Effects of Combined Therapy with SGLT2i and GLP-1RAs on Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation in Diabetic Cohorts: One-Year Outcomes from Continuous Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods (Research Design and Methods)
4.1. Laboratory Analysis
4.2. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, A.; Truong, T.; Black-Maier, E.; Green, C.; Campbell, K.B.; Barnett, A.S.; Febre, J.; Loring, Z.; Al-Khatib, S.M.; Atwater, B.D.; et al. Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with diabetes mellitus. Heart Rhythm O2 2020, 1, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmino, M.; Matta, M.; D’ascenzo, F.; Pappone, C.; Santinelli, V.; Bunch, T.J.; Neumann, T.; Schilling, R.J.; Hunter, R.J.; Noelker, G.; et al. Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Europace 2015, 17, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Jiang, C.; He, L.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, M.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Dai, W.; et al. Impact of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor on Recurrence After Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Diabetes: A Propensity-Score Matching Study and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e031269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakasis, P.; Fragakis, N.; Patoulias, D.; Theofilis, P.; Kassimis, G.; Karamitsos, T.; El-Tanani, M.; Rizzo, M. Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists on Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Adv. Ther. 2024, 41, 3749–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardu, C.; Trotta, M.C.; Marfella, L.V.; D’Amico, G.; La Marca, C.; Mauro, C.; Santamaria, M.; Giordano, V.; Turriziani, F.; Rafaniello, C.; et al. Effects of SGLT2i therapy on cardiac electrophysiological properties and arrhythmias in diabetic patients with implantable cardiac defibrillator. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 216, 107759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, H.; Sheth, A.; Nair, A.; Patel, B.; Thakkar, S.; Narasimhan, B.; Mehta, N.; Azad, Z.; Kowlgi, G.N.; Desimone, C.V.; et al. Long-Term Impact of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists on AF Recurrence After Ablation in Obese Patients. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2025, 36, 1808–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardu, C.; Marfella, L.V.; Rinaldi, L.; Sasso, F.C.; Cozzolino, D.; Nappo, F.; Sellitto, C.; Romano, C.; Carusone, C.; D’Onofrio, N.; et al. Effects of combination therapy with SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists on CRT response and clinical outcomes in in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients receiving chronic anti-diabetic medications: A multicenter observational study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2025, 3, 112452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardu, C.; Santulli, G.; Santamaria, M.; Barbieri, M.; Sacra, C.; Paolisso, P.; D’Amico, F.; Testa, N.; Caporaso, I.; Paolisso, G.; et al. Effects of Alpha Lipoic Acid on Multiple Cytokines and Biomarkers and Recurrence of Atrial Fibrillation Within 1 Year of Catheter Ablation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 119, 1382–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, G.; Li, Z.; Tan, W.; Fan, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, G. Effectiveness of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors on atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2024, 413, 132359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishima, H.; Mine, T.; Fukuhara, E.; Kitagaki, R.; Asakura, M.; Ishihara, M. Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Outcomes After Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2022, 8, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Qaoud, M.R.; Kumar, A.; Tarun, T.; Abraham, S.; Ahmad, J.; Khadke, S.; Husami, R.; Kulbak, G.; Sahoo, S.; Januzzi JLJr Neilan, T.G.; et al. Impact of SGLT2 Inhibitors on AF Recurrence After Catheter Ablation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satti, D.I.; Karius, A.; Chan, J.S.K.; Isakadze, N.; Yadav, R.; Garg, K.; Aronis, K.N.; Marine, J.E.; Berger, R.; Calkins, H.; et al. Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2024, 10, 1848–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M.; Bunting, K.V.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Caso, V.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; De Potter, T.J.R.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart. J. 2024, 45, 3314–3414, Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2025, ehaf306. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehaf306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46 (Suppl. S1), S19–S40, Erratum in Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1106. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc23-er05; Erratum in Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1715. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc23-ad08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
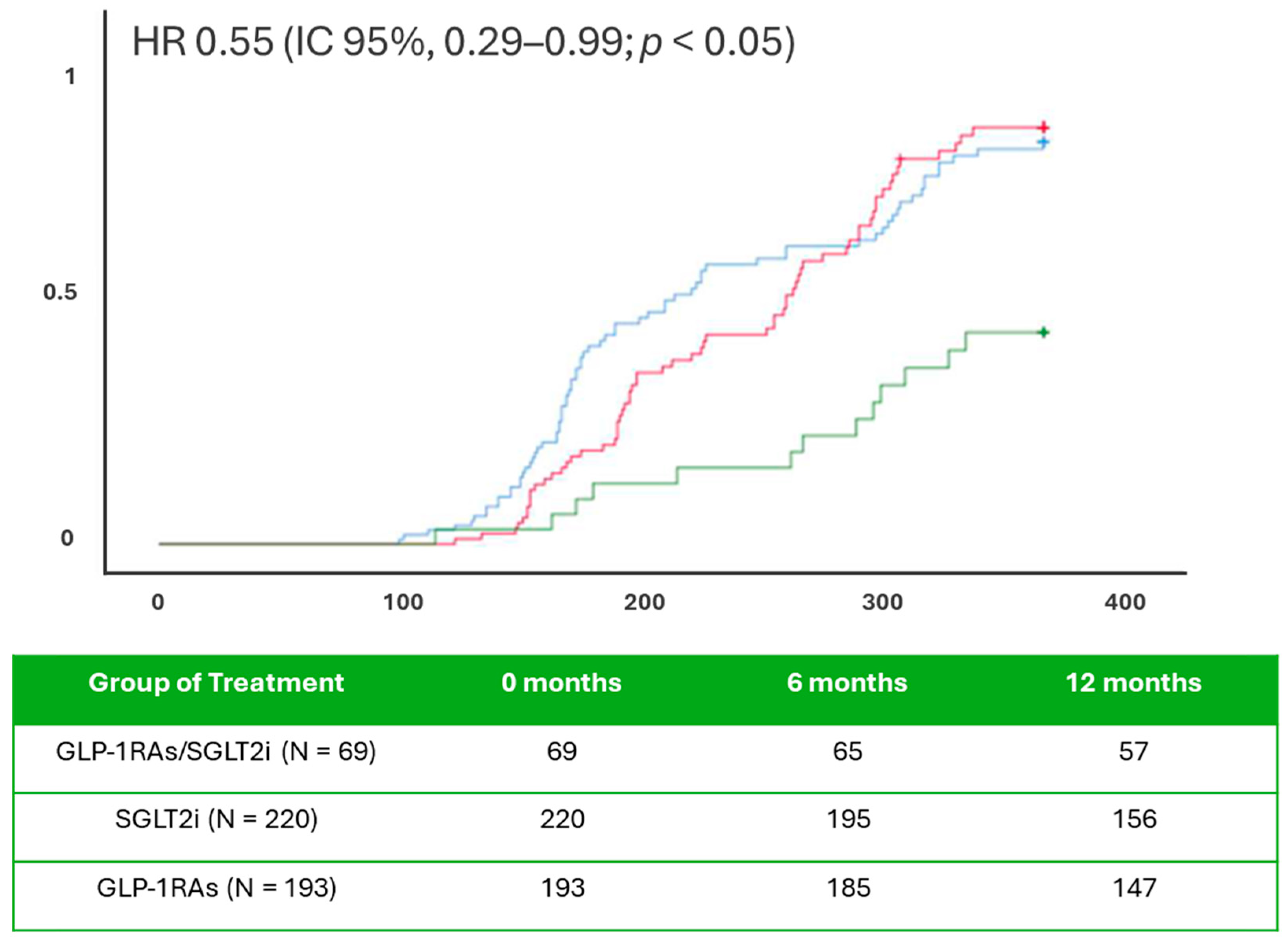
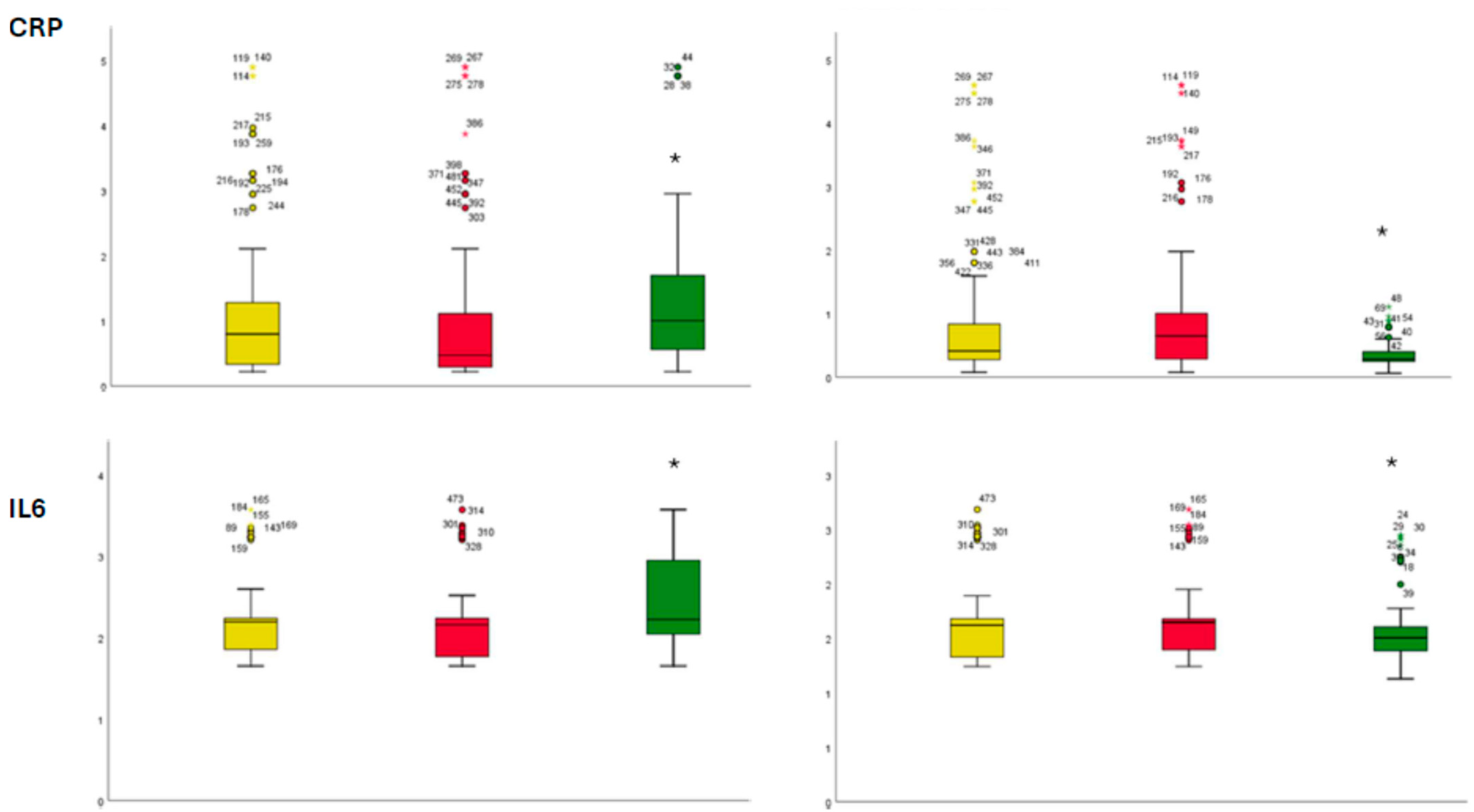
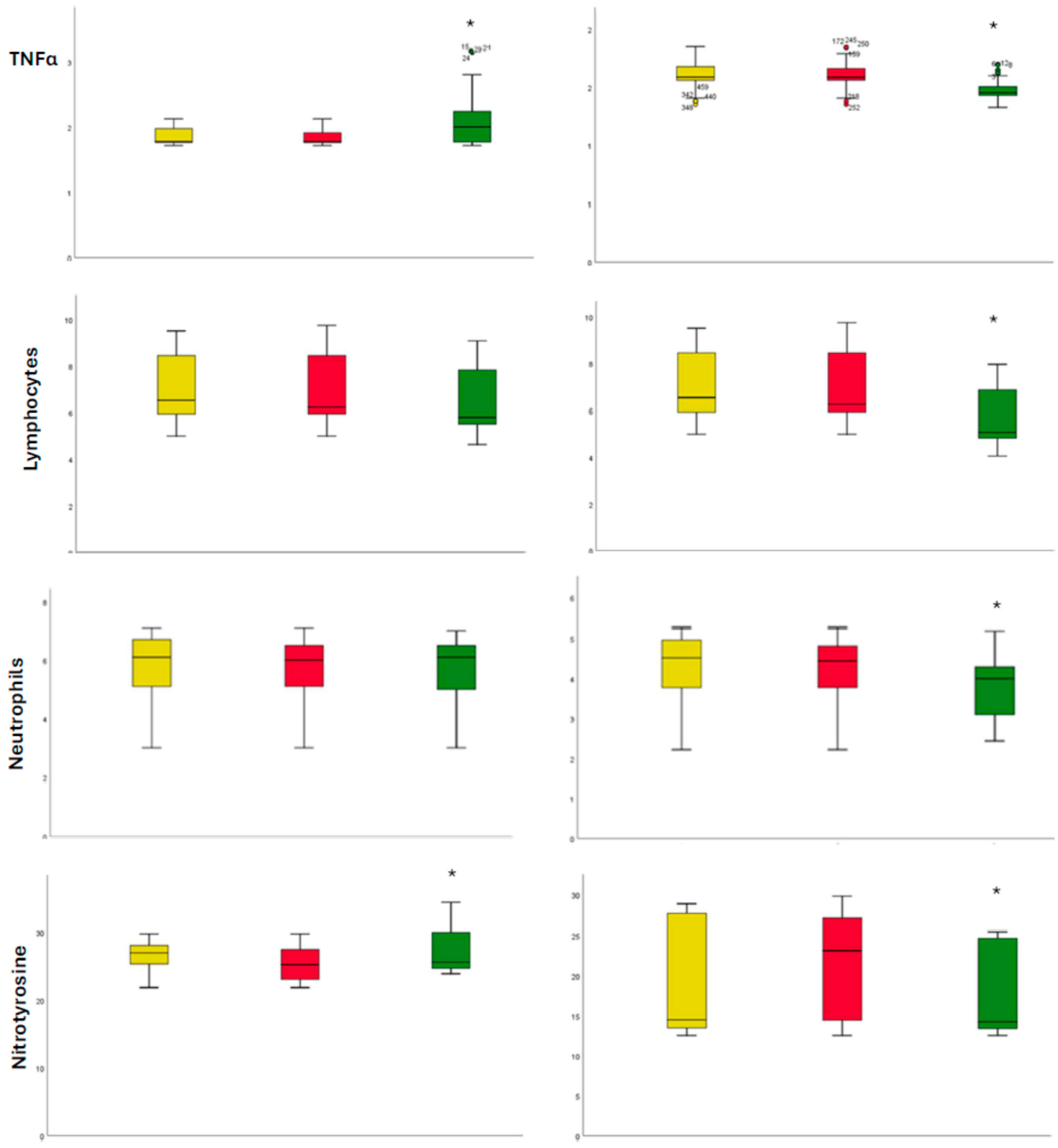
| Baseline | 1 Year of Follow-Up | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | SGLT2i (n 220) | GLP1-RAs (n 193) | GLP1-RAs/SGLT2i (n 69) | SGLT2i (n 220) | GLP1-RAs (n 193) | GLP1-RAs/SGLT2i (n 69) |
| Age (years) | 53.9 ± 8.4 | 54.5 ± 8.1 | 53.8 ± 8.0 | / | / | / |
