Molecular Biomarkers for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease and the Complementary Role of Engineered Nanomaterials: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
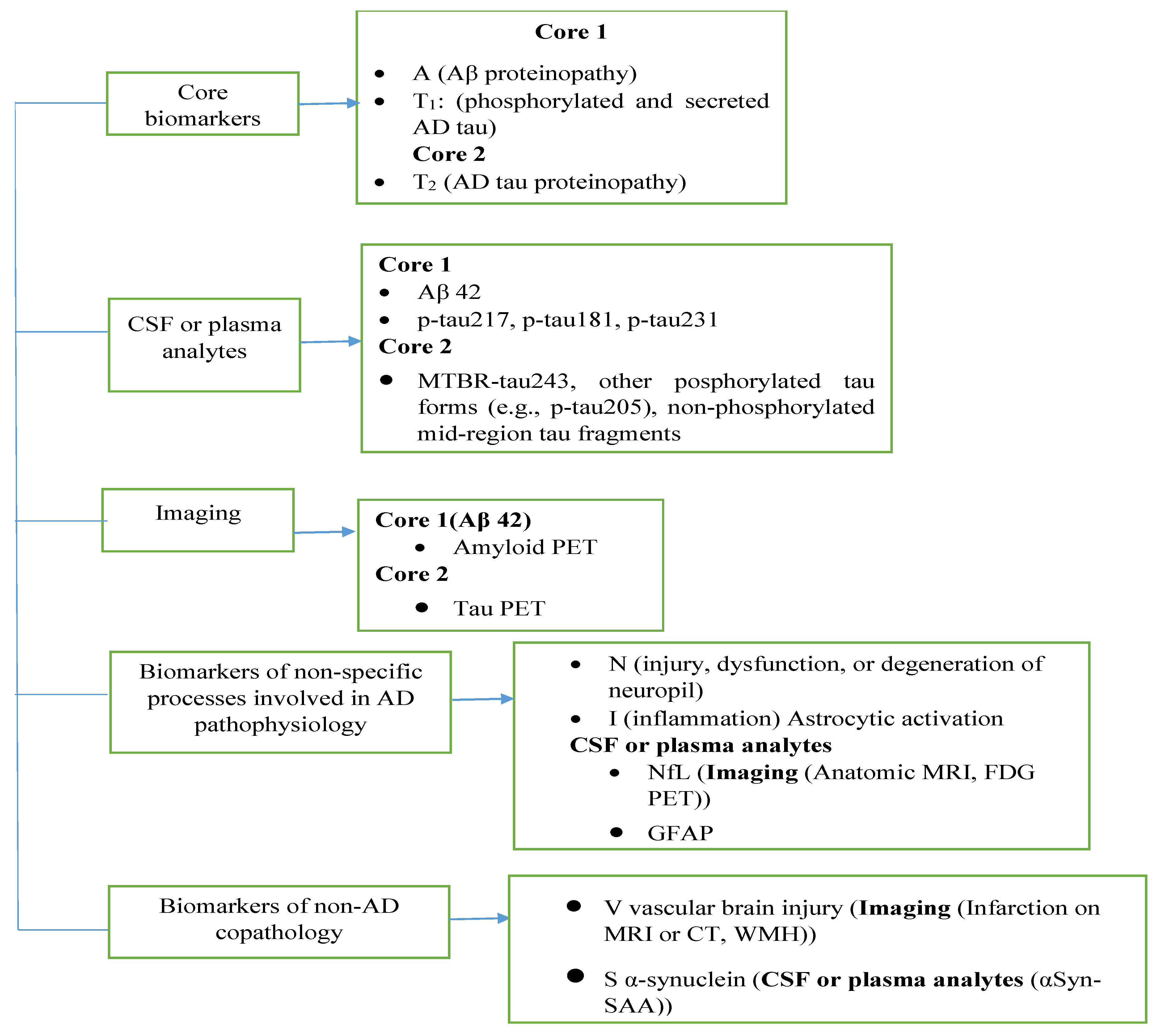
1.1. Overview of AD Biomarkers
1.1.1. Core AD Biomarkers (AD Neuropathologic Change-ADNCP)
- Amyloid-β (Aβ):
- Tau protein:
- Phosphorylated tau (p-tau):
1.1.2. Emerging and Supporting Biomarkers
- Neurofilament Light Chain (NFL):
- Metal ions:
- Apolipoprotein E (ApoE):
1.1.3. Non-Specific or Non-AD Co-Pathology Biomarkers
- Lactoferrin (LF):
- Cortisol:
1.1.4. Diagnostics Criteria and Techniques
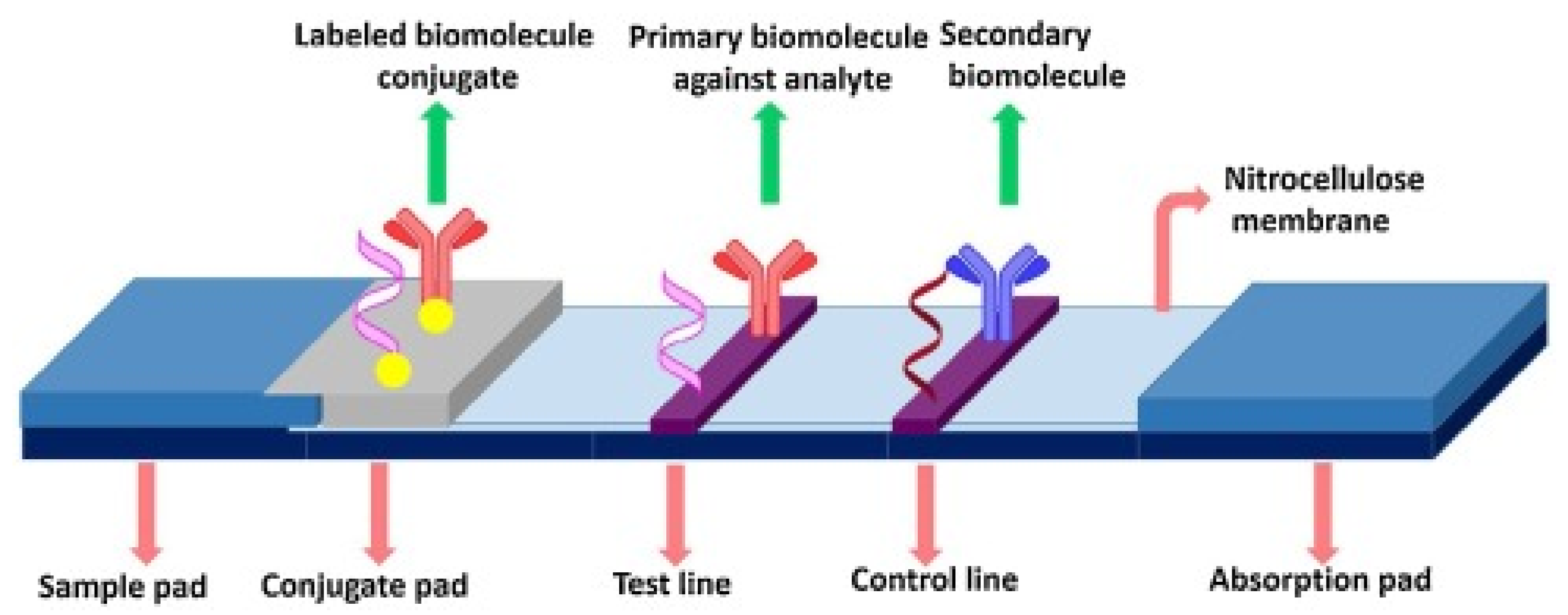
1.2. Biomarker Related Diagnostic Techniques
1.3. Advanced AD Diagnostic Methods
2. Research Method
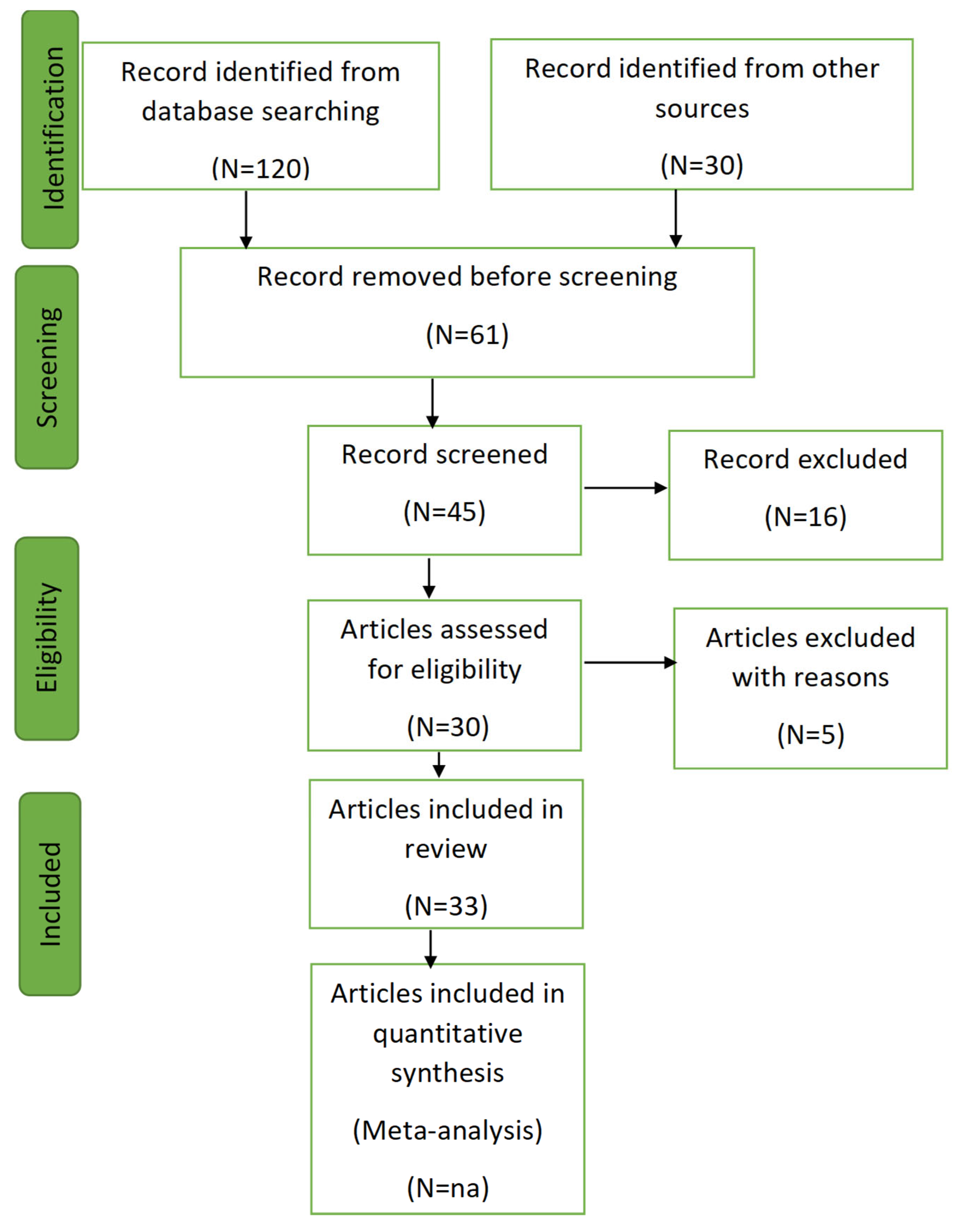
2.1. Search Procedures
2.2. Study Selection and Quality Assessment
2.3. Risk of Bias
- Including only peer-reviewed articles to reduce publication bias;
