Serum and Tissue Light-Chains as Disease Biomarkers in AL Amyloidosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
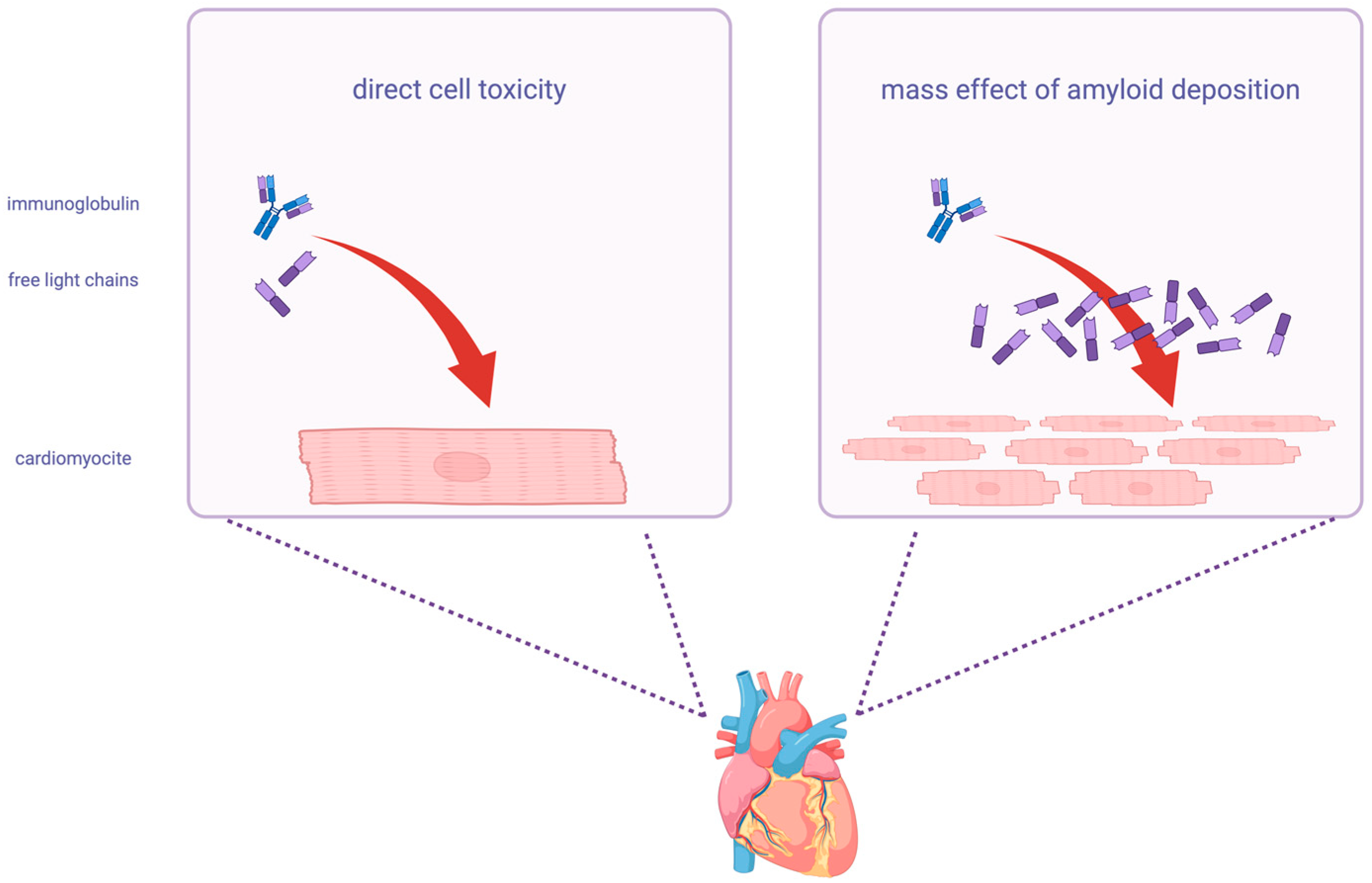
2. Pathogenetic Role of Light-Chains in AL Amyloidosis
3. The Role of Monoclonal Light-Chains in Diagnosis, Risk Prediction and Response Assessment
4. Methods to Measure Circulating Light-Chains
5. Purposes of Measuring Light-Chains in Tissues: Diagnosis, Risk Prediction
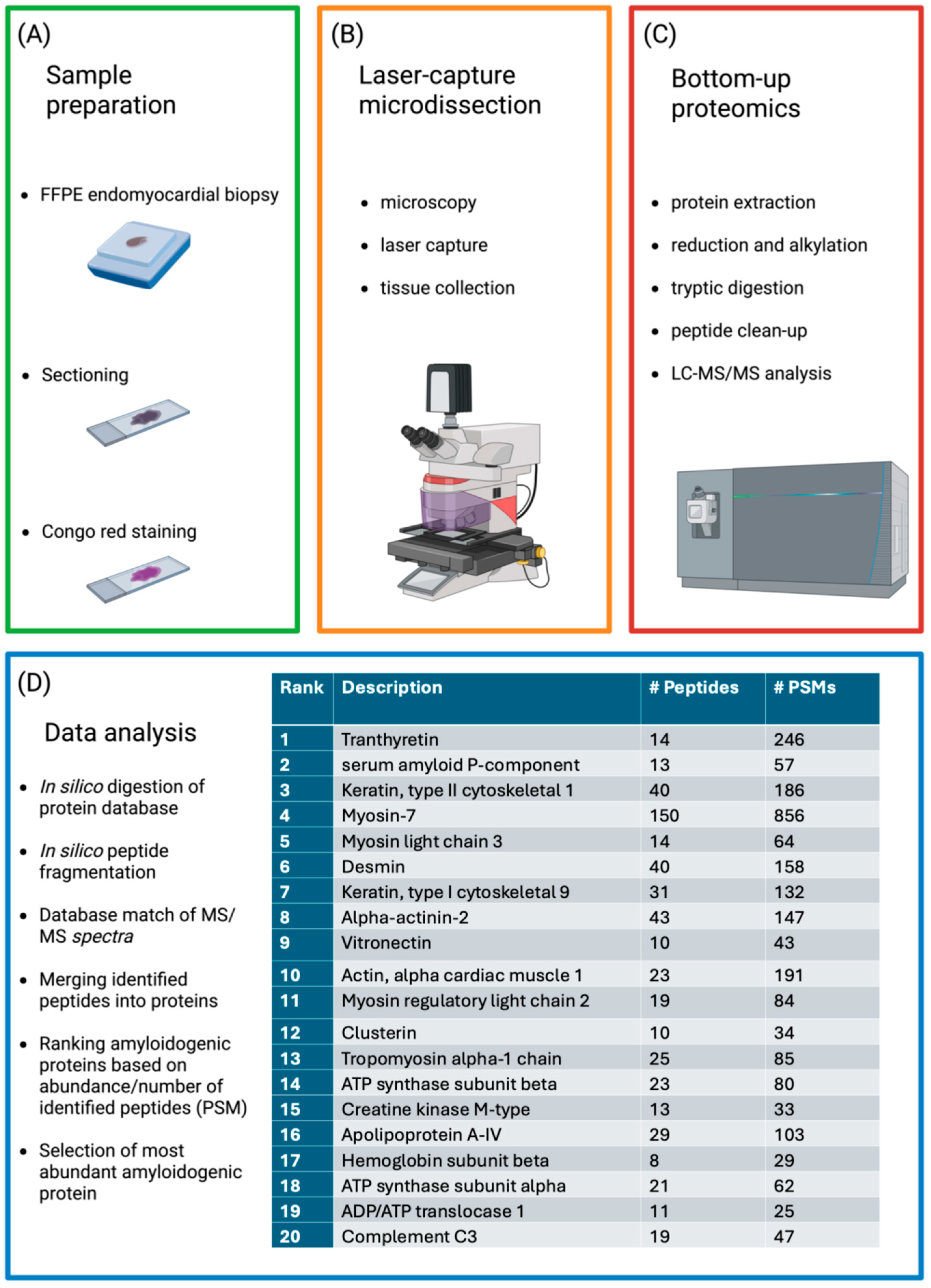
6. Techniques for Tissue Analysis
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Porcari, A.; Bussani, R.; Merlo, M.; Varrà, G.G.; Pagura, L.; Rozze, D.; Sinagra, G. Incidence and Characterization of Concealed Cardiac Amyloidosis Among Unselected Elderly Patients Undergoing Post-mortem Examination. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 749523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, F.U.; Hayer-Hartl, M. Molecular Chaperones in the Cytosol: From Nascent Chain to Folded Protein. Science 2002, 295, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiti, F.; Dobson, C.M. Protein Misfolding, Amyloid Formation, and Human Disease: A Summary of Progress Over the Last Decade. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 27–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, R.; Gillespie, J.R.; Talapatra, A.; Minert, L.J.; Ionescu-Zanetti, C.; Millett, I.; Fink, A.L. Partially Folded Intermediates as Critical Precursors of Light Chain Amyloid Fibrils and Amorphous Aggregates. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 3525–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blancas-Mejía, L.M.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M. Systemic Amyloidoses. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 745–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, M.A.; Dispenzieri, A. Systemic Amyloidosis Recognition, Prognosis, and Therapy. JAMA 2020, 324, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechalekar, A.D.; Whelan, C. Encouraging impact of doxycycline on early mortality in cardiac light chain (AL) amyloidosis. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidana, S.; Tandon, N.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Dingli, D.; Jevremovic, D.; Morice, W.G.; Kapoor, P.; Kourelis, T.V.; Lacy, M.Q.; et al. Prognostic significance of circulating plasma cells by multi-parametric flow cytometry in light chain amyloidosis. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baden, E.M.; Randles, E.G.; Aboagye, A.K.; Thompson, J.R.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M. Structural insights into the role of mutations in amyloidogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gottwald, J.; Röcken, C. The amyloid proteome: A systematic review and proposal of a protein classification system. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 56, 526–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurizi, N.; Rella, V.; Fumagalli, C.; Salerno, S.; Castelletti, S.; Dagradi, F.; Torchio, M.; Marceca, A.; Meda, M.; Gasparini, M.; et al. Prevalence of cardiac amyloidosis among adult patients referred to tertiary centres with an initial diagnosis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 300, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quock, T.P.; Yan, T.; Chang, E.; Guthrie, S.; Broder, M.S. Epidemiology of AL amyloidosis: A real-world study using US claims data. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Rivas, G.; Bender, S.; Sirac, C. Understanding AL amyloidosis with a little help from in vivo models. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1008449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comenzo, R.L.; Zhang, Y.; Martinez, C.; Osman, K.; Herrera, G.A. The tropism of organ involvement in primary systemic amyloidosis: Contributions of Ig VL germ line gene use and clonal plasma cell burden. Blood 2001, 98, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.J.; Nau, A.N.; Wong, S.; Spencer, B.H.; Shen, Y.; Hua, A.; Bullard, M.J.; Sanchorawala, V.; Prokaeva, T. An updated AL-base reveals ranked enrichment of immunoglobulin light chain variable genes in AL amyloidosis. Amyloid 2025, 32, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, J.; Berghaus, N.; Schreiner, S.; Hegenbart, U.; Schönland, S.O.; Wiese, S.; Huhn, S.; Haupt, C. Identification of AL proteins from 10 λ-AL amyloidosis patients by mass spectrometry extracted from abdominal fat and heart tissue. Amyloid 2023, 30, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.A.; Jain, M.; Pimentel, D.R.; Wang, B.; Connors, L.H.; Skinner, M.; Apstein, C.S.; Liao, R. Human Amyloidogenic Light Chains Directly Impair Cardiomyocyte Function Through an Increase in Cellular Oxidant Stress. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapezzi, C.; Merlini, G.; Quarta, C.C.; Riva, L.; Longhi, S.; Leone, O.; Salvi, F.; Ciliberti, P.; Pastorelli, F.; Biagini, E.; et al. Systemic Cardiac Amyloidoses. Circulation 2009, 120, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavatelli, F.; Imperiini, E.; Orrù, S.; Rognoni, P.; Sarnataro, D.; Palladini, G.; Malpasso, G.; Soriano, M.E.; Di Fonzo, A.; Valentini, V.; et al. Novel mitochondrial protein interactors of immunoglobulin light chains causing heart amyloidosis. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 4614–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladini, G.; Jaccard, A.; Milani, P.; Lavergne, D.; Foli, A.; Bender, S.; Lavatelli, F.; Bosoni, T.; Valentini, V.; Pirolini, L.; et al. Circulating free light chain measurement in the diagnosis, prognostic assessment and evaluation of response of AL amyloidosis: Comparison of Freelite and N latex FLC assays. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 1734–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Guan, J.; Plovie, E.; Seldin, D.C.; Connors, L.H.; Merlini, G.; Falk, R.H.; MacRae, C.A.; Liao, R. Human amyloidogenic light chain proteins result in cardiac dysfunction, cell death, and early mortality in zebrafish. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2013, 305, H95–H103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diomede, L.; Rognoni, P.; Lavatelli, F.; Romeo, M.; del Favero, E.; Cantù, L.; Ghibaudi, E.; di Fonzo, A.; Corbelli, A.; Fiordaliso, F.; et al. A Caenorhabditis elegans–based assay recognizes immunoglobulin light chains causing heart amyloidosis. Blood 2014, 123, 3543–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchorawala, V. Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 2295–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, R.T.; Olatoye, O.O.; Randles, E.G.; Howell, K.G.; DiCostanzo, A.C.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M. Role of mutations in the cellular internalization of amyloidogenic light chains into cardiomyocytes. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monis, G.F.; Schultz, C.; Ren, R.; Eberhard, J.; Costello, C.; Connors, L.; Skinner, M.; Trinkaus-Randall, V. Role of Endocytic Inhibitory Drugs on Internalization of Amyloidogenic Light Chains by Cardiac Fibroblasts. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 1939–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, F.; Lavatelli, F.; Di Silvestre, D.; Valentini, V.; Palladini, G.; Merlini, G.; Mauri, P. Shotgun Protein Profile of Human Adipose Tissue and Its Changes in Relation to Systemic Amyloidoses. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 5642–5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, F.J.; Kisilevsky, R. Immunoglobulin light chains, glycosaminoglycans, and amyloid. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2000, 57, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Kyle, R.; Merlini, G.; Miguel, J.S.; Ludwig, H.; Hajek, R.; Palumbo, A.; Jagannath, S.; Blade, J.; Lonial, S.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group guidelines for serum-free light chain analysis in multiple myeloma and related disorders. Leukemia 2009, 23, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, A.C.; Landgren, O. Polyclonal Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains as a PotentialBiomarker of Immune Stimulation and Inflammation. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 1387–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwogbo, O.V.; Jin, Y.; Sliker, T.; Wilhite, D.; Singh, G. Analysis of Multiple Bands on Serum Protein Immunofixation Electrophoresis: Challenge in Interpretation of Clonality in a Patient with Light Chain–Predominant Multiple Myeloma. Lab. Med. 2021, 52, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, P.; Basset, M.; Russo, F.; Foli, A.; Merlini, G.; Palladini, G. Patients with light-chain amyloidosis and low free light-chain burden have distinct clinical features and outcome. Blood 2017, 130, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlini, G.; Palladini, G. Amyloidosis: Is a cure possible? Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, iv63–iv66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochtler, T.; Hegenbart, U.; Heiss, C.; Benner, A.; Cremer, F.; Volkmann, M.; Ludwig, J.; Perz, J.B.; Ho, A.D.; Goldschmidt, H.; et al. Evaluation of the serum-free light chain test in untreated patients with AL amyloidosis. Haematologica 2008, 93, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradwell, A.R.; Carr-Smith, H.D.; Mead, G.P.; Tang, L.X.; Showell, P.J.; Drayson, M.T.; Drew, R. Highly Sensitive, Automated Immunoassay for Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains in Serum and Urine. Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Andújar, A.; Robles, P.; Cibeira, M.T.; Montagud-Marrahi, E.; Guillen, E.; Xipell, M.; Blasco, M.; Poch, E.; Rosiñol, L.; Bladé, J.; et al. The renal range of the κ/λ sFLC ratio: Best strategy to evaluate multiple myeloma in patients with chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.C.; Dispenzieri, A.; Scott, C.G.; Lin, G.; Jaffe, A.S.; Klarich, K.W.; Grogan, M. Utility of the Serum Free Light Chain Assay in the Diagnosis of Light Chain Amyloidosis in Patients with Heart Failure. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Hayman, S.R.; Buadi, F.K.; Colby, C.; Laumann, K.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Leung, N.; Dingli, D.; et al. Revised Prognostic Staging System for Light Chain Amyloidosis Incorporating Cardiac Biomarkers and Serum Free Light Chain Measurements. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladini, G.