| Male, n (%) | 142 (64.5) | 119 (61.7) | 42 (60.9) | / | / | / |
| White | 210 (95.4) | 182 (94.3) | 66 (95.6) | / | / | / |
| Black or African American | 10 (4.5) | 11 (5.7) | 3 (4.4) | / | / | / |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 26.6 ± 5.95 | 26.1 ± 5.62 | 25.5 ± 5.44 | 26.4 ± 5.47 | 26.0 ±5.58 | 25.2 ± 5.3 |
| Waist to hip ratio | 0.89 ± 0.06 | 0.88 ± 0.07 | 0.88 ± 0.05 | 0.91 ± 0.07 | 0.90 ± 0.07 | 0.90 ± 0.06 |
| Heart rate, bpm | 75 ± 7 | 76 ± 6 | 77 ± 7 | 73 ± 6 | 74 ± 7 | 70 ± 7 * |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 124 (56.4) | 127 (65.8) | 41 (59.4) | 130 (59.1) | 129 (66.8) | 47 (68.1) |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 77 (35%) | 83 (43.0) | 38 (55.1) | 99 (45) | 103 (53.4) | 41 (59.4) |
| Ischemic heart disease, n (%) | 130 (59.1) | 120 (62.2) | 44 (63.8) | 137 (62.3) | 127 (65.8) | 45 (65.2) |
| Thyroid disorder, n (%) disorders | 45 (20.4) | 37 (19.2) | 15 (21.7) | 49 (22.3) | 45 (23.3) | 17 (24.6) |
| CKD stage 3 | 23 (10.5) | 18 (9.3) | 7 (10.1) | 27 (12.3) | 29 (15.0) | 9 (13.0) |
| CKD stage 4 | 5 (2.3) | 4 (2.1) | 1 (1.5) | 6 (2.7) | 5 (2.6) | 2 (2.9) |
| Laboratory values | ||||||
| HbA1c (%) | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 6.6 ± 0.3 | 8.0 ± 0.4 * | 6.4 ± 0.3 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 7.2 ± 0.4 * |
| Glycemia, mg/dL | 140 ± 25 | 142 ± 27 | 155 ± 30 * | 130 ± 22 | 132 ± 23 | 145 ± 28 * |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 68.9 ± 21.3 | 70.8 ± 20.8 | 61.6 ± 21.7 * | 76.8 ± 27.6 | 72.4 ± 28.1 | 72.3 ± 33.3 |
| LDL, mg/dL | 72.4 ± 21.4 | 74.1 ± 21.0 | 76.2 ± 18.1 | 65.9 ± 19.4 | 67.3 ± 19.0 | 69.4 ± 16.3 |
| BNP, pg/mL | 66.9 ± 46.5 | 68.2 ± 48.3 | 70.1 ± 70.1 | 56.3 ± 38.1 | 58.5 ± 39.7 | 53.3 ± 39.6 |
| LVEF (%) | 55.1 ± 5.2 | 55.5 ± 5.0 | 54.2 ± 5.2 | 55.8 ± 4.8 | 56.4 ± 5.4 | 56.4 ± 5.2 |
