Therapeutic Potential and Cancer Cell Death-Inducing Effects of Apigenin and Its Derivatives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pharmacological Properties
2.1. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
2.2. Anticancer Properties
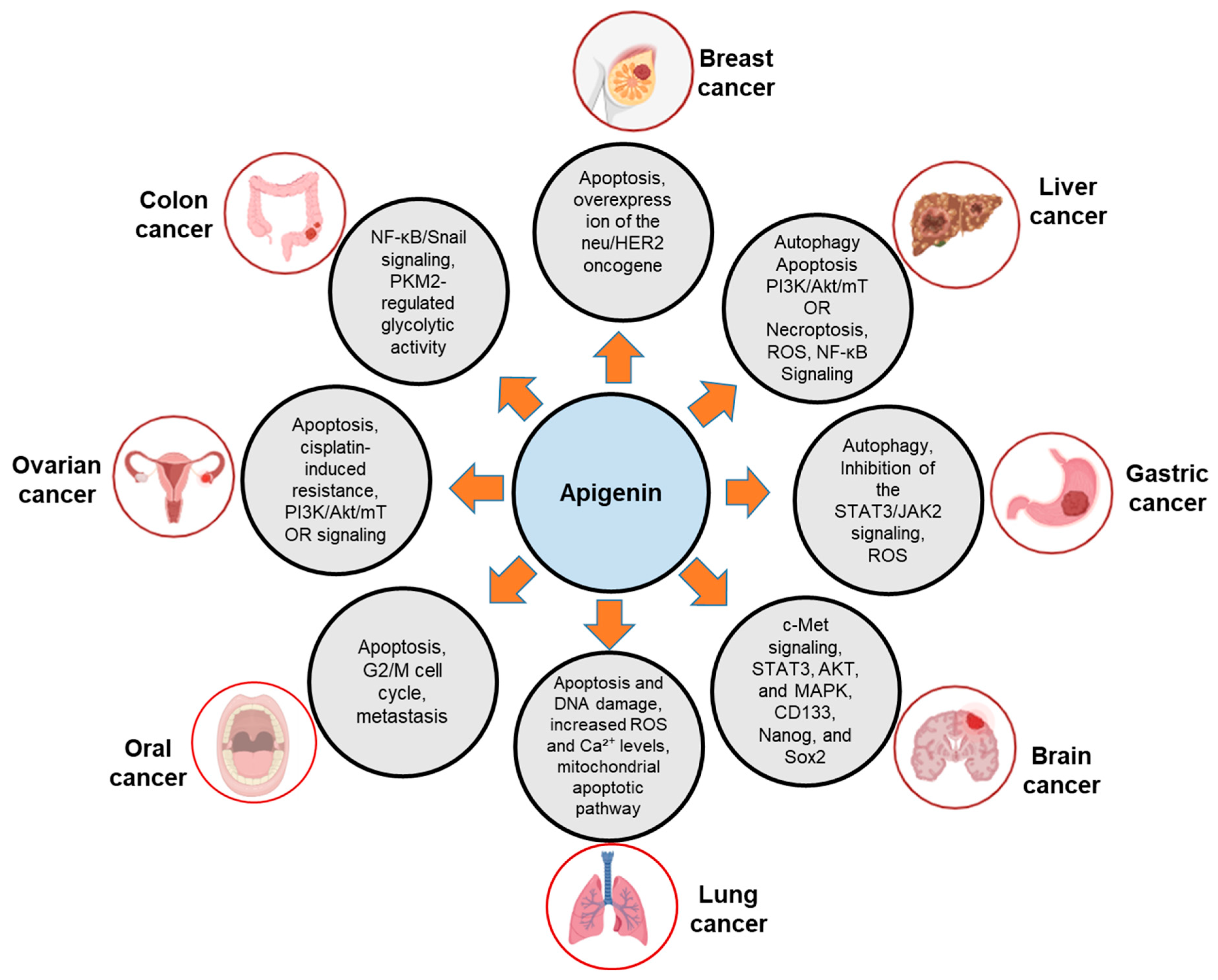
2.2.1. Anti-Breast Cancer Activity
2.2.2. Anti-Liver Cancer Activity
2.2.3. Anti-Gastric Cancer Activity
2.2.4. Anti-Brain Cancer Activity
2.2.5. Anti-Lung Cancer Activity
2.2.6. Anti-Oral Cancer Activity
2.2.7. Anti-Ovarian and Anti-Cervical Cancer Activity
2.2.8. Anti-Colon Cancer Activity
2.3. Regulation of Signaling Pathways in Cancer Therapy
2.3.1. ERK/MAPK Signaling Pathway
2.3.2. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway
2.3.3. NF-κB Signaling Pathway
2.3.4. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling
3. Synergistic Effect
4. Bioavailability
5. Clinical Trials and Patents
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Jakstas, V.; Savickas, A.; Bernatoniene, J. Flavonoids as anticancer agents. Nutrients 2020, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, B.; Venditti, A.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Kręgiel, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B.; Novellino, E.; et al. The Therapeutic Potential of Apigenin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Aslam Gondal, T.; Atif, M.; Shahbaz, M.; Batool Qaisarani, T.; Hanif Mughal, M.; Salehi, B.; Martorell, M.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Apigenin as an Anticancer Agent. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1812–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Feng, X.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lan, Y.; Tang, R.; Jiang, T.; Zheng, L.; Liu, G. Apigenin as an Emerging Hepatoprotective Agent: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1508060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, G.; Yin, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, N.; Peng, J. Apigenin-7-Glucoside-Loaded Nanoparticle Alleviates Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion by ATF3/SLC7A11-Mediated Ferroptosis. J. Control. Release 2024, 366, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaye, P.M.; Mojaveri, M.R.; Ahmadian, R.; Jahromi, M.S.; Bahramsoltani, R. Apigenin and Its Dermatological Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Phytochemistry 2022, 203, 113390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ran, H.; Feng, Q.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, S.; Sun, Y.; Hou, D. Unveiling the Differences between Vitexin and Isovitexin: From the Perspective of Sources, Green Advanced Extraction Technologies, Biological Activities, and Safety. Food Chem. 2025, 485, 144600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S.J.; Crespo, J.F.; Cabanillas, B. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Flavonoids. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim, K.E.; Tagliaferro, A.R.; Bobilya, D.J. Flavonoid Antioxidants: Chemistry, Metabolism and Structure–Activity Relationships. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birt, D.F.; Hendrich, S.; Wang, W. Dietary Agents in Cancer Prevention: Flavonoids and Isoflavonoids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 90, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foti, M.C. Antioxidant Properties of Phenols. