Regulation of PHD2 by HIF-1α in Erythroid Cells: Insights into Erythropoiesis Under Hypoxia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
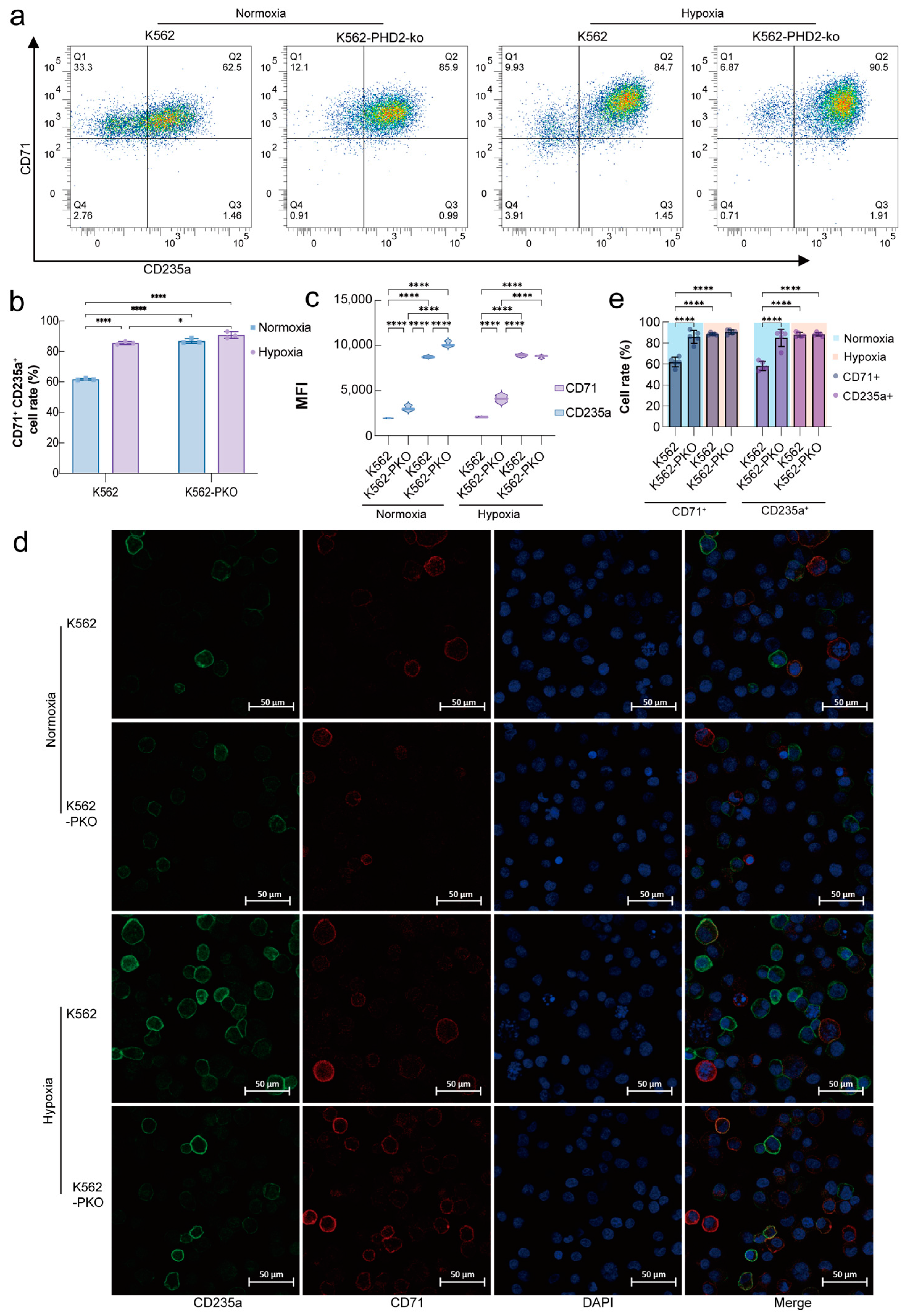
2.1. PHD2 Knockdown and Hypoxia Stimulation Promote Erythroid Differentiation
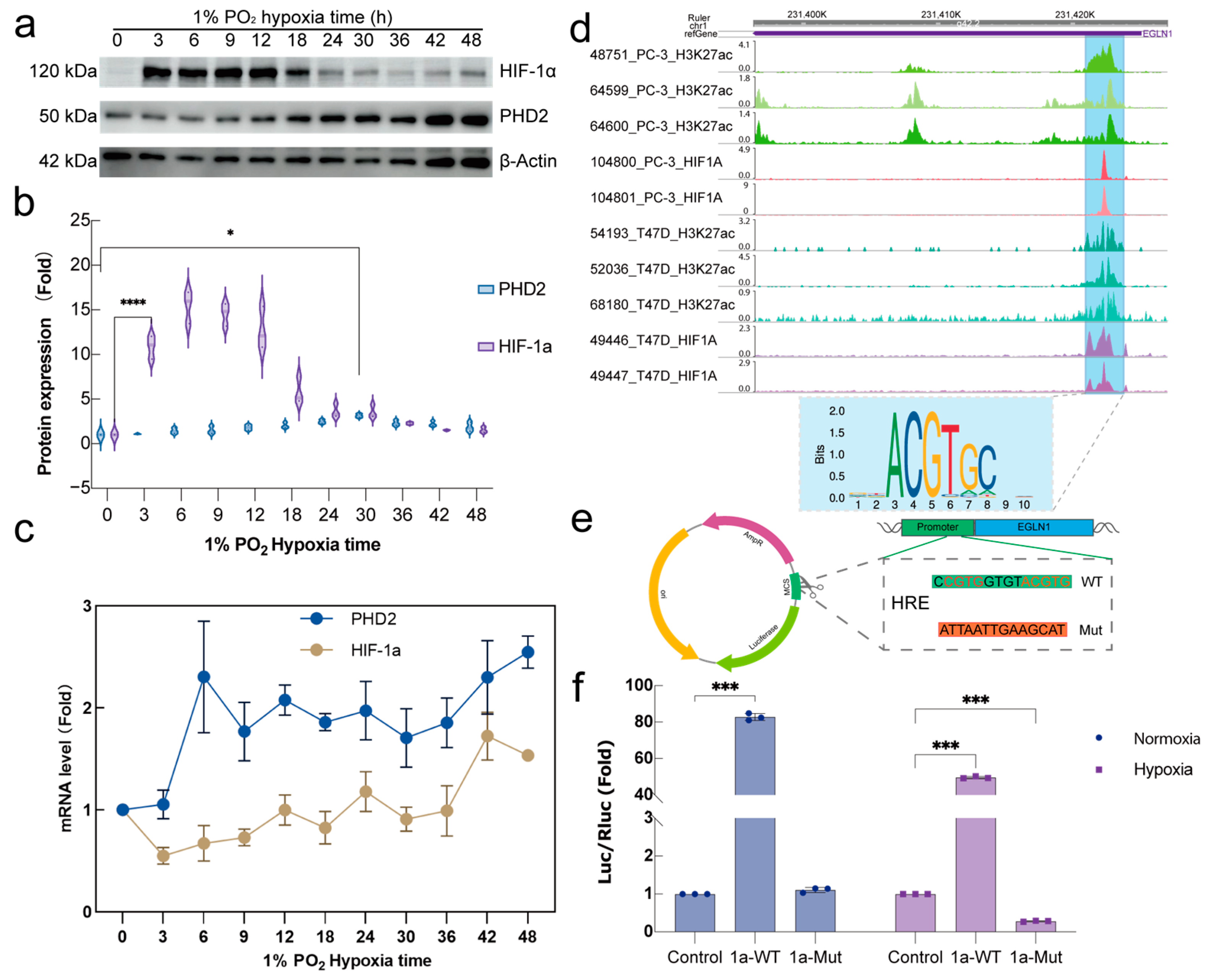
2.2. HIF-1α Regulate PHD2 Transcription via a Specific Motif
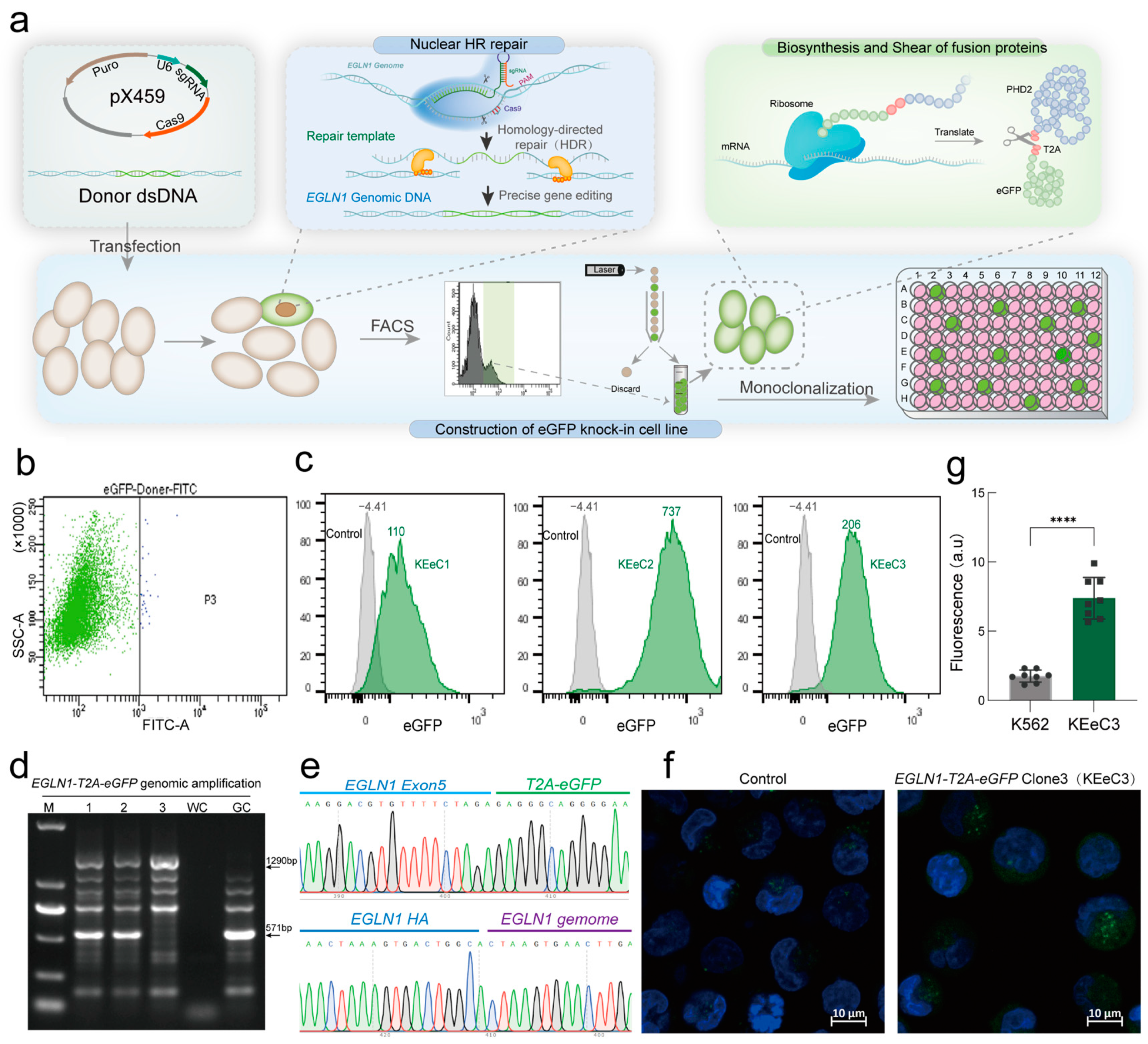
2.3. Establishment of a Fluorescent Reporter Model for Endogenous PHD2 Expression
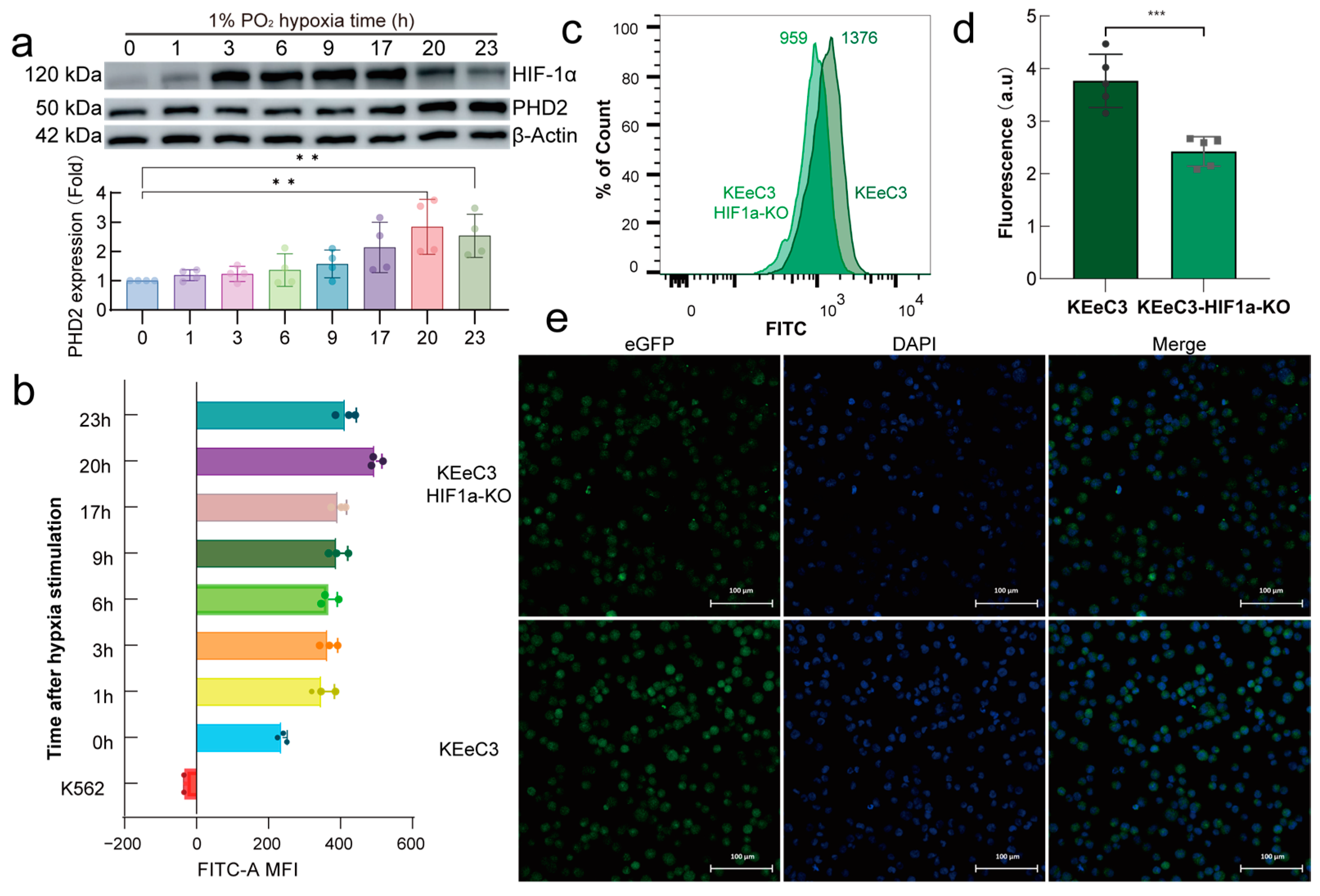
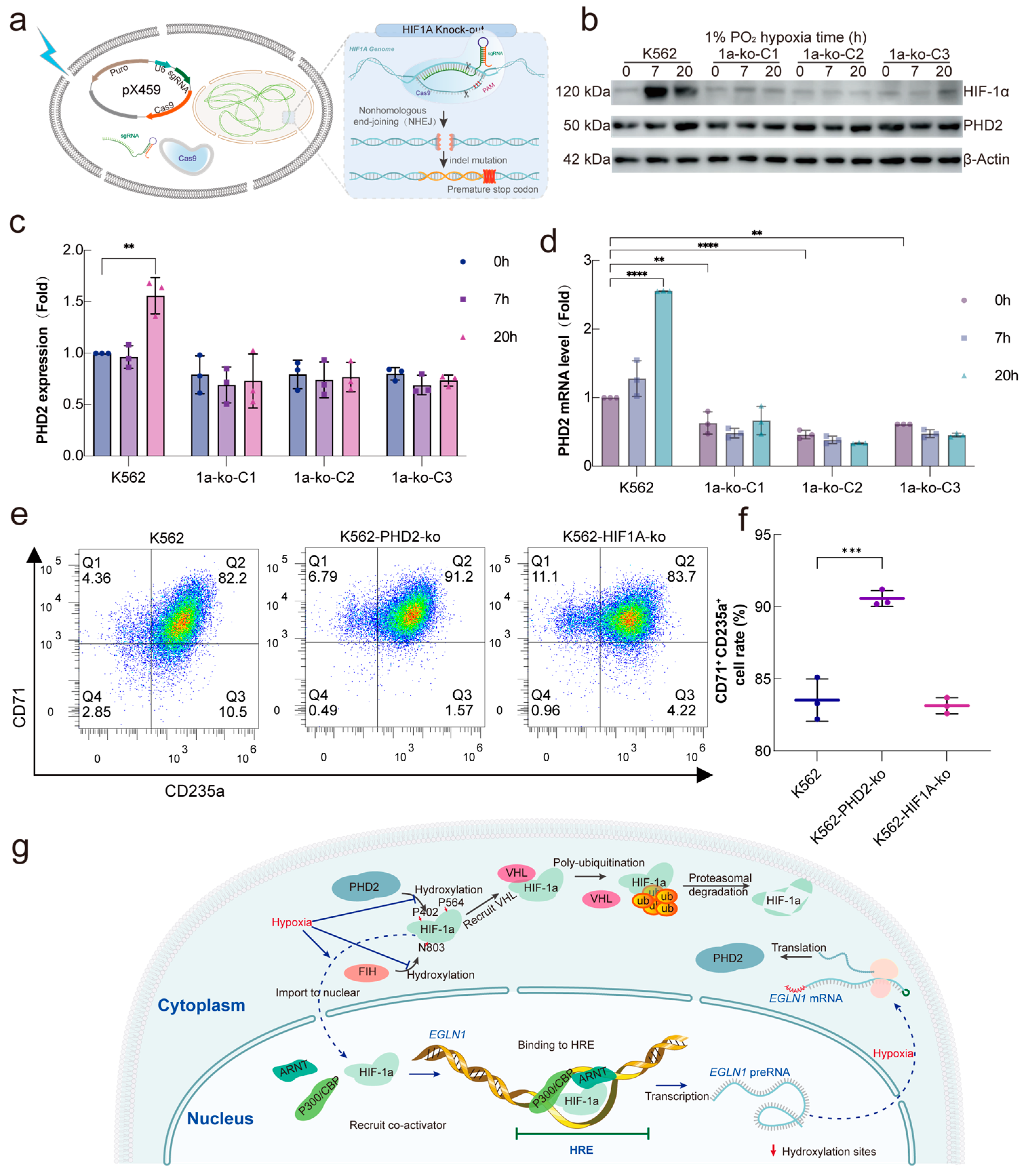
2.4. HIF-1α Regulates Endogenous PHD2 Expression Under Normoxia Conditions
2.5. HIF-1α Is a Major Transcriptional Regulator of PHD2 in Hypoxia
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmids and Cloning
4.2. Mammalian Cell Culture
4.3. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
4.4. Immunoblot and Antibodies
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.6. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.7. Statistical Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fico, F.; Santamaria-Martínez, A. TGFBI modulates tumour hypoxia and promotes breast cancer metastasis. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 3198–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Yang, F.; Shao, C.; Wei, K.; Xie, M.; Shen, H.; Shu, Y. Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.; Li, Y.; Jian, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wei, M. The hypoxia-driven crosstalk between tumor and tumor-associated macrophages: Mechanisms and clinical treatment strategies. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richalet, J.-P.; Hermand, E.; Lhuissier, F.J. Cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology at high altitude. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2024, 21, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factors: Roles in cardiovascular disease progression, prevention, and treatment. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Gu, Y.; Shao, H.; Ma, W.; Li, G.; Guo, M.; Shao, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Intermittent hypoxia protects against hypoxic-ischemic brain damage by inducing functional angiogenesis. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2023, 43, 1656–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucşan, A.N.; Veatch, A.; Singh, D.K.; Akter, S.; Golden, N.A.; Kirkpatrick, M.; Threeton, B.; Moodley, C.; Ahmed, M.; Doyle, L.A.; et al. Response to Hypoxia and the Ensuing Dysregulation of Inflammation Impacts Mycobacterium tuberculosis Pathogenicity. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, K.; Taylor, C.T. The impact of hypoxia on bacterial infection. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 2260–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonson, T.S.; Yang, Y.; Huff, C.D.; Yun, H.; Qin, G.; Witherspoon, D.J.; Bai, Z.; Lorenzo, F.R.; Xing, J.; Jorde, L.B.; et al. Genetic evidence for high-altitude adaptation in Tibet. Science 2010, 329, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.-L.; Simonson, T.S.; Cooksey, R.C.; Tanna, U.; Qin, G.; Huff, C.D.; Witherspoon, D.J.; Xing, J.; Zhengzhong, B.; Prchal, J.T.; et al. Metabolic insight into mechanisms of high-altitude adaptation in Tibetans. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 106, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foll, M.; Gaggiotti, O.E.; Daub, J.T.; Vatsiou, A.; Excoffier, L. Widespread signals of convergent adaptation to high altitude in Asia and america. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 95, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. Angiogenesis in ischemic and neoplastic disorders. Annu. Rev. Med. 2003, 54, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, M.; Kondo, K.; Yang, H.; Kim, W.; Valiando, J.; Ohh, M.; Salic, A.; Asara, J.M.; Lane, W.S.; Kaelin, W.G. HIFalpha targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: Implications for O2 sensing. Science 2001, 292, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaelin, W.G.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Oxygen sensing by metazoans: The central role of the HIF hydroxylase pathway. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minervini, G.; Quaglia, F.; Tosatto, S.C.E. Insights into the proline hydroxylase (PHD) family, molecular evolution and its impact on human health. Biochimie 2015, 116, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strocchi, S.; Reggiani, F.; Gobbi, G.; Ciarrocchi, A.; Sancisi, V. The multifaceted role of EGLN family prolyl hydroxylases in cancer: Going beyond HIF regulation. Oncogene 2022, 41, 3665–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardie, B.; Percy, M.J.; Hoogewijs, D.; Chowdhury, R.; Bento, C.; Arsenault, P.R.; Richard, S.; Almeida, H.; Ewing, J.; Lambert, F.; et al. The role of PHD2 mutations in the pathogenesis of erythrocytosis. Hypoxia 2014, 2, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnema, M.; Song, D.; Guan, W.; Janssen, J.W.H.; van Wijk, R.; Navalsky, B.E.; Peng, K.; Donker, A.E.; Stegmann, A.P.A.; Lee, F.S. Loss-of-function zinc finger mutation in the EGLN1 gene associated with erythrocytosis. Blood 2018, 132, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delamare, M.; Le Roy, A.; Pacault, M.; Schmitt, L.; Garrec, C.; Maaziz, N.; Myllykoski, M.; Rimbert, A.; Karaghiannis, V.; Aral, B.; et al. Characterization of genetic variants in the EGLN1/PHD2 gene identified in a European collection of patients with erythrocytosis. Haematologica 2023, 108, 3068–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, C.C.; Taylor, C.T. Targeting the HIF pathway in inflammation and immunity. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, S.; Nesper, J.; Hasgall, P.A.; Wirthner, R.; Nytko, K.J.; Edlich, F.; Katschinski, D.M.; Stiehl, D.P.; Wenger, R.H.; Camenisch, G. The peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerase FKBP38 determines hypoxia-inducible transcription factor prolyl-4-hydroxylase PHD2 protein stability. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 3758–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Navalsky, B.E.; Guan, W.; Ingersoll, C.; Wang, T.; Loro, E.; Eeles, L.; Matchett, K.B.; Percy, M.J.; Walsby-Tickle, J.; et al. Tibetan PHD2, an allele with loss-of-function properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 12230–12238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, J.D.; Brown, M.C.; Dobrikov, M.I.; Dobrikova, E.Y.; Gemberling, S.L.; Zhang, Q.; Gromeier, M. Regulation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α during Hypoxia by DAP5-Induced Translation of PHD2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2018, 38, e00647-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, P.; Chang, C.; Pursell, B.; Mercurio, A.M. Estrogen receptor β sustains epithelial differentiation by regulating prolyl hydroxylase 2 transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4708–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.Y.; Wilkes, S.; Yang, H. CD71 is selectively and ubiquitously expressed at high levels in erythroid precursors of all maturation stages: A comparative immunochemical study with glycophorin A and hemoglobin A. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2011, 35, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulier, A.L.; Sankaran, V.G. Molecular and cellular mechanisms that regulate human erythropoiesis. Blood 2022, 139, 2450–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Takada, M.; Fan, C.; Zheng, X.; Wen, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Pestell, R.G.; et al. EglN2 associates with the NRF1-PGC1α complex and controls mitochondrial function in breast cancer. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 2953–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ci, X.; Ahmed, M.; Hua, J.T.; Soares, F.; Lin, D.; Puca, L.; Vosoughi, A.; Xue, H.; Li, E.; et al. ONECUT2 is a driver of neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Wan, C.; Mei, S.; Qin, Q.; Wu, Q.; Sun, H.; Chen, C.-H.; Brown, M.; Zhang, X.; Meyer, C.A.; et al. Cistrome Data Browser: Expanded datasets and new tools for gene regulatory analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D729–D735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L.; Wang, G.L. A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol. Cell Biol. 1992, 12, 5447–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, P.H.; Wiesener, M.S.; Chang, G.W.; Clifford, S.C.; Vaux, E.C.; Cockman, M.E.; Wykoff, C.C.; Pugh, C.W.; Maher, E.R.; Ratcliffe, P.J. The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 1999, 399, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, F.S. Hypoxia Inducible Factor pathway proteins in high-altitude mammals. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2024, 49, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, F.R.; Huff, C.; Myllymäki, M.; Olenchock, B.; Swierczek, S.; Tashi, T.; Gordeuk, V.; Wuren, T.; Ri-Li, G.; McClain, D.A.; et al. A genetic mechanism for Tibetan high-altitude adaptation. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashi, T.; Scott Reading, N.; Wuren, T.; Zhang, X.; Moore, L.G.; Hu, H.; Tang, F.; Shestakova, A.; Lorenzo, F.; Burjanivova, T.; et al. Gain-of-function EGLN1 prolyl hydroxylase (PHD2 D4E:C127S) in combination with EPAS1 (HIF-2α) polymorphism lowers hemoglobin concentration in Tibetan highlanders. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Peng, K.; Palmer, B.E.; Lee, F.S. The ribosomal chaperone NACA recruits PHD2 to cotranslationally modify HIF-α. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e112059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, G.; Duplan, E.; Boyer, N.; Vigne, P.; Frelin, C. Hypoxia up-regulates prolyl hydroxylase activity: A feedback mechanism that limits HIF-1 responses during reoxygenation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38183–38187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, A.C.R.; Gleadle, J.M.; McNeill, L.A.; Hewitson, K.S.; O’Rourke, J.; Mole, D.R.; Mukherji, M.; Metzen, E.; Wilson, M.I.; Dhanda, A.; et al. C. elegans EGL-9 and Mammalian Homologs Define a Family of Dioxygenases that Regulate HIF by Prolyl Hydroxylation. Cell 2001, 107, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, C.L.; Liu, X.Q.; Kosinski, P.A.; Garay, M.; Bowen, B.R. Differential regulation of HIF-1 alpha prolyl-4-hydroxylase genes by hypoxia in human cardiovascular cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 303, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marxsen, J.H.; Stengel, P.; Doege, K.; Heikkinen, P.; Jokilehto, T.; Wagner, T.; Jelkmann, W.; Jaakkola, P.; Metzen, E. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) promotes its degradation by induction of HIF-α-prolyl-4-hydroxylases. Biochem. J. 2004, 381, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzen, E.; Stiehl, D.P.; Doege, K.; Marxsen, J.H.; Hellwig-Bürgel, T.; Jelkmann, W. Regulation of the prolyl hydroxylase domain protein 2 (phd2/egln-1) gene: Identification of a functional hypoxia-responsive element. Biochem. J. 2005, 387, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, A.L.; Vignali, D.A.A. Development of 2A peptide-based strategies in the design of multicistronic vectors. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2005, 5, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowman, S.J.; Koh, M.Y. Revisiting the HIF Switch in the Tumor and its Immune Microenvironment. Trends Cancer 2022, 8, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Xu, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, N.; Qi, Y.; Tang, F.; Ge, R. Regulation of PHD2 by HIF-1α in Erythroid Cells: Insights into Erythropoiesis Under Hypoxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020762
Wang S, Xu Q, Liu W, Zhang N, Qi Y, Tang F, Ge R. Regulation of PHD2 by HIF-1α in Erythroid Cells: Insights into Erythropoiesis Under Hypoxia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(2):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020762
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shunjuan, Qiying Xu, Wenjing Liu, Na Zhang, Yuelin Qi, Feng Tang, and Rili Ge. 2025. "Regulation of PHD2 by HIF-1α in Erythroid Cells: Insights into Erythropoiesis Under Hypoxia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 2: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020762
APA StyleWang, S., Xu, Q., Liu, W., Zhang, N., Qi, Y., Tang, F., & Ge, R. (2025). Regulation of PHD2 by HIF-1α in Erythroid Cells: Insights into Erythropoiesis Under Hypoxia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(2), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020762