| left atrial volume, mL | 35.5 ± 8.4 | 35.7 ± 8.5 | 36.2 ± 9.6 | 34.4 ± 7.8 | 34.1 ± 7.3 | 34.3 ± 6.8 |
| Drug therapy | ||||||
| Amiodaron, n (%) | 29 (13.2) | 23 (11.9) | 10 (14.5) | 22 (10) | 19 (9.8) | 6 (8.7) |
| Flecainide, n (%) | 162 (73.6) | 149 (77.2) | 54 (78.3) | 109 (49.5) | 101 (52.3) | 24 (34.8) * |
| Beta blockers, n (%) | 153 (69.5) | 144 (74.6) | 48 (69.6) | 162 (73.6) | 150 (77.7) | 51 (73.9) |
| Calcium blockers, n (%) | 12 (5.5) | 9 (4.8) | 3 (4.3) | 19 (8.6) | 18 (9.6) | 5 (7.2) |
| Anticoagulants, n (%) | 198 (90) | 181 (93.8) | 63 (91.3) | 205 (93.2) | 184 (95.3) | 65 (94.2) |
| Anti-platelets, n (%) | 98 (44.5) | 90 (46.6) | 34 (49.3) | 106 (48.2) | 94 (48.7) | 37 (53.6) |
| Metformin, n (%) | 119 (54.1) | 99 (51.3) | 40 (57.9) | 134 (60.9) | 112 (58) | 44 (63.8) |
| Insulin, n (%) | 75 (34.1) | 57 (29.5) | 24 (34.8) | 84 (38.2) | 64 (33.2) | 28 (40.6) |
| Digitalis, n (%) | 43 (19.5) | 40 (20.7) | 16 (23.2) | 49 (22.3) | 46 (23.8) | 21 (30.4) |
| ACEi, n (%) | 51 (23.2) | 50 (25.9) | 12 (17.4) | 55 (25) | 54 (28) | 16 (23.2) |
| ARBs, n (%) | 63 (28.6) | 62 (32.1) | 24 (34.8) | 74 (33.6) | 72 (37.3) | 27 (39.1) |
| ARNI, n (%) | 17 (7.7) | 18 (9.3) | 8 (11.6) | 25 (11.4) | 26 (13.4) | 10 (14.4) |
| Dihydropyridines, n (%) | 22 (10) | 19 (9.8) | 7 (10.1) | 29 (13.2) | 28 (14.5) | 9 (13.0) |
| Loop diuretics, n (%) | 81 (36.8) | 75 (38.9) | 30 (435.5) | 89 (40.5) | 90 (46.6) | 30 (43.5) |
| Thiazides, n (%) | 34 (15.5) | 32 (16.6) | 15 (21.7) | 40 (18.2) | 37 (19.2) | 16 (23.2) |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Factor | HR | CI 95% | p Value | HR | CI 95% | p Value |
| Age | 1.001 | 0.990–1.012 | 0.897 | 0.999 | 0.986–1.012 | 0.887 |
| BNP | 1.109 | 1.060–1.220 | 0.040 * | 1.040 | 1.001–1.080 | 0.006 * |
| CRP | 1.451 | 1.176–1.734 | 0.038 * | 1.223 | 1.143–1.309 | 0.001 * |
