Autoimmune Encephalitis with Neuronal Surface Autoantibodies and Other Suspected Cases of Autoimmune Etiology: A Single-Center Experience in Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographic and Diagnostic Characteristics of the Study Cohort
2.1.1. Autoantibody Profiles and CSF Antibody Testing
2.1.2. CSF Analysis
2.1.3. MRI Findings
2.1.4. Neoplasm Associations
2.1.5. Immunosuppressive Treatment
2.2. Clinical Presentation and Supportive Investigations
2.2.1. Findings in AE Patients
Characteristics of Ab-Positive AE Patients
Characteristics of Ab-Negative AE Patients
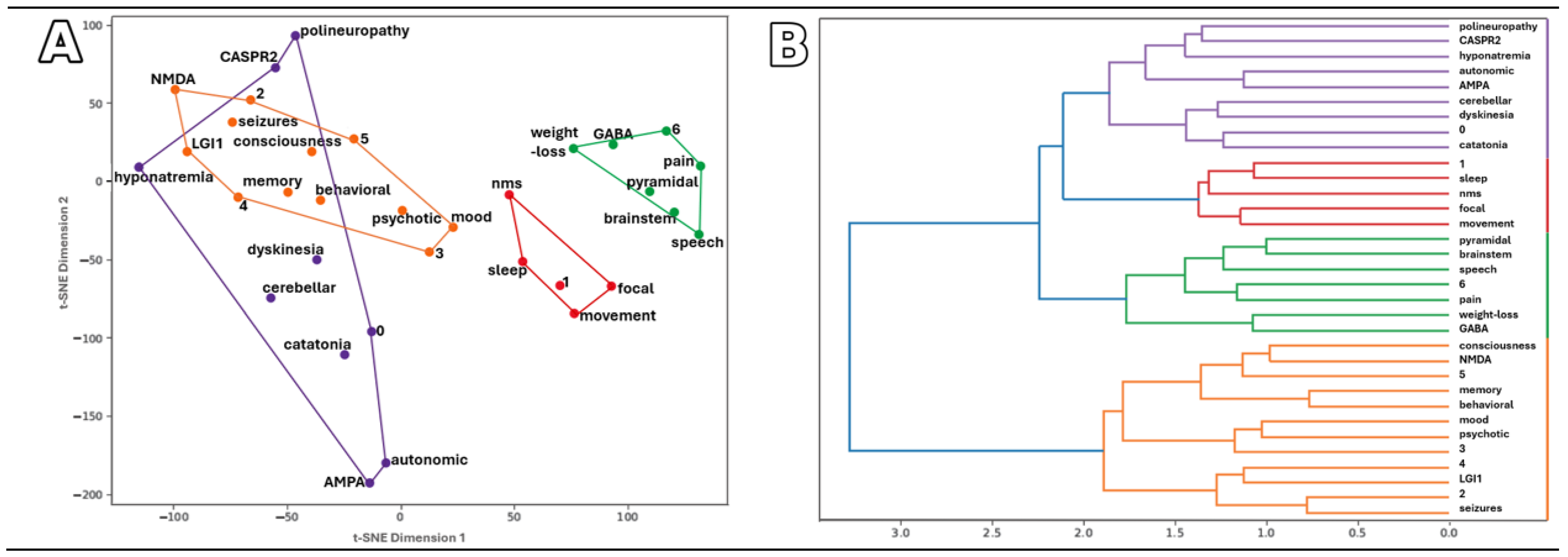
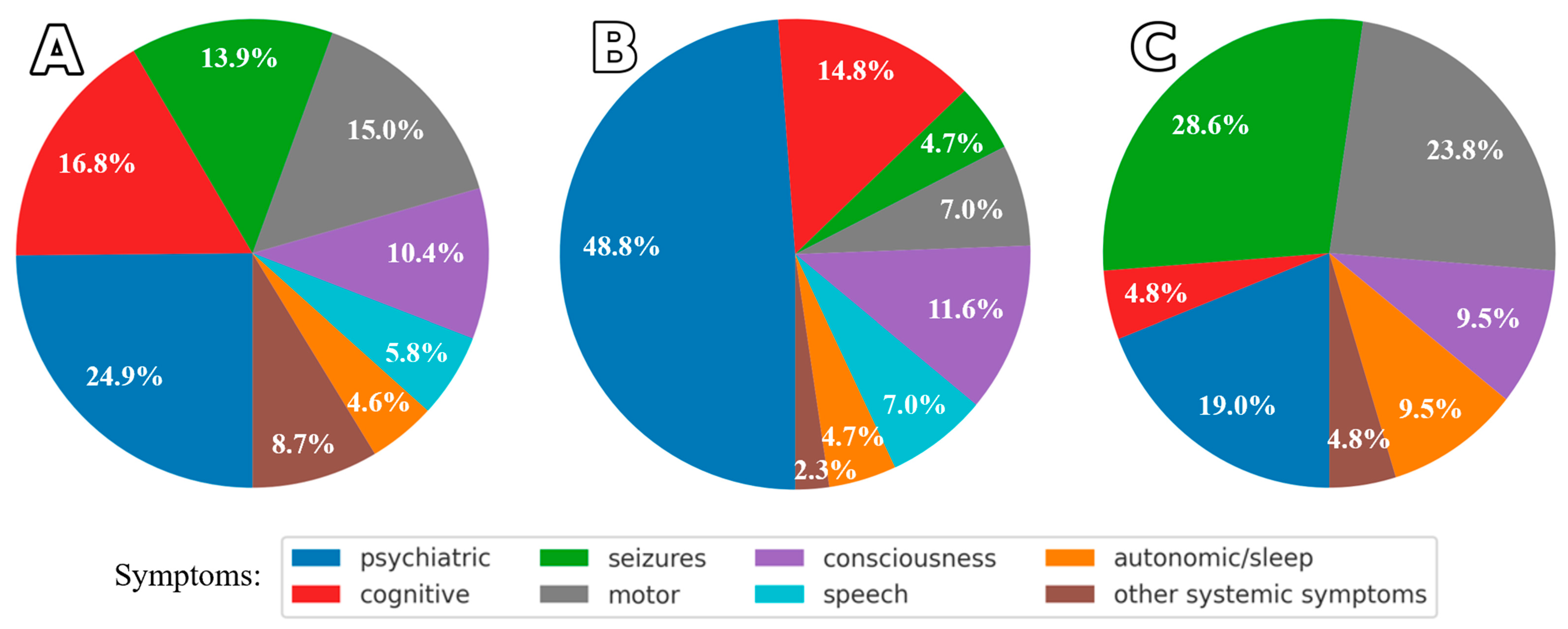
Symptom Patterns and Similarities in AE Patients
2.2.2. Findings in Ab-Positive Patients Without AE
3. Discussion
3.1. Antibody-Positive AE
3.2. Antibody-Negative AE
3.3. Antibody-Positive, Non-AE Presentations
3.4. Comparison of Symptom Profiles Across Study Subgroups
4. Materials and Methods
- Ab-positive AE: meeting clinical criteria for AE with detectable Abs (n = 47);
- Ab-negative AE: meeting clinical criteria for AE without detectable Abs (n = 7);
- Ab-positive, not AE: Ab positivity without meeting clinical criteria for AE (n = 11) (see Figure 3).
4.1. Autoantibody Testing
4.2. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Limitation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ab | autoantibody (antibody) |
| AE | autoimmune encephalitis |
| AMPAR | α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid receptor |
| CASPR2 | contactin-associated protein-like 2 |
| CBA | cell-based assay |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| FBDS | faciobrachial dystonic seizures |
| GABABR | γ-Aminobutyric acid receptor-B |
| HSV-1 | herpes simplex virus 1 |
| IVIG | intravenous immunoglobulin |
| LE | limbic encephalitis |
| LGI1 | components of the voltage-gated potassium channel complex, including leucine-rich glioma-inactivated protein 1 |
| MP | methylprednisolone |
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| NMDAR | N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor |
| PLEX | plasma exchange |
| RPD | rapidly progressive dementia |
| SCLC | a small-cell lung carcinoma |
References
- Hughes, E.G.; Peng, X.; Gleichman, A.J.; Lai, M.; Zhou, L.; Tsou, R.; Parsons, T.D.; Lynch, D.R.; Dalmau, J.; Balice-Gordon, R.J. Cellular and synaptic mechanisms of anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 5866–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planagumà, J.; Leypoldt, F.; Mannara, F.; Gutiérrez-Cuesta, J.; Martín-García, E.; Aguilar, E.; Titulaer, M.J.; Petit-Pedrol, M.; Suárez-Calvet, M.; Saiz, A.; et al. Human N-methyl D-aspartate receptor antibodies alter memory and behavior in mice. Brain 2015, 138, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbatemarco, J.R.; Yan, C.; Kunchok, A.; Rae-Grant, A. Antibody-mediated autoimmune encephalitis: A practical approach. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2021, 88, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Meng, Y.; Najjar, A.; Lado, F.; Najjar, S. Autoimmune encephalitis: A physician’s guide to the clinical spectrum diagnosis and management. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simabukuro, M.M.; Silva, G.D.D.; Castro, L.H.M.; Lucato, L.T. A critical review and update on autoimmune encephalitis: Understanding the alphabet soup. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2022, 80, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, C.E.; Binks, S.; Irani, S.R. Autoimmune encephalitis: Clinical spectrum and management. Pract. Neurol. 2021, 21, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.H.F.; Disserol, C.C.D.; de Freitas Dias, B.; Marques, A.C.; Cardoso, M.D.; Silva, P.V.C.; Toso, F.F.; Dutra, L.A. Recent advances in autoimmune encephalitis. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2024, 82, s00441793933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, J.E.; Carlson, N.G.; Abbatemarco, J.R.; Herdlevær, I.; Clardy, S.L.; Vedeler, C.A. Paraneoplastic and other autoimmune encephalitides: Antineuronal antibodies, T lymphocytes, and questions of pathogenesis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 12, 744653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinmaz, N.; Nguyen, T.; Tea, F.; Dale, R.C.; Brilot, F. Mapping autoantigen epitopes: Molecular insights into autoantibody-associated disorders of the nervous system. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, M.; Wu, X.; Hong, D. Clinical characteristics of autoimmune encephalitis with co-existence of multiple anti-neuronal antibodies. BMC Neurol. 2024, 24, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus, F.; Dalmau, J. Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes in the era of immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus, F.; Titulaer, M.J.; Balu, R.; Benseler, S.; Bien, C.G.; Cellucci, T.; Cortese, I.; Dale, R.C.; Gelfand, J.M.; Geschwind, M.; et al. A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.C.; Lin, M.I.; Wenig, W.C.; Lee, W.T. Neuropsychiatric disorders due to limbic encephalitis: Immunologic aspect. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, D.; Pittock, S.J.; Kelly, C.R.; McKeon, A.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; Lennon, V.A.; Gadoth, A.; Smith, C.Y.; Bryant, S.C.; Klein, C.J.; et al. Autoimmune encephalitis epidemiology and a comparison to infectious encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braczkowski, M.; Soszyński, D.; Sierakowska, A.; Braczkowski, R.; Kufel, K.; Łabuz-Roszak, B. Autoimmune encephalitis with antibodies: Anti-NMDAR, anti-AMPAR, anti-GQ1b, anti-DPPX, anti-CASPR2, anti-LGI1, anti-RI, anti-Yo, anti-Hu, anti-CV2 and anti-GABAAR, in the course of psychoses, neoplastic diseases, and paraneoplastic syndromes. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, Z.; Bóné, B.; Orsi, G.; Szots, M.; Nagy, F.; Csépány, T.; Mezei, Z.; Rajda, C.; Simon, D.; Najbauer, J.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of neuronal surface antibody-mediated autoimmune encephalitis patients in a national cohort. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 611597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Yang, H.; Wang, Q. Neuronal surface antibody-mediated autoimmune encephalitis (limbic encephalitis) in China: A multiple-center, retrospective study. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 621599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Armangué, T.; Planagumà, J.; Radosevic, M.; Mannara, F.; Leypoldt, F.; Geis, C.; Lancaster, E.; Titulaer, M.J.