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Kumar, S.; Wechalekar, A.; Hawkins, P.N.; Schönland, S.; Hegenbart, U.; Comenzo, R.; Kastritis, E.; et al. New Criteria for Response to Treatment in Immunoglobulin Light Chain Amyloidosis Based on Free Light Chain Measurement and Cardiac Biomarkers: Impact on Survival Outcomes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4541–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponi, L.; Koni, E.; Romiti, N.; Paolicchi, A.; Franzini, M. Different immunoreactivity of monomers and dimers makes automated free light chains assays not equivalent. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 57, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caponi, L.; Koni, E.; Romiti, N.; Paolicchi, A.; Franzini, M. Free light chain UV quantification compared with immunochemical measurement: How dimers and monomers may influence the results. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 510, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caponi, L.; Franzini, M.; Koni, E.; Masotti, S.; Petrini, M.; Paolicchi, A. Discrepancy between FLC assays: Only a problem of quantification? Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1111–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kaplan, B.; Jacobs, J.F. FLC polymerization: Another hurdle towards standardization of FLC measurements. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 515, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camerini, L.; Aimo, A.; Pucci, A.; Castiglione, V.; Musetti, V.; Masotti, S.; Caponi, L.; Vergaro, G.; Passino, C.; Clerico, A.; et al. Serum and tissue light-chains as disease biomarkers and targets for treatment in AL amyloidosis. Vessel. Plus 2022, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.T.; Kumar, S.K.; Dispenzieri, A.; Kyle, R.A.; Katzmann, J.A.; Rajkumar, S.V. Serum free light chain ratio as a biomarker for high-risk smoldering multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2013, 27, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Kyle, R.A.; Katzmann, J.A.; Therneau, T.M.; Larson, D.; Benson, J.; Clark, R.J.; Melton, L.J., 3rd; Gertz, M.A.; Kumar, S.K.; et al. Immunoglobulin free light chain ratio is an independent risk factor for progression of smoldering (asymptomatic) multiple myeloma. Blood 2008, 111, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotten, S.W.; Shajani-Yi, Z.; Cervinski, M.A.; Voorhees, T.; Tuchman, S.A.; Korpi-Steiner, N. Reference intervals and diagnostic ranges for serum free κ and free λ immunoglobulin light chains vary by instrument platform: Implications for classification of patient results in a multi-center study. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 58, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercammen, M.; Meirlaen, P.; Broodtaerts, L.; Broek, I.V.; Bossuyt, X. Effect of sample dilution on serum free light chain concentration by immunonephelometric assay. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, S.; Wassef, N.L.; Salter, S.J.; Sachchithanantham, S.; Lane, T.; Foard, D.; Whelan, C.J.; Lachmann, H.J.; Gillmore, J.D.; Hawkins, P.N.; et al. Comparison of Free Light Chain Assays. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 146, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schieferdecker, A.; Hörber, S.; Ums, M.; Besemer, B.; Bokemeyer, C.; Peter, A.; Weisel, K. Comparison of three different serum-free light-chain assays—Implications on diagnostic and therapeutic monitoring of multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daves, M.; Piccin, A.; Roccaforte, V.; Lippi, G. Comparison of Freelite and N-Latex serum free light chain assays. Biochem. Medica 2021, 31, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, C.K.; Swarttouw, T.; Angelino, C.M.d.K.; Jacobs, J.F.; Russcher, H. Method comparison of four clinically available assays for serum free light chain analysis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 58, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponi, L.; Romiti, N.; Koni, E.; Di Fiore, A.; Paolicchi, A.; Franzini, M. Inter-assay variability in automated serum free light chain assays and their use in the clinical laboratory. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Wu, A.H. Analytical and clinical concordance of free light chain assay. Pract. Lab. Med. 2019, 13, e00112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muluhngwi, P.; Sharp, C.N.; Pozzi, N.; Elin, R.J.; Jortani, S.A. Verification of Newly FDA-Approved Kappa and Lambda Free Light Chain Assays on a Previously Untested Platform. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2019, 4, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.P.; Heaney, J.L.; Shemar, M.; Baldwin, D.; Griffin, A.E.; Oldridge, E.; Goodall, M.; Afzal, Z.; Plant, T.; Cobbold, M.; et al. Development of a rapid and quantitative lateral flow assay for the simultaneous measurement of serum κ and λ immunoglobulin free light chains (FLC): Inception of a new near-patient FLC screening tool. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.F.; Angelino, C.M.d.K.; Brouwers, H.M.; Croockewit, S.A.; Joosten, I.; van der Molen, R.G. Evaluation of a new free light chain ELISA assay: Bringing coherence with electrophoretic methods. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillon, H.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Attal, M.; Moreau, P.; Decaux, O.; Dejoie, T. Comparison of Sebia Free Light Chain Assay with Freelite Assay for the Clinical Management of Diagnosis, Response, and Relapse Assessment in Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019, 19, e228–e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzmann, A.J.; Kyle, A.R.; Benson, J.; Larson, D.R.; Snyder, M.R.; Lust, A.J.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Dispenzieri, A. Screening Panels for Detection of Monoclonal Gammopathies. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1517–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.; Kyle, R.; Fermand, J.-P.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Miguel, J.S.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Ludwig, H.; Joshua, D.; Mehta, J.; Gertz, M.; et al. Consensus recommendations for standard investigative workup: Report of the International Myeloma Workshop Consensus Panel 3. Blood 2011, 117, 4701–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnidge, D.R.; Tschumper, R.C.; Theis, J.D.; Snyder, M.R.; Jelinek, D.F.; Katzmann, J.A.; Dispenzieri, A.; Murray, D.L. Monitoring M-Proteins in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Using Heavy-Chain Variable Region Clonotypic Peptides and LC–MS/MS. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 1905–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergen, H.R.; Dasari, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Mills, J.R.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M.; Tschumper, R.C.; Jelinek, D.F.; Barnidge, D.R.; Murray, D.L. Clonotypic Light Chain Peptides Identified for Monitoring Minimal Residual Disease in Multiple Myeloma without Bone Marrow Aspiration. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnidge, D.R.; Dasari, S.; Botz, C.M.; Murray, D.H.; Snyder, M.R.; Katzmann, J.A.; Dispenzieri, A.; Murray, D.L. Using Mass Spectrometry to Monitor Monoclonal Immunoglobulins in Patients with a Monoclonal Gammopathy. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnidge, D.R.; Krick, T.P.; Griffin, T.J.; Murray, D.L. Using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry to detect monoclonal immunoglobulin light chains in serum and urine. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 29, 2057–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.L. Bringing mass spectrometry into the care of patients with multiple myeloma. Int. J. Hematol. 2022, 115, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomsztyk, J.; Ravichandran, S.; Giles, H.V.; Wright, N.J.; Berlanga, O.; Khwaja, J.; Mahmood, S.; Wisniowski, B.; Cohen, O.C.; Foard, D.; et al. Complete responses in AL amyloidosis are unequal: The impact of free light chain mass spectrometry in AL amyloidosis. Blood 2024, 143, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, D.L.; Puig, N.; Kristinsson, S.; Usmani, S.Z.; Dispenzieri, A.; Bianchi, G.; Kumar, S.; Chng, W.J.; Hajek, R.; Paiva, B.; et al. Mass spectrometry for the evaluation of monoclonal proteins in multiple myeloma and related disorders: An International Myeloma Working Group Mass Spectrometry Committee Report. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillmore, J.D.; Hawkins, P.N. Amyloidosis and the respiratory tract. Thorax 1999, 54, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, F.; Lavatelli, F.; Di Silvestre, D.; Valentini, V.; Rossi, R.; Palladini, G.; Obici, L.; Verga, L.; Mauri, P.; Merlini, G. Reliable typing of systemic amyloidoses through proteomic analysis of subcutaneous adipose tissue. Blood 2012, 119, 1844–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrana, J.A.; Gamez, J.D.; Madden, B.J.; Theis, J.D.; Bergen, H.R.; Dogan, A. Classification of amyloidosis by laser microdissection and mass spectrometry–based proteomic analysis in clinical biopsy specimens. Blood 2009, 114, 4957–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavatelli, F.; Perlman, D.H.; Spencer, B.; Prokaeva, T.; McComb, M.E.; Théberge, R.; Connors, L.H.; Bellotti, V.; Seldin, D.C.; Merlini, G.; et al. Amyloidogenic and Associated Proteins in Systemic Amyloidosis Proteome of Adipose Tissue. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxbaum, J.N.; Linke, R.P. A Molecular History of the Amyloidoses. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 421, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucci, A.; Aimo, A.; Musetti, V.; Barison, A.; Vergaro, G.; Genovesi, D.; Giorgetti, A.; Masotti, S.; Arzilli, C.; Prontera, C.; et al. Amyloid Deposits and Fibrosis on Left Ventricular Endomyocardial Biopsy Correlate with Extracellular Volume in Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e020358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, T.; Gilbertson, A.J.; Mangione, P.P.; Rowczenio, D.; Rendell, N.B.; Canetti, D.; Lachmann, H.J.; Wechalekar, A.D.; Bass, P.; Hawkins, P.N.; et al. The complementary role of histology and proteomics for diagnosis and typing of systemic amyloidosis. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2019, 5, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.L.; Eulitz, M.; Hrncic, R.; Sletten, K.; Westermark, P.; Williams, T.; Macy, S.D.; Wooliver, C.; Wall, J.; Weiss, D.T.; et al. Chemical Typing of Amyloid Protein Contained in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Biopsy Specimens. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 116, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladini, G.; Milani, P.; Merlini, G. Management of AL amyloidosis in 2020. Blood 2020, 136, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, M.; Tholey, A.; Kristen, A.; Röcken, C. MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging: A Novel Tool for the Identification and Classification of Amyloidosis. Proteomics 2017, 17, 1700236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Theis, J.D.; Vrana, J.A.; Rech, K.L.; Dao, L.N.; Howard, M.T.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Hasadsri, L.; Highsmith, W.E.; et al. Amyloid Typing by Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Practice: A Comprehensive Review of 16,175 Samples. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 1852–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitia, R.; Palladini, G.; Merlini, G. Bortezomib in the treatment of AL amyloidosis: Targeted therapy? Haematologica 2007, 92, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, G.; Zhang, Y.; Comenzo, R.L. AL Amyloidosis: Current Chemotherapy and Immune Therapy Treatment Strategies. JACC CardioOncol. 2021, 3, 467–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musetti, V.; Greco, F.; Castiglione, V.; Aimo, A.; Palmieri, C.; Genovesi, D.; Giorgetti, A.; Emdin, M.; Vergaro, G.; McDonnell, L.A.; et al. Tissue Characterization in Cardiac Amyloidosis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Assay | Antisera | Method | Platform | Strengths | Possible Weaknesses | Quantification Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freelite® FLC | Polyclonal | - Nephelometric - Turbidimetric | - BN II System - Optilite | - Reference method for IMWG - First developed method - Long-standing on the market | Lot-to-lot and platform variability Underestimation due to antigen excess (hook effect) Poor linearity after dilution | Absolute quantification, but limited accuracy at very high concentrations |
| N Latex FLC | Monoclonal | Nephelometric | BN II System | High sensitivity |
|
|
| Diazyme human kappa/lambda FLC | Polyclonal | Turbidimetric | Advia 1800 | High sensitivity |
|
|
| Seralite® FLC | Monoclonal | Lateral flow immunoassay | ADxRL5 | - Reduced false negatives - Coupled measurement of kappa–lambda |
|
|
| Sebia FLC ELISA kappa/lambda | Polyclonal | ELISA sandwich | AP22 Elite | - Larger measurement interval - Reduced repetitions needed for FLC quantification |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aimo, A.; Ferrari Chen, Y.F.; Chianca, M.; Mori, F.; Pucci, A.; Castiglione, V.; Musetti, V.; Caponi, L.; Fabiani, I.; Vergaro, G.; et al. Serum and Tissue Light-Chains as Disease Biomarkers in AL Amyloidosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199511
Aimo A, Ferrari Chen YF, Chianca M, Mori F, Pucci A, Castiglione V, Musetti V, Caponi L, Fabiani I, Vergaro G, et al. Serum and Tissue Light-Chains as Disease Biomarkers in AL Amyloidosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199511
Chicago/Turabian StyleAimo, Alberto, Yu Fu Ferrari Chen, Michela Chianca, Francesco Mori, Angela Pucci, Vincenzo Castiglione, Veronica Musetti, Laura Caponi, Iacopo Fabiani, Giuseppe Vergaro, and et al. 2025. "Serum and Tissue Light-Chains as Disease Biomarkers in AL Amyloidosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199511
APA StyleAimo, A., Ferrari Chen, Y. F., Chianca, M., Mori, F., Pucci, A., Castiglione, V., Musetti, V., Caponi, L., Fabiani, I., Vergaro, G., Franzini, M., Emdin, M., & Cardinale, D. (2025). Serum and Tissue Light-Chains as Disease Biomarkers in AL Amyloidosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199511







