Lysosomal Network Defects in Early-Onset Parkinson’s Disease Patients Carrying Rare Variants in Lysosomal Hydrolytic Enzyme Genes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical and Genetic Findings
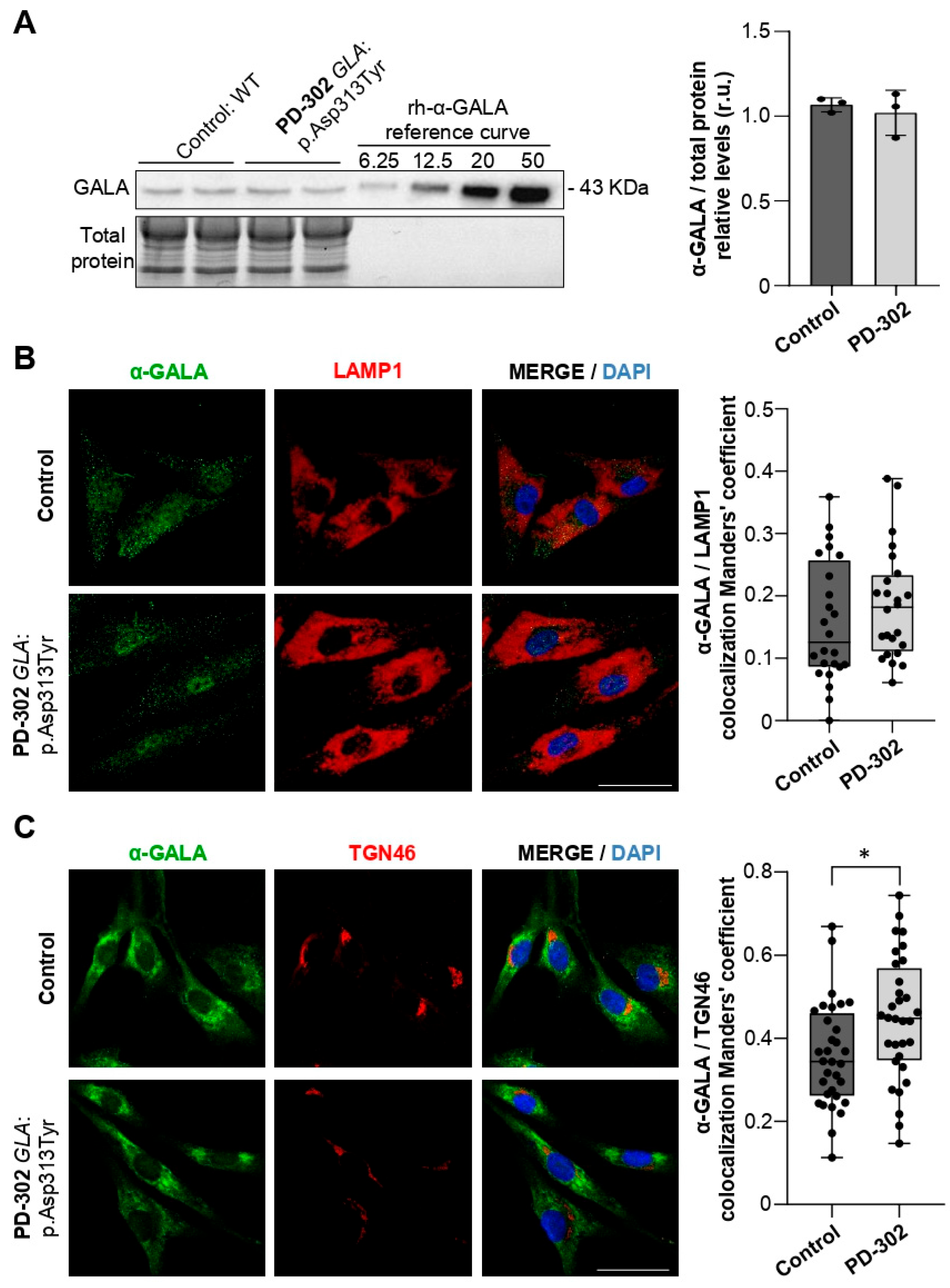
2.2. Patient Carrying the GLA:p.Asp313Tyr Variant Shows Partial Retention of GALA in the Trans-Golgi Network
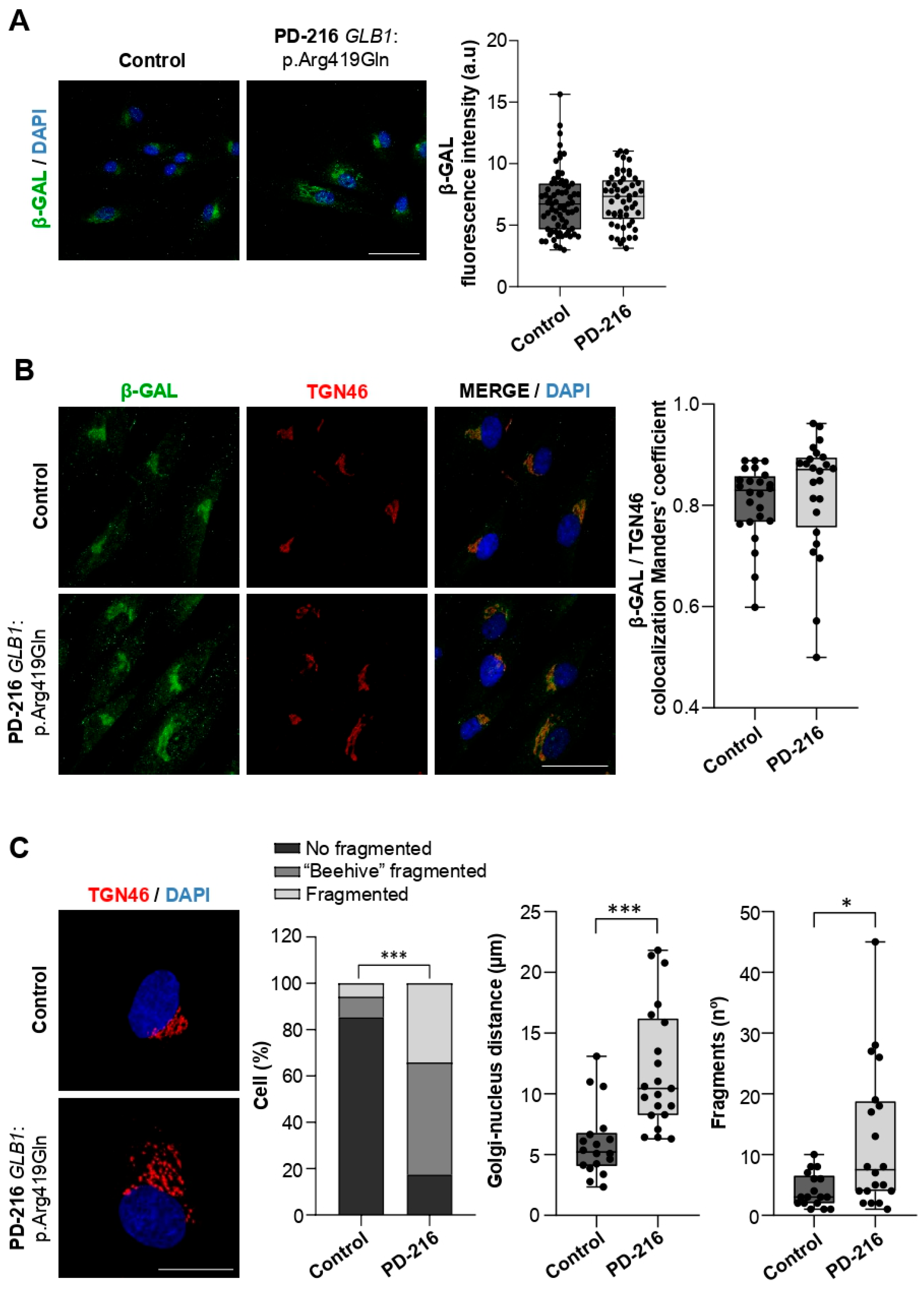
2.3. The Patient Carrying GLB1:p.Arg419Gln Shows Trans-Golgi Network Defects
2.4. Variants in Genes Encoding Lysosomal Hydrolases Are Linked to Changes in Lysosomal Morphology and pH Levels
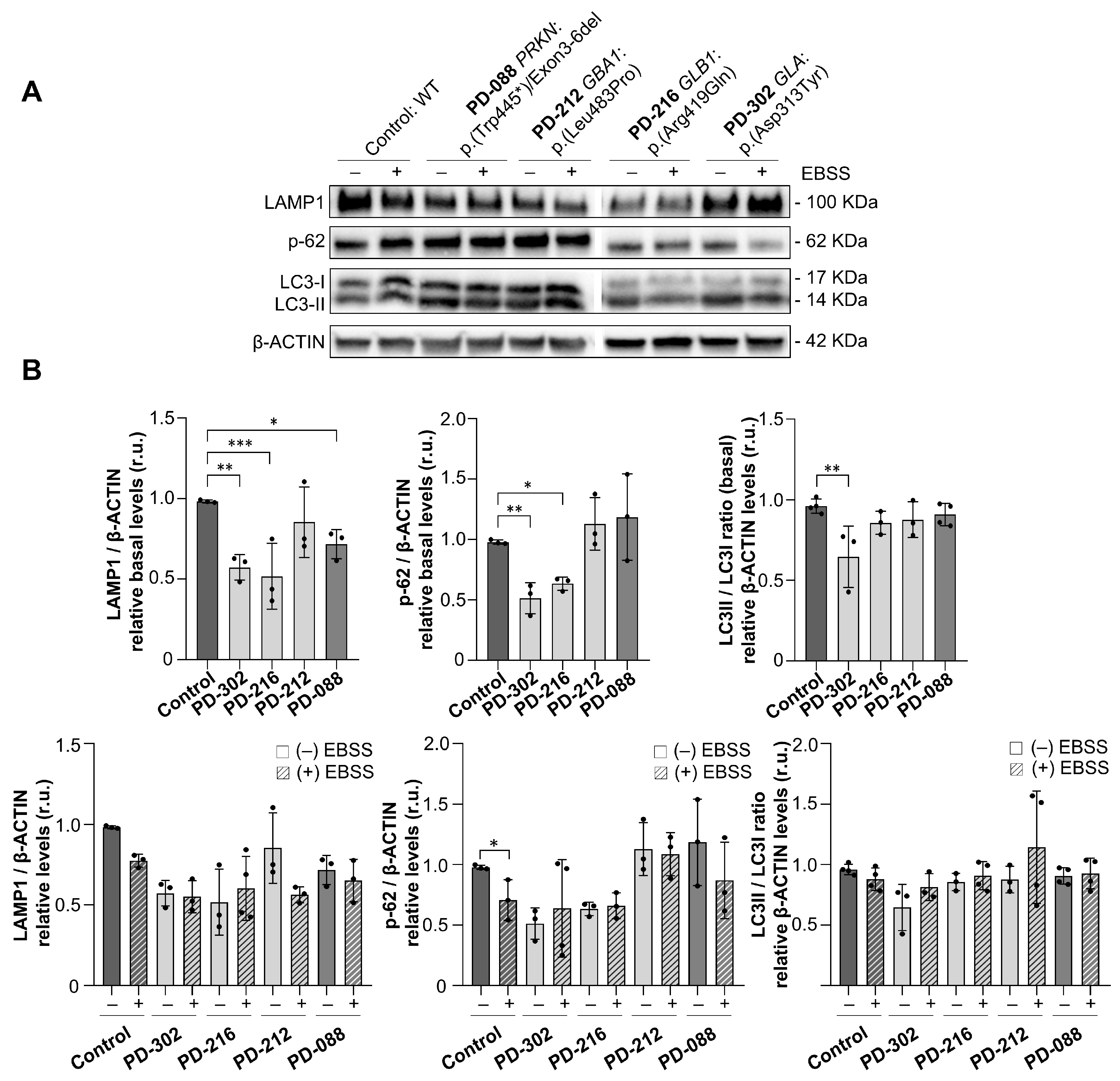
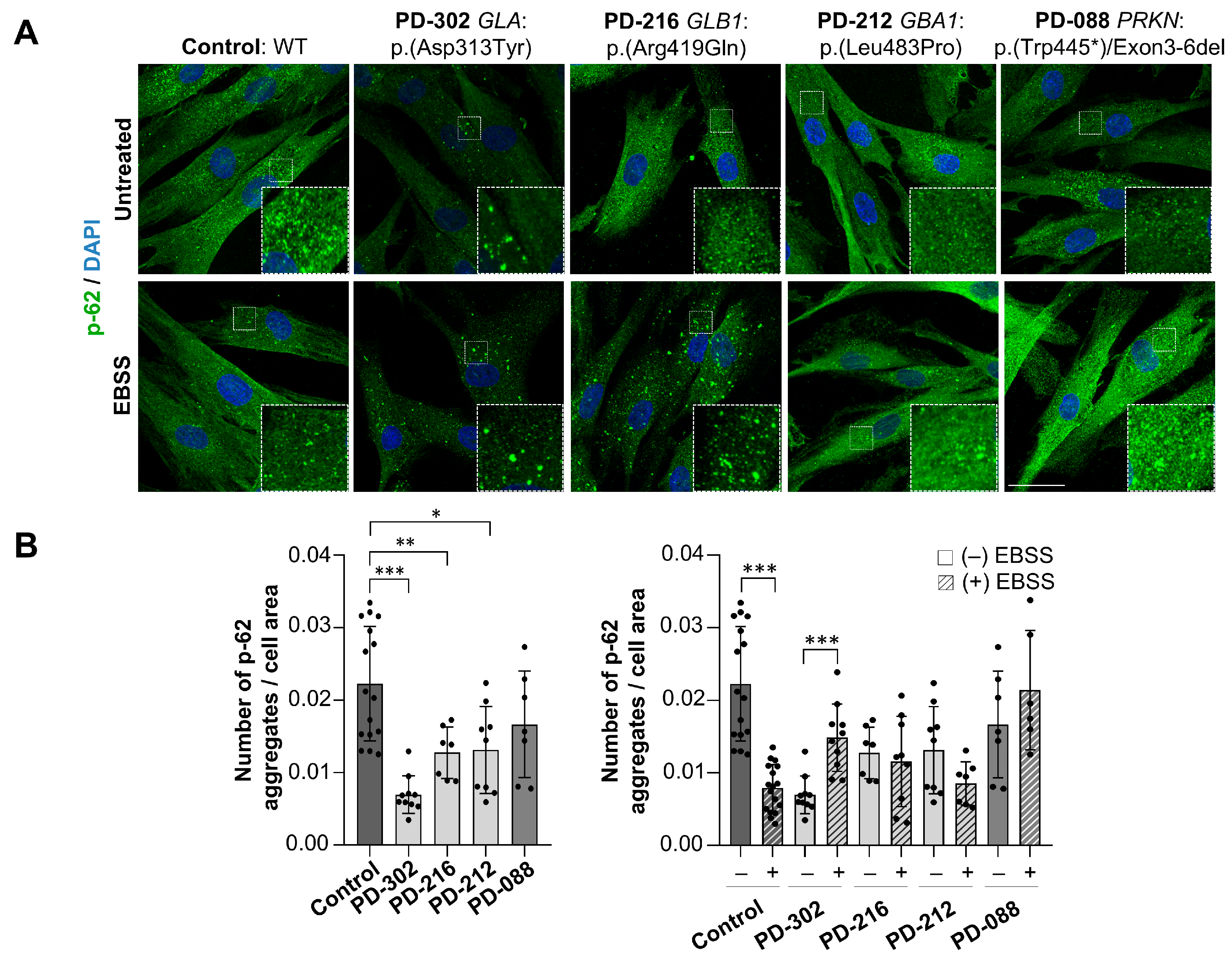
2.5. Impaired Autophagic Flux in Patients with Variants in Lysosomal Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Whole Exome Sequencing
4.2.1. Variant Calling and Annotation
4.2.2. Variant Filtering and Priorization
4.3. Skin Biopsy and Fibroblast Culture
Treatments
4.4. Western Blot Assays
4.5. Immunofluorescence
4.6. Lysosomal pH Analysis
4.7. Image Acquisition and Super-Resolution Images Analysis
4.7.1. Colocalization Analysis
4.7.2. Lysosomes Analysis
4.7.3. Golgi Apparatus Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GALA | α-galactosidase A |
| β-GAL | β-galactosidase |
| B | Benign |
| EOPS | Early Onset Parkinsonian Syndromes |
| EOPD | Early Onset Parkinson Diseases |
| FS | Fabry disease |
| Gb3 | Globotriaosylceramide |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| LP | Likely pathogenic |
| LSD | Lysosomal storage disorder |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PS | Parkinsonian syndromes |
| WES | Whole-exome sequencing |
| VUS | Variant of uncertain significance |
References
- Blauwendraat, C.; Nalls, M.A.; Singleton, A.B. The Genetic Architecture of Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.F.; Saad, M.; Bras, J.; Bettella, F.; Nicolaou, N.; Simón-Sánchez, J.; Mittag, F.; Büchel, F.; Sharma, M.; Gibbs, J.R.; et al. Using Genome-Wide Complex Trait Analysis to Quantify “missing Heritability” in Parkinson’s Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 4996–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funayama, M.; Nishioka, K.; Li, Y.; Hattori, N. Molecular Genetics of Parkinson’s Disease: Contributions and Global Trends. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 68, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, K.J.; Paul, K.C.; Wong, D.; Kusters, C.D.J.; Bronstein, J.M.; Ritz, B.; Fogel, B.L. Lysosomal Genes Contribute to Parkinson’s Disease near Agriculture with High Intensity Pesticide Use. npj Park. Dis. 2024, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Romero, A.; Montpeyó, M.; Martinez-Vicente, M. The Emerging Role of the Lysosome in Parkinson’s Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robak, L.A.; Jansen, I.E.; van Rooij, J.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Kraaij, R.; Jankovic, J.; Heutink, P.; Shulman, J.M.; Nalls, M.A.; Plagnol, V.; et al. Excessive Burden of Lysosomal Storage Disorder Gene Variants in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2017, 140, 3191–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asselta, R.; Rimoldi, V.; Siri, C.; Cilia, R.; Guella, I.; Tesei, S.; Soldà, G.; Pezzoli, G.; Duga, S.; Goldwurm, S. Glucocerebrosidase Mutations in Primary Parkinsonism. Park. Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidransky, E.; Nalls, M.A.; Aasly, J.O.; Aharon-Peretz, J.; Annesi, G.; Barbosa, E.R.; Bar-Shira, A.; Berg, D.; Bras, J.; Brice, A.; et al. Multicenter Analysis of Glucocerebrosidase Mutations in Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanin, E.; Landoulsi, Z.; Pachchek, S.; Zelimkhanov, G.; Wollscheid-Lengeling, E.; Wilmes, P.; Boas, L.V.; Vega, C.; Vaillant, M.; Tsurkalenko, O.; et al. Penetrance of Parkinson’s Disease in GBA1 Carriers Depends on Variant Severity and Polygenic Background. npj Park. Dis. 2025, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Nalls, M.A.; Hallgrímsdóttir, I.B.; Hunkapiller, J.; van der Brug, M.; Cai, F.; Kerchner, G.A.; Ayalon, G.; Bingol, B.; Sheng, M.; et al. A Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies Identifies 17 New Parkinson’s Disease Risk Loci. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfner, F.; Mueller, S.H.; Szymczak, S.; Junge, O.; Tittmann, L.; May, S.; Lohmann, K.; Grallert, H.; Lieb, W.; Strauch, K.; et al. Rare Variants in Specific Lysosomal Genes Are Associated With Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 1245–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuervo, A.M.; Stafanis, L.; Fredenburg, R.; Lansbury, P.T.; Sulzer, D. Impaired Degradation of Mutant α-Synuclein by Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy. Science 2004, 305, 1292–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzi, T.; Xilouri, M.; Vekrellis, K.; Stefanis, L. Wild Type α-Synuclein Is Degraded by Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy and Macroautophagy in Neuronal Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23542–23556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Kassubek, J.; Hold, S.T.; Kasper, D.C.; Mayer, B.; Müller, K.; Freischmidt, A.; Siebert, R.; Braak, H.; Ludolph, A.C.; et al. Morbus Fabry and Parkinson’s Disease—More Evidence for a Possible Genetic Link. Mov. Disord. 2024, 39, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsini, W.; Giuliacci, G.; Torricelli, F.; Pelo, E.; Martinelli, F.; Scordo, M.R. Anderson-Fabry Disease with Cerebrovascular Complications in Two Italian Families. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 23, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechner, S.; Luzzi, C.; Mannucci, M.; Massi, D.; Borsini, W. Diagnosis of Anderson-Fabry’s Disease in over Seventy-Year-Old Women: Description of Two Cases. