Systemic Inflammation at the Crossroad of Major Depressive Disorder and Comorbidities: A Narrative Review
Abstract
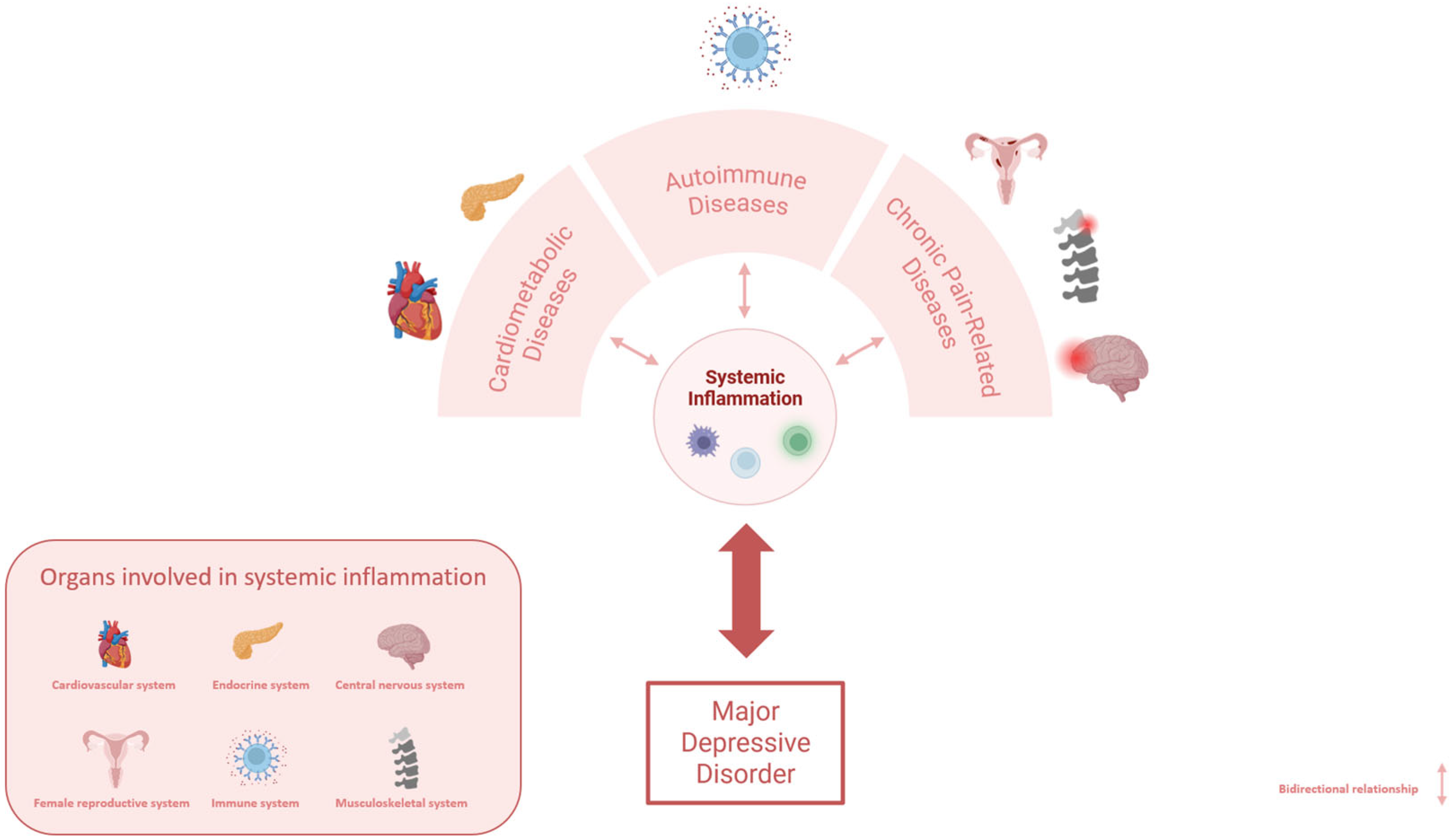
1. Introduction: Role of Inflammation in the Pathophysiology of Major Depressive Disorder
| Disease | Inflammation-Related Proteins | References | Inflammation-Related Genes | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major Depressive Disorder | Upregulated: CCL3; CCL4; CCL8; CCL11; CRP; IL-1β; IL-2; IL-6; IL-8; IL-10; IL-12; IL-13; IL-15; TNF-α | [5,8,9,13,16,17,18,20] | Upregulated: CCL2; FKBP5; GR; IL-1β; IL-1R1; IL-6; TNF-α; TNFR1; TNFR2 | [7,9,10,11] | |
| Downregulated: CCL17; IL-5; IL-16; TNF-β | Downregulated: GR; IL4; SOCS1; SOCS2; SOCS3 | ||||
| Cardiometabolic Diseases | Heart Failure | Upregulated: hs-CRP; IL-1β; IL-6; IL-8; TNF-α | [21,22,23,24,25] | Upregulated: TNF-α | [25] |
| Ischemic Heart Disease | Upregulated: IL-6 | [26] | Upregulated: IL-1 | [27] | |
| Coronary Arthery/Heart Disease | - | - | Upregulated: TNF-α | [28] | |
| Myocardial Infartion | Upregulated: CRP; IL-6; IL-8; TNF-α | [29,30] | Upregulated: TNF-α | [31] | |
| Hypertension | Upregulated: CRP; hs-CRP; IL-6; TNF-α | [32] | - | - | |
| Ischemic Stroke | Upregulated: CRP; IL-6; IL-8; TNF-α | [33,34,35,36] | - | - | |
| Diabetes | Upregulated: hs-CRP; IL-6; TNF-α | [37,38,39] | Upregulated: CCL2; CRP; IL-1β; IL-6; TNF-α | [40] | |
| Autoimmune Diseases | Rheumatoid Arthritis | Upregulated: IL-1β; IL-6; TNF-α | [41,42,43,44] | Upregulated: TNF-α | [44] |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | Upregulated: IFN-γ; IL-12; IL-17; IL-23; TNF-α | [45] | - | - | |
| Psoriasis Vulgaris | Upregulated: IL-6; IL-17; TNF-α | [41] | - | - | |
| Multiple Sclerosis | Upregulated: CCL4; CCL22; CXCL10; IL-6; IL-12 Downregulated: IL-10 | [46,47] | Upregulated: IFN-γ; TNF-α | [48] | |
| Downregulated: IL-10 | |||||
| Chronic Pain-Related Diseases | Low Back Pain | Upregulated: CRP; IL-1β; IL-6; TNF-α | [49,50] | - | - |
| Fibromyalgia | Upregulated: hs-CRP; IL-6; IL-8; TNF-α | [51,52] | - | - | |
| Migraine | Upregulated: IL-1β; IL-6; IL-8 TNF-α | [53] | - | - | |
| Chronic Fatigue/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis | Upregulated: CCL24; CXCL-10; hs-CRP; IFN-γ; IL-7; IL-8; TNF-α | [54,55,56,57] | - | - | |
| Endometriosis | Upregulated: IL-1;IL-2; IL-8; IL-33; TNF-α | [58] | - | - | |
2. Antidepressant Treatments: How the Inflammation May Modulate and Predict Their Efficacy
3. Inflammation as a Triggering Mechanism of Comorbidities in MDD
3.1. Alterations in Cytokine Patterns Are Associated with the Development of Several Cardiometabolic Disorders and Their Co-Occurrence with MDD
3.1.1. Cardiovascular Disorders
3.1.2. Diabetes
3.2. Immune System Dysregulation and Elevated Levels of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Are Shared Biomarkers Between Autoimmune Diseases and MDD
3.2.1. Rheumatoid Arthritis
3.2.2. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
3.2.3. Psoriasis Vulgaris
3.2.4. Multiple Sclerosis
3.2.5. Inflammation as Both a Limit and a Target for AD Treatment in the Presence of Autoimmune Comorbidities
3.3. Alterations in the Kynurenine Pathway and Cytokine Patterns Characterize Both Chronic Pain Conditions and MDD
3.3.1. Low Back Pain
3.3.2. Fibromyalgia
3.3.3. Migraine
3.3.4. Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Endometriosis
3.3.5. Involvement of Kynurenine Pathway in Chronic Pain Conditions
3.3.6. Chronic Pain Impacts on AD Successful Rate in MDD Patients
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTH | Adrenocorticotropic Hormone |
| AD | Antidepressant |
| ASC | apoptosis-associated speck-like protein |
| CAD | Coronary Artery Disease |
| CCL | C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand |
| CFS/ME | Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis |
| CHD | Coronary Heart Disease |
| CMDs | Cardiometabolic Diseases |
| CRH | Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| CVDs | Cardiovascular Diseases |
| CXCL | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligands |
| FKBP5 | FKBP prolyl isomerase 5 |
| GCs | Glucocorticoids |
| GR | Glucocorticoids Receptor |
| HDRS | Hamilton Depression Rating Scale |
| HF | Heart Failure |
| HPA axis | Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis |
| hs-CRP | high sensitivity CRP |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| IHD | Ischemic Heart Disease |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LBP | Low Back Pain |
| MADRS | Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale |
| MDD | Major Depressive Disorder |
| MI | Myocardial Infarction |
| mRNA | messanger Ribonucleic Acid |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| NAD(P)+ | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphorylated |
| NLRP3 | Nod-like receptor protein 3 |
| PV | Psoriasis Vulgaris |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| SLE | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |
| SOCS | Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling |
| SSRI | selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor |
| Th1 | T helper type 1 |
| Th2 | T helper type 2 |
| Th17 | T helper type 17 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha |
| TNFR | Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor |
| TRD | Treatment Resistant Depression |
| T1D | Type 1 Diabetes |
| T2D | Type 2 Diabetes |
References
- Otte, C.; Gold, S.M.; Penninx, B.W.; Pariante, C.M.; Etkin, A.; Fava, M.; Mohr, D.C.; Schatzberg, A.F. Major Depressive Disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, S. Epidemiology of Suicide and the Psychiatric Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Benedetto, M.G.; Landi, P.; Mencacci, C.; Cattaneo, A. Depression in Women: Potential Biological and Sociocultural Factors Driving the Sex Effect. Neuropsychobiology 2024, 83, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xia, M.; Li, B. Major Depressive Disorder: Hypothesis, Mechanism, Prevention and Treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osimo, E.F.; Baxter, L.J.; Lewis, G.; Jones, P.B.; Khandaker, G.M. Prevalence of Low-Grade Inflammation in Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of CRP Levels. Psychol. Med. 2019, 49, 1958–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, K.M.; Kaspersen, K.A.; Mikkelsen, S.; Pedersen, O.B.; Petersen, M.S.; Thørner, L.W.; Hjalgrim, H.; Rostgaard, K.; Ullum, H.; Erikstrup, C. Low-Grade Inflammation Is Negatively Associated with Physical Health-Related Quality of Life in Healthy Individuals: Results from The Danish Blood Donor Study (DBDS). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214468, Correction in PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216339. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0216339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, A.; Gennarelli, M.; Uher, R.; Breen, G.; Farmer, A.; Aitchison, K.J.; Craig, I.W.; Anacker, C.; Zunsztain, P.A.; McGuffin, P.; et al. Candidate Genes Expression Profile Associated with Antidepressants Response in the GENDEP Study: Differentiating between Baseline “predictors” and Longitudinal “Targets”. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Hua, S.; Wang, W.; Fan, W.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C. Identification of TNFA Influencing MDD Risk and Clinical Features in Han Chinese. Cytokine 2020, 129, 155030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sforzini, L.; Cattaneo, A.; Ferrari, C.; Turner, L.; Mariani, N.; Enache, D.; Hastings, C.; Lombardo, G.; Nettis, M.A.; Nikkheslat, N.; et al. Higher Immune-Related Gene Expression in Major Depression Is Independent of CRP Levels: Results from the BIODEP Study. