Cinnamaldehyde Inhibits Leptin-Induced MMP-1 by Modulating Leptin Receptor/STAT3 and Blocking RhoA/NF-κB Pathways in Human Intervertebral Disc Stem Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
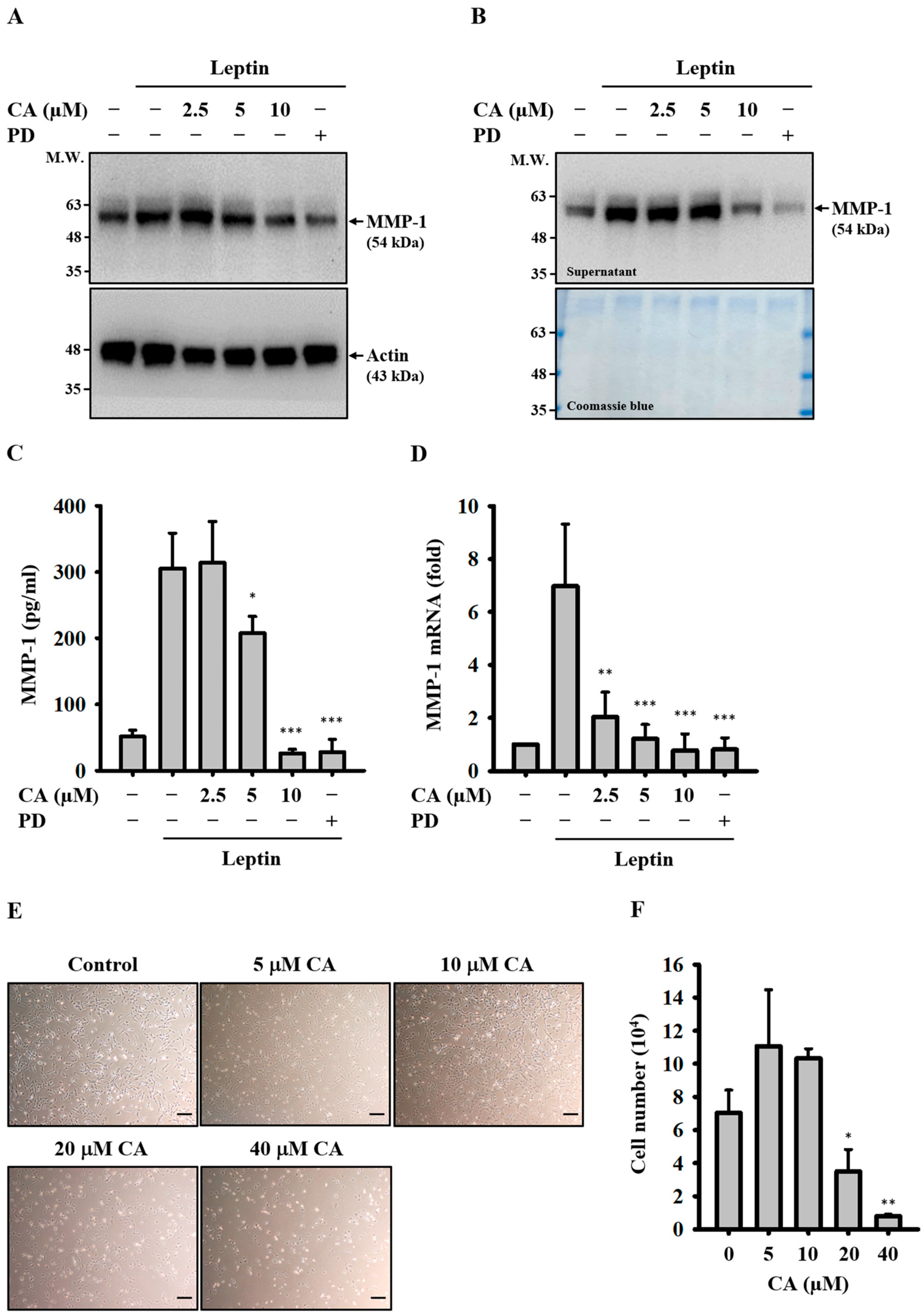
2.1. Effect of CA on Leptin-Induced MMP-1 Expression
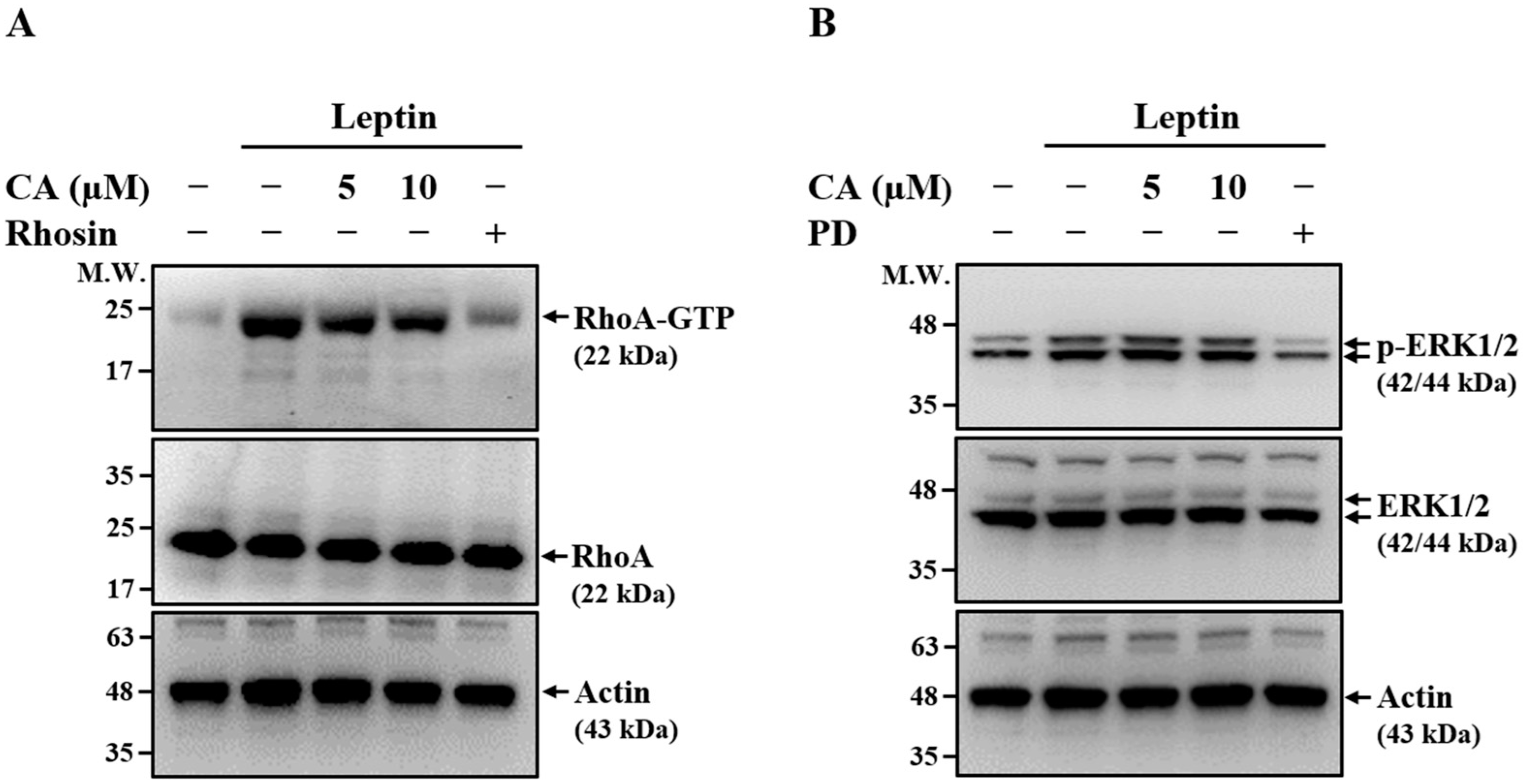
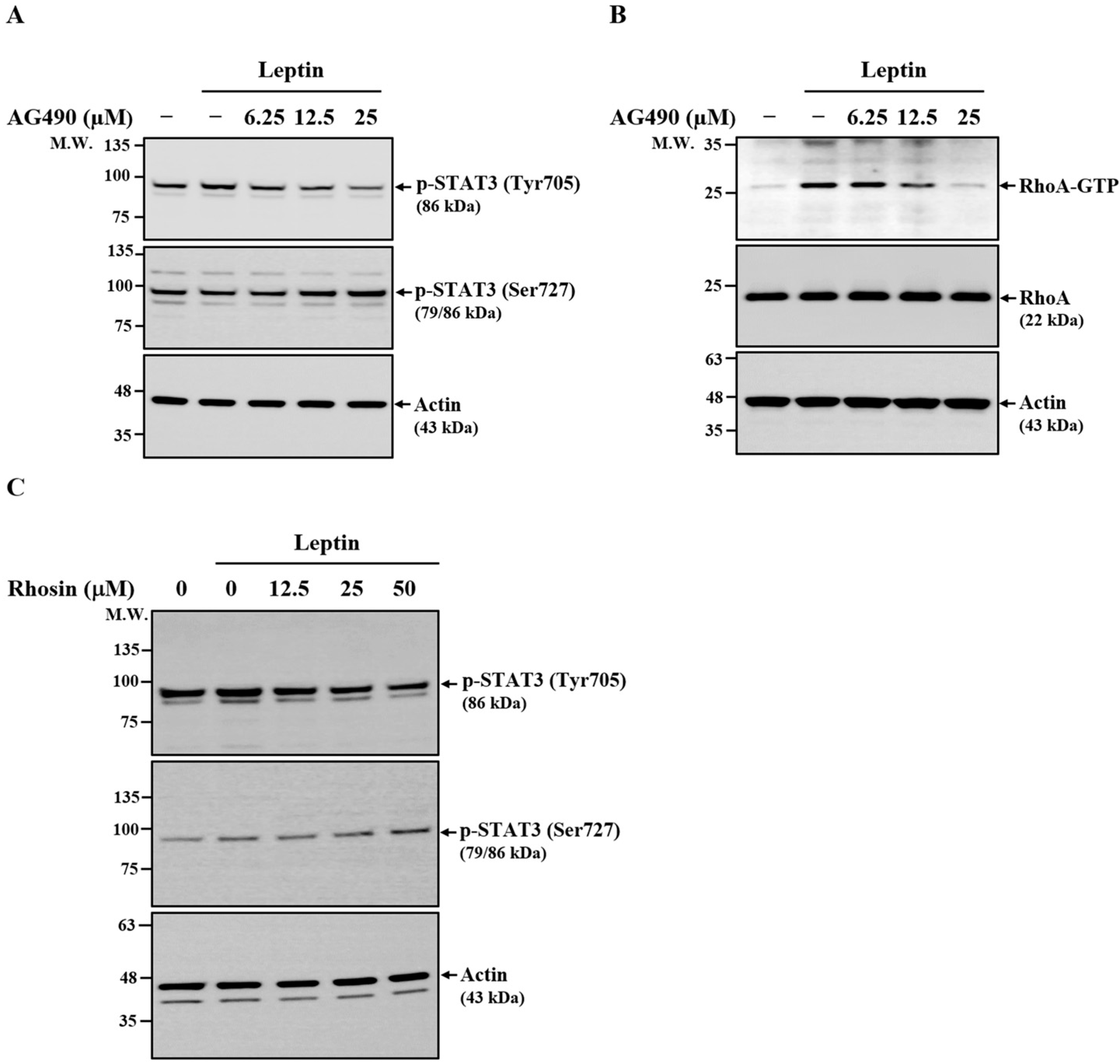
2.2. Effect of CA on Leptin-Induced Activation of RhoA and ERK1/2
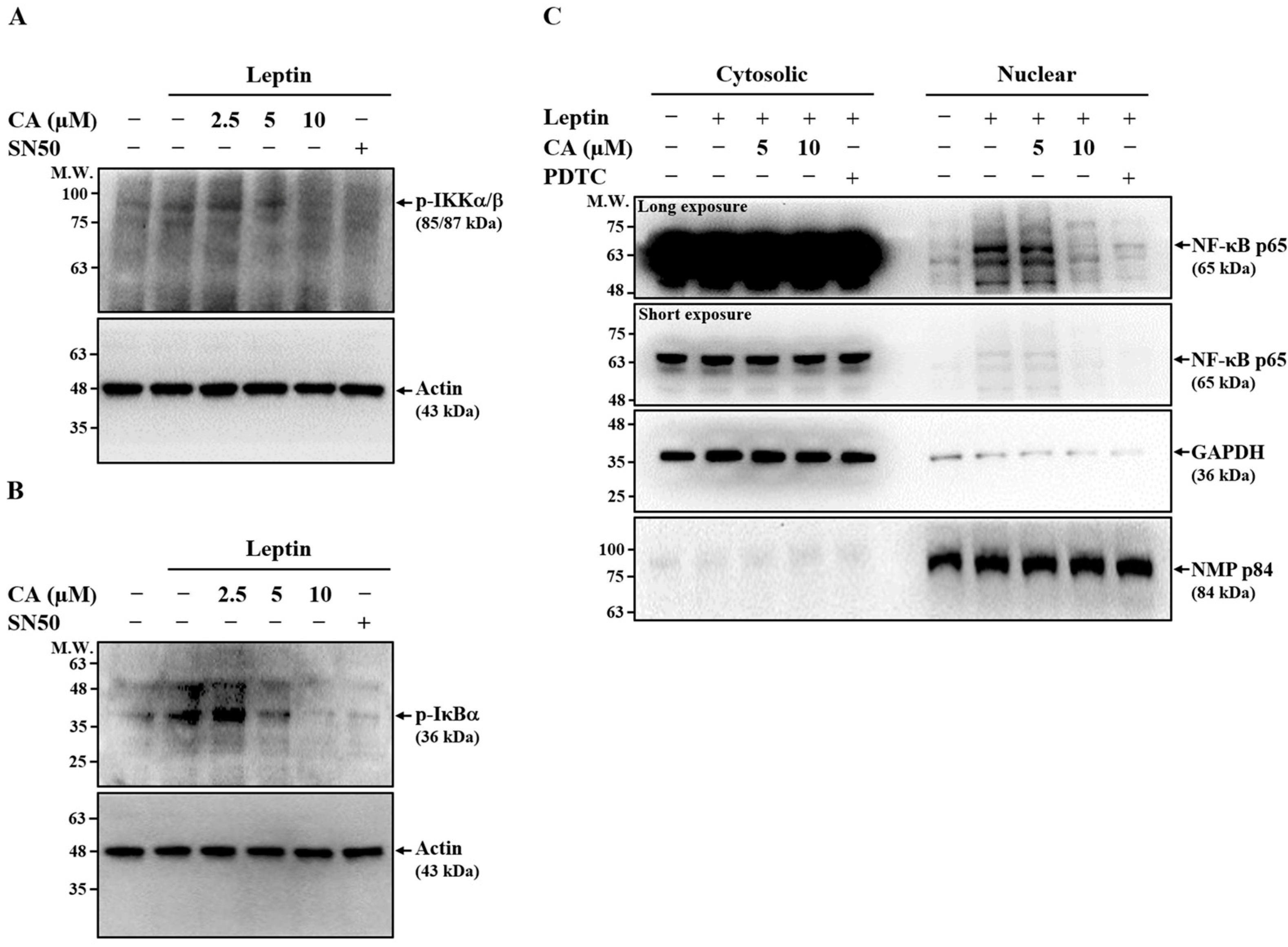
2.3. Effect of CA on Leptin-Induced Activation of NF-κB
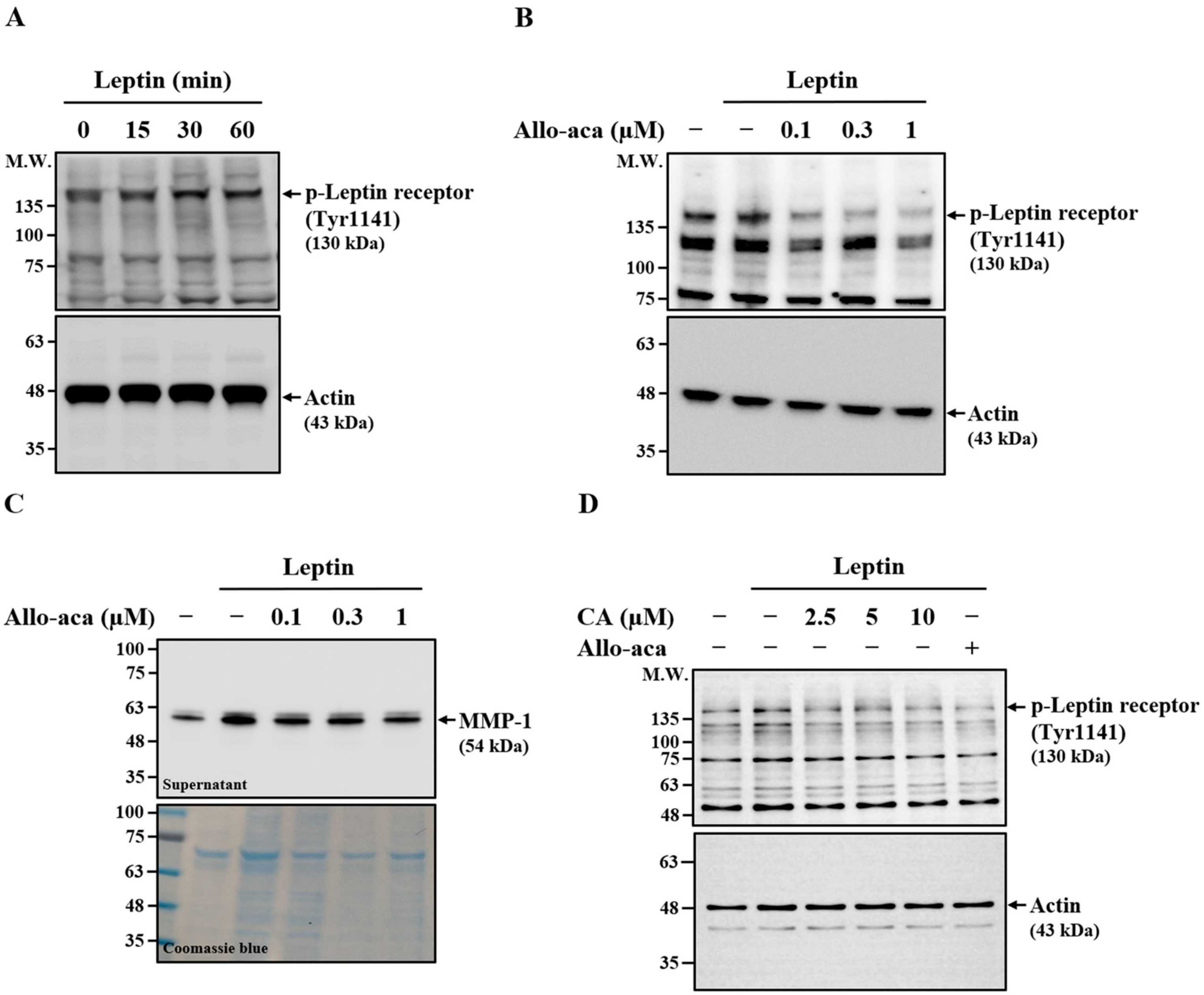
2.4. Effect of CA on Leptin-Induced Phosphorylation of Leptin Receptor
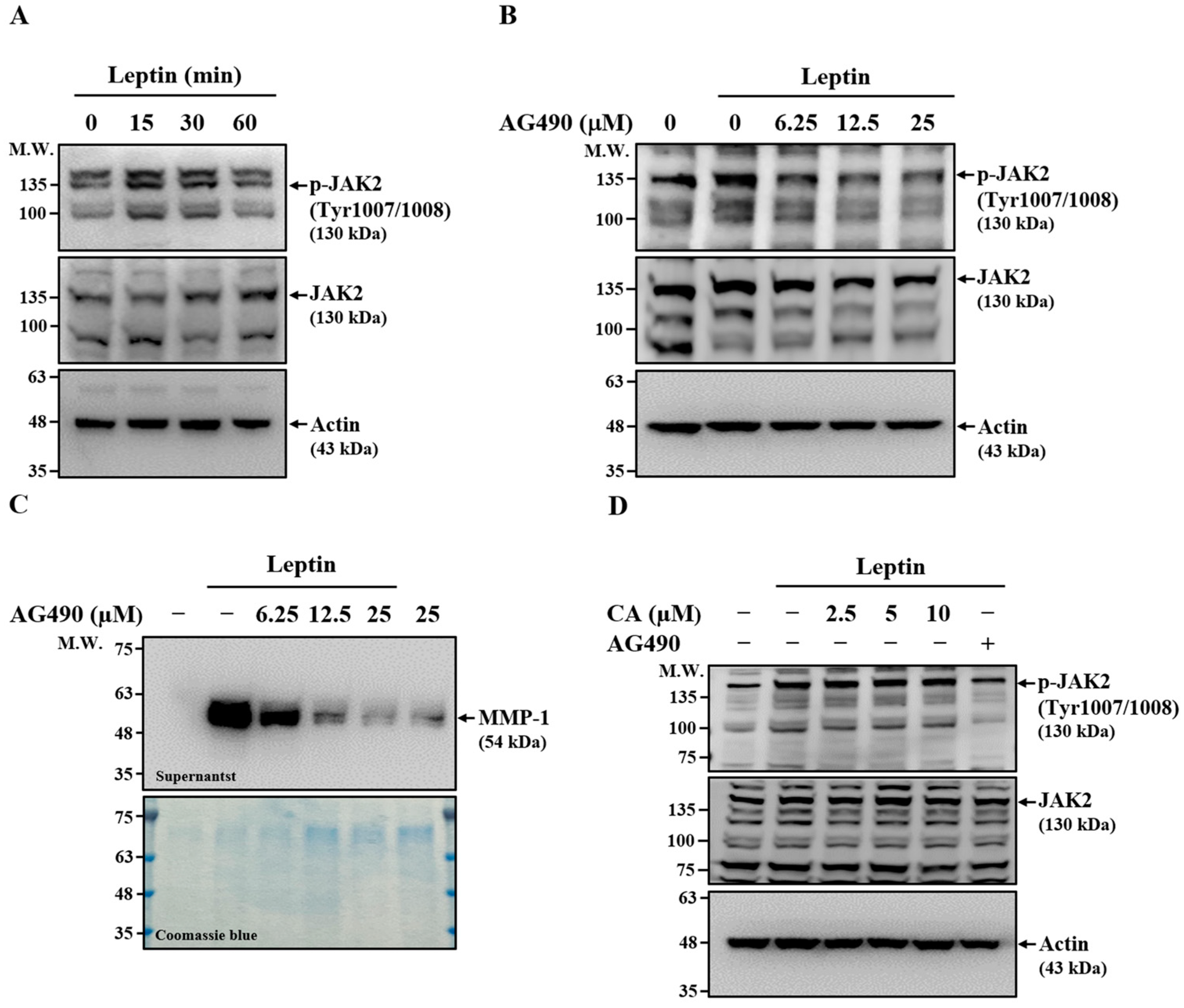
2.5. Effect of CA on Leptin-Induced Activation of JAK2
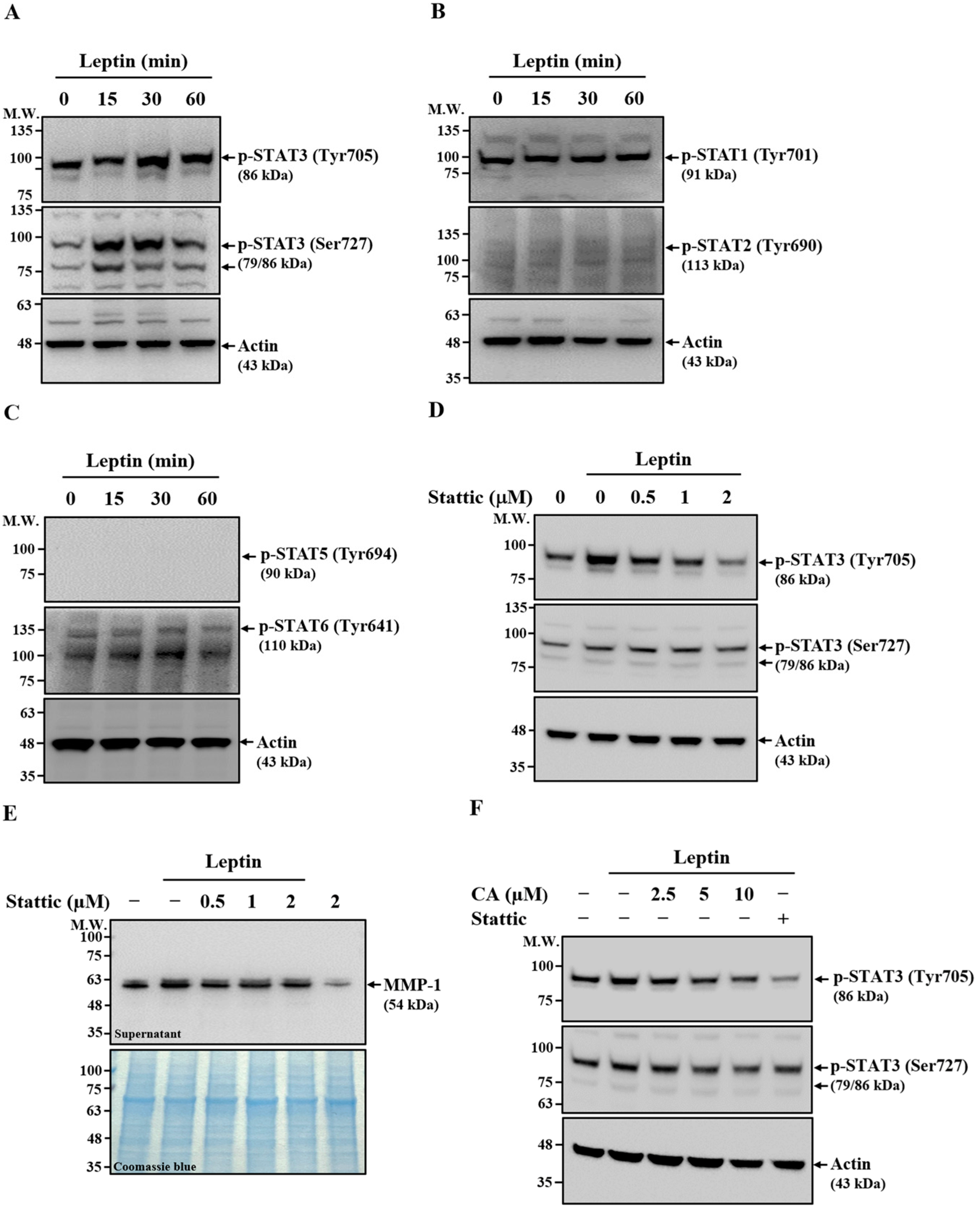
2.6. Effect of CA on Leptin-Induced Activation of STAT3
2.7. Relationship Between JAK2, RhoA, and STAT3 in Leptin-Activated SV40 Cells
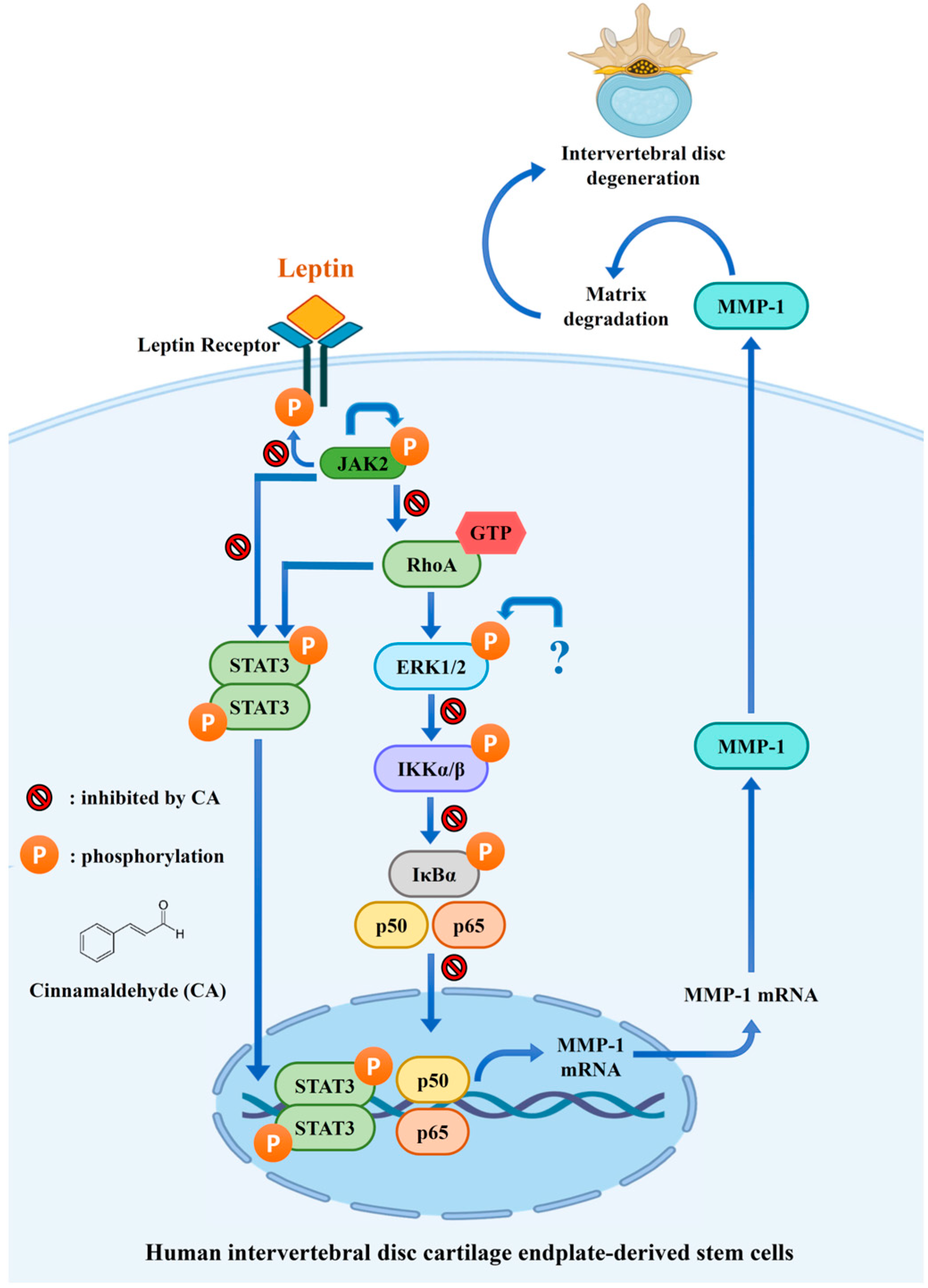
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Effect of CA on Leptin-Induced MMP-1 Expression
4.4. Effect of CA on Leptin-Induced Activation of RhoA
4.5. Effect of CA on Leptin-Induced Phosphorylation of ERK1/2
4.6. Effect of CA on Leptin-Induced Activation of NF-κB
4.7. Effect of CA on Leptin-Induced Phosphorylation of Leptin Receptor, JAK2, and STATs
4.8. Relationship Between JAK2, RhoA and STAT3 in Leptin-Activated SV40 Cells
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IVD | Intervertebral disc |
| MMP-1 | Matrix metalloproteinase-1 |
| SV40 cells | Human intervertebral disc cartilage endplate-derived stem cells |
| RhoA | Ras homolog family member A |
| JAK2 | Janus Kinase 2 |
| STAT | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| CA | Cinnamaldehyde |
| PD | PD98059 |
| PDTC | Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate |
| NLRP3 | NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 |
| NMP p84 | Nuclear matrix protein p84 |
