Abstract
Liver tumors represent a serious clinical health problem that threatens human life. Previous studies have demonstrated that the pathogenesis of liver tumors is complex and influenced by various factors, highlighting limitations in both basic pathological research and clinical treatment. Traditional research methods often begin with the discovery of phenomena and gradually progress to the development of animal models and human trials. Among these, liver tumor animal models play a critical role in advancing related research. The zebrafish liver closely resembles the human liver in structure, function, and regenerative capacity. Additionally, the high transparency and rapid development of zebrafish embryos and larvae make them ideal model organisms for studying liver tumors. This review systematically summarizes recent methods for constructing zebrafish liver tumor models, including transplantation, transgenesis, induction, and gene knockout. Furthermore, the present paper explores the applications of these models in the study of liver cancer pathogenesis, metastasis, the tumor microenvironment, drug screening, and other related areas. By comparing the advantages and limitations of various models and integrating their distinct characteristics, this review provides insights for developing a novel liver tumor model that better aligns with clinical needs. This approach will offer valuable reference information for further in-depth studies of the pathological mechanisms of liver tumors and the development of new therapeutic drugs or strategies.
1. Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a malignant tumor that originates in the liver and is the sixth most common malignancy worldwide. Currently, treatment options for liver tumors are inadequate. According to a World Health Organization (WHO) survey in 2020, the mortality rate associated with liver tumors ranks third among the causes of death from malignant tumors. HCCs can be categorized into several pathological types, including HCC, cholangiocarcinoma, and mixed hepatocellular–cholangiocarcinoma, with HCC being the most prevalent, accounting for 75–85% of all primary liver cancers globally. In China, this proportion is even higher, reaching nearly 93%. Risk factors for HCC include chronic infections with hepatitis B and C viruses, alcohol addiction, metabolic liver diseases—particularly nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—and exposure to dietary toxins such as aflatoxins and aristolochic acid [1]. Notably, variations in etiology, tumor growth kinetics, metastatic propensity, and prognosis can arise within the same cohort of patients with HCC due to diverse inducing factors. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of the underlying causes and mechanisms governing metastasis and proliferation is crucial for tailoring personalized treatment strategies and prognostic assessments in HCC management. In this context, the use of diverse animal models is essential, facilitating profound exploration into the pathogenesis of HCCs.
Animal models are widely utilized in biological research because of their distinct characteristics in morphology, genetics, physiology, and behavior. These animals share numerous similarities with humans and serve as crucial tools in biological and medical studies. Common animal models for HCC include mice, rats, rabbits, macaques, and pigs. Each model has advantages and disadvantages, and no single model can completely replicate human clinical symptoms [2]; thus, various animal disease models should complement each other’s strengths and weaknesses (Table 1).

Table 1.
Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of different liver cancer animal models.
In recent years, zebrafish have emerged as a novel model offering unique advantages, such as a short breeding time, small space requirements, low cost, and a transparent body structure that facilitates the observation of transplanted cells without an immune response from embryos [11]. This makes zebrafish an effective supplement to traditional animal models. Compared with that of rodents, the transparency of zebrafish embryos and larvae provides unique advantages for real-time high-resolution imaging at both the whole-body and cellular levels in vivo, enhancing the observation of cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. However, similar to mice and humans, adult zebrafish have limited spatial resolution due to the turbidity of their skin and subcutaneous structures. Current in vivo imaging technologies, such as bioluminescence, positron emission tomography (PET), computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), face challenges in terms of resolution, sensitivity, or the need for expensive equipment [12]. Nonetheless, advancements in biotechnology have led to the development of specific zebrafish models that address these shortcomings. For example, casper zebrafish—a highly transparent adult zebrafish model—and a double transgenic model combining the nacre mutant and roy orbison (roy) zebrafish exhibit nearly complete transparency in adults [12]. Furthermore, the use of isoetharine to inhibit melanin synthesis in zebrafish can also produce transparent specimens, which is particularly useful for imaging the eyes [13].
Although zebrafish and humans have different body structures, their liver functions are highly similar [14]. Comparative analyses of the transcriptomes of hepatocytes from zebrafish, mice, and humans show that the orthologous cell types in zebrafish are completely conserved, with functions closely resembling those of humans [15]. The experimental results indicate that the incidence of HCC induced by oncogenes in zebrafish models approaches 100% [16]. The zebrafish liver tumor model is invaluable for studying the early processes of tumor occurrence and long-term tumor development. As related research has progressed, an increasing number of zebrafish models constructed through various methods have been applied to specific experiments. This review aims to summarize, classify, analyze, and explore studies of zebrafish liver tumor models in recent years, providing a fresh perspective on liver cancer research.
2. Application of the Zebrafish Liver Tumor Model in Different HCC Exploration Scenarios
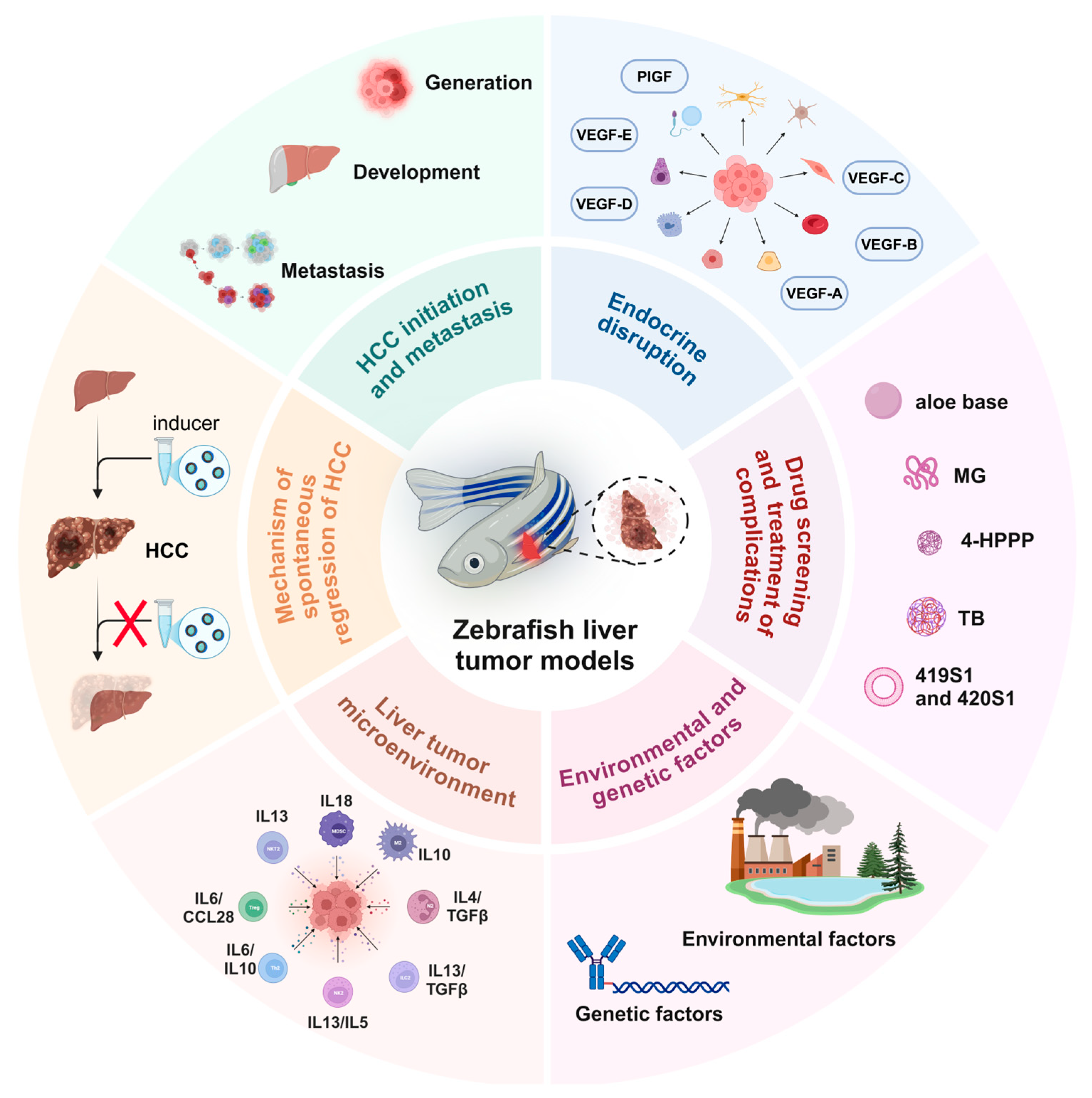
The zebrafish model for studying liver cancer has been successfully utilized to explore and evaluate various aspects of carcinogenesis, including tumor growth, tumor focus formation, proliferation, cancer stem cell dynamics, metastasis (migration, dissemination, extravasation, and infiltration), angiogenesis, and the tumor microenvironment (Figure 1). It is worth noting that the zebrafish model breaks through some of the limitations of traditional models in research. For example, the dynamic observation of cancer cell metastasis in the zebrafish transplantation model, the repeated induction of single transgene and inducer in the same individual, and the dynamic transformation study of liver disease and liver tumors make the study of the zebrafish model more feasible.
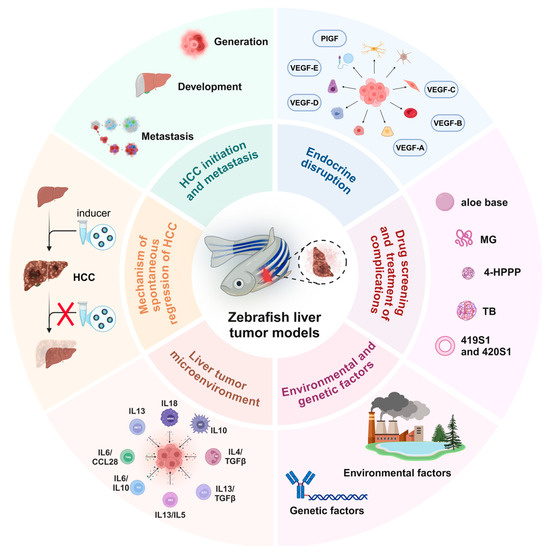
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the application of the zebrafish liver tumor model in different liver cancer exploration scenarios. 4-HPPP: 4-phenoxyphenol derivative; MG: methyl gallate; TB: teabrownin.