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 1673–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leopoldini, M.; Russo, N.; Toscano, M. The Molecular Basis of Working Mechanism of Natural Polyphenolic Antioxidants. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 288–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.S.; Mantas, A.; Chass, G.A.; Ferretti, F.H.; Estrada, M.; Zamarbide, G.; Csizmadia, I.G. Ab Initio and DFT Conformational Analysis of Selected Flavones: 5,7-Dihydroxyflavone (Chrysin) and 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone. Can. J. Chem. 2002, 80, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Min, J.-W.; Kong, W.-L.; He, X.-H.; Li, J.-X.; Peng, B.-W. A review on the pharmacological effects of vitexin and isovitexin. Phytother. Res 2016, 115, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.T.; Chen, C.T.; Chieng, K.T.; Huang, S.H.; Chiang, B.H.; Wang, L.F.; Kuo, H.S.; Lin, C.M. Inhibitory effects of a rice hull constituent on tumor necrosis factor α, prostaglandin E2, and cyclooxygenase-2 production in lipopolysaccharide-activated mouse macrophages. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1042, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Borghi, S.M.; Carvalho, T.T.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Hohmann, M.S.; Pinge-Filho, P.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Vitexin inhibits inflammatory pain in mice by targeting TRPV1, oxidative stress, and cytokines. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, C.L.; Macho, A.; Arunachalam, K.; de Almeida, D.A.T.; Rosa, S.I.G.; Pavan, E.; Balogun, S.O.; Damazo, A.S.; de Oliveira Martins, D.T. Vitexin inhibits inflammation in murine ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 97, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yu, T.; Liu, J.; Gu, L. Vitexin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by controlling the Nrf2 pathway. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196405. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.-H.; Min, S.-Y.; Yu, H.-W.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, Y.-J. Effects of apigenin on RBL-2H3, RAW264. 7, and HaCaT cells: Anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory, and skin-protective activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Youn, J.; Kim, K.; Joo, D.H.; Shin, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.K.; An, I.-S.; Kwon, S.; Youn, H.J. Apigenin inhibits UVA-induced cytotoxicity in vitro and prevents signs of skin aging in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yue, R.F.; Jin, Z.; He, L.M.; Shen, R.; Du, D.; Tang, Y.Z. Efficiency comparison of apigenin-7-O-glucoside and trolox in antioxidative stress and anti-inflammatory properties. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Najafipour, R.; Momeni, A.M.; Mirmazloomi, Y.; Moghbelinejad, S.; Medicine, C. Vitexin induces apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells through the regulation of specific miRNAs expression. Int. J. Mol. Cell. Med. 2022, 11, 197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghazy, E.; Taghi, H.S. The autophagy-inducing mechanisms of vitexin, cinobufacini, and physalis alkekengi hydroalcoholic extract against breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2022, 53, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Way, T.-D.; Kao, M.-C.; Lin, J.