Comparative Transcriptomics Provides Insight into the Neuroendocrine Regulation of Spawning in the Black-Lip Rock Oyster (Saccostrea echinata)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
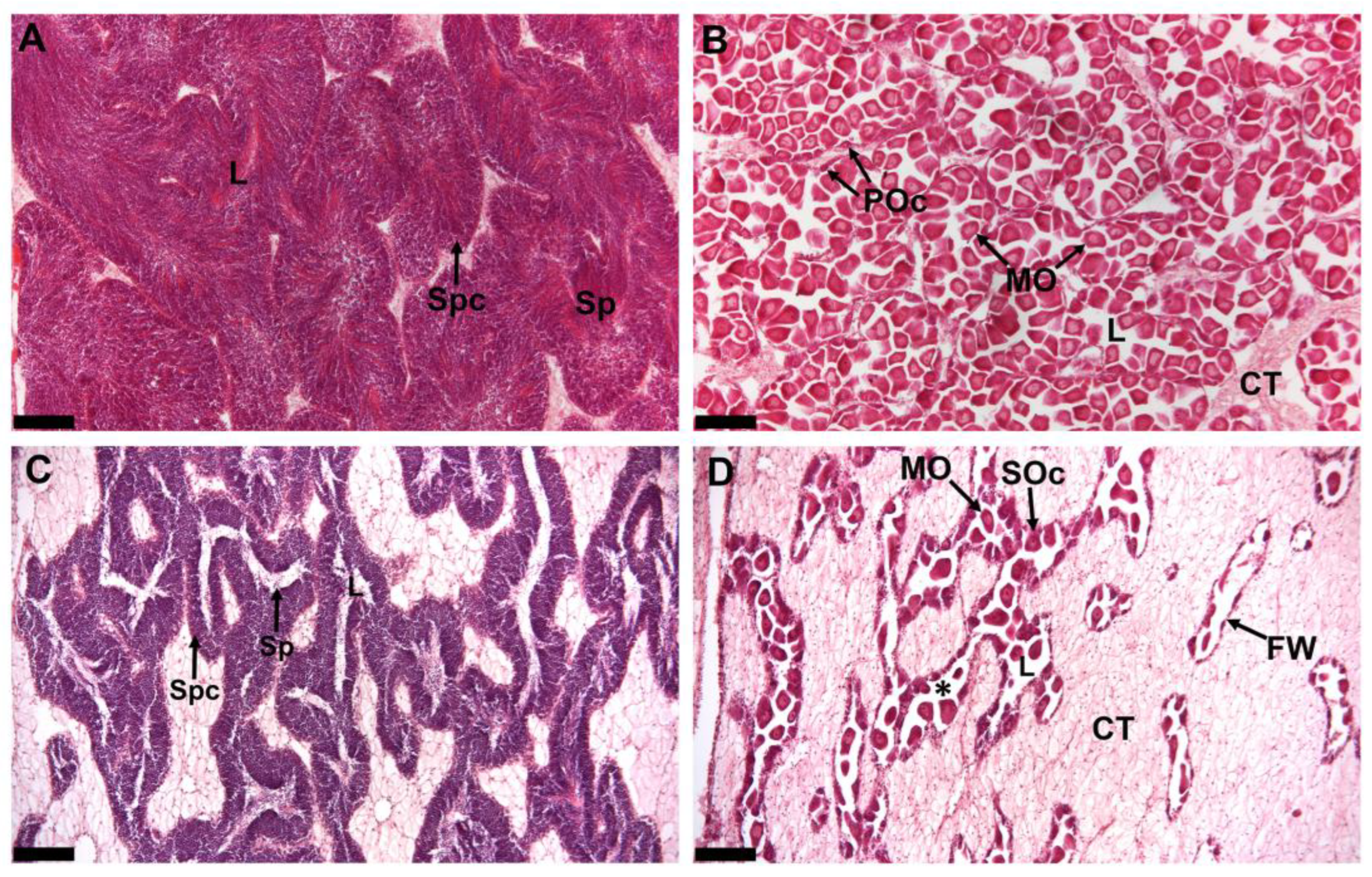
2.1. Gonad Histology at Pre- and Post-Spawn S. echinata
2.2. Overview of Reference Transcriptome Assembly
2.3. Targeted Characterisation of Neuropeptide and Reproductive-Associated Genes
2.4. Tissue Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) and Functional Annotation
2.4.1. Visceral Ganglia (VG)
2.4.2. Gonads
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals and Sample Collection
4.2. Gonad Histology
4.3. RNA Extraction, Library Construction, and RNA Sequencing
4.4. Reference Transcriptome Assembly and Annotation
4.5. Targeted Identification of Neuropeptide and Reproductive-Associated Genes
4.6. Differential Gene Expression Analysis and Annotation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QLD | Queensland |
| US/USA | United States/United States of America |
| VG | Visceral Ganglia |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| GC | Guanine–Cytosine content |
| BUSCO | Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs |
| NPY | Neuropeptide Y |
| CCAP | Crustacean Cardioactive Peptide |
| CCK | Cholecystokinin |
| DEG | Differentially Expressed Gene |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| 5HT | 5-Hydroxytryptamine |
| QRFP | Pyroglutamylated RFamide Peptide |
| ALK | Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase |
| FC | Fold Change |
| TPM | Transcripts Per Million |
| ADAM | A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase |
| NCBI | National Centre for Biotechnology Information |
| NROBA | Neuropeptide Receptor of Bivalves |
| TSSK | Testis-Specific Serine/Threonine Kinase |
| ER | Oestrogen Receptor |
| AEC | Adenylate energy charge |
| VP/OT | Vasopressin-type/oxytocin |
| AST | Allatostatin |
| GPCR | G-Protein Coupled Receptor |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| LPB | Larvae, Post-larvae, and Broodstock |
| MA | Massachusetts |
| FASTQ | FastQ format |
| CLC | CLC genomics workbench software |
| SL | Sociedad Limitada |
| CD-HIT | Cluster Database at High Identity with Tolerance |
| ORF | Open Reading Frame |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| FRDC | Fisheries Research and Development Corporation |
| BIRC | Bribie Island Research Centre |
References
- FAO. Fao Fisheries and Aquaculture—Fishstatj—Software for Fishery and Aquaculture Statistical Time Series; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Division: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, L.; Myers, A. 2020–2025 Oyster Australia Strategic Plan, Project No. 2019-208–2020-25 Strategic Plan for the Australian Oyster Industry; Fisheries Research and Development Corporation: Canberra, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Green, T.J.; Raftos, D.; O’Connor, W.; Adlard, R.D.; Barnes, A.C. Disease