| RT | Reverse transcribed |
| qPCR | Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
References
- Lyu, F.J.; Cui, H.; Pan, H.; Mc Cheung, K.; Cao, X.; Iatridis, J.C.; Zheng, Z. Painful intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation: From laboratory evidence to clinical interventions. Bone Res. 2021, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, T.; Iwasaki, N.; Sudo, H. Causes of and Molecular Targets for the Treatment of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: A Review. Cells 2022, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska, A.; Touli, E.; Hitzl, W.; Greutert, H.; Ferguson, S.J.; Wuertz-Kozak, K.; Hausmann, O.N. Inflammaging in cervical and lumbar degenerated intervertebral discs: Analysis of proinflammatory cytokine and TRP channel expression. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannata, F.; Vadalà, G.; Ambrosio, L.; Fallucca, S.; Napoli, N.; Papalia, R.; Pozzilli, P.; Denaro, V. Intervertebral disc degeneration: A focus on obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, V.; Pino, J.; González-Gay, M.Á.; Lago, F.; Karppinen, J.; Tervonen, O.; Mobasheri, A.; Gualillo, O. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Gris, D.; Lei, Y.; Jha, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, M.T.; Brickey, W.J.; Ting, J.P. Fatty acid-induced NLRP3-ASC inflammasome activation interferes with insulin signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruze, R.; Liu, T.; Zou, X.; Song, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, R.; Yin, X.; Xu, Q. Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Connections in epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatments. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1161521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Mi, J.; Peng, Y.; Han, H.; Liu, Z. Causal Associations of Obesity with the Intervertebral Degeneration, Low Back Pain, and Sciatica: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 740200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Lu, W.; Zeng, Q.; Li, D.; Ding, L.; Wu, J. High glucose-induced excessive reactive oxygen species promote apoptosis through mitochondrial damage in rat cartilage endplate cells. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 2476–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Leon, V.; Perez-Lois, R.; Villalon, M.; Prida, E.; Muñoz-Moreno, D.; Fernø, J.; Quiñones, M.; Al-Massadi, O.; Seoane, L.M. Novel mechanisms involved in leptin sensitization in obesity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 223, 116129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.T.; Yue, C.T.; Teng, M.S.; Tzeng, I.S.; Li, T.C.; Tai, P.A.; Huang, K.F.; Chen, C.Y.; Ko, Y.L. Immuohistochemical score of matrix metalloproteinase-1 may indicate the severity of symptomatic cervical and lumbar disc degeneration. Spine J. 2020, 20, 124–137, Correction in Spine J. 2020, 20, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, K.F.; Li, L.H.; Yu, H.C.; Wong, W.T.; Hsu, H.T. Leptin Induces MMP-1 Expression Through the RhoA/ERK1/2/NF-κB Axis in Human Intervertebral Disc Cartilage Endplate-Derived Stem Cells. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 5235–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yu, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.; Zhan, F.; Yu, X.; Wang, S.; He, F.; Han, Y.; Zhao, H. The treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration using Traditional Chinese Medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 113117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, A.; Ziadlou, R.; Lang, G.; Pfannkuche, J.; Cui, S.; Li, Z.; Richards, R.G.; Alini, M.; Grad, S. Small molecule-based treatment approaches for intervertebral disc degeneration: Current options and future directions. Theranostics 2021, 11, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.T.; Chen, P.F.; Chang, S.C. Antibacterial activity of leaf essential oils and their constituents from Cinnamomum osmophloeum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 77, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.K.; Hua, K.F.; Hsu, H.Y.; Cheng, S.S.; Lin, I.F.; Chen, C.J.; Chen, S.T.; Chang, S.T. Cinnamaldehyde inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines secretion from monocytes/macrophages through suppression of intracellular signaling. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Wong, W.T.; Weng, Y.M.; Ho, C.L.; Hsu, H.T.; Hua, K.F.; Wu, C.H.; Li, L.H. Cinnamaldehyde, A Bioactive Compound from the Leaves of Cinnamomum osmophloeum Kaneh, Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice by Inhibiting the NLRP3 Inflammasome. J. Physiol. Investig. 2024, 67, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.F.; Lin, Y.B.; Chiu, H.W.; Wong, W.T.; Ka, S.M.; Wu, C.H.; Lin, W.Y.; Wang, C.C.; Hsu, C.H.; Hsu, H.T.; et al. Cinnamaldehyde inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome by preserving mitochondrial integrity and augmenting autophagy in Shigella sonnei-infected macrophages. J. Inflamm. 2024, 21, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, K.F.; Chiu, H.W.; Chen, M.M.; Wong, W.T.; Tsai, W.C.; Lin, W.Y.; Wu, C.H.; Wang, C.C.; Hsu, C.H.; Chernikov, O.V.; et al. Cinnamaldehyde inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome and inflammatory response by reducing oxidative stress in Neisseria gonorrhoeae-infected macrophages. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Khare, P.; Jagtap, S.; Jain, Y.; Baboota, R.K.; Mangal, P.; Boparai, R.K.; Bhutani, K.K.; Sharma, S.S.; Premkumar, L.S.; Kondepudi, K.K.; et al. Cinnamaldehyde supplementation prevents fasting-induced hyperphagia, lipid accumulation, and inflammation in high-fat diet-fed mice. Biofactors 2016, 42, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, H.; Duan, M.; Liu, R.