- Applying strictly the inclusion/exclusion criteria to minimize selection bias;
- Conducting independent duplicate screening and quality assessment to reduce reviewer bias.
2.4. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- Studies published between January 2021 and September 2025 to ensure the inclusion of the most recent advances.
- Articles reporting original research on diagnostic biomarkers or techniques for AD.
- Provided quantitative outcomes, particularly specifying the limits of detection (LOD) for at least one AD biomarkers.
- Articles published in peer-reviewed journals and indexed in at least one major database (e.g., PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus).
- Available in full-text format in English language.
- Published in languages other than English;
- Limited to abstracts only, without access to full text;
- Non-original research articles such as meta-analyses, conference abstract, or editorials, etc.;
- Studies focusing on diseases other than AD or that did not evaluate diagnostics biomarkers relevant to AD;
- Articles that did not provide measurable analytical performance (e.g., LOD, sensitivity, or specificity).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Research Questions
- What is the global distribution of AD across populations by age and geographic regions?
- What emerging biomarkers are being explored for the diagnosis of AD?
- What advancements in diagnostic techniques for AD have been developed recently?
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Screening Process
- Initial Filtering: Titles and abstracts were reviewed to remove irrelevant articles.
- Categorization: Articles were classified into:
- Primary Articles: Reporting original experimental or observational data.
- Methods Papers: Describing or evaluating techniques for biomarker detection.