2.1. Mechanisms of Occurrence and Metastasis of HCC
The occurrence of tumors can be clearly divided into three independent stages: tumor formation, progression, and metastasis. The most common gene mutations associated with tumor formation include TERT (telomerase reverse transcriptase) promoter mutations, TP53, CTNNB1 (Catenin Beta 1), AXIN1, ARID1A, ARID2, and other mutations accounting for less than 10% of mutations [17]. Current studies using zebrafish models have successfully demonstrated that genes such as TP53 [18], CTNNB1 [19], and ARID1A [20] play key roles in the development of HCC. However, the phenotypes associated with the AXIN1 gene in zebrafish models are not directly linked to liver tumors. For example, mutations in the GSK3 binding domain of zebrafish Masterblind/Axin1 result in reduced or absent eyes and telencephalon, alongside an expansion of telencephalic fates to the anterior part of the brain [21]. Additionally, increased maternal expression of Axin1 and Axin2 contributes to the ventralization phenotype observed in the ichabod zebrafish mutant [22]. During HCC progression, several pathways are involved, including telomere maintenance, the P53 pathway, the Wnt pathway, the cell cycle, the Ras/MAPK pathway, and the AKT/mTOR pathway, as well as epigenetic and chromatin remodeling processes, oxidative stress, and angiogenesis [17]. The zebrafish model can effectively reproduce the effects of most of these pathways on liver tumors, highlighting its importance in studying cell signaling pathway activation.
Cancer cell migration within the body is a significant factor contributing to poor clinical prognosis [23]. Given the complexity of metastasis, it is essential to utilize experimental models that can represent and manipulate each step of the metastatic process individually [24]. For example, TWIST1 is one of the key genes involved in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which is critical in embryonic development, tumor progression, and metastasis. However, the role of the TWIST1 gene in liver tumor metastasis in vivo remains unclear [23]. In a study by Jeng-Wei Lu et al., two double-transgenic zebrafish models, twist1a+/kras+ [23] and twist1a+/xmrk+ [25], were constructed to investigate how crosstalk between signaling pathways can enhance the migration and dissemination of cancer cells. In recent years, various factors influencing cell migration in vivo have been validated in zebrafish models, including the knockdown of MAT2B in cells [26], the downregulation of p-Met and p-AKT protein expression [27], the activation of β-catenin ubiquitination, and proteasomal degradation [28], as well as the overexpression of LGR5 [29] and induction of TAp73β expression [30]. All these factors can significantly impact the migration and spread of cancer cells in vivo. In future research on cancer cell metastasis and invasion, the zebrafish model remains a valuable animal model to consider.
2.2. Research on the Mechanism of Spontaneous Regression in Liver Cancer
The regression of liver tumors in clinical practice may be closely related to the treatment methods employed [31]. Common treatment options include surgical resection, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, and ablation therapy. These approaches aim to eliminate tumor cells and can promote the gradual regression of tumors. In 2002, medical journals published an average of more than four papers per month on spontaneous cancer regression [32]. However, the reported cases are often difficult to reproduce in clinical practice [33,34]. In several liver tumor models induced in transgenic zebrafish, similar phenomena have been consistently observed. When the chemical inducer is withdrawn, the liver tumors in the zebrafish model tend to regress. After several weeks of tumor regression, the tumor-affected livers often revert to histologically normal livers, and tumors can be reinduced by reexposing the fish to the inducing agent, thereby reactivating oncogene expression [35].
The mechanisms underlying tumor regression in different transgenic zebrafish models may vary. (1) Tumor liver cells can be eliminated through cell death, inhibiting tumor cell pathways and allowing normal liver cells to eventually replace tumor liver cells through proliferation and differentiation. In a study by Anh Tuan Nguyen et al., withdrawal of mifepristone resulted in tumor regression in transgenic fish by inducing cell death and inhibiting Ras through targeting its downstream effectors, including the Raf–MEK–ERK and PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathways, which drive liver tumorigenesis [36]. (2) Tumor liver cells may directly revert to normal liver cells. Research by Zhen Li et al. revealed that in addition to the complete replacement of HCC cells by newly generated normal hepatocytes, intermediate phenotypes such as adenomas or hyperplasia were observed in many regression samples, indicating that during tumor regression, some HCC cells can be directly restored to normal liver cells [37]. These findings suggest that some liver tumors may rely on mutations in a single gene for initiation and development. By inhibiting key oncogenes or oncogenic pathways, it may be possible to revert tumor cells back to a normal state.
2.3. Liver Tumor Microenvironment
Abnormal lipid accumulation in hepatocytes increases oxidative stress and leads to lipotoxicity, triggering liver inflammation, which is a hallmark of the progression from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) to HCC. Immune cell populations, including neutrophils and macrophages, provide growth factors, matrix remodeling factors, and inflammatory mediators to the tumor microenvironment (TME), facilitating tumor growth [38]. Current research indicates that both the innate and adaptive immune systems play key roles in the progression of HCC. Further in-depth research is needed to analyze immune responses and liver tumorigenesis in living intact animals. The optical clarity and genetic tractability of zebrafish larvae make them an attractive model for studying the liver microenvironment and immune cell composition using noninvasive fluorescence in vivo imaging [39]. Although the crosstalk between tumors and their local microenvironment has been well studied, the impact of tumors on distant tissues remains understudied [16]. In a study by Yan Li et al., progressive destruction of the intestinal structure was observed in tumor-bearing zebrafish, characterized by villus damage, thinning of the intestinal wall, an increased number of goblet cells, decreased goblet cell size, and eosinophil infiltration, with some fish exhibiting an inflammatory bowel phenotype [16]. This study provides a broader organ-scale view of the liver tumor microenvironment and represents the first systematic characterization of intestinal disruption under liver tumor conditions, targeting intestinal inflammation as a potential approach to managing cancer cachexia.
Research findings regarding the role of neutrophils in tumor progression are conflicting. Some studies highlight the antitumor capabilities of neutrophils in vitro, in vivo, and in clinical contexts, whereas others suggest that neutrophil infiltration may promote tumor progression [40]. For example, Chuan Yan et al. demonstrated that inflammatory signals from oncogenic hepatocytes lead to the rapid recruitment of neutrophils to the oncogenic liver, suggesting that neutrophils promote early liver carcinogenesis [41]. In contrast, Zhen Li et al. reported that neutrophils and macrophages were enriched during both tumor progression and regression. Although these immune cells are relatively evenly distributed in HCC, they accumulate locally during tumor regression, particularly macrophages, which show a dominant vascular association in late regression. These findings suggest that these immune cells may play distinct roles in tumor progression and regression [9]. The mechanistic relationships among different immune cells in the tumor microenvironment are not merely one-way interactions; there may be feedback loops that complicate these dynamics. The zebrafish model offers unique advantages for such research and will be an indispensable tool for uncovering these complex mechanisms.
2.4. Drug Screening and Individualized Treatment of Complications
One significant advantage of zebrafish models over rodent models is the ability to conduct high-throughput in vivo chemical screening. This allows researchers to use zebrafish liver tumor models for new drug discovery and preclinical drug screening, evaluating the efficacy and potential toxic side effects of candidate drugs against liver cancer. Over the past 20 years, various studies have demonstrated the therapeutic potential of a range of natural and chemically synthesized products for treating HCC, including aloe base, a 4-phenoxyphenol derivative, MG, TB, bortezomib, and two polytyrosine kinase inhibitors (419S1 and 420S1) [2]. Although there are some limitations in the clinical application of these drugs, this is mainly manifested in physiological differences, drug dose conversion, and drug delivery route differences, so the relevant candidate drugs need to be further verified, such research has the potential to open new avenues for the development of specific therapies. In the study by Marlon E.P. Rosa and colleagues, it was found that anacardic acid (2-hydroxy-6-alkylbenzoic acid, AA) exhibits hydrophobic properties, making it challenging to deliver in aqueous systems. To address this, a natural polymer was developed as an active encapsulation matrix in zebrafish studies. In vivo experiments demonstrated no acute toxicity or changes in locomotor activity in zebrafish treated with this formulation [42]. Through these screening techniques, new angiogenesis inhibitors, such as IROFULVEN and endostatin-mimetic peptide 011, have been identified [9].
Another promising direction for future research is the use of different induced zebrafish models to conduct personalized treatment studies based on individual responses to drugs, which could guide treatment options for clinical liver cancer patients. Cancer anorexia cachexia syndrome (CACS) is a multifactorial syndrome associated with tumors characterized by weight loss, anorexia, and generalized muscle and fat mass atrophy, severely impacting treatment efficacy and quality of life [43]. Sarcopenia, a progressive systemic disease of skeletal muscle, leads to accelerated losses in muscle mass and function and is associated with increased adverse outcomes, including falls, functional decline, frailty, and death [44]. Symptoms such as anorexia make it challenging to implement nutritional strategies in other model animals; however, these strategies can be effectively applied in zebrafish. In studies using the krasV12 transgenic zebrafish model, liver tumors were induced using tetracycline or its analogs, resulting in sustained and severe skeletal muscle atrophy, as evidenced by a gradual decrease in the muscle fiber cross-sectional area (MFCSA). Increased food supplementation was found to accelerate liver carcinogenesis and muscle atrophy, demonstrating a strong correlation between HCC and muscle atrophy [45]. Research by Fei Fei et al. revealed that normalizing insulin-like growth factor 1 (Igf1) expression and disrupting leptin signaling could significantly alleviate anorexia, muscle atrophy, and lipoatrophy in a Ras- and Myc-driven HCC zebrafish model [43]. Given that cancer cachexia affects up to 80% of patients with advanced solid tumors [45], addressing this issue is crucial. The use of zebrafish models can enhance the design of future clinical trials and help stage cancer patients based on the degree of cachexia. This approach enables the early initiation of nutritional, metabolic, and pharmacological support before severe weight loss occurs [46].
