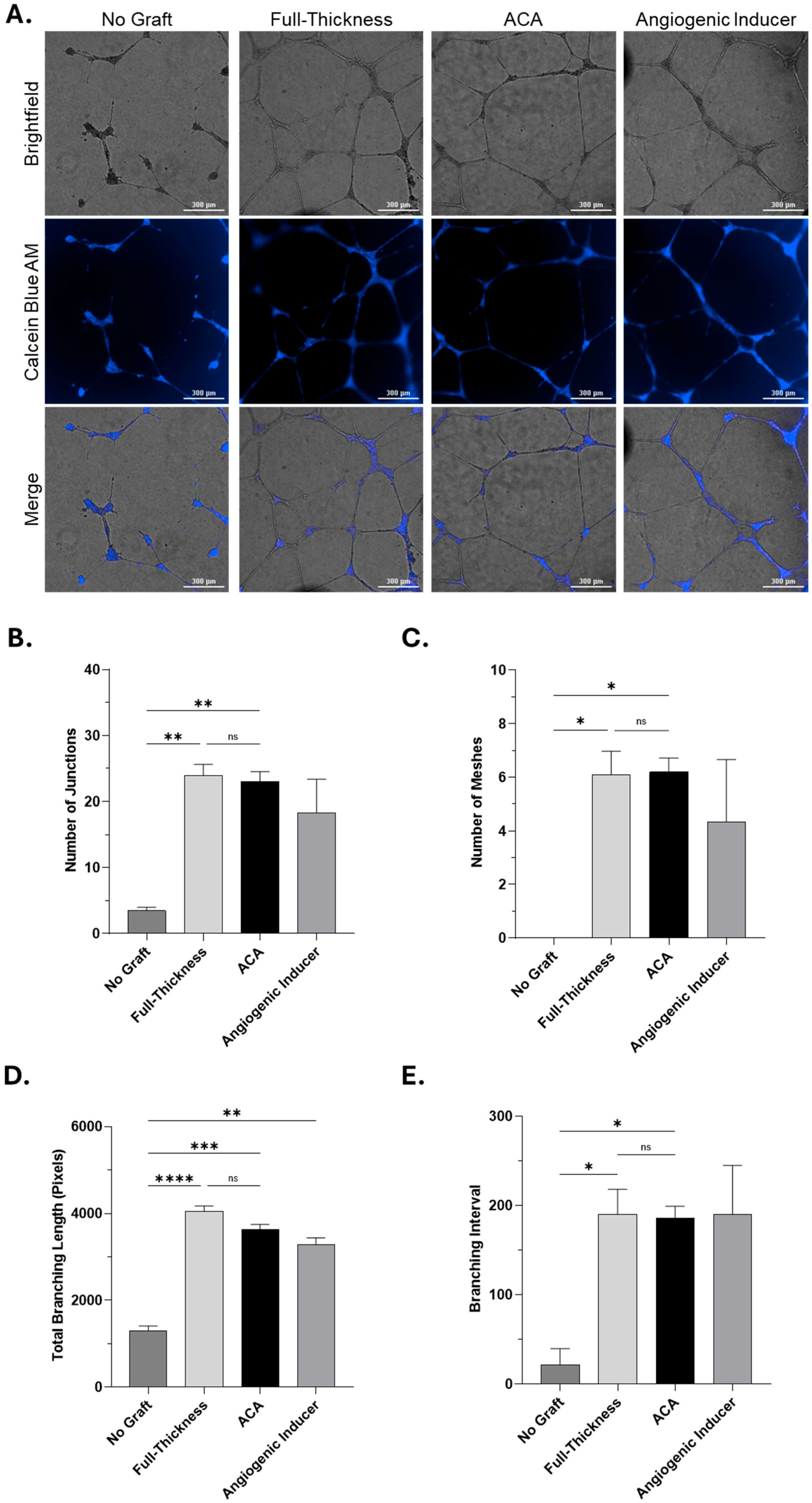
| Mechanisms | GO Pathways [Pathway Identifier (Description)] |
|---|---|
| Wound Repair | GO:0042060 (wound healing); GO:1903689 (regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells); GO:0035313 (wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells); GO:0061045 (negative regulation of wound healing); GO:0090303 (positive regulation of wound healing) |
| Angiogenesis | GO:0001525 (angiogenesis); GO:0048646 (anatomical structure formation involved in morphogenesis); GO:0048514 (blood vessel morphogenesis); GO:0001568 (blood vessel development); GO:0001944 (vasculature development); GO:0035239 (tube morphogenesis); GO:0035295 (tube development); GO:0060055 (angiogenesis involved in wound healing); GO:0061042 (vascular wound healing); GO:0061043 (regulation of vascular wound healing); GO:0002040 (sprouting angiogenesis); GO:1903672 (positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis); GO:1903670 (regulation of sprouting angiogenesis); GO:1903671 (negative regulation of sprouting angiogenesis); GO:0001569 (branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis); GO:1905553 (regulation of blood vessel branching); GO:1905554 (negative regulation of blood vessel branching); GO:1905555 (positive regulation of blood vessel branching); GO:0045766 (positive regulation of angiogenesis); GO:0016525 (negative regulation of angiogenesis); GO:0045765 (regulation of angiogenesis); GO:1903672 (positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis); GO:1905555 (positive regulation of blood vessel branching); GO:0035470 (positive regulation of vascular wound healing) |
| Hemostasis | GO:0007599 (hemostasis); GO:0007596 (blood coagulation); GO:0072378 (blood coagulation, fibrin clot formation); GO:0072377 (blood coagulation, common pathway); GO:0030194 (positive regulation of blood coagulation); GO:1900047 (negative regulation of hemostasis); GO:1900046 (regulation of hemostasis); GO:1900048 (positive regulation of hemostasis); GO:0030195 (negative regulation of blood coagulation); GO:0071892 (thrombocyte activation); GO:0030193 (regulation of blood coagulation); GO:0030168 (platelet activation); GO:2000268 (positive regulation of blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway); GO:2000265 (positive regulation of blood coagulation, extrinsic pathway); GO:2000262 (positive regulation of blood coagulation, common pathway); GO:0002543 (activation of blood coagulation via clotting cascade) |
| Inflammatory Response | GO:0006954 (inflammatory response); GO:0090594 (inflammatory response to wounding); GO:0002544 (chronic inflammatory response); GO:0002526 (acute inflammatory response); GO:0002246 (wound healing involved in inflammatory response); GO:0002247 (clearance of damaged tissue involved in inflammatory response wound healing); GO:0106015 (negative regulation of inflammatory response to wounding); GO:0106016 (positive regulation of inflammatory response to wounding); GO:0106014 (regulation of inflammatory response to wounding); GO:1903034 (regulation of response to wounding); GO:0061041 (regulation of wound healing); GO:1903036 (positive regulation of response to wounding); GO:1903035 (negative regulation of response to wounding); GO:0009611 (response to wounding) |
| Proliferation | GO:0008283 (cell population proliferation); GO:0008284 (positive regulation of cell population proliferation); GO:0008285 (negative regulation of cell population proliferation); GO:0042127 (regulation of cell population proliferation); GO:0002043 (blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis); GO:0048144 (fibroblast proliferation); GO:0048145 (regulation of fibroblast proliferation); GO:0048146 (positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation); GO:0048147 (negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation) |