Prevention Strategies for Qx Disease (Marteilia sydneyi) of Sydney Rock Oysters (Saccostrea glomerata). J. Shellfish Res. 2011, 30, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dove, M.C.; Nell, J.A.; O’Connor, W.A. Evaluation of the Progeny of the Fourth-Generation Sydney Rock Oyster Saccostrea glomerata (Gould, 1850) Breeding Lines for Resistance to Qx Disease (Marteilia sydneyi) and Winter Mortality (Bonamia roughleyi). Aquac. Res. 2013, 44, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul-Pont, I.; Dhand, N.K.; Whittington, R.J. Influence of Husbandry Practices on Oshv-1 Associated Mortality of Pacific Oysters Crassostrea gigas. Aquaculture 2013, 412, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugalde, S.C.; Preston, J.; Ogier, E.; Crawford, C. Analysis of Farm Management Strategies Following Herpesvirus (Oshv-1) Disease Outbreaks in Pacific Oysters in Tasmania, Australia. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willer, D.F.; Aldridge, D.C. Sustainable Bivalve Farming Can Deliver Food Security in the Tropics. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J. A National Industry Response to Pacific Oyster Mortality Syndrome (Poms); Agribusiness Tasmania: Launceston, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cobcroft, J.; Bell, R.; Fitzgerald, J.; Diedrich, A.; Jerry, D. Northern Australia Aquaculture Industry Situational Analysis Project; Cooperative Research Centre for Developing Northern Australia: Aitkenvale, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nowland, S.J.; Silva, C.N.S.; Southgate, P.C.; Strugnell, J.M. Mitochondrial and Nuclear Genetic Analyses of the Tropical Black-Lip Rock Oyster (Saccostrea echinata) Reveals Population Subdivision and Informs Sustainable Aquaculture Development. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, C. Comparative De Novo Transcriptome Analysis of the Australian Black-Lip and Sydney Rock Oysters Reveals Expansion of Repetitive Elements in Saccostrea Genomes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coeroli, M.; De Gaillande, D.; Landret, J.P. Recent Innovations in Cultivation of Molluscs in French Polynesia. Aquaculture 1984, 39, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southgate, P.C.; Lee, P.S. Hatchery Rearing of the Tropical Blacklip Oyster Saccostrea echinata (Quoy and Gaimard). Aquaculture 1998, 169, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowland, S.J.; O’Connor, W.; Southgate, P.C. Embryonic, Larval, and Early Postlarval Development of the Tropical Black-Lip Rock Oyster Saccostrea echinata. J. Shellfish Res. 2018, 37, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowland, S.; Hartley, C.; Osborne, M.; Schipp, G.; O’Connor, W.; Southgate, P. Hatchery Protocol for the Blacklip Rock Oyster Saccostrea echinata (Quoy and Gaimard, 1835); Northern Territory Government: Palmerston, Australia, 2021.