-K. Apigenin induces apoptosis through proteasomal degradation of HER2/neu in HER2/neu-overexpressing breast cancer cells via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4479–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-D.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.-P.; Xu, Y.-J.; Yu, Y.; Ding, Y.-J.; Yu, W.-L.; Zhang, R.-X.; Zhang, H.-M.; Du, H.-Y.J.O. Vitexin suppresses autophagy to induce apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma via activation of the JNK signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 84520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Mohan, C.D.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Rangappa, S.; Sethi, G.; Siveen, K.S.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Basappa, S.J.B. Vitexin abrogates invasion and survival of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through targeting STAT3 signaling pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 175, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Pi, C.; Wang, G.J.B. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway by apigenin induces apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, C.; Huijuan, W.; Zhao, H.; Liu, W.; Xiang, Z.; Wang, Q.J.P.-R. Apigenin, a flavonoid constituent derived from P. villosa, inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth by CyclinD1/CDK4 regulation via p38 MAPK-p21 signaling. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, P.B.; Abusaliya, A.; Kim, H.H.; Ha, S.E.; Park, M.Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Vetrivel, P.; Heo, J.D.; Kim, J.-A.; Won, C.K.J.C. Apigetrin promotes TNFα-induced apoptosis, necroptosis, G2/M phase cell cycle arrest, and ROS generation through inhibition of NF-κB pathway in Hep3B liver cancer cells. Cancers 2022, 11, 2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, P.B.; Kim, H.H.; Abusaliya, A.; Jeong, S.H.; Park, M.Y.; Kim, H.-W.; Seong, J.K.; Ahn, M.; Park, K.I.; Heo, J.D.J.B. Inhibition of cell proliferation and cell death by apigetrin through death receptor-mediated pathway in hepatocellular cancer cells. Biomedicines 2023, 13, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.W.; Lee, H.G. Apigenin induces autophagy and cell death by targeting EZH2 under hypoxia conditions in gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Lu, N.-N.; Feng, L. Apigetrin inhibits gastric cancer progression through inducing apoptosis and regulating ROS-modulated STAT3/JAK2 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 498, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, X.; Su, F.; Xu, L. Effects of vitexin, a natural flavonoid glycoside, on the proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis of human U251 glioblastoma cells. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 3129155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Li, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Jin, X. Vitexin induces G2/M-phase arrest and apoptosis via Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human glioblastoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 17, 4599–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Ding, Y.-H.; Sang, C.-S.; Lin, Z.-X.; Dong, J.; Fu, X.-A. Vitexin enhances radiosensitivity of mouse subcutaneous xenograft glioma by affecting the miR-17-5p/miR-130b-3p/PTEN/HIF-1α pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 200, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Jung, N.; Lee, S.; Sohng, J.K.; Jung, H.J. Apigenin inhibits cancer stem cell-like phenotypes in human glioblastoma cells via suppression of c-met signaling. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, H.; Luo, S. Vitexin induces apoptosis through mitochondrial pathway and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.-F.; Chie, Y.-J.; Yang, M.-S.; Lu, K.-W.; Fu, J.-J.; Yang, J.-S.; Chen, H.-Y.; Hsia, T.-C.; Ma, C.-Y.; Ip, S.-W.J.H.; et al. Apigenin induces apoptosis in human lung cancer H460 cells through caspase-and mitochondria-dependent pathways. Anticancer Res. 2011, 30, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Zha, D.; Cai, F.; Zhang, W.; He, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhuang, H.; Hua, Z.-C. Apigenin potentiates TRAIL therapy of non-small cell lung cancer via upregulating DR4/DR5 expression in a p53-dependent manner. Oncotarget 2016, 6, 35468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-H.; Cheng, C.-W.; Yang, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-S.; Hung, W.-Y.; Chow, J.-M.; Chen, P.-S.; Hsiao, M.; Lee, W.-J.; Chien, M.-H.; et al. Downregulating CD26/DPPIV by apigenin modulates the interplay between Akt and Snail/Slug signaling to restrain metastasis of lung cancer with multiple EGFR statuses. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res 2018, 37, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.-F.; Chie, Y.-J.; Yang, M.-S.; Lee, C.-S.; Fu, J.-J.; Yang, J.-S.; Tan, T.-W.; Wu, S.-H.; Ma, Y.-S.; Ip, S.-W. Apigenin induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in human lung cancer A549 cells through Bax-and Bcl-2-triggered mitochondrial pathway. Anticancer Res. 2010, 36, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Liao, P.; Pan, Y.; Chen, S.; Chou, S.; Chou, M. The novel p53-dependent metastatic and apoptotic pathway induced by vitexin in human oral cancer OC2 cells. Anticancer Res. 2013, 27, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggioni, D.; Garavello, W.; Rigolio, R.; Pignataro, L.; Gaini, R.; Nicolini, G. Apigenin impairs oral squamous cell carcinoma growth in vitro inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, N.; Guo, W.; Qi, J.; Hu, Z.; Su, S.; Tang, P.; Zhou, X. Purified vitexin compound 1 serves as a promising antineoplastic agent in ovarian cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 734708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-d.; Hu, X.-w.; Wang, Y.-t.; Fang, J. Apigenin inhibits proliferation of ovarian cancer A2780 cells through Id1. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Ding, Z.; Yao, Y.; Ren, F.; Yin, M.; Yang, S.; Chen, A. Apigenin induces apoptosis and counteracts cisplatin-induced chemoresistance via Mcl-1 in ovarian cancer cells. Front. Oncol. 2020, 20, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-W.; Meng, D.; Fang, J. Apigenin inhibited migration and invasion of human ovarian cancer A2780 cells through focal adhesion kinase. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Cheng, L.; Han, S.; Che, H. Apigenin inhibits histamine-induced cervical cancer tumor growth by regulating estrogen receptor expression. Molecules 2020, 25, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.P.; Bonfim-Mendonca, P.d.S.; Gimenes, F.; Ratti, B.A.; Kaplum, V.; Bruschi, M.L.; Nakamura, C.V.; Silva, S.O.; Maria-Engler, S.S.; Consolaro, M.E. Oxidative stress triggered by apigenin induces apoptosis in a comprehensive panel of human cervical cancer-derived cell lines. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1512745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; He, Y.; Shi, H.; Han, C.; Zhu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Hua, D. Investigating the molecular mechanism of vitexin targeting CDK1 to inhibit colon cancer cell proliferation via GEO chip data mining, computer simulation, and biological activity verification. Life Sci. 2025, 398, 1637–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, L. Apigenin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human colon cancer cells through NF-κB/Snail signaling pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sain, A.; Khamrai, D.; Kandasamy, T.; Naskar, D. Apigenin exerts anti-cancer effects in colon cancer by targeting HSP90AA1. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2025, 43, 3557–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Shi, J.; Yang, P.; Jia, B.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Apigenin restrains colon cancer cell proliferation via targeted blocking of pyruvate kinase M2-dependent glycolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8136–8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Nakai, N.; Yanagita, T.; Ando, N.; Okubo, T.; Saito, K.; Shiga, K.; Hirokawa, T.; Hara, M. Apigenin induces apoptosis by suppressing Bcl-xl and Mcl-1 simultaneously via signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling in colon cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, D. Apigenin suppresses the low oxaliplatin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via LINC00857. Front. Oncol. 2024, 13, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-J.; Pan, W.-W.; Liu, S.-B.; Shen, Z.-F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.-L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Cao, J.; Wang, J.; Lian, H. Protective effect of vitexin reduces sevoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis through HIF-1α, VEGF and p38 MAPK signaling pathway in vitro and in newborn rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 15, 3117–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Han, X.; Cheng, W.; Ni, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Song, Z. Apigenin inhibits proliferation and invasion, and induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human melanoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2277–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; MacLennan, G.T.; Fu, P.; Gupta, S. Apigenin attenuates insulin-like growth factor-I signaling in an autochthonous mouse prostate cancer model. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, H.; Chen, M.; Takahashi, H.; King, J.; Reber, H.A.; Hines, O.J.; Pandol, S.; Eibl, G. Apigenin inhibits NNK-induced focal adhesion kinase activation in pancreatic cancer cells. Pancreas 2012, 41, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Chang, C.; Lee, K.; Lin, H.; Chen, T.; Wan, L. Flavones inhibit breast cancer proliferation through the Akt/FOXO3a signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Sun, H.; Zha, W.; Cui, W.; Xu, L.; Min, Q.; Wu, J. Apigenin attenuates adriamycin-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 2590676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Vetrivel, P.; Ha, S.E.