| Cell Migration | GO:0016477 (cell migration); GO:0048870 (cell motility); GO:0002042 (cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis); GO:0044319 (wound healing, spreading of cells); GO:0035313 (wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells); GO:1903689 (regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells); GO:1903691 (positive regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells); GO:1903690 (negative regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells); GO:0040039 (inductive cell migration); GO:0050900 (leukocyte migration); GO:0030595 (leukocyte chemotaxis); GO:0002685 (regulation of leukocyte migration); GO:0002523 (leukocyte migration involved in inflammatory response); GO:0035701 (hematopoietic stem cell migration); GO:2000471 (regulation of hematopoietic stem cell migration); GO:2000473 (positive regulation of hematopoietic stem cell migration); GO:2000472 (negative regulation of hematopoietic stem cell migration); GO:0038089 (positive regulation of cell migration by vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway); GO:0038033 (positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis by VEGF-activated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway); GO:0038090 (positive regulation of cell migration by VEGF-activated platelet derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway); GO:0030335 (positive regulation of cell migration); GO:1904849 (positive regulation of cell chemotaxis to fibroblast growth factor); GO:0010595 (positive regulation of endothelial cell migration); GO:1904859 (positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis to vascular endothelial growth factor); GO:0010634 (positive regulation of epithelial cell migration); GO:0010763 (positive regulation of fibroblast migration); GO:1905212 (positive regulation of fibroblast chemotaxis); GO:0043542 (endothelial cell migration); GO:0043534 (blood vessel endothelial cell migration); GO:0035767 (endothelial cell chemotaxis); GO:0010594 (regulation of endothelial cell migration); GO:0060326 (cell chemotaxis); GO:1990956 (fibroblast chemotaxis); GO:0035441 (cell migration involved in vasculogenesis) |
| Tissue Remodeling | GO:0048771 (tissue remodeling; GO:0034103 (regulation of tissue remodeling); GO:0002248 (connective tissue replacement involved in inflammatory response wound healing); GO:1904596 (regulation of connective tissue replacement involved in inflammatory response wound healing); GO:0001974 (blood vessel remodeling); GO:0060312 (regulation of blood vessel remodeling); GO:0060313 (negative regulation of blood vessel remodeling); GO:2000504 (positive regulation of blood vessel remodeling); GO:0034105 (positive regulation of tissue remodeling); GO:0034104 (negative regulation of tissue remodeling); GO:1905205 (positive regulation of connective tissue replacement); GO:1905204 (negative regulation of connective tissue replacement); GO:0034102 (erythrocyte clearance); GO:0034106 (regulation of erythrocyte clearance); GO:0034107 (negative regulation of erythrocyte clearance); GO:0034108 (positive regulation of erythrocyte clearance); GO:0097709 (connective tissue replacement); GO:1905204 (negative regulation of connective tissue replacement); GO:1905205 (positive regulation of connective tissue replacement); GO:0002247 (clearance of damaged tissue involved in inflammatory response wound healing); GO:1904598 (positive regulation of connective tissue replacement involved in inflammatory response wound healing); GO:1904597 (negative regulation of connective tissue replacement involved in inflammatory response wound healing) |