- Nowland, S.J.; O’Connor, W.A.; Penny, S.S.; Southgate, P.C. Monsoonally Driven Reproduction in the Tropical Black-Lip Rock Oyster Saccostrea echinata (Quoy & Gaimard, 1835) in Northern Australia. J. Shellfish Res. 2019, 38, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Nowland, S.J.; O’Connor, W.A.; Southgate, P.C. Optimizing Stocking Density and Microalgae Ration Improves the Growth Potential of Tropical Black-Lip Oyster, Saccostrea echinata, Larvae. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2019, 50, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowland, S.J.; O’Connor, W.A.; Penny, S.S.; Osborne, M.W.J.; Southgate, P.C. Water Temperature and Salinity Synergistically Affect Embryonic and Larval Development of the Tropical Black-Lip Rock Oyster Saccostrea echinata. Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowland, S.J.; O’Connor, W.A.; Elizur, A.; Southgate, P.C. Evaluating Spawning Induction Methods for the Tropical Black-Lip Rock Oyster, Saccostrea echinata. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartenstein, V. The Neuroendocrine System of Invertebrates: A Developmental and Evolutionary Perspective. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 190, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.J.; Favrel, P.; Rotgans, B.A.; Wang, T.; Zhao, M.; Sohail, M.; O’Connor, W.A.; Elizur, A.; Henry, J.; Cummins, S.F. Neuropeptides Encoded by the Genomes of the Akoya Pearl Oyster Pinctata fucata and Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas: A Bioinformatic and Peptidomic Survey. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, V.V.; Ntalamagka, N.; O’Connor, W.; Wang, T.; Powell, D.; Cummins, S.F.; Elizur, A. Reproductive Neuropeptides That Stimulate Spawning in the Sydney Rock Oyster (Saccostrea glomerata). Peptides 2016, 82, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galtsoff, P.S. The American Oyster, Crassostrea virginica Gmelin; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1964; Volume 64.
- Yurchenko, O.V.; Skiteva, O.I.; Voronezhskaya, E.E.; Dyachuk, V.A. Nervous System Development in the Pacific Oyster, Crassostrea gigas (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Front. Zool. 2018, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinamani, P. Reproductive Cycle and Gonadial Changes in the New Zealand Rock Oyster Crassostrea glomerata. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1974, 8, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, Z. Transcriptomics Analysis of Crassostrea hongkongensis for the Discovery of Reproduction-Related Genes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Realis-Doyelle, E.; Schwartz, J.; Cabau, C.; Le Franc, L.; Bernay, B.; Riviere, G.; Klopp, C.; Favrel, P. Transcriptome Profiling of the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas Visceral Ganglia over a Reproduction Cycle Identifies Novel Regulatory Peptides. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, C.; Wei, J.; Qin, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Three Gonadal Development Stages Reveals Potential Genes Involved in Gametogenesis of the Fluted Giant Clam (Tridacna squamosa). BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teaniniuraitemoana, V.; Huvet, A.; Levy, P.; Klopp, C.; Lhuillier, E.; Gaertner-Mazouni, N.; Gueguen, Y.; Le Moullac, G. Gonad Transcriptome Analysis of Pearl Oyster Pinctada margaritifera: Identification of Potential Sex Differentiation and Sex Determining Genes. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbach, J.P.H. What Are Neuropeptides? In Neuropeptides: Methods and Protocols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Veenstra, J.A. Neurohormones and Neuropeptides Encoded by the Genome of Lottia gigantea, with Reference to Other Mollusks and Insects. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 167, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Li, R.; Xie, X.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L.; Bao, Z. Identification and Characterization of Neuropeptides by Transcriptome and Proteome Analyses in a Bivalve Mollusc Patinopecten yessoensis. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pales Espinosa, E.; Farhat, S.; Allam, B. In Silico Identification of Neuropeptide Genes Encoded by the Genome of Crassostrea virginica with a Special Emphasis on Feeding-Related Genes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2025, 301, 111792. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, E.R.B. Dax1: Increasing Complexity in the Roles of This Novel Nuclear Receptor. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 265–266, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, A.; Zanaria, E.; Hacker, A.; Lovell-Badge, R.; Camerino, G. Mouse Dax1 Expression Is Consistent with a Role in Sex Determination as Well as in Adrenal and Hypothalamus Function. Nat. Genet. 