2.5. Interference of Sex Hormones on Liver Tumors
Sex differences in primary liver cancer have been well documented, with the incidence in men being 2–8 times greater than that in women [47]. Traditionally, this sex bias has been attributed to men’s increased susceptibility to known risk factors for HCC, such as heavy alcohol consumption and unhealthy diets. However, experiments in laboratory mice have also demonstrated that males are more susceptible to HCC than females, with 100% of males and only 30% of females developing HCC under chronic carcinogen exposure [48]. This phenomenon has been replicated in transgenic zebrafish models, prompting further investigation into the mechanisms underlying sex differences associated with HCC.
Numerous studies using zebrafish models have consistently reported these differences. Research conducted by Xiaojing Huo et al. revealed that larval oncogenic hepatocytes exhibit cancer stem cell characteristics. Female oncogenic hepatocytes resemble mild human HCC subtypes, whereas male oncogenic hepatocytes align more closely with severe HCC subtypes, mirroring the sex differences observed in both zebrafish and humans [49]. Further research by Yan Li and colleagues demonstrated that estrogen treatment has tumor-suppressive effects in the early stages of tumor development by inhibiting cell proliferation, whereas androgens promote tumor growth by increasing cell proliferation [50]. The roles of sex hormones in liver tumorigenesis and regression were explored using the inducible double-transgenic zebrafish Myc/xmrk. Hankun Li et al. treated Myc/xmrk fish with androgens or estrogens and reported that the male hormone 11-ketotestosterone (KT11) generally stimulated HCC progression in female Myc/xmrk fish and delayed tumor regression. Conversely, estrogen (E2) delayed HCC progression and accelerated regression in male Myc/xmrk fish, indicating that sex hormones significantly influence both tumor progression and regression, contributing to the observed sex differences [51]. Although current research confirms that sex hormones affect liver tumor diseases, it also highlights that the tumorigenic impact of these hormones is limited, as animal models continue to develop HCC despite hormonal interventions. More relevant research is needed to enhance the clinical applicability of these findings.
2.6. Research on the Impact of Genetic and Environmental Factors on Liver Cancer
Genetic and environmental factors play crucial roles in the occurrence of liver cancer. The significance of hMOF (human males absent on the first, KAT8) in vascular invasion of HCC is highlighted in the study by Nicolas Poté et al., which supports the transcriptional activation of key genes involved in this process [52]. These findings underscore the major role of epigenetic changes in HCC progression and provide valuable insights for future targeted therapies. The zebrafish model is particularly useful for exploring the impact of environmental factors, including chemicals, nutritional influences, and toxins, on liver cancer. While mammalian models often provide insights into the stress effects of environmental factors on humans, zebrafish offer unique advantages in certain studies. Given that a significant proportion of tumors are thought to originate from environmental exposures, the potential carcinogenic risks associated with these factors must be thoroughly assessed, as outlined by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) [53]. The complexity of potential environmental factors necessitates experimental designs that can address the interactions between multiple elements. Owing to their efficiency and rapid development, zebrafish models are particularly well suited for this purpose. In fact, zebrafish have emerged as one of the primary model organisms for the preliminary screening of environmental carcinogens, making them valuable tools in cancer research. The earliest environmental factors studied in zebrafish mainly focused on pollutants of global concern, such as persistent organic pollutants (POPs) [54] and heavy metals [55], and then gradually expanded to endocrine disrupters [56], new pollutants [57], and physical factors.
3. Construction of a Zebrafish Liver Tumor Model Through Transplantation Methods
3.1. Transplantation Methods
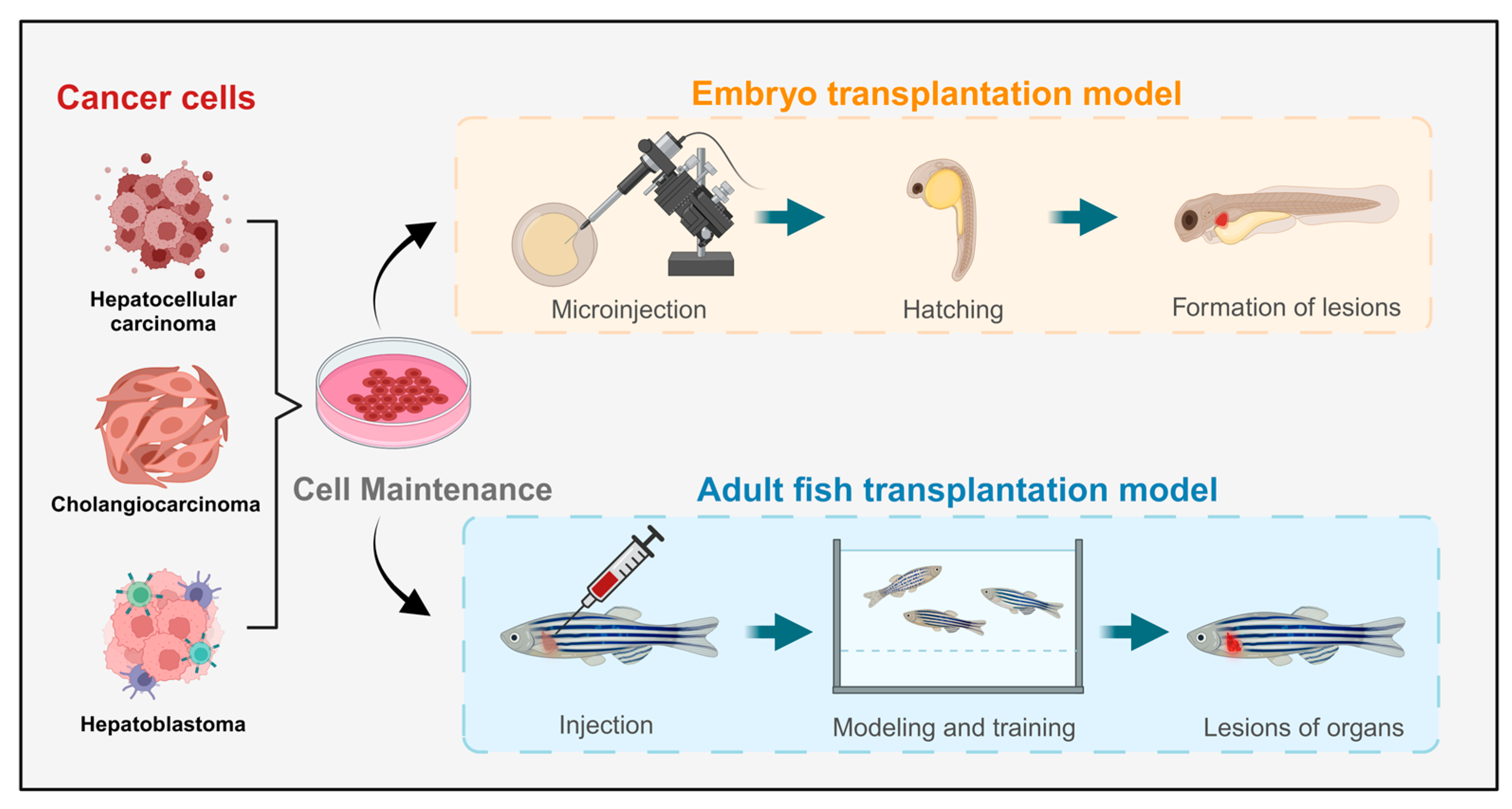
Currently, the predominant method for constructing liver cancer model animals is xenotransplantation, which is widely used and has a high success rate [58]. Xenograft models of liver cancer closely resemble human cancer cell lines at the cellular level. By implanting tumor cells or tissues marked with fluorescent proteins into model animals, researchers can observe the proliferation and metastasis of cancer cells in vivo, aiding in predictions of human liver cancer development, treatment efficacy, and drug screening (Figure 2). Notably, zebrafish have low-level or absent immune systems during their embryonic and early juvenile stages, making them particularly amenable to xenograft models and more receptive to transplanted cells. This characteristic has garnered significant attention for xenograft zebrafish models, leading to rapid advancements in related research fields [59]. However, these models have limitations, including potential trauma responses from implantation surgery and anatomical differences between zebrafish and mammals, which need to be addressed for more accurate results.
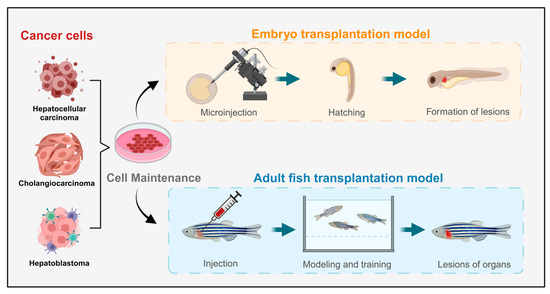
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the liver tumor zebrafish model constructed through transplantation methods.
3.2. Embryo Transfer Model
Zebrafish serve as a high-throughput in vivo model, enhancing success rates in later stages of preclinical drug development and reducing the economic and time costs associated with the screening process. Among the animal models constructed through transplantation methods, zebrafish models offer several significant advantages in the larval stage compared with rodents. Additionally, the unique immune deficiency stages of zebrafish eliminate the need for immunosuppressive treatments when xenograft models are constructed, thereby reducing potential interference in the construction process. In a study by Federica Tonon et al., a novel, rapid, and cost-effective zebrafish HCC xenograft model was developed by microinjecting the HCC cell line JHH6 into the yolk sac of zebrafish embryos for drug screening purposes [27]. An increasing number of researchers have recently explored the use of microinjection to transfer liver cancer cells into zebrafish embryos, resulting in improved construction standards for these models. Zebrafish models are gaining prominence in the fields of tumor xenograft models, developmental biology, genetics, and cancer research, occupying an increasingly important position in scientific inquiry.
3.3. Adult Fish Transplant Model
The embryo transplant model is limited to the early stages of embryonic development, and models constructed at this stage may not guarantee continued growth and development. Consequently, some research may necessitate the use of more mature organs or adult samples. To address this, researchers have explored injecting cells into the tissues or organs of adult zebrafish to create adult fish transplant models of liver tumors. In a study by Jianhong Yang et al., fluorescently labeled HepG2 cells were successfully introduced into the small intersegmental blood vessels of transgenic zebrafish. The results revealed that some tumor cells remained quiescent, whereas others underwent apoptosis or fragmentation. Notably, tumor cells with strong metastatic potential were able to penetrate and extravasate from host blood vessels into adjacent tissues within 24 h [60]. Although the stability of adult zebrafish models constructed using transplantation methods has yet to be fully established, these models represent promising avenues for development and application and could play irreplaceable roles in the study of certain cases of nonspontaneous liver tumors.