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 18, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomizawa, Y.; Okuzumi, A.; Shiotsuki, H.; Noda, K.; Hattori, N.; Okuma, Y. A Patient with the GLA p.E66Q Mutation Exhibiting Vascular Parkinsonism and Bilateral Pulvinar Lesions. Intern. Med. 2015, 54, 2503–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalay, R.N.; Wolf, P.; Levy, O.A.; Kang, U.J.; Waters, C.; Fahn, S.; Ford, B.; Kuo, S.H.; Vanegas, N.; Shah, H.; et al. Alpha Galactosidase A Activity in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 112, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, Y.; Nawashiro, K.; Ohdake, R.; Tatebe, H.; Shima, S.; Ueda, A.; Yoshimoto, J.; Ito, M.; Tokuda, T.; Mutoh, T.; et al. Enzymatic Properties and Clinical Associations of Serum Alpha-Galactosidase A in Parkinson’s Disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2023, 10, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yekedüz, M.K.; Yilmaz, R.; Kayis, G.; Doğulu, N.; Öncül, Ü.; Abali, T.; Temizyurek, A.D.; Çelik, G.; Çöklü, H.; Gemci, E.; et al. Genetic Variants of GBA and GLA in a Turkish Cohort of Parkinson’s Disease: A Preliminary Report. Park. Relat. Disord. 2023, 110, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiyrzhanov, R.; Guliyeva, U.; Gulieva, S.; Salayev, K.; Mursalova, A.; Allahyarova, P.; Ferla, M.P.; Houlden, H. GM1-Gangliosidosis Type III Associated Parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2021, 8, S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koya Kutty, S.; Magrinelli, F.; Milner, A.V.; Bhatia, K.P. Abnormal DaTscan in GM1-Gangliosidosis Type III Manifesting with Dystonia-Parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2022, 9, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vela-Desojo, L.; Pascual, A.; Montal, V.; Guerrero, C.; Osuna-López, M.; Guallar, V.; Palau, F.; Hoenicka, J. A New LRRK2 Variant in a Family with Parkinson’s Disease Affects Binding to RAB8A. npj Park. Dis. 2025, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, C.; Lang, A.; van de Warrenburg, B.P.; Sue, C.M.; Tabrizi, S.J.; Bertram, L.; Mercimek-Mahmutoglu, S.; Ebrahimi-Fakhari, D.; Warner, T.T.; Durr, A.; et al. Nomenclature of Genetic Movement Disorders: Recommendations of the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society Task Force. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 436–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittke, C.; Petkovic, S.; Dobricic, V.; Schaake, S.; Arzberger, T.; Compta, Y.; Englund, E.; Ferguson, L.W.; Gelpi, E.; Roeber, S.; et al. Genotype–Phenotype Relations for the Atypical Parkinsonism Genes: MDSGene Systematic Review. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veen, S.; Zutt, R.; Klein, C.; Marras, C.; Berkovic, S.F.; Caviness, J.N.; Shibasaki, H.; de Koning, T.J.; Tijssen, M.A.J. Nomenclature of Genetically Determined Myoclonus Syndromes: Recommendations of the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society Task Force. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1602–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Anheim, M.; Durr, A.; Klein, C.; Koenig, M.; Synofzik, M.; Marras, C.; van de Warrenburg, B.P. The Genetic Nomenclature of Recessive Cerebellar Ataxias. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1056–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, L.M.; Junker, J.; Loens, S.; Baumann, H.; Olschewski, L.; Schaake, S.; Madoev, H.; Petkovic, S.; Kuhnke, N.; Kasten, M.; et al. Genotype–Phenotype Relations for Isolated Dystonia Genes: MDSGene Systematic Review. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1086–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinnah, H.A.; Albanese, A.; Bhatia, K.P.; Cardoso, F.; Da Prat, G.; de Koning, T.J.; Espay, A.J.; Fung, V.; Garcia-Ruiz, P.J.; Gershanik, O.; et al. Treatable Inherited Rare Movement Disorders. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.R.; Williams, E.; Foulger, R.E.; Leigh, S.; Daugherty, L.C.; Niblock, O.; Leong, I.U.S.; Smith, K.R.; Gerasimenko, O.; Haraldsdottir, E.; et al. PanelApp Crowdsources Expert Knowledge to Establish Consensus Diagnostic Gene Panels. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, H.; Fujisawa, C.; Bhadhprasit, W. Inherited Copper Transport Disorders: Biochemical Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacik, P.; Sanchez-Contreras, M.; Rademakers, R.; Dickson, D.W.; Wszolek, Z.K. Genetic Disorders with Tau Pathology: A Review of the Literature and Report of Two Patients with Tauopathy and Positive Family Histories. Neurodegener. Dis. 2016, 16, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenson, P.D.; Ball, E.V.; Mort, M.; Phillips, A.D.; Shiel, J.A.; Thomas, N.S.T.; Abeysinghe, S.; Krawczak, M.; Cooper, D.N. Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD®): 2003 Update. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekawade, A.; Velinder, M.; Ward, A.; Disera, T.; Miller, C.; Qiao, Y.; Marth, G. Genepanel.Iobio—An Easy to Use Web Tool for Generating Disease- And Phenotype-Associated Gene Lists. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seal, R.L.; Braschi, B.; Gray, K.; Jones, T.E.M.; Tweedie, S.; Haim-Vilmovsky, L.; Bruford, E.A. Genenames.Org: The HGNC Resources in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1003–D1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Schindler, C.; Jia, R.; Jarnik, M.; Backlund, P.; Bonifacino, J.S. BORC, a Multisubunit Complex That Regulates Lysosome Positioning. Dev. Cell 2015, 33, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmoise, A.; Teneberg, S.; Bouzonville, L.; Brady, R.O.; Beck, M.; Kaufmann, S.H.E.; Winau, F. Lysosomal α-Galactosidase Controls the Generation of Self Lipid Antigens for Natural Killer T Cells. Immunity 2010, 33, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guce, A.I.; Clark, N.E.; Salgado, E.N.; Ivanen, D.R.; Kulminskaya, A.A.; Brumer, H.; Garman, S.C. Catalytic Mechanism of Human α-Galactosidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 3625–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.G.; Osman, N.; McKenzie, I.F.C.; Sandrin, M.S. Reduction of α-Gal Expression by Relocalizing α-Galactosidase to the Trans-Golgi Network and Cell Surface. Glycobiology 2002, 12, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Hakamata, W.; Tanaka, A.; Hirano, T.; Nishio, T. Discovery of Human Golgi β-Galactosidase with No Identified Glycosidase Using a QMC Substrate Design Platform for Exo-Glycosidase. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Abshana, L.P.; Mendivil-Perez, M.; Jimenez-Del-Rio, M.; Velez-Pardo, C. The GBA1 K198E Variant Is Associated with Suppression of Glucocerebrosidase Activity, Autophagy Impairment, Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Damage, and Apoptosis in Skin Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkevich, K.; Gan-Or, Z. Autophagy Lysosomal Pathway Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease; Evidence from Human Genetics. Park. Relat. Disord. 2020, 73, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imberechts, D.; Kinnart, I.; Wauters, F.; Terbeek, J.; Manders, L.; Wierda, K.; Eggermont, K.; Madeiro, R.F.; Sue, C.; Verfaillie, C.; et al. DJ-1 Is an Essential Downstream Mediator in PINK1/Parkin-Dependent Mitophagy. Brain 2022, 145, 4368–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalls, M.A.; Blauwendraat, C.; Vallerga, C.L.; Heilbron, K.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Chang, D.; Tan, M.; Kia, D.A.; Noyce, A.J.; Xue, A.; et al. Identification of Novel Risk Loci, Causal Insights, and Heritable Risk for Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, B.R.; Maddison, D.C.; Smith, G.A.; Peters, O.M. Autophagic and Endo-Lysosomal Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Disease. Mol. Brain 2019, 12, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, S.R.L.; Schapira, A.H.V. Glucocerebrosidase Mutations and Parkinson Disease. J. Neural Transm. 2022, 129, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrahin, A.; Horowitz, M.; Istaiti, M.; Skrahina, V.; Lukas, J.; Yahalom, G.; Cohen, M.E.; Revel-Vilk, S.; Goker-Alpan, O.; Becker-Cohen, M.; et al. GBA1-Associated Parkinson’s Disease Is a Distinct Entity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effraimidis, G.; Rasmussen, Å.K.; Bundgaard, H.; Sørensen, S.S.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U. Is the Alpha-Galactosidase A Variant p.Asp313Tyr (p.D313Y) Pathogenic for Fabry Disease? A Systematic Review. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2020, 43, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackova, A.; Beetz, C.; Oppermann, S.; Bauer, P.; Pavelekova, P.; Lorincova, T.; Ostrozovicova, M.; Kulcsarova, K.; Cobejova, J.; Cobej, M.; et al. Prevalence of Fabry Disease among Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Dis. 2022, 2022, 1014950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaaboune, S.R.; Wang, Y. Golgi Defect as a Major Contributor to Lysosomal Dysfunction. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1386149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, R.O.; Kanfer, J.N.; Shapiro, D. Metabolism of Glucocerebrosides II. Evidence of an Enzymatic Deficiency in Gaucher’s Disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1965, 18, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsford, A.H.; Ryan, T.A.; Raimondi, A.; Cocucci, E.; Wycislo, S.A.; Fröhlich, F.; Swan, L.E.; Stagi, M. Live Imaging of Intra-Lysosome PH in Cell Lines and Primary Neuronal Culture Using a Novel Genetically Encoded Biosensor. Autophagy 2021, 17, 1500–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashrazm, F.; Hammond, D.; Perera, G.; Dobson-Stone, C.; Mueller, N.; Pickford, R.; Kim, W.S.; Kwok, J.B.; Lewis, S.J.G.; Halliday, G.M.; et al. Reduced Glucocerebrosidase Activity in Monocytes from Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosta, F.; Kostic, V.S.; Davidovic, K.; Kresojević, N.; Sarro, L.; Svetel, M.; Stanković, I.; Comi, G.; Klein, C.; Filippi, M. White Matter Abnormalities in Parkinson’s Disease Patients with Glucocerebrosidase Gene Mutations. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmes, R.; ten Brink, C.; Oorschot, V.; Veenendaal, T.; Jonker, C.; van der Sluijs, P.; Klumperman, J. Vps33B Is Required for Delivery of Endocytosed Cargo to Lysosomes. Traffic 2015, 16, 1288–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabio, A.; Bonifacino, J.S. Lysosomes as Dynamic Regulators of Cell and Organismal Homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scerra, G.; De Pasquale, V.; Pavone, L.M.; Caporaso, M.G.; Mayer, A.; Renna, M.; D’Agostino, M. Early Onset Effects of Single Substrate Accumulation Recapitulate Major Features of LSD in Patient-Derived Lysosomes. iScience 2021, 24, 102707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrer, M.; Chan, P.; Chen, R.; Tan, L.; Lincoln, S.; Hernandez, D.; Forno, L.; Gwinn-Hardy, K.; Petrucelli, L.; Hussey, J.; et al. Lewy Bodies and Parkinsonism in Families with Parkin Mutations. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramstaller, P.P.; Schlossmacher, M.G.; Jacques, T.S.; Scaravilli, F.; Eskelson, C.; Pepivani, I.; Hedrich, K.; Adel, S.; Gonzales-McNeal, M.; Hilker, R.; et al. Lewy Body Parkinson’s Disease in a Large Pedigree with 77 Parkin Mutation Carriers. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 58, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickrell, A.M.; Huang, C.H.; Kennedy, S.R.; Ordureau, A.; Sideris, D.P.; Hoekstra, J.G.; Harper, J.W.; Youle, R.J. Endogenous Parkin Preserves Dopaminergic Substantia Nigral Neurons Following Mitochondrial DNA Mutagenic Stress. Neuron 2015, 87, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gialluisi, A.; Reccia, M.G.; Modugno, N.; Nutile, T.; Lombardi, A.; Di Giovannantonio, L.G.; Pietracupa, S.; Ruggiero, D.; Scala, S.; Gambardella, S.; et al. Identification of Sixteen Novel Candidate Genes for Late Onset Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarious, M.B.; Lake, J.; Pitz, V.; Fu, A.Y.; Guidubaldi, J.L.; Solsberg, C.W.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Leonard, H.L.; Kim, J.J.; Billingsley, K.J.; et al. Large-Scale Rare Variant Burden Testing in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2023, 146, 4622–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Splinter, K.; Adams, D.R.; Bacino, C.A.; Bellen, H.J.; Bernstein, J.A.; Cheatle-Jarvela, A.M.; Eng, C.M.; Esteves, C.; Gahl, W.A.; Hamid, R.; et al. Effect of Genetic Diagnosis on Patients with Previously Undiagnosed Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P.; et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, M.J.S.; Gamieldien, J. A Practical Guide to Filtering and Prioritizing Genetic Variants. Biotechniques 2017, 62, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, D.L.; Cooper, G.M.; Schmutz, J.; Dickson, M.; Gonzales, E.; Tsai, M.; Karra, K.; Davydov, E.; Batzoglou, S.; Myers, R.M.; et al. Evolutionary Constraint Facilitates Interpretation of Genetic Variation in Resequenced Human Genomes. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubach, M.; Maass, T.; Nazaretyan, L.; Röner, S.; Kircher, M. CADD v1.7: Using Protein Language Models, Regulatory CNNs and Other Nucleotide-Level Scores to Improve Genome-Wide Variant Predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1143–D1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. Mutationtaster2: Mutation Prediction for the Deep-Sequencing Age. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.C.; Henikoff, S. SIFT: Predicting Amino Acid Changes That Affect Protein Function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3812–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihab, H.A.; Rogers, M.F.; Gough, J.; Mort, M.; Cooper, D.N.; Day, I.N.M.; Gaunt, T.R.; Campbell, C. An Integrative Approach to Predicting the Functional Effects of Non-Coding and Coding Sequence Variation. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A Method and Server for Predicting Damaging Missense Mutations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, K.; Kyriazopoulou Panagiotopoulou, S.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B.; et al. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukedal, H.; Corsi, G.I.; Gadekar, V.P.; Doncheva, N.T.; Kedia, S.; de Haan, N.; Chandrasekaran, A.; Jensen, P.; Schiønning, P.; Vallin, S.; et al. Golgi Fragmentation—One of the Earliest Organelle Phenotypes in Alzheimer’s Disease Neurons. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1120086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Majeed, W.; Kudlyk, T.; Lupashin, V.; Storrie, B. Identification of Rab41/6d Effectors Provides an Explanation for the Differential Effects of Rab41/6d and Rab6a/a’ on Golgi Organization. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yan, B.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Zhang, A.; Xu, X.; Dong, H. Decreased Activities of Lysosomal Acid Alpha-D-Galactosidase A in the Leukocytes of Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 271, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Pang, S.; Feng, X.; Zhang, A.; Li, J.; Gu, K.; Huang, J.; Dong, H.; Yan, B. Genetic Analysis of Lysosomal Alpha-Galactosidase A Gene in Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 500, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.P.; Boutin, M.; Tse, T.E.; Lu, H.; Haley, E.D.; Ouyang, X.; Zhang, J.; Auray-Blais, C.; Shacka, J.J. The Lysosomal Enzyme Alpha-Galactosidase A Is Deficient in Parkinson’s Disease Brain in Association with the Pathologic Accumulation of Alpha-Synuclein. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 110, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perillo, S.; Palmieri, G.R.; del Moral, M.O.; De Michele, G.; Giglio, A.; Cuomo, N.; Pane, C.; Bauer, P.; De Michele, G.; De Rosa, A. Screening for Fabry Disease in a Series of Parkinson’s Disease Patients and Literature Review. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 44, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| P | General Information | Scores | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene/ MIM Phenotype | Pathways | Variant | INH | ACMG | CADD | Freq. | ACMG | CADD | Freq. | MT | PolP2 | SIFT | F-MKL | S-AI | GERP | Z/pLI | BE | T | |