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L. Cinnamaldehyde Improves Metabolic Functions in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice by Regulating Gut Microbiota. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2021, 15, 2339–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Mazhar, M. Cinnamaldehyde and its combination with deferoxamine ameliorate inflammation, ferroptosis and hematoma expansion after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2025, 22, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Z.; Fan, B.; Wang, C.; Tian, Z. Cinnamaldehyde alleviates pulmonary hypertension by affecting vascular remodeling through the TLR4/NF-kB/HIF-1a pathway. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2025, 47, 2486829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Lin, D.; He, L.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Huang, S. Cinnamaldehyde mitigates acute myocardial infarction by regulating ferroptosis through the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 150, 114262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashisth, C.; Kumar Verma, N.; Afshari, M.; Bendi, A.; Raghav, N. Cinnamaldehyde as a Potential Cathepsin-B Inhibitor: A Comparative Investigation with some Commercial Anticancer Drugs. Chem. Biodivers. 2025, 22, e202401985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.K.; Ahima, R.S. Leptin signaling. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Li, J.; Fu, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway: From bench to clinic. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Du, J.; Huang, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, X.; He, B. From hyperglycemia to intervertebral disc damage: Exploring diabetic-induced disc degeneration. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1355503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Fernández, C.; Francisco, V.; Pino, J.; Mera, A.; González-Gay, M.A.; Gómez, R.; Lago, F.; Gualillo, O. Molecular Relationships among Obesity, Inflammation and Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Are Adipokines the Common Link? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Ren, J.Z.; Meng, X.Q.; Pang, C.G.; Duan, G.Q.; Zhang, J.X.; Zou, H.; Yang, H.Z.; Ji, J.J. Expression profiles of MMP-1 and TIMP-1 in lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 19080–19086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Soskic, S.; Essack, M.; Arya, S.; Stewart, A.J.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 585887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederico, M.J.S.; Sulis, P.M.; Pereira, L.L.; Rey, D.; Aragón, M.; Silva, F.R.M.B. Potential Effect of Cinnamaldehyde on Insulin Resistance Is Mediated by Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.H.; Ma, R.X.; Wu, J.T.; Du, S.Q.; Lv, Y.Y.; Yu, H.N.; Zhang, W.; Mao, S.M.; Liu, G.Y.; Bu, Y.T.; et al. Cinnamaldehyde Alleviates Bone Loss by Targeting Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Damage via the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway in BMSCs and Ovariectomized Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 17362–17378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Zhang, H.; Jia, C.; Zhang, R.; Shen, C. Epigenetic modifications of inflammation in intervertebral disc degeneration. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 87, 101902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, X.; Escames, G.; Lei, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Jing, T.; Yao, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Contributions to inflammation-related diseases. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2023, 28, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Jin, S.H.; Wang, M.Y.; Jin, X.L.; Lv, C.; Deng, Y.F.; Wang, J.L. Enhanced NLRP3, caspase-1, and IL- 1β levels in degenerate human intervertebral disc and their association with the grades of disc degeneration. Anat. Rec. 2015, 298, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risbud, M.V.; Shapiro, I.M. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: Pain and disc content. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chang, X.; Fu, S. Role of Pyroptosis in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Its Therapeutic Implications. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao-Yang, G.; Peng, C.; Hai-Hong, Z. Roles of NLRP3 inflammasome in intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Qiu, J.; Jiang, T.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, X.; He, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Feng, X.; et al. Maltol ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration through inhibiting PI3K/AKT/NF-kappaB pathway and regulating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, K.; Ying, J.; Xu, H.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, H.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Wang, P.; Jin, H.; Li, J.; et al. Aucubin Alleviates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Repressing NF-kappaB-NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Endplate Chondrocytes. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 5899–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, S.; Ishida-Takahashi, R.; Tawara, I.; Hu, J.; Patterson, C.M.; Jones, J.C.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Myers, M.G., Jr. Insufficiency of Janus kinase 2-autonomous leptin receptor signals for most physiologic leptin actions. Diabetes 2010, 59, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, M.; De Santo, M.; Comandè, A.; Belsito, E.L.; Andò, S.; Liguori, A.; Leggio, A. Leptin-Activity Modulators and Their Potential Pharmaceutical Applications. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Correa, A.A.; Estrada, J.A.; Contreras, I. Leptin Signaling in the Control of Metabolism and Appetite: Lessons from Animal Models. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 66, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Arita, S.; Ogawa, T.; Takenouchi, A.; Inagaki-Ohara, K. Augmented leptin-induced trefoil factor 3 expression and epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation differentially influences neoplasia progression in the stomach and colorectum of dietary fat-induced obese mice. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2022, 729, 109379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.H.; Li, J.H.; Zhao, Y.L.; Wang, G.S. Effect and Safety of Cinnamaldehyde on Immunosuppressed Mice with Invasive Pulmonary Candidiasis. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 27, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, K.-F.; Yu, H.-C.; Hsu, H.-T. Cinnamaldehyde Inhibits Leptin-Induced MMP-1 by Modulating Leptin Receptor/STAT3 and Blocking RhoA/NF-κB Pathways in Human Intervertebral Disc Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199819
Hua K-F, Yu H-C, Hsu H-T. Cinnamaldehyde Inhibits Leptin-Induced MMP-1 by Modulating Leptin Receptor/STAT3 and Blocking RhoA/NF-κB Pathways in Human Intervertebral Disc Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199819
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Kuo-Feng, Hsin-Chiao Yu, and Hsien-Ta Hsu. 2025. "Cinnamaldehyde Inhibits Leptin-Induced MMP-1 by Modulating Leptin Receptor/STAT3 and Blocking RhoA/NF-κB Pathways in Human Intervertebral Disc Stem Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199819
APA StyleHua, K.-F., Yu, H.-C., & Hsu, H.-T. (2025). Cinnamaldehyde Inhibits Leptin-Induced MMP-1 by Modulating Leptin Receptor/STAT3 and Blocking RhoA/NF-κB Pathways in Human Intervertebral Disc Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199819