3.4. Application Effects of Zebrafish Models Constructed Through Transplantation
Dozens of xenograft zebrafish liver cancer models have been developed to date. Models constructed from different cell lines and injection sites exhibit distinct characteristics and varying applicability. Recent experimental studies have shown that yolk sac microinjection is the most successful method for constructing these transplantation models. The following sections evaluate the applications and effects of xenograft zebrafish models in related fields over the past five years (Table 2).

Table 2.
Application and evaluation of the zebrafish model constructed through transplantation methods.
4. Transgenic Methods for Constructing a Zebrafish Liver Tumor Model
4.1. Transgenic Methods
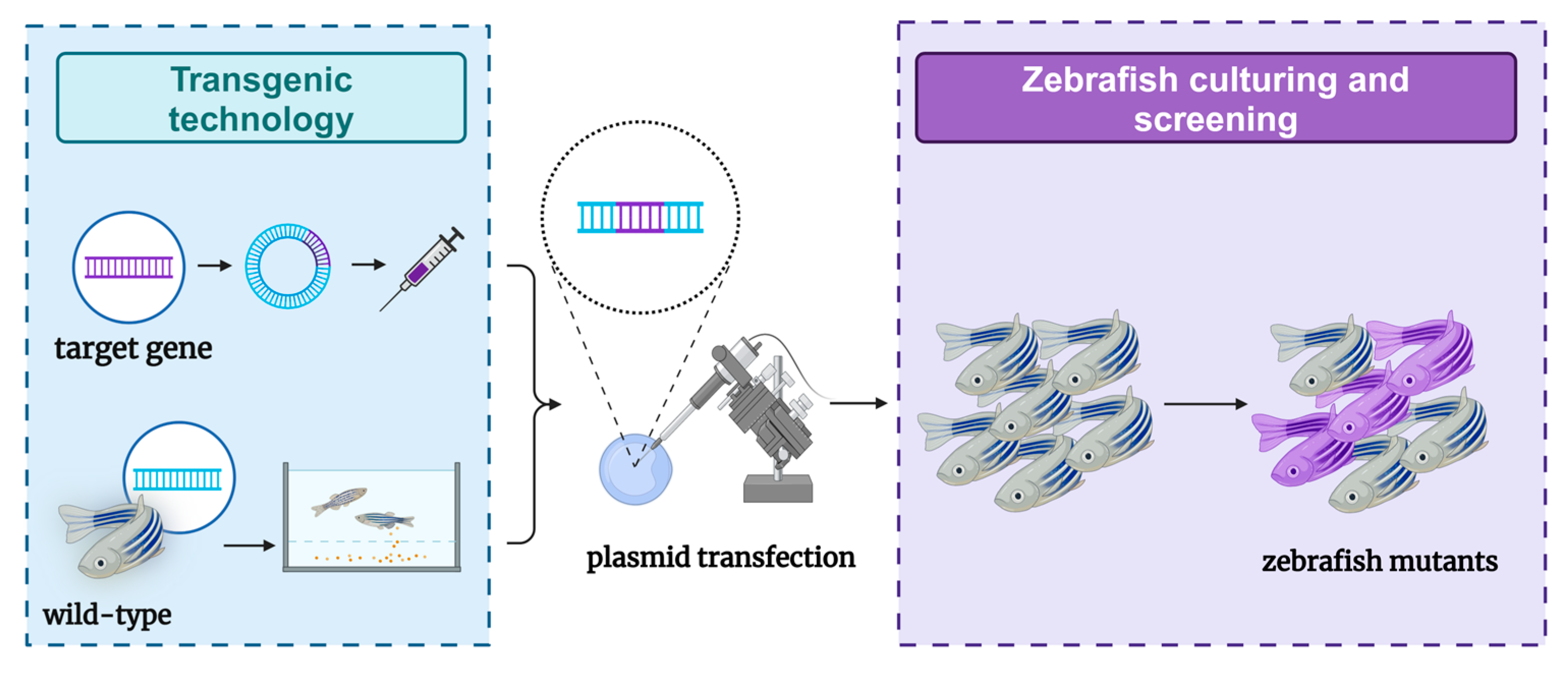
The production of genetically modified organisms is invaluable for studying the genetic basis of embryonic development in both mammalian and invertebrate species [66]. Comparisons with the human reference genome revealed that approximately 70% of human genes have at least one clear zebrafish ortholog, and approximately 85% of disease-causing genes have zebrafish counterparts [67,68]. Due to these similarities, zebrafish are considered promising transgenic research models for studying various human diseases, including genetic disorders. However, the research process has faced challenges. In 1988, the first transgenic zebrafish were successfully created by microinjecting plasmid DNA carrying foreign genes into fertilized eggs [14]. Unfortunately, the transgenic zebrafish produced by this method lacked stability. It was not until 2011 that stable transgenic zebrafish models capable of expressing liver cancer were reported [69]. Currently, researchers have successfully constructed several liver tumor models by expressing transgenes in zebrafish livers, primarily using three common types of oncogenes: kras, xmrk, and Myc. These transgenic zebrafish typically develop hepatocellular adenomas (HCAs) that can progress to HCC and other liver tumors of varying severity. Together, these three zebrafish liver cancer models account for nearly half (47.2%) of human HCC cases, with a significant correlation observed between some human HCCs and these oncogene-addicted zebrafish tumors [70]. Transgenic zebrafish have a high success rate and high stability in the construction of liver tumor models (Figure 3). Owing to their rapid reproduction rate, zebrafish play a crucial role in the early exploration of clinical treatments. However, due to limitations in transgenic technology—such as gene superposition effects—liver tumors induced by specific genes cannot fully represent the relevant pathogenesis. Therefore, additional models are needed to support related research.
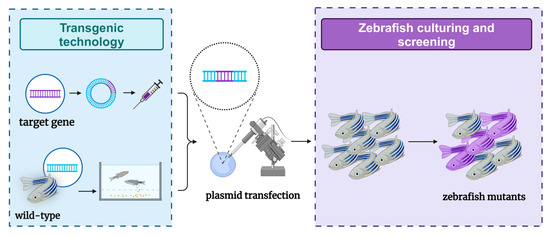
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the zebrafish model of liver tumors constructed through transgenic methods.
4.2. krasV12 Gene Overexpression Model
Cross-species comparisons of cancer transcriptomes have further elucidated HCC-specific gene signatures and liver cancer progression signatures that are evolutionarily conserved between humans and zebrafish [69]. One of the most significant transgenic zebrafish liver tumor models is the krasV12 gene overexpression model, which involves the transformation of zebrafish liver cells through krasV12 overexpression. This model represents one of the earliest stable transgenic zebrafish liver tumor models. In a study by Anh Tuan Nguyen et al., the molecular mechanisms underlying progressive Ras-induced HCC were explored using the liver-specific fatty acid-binding protein 10 (fabp10) promoter, which drives oncogenic krasV12 expression specifically in zebrafish livers [69]. Ras has been identified as a potent oncogene and a central regulator of multiple signal transduction pathways in human cancer, with activation occurring in more than half of HCC cases [36]. Consequently, the krasV12 overexpression model effectively mirrors many clinical features of liver tumors. This zebrafish liver cancer model excels in various applications, including studies of tumorigenesis, oncogene addiction, tumor microenvironment interactions, sex differences, cancer cachexia, and drug screening. However, although it reveals several molecular mechanisms of Ras-driven liver tumorigenesis and recapitulates typical features of human HCC, the constitutive high-level expression of Ras often leads to early tumorigenesis and premature mortality. In contrast, low-Krasv12-expressing strains exhibit delayed tumor onset and a lower incidence of tumors (approximately 30%), which may limit the model’s utility for large-scale research and drug screening [36]. Despite these challenges, ongoing efforts are aiming to develop improved zebrafish liver tumor models, building on the foundational krasV12 model.
4.3. xmrk Model
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and its ligand EGF have emerged as promising targets for human liver cancer therapy. The xmrk gene is a naturally occurring mutation of the EGFR subtype EGFRb found in fish of the genus Xiphophorus (including flatfish and swordtail fish) [43]. This mutation features two alterations in its extracellular domain, leading to constitutive autophosphorylation and activation of downstream signaling pathways [43]. The xmrk model employs the Tet-on system to achieve liver-specific expression of the superactive fish oncogene xmrk, resulting in the construction of transgenic zebrafish capable of inducing liver cancer [43]. In both juvenile and adult xmrk transgenic fish, liver tumors are rapidly induced with 100% penetrance through continuous induction over varying time periods [43]. Remarkably, this model exhibits most of the histological characteristics of human HCC and displays a unique phenomenon of rapid tumor regression once the inducer is removed. This model provides an ideal experimental framework for studying the initiation and maintenance of HCC driven by a single oncogene, paving the way for the development of treatments targeting oncogene addiction or related oncogenic pathways.
4.4. Myc Overexpression Model
Both xmrk and Myc serve as oncogene-related biomarkers for HCC. The Myc model utilizes the Tet-on system for liver-specific expression of mouse Myc, creating a transgenic zebrafish liver tumor model [71]. This model involves dose-dependent Myc expression, which leads to liver hyperplasia that ultimately progresses to hepatocellular adenoma and liver cancer with prolonged induction [71]. Research by Pal Kaposi-Novak et al. indicated that the activation of the Myc transcriptional signature is closely associated with the malignant transformation of precancerous liver lesions [72]. The transcriptome of Myc-induced zebrafish liver tumors is highly similar to the transcriptomes of various stages of human liver disease, including low-grade dysplastic nodules (LGDNs), high-grade dysplastic nodules (HGDNs), and various stages of HCC (very early HCC, early HCC, late HCC, and advanced HCC) [71]. Like in the xmrk model, the transient inactivation of Myc due to the cessation of inducers results in tumor regression and the differentiation of cancer cells into mature bone cells [71]. However, reactivation of Myc does not restore malignancy but instead induces apoptosis [73]. These findings suggest that the Myc overexpression model possesses unique characteristics that differentiate it from other zebrafish liver tumor models, offering potential avenues for developing targeted therapies for specific cancers.