1996, 12, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Clifford, V.; Western, P.S.; Wilcox, S.A.; Bell, K.S.; Sinclair, A.H. Cloning and Expression of a Dax1 Homologue in the Chicken Embryo. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 24, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, J.; Takase, M.; Nakamura, M. Expression of Dax-1 during Gonadal Development of the Frog. Gene 2001, 280, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-S.; Kobayashi, T.; Senthilkumaran, B.; Sakai, F.; Sudhakumari, C.C.; Suzuki, T.; Yoshikuni, M.; Matsuda, M.; Morohashi, K.-I.; Nagahama, Y. Molecular Cloning of Dax1 and Shp cDNAs and Their Expression Patterns in the Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 297, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Yu, H.; Li, Q. Genome Survey and Characterization of Reproduction-Related Genes in the Pacific Oyster. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2017, 61, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erber, R.; Meyer, J.; Taubert, H.; Fasching, P.A.; Wach, S.; Häberle, L.; Gaß, P.; Schulz-Wendtland, R.; Landgraf, L.; Olbricht, S.; et al. Piwil1 and Piwil2 Expression in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jehn, J.; Gebert, D.; Pipilescu, F.; Stern, S.; Kiefer, J.S.T.; Hewel, C.; Rosenkranz, D. Piwi Genes and Pirnas Are Ubiquitously Expressed in Mollusks and Show Patterns of Lineage-Specific Adaptation. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ichikawa, Y.; Igarashi, Y.; Yoshitake, K.; Kinoshita, S.; Omori, F.; Maeyama, K.; Nagai, K.; Watabe, S.; Asakawa, S. Piwi-Interacting Rna (Pirna) Expression Patterns in Pearl Oyster (Pinctada fucata) Somatic Tissues. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Ji, A.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, D.; Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Z. Piwi1 Is Essential for Gametogenesis in Mollusk Chlamys farreri. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, B.; Du, H. A Review on Sox Genes in Fish. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1986–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Li, Q.; Yu, H. Gonad Transcriptome Analysis of the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas Identifies Potential Genes Regulating the Sex Determination and Differentiation Process. Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pei, J.; Xiong, L.; Guo, S.; Cao, M.; Kang, Y.; Bao, P.; Wu, X.; Chu, M.; Liang, C. Identification of the TSSK4 Alternative Spliceosomes and Analysis of the Function of the TSSK4 Protein in Yak (Bos grunniens). Animals 2022, 12, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, P.; Hoogerbrugge, J.; Baarends, W.M.; Grootegoed, J.A. Evolution of Testis—Specific Kinases Tssk 1b and Tssk 2 in Primates. Andrology 2013, 1, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-L.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.-G.; Cui, L.-B.; Zhang, Z.-F. Gonadogenesis in Scallop Chlamys farreri and Cf-Foxl2 Expression Pattern during Gonadal Sex Differentiation. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Kim, S.J.; Park, C.J.; Nam, Y.K. Characterization of Testis-Specific Serine/Threonine Kinase 1-like (Tssk1-like) Gene and Expression Patterns in Diploid and Triploid Pacific Abalone (Haliotis discus hannai; Gastropoda; Mollusca) Males. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Wei, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, T.; Liu, L.; Xing, Q.; Wang, S.; Bao, Z. Expression of the Testis-Specific Serine/Threonine Kinases Suggests Their Role in Spermiogenesis of Bay Scallop Argopecten irradians. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 657559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.; Subramanian, S.; Suwansa-ard, S.; Zhao, M.; O’Connor, W.; Raftos, D.; Elizur, A. The Genome of the Oyster Saccostrea Offers Insight into the Environmental Resilience of Bivalves. DNA Res. 2018, 25, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutet, I.; Moraga, D.; Marinovic, L.; Obreque, J.; Chavez-Crooker, P. Characterization of Reproduction-Specific Genes in a Marine Bivalve Mollusc: Influence of Maturation Stage and Sex on Mrna Expression. Gene 2008, 407, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Militz, T.A.; Braley, R.D.; Schoeman, D.S.; Southgate, P.C. Larval and Early Juvenile Culture of Two Giant Clam (Tridacninae) Hybrids. Aquaculture 2019, 500, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, L.; Leonardi, M.; Morin, V.; Quiñones, R.A. Induction of Vitellogenin-like Lipoproteins in the Mussel Aulacomya ater under Exposure to 17β-Estradiol. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr. 2012, 47, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.K.A.; MacFarlane, G.R.; Kong, R.Y.C.; O’Connor, W.A.; Yu, R.M.K. Mechanistic Insights into Induction of Vitellogenin Gene Expression by Estrogens in Sydney Rock Oysters, Saccostrea glomerata. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 174, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, M.G.; Matozzo, V. Vitellogenin Induction as a Biomarker of Exposure to Estrogenic Compounds in Aquatic Environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porte, C.; Janer, G.; Lorusso, L.C.; Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Fossi, M.C.; Canesi, L. Endocrine Disruptors in Marine Organisms: Approaches and Perspectives. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 143, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Zeng, Z.; Kong, D.; Hou, L.; Huang, H.; Ke, C. Vitellogenin of Fujian Oyster, Crassostrea angulata: Synthesized in the Ovary and Controlled by Estradiol-17β. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 202, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Nakamura, A.M.; Mori, K.; Kayano, T. Molecular Characterization of a Cdna Encoding Putative Vitellogenin from the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas. Zool. Sci. 2003, 20, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ni, H.; Rong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yan, S.; Liao, X.; Dong, Z. Gonad Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Differences in Gene Expression Related to Sex-Biased and Reproduction of Clam Cyclina sinensis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1110587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.R.; Habibi, H.R. Estrogen Receptor Function and Regulation in Fish and Other Vertebrates. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 192, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.P. Do Mollusks Use Vertebrate Sex Steroids as Reproductive Hormones? Part I: Critical Appraisal of the Evidence for the Presence, Biosynthesis and Uptake of Steroids. Steroids 2012, 77, 1450–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Han, L.; Miao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Pan, L. Estrogen Receptor Knockdown Suggests Its Role in Gonadal Development Regulation in Manila Clam Ruditapes philippinarum. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2024, 243, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leininger, S.; Adamski, M.; Bergum, B.; Guder, C.; Liu, J.; Laplante, M.; Bråte, J.; Hoffmann, F.; Fortunato, S.; Jordal, S. Developmental Gene Expression Provides Clues to Relationships Between Sponge and Eumetazoan Body Plans. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, B.W.; McCallum, C.M.; Moens, C.B. Nanos1 Is Required to Maintain Oocyte Production in Adult Zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 2007, 305, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, H. Nanos Maintains Germline Stem Cell Self-Renewal by Preventing Differentiation. Science 2004, 303, 2016–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, J.S.; Chan, X.Y.; Kingsley, E.P.; Duan, Y.; Lambert, J.D. Nanos Is Required in Somatic Blast Cell Lineages in the Posterior of a Mollusk Embryo. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kranz, A.M.; Tollenaere, A.; Norris, B.J.; Degnan, B.M.; Degnan, S.M. Identifying the Germline in an Equally Cleaving Mollusc: Vasa and Nanos Expression during Embryonic and Larval Development of the Vetigastropod Haliotis asinina. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2010, 314, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Masaoka, T.; Fujiwara, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Satoh, N.; Awaji, M. Reproduction-Related Genes in the Pearl Oyster Genome. Zool. Sci. 2013, 30, 826–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Li, Q.; Yu, H.; Kong, L. Oocyte Maturation and Origin of the Germline as Revealed by the Expression of Nanos-like in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas. Gene 2018, 663, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelin, C.; Kellner, K.; Mathieu, M. Storage Metabolism in the Pacific Oyster (Crassostrea gigas) in Relation to Summer Mortalities and Reproductive Cycle (West Coast of France). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 125, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C.; Abad, M.; Sedano, F.; Garcia-Martin, L.O.; Sanchez Lopez, J.L. Influence of Seasonal Environmental Changes on the Gamete Production and Biochemical Composition of Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg) in Suspended Culture in El Grove, Galicia, Spain. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1992, 155, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdue, J.A.; Beattie, J.H.; Chew, K.K. Some Relationships between Gametogenic Cycle and Summer Mortality Phenomenon in the Pacific Oyster (Crassostrea gigas) in Washington State. J. Shellfish Res. 1981, 1, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Qin, J.G.; Abbott, C.A.; Li, X.; Benkendorff, K. Synergistic Impacts of Heat Shock and Spawning on the Physiology and Immune Health of Crassostrea gigas: An Explanation for Summer Mortality in Pacific Oysters. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 293, R2353–R2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschraegen, K.; Herman, P.M.J.; Van Gansbeke, D.; Braeckman, A. Measurement of the Adenylate Energy Charge in Nereis diversicolor and Nephtys sp. (Polychaeta: Annelida): Evaluation of the Usefulness of Aec in Pollution Monitoring. Mar. Biol. 1985, 86, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qin, J.G.; Li, X.; Benkendorff, K. Assessment of Metabolic and Immune Changes in Postspawning Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas: Identification of a Critical Period of Vulnerability After Spawning. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, e155–e165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.C. Cellular Defense Mechanisms in Oysters. In Recent Advances in Marine Biotechnology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.S.; Beaven, A.E. Antibacterial Activities of Oyster (Crassostrea virginica) and Mussel (Mytilus edulis and Geukensia demissa) Plasma. Aquat. Living Resour. 2001, 14, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qin, J.G.; Li, X.; Benkendorff, K. Spawning-Dependent Stress Responses in Pacific Oysters Crassostrea gigas: A Simulated Bacterial Challenge in Oysters. Aquaculture 2009, 293, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubos, M.-P.; Zels, S.; Schwartz, J.; Pasquier, J.; Schoofs, L.; Favrel, P. Characterization of a Tachykinin Signalling System in the Bivalve Mollusc Crassostrea gigas. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 266, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rato, A.; Joaquim, S.; Matias, D.; Hubbard, P.C. The Roles of Chemical Cues in the Life Cycle of Bivalves: Spawning, Settlement, and Metamorphosis. Rev. Aquac. 2025, 17, e13007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xu, F.; Qu, T.; Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Que, H.; Zhang, G. Identification of Thyroid Hormones and Functional Characterization of Thyroid Hormone Receptor in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas Provide Insight into Evolution of the Thyroid Hormone System. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegener, C.; Chen, J. Allatostatin A Signalling: Progress and New Challenges from a Paradigmatic Pleiotropic Invertebrate Neuropeptide Family. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 920529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetan, J.; Kornthong, N.; Duangprom, S.; Phanthong, P.; Kruangkum, T.; Sobhon, P. The Oxytocin/Vasopressin-like Peptide Receptor mRNA in the Central Nervous System and Ovary of the Blue Swimming Crab, Portunus pelagicus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2021, 258, 110983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odekunle, E.A.; Elphick, M.R. Comparative and Evolutionary Physiology of Vasopressin/Oxytocin-Type Neuropeptide Signaling in Invertebrates. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 225. [Google Scholar]
- Van Kesteren, R.E.; Smit, A.B.; De Lange, R.P.; Kits, K.S.; Van Golen, F.A.; Van Der Schors, R.C.; Burke, J.F.; Geraerts, W.P. Structural and Functional Evolution of the Vasopressin/Oxytocin Superfamily: Vasopressin-Related Conopressin Is the Only Member Present in Lymnaea, and Is Involved in the Control of Sexual Behavior. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 5989–5998. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Kesteren, R.E.; Tensen, C.P.; Smit, A.B.; Van Minnen, J.; Van Soest, P.F.; Kits, K.S.; Meyerhof, W.; Richter, D.; Van Heerikhuizen, H.; Vreugdenhil, E. A Novel G Protein-Coupled Receptor Mediating Both Vasopressin-and Oxytocin-like Functions of Lys-Conopressin in Lymnaea stagnalis. Neuron 1995, 15, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, G.E.; Farnsworth, D.E.; Siegel, N.R.; Fok, K.F.; Feyereisen, R. Identification of an Allatostatin from Adult Diploptera punctata. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 163, 1243–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhead, A.P.; Stay, B.; Seidel, S.L.; Khan, M.A.; Tobe, S.S. Primary Structure of Four Allatostatins: Neuropeptide Inhibitors of Juvenile Hormone Synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 5997–6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audsley, N.; Weaver, R.J. Neuropeptides Associated with the Regulation of Feeding in Insects. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 162, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabeau, O.; Joly, J.-S. Molecular Evolution of Peptidergic Signaling Systems in Bilaterians. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2028–E2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elphick, M.R.; Mirabeau, O.; Larhammar, D. Evolution of Neuropeptide Signalling Systems. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb151092, Correction in J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb193342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdol, M.; Moreira, R.; Cruz, F.; Gómez-Garrido, J.; Vlasova, A.; Rosani, U.; Venier, P.; Naranjo-Ortiz, M.A.; Murgarella, M.; Greco, S.; et al. Massive Gene Presence-Absence Variation Shapes an Open Pan-Genome in the Mediterranean Mussel. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cardoso, J.C.R.; Peng, M.; Inácio, J.P.S.; Power, D.M. Evolution and Potential Function in Molluscs of Neuropeptide and Receptor Homologues of the Insect Allatostatins. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 725022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Fang, X.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Luo, R.; Xu, F.; Yang, P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Qi, H.; et al. The Oyster Genome Reveals Stress Adaptation and Complexity of Shell Formation. Nature 2012, 490, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabe, H.B.; Guerreiro, A.d.S.; Sandrini, J.Z. Molecular and Biochemical Effects of the Antifouling DCOIT in the Mussel Perna perna. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 239, 108870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abele, D.; Heise, K.; Portner, H.O.; Puntarulo, S. Temperature-Dependence of Mitochondrial Function and Production of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Intertidal Mud Clam Mya arenaria. J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bao, Z.; Lin, Z.; Xue, Q. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Superoxide Dismutases in Four Oyster Species Reveals Functional Differentiation in Response to Biotic and Abiotic Stress. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-Hit: A Fast Program for Clustering and Comparing Large Sets of Protein or Nucleotide Sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seppey, M.; Manni, M.; Zdobnov, E.M. Busco: Assessing Genome Assembly and Annotation Completeness. In Gene Prediction: Methods and Protocols; Kollmar, M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 227–245. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De Novo Transcript Sequence Reconstruction from Rna-Seq Using the Trinity Platform for Reference Generation and Analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talón, M.; Robles, M. Blast2go: A Universal Tool for Annotation, Visualization and Analysis in Functional Genomics Research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.-Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. Interproscan 5: Genome-Scale Protein Function Classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedhart, J.; Luijsterburg, M.S. Volcanoser Is a Web App for Creating, Exploring, Labeling and Sharing Volcano Plots. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Contig ID | Gene Name | Female VG | Male VG | Female Gonad | Male Gonad |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146852 | Allatotropin | ● | ● | ||
| 140434 | APGWa | ● | ● | ||
| 46225 | Buccalin | ● | ● | ||
| 71066 | CCAP-1 | ● | ● | ||
| 91581 | CCAP-2 | ● | ● | ||
| 120340 | CCK | ● | ● | ||
| 136993 | Conopressin | ● | ● | ||
| 113456 | GGNG | ● | ● | ||
| 98593 | LASGLVamide | ● | ● | ● * | |
| 86141 | LFRFa | ● | ● | ||
| 74205 | LFRYa | ● | |||
| 51782 | LRNFVamide | ● | ● | ||
| 86374 | Luqin | ● | ● | ||
| 139379 | Myomodulin | ● | |||
| 39729 | NdWFamide | ● | |||
| 137757 | Pedal peptide-1 | ● | ● | ||
| 98593 | Pedal peptide-2 | ● | ● | ● | |
| 80267 | PKYMDT | ● | ● | ||
| 125782 | Pyrokinin | ● | ● | ||
| 86374 | Wwamide | ● | ● |
| Contig ID | Gene Name | Female VG | Male VG | Female Gonad | Male Gonad |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gonad development | |||||
| 448 | Adenosine deaminase-like | ● | ● | ||
| 5174 | Calcineurin-beta | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| 2311 | Catenin-beta | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| 41577 | Cytidine deaminase-like (CDA) | ● | ● | ||
| 2102 | Dax1 | ● | ● | ● * | ● |
| 34255 | Forkhead box protein L2-like (Foxl2) | ● | |||
| 13580 | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 (IGFBF7) | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| 19979 | Insulin-like peptide receptor (IR) | ● # | |||
| 1086 | Piwi 1-like | ● * | ● | ||
| 7116 | Prohibitin 1-like | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| 1911 | Prohibitin 2-like | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| 2769 | Transcription factor SOX-11-like (Sox11) | ● * | |||
| 24745 | Transcription factor SOX-9-like (Sox9) | ● | ● | ● | |
| 1218 | Transforming growth factor-beta | ● | ● | ||
| 150 | Vasa | ● | |||
| Spermatogenesis | |||||
| 80733 | Spermatogenesis and centriole associated 1 (SCA) | ● | |||