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; et al. An update on anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis for neurologists and psychiatrists: Mechanisms and models. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wang, H. Biomarkers on anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. Brain Netw. Disord. 2025, 1, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titulaer, M.J.; McCracken, L.; Gabilondo, I.; Armangué, T.; Glaser, C.; Iizuka, T.; Honig, L.S.; Benseler, S.M.; Kawachi, I.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; et al. Treatment and prognostic factors for long-term outcome in patients with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: An observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Lin, J.; Li, A.; Guo, K.; Zhou, D.; Hong, Z. Long-term functional outcomes and relapse of anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: A cohort study in Western China. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilligan, M.; Thakolwiboon, S.; Orozco, E.; Banks, S.; Flanagan, E.P.; Lopez-Chiriboga, S.; Tillema, J.M.; Mills, J.R.; Pittock, S.J.; Valencia Sanchez, C.; et al. Autoimmune brainstem encephalitis: Clinical associations, outcomes, and proposed diagnostic criteria. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2025, 12, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Q.; Wang, K.; Tian, Y. Progressive cortical and sub-cortical alterations in patients with anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Yan, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. Overlapping anti-NMDAR encephalitis and multiple sclerosis: A case report and literature review. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1088801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumez, P.; Villagrán-García, M.; Bani-Sadr, A.; Benaiteau, M.; Peter, E.; Farina, A.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Ruitton-Allinieu, M.C.; Cotton, F.; et al. Specific clinical and radiological characteristics of anti-NMDA receptor autoimmune encephalitis following herpes encephalitis. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 6692–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armangué, T.; Olivé-Cirera, G.; Martínez-Hernandez, E.; Rodes, M.; Peris-Sempere, V.; Guasp, M.; Ruiz, R.; Palou, E.; González, A.; Marcos, M.Á.; et al. Neurologic complications in herpes simplex encephalitis: Clinical, immunological and genetic studies. Brain 2023, 146, 4306–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salovin, A.; Glanzman, J.; Roslin, K.; Armangue, T.; Lynch, D.R.; Panzer, J.A. Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis and nonencephalitic HSV-1 infection. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 5, e458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Tartaglia, S.; Dentoni, M.; Fabris, M.; Bax, F.; Belluzzo, M.; Verriello, L.; Bagatto, D.; Gastaldi, M.; Tocco, P.; et al. Central nervous system immune-related disorders after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination: A multicenter study. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1344184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayadnasiri, M.; Layeghi, F. Anti-N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor encephalitis following fourth dose of COVID-19 vaccination: A case report. Neurol. India 2024, 72, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, E. Autoantibody encephalitis: Presentation, diagnosis, and management. J. Clin. Neurol. 2022, 18, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, S.; Al-Diwani, A.; Waters, P.; Irani, S.R. The autoantibody-mediated encephalitides: From clinical observations to molecular pathogenesis. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 1689–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, Z.; Su, M.; Ni, J.; Wei, M.; Shi, J.; Tian, J. Clinical features and therapeutic effects of anti-leucine-rich glioma inactivated 1 encephalitis: A systematic review. Front. Neurol. 2022, 12, 791014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, N. Current nosology of neural autoantibody-associated dementia. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 711195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Huang, Z.; Lian, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J. A rare case of anti-LGI1 limbic encephalitis with concomitant positive NMDAR antibodies. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmau, J.; Graus, F. Diagnostic criteria for autoimmune encephalitis: Utility and pitfalls for antibody-negative disease. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, X.; Li, D.; Yuan, R.; Zhai, Y.; Teng, J.; Deng, W. Clinical features and factors associated with outcomes of antibody-negative autoimmune encephalitis in patients requiring intensive care. Crit. Care 2025, 29, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojžišová, H.; Krýsl, D.; Hanzalová, J.; Dargvainiene, J.; Wandinger, K.P.; Leypoldt, F.; Elišák, M.; Marusič, P. Antibody-negative autoimmune encephalitis: A single-center retrospective analysis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 10, e200170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abboud, H.; Probasco, J.; Irani, S.R.; Ances, B.; Benavides, D.R.; Bradshaw, M.; Christo, P.P.; Dale, R.C.; Fernandez-Fournier, M.; Flanagan, E.P.; et al. Autoimmune Encephalitis Alliance Clinicians Network. Autoimmune encephalitis: Proposed recommendations for symptomatic and long-term management. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Das, A.; Das, A.; Mulmuley, M. Antibody negative autoimmune encephalitis- does it differ from definite one? Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2019, 22, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, E.P.; Geschwind, M.D.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; Blackburn, K.M.; Turaga, S.; Binks, S.; Zitser, J.; Gelfand, J.M.; Day, G.S.; Dunham, S.R.; et al. Autoimmune encephalitis misdiagnosis in adults. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinoto, A.; Zara, P.; Mariotto, S.; Ferrari, S.; Flanagan, E.P.; Budhram, A.; Orellana, D.; Turilli, D.; Solla, P.; Day, G.S.; et al. Autoimmune encephalitis misdiagnosis and mimics. J. Neuroimmunol. 2023, 378, 578071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbistat. Demografia per età—Mokotów District. Available online: https://ugeo.urbistat.com/AdminStat/it/pl/demografia/eta/mokotow---district/1465058/4 (accessed on 25 September 2025).