4.5. Multitransgenic Model
To date, dozens of inducible transgenic zebrafish have been successfully constructed using native inducible gene promoters or chimeric promoters that incorporate well-characterized responsive cis elements [72]. With advancements in zebrafish transgenic technology, researchers have started to explore the construction of multitransgenic models. Double transgenic technology allows the introduction of two different genes into the target organism, enabling the simultaneous expression of multiple traits and facilitating more complex functional enhancements. For example, the transparency of casper double mutant zebrafish has improved due to the interaction of two genes, allowing for direct visualization of organs such as the heart, intestines, liver, and gallbladder using a standard stereomicroscope [12]. Currently, multitransgenic zebrafish combining fluorescent genes with liver disease genes have also been reported. Research indicates that when there is potential complementarity or synergy between two genes, this effect can be more effectively realized through double transgene technology. For example, a study by Jerry D. Monroe et al. demonstrated that the induction of xmrk, Myc, and xmrk/Myc can lead to different stages of HCC. During tumor progression, lipid deposition and grade generally increase, whereas triglyceride levels decrease. In the double transgenic model, Myc appears to regulate lipid species levels in early HCC stages, whereas xmrk may take over this regulation in later stages, with the complementary effects of the two genes enhancing the speed and extent of tumorigenesis [73]. Additionally, a study by Jeng-Wei Lu et al. revealed that the tumor metastasis rate in twist1a+/kras+ double transgenic zebrafish was more than 20% greater than that in single transgenic zebrafish, demonstrating that different genes can cooperate to induce tumor metastasis [23].
4.6. Application Effects of Zebrafish Models Constructed Through Transgenic Methods
In recent years, as clinical research has advanced, the limitations of single transgenic models have become increasingly apparent, leading researchers to explore the use of multiple transgene combinations to construct more relevant models for research applications. These multitransgenic zebrafish models offer greater complexity and can more accurately replicate human disease processes, allowing for more comprehensive studies of disease mechanisms and therapeutic testing. Below is an overview of recent applications and evaluations of multitransgenic zebrafish models in various research fields over the past five years (Table 3).

Table 3.
Application and evaluation of the transgenic zebrafish model.
5. Construction of Zebrafish Liver Tumor Models Through Induction Methods
5.1. Induction Methods
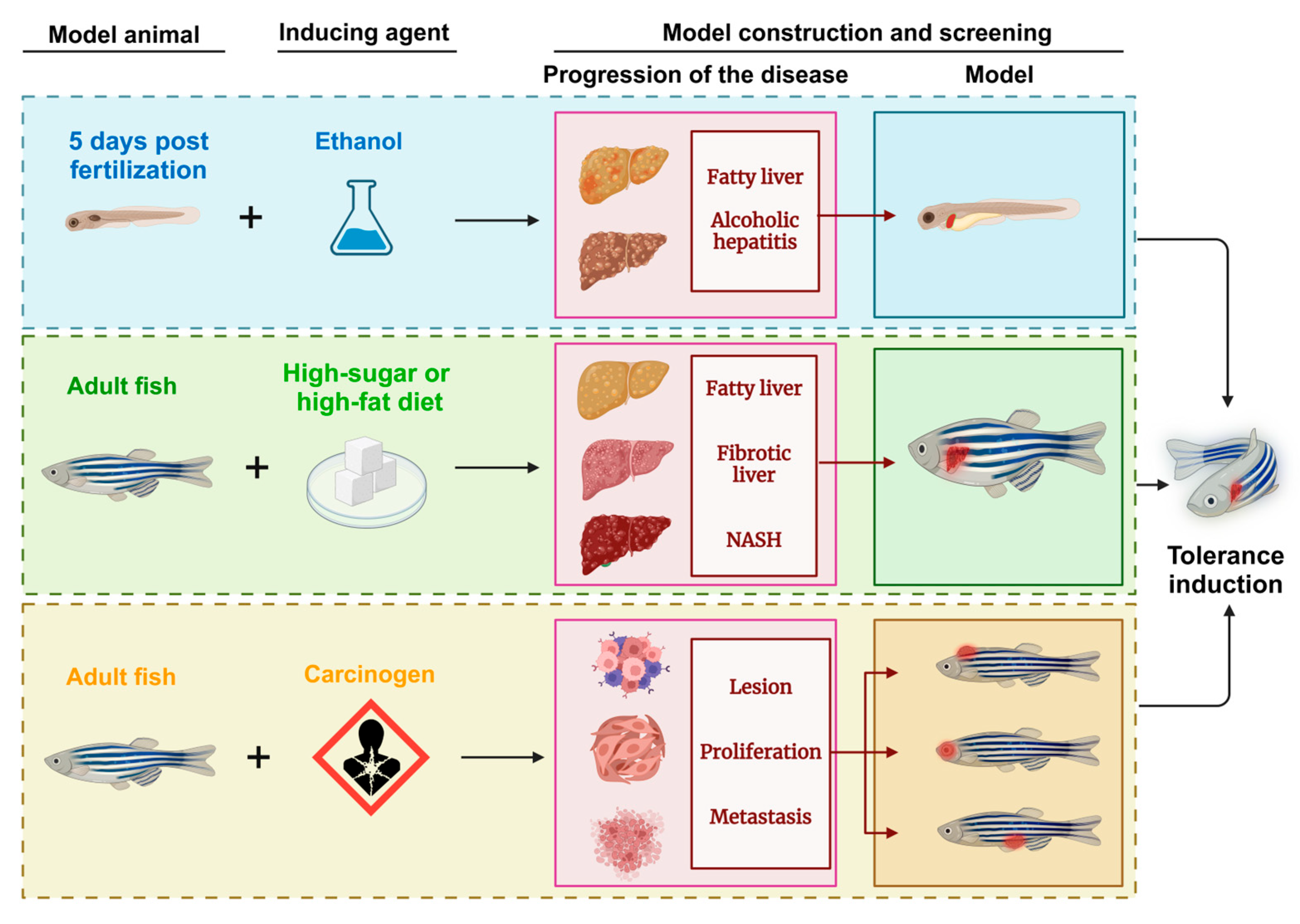
Inducible zebrafish liver cancer models have become valuable for verifying cancer-related pathogenesis at the histological, transcriptomic [78], and molecular levels. This approach focuses on both eliminating and preventing cancer factors and constructs models through the use of chemicals, heavy metals, and radiation to simulate carcinogenic environments. Through repeated exposure and subsequent expression, an in vivo model closely resembling human liver cancer characteristics was generated. Early work by JAN M. Spitsberg [79] in the late 20th century using N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG) to induce liver tumors laid the groundwork for modern inducible zebrafish cancer models and highlighted their potential in cancer research. Induced zebrafish models not only exhibit clinical parallels to human liver tumors but also serve as early detection tools for environmental carcinogens. They provide insight into the complexities of the impact of carcinogens, simulating the multifactorial progression of liver cancer in a way that reflects real-world exposures. Although conventional induced models have several limitations—namely, difficulty in isolating single cancer pathways owing to the broad effects of carcinogens—they continue to be indispensable. By integrating recent technological advancements, researchers have enhanced the scope and application of these models, enabling their use in diverse aspects of clinical research and reinforcing their role in understanding and combating liver cancer (Figure 4).
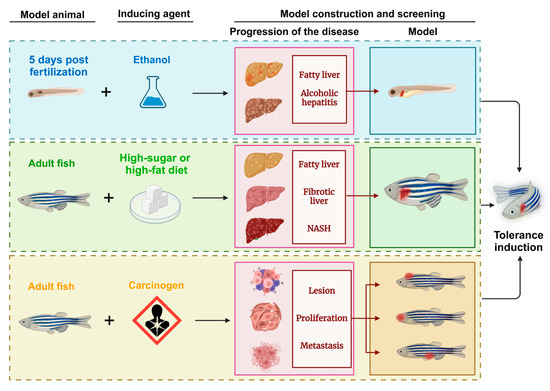
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the zebrafish model of liver tumors generated through induction methods. NASH: nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
5.2. Chemical Induction Model
Liver cancer is caused primarily by alcoholism, chronic hepatitis B and C infections, and exposure to environmental toxins [80]. Zebrafish models are induced with carcinogens to mimic liver disease progression into tumors. However, due to the nonspecific nature of carcinogen effects and the physiological and immune differences between zebrafish and humans, these induced models often fail to consistently replicate isolated liver conditions, which complicates their application in liver cancer research. Diethylnitrosamine (DEN), a hepatotoxic and hepatocarcinogenic compound, has been instrumental in the development of HCC models in various species [80,81]. In studies by Jegannathan Srimathi Devi and colleagues, DEN successfully induced liver fibrosis in zebrafish, showing its potential for inducing liver disease in non-mammalian animals [82]. This zebrafish model exhibited key liver pathologies, including fatty tissue lesions, peritoneal effusion, and tumor development in the liver, making it a practical and efficient model for investigating liver cancer.
However, the prolonged induction period and inconsistent lesion progression limit the effectiveness of purely carcinogen-induced models. Recent advancements in transgenic technology have led to combined models in which chemical induction and genetic modifications stabilize liver tumor models in zebrafish. For example, Reboredo et al. explored transgene expression changes in the liver by combining the rtTA2(S)-M2 and GLp65 transactivators with doxycycline and mifepristone for a more precise induction control [83]. Mifepristone, an antiprogestogen agent, was also used to regulate gene expression via the LexPR system, increasing the model’s specificity [84]. These combined inducible zebrafish models have become pivotal in liver cancer research, offering stable lesion progression and accurate control of life cycle expression. Their applications have expanded to include drug screening, and some models have demonstrated the potential for tumor regression—a rare phenomenon in clinical settings. Understanding the mechanisms behind this regression could unlock new pathways for cancer treatment, making these models valuable for future explorations in liver cancer therapy.
5.3. Dietary Induction Model
The pathogenesis of HCC involves a progressive sequence of liver damage starting with hepatitis or fatty liver disease, advancing to fibrosis, and finally to cirrhosis, which can evolve into HCC over decades [9]. Researchers have leveraged zebrafish to model this stepwise progression by establishing both alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and diet-induced obesity (DIO) models, simulating aspects of NAFLD. These models provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of primary liver tumor development.