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizavi, H.S.; Ren, X.; Zhang, H.; Bhaumik, R.; Pandey, G.N. Abnormal Gene Expression of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Their Membrane-Bound Receptors in the Lymphocytes of Depressed Patients. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 240, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Shinagawa, S.; Nagata, T.; Shigeta, M.; Kondo, K. Suppressors of Cytokine Signaling Are Decreased in Major Depressive Disorder Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler-Forsberg, O.; Buttenschøn, H.N.; Tansey, K.E.; Maier, W.; Hauser, J.; Dernovsek, M.Z.; Henigsberg, N.; Souery, D.; Farmer, A.; Rietschel, M.; et al. Association between C-Reactive Protein (CRP) with Depression Symptom Severity and Specific Depressive Symptoms in Major Depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 62, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Emon, M.P.Z.; Shahriar, M.; Nahar, Z.; Islam, S.M.A.; Bhuiyan, M.A.; Islam, S.N.; Islam, M.R. Higher Levels of Serum IL-1β and TNF-α Are Associated with an Increased Probability of Major Depressive Disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 295, 113568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.; Wang, G.; Cui, Y.; Meng, P.; Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y. Association between Inflammatory Cytokines and Symptoms of Major Depressive Disorder in Adults. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1110775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmin, N.; Roknuzzaman, A.S.M.; Mouree, T.Z.; Islam, M.R.; Al Mahmud, Z. Evaluation of Serum Interleukin-12 and Interleukin-4 as Potential Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, K.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; et al. Inflammatory Cytokines, Complement Factor H and Anhedonia in Drug-Naïve Major Depressive Disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 95, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Liang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, F.; Ge, J.; Xia, Q. Serum Cytokines-Based Biomarkers in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Therapeutic Response in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 118, 110108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.; Roknuzzaman, A.S.M.; Shahriar, M.; Islam, S.M.A.; Bhuiyan, M.A.; Qusar, M.M.A.S.; Kabir, E.R.; Islam, R. Evaluation of Serum MIP-1β and MCP-2 Levels in Major Depressive Disorder: A Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0305734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrati, E.; Eftekhar, S.P.; Mosaed, R.; Shiralizadeh Dini, S.; Namazi, M. Understanding the Kynurenine Pathway: A Narrative Review on Its Impact across Chronic Pain Conditions. Mol. Pain 2024, 20, 17448069241275097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheiran Pereira, G.; Piton, E.; Moreira dos Santos, B.; Ramanzini, L.G.; Muniz Camargo, L.F.; Menezes da Silva, R.; Bochi, G.V. Microglia and HPA Axis in Depression: An Overview of Participation and Relationship. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 23, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, R.; Perticone, M.; Suraci, E.; Sciacqua, A.; Sesti, G.; Perticone, F. Endothelial Dysfunction and C-Reactive Protein Predict the Incidence of Heart Failure in Hypertensive Patients. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuzzello, C.; Di Vito, L.; Melchionna, R.; Melillo, G.; Silvestri, L.; Cesareo, E.; Crea, F.; Liuzzo, G.; Facchiano, A.; Capogrossi, M.C.; et al. Increase of Plasma IL-9 and Decrease of Plasma IL-5, IL-7, and IFN-γ in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, Y.C.; Kieneker, L.M.; van Hassel, G.; Binnenmars, S.H.; Nolte, I.M.; van Zanden, J.J.; van der Meer, P.; Navis, G.; Voors, A.A.; Bakker, S.J.L.; et al. Interleukin 6 and Development of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction in the General Population. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e018549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Ge, J.; Li, X. Association of IL-1β Polymorphisms and Plasma Levels with Chronic Heart Failure: A Case-Control Study in Chinese Patients. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2018, 16, 205873921881868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre-Amione, G.; Kapadia, S.; Lee, J.; Durand, J.-B.; Bies, R.D.; Young, J.B.; Mann, D.L. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors in the Failing Human Heart. Circulation 1996, 93, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altyar, A.E.; Bhardwaj, S.; Ghaboura, N.; Kaushik, P.; Alenezi, S.K.; Mantargi, M.J.S.; Afzal, M. Role of IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α as Potential Biomarkers in Ischemic Heart Disease: A Comparative Study of Patients with CAD and Non-CAD. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, G.; Francis, S.E.; Suvarna, K.; Blakemore, S.; Ward, C.; Wallace, D.; Braddock, M.; Crossman, D. Differential Gene Expression in Coronary Arteries from Patients Presenting with Ischemic Heart Disease: Further Evidence for the Inflammatory Basis of Atherosclerosis. Am. Heart J. 2005, 150, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Carter, P.; Bruzelius, M.; Vithayathil, M.; Kar, S.; Mason, A.M.; Lin, A.; Burgess, S.; Larsson, S.C. Effects of Tumour Necrosis Factor on Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katkenov, N.; Mukhatayev, Z.; Kozhakhmetov, S.; Sailybayeva, A.; Bekbossynova, M.; Kushugulova, A. Systematic Review on the Role of IL-6 and IL-1β in Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2024, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasucci, L.M.; Koenig, W.; Mair, J.; Mueller, C.; Plebani, M.; Lindahl, B.; Rifai, N.; Venge, P.; Hamm, C.; Giannitsis, E.; et al. How to Use C-Reactive Protein in Acute Coronary Care. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 3687–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Yuan, Y.; Li, J.; Gionfriddo, M.R.; Huang, R. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Its Role as a Mediator in Myocardial Infarction: A Brief Review. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2015, 1, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayedi, A.; Rahimi, K.; Bautista, L.E.; Nazarzadeh, M.; Zargar, M.S.; Shab-Bidar, S. Inflammation Markers and Risk of Developing Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Heart 2019, 105, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, N.S.; Callas, P.W.; Judd, S.E.; McClure, L.A.; Kissela, B.; Zakai, N.A.; Cushman, M. Inflammatory Cytokines and Ischemic Stroke Risk: The REGARDS Cohort. Neurology 2019, 92, E2375–E2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, H.A.; Daker, L.I.; Abbass, M.M.; Abd El Fattah, A.A. The Relationship between the Severity of Disability and Serum IL-8 in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. Egyp. J. Neurol. Psychiatr. Neurosurg. 2018, 54, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amezcua-Castillo, E.; González-Pacheco, H.; Sáenz-San Martín, A.; Méndez-Ocampo, P.; Gutierrez-Moctezuma, I.; Massó, F.; Sierra-Lara, D.; Springall, R.; Rodríguez, E.; Arias-Mendoza, A.; et al. C-Reactive Protein: The Quintessential Marker of Systemic Inflammation in Coronary Artery Disease—Advancing toward Precision Medicine. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Leyte, D.J.; Zepeda-García, O.; Domínguez-Pérez, M.; González-Garrido, A.; Villarreal-Molina, T.; Jacobo-Albavera, L. Endothelial Dysfunction, Inflammation and Coronary Artery Disease: Potential Biomarkers and Promising Therapeutical Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshikawa, T.; Okamoto, N.; Natsuyama, T.; Fujii, R.; Ikenouchi, A.; Honma, Y.; Harada, M.; Yoshimura, R. Associations of Serum Cytokines, Growth Factors, and High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Levels in Patients with Major Depression with and without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Explanatory Investigation. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2022, 18, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, N.; Hoshikawa, T.; Honma, Y.; Chibaatar, E.; Ikenouchi, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshimura, R. Effect Modification of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α on the Kynurenine and Serotonin Pathways in Major Depressive Disorder on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2023, 274, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.M.; Perlman, G.; Kim, N.; Wu, C.Y.; Daher, V.; Zhou, A.; Mathers, E.H.; Anita, N.Z.; Lanctôt, K.L.; Herrmann, N.; et al. Depression in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Blood Inflammatory Markers. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2021, 134, 105448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burhans, M.S.; Hagman, D.K.; Kuzma, J.N.; Schmidt, K.A.; Kratz, M. Contribution of Adipose Tissue Inflammation to the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialek, K.; Czarny, P.; Strycharz, J.; Sliwinski, T. Major Depressive Disorders Accompanying Autoimmune Diseases-Response to Treatment. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 95, 109678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Liu, Y.; Jia, H.; Yao, L.; Zhang, S.; Tian, F. Analysis of Potential Diagnostic Markers and Therapeutic Targets for Rheumatoid Arthritis with Comorbid Depression Immunologic Indicators. Behav. Brain Res. 2024, 471, 115098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koper-Lenkiewicz, O.M.; Gińdzieńska-Sieśkiewicz, E.; Kamińska, J.; Milewska, A.J.; Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Matowicka-Karna, J. Could IL-1β, IL-6, IFN-γ, and SP-Selectin Serum Levels Be Considered as Objective and Quantifiable Markers of Rheumatoid Arthritis Severity and Activity? Reumatologia 2022, 60, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, M.; Baron, B. The Role of TNF-α in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Focus on Regulatory T Cells. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2016, 2, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, P.; Macovei, L.A.; Mihai, I.R.; Cardoneanu, A.; Burlui, M.A.; Rezus, E. Cytokines in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus—Focus on TNF-α and IL-17. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallaur, A.P.; Oliveira, S.R.; Simao, A.N.C.; De Almeida, E.R.D.; Morimoto, H.K.; Lopes, J.; De Carvalho Jennings Pereira, W.L.; Andrade, R.M.; Pelegrino, L.M.; Borelli, S.D.; et al. Cytokine Profile in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Patients and the Association between Progression and Activity of the Disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaibullin, T.; Ivanova, V.; Martynova, E.; Cherepnev, G.; Khabirov, F.; Granatov, E.; Rizvanov, A.; Khaiboullina, S. Elevated Levels of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahl, K.G.; Kruse, N.; Faller, H.; Weiß, H.; Rieckmann, P. Expression of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Interferon-γ MRNA in Blood Cells Correlates with Depression Scores during an Acute Attack in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2002, 27, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, E.M.; Neves, J.R.; Laranjeira, M.; Reis, J. The Importance of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Non-Specific Acute and Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review. Eur. Spine J. 2023, 32, 3230–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risbud, M.V.; Shapiro, I.M. Role of Cytokines in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Pain and Disc Content. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.H.; Hsu, J.W.; Huang, K.L.; Su, T.P.; Bai, Y.M.; Li, C.T.; Yang, A.C.; Chang, W.H.; Chen, T.J.; Tsai, S.J.; et al. Bidirectional Association between Depression and Fibromyalgia Syndrome: A Nationwide Longitudinal Study. J. Pain 2015, 16, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groven, N.; Reitan, S.K.; Fors, E.A.; Guzey, I.C. Kynurenine Metabolites and Ratios Differ between Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, Fibromyalgia, and Healthy Controls. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2021, 131, 105287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musubire, A.K.; Cheema, S.; Ray, J.C.; Hutton, E.J.; Matharu, M. Cytokines in Primary Headache Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Headache Pain. 2023, 24, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.G.; Holmes, T.H.; Anderson, J.N.; Maecker, H.T.; Rosenberg-Hasson, Y.; Valencia, I.J.; Chu, L.; Younger, J.W.; Tato, C.M.; Davis, M.M. Cytokine Signature Associated with Disease Severity in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7150–E7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groven, N.; Fors, E.A.; Reitan, S.K. Patients with Fibromyalgia and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Show Increased HsCRP Compared to Healthy Controls. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 81, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardcastle, S.L.; Brenu, E.W.; Johnston, S.; Nguyen, T.; Huth, T.; Ramos, S.; Staines, D.; Marshall-Gradisnik, S. Serum Immune Proteins in Moderate and Severe Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis Patients. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 12, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Twisk, F.N.M.; Ringel, K. Inflammatory and Cell-Mediated Immune Biomarkers in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Depression: Inflammatory Markers Are Higher in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome than in Depression. Psychother. Psychosom. 2012, 81, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Stratopoulou, C.A.; Dolmans, M.M. Pathogenesis of Endometriosis: New Insights into Prospective Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodburn, S.C.; Bollinger, J.L.; Wohleb, E.S. The Semantics of Microglia Activation: Neuroinflammation, Homeostasis, and Stress. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sagar, A.P.; Kéri, S. Microglial Markers in the Frontal Cortex Are Related to Cognitive Dysfunctions in Major Depressive Disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 241, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, E.; Wilson, A.A.; Mizrahi, R.; Rusjan, P.M.; Miler, L.; Rajkowska, G.; Suridjan, I.; Kennedy, J.L.; Rekkas, P.V.; Houle, S.; et al. Role of Translocator Protein Density, a Marker of Neuroinflammation, in the Brain during Major Depressive Episodes. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulska, J.; Juszczyk, G.; Gawrońska-Grzywacz, M.; Herbet, M. HPA Axis in the Pathomechanism of Depression and Schizophrenia: New Therapeutic Strategies Based on Its Participation. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wu, H. Structural Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly and Activation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 41, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.N.; Zhang, H.; Sharma, A.; Ren, X. Innate Immunity Receptors in Depression and Suicide: Upregulated NOD-like Receptors Containing Pyrin (NLRPs) and Hyperactive Inflammasomes in the Postmortem Brains of People Who Were Depressed and Died by Suicide. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2021, 46, E538–E547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcocer-Gómez, E.; de Miguel, M.; Casas-Barquero, N.; Núñez-Vasco, J.; Sánchez-Alcazar, J.A.; Fernández-Rodríguez, A.; Cordero, M.D. NLRP3 Inflammasome Is Activated in Mononuclear Blood Cells from Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 36, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinstein, L.; Endter, K.; Hedrich, C.M.; Reinke, S.; Luksch, H.; Schulze, F.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Cooper, M.A.; Rösen-Wolff, A.; Winkler, S. An Optimized Whole Blood Assay Measuring Expression and Activity of NLRP3, NLRC4 and AIM2 Inflammasomes. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 191, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwano, N.; Kato, T.A.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Sato-Kasai, M.; Shimokawa, N.; Hayakawa, K.; Ohgidani, M.; Sagata, N.; Kubo, H.; Sakurai, T.; et al. Neuron-Related Blood Inflammatory Markers as an Objective Evaluation Tool for Major Depressive Disorder: An Exploratory Pilot Case-Control Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 240, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derry, H.M.; Padin, A.C.; Kuo, J.L.; Hughes, S.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Sex Differences in Depression: Does Inflammation Play a Role? Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2015, 17, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarkas, D.A.; Villeneuve, A.H.; Daneshmend, A.Z.B.; Villeneuve, P.J.; McQuaid, R.J. Sex Differences in the Inflammation-Depression Link: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 121, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Chang, K.A. Sex Difference in Peripheral Inflammatory Biomarkers in Drug-Naïve Patients with Major Depression in Young Adulthood. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moieni, M.; Irwin, M.R.; Jevtic, I.; Olmstead, R.; Breen, E.C.; Eisenberger, N.I. Sex Differences in Depressive and Socioemotional Responses to an Inflammatory Challenge: Implications for Sex Differences in Depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Chi, V.T.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Yao, Z.; Wu, H.; Bao, X.; Gu, Y.; et al. Association between Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Depressive Symptoms among Chinese Adults: A Population Study from the TCLSIH Cohort Study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 103, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolini, M.; Harrington, Y.; Raffaelli, L.; Poletti, S.; Zanardi, R.; Colombo, C.; Benedetti, F. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Antidepressant Treatment Response in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: Effect of Sex and Hippocampal Volume. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2023, 76, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, A.; Ferrari, C.; Turner, L.; Mariani, N.; Enache, D.; Hastings, C.; Kose, M.; Lombardo, G.; McLaughlin, A.P.; Nettis, M.A.; et al. Whole-Blood Expression of Inflammasome- and Glucocorticoid-Related MRNAs Correctly Separates Treatment-Resistant Depressed Patients from Drug-Free and Responsive Patients in the BIODEP Study. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 232, Erratum in Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 352. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-020-01044-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swoboda, C.; Deloch, L.; von Zimmermann, C.; Richter-Schmidinger, T.; Lenz, B.; Kornhuber, J.; Mühle, C. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor in Major Depressive Disorder: A Multilevel Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, F.; Poletti, S.; Vai, B.; Mazza, M.G.; Lorenzi, C.; Brioschi, S.; Aggio, V.; Branchi, I.; Colombo, C.; Furlan, R.; et al. Higher Baseline Interleukin-1β and TNF-α Hamper Antidepressant Response in Major Depressive Disorder. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 42, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yan, D.; Liao, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.X.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, L.J. Effect of Fluvoxamine on Plasma Interleukin-6 in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: A Prospective Follow-up Study. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1163754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessa, C.; Janssens, J.; Coppens, V.; El Abdellati, K.; Vergaelen, E.; van den Ameele, S.; Baeken, C.; Zeeuws, D.; Milaneschi, Y.; Lamers, F.; et al. Efficacy of Inflammation-Based Stratification for Add-on Celecoxib or Minocycline in Major Depressive Disorder: Protocol of the INSTA-MD Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Randomised Clinical Trial. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2024, 41, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, G.; Nettis, M.A.; Hastings, C.; Zajkowska, Z.; Mariani, N.; Nikkheslat, N.; Worrell, C.; Enache, D.; McLaughlin, A.; Kose, M.; et al. Sex Differences in a Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial with Minocycline in Treatment-Resistant Depressed Patients: CRP and IL-6 as Sex-Specific Predictors of Treatment Response. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2022, 26, 100561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raison, C.L.; Rutherford, R.E.; Woolwine, B.J.; Shuo, C.; Schettler, P.; Drake, D.F.; Haroon, E.; Miller, A.H. A Randomized Controlled Trial of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Antagonist Infliximab for Treatment-Resistant Depression: The Role of Baseline Inflammatory Biomarkers. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian, F.; Bagheri, S.; Moradi, K.; Keykhaei, M.; Etemadi, A.; Shalbafan, M.; Shariati, B.; Vaseghi, S.; Samsami, F.S.; Akhondzadeh, S. Evidence for Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Adalimumab in Treatment of Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: A Pilot, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 45, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Zhang, S.; Duan, Y. Depression Symptoms Predict Worse Clinical Response to Etanercept Treatment in Psoriasis Patients. Dermatology 2019, 235, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiosano, S.; Yavne, Y.; Watad, A.; Langevitz, P.; Lidar, M.; Feld, J.; Tishler, M.; Aamar, S.; Elkayam, O.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; et al. The Impact of Tocilizumab on Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2020, 50, e13268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappelmann, N.; Lewis, G.; Dantzer, R.; Jones, P.B.; Khandaker, G.M. Antidepressant Activity of Anti-Cytokine Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials of Chronic Inflammatory Conditions. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaholimihaso, T.; Bouazzaoui, F.; Kaladjian, A. Curcumin in Depression: Potential Mechanisms of Action and Current Evidence-A Narrative Review. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 572533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.J.; Pei, L.B.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, Z.Y.; Yang, J.L. Chronic Supplementation of Curcumin Enhances the Efficacy of Antidepressants in Major Depressive Disorder: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 35, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Li, J.M.; Ruan, Y.M.; Yan, W.J.; Zhong, S.Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, L.L.; Wu, R.; Wang, B.; et al. Glycyrrhizic Acid as an Adjunctive Treatment for Depression through Anti-Inflammation: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 265, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Dou, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Fan, H.; Fan, N.; Yang, X.; Ma, X. Efficacy and Acceptability of Anti-Inflammatory Agents in Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1407529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavyani, Z.; Musazadeh, V.; Fathi, S.; Hossein Faghfouri, A.; Dehghan, P.; Sarmadi, B. Efficacy of the Omega-3 Fatty Acids Supplementation on Inflammatory Biomarkers: An Umbrella Meta-Analysis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, S.; Manohar, K.; Shariff, A.; Kinattingal, N.; Wani, S.U.D.; Alshehri, S.; Imam, M.T.; Shakeel, F.; Krishna, K.L. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Supplementation in the Treatment of Depression: An Observational Study. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suneson, K.; Söderberg Veibäck, G.; Lindahl, J.; Tjernberg, J.; Ståhl, D.; Ventorp, S.; Ängeby, F.; Lundblad, K.; Wolkowitz, O.M.; Lindqvist, D. Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Inflamed Depression-A Match/Mismatch Study. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 118, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Xie, B.; Zhang, H.; He, Q.; Guo, L.; Subramaniapillai, M.; Fan, B.; Lu, C.; Mclntyer, R.S. Efficacy of Omega-3 PUFAs in Depression: A Meta-Analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 190, Erratum in Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, P.E.; Fournier, A.A.; Sisitsky, T.; Simes, M.; Berman, R.; Koenigsberg, S.H.; Kessler, R.C. The Economic Burden of Adults with Major Depressive Disorder in the United States (2010 and 2018). Pharmacoeconomics 2021, 39, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuomo, A.; Koukouna, D.; Pardossi, S.; Pinzi, M.; Rescalli, M.B.; Pierini, C.; Fagiolini, A. Depression and Physical Comorbidities: An Integrated Review of Challenges and Treatment Approaches. Riv. Psichiatr. 2025, 60, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Tu, S.; Sheng, J.; Shao, A. Depression in Sleep Disturbance: A Review on a Bidirectional Relationship, Mechanisms and Treatment. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 2324–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaipisuttikul, P.; Ittasakul, P.; Waleeprakhon, P.; Wisajun, P.; Jullagate, S. Psychiatric Comorbidities in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2014, 10, 2097–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, A.M.; Brister, T.S.; Duckworth, K.; Foxworth, P.; Fulwider, T.; Suthoff, E.D.; Werneburg, B.; Aleksanderek, I.; Reinhart, M.L. Impact of Major Depressive Disorder on Comorbidities: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2022, 83, E1–E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäbitz, W.-R.; Glatz, K.; Schuhan, C.; Sommer, C.; Berger, C.; Schwaninger, M.; Hartmann, M.; Goebel, H.H.; Meinck, H.-M. Higher Incidence of Depression Preceding the Onset of Parkinson’s Disease: A Register Study. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáiz-Vázquez, O.; Gracia-García, P.; Ubillos-Landa, S.; Puente-Martínez, A.; Casado-Yusta, S.; Olaya, B.; Santabárbara, J. Depression as a Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review of Longitudinal Meta-Analyses. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’neil, A.; Fisher, A.J.; Kibbey, K.J.; Jacka, F.N.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Williams, L.J.; Stuart, A.L.; Berk, M.; Lewandowski, P.A.; Taylor, C.B.; et al. Depression Is a Risk Factor for Incident Coronary Heart Disease in Women: An 18-Year Longitudinal Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 196, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyness, J.M.; Niculescu, A.; Tu, X.; Reynolds, C.F.; Caine, E.D. The Relationship of Medical Comorbidity and Depression in Older, Primary Care Patients. Psychosomatics 2006, 47, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.; Dalla, E.; Mehra, A.; Chakrabarti, S.; Avasthi, A. Physical Comorbidity and Its Impact on Symptom Profile of Depression among Elderly Patients Attending Psychiatry Services of a Tertiary Care Hospital. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2017, 39, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, B.S.; Butters, M.A.; Albert, S.M.; Dew, M.A.; Reynolds, C.F. Late-Life Depression and Risk of Vascular Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Community-Based Cohort Studies. Br. J. Psychiatry 2013, 202, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, B.S.; Reynolds, C.F.; Butters, M.A.; Dew, M.A.; Firmo, J.O.A.; Lima-Costa, M.F.; Castro-Costa, E. The effect of gender, age, and symptom severity in late-life depression on the risk of all-cause mortality: The bambuí cohort study of aging. Depress. Anxiety 2014, 31, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, M.; Köhler-Forsberg, O.; Turner, M.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Wrobel, A.; Firth, J.; Loughman, A.; Reavley, N.J.; McGrath, J.J.; Momen, N.C.; et al. Comorbidity between Major Depressive Disorder and Physical Diseases: A Comprehensive Review of Epidemiology, Mechanisms and Management. World Psychiatry 2023, 22, 366–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990-2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021, Correction in J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1958–1959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2021.02.039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstedt, J.; Pasman, J.A.; Ma, Z.; Harder, A.; Yao, S.; Parker, N.; Treur, J.L.; Smit, D.J.A.; Frei, O.; Shadrin, A.A.; et al. Distinct Biological Signature and Modifiable Risk Factors Underlie the Comorbidity between Major Depressive Disorder and Cardiovascular Disease. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 3, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.K.; Barton, D.A. Depression and the Link with Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Psychiatry 2016, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Qamar, A.; Vaduganathan, M.; Charney, D.S.; Murrough, J.W. Screening and Management of Depression in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1827–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, L.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Shi, L.; Luo, M. Prevalence of Depression in Myocardial Infarction; A PRISMA-Compliant Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e14596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrels, E.; Kainth, T.; Silva, B.; Yadav, G.; Gill, G.; Salehi, M.; Gunturu, S. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Post-Myocardial Infarction Depression: A Narrative Review. Front Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1225794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, M.; Marshall, I.J.; Wolfe, C.D.; Wang, Y.; Connell, M.D. Prevalence and Natural History of Depression after Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1004200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towfighi, A.; Ovbiagele, B.; El Husseini, N.; Hackett, M.L.; Jorge, R.E.; Kissela, B.M.; Mitchell, P.H.; Skolarus, L.E.; Whooley, M.A.; Williams, L.S. Poststroke Depression: A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2017, 48, e30–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoni, S.; Kernic, M.A.; Malloy, K.; Ali, T.; Zhang, Y.; Cole, S.A.; Fretts, A.M. Depression and Incident Hypertension: The Strong Heart Family Study. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2025, 22, E06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukhari, F.Z.; Belayachi, S.; Essayagh, F.; Terkiba, O.; Naji, A.A.; Amine, M.; Lambaki, A.; Essayagh, M.; Essayagh, S.; Essayagh, T. Self-Reported Depression and Its Risk Factors among Hypertensive Patients, Morocco: A Cross-Sectional Study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedland, K.E.; Carney, R.M.; Rich, M.W.; Steinmeyer, B.C.; Skala, J.A.; Dávila-Román, V.G. Depression and Multiple Rehospitalizations in Patients with Heart Failure. Clin. Cardiol. 