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, J.-A.; Kim, G.S. Apigetrin induces extrinsic apoptosis, autophagy and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in AGS human gastric cancer cell. Acta Gen. Subj. 2020, 83, 108427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Shankar, E.; Fu, P.; MacLennan, G.T.; Gupta, S. Suppression of NF-κB and NF-κB-regulated gene expression by apigenin through IκBα and IKK pathway in TRAMP mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuelli, L.; Benvenuto, M.; Mattera, R.; Di Stefano, E.; Zago, E.; Taffera, G.; Tresoldi, I.; Giganti, M.G.; Frajese, G.V.; Berardi, G. In vitro and in vivo anti-tumoral effects of the flavonoid apigenin in malignant mesothelioma. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Niu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shu, G.; Yin, G. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: Function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jin, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.-Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H. Vitexin protects against high glucose-induced endothelial cell apoptosis and oxidative stress via Wnt/β-catenin and Nrf2 signalling pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 130, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Song, Y.; Yao, J.; Huang, K.; Zhu, X. Apigenin suppresses colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 11, 3075–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-M.; Chen, H.-H.; Lin, C.-A.; Wu, H.-C.; Sheu, J.J.-C.; Chen, H.-J. Apigenin-induced lysosomal degradation of β-catenin in Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncotarget 2017, 7, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, A.; Farabegoli, F.; Iori, R.; Orlandi, M.; De Nicola, G.R.; Bagatta, M.; Angelino, D.; Gennari, L.; Ninfali, P. Vitexin-2-O-xyloside, raphasatin and (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate synergistically affect cell growth and apoptosis of colon cancer cells. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, H.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Huang, W. Vitexin Inhibits TNBC Progression and Metastasis by Modulating Macrophage Polarization Through EGFR Signaling. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 47, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpa, E.-S.; Emanuelli, M.; Frati, A.; Pozzi, V.; Antonini, E.; Diamantini, G.; Di Ruscio, G.; Sartini, D.; Armeni, T.; Palma, F.; et al. Betacyanins enhance vitexin-2-O-xyloside mediated inhibition of proliferation of T24 bladder cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 7, 4772–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şirin, N.; Elmas, L.; Seçme, M.; Dodurga, Y. Investigation of possible effects of apigenin, sorafenib and combined applications on apoptosis and cell cycle in hepatocellular cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 737, 144428. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; He, W.; Xia, S.