| 89650 | Spermatogenesis-associated protein 48 (SPATA48) | ● | |||
| 56798 | Spermatogenesis-associated protein 7-like (SPATA7) | ● | |||
| 103099 | Testis-specific serine/threonine-protein kinase 1-like (Tssk1) | ● | |||
| 21110 | Testis-specific serine/threonine-protein kinase 4-like (Tssk4) | ● | |||
| 88892 | Testis-specific serine/threonine-protein kinase 5-like (Tssk5) | ● | |||
| Ovarian development | |||||
| 56406 | Oestrogen receptor (ER) | ● | ● | ||
| 22711 | Nanos 1- like | ● * | |||
| 17 | Vitellogenin (Vg) | ● | |||
| Sex and Stage | Contig ID | Description | Log2 FC (TPM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female Pre-spawn | 47778 | Thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor-like | 5.75 |
| 32718 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(s) subunit alpha-like | 4.68 | |
| 5974 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3-like | 4.28 | |
| 28837 | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor Ror2-like | 3.90 | |
| 15516 | ADAM 17-like protease | 3.74 | |
| 26931 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor 8 | 3.72 | |
| 39055 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR5-like isoform X1 | 3.55 | |
| 59795 | Uncharacterised protein LOC133181846 | 3.47 | |
| 25097 | Probable nuclear hormone receptor HR38 | 3.43 | |
| 18453 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3-like | 3.30 | |
| 3895 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3 | 3.29 | |
| 3692 | Protein timeless-like | 3.10 | |
| 13401 | ALK tyrosine kinase receptor-like isoform X2 | 3.10 | |
| 2417 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(s) subunit alpha-like | 3.09 | |
| 39896 | Dual specificity protein phosphatase 1-like | 3.05 | |
| 63391 | 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor | 3.05 | |
| 22655 | Tachykinin-like peptides receptor 99D | 3.03 | |
| 11835 | Proline-rich protein 5-like isoform X2 | 3.00 | |
| 5768 | Hypoxia up-regulated protein 1-like isoform X1 | 2.94 | |
| 28224 | ALK tyrosine kinase receptor-like | 2.83 | |
| 15622 | Activin receptor type-1-like isoform X2 | 2.70 | |
| 9750 | Cell division control protein 6 homologue | 2.63 | |
| 9970 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SIK1-like | 2.53 | |
| 11308 | Neurogenic locus notch homologue protein 1-like isoform X2 | 2.50 | |
| 20191 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha isoform-like | 2.38 | |
| 8892 | Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor L3-like isoform X1 | 2.16 | |
| 20967 | Glypican-6-like | 2.14 | |
| 23152 | QRFP-like peptide receptor | 2.13 | |
| 1932 | Repulsive guidance molecule A-like | 2.11 | |
| Male Pre-spawn | 44229 | Mesotocin receptor-like | 6.74 |
| 32219 | Protein immune deficiency | 5.02 | |
| 67392 | Allatostatin-A receptor-like | 4.86 | |
| 152920 | Protein IMPACT homologue | 4.69 | |
| 64014 | Uncharacterised protein LOC133197027 | 4.14 | |
| 83878 | Allatostatin-A receptor-like | 3.33 | |
| 33855 | Death domain-containing protein CRADD-like | 3.20 | |
| 23863 | Uncharacterised protein LOC133197027 | 2.45 | |
| Male Post-spawn | 64930 | Tumour necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11 isoform X1 | 2.54 |
| 8051 | Orexin receptor type 2-like | 3.23 | |
| 16500 | Ras-related protein Rab-39B-like | 3.98 | |
| 27769 | G-protein coupled receptor dmsr-1-like | 4.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zafar, M.A.; Suwansa-ard, S.; Mellor, A.; Wingfield, M.; Reiher, K.; Elizur, A.; Cummins, S.F. Comparative Transcriptomics Provides Insight into the Neuroendocrine Regulation of Spawning in the Black-Lip Rock Oyster (Saccostrea echinata). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10032. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010032
Zafar MA, Suwansa-ard S, Mellor A, Wingfield M, Reiher K, Elizur A, Cummins SF. Comparative Transcriptomics Provides Insight into the Neuroendocrine Regulation of Spawning in the Black-Lip Rock Oyster (Saccostrea echinata). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10032. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleZafar, Md Abu, Saowaros Suwansa-ard, Aiden Mellor, Max Wingfield, Karl Reiher, Abigail Elizur, and Scott F. Cummins. 2025. "Comparative Transcriptomics Provides Insight into the Neuroendocrine Regulation of Spawning in the Black-Lip Rock Oyster (Saccostrea echinata)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10032. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010032
APA StyleZafar, M. A., Suwansa-ard, S., Mellor, A., Wingfield, M., Reiher, K., Elizur, A., & Cummins, S. F. (2025). Comparative Transcriptomics Provides Insight into the Neuroendocrine Regulation of Spawning in the Black-Lip Rock Oyster (Saccostrea echinata). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10032. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010032