2016, 39, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.C.; Singh, K.; Nitin, R.; Davis, L.K.; Wray, N.R.; Shah, S. Sex-Specific Association between Genetic Risk of Psychiatric Disorders and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2024, e004685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolewska-Nowak, J.; Wachowska, K.; Nowak, A.; Orzechowska, A.; Szulc, A.; Płaza, O.; Gałecki, P. Exploring the Heart–Mind Connection: Unraveling the Shared Pathways between Depression and Cardiovascular Diseases. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, M.A.; Paneni, F.; Libby, P.; Frantz, S.; Stähli, B.E.; Templin, C.; Mengozzi, A.; Wang, Y.J.; Kündig, T.M.; Räber, L.; et al. Inflammation in Acute Myocardial Infarction: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, K.; Zhao, R.; Hu, J.; Hao, Z.; Wang, F.; Lu, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y. Inflammatory Biomarkers of Coronary Heart Disease. Front. Biosci. 2018, 10, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simats, A.; Liesz, A. Systemic Inflammation after Stroke: Implications for Post-stroke Comorbidities. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e16269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shou, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, D. Immuno-Inflammatory Pathogenesis in Ischemic Heart Disease: Perception and Knowledge for Neutrophil Recruitment. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1411301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, X.; Meng, X.; Zhou, X. Role of Inflammation, Immunity, and Oxidative Stress in Hypertension: New Insights and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1098725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsioufis, P.; Theofilis, P.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D. The Impact of Cytokines in Coronary Atherosclerotic Plaque: Current Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwa, D.N.; Pathak, A.; Agrawal, A. IL-6 Regulates Induction of C-Reactive Protein Gene Expression by Activating STAT3 Isoforms. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 146, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Koyama, Y.; Shimada, S. Inflammation from Peripheral Organs to the Brain: How Does Systemic Inflammation Cause Neuroinflammation? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 903455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Baranova, A.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, F. Bidirectional Associations between Mental Disorders, Antidepressants and Cardiovascular Disease. BMJ Mental Health 2024, 27, e300975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avan, A.; Tavakoly Sany, S.B.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Rahimi, H.R.; Tajfard, M.; Ferns, G. Serum C-Reactive Protein in the Prediction of Cardiovascular Diseases: Overview of the Latest Clinical Studies and Public Health Practice. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 8508–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Buring, J.E.; Shih, J.; Matias, M.; Hennekens, C.H. Prospective Study of C-Reactive Protein and the Risk of Future Cardiovascular Events Among Apparently Healthy Women. Circulation 1998, 98, 731–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, S.; Ding, H.; Fan, H.; Hou, S. Cumulative Exposure to High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Predicts the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aul, P.; Idker, M.R.; Ifai, A.R.; Ynda, L.; Ose, R.; Ulie, J.; Uring, E.B.; Ook, A.R.C. Comparison of C-Reactive Protein and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels in the Prediction of First Cardiovascular Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartorius, N. Depression and Diabetes. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.L.; Abate, D.; Abate, K.H.; Abay, S.M.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 354 Diseases and Injuries for 195 Countries and Territories, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, Regional and Country-Level Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2021 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, G.; Raschi, E.; Hafez, G.; Matura, S.; Schiweck, C.; Poluzzi, E.; Lunghi, C. The Interface of Depression and Diabetes: Treatment Considerations. Transl. Psychiatry 2025, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Liu, D.-L.; Zeng, X.-X.; Pan, X.-R.; Peng, J. Bidirectional Relationship between Diabetes Mellitus and Depression: Mechanisms and Epidemiology. World J. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herder, C.; Zhu, A.; Schmitt, A.; Spagnuolo, M.C.; Kulzer, B.; Roden, M.; Hermanns, N.; Ehrmann, D. Associations between Biomarkers of Inflammation and Depressive Symptoms-Potential Differences between Diabetes Types and Symptom Clusters of Depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2025, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prigge, R.; Wild, S.H.; Jackson, C.A. Depression, Diabetes, Comorbid Depression and Diabetes and Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality: A Prospective Cohort Study. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1450–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounthavong, M.; Medina, A.; Wallace, B.M.; Sepassi, A.; Morello, C.M. Impact of Increasing Number of Mental Health Conditions on Healthcare Costs and Resource Utilization among Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Pharm. Health Serv. Res. 2024, 15, rmae008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangethe, A.; Lawrence, D.F.; Touya, M.; Chrones, L.; Polson, M.; Evangelatos, T. Incremental Burden of Comorbid Major Depressive Disorder in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes or Cardiovascular Disease: A Retrospective Claims Analysis. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2021, 21, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, B.R.; de Araujo Borba, L.; Borges de Souza, P.; Gil-Mohapel, J.; Rodrigues, A.L.S. Role of Inflammatory Mechanisms in Major Depressive Disorder: From Etiology to Potential Pharmacological Targets. Cells 2024, 13, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnaruc, A.M.; Roberge, M.; Giroux, I.; Aguer, C. The Bidirectional Link between Major Depressive Disorder and Type 2 Diabetes: The Role of Inflammation. Endocrines 2024, 5, 478–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedosugova, L.V.; Markina, Y.V.; Bochkareva, L.A.; Kuzina, I.A.; Petunina, N.A.; Yudina, I.Y.; Kirichenko, T.V. Inflammatory Mechanisms of Diabetes and Its Vascular Complications. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.; Akash, M.S.H. Mechanisms of Inflammatory Responses and Development of Insulin Resistance: How Are They Interlinked? J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dludla, P.V.; Mabhida, S.E.; Ziqubu, K.; Nkambule, B.B.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E.; Hanser, S.; Basson, A.K.; Pheiffer, C.; Kengne, A.P. Pancreatic β-Cell Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes: Implications of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsalamandris, S.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Oikonomou, E.; Papamikroulis, G.A.; Vogiatzi, G.; Papaioannou, S.; Deftereos, S.; Tousoulis, D. The Role of Inflammation in Diabetes: Current Concepts and Future Perspectives. Eur. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 14, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, B.; Shelton, R.C.; Dwivedi, Y. DNA Methylation and Expression of Stress Related Genes in PBMC of MDD Patients with and without Serious Suicidal Ideation. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 89, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianotti, L.; Belcastro, S.; D’Agnano, S.; Tassone, F. The Stress Axis in Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus: An Update. Endocrines 2021, 2, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Silva, E.; de Melo, M.G.; Maes, M.; Filho, A.J.M.C.; Macedo, D.; Peixoto, C.A. Shared Metabolic and Neuroimmune Mechanisms Underlying Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Major Depressive Disorder. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 111, 110351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alruwaili, N.S.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Albuhadily, A.K.; Ragab, A.E.; Alenazi, A.A.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; Batiha, G.E.-S. Antidepressants and Type 2 Diabetes: Highways to Knowns and Unknowns. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 15, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopan, S.; Larsen, E.R. Use of Antidepressants in Patients with Depression and Comorbid Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2017, 29, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottilil, S.; Mathur, P. The Influence of Inflammation on Cardiovascular Disease in Women. Front. Glob. Womens Health 2022, 3, 979708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euesden, J.; Danese, A.; Lewis, C.M.; Maughan, B. A Bidirectional Relationship between Depression and the Autoimmune Disorders-New Perspectives from the National Child Development Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, D.; Su, Q.; Shi, J. The Role of Inflammation in Autoimmune Disease: A Therapeutic Target. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1267091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hässler, S.; Lorenzon, R.; Binvignat, M.; Ribet, C.; Roux, A.; Johanet, C.; Amouyal, C.; Amselem, S.; Berenbaum, F.; Benveniste, O.; et al. Clinical Correlates of Lifetime and Current Comorbidity Patterns in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2024, 149, 103318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benros, M.E.; Waltoft, B.L.; Nordentoft, M.; Ostergaard, S.D.; Eaton, W.W.; Krogh, J.; Mortensen, P.B. Autoimmune Diseases and Severe Infections as Risk Factors for Mood Disorders a Nationwide Study. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauden, A.; Geishin, A.; Merzon, E.; Korobeinikov, A.; Green, I.; Golan-Cohen, A.; Vinker, S.; Manor, I.; Weizman, A.; Magen, E. Higher Rates of Allergies, Autoimmune Diseases and Low-Grade Inflammation Markers in Treatment-Resistant Major Depression. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2021, 16, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.K.; Brinton, R.D. Autoimmune Disease in Women: Endocrine Transition and Risk Across the Lifespan. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, C.; Sun, S.; Mi, G.; Liu, C.; Ding, G.; Wang, C.; Tang, F. Elucidating the Bidirectional Association between Autoimmune Diseases and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Ment. Health 2024, 27, e301252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortona, E.; Pierdominici, M.; Maselli, A.; Veroni, C.; Aloisi, F.; Shoenfeld, Y. Monographic Section Sex-Based Differences in Autoimmune Diseases. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanità 2016, 52, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, C.E.; Popescu, C.C.; Agache, M.; Dinache, G.; Codreanu, C. Depression in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Narrative Review-Diagnostic Challenges, Pathogenic Mechanisms and Effects. Medicina 2022, 58, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallerand, I.A.; Lewinson, R.T.; Frolkis, A.D.; Lowerison, M.W.; Kaplan, G.G.; Swain, M.G.; Bulloch, A.G.M.; Patten, S.B.; Barnabe, C. Depression as a Risk Factor for the Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Cohort Study. RMD Open 2018, 4, e000670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakes, D.H.; Fawcett, E.J.; Yick, J.J.J.; Coles, A.R.L.; Seim, R.B.; Miller, K.; LaSaga, M.S.; Fawcett, J.M. Beyond Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis of the Prevalence of Anxiety and Depressive Disorders in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2025, 184, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitrzak-Węglarz, M.; Rybakowski, J.; Szczepankiewicz, A.; Kapelski, P.; Lesicka, M.; Jabłońska, E.; Reszka, E.; Pawlak, J. Identification of Shared Disease Marker Genes and Underlying Mechanisms between Major Depression and Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 168, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerurkar, L.; Siebert, S.; McInnes, I.B.; Cavanagh, J. Rheumatoid Arthritis and Depression: An Inflammatory Perspective. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, L.; Chasset, F.; Martin, T. Immunopathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: An Update. Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Yusoff, F.; Wong, K.K.; Mohd Redzwan, N. Th1, Th2, and Th17 Cytokines in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Autoimmunity 2020, 53, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, A.; Soltani, H.; Faezi, S.T.; Baghdadi, A.; Soleymani Salehabadi, H.; Bashiri, H.; Hemayati, R.; Mansouri, M.; Motaghi, M.; Nejadhosseinian, M. Depression, Anxiety, and Quality of Life in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheumatology 2023, 61, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanati, A.; Marani, A.; Martina, E.; Diotallevi, F.; Radi, G.; Offidani, A. Psoriasis as an Immune-Mediated and Inflammatory Systemic Disease: From Pathophysiology to Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintermann, G.B.; Bierling, A.L.; Peters, E.M.J.; Abraham, S.; Beissert, S.; Weidner, K. Psychosocial Stress Affects the Change of Mental Distress under Dermatological Treatment-A Prospective Cohort Study in Patients with Psoriasis. Stress. Health 2023, 40, e3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzanfar, D.; Dowlati, Y.; French, L.E.; Lowes, M.A.; Alavi, A. Inflammation: A Contributor to Depressive Comorbidity in Inflammatory Skin Disease. Skin. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 31, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, D.S.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Calabresi, P.A. Multiple Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peres, D.S.; Rodrigues, P.; Viero, F.T.; Frare, J.M.; Kudsi, S.Q.; Meira, G.M.; Trevisan, G. Prevalence of Depression and Anxiety in the Different Clinical Forms of Multiple Sclerosis and Associations with Disability: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2022, 24, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina Galindo, L.S.; Gonzalez-Escamilla, G.; Fleischer, V.; Grotegerd, D.; Meinert, S.; Ciolac, D.; Person, M.; Stein, F.; Brosch, K.; Nenadić, I.; et al. Concurrent Inflammation-Related Brain Reorganization in Multiple Sclerosis and Depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 119, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiropoulos, L.A.; Rozenblat, V.; Baes, N. Inflammatory Proteins Related to Depression in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2025, 43, 100939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Studer, V.; Motta, C.; Polidoro, S.; Perugini, J.; Macchiarulo, G.; Mara Giovannetti, A.; Lorena Pareja-Gutierrez, P.; Calò, A.; Colonna, I.; et al. Neuroinflammation Drives Anxiety and Depression in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Neurology 2017, 89, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo-Braga, M.; Cornaby, C.; Cortez, A.; Bernardes, M.; Terroso, G.; Figueiredo, M.; Mesquita, C.D.S.; Costa, L.; Poole, B.D. Influence of Biological Therapeutics, Cytokines, and Disease Activity on Depression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 5954897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, R.G.; Feldman, S.R.; Han, C.; Schenkel, B.; Szapary, P.; Hsu, M.C.; Ortonne, J.P.; Gordon, K.B.; Kimball, A.B. Ustekinumab Significantly Improves Symptoms of Anxiety, Depression, and Skin-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis: Results from a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase III Trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 63, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rometsch, C.; Martin, A.; Junne, F.; Cosci, F. Chronic Pain in European Adult Populations: A Systematic Review of Prevalence and Associated Clinical Features. Pain. 2024, 166, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohayon, M.M.; Schatzberg, A.F. Chronic Pain and Major Depressive Disorder in the General Population. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2010, 44, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnow, B.A.; Hunkeler, E.M.; Blasey, C.M.; Lee, J.; Constantino, M.J.; Fireman, B.; Kraemer, H.C.; Dea, R.; Robinson, R.; Hayward, C. Comorbid Depression, Chronic Pain, and Disability in Primary Care. Psychosom. Med. 2006, 68, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treede, R.D.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Finnerup, N.B.; First, M.B.; et al. A Classification of Chronic Pain for ICD-11. Pain. 2015, 156, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.X.; Zhai, M.N.; Zhu, M.; He, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.J. Inflammation in Pathogenesis of Chronic Pain: Foe and Friend. Mol. Pain. 2023, 19, 17448069231178176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, R.; Atzeni, F.; Bazzichi, L.; Beretta, G.; Costantini, E.; Sacerdote, P.; Tassorelli, C. Pain in Women: A Perspective Review on a Relevant Clinical Issue That Deserves Prioritization. Pain. Ther. 2021, 10, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.F.S.; Farkas, O.; Faria, A.V.; Plemel, J.R.; Kerr, B.J. A Recent History of Immune Cell Sex Differences in the Peripheral Nervous System in Persistent Pain States. Brain Behav. Immun. 2025, 128, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Hurwitz, E.L.; Li, J.; de Luca, K.; Tavares, P.; Green, B.; Haldeman, S. Bidirectional Comorbid Associations between Back Pain and Major Depression in US Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünal, Ö.; Akyol, Y.; Tander, B.; Ulus, Y.; Terzi, Y.; Kuru, Ö. The Relationship of Illness Perceptions with Demographic Features, Pain Severity, Functional Capacity, Disability, Depression, and Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 65, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, J.; Maeno, K.; Takada, T.; Kakutani, K.; Yurube, T.; Zhang, Z.; Hirata, H.; Kurakawa, T.; Sakai, D.; Mochida, J.; et al. Fas Ligand Plays an Important Role for the Production of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Intervertebral Disc Nucleus Pulposus Cells. J. Orthop. Res. 2013, 31, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashina, S.; Serrano, D.; Lipton, R.B.; Maizels, M.; Manack, A.N.; Turkel, C.C.; Reed, M.L.; Buse, D.C. Depression and Risk of Transformation of Episodic to Chronic Migraine. J. Headache Pain. 2012, 13, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edvinsson, L.; Haanes, K.A.; Warfvinge, K.; Krause, D.N. CGRP as the Target of New Migraine Therapies-Successful Translation from Bench to Clinic. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, S.; Ossipov, M.H.; Johnson, K.W. The Role of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide in Peripheral and Central Pain Mechanisms Including Migraine. Pain 2017, 158, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.; Brenu, E.W.; Staines, D.; Marshall-Gradisnik, S. The Prevalence of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 5, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, S.B.; Wadsworth, M.; Wessely, S.; Hotopf, M. The Relationship between Prior Psychiatric Disorder and Chronic Fatigue: Evidence from a National Birth Cohort Study. Psychol. Med. 2008, 38, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatomi, Y.; Mizuno, K.; Ishii, A.; Wada, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Tazawa, S.; Onoe, K.; Fukuda, S.; Kawabe, J.; Takahashi, K.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis: An11C-(R)-PK11195 PET Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasar, P.; Ozcan, P.; Terry, K.L. Endometriosis: Epidemiology, Diagnosis and Clinical Management. Curr. Obstet. Gynecol. Rep. 2017, 6, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Hsu, J.W.; Huang, K.L.; Bai, Y.M.; Su, T.P.; Li, C.T.; Yang, A.C.; Chang, W.H.; Chen, T.J.; Tsai, S.J.; et al. Risk of Developing Major Depression and Anxiety Disorders among Women with Endometriosis: A Longitudinal Follow-up Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 190, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.W.; Zhang, X.L.; Yan, X.T.; Qi, C.; Jiang, G.J. Association between Depression and Endometriosis Using Data from NHANES 2005–2006. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.S.; Gude, K.; Perdeaux, E.; Gattrell, W.T.; Becker, C.M. Surgical Outcomes in Patients with Endometriosis: A Systematic Review. J. Gynaecol. Can. 2020, 42, 881–888.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körtési, T.; Nagy-Grócz, G.; Vécsei, L. The Role of Kynurenines in Migraine-Related Neuroimmune Pathways. J. Headache Pain. 2024, 25, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Ma, T.; Fan, H.; Bai, L.; Ma, B.; Qi, S.; Wang, Z.; An, H.; et al. Relationship between the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Pathway and Painful Physical Symptoms in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. J. Psychosom. Res. 2022, 163, 111069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugger, G.; Dold, M.; Bartova, L.; Mitschek, M.M.M.; Souery, D.; Mendlewicz, J.; Serretti, A.; Zohar, J.; Montgomery, S.; Fabbri, C.; et al. Clinical Correlates and Outcome of Major Depressive Disorder and Comorbid Migraine: A Report of the European Group for the Study of Resistant Depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 23, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, S.T.; Jung, C.; Weiner, D.K.; Peciña, M.; Karp, J.F. Opioid Exposure Negatively Affects Antidepressant Response to Venlafaxine in Older Adults with Chronic Low Back Pain and Depression. Pain Med. 2020, 21, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vitali, E.; Cattane, N.; D’Aprile, I.; Petrillo, G.; Cattaneo, A. Systemic Inflammation at the Crossroad of Major Depressive Disorder and Comorbidities: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199382
Vitali E, Cattane N, D’Aprile I, Petrillo G, Cattaneo A. Systemic Inflammation at the Crossroad of Major Depressive Disorder and Comorbidities: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199382
Chicago/Turabian StyleVitali, Erika, Nadia Cattane, Ilari D’Aprile, Giulia Petrillo, and Annamaria Cattaneo. 2025. "Systemic Inflammation at the Crossroad of Major Depressive Disorder and Comorbidities: A Narrative Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199382
APA StyleVitali, E., Cattane, N., D’Aprile, I., Petrillo, G., & Cattaneo, A. (2025). Systemic Inflammation at the Crossroad of Major Depressive Disorder and Comorbidities: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199382