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Bai, J.; Li, N.; Chen, L.; Yang, B. Apigenin enhanced antitumor effect of cisplatin in lung cancer via inhibition of cancer stem cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 73, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, K.; Banerjee, S.; Mandal, M. Dual drug loaded liposome bearing apigenin and 5-Fluorouracil for synergistic therapeutic efficacy in colorectal cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 180, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristou, F.; Anninou, N.; Koukoulis, G.; Paraskakis, S.; Sertaridou, E.; Tsalikidis, C.; Pitiakoudis, M.; Simopoulos, C.; Tsaroucha, A. Differential effects of cisplatin combined with the flavonoid apigenin on HepG2, Hep3B, and Huh7 liver cancer cell lines. Toxicol. In Vitro 2021, 866, 503352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilakarathna, S.H.; Rupasinghe, H.V. Flavonoid Bioavailability and Attempts for Bioavailability Enhancement. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3367–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Almatroodi, S.A.; Almatroudi, A.; Allemailem, K.S.; Joseph, R.J.; Khan, A.A.; Alrumaihi, F.; Alsahli, M.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Tamarix articulata Leaf Extract: An Effective Approach for Attenuation of Oxidative Stress-Mediated Diseases. Int. J. Food Sci. 2020, 24, 677–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, M.J.; Renouf, M.; Cruz-Hernandez, C.; Actis-Goretta, L.; Thakkar, S.K.; da Pinto, M. Bioavailability of Bioactive Food Compounds: A Challenging Journey to Bioefficacy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 588–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradolatto, A.; Basly, J.P.; Bergès, R.; Teyssier, C.; Chagnon, M.C.; Siess, M.H.; Canivenc-Lavier, M.C. Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism of Apigenin in Female and Male Rats after a Single Oral Administration. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, T.; Li, S. Encapsulation of Vitexin-Rhamnoside Based on Zein/Pectin Nanoparticles Improved Its Stability and Bioavailability. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100419. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, Y.; Lv, H.; Zhang, H.; Liang, T.; Zhou, G.; Huang, L.; Tian, Y.; Liang, W. Apigenin in Cancer Therapy: From Mechanism of Action to Nano-Therapeutic Agent. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 168, 113385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gates, M.A.; Tworoger, S.S.; Hecht, J.L.; De Vivo, I.; Rosner, B.; Hankinson, S.E. A Prospective Study of Dietary Flavonoid Intake and Incidence of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 2225–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lee, I.M.; Zhang, S.M.; Blumberg, J.B.; Buring, J.E.; Sesso, H.D. Dietary Intake of Selected Flavonols, Flavones, and Flavonoid-Rich Foods and Risk of Cancer in Middle-Aged and Older Women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
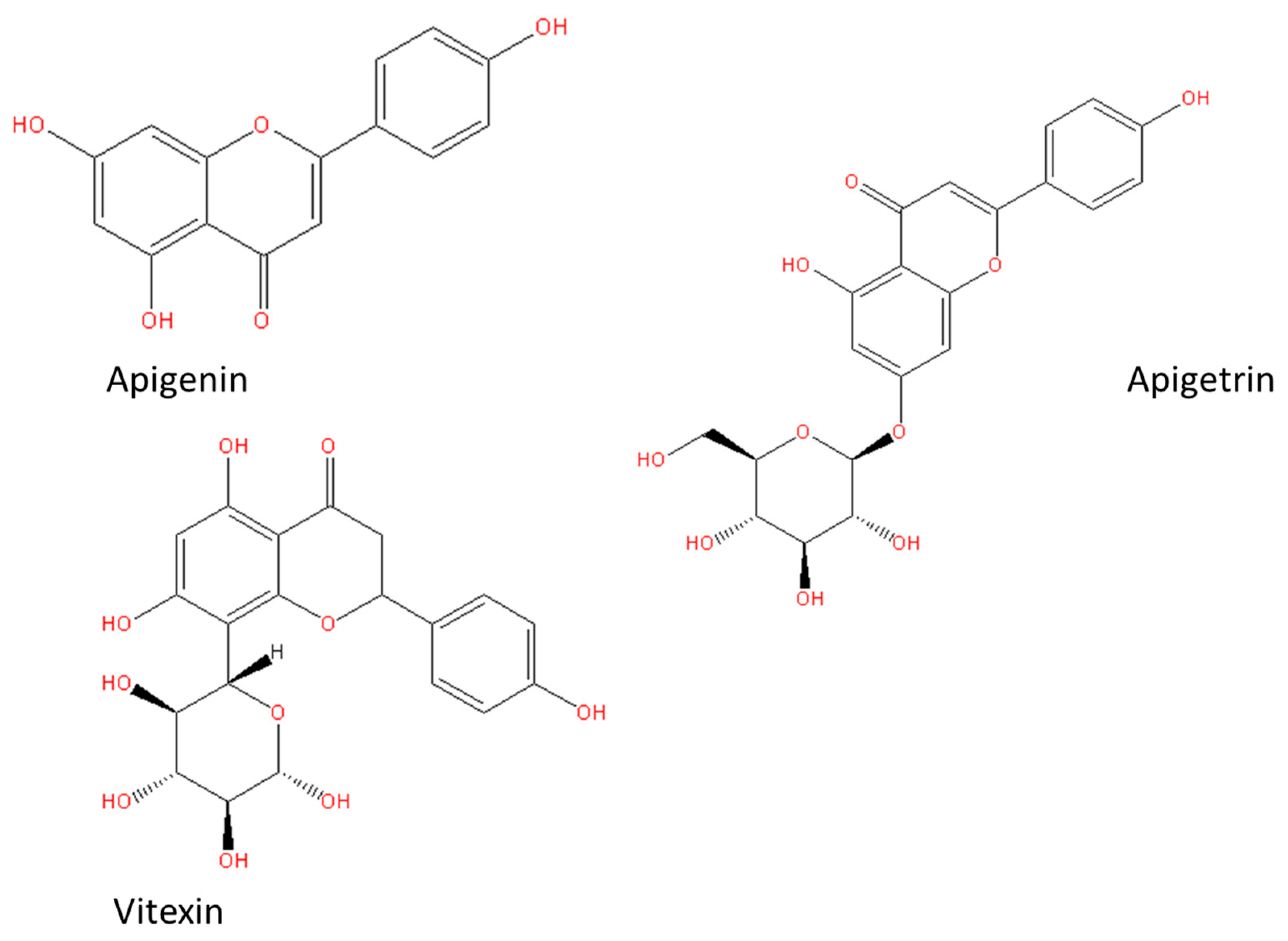




| Cancer | Outcome of the Study | Type of Cells | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breast Cancer | Vitexin induced apoptosis and elevated caspase 3 and caspase 8 protein expressions | MCF-7 | [22] |
| Vitexin induces autophagy, anticancer, leading to significantly elevated expression levels of ATG, Beclin-1, and LC3-II when compared with controls. | CRL7242 | [23] | |
| Apigenin induces apoptosis with overexpression of the neu/HER2 oncogene. | MDA-MB-453, BT-474, SKBr-3 | [24] | |
| Liver Cancer | The invasion and viability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells were suppressed by vitexin via modulation of the STAT3 pathway. | HepG2 | [26] |
