Influence of Lifestyle on Brain Sensitivity to Circulating Insulin-like Growth Factor 1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Lifestyle Modulates Mood
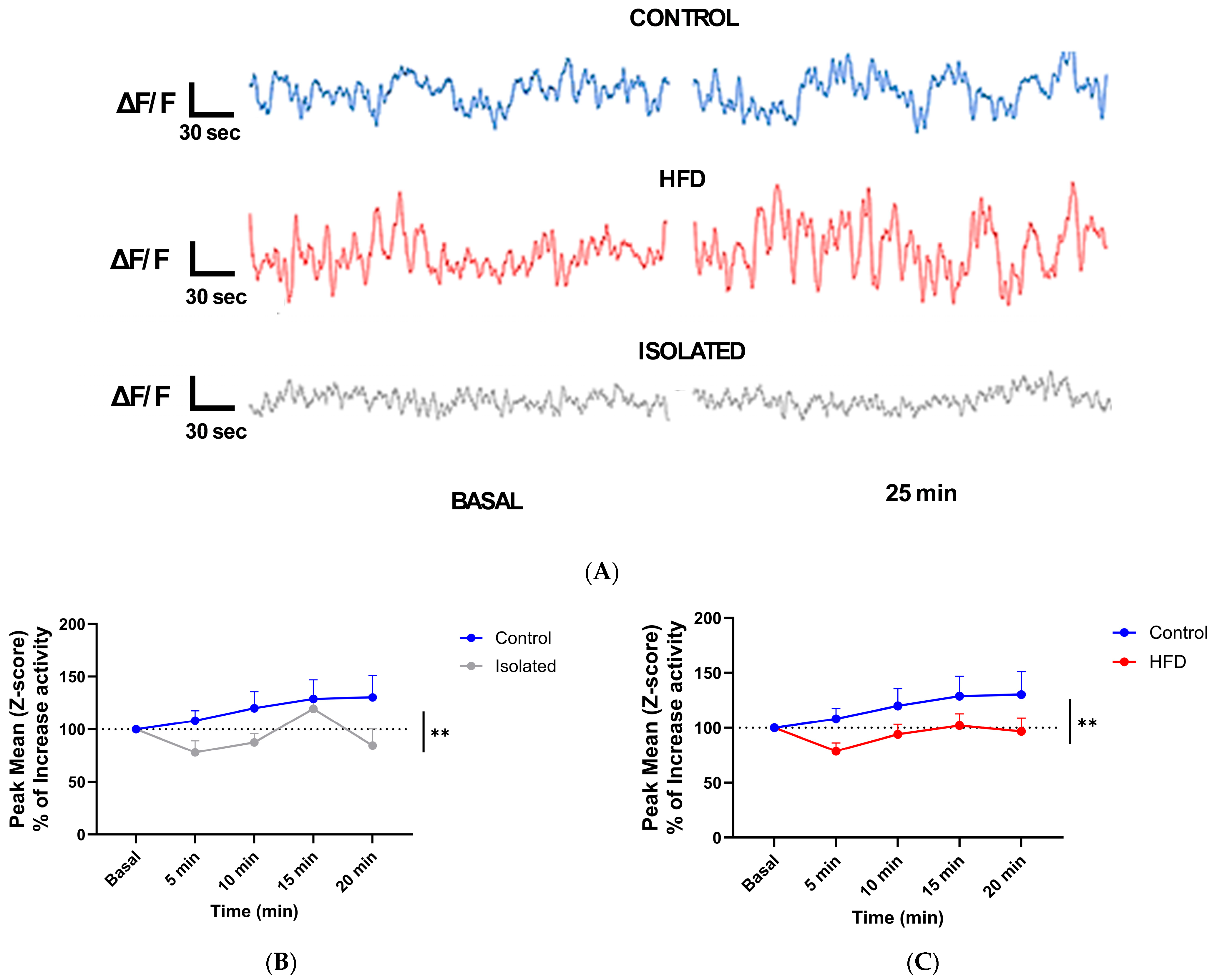
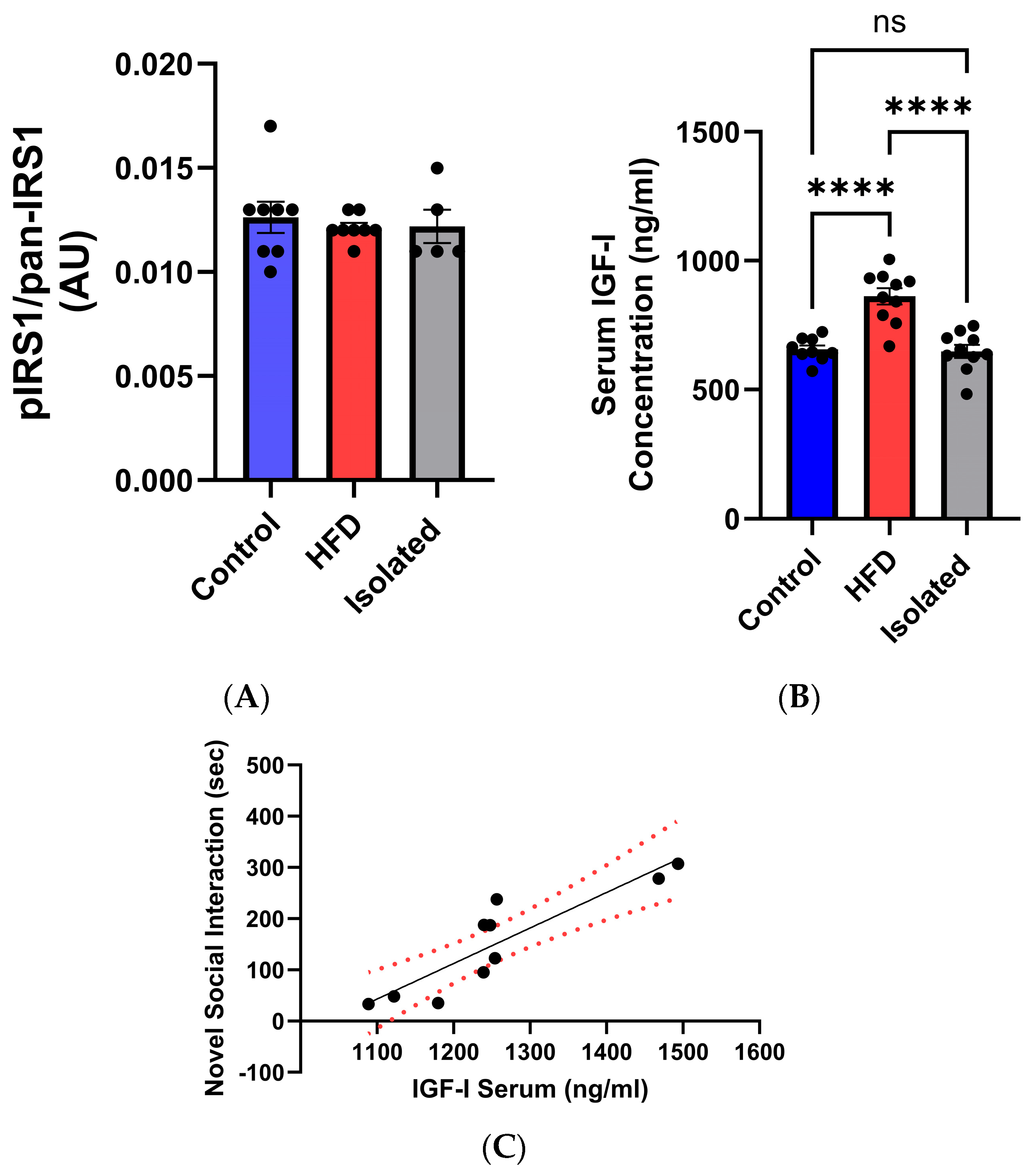
2.2. Lifestyle Modulates Neuronal Responses to Systemic IGF-1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Behavioral Tests
4.4. Ca++ Fiber-Photometry
4.5. Immunoassays
4.6. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattson, M.P.; Arumugam, T.V. Hallmarks of Brain Aging: Adaptive and Pathological Modification by Metabolic States. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1176–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.M.; Santi, A.; Torres Aleman, I. Insulin Peptides as Mediators of the Impact of Life Style in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Plast. 2018, 4, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.M.; Torres-Aleman, I. The many faces of insulin-like peptide signalling in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, T.; Piriz, J.; Duflot, S.; Fernandez, A.M.; Gaitan, G.; Gomez-Pinedo, U.; Verdugo, J.M.; Leroy, F.; Soya, H.; Nunez, A.; et al. Neuronal activity drives localized blood-brain-barrier transport of serum insulin-like growth factor-I into the CNS. Neuron 2010, 67, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.M.; Reinhardt, R.R.; Lee, W.H.; Joncas, G.; Patel, S.C.; Bondy, C.A. Insulin-like growth factor 1 regulates developing brain glucose metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10236–10241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, M.; Milaneschi, Y.; Penninx, B.W.; Drent, M.L. Plasma insulin-like growth factor I levels are higher in depressive and anxiety disorders, but lower in antidepressant medication users. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 68, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo, J.L.; Piriz, J.; Llorens-Martin, M.V.; Fernandez, A.M.; Bolos, M.; LeRoith, D.; Nunez, A.; Torres-Aleman, I. Central actions of liver-derived insulin-like growth factor I underlying its pro-cognitive effects. Mol. Psychiatry 2007, 12, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegarra-Valdivia, J.A.; Santi, A.; Fernandez de Sevilla, M.E.; Nunez, A.; Torres Aleman, I. Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Deficiency Associates to Alzheimer’s Disease Co-Morbidities. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 69, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, A.; Bot, M.; Aleman, A.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Aleman, I.T. Circulating insulin-like growth factor I modulates mood and is a biomarker of vulnerability to stress: From mouse to man. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitschelen, M.; Yan, H.; Farley, J.A.; Warrington, J.P.; Han, S.; Herenu, C.B.; Csiszar, A.; Ungvari, Z.; Bailey-Downs, L.C.; Bass, C.E.; et al. Long-term deficiency of circulating and hippocampal insulin-like growth factor I induces depressive behavior in adult mice: A potential model of geriatric depression. Neuroscience 2011, 185, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, C.P.; Grimberg, A. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I is a Marker for the Nutritional State. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Rev. 2015, 13, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deuschle, M.; Blum, W.F.; Strasburger, C.J.; Schweiger, U.; Weber, B.; Korner, A.; Standhardt, H.; Gotthardt, U.; Schmider, J.; Pflaum, C.D.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) plasma concentrations are increased in depressed patients. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1997, 22, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Golde, D.W.; Bailey, R.; Geffner, M.E. Insulin-like growth factor-I resistance. Endocr. Rev. 1998, 19, 625–646. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero-Labrador, R.; Trueba-Saiz, A.; Martinez-Rachadell, L.; Fernandez de Sevilla, M.E.; Zegarra-Valdivia, J.A.; Pignatelli, J.; Diaz-Pacheco, S.; Fernandez, A.M.; Torres Aleman, I. Circulating Insulin-Like Growth Factor I is Involved in the Effect of High Fat Diet on Peripheral Amyloid β Clearance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatelli, J.; de Sevilla, M.E.F.; Sperber, J.; Horrillo, D.; Medina-Gomez, G.; Aleman, I.T. Insulin-like Growth Factor I Couples Metabolism with Circadian Activity through Hypothalamic Orexin Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H.; Akam, T.; Patriarchi, T.; Blanco-Pozo, M.; Burgeno, L.M.; Mohebi, A.; Cragg, S.J.; Walton, M.E. Lights, fiber, action! A primer on in vivo fiber photometry. Neuron 2024, 112, 718–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botterill, J.J.; Khlaifia, A.; Appings, R.; Wilkin, J.; Violi, F.; Premachandran, H.; Cruz-Sanchez, A.; Canella, A.E.; Patel, A.; Zaidi, S.D.; et al. Dorsal peduncular cortex activity modulates affective behavior and fear extinction in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2024, 49, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Shwani, T.; Liu, J.; Zhong, P.; Yang, F.; Schatz, K.; Zhang, F.; Pralle, A.; Yan, Z. Molecular and cellular mechanisms for differential effects of chronic social isolation stress in males and females. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 3056–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, C.J.; Reichelt, A.C.; Hall, P.A. The Prefrontal Cortex and Obesity: A Health Neuroscience Perspective. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2019, 23, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Garzon, E.; Fernandez, A.M.; Perez-Alvarez, A.; Genis, L.; Bascunana, P.; Fernandez de la Rosa, R.; Delgado, M.; Angel Pozo, M.; Moreno, E.; McCormick, P.J.; et al. The insulin-like growth factor I receptor regulates glucose transport by astrocytes. Glia 2016, 64, 1962–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macauley, S.L.; Stanley, M.; Caesar, E.E.; Yamada, S.A.; Raichle, M.E.; Perez, R.; Mahan, T.E.; Sutphen, C.L.; Holtzman, D.M. Hyperglycemia modulates extracellular amyloid-beta concentrations and neuronal activity in vivo. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 2463–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trueba-Saiz, A.; Cavada, C.; Fernandez, A.M.; Leon, T.; Gonzalez, D.A.; Fortea, O.J.; Lleo, A.; Del, S.T.; Nunez, A.; Torres-Aleman, I. Loss of serum IGF-I input to the brain as an early biomarker of disease onset in Alzheimer mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2013, 3, e330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegarra-Valdivia, J.A.; Fernandes, J.; Fernandez de Sevilla, M.E.; Trueba-Saiz, A.; Pignatelli, J.; Suda, K.; Martinez-Rachadell, L.; Fernandez, A.M.; Esparza, J.; Vega, M.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor I sensitization rejuvenates sleep patterns in old mice. Geroscience 2022, 44, 2243–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, M.W.; Sakaue, H.; Wang, L.; Alessi, D.R.; Roth, R.A. Modulation of insulin-stimulated degradation of human insulin receptor substrate-1 by Serine 312 phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 8199–8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbot, K.; Wang, H.Y.; Kazi, H.; Han, L.Y.; Bakshi, K.P.; Stucky, A.; Fuino, R.L.; Kawaguchi, K.R.; Samoyedny, A.J.; Wilson, R.S.; et al. Demonstrated brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease patients is associated with IGF-1 resistance, IRS-1 dysregulation, and cognitive decline. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1316–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.J.; Koffer, R.E. Lonely days: Linking day-to-day loneliness to biological and functional aging. Health Psychol. 2025, 44, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carro, E.; Trejo, J.L.; Busiguina, S.; Torres-Aleman, I. Circulating insulin-like growth factor I mediates the protective effects of physical exercise against brain insults of different etiology and anatomy. J. Neurosci 2001, 21, 5678–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickx, H.; McEwen, B.S.; van der Ouderaa, F. Metabolism, mood and cognition in aging: The importance of lifestyle and dietary intervention. Neurobiol. Aging 2005, 26 (Suppl. 1), 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, A.D.; Uchino, B.N.; Wethington, E. Loneliness and Health in Older Adults: A Mini-Review and Synthesis. Gerontology 2016, 62, 443–449. [Google Scholar]