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Antibody Profile | Ab-Positive AE (n = 47) | Ab-Positive, Not AE (n = 11) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMDAR | LGI1 | CASPR2 | GABABR | AMPAR | NMDAR | CASPR2 | |
| Total Abs (N = 59) | n = 24 | n = 13 | n = 8 | n = 2 | n = 1 | n = 7 | n = 4 |
| Age: median (Q1–Q3), range [y] | 51.5 (38.8–65.2), 22–84 | 52.0 (40.0–69.0), 16–77 | 70.0 (59.8–73.8), 21–78 | 66.0 (65.5–66.5), 65–67 | 65 * | 48.0 (29.0–60.5), 20–66 | 24,5 (20.5–29.8), 19–35 |
| Serum+ & CSF+ | 7 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Serum+ & CSF–/NT | 8/8 | 2/4 | 6/1 | 0/2 | 1/0 | 0/7 | 2/2 |
| Serum– & CSF+ | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Abs in Females (N = 32) | n = 16 | n = 4 | n = 3 | n = 2 | n = 1 | n = 3 | n = 3 |
| Age: median (Q1–Q3), range [y] | 54.5 (38.2–65.5), 22–77 | 69.5 (55.0–71.5), 16–73 | 76.0 (48.5–77.0), 21–78 | 66.0 (65.5–66.5), 65–67 | 65 * | 65.0 (44.0–65.5), 23–66 | 28,0 (23.5–31.5), 19–35 |
| Serum+ & CSF+ | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Serum+ & CSF–/NT | 3/7 | 2/2 | 3/0 | 0/2 | 1/0 | 0/3 | 2/1 |
| Serum– & CSF+ | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Abs in Males (N = 27) | n = 8 | n = 9 | n = 5 | n = 0 | n = 0 | n = 4 | n = 1 |
| Age: median (Q1–Q3), range [y] | 44.0 (40.2–55.5), 23–84 | 50.0 (40.0–66.0), 23–77 | 67.0 (67.0–73.0), 38–73 | – | – | 41.5 (31.25–50.0), 20–56 | 21 * |
| Serum+ & CSF+ | 2 | 7 | 1 | – | – | 0 | 0 |
| Serum+ & CSF–/NT | 5/1 | 0/2 | 3/1 | – | – | 0/4 | 0/1 |
| Cerebrospinal Fluid | Ab-Positive AE | Ab-Negative AE | Ab-Positive, Not AE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (N = 47) | Female (n = 26) | Male (n = 21) | Total (N = 7) | Female (n = 3) | Male (n = 4) | Total (N = 11) | Female (n = 6) | Male (n = 5) | |
| Pleocytosis (cells/μL) | |||||||||
| 0–5 (NR) | 29 | 18 | 11 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 8 | 6 | 2 |
| 6–50 | 9 | 3 | 6 | 2 | – | 2 | – | – | – |
| >50 | 3 | 3 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| NT | 6 | 2 | 4 | – | – | – | 3 | – | 3 |
| Protein (mg/dL) | |||||||||
| <45 (NR) | 21 | 12 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 45–100 | 13 | 5 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| >100 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| NT | 13 | 9 | 4 | – | – | – | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| IgG Index | |||||||||
| <0.7 (N) | 30 | 19 | 11 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 2 |
| >0.7 | 10 | 5 | 5 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| NT | 7 | 2 | 5 | – | – | – | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| Oligoclonal Bands | |||||||||
| Type I | 14 | 10 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Type II | 6 | 3 | 3 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Type III | 4 | 2 | 2 | – | – | – | 2 | 2 | – |
| Type IV | 6 | 1 | 5 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Type V | 1 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| NT | 16 | 9 | 7 | 3 | – | 3 | 7 | 3 | 4 |
| MRI Findings | Ab-Positive AE (N = 47) | Ab-Negative AE (N = 7) | Ab Positive, Not AE (N = 11) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Associated Ab | n | n | Associated Ab | |
| No abnormalities detected | 14 | anti-NMDAR (n = 7) anti-CASPR2 (n = 3) anti-LGI1 (n = 2) anti-GABABR (n = 1) anti-NMDAR/LGI1 (n = 1) | 1 | 5 | anti-NMDAR (n = 4) anti-CASPR2 (n = 1) |
| Vasogenic edema/injury | 16 | anti-NMDAR (n = 8) anti-CASPR2 (n = 4) anti-LGI1 (n = 3) anti-AMPAR/Hu (n = 1) | 1 | 3 | anti-CASPR2 (n = 2) anti-NMDAR (n = 1) |
| Limbic inflammation | 14 | anti-LGI1 (n = 7) anti-NMDAR (n = 6) anti-GABABR (n = 1) | 5 | – | – |