| Apigenin caused apoptosis and autophagy by suppressing the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. | HCCLM3 | [27] | |
| Apigenin induces necroptosis and apoptosis through NF-κB signaling. | Hep3B | [29] | |
| Apigenin regulated cell cycle progression and promoted apoptosis. | SCC-25 | [30] | |
| Apigenin effectively inhibits metastasis triggered by low-dose oxaliplatin (OXA), primarily by downregulating the expression of LINC00857. | SCC-25 | [55] | |
| VB1 exerted anti-neoplastic activities in vitro by inhibiting proliferation, inducing apoptosis, and arresting the cell cycle at G2/M phase. | HO8910 | [44] | |
| Ovarian Cancer | Apigenin inhibits proliferation through Id1 by activating transcription factor 3+ | Hela Siha | [45] |
| Apigenin induced apoptosis and overcame cisplatin-induced resistance in ovarian cancer cells by targeting the Mcl-1 protein. | A2780 | [46] | |
| Apigenin suppresses the expression of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and reduces the migration and invasion. | SKOV3 | [47] | |
| Apigenin was shown to reduce histamine-induced dysregulation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) signaling. | A2780 | [48] | |
| Apigenin exhibits a selective, dose-dependent cytotoxicity and promotes apoptosis. | HeLa | [49] | |
| Vitexin inhibits HCT-116 colon cancer cell proliferation by downregulating CDK1/cyclin B, leading to G2/M-phase cell cycle arrest. | HCT-116 | [50] | |
| Apigenin was shown to suppress epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), along with the migration and invasion capabilities. | HCT-116, LOVO | [51] | |
| Colon Cancer | Apigenin treatment decreased the expression of HSP90AA1. | COLO-205 | [52] |
| Apigenin suppresses the proliferation of colon cancer cells by interfering with PKM2-regulated glycolytic activity. | HCT116 | [53] | |
| Apigenin triggers apoptosis by concurrently reducing Bcl-xL and Mcl-1 levels via STAT3 inhibition. | HT29, DLD-1 | [54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhosale, P.B.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, H.H.; Heo, J.D.; Hwang, K.H.; Moon, Y.G.; Ahn, M.; Seong, J.K.; Won, C.; Kim, G.S. Therapeutic Potential and Cancer Cell Death-Inducing Effects of Apigenin and Its Derivatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10084. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010084
Bhosale PB, Jeong SH, Kim HH, Heo JD, Hwang KH, Moon YG, Ahn M, Seong JK, Won C, Kim GS. Therapeutic Potential and Cancer Cell Death-Inducing Effects of Apigenin and Its Derivatives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10084. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010084
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhosale, Pritam Bhagwan, Se Hyo Jeong, Hun Hwan Kim, Jeong Doo Heo, Kwang Hyun Hwang, Yeon Gyu Moon, Meejung Ahn, Je Kyung Seong, Chungkil Won, and Gon Sup Kim. 2025. "Therapeutic Potential and Cancer Cell Death-Inducing Effects of Apigenin and Its Derivatives" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10084. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010084
APA StyleBhosale, P. B., Jeong, S. H., Kim, H. H., Heo, J. D., Hwang, K. H., Moon, Y. G., Ahn, M., Seong, J. K., Won, C., & Kim, G. S. (2025). Therapeutic Potential and Cancer Cell Death-Inducing Effects of Apigenin and Its Derivatives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10084. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010084