Zebrafish larvae are especially suitable for studying ALD due to their ability to metabolize alcohol, with the liver reaching maturity at four days postfertilization (DPF). ALD can be induced by adding ethanol to the larval breeding environment, effectively inducing alcohol-related liver damage. However, a key challenge in this model is maintaining sufficient food intake in ethanol-exposed larvae, a difficulty that prevents the sustained induction of ALD, combined with the progressive development of HCC—a challenge that remains for future research. NAFLD, which encompasses simple steatosis to NASH with chronic inflammation, can lead to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and eventually HCC [24]. In zebrafish, diet-induced obesity models provide a robust approach to studying NAFLD by simulating human dietary habits. Feeding zebrafish a high-sugar or high-fat diet induces NAFLD-related diseases, and with extended exposure, disease severity increases, including the risk of related comorbidities. These diet-induced zebrafish models closely replicate the primary pathogenesis of hepatocellular tumors in humans, offering an accessible and representative platform for investigating dietary impacts on liver disease progression.
5.4. Application Effects of Zebrafish Models Constructed Through Induction Methods
Induced zebrafish liver cancer models, developed through exposure to carcinogens, provide an essential platform for clinical research because of their alignment with the pathogenesis of human liver diseases. These models offer unique insights into disease progression by replicating the stages and mechanisms of HCC development observed in human cases, from initial hepatic damage to tumor formation. Despite the variability in their construction compared with those of genetically stable models, such as transgenic approaches, their relevance to environmentally and chemically induced liver cancer makes them a cornerstone in the study of clinically relevant disease pathways. Recent advancements in zebrafish modeling have led to the development of standardized protocols that improve the consistency and reproducibility of induced models. These standards focus on optimal carcinogen types, dosages, and exposure durations, as well as postexposure care, which have collectively enhanced the reliability and applicability of induced liver cancer models in research. This rigorous approach enables researchers to simulate pathophysiological changes leading to liver cancer more accurately, creating a bridge between experimental models and human clinical conditions. In the last five years, induced zebrafish models have become increasingly instrumental in assessing environmental carcinogens, examining potential chemopreventive agents, and understanding the molecular underpinnings of liver carcinogenesis. The following sections detail the application and impact of these models in recent research, highlighting their contributions to advancing our understanding of liver cancer etiology and intervention strategies (Table 4).

Table 4.
Application and evaluation of induction methods for constructing zebrafish models.
6. Gene Knockout Methods for Constructing Zebrafish Liver Tumor Models
6.1. Gene Knockout Methods
Gene knockout technology enables targeted manipulation of endogenous DNA, reducing or eliminating the expression of specific proteins [86]. This technique is invaluable for constructing precise animal models that reflect the mechanisms of human diseases, especially in the study of genetic and complex polygenic diseases. To achieve a reliable model, factors such as accuracy, reproducibility, cost-effectiveness, and usability across research fields are crucial [9]. Recent advancements in gene-editing tools, including zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs) [31], transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) [32], and CRISPR/Cas systems [34], have transformed model development, with CRISPR/Cas9 being especially effective and widely adopted in zebrafish research [33]. CRISPR/Cas9 has facilitated rapid and precise gene knockout, allowing researchers to silence specific tumor suppressor genes, such as Tp53 and PTEN, which are implicated in the pathogenesis of HCC. Through this technology, researchers can investigate how gene deletions contribute to liver cancer development in zebrafish, providing insights into gene function and disease mechanisms (Figure 5). Gene knockout zebrafish models offer high potential for understanding the genetic factors involved in liver cancer and other diseases; however, challenges remain. Off-target effects and the unintended silencing of genes across generations can limit precision. Additionally, compensatory mechanisms within organisms may offset the effects of gene knockouts, potentially confounding results. Due to these limitations, knockout zebrafish models are still emerging as research tools and are used selectively in studies requiring intricate analysis of gene–disease interactions.
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of zebrafish models of liver tumors generated through knockout methods. sg RNA: single-guide RNA; TSS: transcription start site.
6.2. p53 Mutation Model
The p53 tumor suppressor gene is essential for regulating apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and DNA damage repair, with mutations leading to its inactivation in approximately 50% of human cancers [47]. In the liver, p53 ablation exacerbates liver pathology and polyploidization, even though it does not significantly affect other tissues, such as the kidney, germ cells, or brain [48]. Initial studies with p53-mutant zebrafish models did not reveal tumor formation in liver tissue from p53 mutation alone. However, research by Jeng-Wei Lu et al. demonstrated that combining HBx (hepatitis B virus X protein) with p53 mutations induces HCC in zebrafish through the activation of the src pathway, with HBx inducing tumorigenesis only in the presence of p53 mutations [49]. This HBx/p53 mutant model mirrors aspects of human HCC, providing a valuable in vivo platform for potential liver cancer drug screening. The zebrafish p53-HBx model represents a major step toward replicating human HCC, but the widespread roles of p53 in stem cell proliferation, differentiation, and overall development complicate its use. No current model can entirely eliminate the growth variations introduced by p53 mutations, which limits the model’s reliability and application scope in research [44]. Therefore, although promising, these models require further refinement for broader applications.
6.3. PTEN Knockout Model
The PTEN tumor suppressor gene, known for its dual protein and lipid phosphatase activities, is one of the most commonly mutated genes in sporadic cancers [45]. Its tumor-suppressive properties rely mainly on its lipid phosphatase function, which negatively regulates the PI3K–AKT–mTOR signaling pathway [45]. In a study by Juanjuan Luo et al., researchers used the CRISPR/Cas9 system to create a transgenic zebrafish strain with PTEN-specific mutations to genetically induce liver tumorigenesis [46]. The results showed that PTEN loss alone was insufficient to induce liver cancer in zebrafish, highlighting that PTEN depletion alone may not always trigger tumorigenesis in certain tissues. Further investigations by Luo’s team employed CRISPR/Cas9 to generate zebrafish models with dual mutations in PTEN and p53. These models presented greater incidences of tumors, higher histological grades, and shorter survival times than single-gene mutation models did, suggesting a synergistic interaction between the PTEN and p53 pathways in promoting tumor initiation and progression [46]. This dual mutation model underscores the cooperative role of PTEN and p53 in hepatocarcinogenesis in zebrafish, providing a compelling basis for a more detailed exploration of the mechanistic pathways underlying liver cancer and potential therapeutic targets.
6.4. Application Effects of Zebrafish Models Constructed Through Gene Knockout Methods
In the early stages of zebrafish liver cancer model development, the limitations of gene knockout technology pose challenges, restricting the application of knockout models. However, recent advancements in gene editing methods, including CRISPR/Cas9, TALENs, and ZFNs, have revitalized interest in these models, enabling a more precise and effective knockout of specific genes. Current studies suggest that silencing or reducing the expression levels of certain tumor suppressor genes, such as p53 and PTEN, can play a critical role in liver tumor development. This aligns with findings from knockout models, which help to delineate how individual gene loss contributes to cancer initiation and progression. Compared with other construction methods, knockout zebrafish models tend to focus on the specific loss of one or a few genes, somewhat limiting their scope. However, they are invaluable in pinpointing the specific roles of genes in cancer pathology. These models are particularly useful for investigating the functional impact of gene deletions on tumor development, making them ideal for mechanistic studies in liver cancer research. The following is an application and effectiveness evaluation of induced knockout zebrafish models in liver cancer research from recent years (Table 5).

Table 5.
Application and evaluation of gene knockout methods for constructing zebrafish models.
7. Conclusions
Research on zebrafish liver tumor models provides a powerful tool for exploring the pathogenesis of liver cancer and preclinical drug screening. Zebrafish liver cancer models constructed through transplantation, transgenesis, induction, gene knockout, and other methods have shown great potential in terms of tumor formation, development, metastasis, and treatment response, such as the following: (1) xenotransplantation has a low immune expression stage and can be used to conduct in-depth research on the invasiveness of liver cancer cells; (2) models combining transgenes and drug induction help to explore the unique spontaneous regression mechanism of zebrafish liver tumors; and (3) zebrafish models facilitate real-time observation of tumor growth and metastasis processes and are suitable for high-throughput screening of potential therapeutic drugs. However, these models also have limitations such as certain biological differences, differences in metabolic pathways, and poor prediction ability for some drug responses. Therefore, future research should consider combining the advantages of multiple animal models to compensate for the shortcomings of a single model and further improve the clinical translation potential of liver cancer research. For example, the zebrafish model for candidate drug screening combined with a mouse model and cell in vitro validation can greatly shorten the development cycle of new drugs. Future research should also strengthen the application of zebrafish models in personalized treatment, especially in high-throughput drug screening, tumor microenvironment research, and the treatment of complications. By continuously optimizing the construction method of zebrafish models and promoting the development of gene editing technology, more precise treatment strategies and better prognosis management for patients with liver cancer are expected.