| Demyelinating changes | 2 | anti-NMDAR (n = 2) | – | 1 | anti-NMDAR (n = 1) |
| Neoplastic changes | – | – | – | 2 | anti-NMDAR (n = 1) anti-CASPR2 (n = 1) |
| Neoplasm Distribution | Ab-Positive AE (N = 47) | Ab-Negative AE (N = 7) | Ab-Positive, Not AE (N = 11) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Associated Ab | n | n | Associated Ab | |
| Ovarian tumor: carcinoma/teratoma | 2:1/1 | anti-NMDAR | 1:0/1 | – | – |
| Renal cell carcinoma | 1 | anti-NMDAR | – | – | – |
| Nasopharynx carcinoma | 1 | anti-LGI1 | – | – | – |
| Breast carcinoma | 1 | anti-NMDAR | – | – | – |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | 1 | anti-AMPAR/Hu | – | 1 | anti-NMDAR |
| Small cell lung cancer | 1 | anti-GABABR | – | – | – |
| Myeloma | 2 | anti-NMDAR anti-CASRP2 | – | – | – |
| Melanoma | 1 | anti-LGI1 | – | – | – |
| Brain neoplasm | – | – | – | 2 | anti-NMDAR anti-CASPR2 |
| Not detected/Unknown | 30/7 | – | – | 8/1 | – |
| Treatment Modality | Details | AE (N = 54) | Ab-Positive, Not AE (N = 11) |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | n | ||
| Methylprednisolone (MP) | 5 × 1 g IV | 33 | 4 |
| Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG) | 2 g/kg | 26 | 2 |
| Plasma Exchange (PLEX) | 5–7 sessions, every other day | 10 | – |
| Cyclophosphamide (CYC) | 1000 mg, 3–5 cycles every 4 weeks | 11 | – |
| Rituximab | As per protocol | 1 | – |
| Prolonged immunosuppressive treatment | 1–5 years | 28 | 3 |
| Oral steroids | Prednisone 1 mg/kg, 3–24 months | 16 | 3 |
| Other immunosuppressant | Azathioprine | 7 | 1 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | 1 | – | |
| Methotrexate | 4 | – | |
| No treatment | — | 7 | 5 |
| Autoantibody | n | Sex/Age | Initial Symptoms | Final Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-NMDAR (N = 7) | 1 | F/28 | first seizure | primary generalized epilepsy |
| 3 | F/23, M/27, M/56 | first seizure | epilepsy of unknown etiology | |
| 1 | M/35 | initial psychotic episode | catatonic schizophrenia | |
| 1 | F/65 | limb paresis, ataxia, mild memory impairment | primary progressive MS | |
| 1 | F/66 | hemiparesis, dyskinesia, altered consciousness | ischemic stroke | |
| Anti-CASPR2 (N = 4) | 2 | F/35, M/48 | first seizure | glioma (2 cases) |
| 1 | M/21 | first seizure | epilepsy of unknown etiology | |
| 1 | F/19 | behavioral disturbances | borderline personality disorder |
| Clinical Characteristic | Ab-Positive AE | Ab-Negative AE | Ab-Positive, Not AE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (N = 54) | Female (n = 29) | Male (n = 25) | Total (N = 7) | Female (n = 3) | Male (n = 4) | Total (N = 11) | Female (n = 6) | Male (n = 5) | |
| Age, median (Q1–Q3), range [y] | 61.0 (41.0–68.5), 16–84 | 64.5 (41.25–70.25), 16–78 | 52.0 (42.0–67.0), 23–84 | 55.0 (38.5–64.0), 26–80 | 55.0 (40.5–62.0), 26–69 | 50.0 (39.8–64.3), 36–80 | 35.0 (22.0–52.0), 19–66 | 31.5 (24.2–57.5), 19–66 | 35.0 (21.0–48.0), 20–56 |
| Symptoms | |||||||||
| Altered consciousness | 18 | 11 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Behavioral (psychiatric) | 22 | 14 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | – |
| Psychotic | 10 | 7 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Anxiety/Depression/Bipolar disorder | 4/2/1 | 3/2/1 | 1/0/0 | 4/1/0 | 1/0/0 | 3/1/0 | 1/0/0 | 1/0/0 | – |
| Neuroleptic malignant syndrome | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | – | – | – |
| Catatonia | 2 | 1 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Memory disorders/Dementia | 20/9 | 9/4 | 11/5 | 6/0 | 2/0 | 4/0 | 1/0 | 0 | 1/0 |
| Seizures/Status epilepticus/Myoclonus | 16/7/1 | 7/5/1 | 9/2/0 | 1/1/0 | 1/1/0 | 0 | 6/0/0 | 3/0/0 | 3/0/0 |
| Speech disorders | 10 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | – | – | – |
| Parkinson’s syndrome/Dyskinesia/PSP-like | 4/7/1 | 1/4/1 | 3/3/0 | – | – | – | 0/1/0 | 0/1/0 | – |
| Lower limb paresis | 5 | 3 | 2 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Pyramidal syndrome | 1 | 1 | 0 | – | – | – | 1 | 1 | – |
| Focal symptoms | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | – |
| Cerebellar syndrome | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | – | – | – |
| Brainstem: oculomotor/urinary/dysphagia | 1/4/1 | 1/3/1 | 0/1/0 | 1/0/0 | 1/0/0 | 0/0/0 | 1/0/0 | 1/0/0 | – |
| Autonomic dysfunction | 4 | 3 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Sleep disorders | 4 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Pain/Paresthesia | 2/1 | 0/1 | 2/0 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Polyneuropathy | 1 | 0 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Hyponatremia | 5 | 5 | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Weight loss | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | – | – | – |
| Outcome | |||||||||
| Complete recovery | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | – |
| One-time relapse | 4 | 3 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Epilepsy | 16 | 5 | 11 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 3 |
| Memory disorders | 15 | 7 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 2 | – | – | |
| Psychiatric symptoms | 9 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Multiple sclerosis | 2 | 2 | 0 | – | – | – | 1 | 1 | – |
| Death | 14 | 11 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | – | 1 |
| Final diagnosis | |||||||||
| LE | 34 | 20 | 14 | 7 | 3 | 4 | – | – | – |
| RPD | 6 | 2 | 4 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Brainstem AE | 3 | 2 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Cortico-subcortical AE | 2 | 1 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Cerebellitis AE | 2 | 1 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Epilepsy | – | – | – | – | – | – | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| Glioma | – | – | – | – | – | – | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Stroke | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Schizophrenia | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Borderline personality | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurkowska-Jastrzębska, I.; Polanowska, K.; Kurczych, K.; Cudna, A.; Sienkiewicz-Jarosz, H.; Piechal, A. Autoimmune Encephalitis with Neuronal Surface Autoantibodies and Other Suspected Cases of Autoimmune Etiology: A Single-Center Experience in Poland. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199541
Kurkowska-Jastrzębska I, Polanowska K, Kurczych K, Cudna A, Sienkiewicz-Jarosz H, Piechal A. Autoimmune Encephalitis with Neuronal Surface Autoantibodies and Other Suspected Cases of Autoimmune Etiology: A Single-Center Experience in Poland. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199541
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurkowska-Jastrzębska, Iwona, Katarzyna Polanowska, Katarzyna Kurczych, Agnieszka Cudna, Halina Sienkiewicz-Jarosz, and Agnieszka Piechal. 2025. "Autoimmune Encephalitis with Neuronal Surface Autoantibodies and Other Suspected Cases of Autoimmune Etiology: A Single-Center Experience in Poland" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199541
APA StyleKurkowska-Jastrzębska, I., Polanowska, K., Kurczych, K., Cudna, A., Sienkiewicz-Jarosz, H., & Piechal, A. (2025). Autoimmune Encephalitis with Neuronal Surface Autoantibodies and Other Suspected Cases of Autoimmune Etiology: A Single-Center Experience in Poland. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199541






