Pharmacodynamic Mechanisms of Cicadae Periostracum in Parkinson’s Disease: A Metabolomics-Based Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
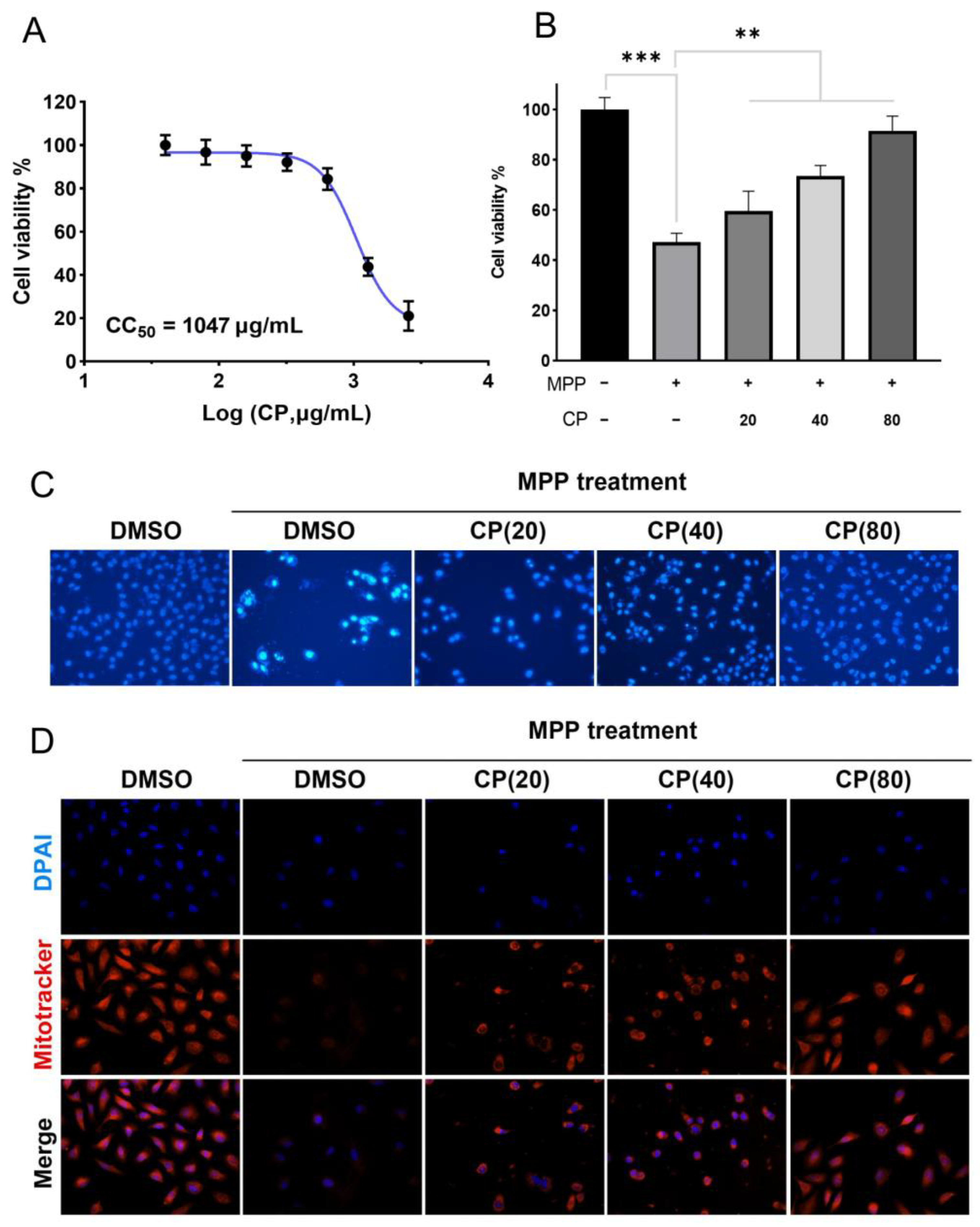
2.1. Cell Experiment Results
2.1.1. CP Can Improve MPP+-Induced Cytotoxicity
2.1.2. CP Can Reduce MPP+-Induced Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells
2.1.3. CP Restores Mitochondrial Membrane Potential of SHSY5Y Cells Induced by MPP+
2.2. Results of Animal Analysis
2.2.1. Behavioral Analysis of CP in the MPTP-Induced PD Mice Model
2.2.2. CP Protects the MPTP-Induced Loss of TH Neurons in the Midbrain and Reduces α-Syn Aggregation in STR
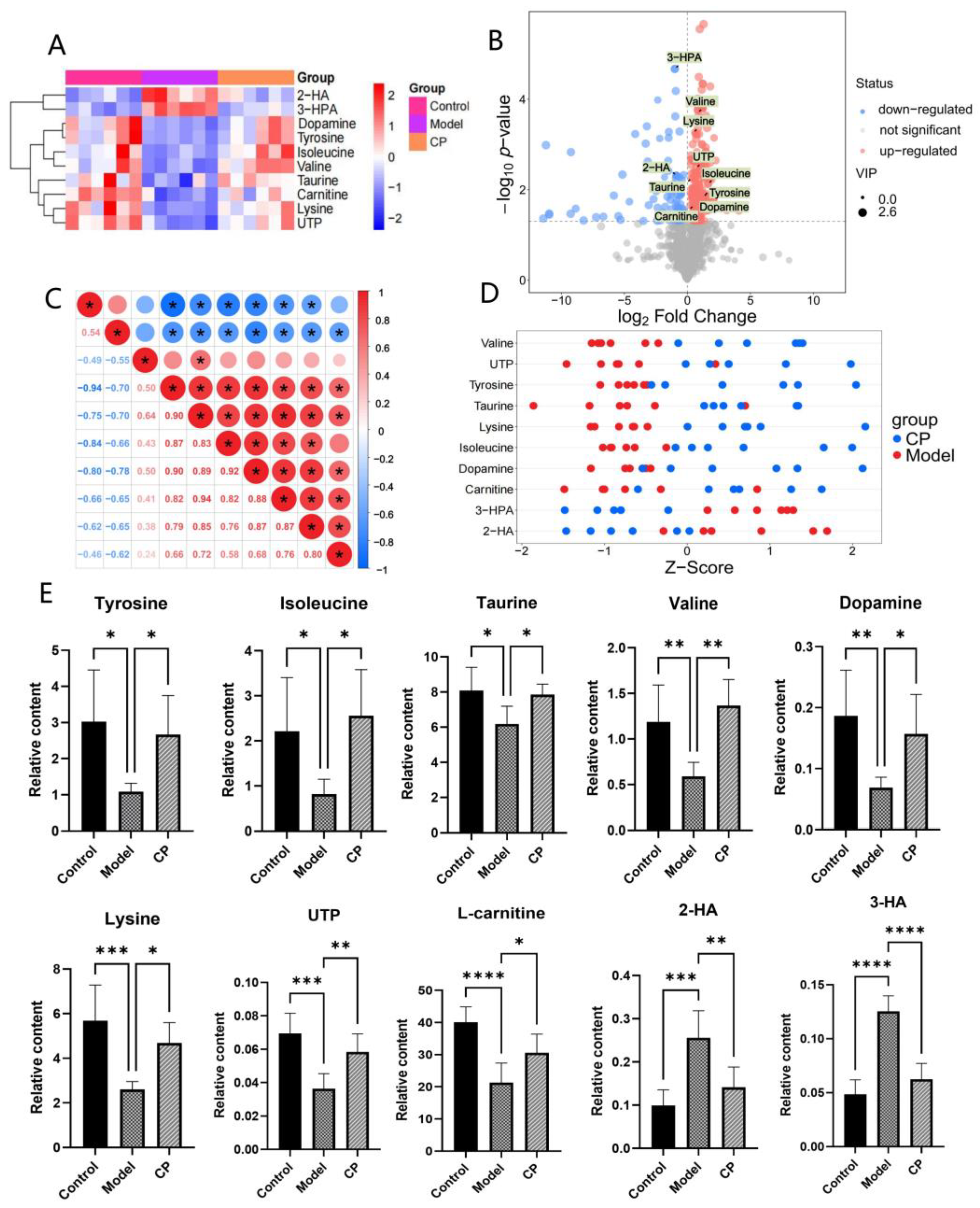
2.3. Results of Metabolomics Analysis
2.3.1. Multivariate Data Analysis
2.3.2. Identification of Endogenous Metabolites
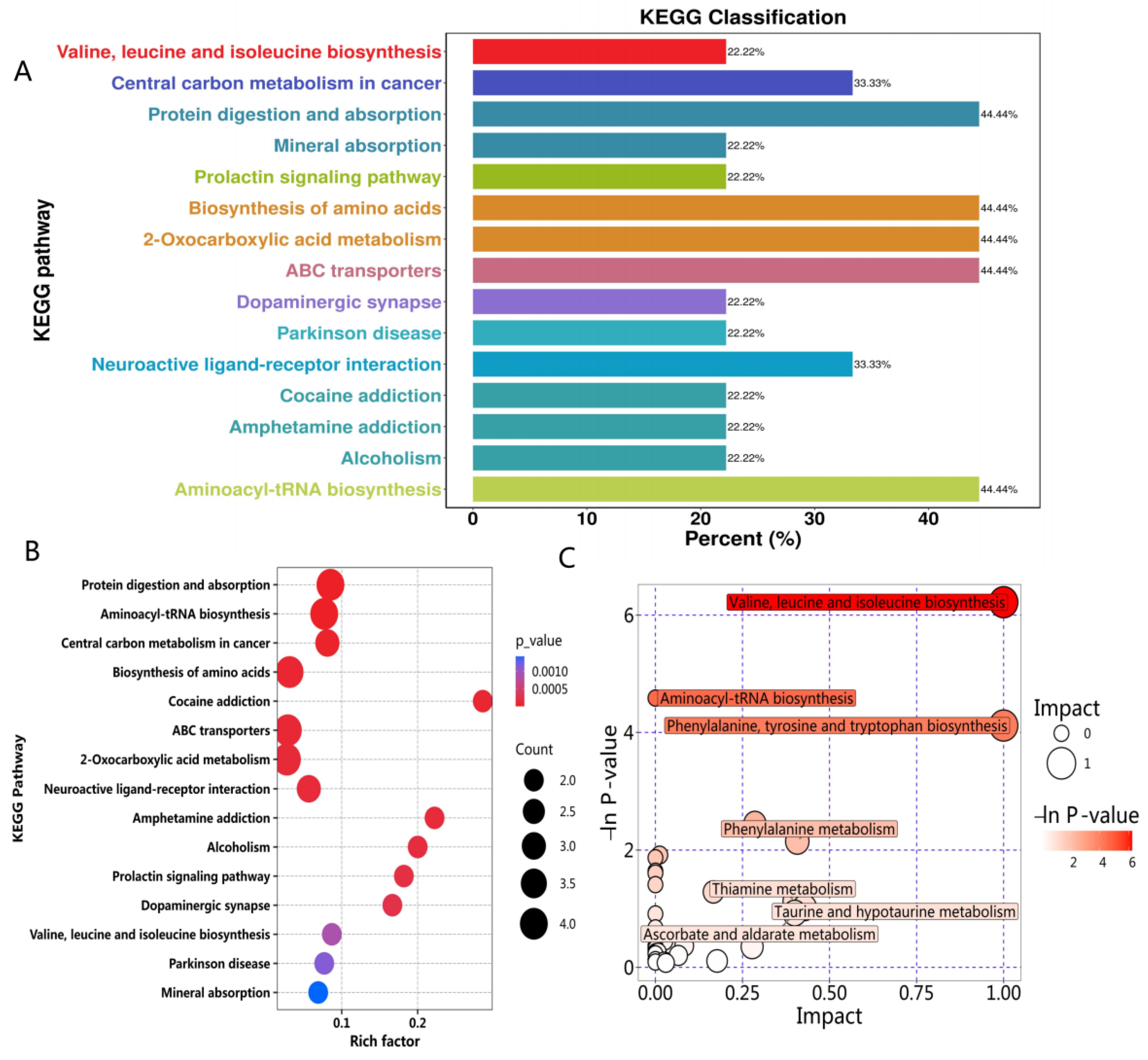
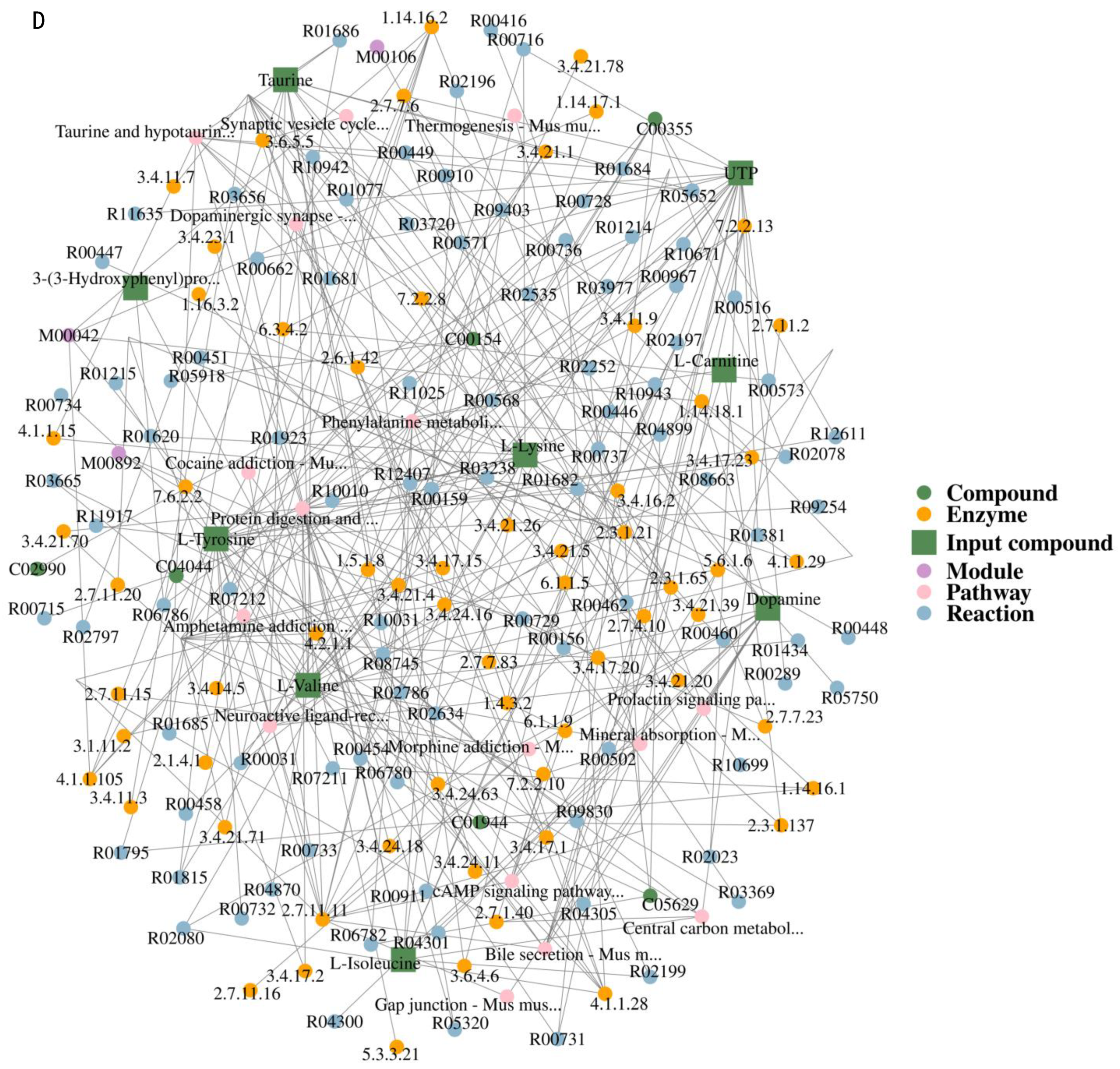
2.3.3. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
2.4. Mechanism Analysis of CP Treating PD
2.4.1. CP Reduces MPP+-Induced Apoptosis in SHSY5Y Cells via Bax/Bcl-2/Caspase-3 Pathway
2.4.2. CP Reduces MPP+-Induced Oxidative Stress in SHSY5Y Cells via Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Experiments
4.1.1. Preparation of Ethanol Crude Extract of CP
4.1.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.1.3. Measurement of Cell Viability
4.1.4. MitoTracker Assay
4.1.5. Hoechst 33342 Assay
4.2. Animal Experiments
4.2.1. Animals and Drug Administration
4.2.2. Pole Test
4.2.3. Rotarod Test
4.2.4. Open Field Test
4.2.5. Preparation of Tissue
4.2.6. Tyrosine Hydroxylase (TH) Immunofluorescence Staining
4.2.7. Immunoblotting Assay
4.3. UPLC-MS Metabolomics Analysis
4.3.1. Sample Preparation
4.3.2. UPLC-Orbitrap/MS Analysis
4.3.3. Data Analysis
4.4. Mechanism Analysis
4.4.1. Determination of Glutathione (GSH) and Malondialdehyde (MDA) Levels in Cells