| Epithelialization | GO:0043616 (keratinocyte proliferation); GO:0010837 (regulation of keratinocyte proliferation); GO:0010838 (positive regulation of keratinocyte proliferation); GO:0010839 (negative regulation of keratinocyte proliferation); GO:0050678 (regulation of epithelial cell proliferation); GO:0050680 (negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation); GO:0050679 (positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation); GO:0050678 (regulation of epithelial cell proliferation); GO:0050673 (epithelial cell proliferation) |
| Anti-Inflammatory Response | GO:0050728 (negative regulation of inflammatory response); GO:0002674 (negative regulation of acute inflammatory response); GO:0106015 (negative regulation of inflammatory response to wounding) |
| Antioxidation Activity | GO:0016209 (antioxidant activity); GO:0098869 (cellular oxidant detoxification); GO:0019430 (removal of superoxide radicals); GO:1904832 (negative regulation of removal of superoxide radicals); GO:1904833 (positive regulation of removal of superoxide radicals); GO:2000121 (regulation of removal of superoxide radicals); GO:0061692 (cellular detoxification of hydrogen peroxide); GO:0004601 (peroxidase activity); GO:0050605 (superoxide reductase activity); GO:0004784 (superoxide dismutase activity); GO:0032542 (sulfiredoxin activity); GO:0004791 (thioredoxin-disulfide reductase (NADPH) activity); GO:0045174 (glutathione dehydrogenase (ascorbate) activity); GO:0004362 (glutathione-disulfide reductase (NADPH) activity) |
| Detoxification | GO:1990748 (cellular detoxification); GO:0098754 (detoxification); GO:0097237 (cellular response to toxic substance); GO:0110052 (toxic metabolite repair); GO:0070458 (cellular detoxification of nitrogen compound) |
| Innate Antimicrobial Immune Response | GO:0045087 (innate immune response); GO:0140546 (defense response to symbiont); GO:0098542 (defense response to other organism); GO:0051707 (response to other organism); GO:0043207 (response to external biotic stimulus); GO:0006952 (defense response); GO:0042742 (defense response to bacterium); GO:0050832 (defense response to fungus); GO:0140367 (antibacterial innate immune response); GO:1900425 (negative regulation of defense response to bacterium); GO:1900426 (positive regulation of defense response to bacterium); GO:0050830 (defense response to Gram-positive bacterium); GO:0070944 (neutrophil-mediated killing of bacterium); GO:0050829 (defense response to Gram-negative bacterium); GO:1900424 (regulation of defense response to bacterium); GO:0070947 (neutrophil-mediated killing of fungus); GO:0061760 (antifungal innate immune response); GO:1900150 (regulation of defense response to fungus); GO:0140976 (host defense response against symbiont-mediated perturbation of plasma membrane integrity); GO:0034050 (symbiont-induced defense-related programmed cell death) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, P.; Guha, S.; Landa, O.; King, A.R.; Valdes Cavazos, D.; Marquez, J.; Hill, S. Native Wound-Repair Proteins Retained in Multilayer Placental CAMPs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010121
Singh P, Guha S, Landa O, King AR, Valdes Cavazos D, Marquez J, Hill S. Native Wound-Repair Proteins Retained in Multilayer Placental CAMPs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010121
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Pragya, Shantanu Guha, Odalis Landa, Andrew Ryan King, Diego Valdes Cavazos, Joanna Marquez, and Shauna Hill. 2025. "Native Wound-Repair Proteins Retained in Multilayer Placental CAMPs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010121
APA StyleSingh, P., Guha, S., Landa, O., King, A. R., Valdes Cavazos, D., Marquez, J., & Hill, S. (2025). Native Wound-Repair Proteins Retained in Multilayer Placental CAMPs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010121