| eGFR | 1.006 | 0.999–1.014 | 0.095 | 0.999 | 0.990–1.008 | 0.795 |
| Flecainide | 0.884 | 0.614–1.273 | 0.507 | 1.118 | 0.729–1.714 | 0.610 |
| Gender | 1.154 | 0.825–1.616 | 0.402 | 1.014 | 0.696–1.477 | 0.943 |
| Hb1Ac | 1.154 | 1.074–1.441 | 0.050 * | 1.010 | 0.909–1.122 | 0.857 |
| Heart rate | 0.997 | 0.974–1.022 | 0.831 | 1.016 | 0.988–1.046 | 0.267 |
| Hypertension | 0.681 | 0.494–0.938 | 0.019 * | 0.934 | 0.619–1.410 | 0.747 |
| Lymphocytes | 1.387 | 0.733–1.956 | 0.090 | 1.086 | 0.931–1.266 | 0.296 |
| LVEF | 0.993 | 0.979–1.007 | 0.324 | 0.994 | 0.978–1.010 | 0.428 |
| SGLT2i/GLP-1RAs | 0.504 | 0.285–0.890 | 0.018 * | 0.443 | 0.231–0.847 | 0.014 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sardu, C.; Marfella, R. Effects of Combined Therapy with SGLT2i and GLP-1RAs on Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation in Diabetic Cohorts: One-Year Outcomes from Continuous Monitoring. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199285
Sardu C, Marfella R. Effects of Combined Therapy with SGLT2i and GLP-1RAs on Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation in Diabetic Cohorts: One-Year Outcomes from Continuous Monitoring. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199285
Chicago/Turabian StyleSardu, Celestino, and Raffaele Marfella. 2025. "Effects of Combined Therapy with SGLT2i and GLP-1RAs on Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation in Diabetic Cohorts: One-Year Outcomes from Continuous Monitoring" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199285
APA StyleSardu, C., & Marfella, R. (2025). Effects of Combined Therapy with SGLT2i and GLP-1RAs on Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Catheter Ablation in Diabetic Cohorts: One-Year Outcomes from Continuous Monitoring. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199285