4.4.2. Pathway Verification
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Simon, D.K.; Tanner, C.M.; Brundin, P. Parkinson Disease Epidemiology, Pathology, Genetics, and Pathophysiology. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2020, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabreira, V.; Massano, J. Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical Review and Update. Acta Med. Port. 2019, 32, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascherio, A.; Schwarzschild, M.A. The epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease: Risk factors and prevention. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degirmenci, Y.; Angelopoulou, E.; Georgakopoulou, V.E.; Bougea, A. Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease: An Updated Overview Focusing on Emerging Pharmaceutical Treatment Approaches. Medicina 2023, 59, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, H.; Bai, Y.; Xiong, F.; Wu, S.; Bi, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Feng, L.; et al. Pharmacodynamical research of extracts and compounds in traditional Chinese medicines for Parkinson’s disease. Fitoterapia 2024, 177, 106086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.M.; Guo, J.L.; Chen, L.; Ho, P.C. Application for proteomics analysis technology in studying animal-derived traditional Chinese medicine: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 191, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yan, Y.-M.; Liao, L.; Wang, S.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.-X. Cicadamides A and B,N-Acetyldopamine Dimers From the InsectPeriostracum cicadae. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X19850019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.C.; Guo, M.F.; Han, Y.; Fan, Y.T.; Zhu, J.H.; Zhu, H.; Xu, J.D.; Shen, H.; Zhou, G.R.; Mao, Q.; et al. Systematic metabolite profiling of N-acetyldopamine oligomers from Cicadae Periostracum in rats by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 192, 113665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, G.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.H. N-Acetyldopamine derivatives from Periostracum Cicadae. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 11, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, T.; Jin, J.; Si, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, X.; Guo, T.; Wei, W. Periostracum Cicadae Extract and N-Acetyldopamine Regulate the Sleep-Related Neurotransmitters in PCPA-Induced Insomnia Rats. Molecules 2024, 29, 3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.S.; Kim, J.S.; Moon, B.C.; Choi, G.; Ryu, S.M.; Lee, J.; Ang, M.J.; Jeon, M.; Moon, C.; Park, G. Cicadidae Periostracum, the Cast-Off Skin of Cicada, Protects Dopaminergic Neurons in a Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 5797512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gątarek, P.; Sekulska-Nalewajko, J.; Bobrowska-Korczaka, B.; Pawełczyk, M.; Jastrzębski, K.; Głąbiński, A.; Kałużna-Czaplińska, J. Plasma Metabolic Disturbances in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, K.C.; Zhang, K.; Walker, D.I.; Sinsheimer, J.; Yu, Y.; Kusters, C.; Del Rosario, I.; Folle, A.D.; Keener, A.M.; Bronstein, J.; et al. Untargeted serum metabolomics reveals novel metabolite associations and disruptions in amino acid and lipid metabolism in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Landolfi, A.; Cavallo, P.; Marciano, F.; Barone, P.; Amboni, M. Metabolomics in Parkinson’s disease. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2021, 104, 107–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, M.; Fadda, P.; Klephan, K.J.; Hull, C.; Teismann, P.; Platt, B.; Riedel, G. Neurochemical, histological, and behavioral profiling of the acute, sub-acute, and chronic MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2023, 164, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebrisi, E.E. Neuroprotective Activities of Curcumin in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagatsu, T.; Nakashima, A.; Watanabe, H.; Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K. Neuromelanin in Parkinson’s Disease: Tyrosine Hydroxylase and Tyrosinase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Xu, G.; Le, W. Comprehensive metabolic profiling of Parkinson’s disease by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zeng, F.; Huang, C.; Pu, Q.; Thomas, E.R.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. The potential role of glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, and amino acid metabolism in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, H.P.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Novoa, I.; Lu, P.D.; Calfon, M.; Sadri, N.; Yun, C.; Popko, B.; Paules, R.; et al. An integrated stress response regulates amino acid metabolism and resistance to oxidative stress. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, V.; Junn, E.; Mouradian, M.M. The role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. J. Park. Dis. 2013, 3, 461–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, S.R.; Chesselet, M.F. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 106–107, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesavardhana, S.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; Kanneganti, T.D. Caspases in Cell Death, Inflammation, and Pyroptosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 567–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Peng, S.; Zhu, X. Baicalein protects against MPP(+)/MPTP-induced neurotoxicity by ameliorating oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells and mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 2021, 87, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.Q.; Guo, L.P.; Zhang, X.B.; Yu, L.Y.; Sun, J.H. Species of Chinese materia medica resources based on the fourth national survey of Chinese materia medica resources. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2024, 49, 3409–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babos, M.B.; Perry, J.D.; Reed, S.A.; Bugariu, S.; Hill-Norby, S.; Allen, M.J.; Corwell, T.K.; Funck, J.E.; Kabir, K.F.; Sullivan, K.A.; et al. Animal-derived medications: Cultural considerations and available alternatives. J. Osteopath. Med. 2021, 121, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Guo, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Deng, Z. Edible and Medicinal Progress of Cryptotympana atrata (Fabricius) in China. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, P.; Gu, Y.; Kil, Y.S.; Baek, S.C.; Kim, K.H.; Han, A.R.; Seo, E.K.; Choi, H.; Chang, J.H.; Nam, J.W. N-Acetyldopamine derivatives from Periostracum Cicadae and their regulatory activities on Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 102, 104095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.M.; Bao, X.H.; Li, J.J.; Li, Y.P.; Zhang, H.X.; Cheng, Y.X. Dimeric N-Acetyldopamine Derivatives Featuring a Seco-Benzene System from the Insects Aspongopus chinensis and Periostracum cicadae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 20690–20700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.Z.; Lee, W.S.; Han, J.M.; Oh, H.W.; Park, D.S.; Tian, G.R.; Jeong, T.S.; Park, H.Y. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of N-acetyldopamine dimers from Periostracum Cicadae. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 7826–7834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Lu, H.; Lee, Y.H. Challenges and emergent solutions for LC-MS/MS based untargeted metabolomics in diseases. Mass. Spectrom. Rev. 2018, 37, 772–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, A.W.; Standaert, D.G. Metabolomics and the search for biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1620–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.G.; Rao, S.; Weir, T.L.; O’Malia, J.; Bazan, M.; Brown, R.J.; Ryan, E.P. Metabolomics and metabolic pathway networks from human colorectal cancers, adjacent mucosa, and stool. Cancer Metab. 2016, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrowolski, S.F.; Phua, Y.L.; Sudano, C.; Spridik, K.; Zinn, P.O.; Wang, Y.; Bharathi, S.; Vockley, J.; Goetzman, E. Comparative metabolomics in the Pah(enu2) classical PKU mouse identifies cerebral energy pathway disruption and oxidative stress. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2022, 136, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruocco, C.; Segala, A.; Valerio, A.; Nisoli, E. Essential amino acid formulations to prevent mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2021, 24, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Metabolite | Mode | Retention Time(s) | m/z | Formula | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-HA | NEG | 41.8 | 159.1025 | C8H16O3 | down |
| 3-HPA | NEG | 62.7 | 165.0555 | C9H10O3 | down |
| Isoleucine | NEG | 161.8 | 130.0872 | C6H13NO2 | up |
| Betaine | POS | 165.3 | 118.0857 | C5H11NO2 | up |
| Methionine | NEG | 172.5 | 148.0436 | C5H11NO2S | up |
| Taurine | NEG | 177.2 | 124.0072 | C2H7NO3S | up |
| S1P(d18:1) | POS | 177.7 | 380.2549 | C18H38NO5P | up |