| PD-302 (WES-Trio) | FBXO7/ PARK 15 (AR) | LY/ATP | p.(Ala248Thr) c.742G>A | M | VUS | 24.5 | 3.97 × 10−6 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 12 |
| LRRK2/ PARK 8 (AD) | LY/VT/NR | p.(Phe1436Leu) c.4306T>C | M | VUS | 24.1 | NF | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 11 | |
| GLA/ FD (XL) & | LY/ATP | p.Asp313Tyr c.937G>T | M | B | 18.3 | 4.46 × 10−3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | |
| PD-227 (WES-Singleton) | ABL2/ - | NR | p.(Arg180Cys) c.538C>T | . | LP | 34.0 | 8.79 × 10−6 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 12 |
| GLA/ FD (XL) & | LY/ATP | p.Asp313Tyr c.937G>T | M | B | 18.3 | 4.46 × 10−3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | |
| BORCS8/ NDOABA (AR) | LY/MAPK | p.(Arg85His) c.254G>A | . | VUS | 22.8 | 1.35 × 10−5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 8 | |
| PD-216 (WES-Trio) | VPS33B/(AR) * | LY/GLG/ ATP | p.(Arg398Cys) c.1192C>T | M | VUS | 33.0 | NF | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 13 |
| GLB1/ (AR) % | LY/ATP/ NR | p.Arg419Gln c.1256G>A | F | LP | 35.0 | 7.06 × 10−6 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 12 | |
| DAPK1/ - | LY/ATP | p.(Arg666Gln) c.1997G>A | M | VUS | 25.4 | 6.22 × 10−5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 10 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pascual, A.; Moulka, T.; de Fàbregues, O.; Repossi, R.; García-Ruiz, P.J.; Ortolano, S.; De Lucca, M.; Vela-Desojo, L.; Alves-Villar, M.; Frías, M.; et al. Lysosomal Network Defects in Early-Onset Parkinson’s Disease Patients Carrying Rare Variants in Lysosomal Hydrolytic Enzyme Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199454
Pascual A, Moulka T, de Fàbregues O, Repossi R, García-Ruiz PJ, Ortolano S, De Lucca M, Vela-Desojo L, Alves-Villar M, Frías M, et al. Lysosomal Network Defects in Early-Onset Parkinson’s Disease Patients Carrying Rare Variants in Lysosomal Hydrolytic Enzyme Genes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199454
Chicago/Turabian StylePascual, Alba, Thaleia Moulka, Oriol de Fàbregues, Roberta Repossi, Pedro J. García-Ruiz, Saida Ortolano, Marisel De Lucca, Lydia Vela-Desojo, Marta Alves-Villar, Marcos Frías, and et al. 2025. "Lysosomal Network Defects in Early-Onset Parkinson’s Disease Patients Carrying Rare Variants in Lysosomal Hydrolytic Enzyme Genes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199454
APA StylePascual, A., Moulka, T., de Fàbregues, O., Repossi, R., García-Ruiz, P. J., Ortolano, S., De Lucca, M., Vela-Desojo, L., Alves-Villar, M., Frías, M., Feliz-Feliz, C., Roldán, M., Olival, J., Fernàndez, G., Palau, F., Pijuan, J., & Hoenicka, J. (2025). Lysosomal Network Defects in Early-Onset Parkinson’s Disease Patients Carrying Rare Variants in Lysosomal Hydrolytic Enzyme Genes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199454