- Frystyk, J.; Brick, D.J.; Gerweck, A.V.; Utz, A.L.; Miller, K.K. Bioactive insulin-like growth factor-I in obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.Y.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, K.R.; Cha, B.S.; Song, Y.D.; Lim, S.K.; Lee, H.C.; Huh, K.B. Effect of obesity on total and free insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, and their relationship to IGF-binding protein (BP)-1, IGFBP-2, IGFBP-3, insulin, and growth hormone. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1997, 21, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasselin, J.; Capuron, L. Chronic low-grade inflammation in metabolic disorders: Relevance for behavioral symptoms. Neuroimmunomodulation 2014, 21, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrodnik, M.; Zhu, Y.; Langhi, L.G.P.; Tchkonia, T.; Krüger, P.; Fielder, E.; Victorelli, S.; Ruswhandi, R.A.; Giorgadze, N.; Pirtskhalava, T.; et al. Obesity-Induced Cellular Senescence Drives Anxiety and Impairs Neurogenesis. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1061–1077.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrooz, F.; Liu, H.; Salim, S. Stress, psychiatric disorders, molecular targets, and more. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2019, 167, 77–105. [Google Scholar]
- Zegarra-Valdivia, J.A.; Pignatelli, J.; Nuñez, A.; Torres Aleman, I. The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor I in Mechanisms of Resilience and Vulnerability to Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Miyazaki, A.; Katagiri, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Idei, T.; Iguchi, T. Relationship between serum insulin-like growth factor-1 levels and Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 1748–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.M.; Elizabeth Forbes, M.; Constance Linville, M.; Riddle, D.R.; Sonntag, W.E.; Brunso-Bechtold, J.K. Stability of local brain levels of insulin-like growth factor-I in two well-characterized models of decreased plasma IGF-I. Growth Factors 2009, 27, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, V.; Werner, E.D.; Giraud, J.; Lee, Y.H.; Shoelson, S.E.; White, M.F. Phosphorylation of Ser307 in insulin receptor substrate-1 blocks interactions with the insulin receptor and inhibits insulin action. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, M.O.; Muller, A.; Bolos, M.; Carro, E.; Perry, M.L.; Portela, L.V.; Souza, D.O.; Torres-Aleman, I. Western Style Diet Impairs Entrance of Blood-Borne Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 into the Brain. Neuromol. Med. 2007, 9, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiyala, K.J.; Prigeon, R.L.; Kahn, S.E.; Woods, S.C.; Schwartz, M.W. Obesity induced by a high-fat diet is associated with reduced brain insulin transport in dogs. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carro, E.; Torres-Aleman, I. Serum insulin-like growth factor I in brain function. Keio J. Med. 2006, 55, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carro, E.; Torres-Aleman, I. The role of insulin and insulin-like growth factor I in the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 490, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappeler, L.; De Magalhaes Filho, C.M.; Dupont, J.; Leneuve, P.; Cervera, P.; Perin, L.; Loudes, C.; Blaise, A.; Klein, R.; Epelbaum, J.; et al. Brain IGF-1 receptors control mammalian growth and lifespan through a neuroendocrine mechanism. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrimi, J.; Spalletti, C.; Baroni, C.; Keceli, G.; Zhu, G.; Caragnano, A.; Matteucci, M.; Chelko, S.; Ramirez-Correa, G.A.; Bedja, D.; et al. Obese mice exposed to psychosocial stress display cardiac and hippocampal dysfunction associated with local brain-derived neurotrophic factor depletion. EBioMedicine 2019, 47, 384–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.E.; Arvanitakis, Z.; Macauley-Rambach, S.L.; Koenig, A.M.; Wang, H.Y.; Ahima, R.S.; Craft, S.; Gandy, S.; Buettner, C.; Stoeckel, L.E.; et al. Brain insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer disease: Concepts and conundrums. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinridders, A.; Ferris, H.A.; Cai, W.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin action in brain regulates systemic metabolism and brain function. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2232–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullmann, S.; Kleinridders, A.; Small, D.M.; Fritsche, A.; Haring, H.U.; Preissl, H.; Heni, M. Central nervous pathways of insulin action in the control of metabolism and food intake. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennard, M.R.; Nandi, M.; Chapple, S.; King, A.J. The glucose tolerance test in mice: Sex, drugs and protocol. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, H.; Lee, Y.B.; Lee, B.; Lee, D. A quantitative analysis of spontaneous alternation behaviors on a Y-maze reveals adverse effects of acute social isolation on spatial working memory. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Sui, G.; Wang, L.; Yang, C.; Wang, F. High-fat diet induced hippocampal CREB dysfunction, cognitive impairment and depression-like behaviors via downregulation of interleukin-2 in the mice. Metab. Brain Dis. 2022, 37, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; An, D.; Xu, H.; Cheng, X.; Wang, S.; Yu, W.; Yu, D.; Zhao, D.; Sun, Y.; Deng, W.; et al. Effects of social isolation and re-socialization on cognition and ADAR1 (p110) expression in mice. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Yao, X.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, D.