Author Contributions
Q.L. and L.J. wrote and drafted the manuscript and figures. R.P. designed and refined this manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Yifei Wang (Shanghai Fei Fan Testing Certification Group Co., Suzhou, China) for suggestions on the concept of this manuscript and financial support. The authors would like to thank the editor and the anonymous reviewers for providing their insightful comments and suggestions to improve the quality of this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| MRI | Resonance imaging |
| TERT | Telomerase reverse transcriptase |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| EMT | Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| 4-HPPP | 4-[4-(4-hydroxyphenoxy)phenoxy]phenol |
| MG | Methyl gallate |
| TB | Theabrownin |
| CACS | Cancer-related anorexia cachexia syndrome |
| MFCSA | Muscle fiber cross-sectional area |
| Igf1 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| KT11 | 11-ketotestosterone |
| fabp10 | Fatty acid binding protein 10 |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| hMOF | Human males absent on the first |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| ADI | Aidi injection |
| SS | Sorbaria sorbifolia |
| PARP1 | Poly(adenosine diphosphate [ADP]-ribose) polymerase 1 |
| WNK1 | With-no-lysine (K)-1 |
| CP | Compound Phyllanthus urinaria L. |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCA | Hospital Corporation of America |
| LGDN | Low-grade dysplastic nodule |
| HGDN | High-grade dysplastic nodule |
| veHCC | Very early HCC |
| eHCC | Early HCC |
| aHCC | Advanced HCC |
| vaHCC | Very advanced HCC |
| MNNG | Methyl-N′-nitro-nitrosoguanidine |
| DEN | Diethyl nitrosamine |
| pGL-VP | Promoter-less green luciferase vector plasmid |
| ALD | Alcoholic liver disease |
| DIO | Diet-induced obesity |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| ZFNs | Zinc finger nucleases |
| TALENs | Transcription activator-like effector nucleases |
References
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonon, F.; Farra, R.; Zennaro, C.; Pozzato, G.; Truong, N.; Parisi, S.; Rizzolio, F.; Grassi, M.; Scaggiante, B.; Zanconati, F.; et al. Xenograft Zebrafish Models for the Development of Novel Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Molecules. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, F.H.F.; Traldi, M.C.C.; Araújo, R.S.S.; Stefano, J.T.; D’albuquerque, L.A.C.; Oliveira, C.P. Preclinical models of liver câncer. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2023, 60, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adwan, H.; Georges, R.; Pervaiz, A.; Berger, M.R. Investigation of Metastasis-Related Genes: A Rat Model Mimicking Liver Metastasis of Colorectal Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascale, F.; Pelage, J.-P.; Wassef, M.; Ghegediban, S.H.; Saint-Maurice, J.-P.; De Baere, T.; Denys, A.; Duran, R.; Deschamps, F.; Pellerin, O.; et al. Rabbit VX2 Liver Tumor Model: A Review of Clinical, Biology, Histology, and Tumor Microenvironment Characteristics. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 871829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; An, S.; Aizimuaji, Z.; Tao, C.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, S.; Wu, J.; Xiao, T.; et al. Integrated analysis of the rhesus monkey liver transcriptome during development and human primary HCC AFP-related gene expression. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 25, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Piao, Y.; Guo, F.; Wei, J.; Chen, Y.; Dai, X.; Zhang, X. Current progress of pig models for liver cancer research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targen, S.; Konu, O. Zebrafish Xenotransplantation Models for Studying Gene Function and Drug Treatment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2021, 52, 1248–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-W.; Ho, Y.-J.; Yang, Y.-J.; Liao, H.-A.; Ciou, S.-C.; Lin, L.-I.; Ou, D.-L. Zebrafish as a disease model for studying human hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12042–12058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrighton, P.J.; Oderberg, I.M.; Goessling, W. There Is Something Fishy About Liver Cancer: Zebrafish Models of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 8, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Wei, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, Q.; Lee, S.M.-Y.; Ge, W.; Luo, K.Q.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y. Apoptosis-Sensing Xenograft Zebrafish Tumor Model for Anticancer Evaluation of Redox-Responsive Cross-Linked Pluronic Micelles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 39775–39786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.M.; Sessa, A.; Burke, C.; Bowman, T.; LeBlanc, J.; Ceol, C.; Bourque, C.; Dovey, M.; Goessling, W.; Burns, C.E.; et al. Transparent adult zebrafish as a tool for in vivo transplantation analysis. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 2, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciag, M.; Wnorowski, A.; Bednarz, K.; Plazinska, A. Evaluation of β-adrenergic ligands for development of pharmacological heart failure and transparency models in zebrafish. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 434, 115812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, N.; Shiraishi, H.; Hanada, T. Zebrafish as a Useful Model System for Human Liver Disease. Cells 2023, 12, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oderberg, I.M.; Goessling, W. Biliary epithelial cells are facultative liver stem cells during liver regeneration in adult zebrafish. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e163929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lee, A.Q.; Lu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Lu, J.-W.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, N.; Liu, D.; Gong, Z. Systematic Characterization of the Disruption of Intestine during Liver Tumor Progression in the xmrk Oncogene Transgenic Zebrafish Model. Cells 2022, 11, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-S.; Huang, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-R.S.; Hsiao, E.; Hsu, T.-A.; Shiao, H.-Y.; Jiaang, W.-T.; Sampurna, B.P.; Lin, K.-H.; Wu, M.-S.; et al. Identification of Novel Anti-Liver Cancer Small Molecules with Better Therapeutic Index Than Sorafenib via Zebrafish Drug Screening Platform. Cancers 2019, 11, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-D.; Tseng, Y.-K.; Yuh, C.-H.; Chen, S.-C. Low concentrations of 4-ABP promote liver carcinogenesis in human liver cells and a zebrafish model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-W.; Lin, L.-I.; Sun, Y.; Liu, D.; Gong, Z. Effect of Lipopolysaccharides on Liver Tumor Metastasis of twist1a/krasV12 Double Transgenic Zebrafish. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Nguyen, A.T.; Spitsbergen, J.M.; Gong, Z. Myc-Induced Liver Tumors in Transgenic Zebrafish Can Regress in tp53 Null Mutation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Mani, S.A.; Donaher, J.L.; Ramaswamy, S.; Itzykson, R.A.; Come, C.; Savagner, P.; Gitelman, I.; Richardson, A.; Weinberg, R.A. Twist, a Master Regulator of Morphogenesis, Plays an Essential Role in Tumor Metastasis. Cell 2004, 117, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccard, H.; Muschel, R.J.; Opdenakker, G. On the dual roles and polarized phenotypes of neutrophils in tumor development and progression. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2012, 82, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.P.; Gong, Z.; Tse, W.K.F. Zebrafish as the toxicant screening model: Transgenic and omics approaches. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 234, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiong, Y.; Cao, W.; Chen, Z.; He, L.; Tong, M.; Zhang, L.; Wu, M. Epidermal growth factor receptor promotes high-fructose nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inducing mitochondrial fission in zebrafish. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 652, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, K.J.; Doggett, K.; Geng, F.; Mieruszynski, S.; Whitehead, L.; Smith, K.A.; Hogan, B.M.; Simons, C.; Baillie, G.J.; Molania, R.; et al. ahctf1 and kras mutations combine to amplify oncogenic stress and restrict liver overgrowth in a zebrafish model of hepatocellular carcinoma. eLife 2023, 12, e73407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordzij, J.G.; de Bruin-Versteeg, S.; Verkaik, N.S.; Vossen, J.M.J.J.; de Groot, R.; Bernatowska, E.; Langerak, A.W.; van Gent, D.C.; van Dongen, J.J.M. The immunophenotypic and immunogenotypic B-cell differentiation arrest in bone marrow of RAG-deficient SCID patients corresponds to residual recombination activities of mutated RAG proteins. Blood 2002, 100, 2145–2152. [Google Scholar]
- Tonon, F.; Zennaro, C.; Dapas, B.; Carraro, M.; Mariotti, M.; Grassi, G. Rapid and cost-effective xenograft hepatocellular carcinoma model in Zebrafish for drug testing. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-H.; Dang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Dong, C.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, Z.; Shi, J.-P. Anti-hepatocellular carcinoma activity of Sorbaria sorbifolia by regulating VEGFR and c-Met/apoptotic pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 324, 117758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xiao, X.; Yan, B.; Yuan, Q.; Dong, X.; Du, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shan, L.; Ding, Z.; Zhou, L.; et al. Green tea-derived theabrownin induces cellular senescence and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma through p53 signaling activation and bypassed JNK signaling suppression. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Jing, W.; Xiong, G.; Ma, D.; Lin, Y.; Lv, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhu, L.; Shen, X.; et al. Inhibiting Src-mediated PARP1 tyrosine phosphorylation confers synthetic lethality to PARP1 inhibition in HCC. Cancer Lett. 2022, 526, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Noyes, M.B.; Zhu, L.J.; Lawson, N.D.; Wolfe, S.A. Targeted gene inactivation in zebrafish using engineered zinc-finger nucleases. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Xiao, A.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, S.; Zhang, B. Heritable gene targeting in zebrafish using customized TALENs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jin, L.; Peng, R. Research Progress on the Construction and Application of a Diabetic Zebrafish Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, G.; Babu, P.E.; Singh, R.; Trehanpati, N. Application of CRISPR-Cas9 based gene editing to study the pathogenesis of colon and liver cancer using organoids. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-W.; Sun, Y.; Lin, L.-I.; Liu, D.; Gong, Z. Exacerbation of Liver Tumor Metastasis in twist1a+/xmrk+ Double Transgenic Zebrafish following Lipopolysaccharide or Dextran Sulphate Sodium Exposure. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Emelyanov, A.; Koh, C.H.V.; Spitsbergen, J.M.; Parinov, S.; Gong, Z. An inducible krasV12 transgenic zebrafish model for liver tumorigenesis and chemical drug screening. Dis. Model. Mech. 2012, 5, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iscan, E.; Ekin, U.; Yildiz, G.; Oz, O.; Keles, U.; Suner, A.; Cakan-Akdogan, G.; Ozhan, G.; Nekulova, M.; Vojtesek, B.; et al. TAp73β Can Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Dedifferentiation. Cancers 2021, 13, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passeri, M.J.; Cinaroglu, A.; Gao, C.; Sadler, K.C. Hepatic Steatosis in Response to Acute Alcohol Exposure in Zebrafish requires Srebp Activation. Hepatology 2009, 49, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Huo, X.; Wang, S.; Feng, Y.; Gong, Z. Stimulation of hepatocarcinogenesis by neutrophils upon induction of oncogenic kras expression in transgenic zebrafish. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, S.; Houseright, R.A.; Graves, A.L.; Golenberg, N.; Korte, B.G.; Miskolci, V.; Huttenlocher, A. Metformin modulates innate immune inflammation and early progression of NAFLD-associated hepatocellular carcinoma in zebrafish. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yang, Q.; Gong, Z. Tumor-Associated Neutrophils and Macrophages Promote Gender Disparity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Zebrafish. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.E.; Rebouças, L.M.; Marques, S.P.; Silva, L.M.; Cunha, F.E.; Costa, P.M.; de Assis, D.A.; Silveira, K.B.; Muniz, C.R.; Trevisan, M.T.; et al. Sodium hyaluronate microcapsules to promote antitumor selectivity of anacardic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 296, 139616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhan, H.; Zeng, Z.; Li, C.; Spitsbergen, J.M.; Meierjohann, S.; Schartl, M.; Gong, Z. Inducible and repressable oncogene-addicted hepatocellular carcinoma in Tet-on xmrk transgenic zebrafish. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elabd, S.; Jabeen, N.A.; Gerber, V.; Peravali, R.; Bourdon, J.-C.; Kancherla, S.; Vallone, D.; Blattner, C. Delay in development and behavioural abnormalities in the absence of p53 in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollander, M.C.; Blumenthal, G.M.; Dennis, P.A. PTEN loss in the continuum of common cancers, rare syndromes and mouse models. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Lu, C.; Feng, M.; Dai, L.; Wang, M.; Qiu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, B.; et al. Cooperation between liver-specific mutations of pten and tp53 genetically induces hepatocarcinogenesis in zebrafish. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2021, 40, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, D.; Mi, T.; Li, R.; Guo, T.; Li, W. Icaritin activates p53 and inhibits aerobic glycolysis in liver cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2024, 392, 110926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.J.; Bona, N.; Smink, J.; Webb, H.K.; Crisp, A.; Garaycoechea, J.I.; Crossan, G.P. p53 regulates diverse tissue-specific outcomes to endogenous DNA damage in mice. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-W.; Yang, W.-Y.; Tsai, S.-M.; Lin, Y.-M.; Chang, P.-H.; Chen, J.-R.; Wang, H.-D.; Wu, J.-L.; Jin, S.-L.C.; Yuh, C.-H. Liver-specific expressions of HBx and src in the p53 mutant trigger hepatocarcinogenesis in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Spitsbergen, J.M.; Gong, Z. Males develop faster and more severe hepatocellular carcinoma than females in krasV12 transgenic zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, F.; Sun, S.; Li, Q.; Pei, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R.; Luo, F.; Yu, M.; Wang, X. Combinatorial Normalization of Liver-Derived Cytokine Pathways Alleviates Hepatic Tumor-Associated Cachexia in Zebrafish. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessy, T. Immunity over inability: The spontaneous regression of cancer. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2011, 2, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Luo, H.; Li, C.; Huo, X.; Yan, C.; Huang, X.; Al-Haddawi, M.; Mathavan, S.; Gong, Z. Transcriptomic analysis of a transgenic zebrafish hepatocellular carcinoma model reveals a prominent role of immune responses in tumour progression and regression. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Limón, G.; Zappia, J.; Muller, M. A realistic mixture of ubiquitous persistent organic pollutants affects bone and cartilage development in zebrafish by interaction with nuclear receptor signaling. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Wu, B.; Chen, L. Combined effects of polyvinyl chloride or polypropylene microplastics with cadmium on the intestine of zebrafish at environmentally relevant concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tank, M.R.; Patel, H.B.; Patel, H.R.; Delvadiya, R.S.; Patel, U.D.; Fefar, D.T.; Chauhan, J.M. Long-term exposure to bisphenol-A causes oxidative stress-related alterations at the genetic and cellular levels in the mature ovary of adult zebrafish. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kong, L.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Effect of functional groups of polystyrene nanoplastics on the neurodevelopmental toxicity of acrylamide in the early life stage of zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 278, 107177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Sun, N.; Liu, Z.; He, F.; Yang, B. Progress in the application of zebra fish model in cancer research. China Med. Her. 2023, 15, 45–48+60. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, L.M.J.; Seftor, E.A.; Bonde, G.; Cornell, R.A.; Hendrix, M.J.C. The fate of human malignant melanoma cells transplanted into zebrafish embryos: Assessment of migration and cell division in the absence of tumor formation. Dev. Dyn. 2005, 233, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Pei, H.; Luo, H.; Fu, A.; Yang, H.; Hu, J.; Zhao, C.; Chai, L.; Chen, X.; Shao, X.; et al. Non-toxic dose of liposomal honokiol suppresses metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through destabilizing EGFR and inhibiting the downstream pathways. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 915–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.H.; Chua, H.L.; Gong, Z.; Lam, T.J.; Sin, Y.M. Development and maturation of the immune system in zebrafish, Danio rerio: A gene expression profiling, in situ hybridization and immunological study. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Huang, Z.; Tao, X.; You, L.; Stalin, A.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; et al. The anti-hepatocellular carcinoma effect of Aidi injection was related to the synergistic action of cantharidin, formononetin, and isofraxidin through BIRC5, FEN1, and EGFR. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Yin, Z.; Wu, Z.; Sheng, Z.; Ma, C.; Chen, R.; Zhang, X.; Tang, K.; Fei, J.; Cao, Z. Probing Synergistic Targets by Natural Compounds for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 715762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Yang, B.; Yao, Y.; Liao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, N.; Tong, G. Autophagic Inhibition of Caveolin-1 by Compound Phyllanthus urinaria L. Activates Ubiquitination and Proteasome Degradation of β-catenin to Suppress Metastasis of Hepatitis B-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 659325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, S.; Kunter, I.; Azbazdar, Y.; Ozhan, G.; Atabey, N.; Karagonlar, Z.F.; Erdal, E. LGR5/R-Spo1/Wnt3a axis promotes stemness and aggressive phenotype in hepatoblast-like hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cell. Signal. 2021, 82, 109972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, G.W.; V1Elkind, J.R.; Mcmurray, J.V.; Westerfield, M. Stable lines of transgenic zebrafish exhibit reproducible patterns of transgene expression. Development 1990, 109, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarne, M. Editorial: Advances in morphogenesis and patterning: Zebrafish as a model organism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1376663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Emelyanov, A.; Koh, C.H.V.; Spitsbergen, J.M.; Lam, S.H.; Mathavan, S.; Parinov, S.; Gong, Z. A high level of liver-specific expression of oncogenic Kras(V12) drives robust liver tumorigenesis in transgenic zebrafish. Dis. Model. Mech. 2011, 4, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Li, Z.; Nguyen, A.T.; Li, C.; Emelyanov, A.; Gong, Z. Xmrk, Kras and Myc Transgenic Zebrafish Liver Cancer Models Share Molecular Signatures with Subsets of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Zhan, H.; Li, C.; Zhou, L.; Yan, C.; Spitsbergen, J.M.; Gong, Z. A transgenic zebrafish liver tumor model with inducible Myc expression reveals conserved Myc signatures with mammalian liver tumors. Dis. Model. Mech. 2013, 6, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaposi-Novak, P.; Libbrecht, L.; Woo, H.G.; Lee, Y.-H.; Sears, N.C.; Coulouarn, C.; Conner, E.A.; Factor, V.M.; Roskams, T.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Central role of c-Myc during malignant conversion in human hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.; Arvanitis, C.; Chu, K.; Dewey, W.; Leonhardt, E.; Trinh, M.; Sundberg, C.D.; Bishop, J.M.; Felsher, D.W. Sustained loss of a neoplastic phenotype by brief inactivation of MYC. Science 2002, 297, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monroe, J.D.; Fraher, D.; Huang, X.; Mellett, N.A.; Meikle, P.J.; Sinclair, A.J.; Lirette, S.T.; Maihle, N.J.; Gong, Z.; Gibert, Y. Identification of novel lipid biomarkers in xmrk- and Myc-induced models of hepatocellular carcinoma in zebrafish. Cancer Metab. 2022, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Iwao, K.; Nagasawa, Y.; Aihara, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Imaoka, S.; Murata, M.; Shimano, T.; Nakamura, Y. Activation of the beta-catenin gene in primary hepatocellular carcinomas by somatic alterations involving exon 3. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 2524–2527. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao, H.-Y.; Hsu, P.-J.; Sampurna, B.P.; Lin, Y.-J.; Lin, K.-H.; Zhao, Y.-N.; Wang, H.-D.; Yuh, C.-H. The Comprehensive Effects of Carassius auratus Complex Formula against Lipid Accumulation, Hepatocarcinogenesis, and COVID-19 Pathogenesis via Stabilized G-Quadruplex and Reduced Cell Senescence. Adv. Biol. 2023, 7, 2200310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, W.; Cheng, C.; Lin, K.; Sampurna, B.P.; Chan, S.; Yuh, C. Low molecular weight fucoidan inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in zebrafish via ASGR/STAT3/HNF4A signaling. Clin. Transl. Med. 2017, 10, e252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, J.-W.; Huo, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Gong, Z. Effects of sex hormones on liver tumor progression and regression in Myc/xmrk double oncogene transgenic zebrafish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 277, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yuan, J.; Liu, S.; Torraca, V.; Liao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Tan, H.; Yao, X.; Hou, X.; Lyu, H.; et al. ILKAP Promotes the Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Inhibiting β-Catenin Degradation and Enhancing the WNT Signaling Pathway. Adv. Biol. 2024, 8, 2300117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Q.; Li, Y.; Gong, Z. Inducible Liver Cancer Models in Transgenic Zebrafish to Investigate Cancer Biology. Cancers 2021, 13, 5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotty, J.; Bablon, P.; Weiss, P.-H.; Soussan, P. Diethylnitrosamine Induction of Hepatocarcinogenesis in Mice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2024, 2769, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srimathi Devi, J.; Haripriya, D.; Arul, S.; Saravanan, K.M.; Bupesh, G. Evaluation of anti-cancer effect of zerumbone and cisplatin on N-nitrosodiethylamine induced hepatic cancer in freshwater fish (Danio rerio). Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 4794–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reboredo, M.; Kramer, M.G.; Smerdou, C.; Prieto, J.; Rivas, J.D.L. Transcriptomic Effects of Tet-On and Mifepristone-Inducible Systems in Mouse Liver. Hum. Gene Ther. 2008, 19, 1233–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deodato, D.; Asad, N.; Dore, T.M. Photorearrangement of Quinoline-Protected Dialkylanilines and the Photorelease of Aniline-Containing Biological Effectors. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 7342–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, D.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Gong, Z.; Liu, C. Perfluorooctane sulfonate promotes doxycycline-induced liver tumor progression in male Krasv12 transgenic zebrafish. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfenberger, L.; Hennerici, T.; Király, G.; Kitzmüller, S.; Vernooij, M.; Zielinski, J.G. Transgenic Mouse Technology in Skin Biology: Generation of Complete or Tissue-Specific Knockout Mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).