| Valine | NEG | 180.3 | 116.0716 | C5H11NO2 | up |
| Tyrosine | POS | 182.2 | 182.0805 | C9H11NO3 | up |
| Dopamine | POS | 182.2 | 136.0752 | C8H11NO2 | up |
| Proline | NEG | 185.4 | 114.0560 | C5H9NO2 | up |
| Threonine | POS | 207.2 | 120.0651 | C4H9NO3 | up |
| Carnitine | POS | 208.7 | 162.1118 | C7H15NO3 | up |
| UTP | POS | 218.2 | 484.9706 | C9H15N2O15P3 | up |
| Serine | NEG | 220.4 | 104.0352 | C3H7NO3 | up |
| Sn-Glycerol 3-phosphate | NEG | 249.4 | 171.0063 | C3H9O6P | up |
| Ornithine | POS | 291.5 | 115.0862 | C5H12N2O2 | up |
| Arginine | POS | 297.5 | 175.1183 | C6H14N4O2 | up |
| Lysine | POS | 298.1 | 147.1124 | C6H14N2O2 | up |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Xiong, F.; Wu, S.; Wei, W.; Wang, H.; Qiao, Y.; Guo, D. Pharmacodynamic Mechanisms of Cicadae Periostracum in Parkinson’s Disease: A Metabolomics-Based Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020544
Li M, Xiong F, Wu S, Wei W, Wang H, Qiao Y, Guo D. Pharmacodynamic Mechanisms of Cicadae Periostracum in Parkinson’s Disease: A Metabolomics-Based Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(2):544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020544
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mengmeng, Fuyu Xiong, Shifei Wu, Wenlong Wei, Hanze Wang, Yajun Qiao, and Dean Guo. 2025. "Pharmacodynamic Mechanisms of Cicadae Periostracum in Parkinson’s Disease: A Metabolomics-Based Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 2: 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020544
APA StyleLi, M., Xiong, F., Wu, S., Wei, W., Wang, H., Qiao, Y., & Guo, D. (2025). Pharmacodynamic Mechanisms of Cicadae Periostracum in Parkinson’s Disease: A Metabolomics-Based Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(2), 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020544