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gao, J.; et al. Long-term high-fat diet consumption by mice throughout adulthood induces neurobehavioral alterations and hippocampal neuronal remodeling accompanied by augmented microglial lipid accumulation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 100, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffman, D.M.; Farias Quipildor, G.; Mao, K.; Zhang, X.; Wan, J.; Apontes, P.; Cohen, P.; Barzilai, N. Central insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) restores whole-body insulin action in a model of age-related insulin resistance and IGF-1 decline. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munive, V.; Zegarra-Valdivia, J.A.; Herrero-Labrador, R.; Fernandez, A.M.; Aleman, I.T. Loss of the interaction between estradiol and insulin-like growth factor I in brain endothelial cells associates to changes in mood homeostasis during peri-menopause in mice. Aging 2019, 11, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarter, M.; Bodewitz, G.; Stephens, D.N. Attenuation of scopolamine-induced impairment of spontaneous alteration behaviour by antagonist but not inverse agonist and agonist beta-carbolines. Psychopharmacology 1988, 94, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández de Sevilla, M.E.; Pignatelli, J.; Zegarra-Valdivia, J.A.; Mendez, P.; Nuñez, A.; Torres Alemán, I. Insulin-like growth factor I mitigates post-traumatic stress by inhibiting AMP-kinase in orexin neurons. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2182–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zegarra-Valdivia, J.A.; Pignatelli, J.; Fernandez de Sevilla, M.E.; Fernandez, A.M.; Munive, V.; Martinez-Rachadell, L.; Nunez, A.; Torres Aleman, I. Insulin-like growth factor I modulates sleep through hypothalamic orexin neurons. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 15975–15990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zegarra-Valdivia, J.; Khan, M.Z.; Putzolu, A.; Cipriani, R.; Pignatelli, J.; Torres Aleman, I. Influence of Lifestyle on Brain Sensitivity to Circulating Insulin-like Growth Factor 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010008
Zegarra-Valdivia J, Khan MZ, Putzolu A, Cipriani R, Pignatelli J, Torres Aleman I. Influence of Lifestyle on Brain Sensitivity to Circulating Insulin-like Growth Factor 1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleZegarra-Valdivia, Jonathan, M. Zahid Khan, Aurora Putzolu, Raffaela Cipriani, Jaime Pignatelli, and Ignacio Torres Aleman. 2025. "Influence of Lifestyle on Brain Sensitivity to Circulating Insulin-like Growth Factor 1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010008
APA StyleZegarra-Valdivia, J., Khan, M. Z., Putzolu, A., Cipriani, R., Pignatelli, J., & Torres Aleman, I. (2025). Influence of Lifestyle on Brain Sensitivity to Circulating Insulin-like Growth Factor 1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010008