3.2. Data Extraction and Reporting
3.3. Comparison of Nanoparticles and Biomarkers
3.4. Comparison of the Performance of the Applied Techniques and Nanoparticles with Respect to Years
3.5. Comparison of the Performance of AD Biomarkers and Nanoparticles Size (nm)
3.6. Global Burden and Epidemiological Trends of AD
4. Challenges and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, S.; Xiao, C.; Li, R.; Lan, Y.; Gong, C.; Feng, C.; Qi, H.; Lin, Y.; Qin, C. The global, regional, and national burdens of dementia in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2021: A trend analysis based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Medicine 2025, 104, e41836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stouffer, K.M.; Grande, X.; Düzel, E.; Johansson, M.; Creese, B.; Witter, M.P.; Miller, M.; Wisse, L.E.M.; Berron, D. Amidst an amygdala renaissance in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2024, 147, 816–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, F.; Safiri, S.; Shamekh, A.; Ebrahimi, A.; Sullman, M.J.; Kolahi, A.-A. Prevalence, deaths and disability-adjusted life years due to Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias in Middle East and North Africa, 1990–2021. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Jiang, C.; Liu, X.; Shi, W.; Bai, J.; Mubarik, S.; Wang, F. Epidemiological and sociodemographic transitions in the global burden and risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias: A secondary analysis of GBD 2021. Int. J. Equity Health 2025, 24, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Jiménez, J.L.; Cantón-Habas, V.; Carrera-González, M.P.; Rich-Ruiz, M.; Ventura, S. A deep learning model for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis based on patient clinical records. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 169, 107814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, C.; Prajapati, B.G.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.; Maheshwari, S. Dendrimers in the management of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Strateg. 2024, 442, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.B.; Kwon, S.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, N.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, S.H. The molecular mechanisms of neuro inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease, the consequence of neural cell death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Xin, Y.; Wang, B. A hybrid multimodal machine learning model for Detecting Alzheimer’s disease. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 170, 108035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcombe, E.A.; Camats-Perna, J.; Silva, M.L.; Valmas, N.; Huat, T.J.; Medeiros, R. Inflammation: The link between comorbidities, genetics, and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflam. 2018, 15, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, J.A.; Potashkin, J.A. The impact of disease comorbidities in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 631770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, L.; Masliah, E. Molecular mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, R12–R20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala-Cunill, A.; Guilarte, M.; Cardona, V. Phenotypes, endotypes and biomarkers in anaphylaxis: Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 18, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascoal, T.A.; Aguzzoli, C.S.; Lussier, F.Z.; Crivelli, L.; Suemoto, C.K.; Fortea, J.; Rosa-Neto, P.; Zimmer, E.R.; Ferreira, P.C.; Bellaver, B. Insights into the use of biomarkers in clinical trials in Alzheimer’s disease. eBioMedicine 2024, 108, 105322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, B.; Ouyang, Z.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, T.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y. Development and validation of machine learning models with blood-based digital biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis: A multicohort diagnostic study. eClinicalMedicine 2025, 81, 103142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milà-Alomà, M.; Ashton, N.J.; Shekari, M.; Salvadó, G.; Ortiz-Romero, P.; Montoliu-Gaya, L.; Benedet, A.L.; Karikari, T.K.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Vanmechelen, E.; et al. Plasma p-tau231 and p- tau217 as state markers of amyloid-β pathology in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1797–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.L.; Tong, G.; Ballard, C. Treatment combinations for Alzheimer’s disease: Current and future pharmacotherapy options. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 67, 779–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, X.; He, Y. Electrochemical Technology for the Detection of Tau Proteins as a Biomarker of Alzheimer’s Disease in Blood. Biosensors 2025, 15, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzavinos, V.; Alexiou, A. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2017, 14, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, N.N.; Wang, H.; Guo, J.; Sharma, M.; Luo, W. The complexity of tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 705, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.A.; Najm, L.; Ladouceur, L.; Ebrahimi, F.; Shakeri, A.; Al-Jabouri, N.; Didar, T.F.; Dellinger, K. Functional nanomaterials for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Recent progress and future perspectives. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2302673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnov, D.S.; Ashton, N.J.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Simrén, J.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Karikari, T.K.; Hiniker, A.; Rissman, R.A.; Salmon, D.P.; et al. Plasma biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease in relation to neuropathology and cognitive change. Acta Neuropathol. 2022, 143, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Su, X.; Chen, M.; Xie, Y.; Li, M. Self-calibrating surface-enhanced Raman scattering-lateral flow immunoassay for determination of amyloid-β biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 245, 115840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurston, R.C.; Maki, P.; Chang, Y.; Wu, M.; Aizenstein, H.J.; Derby, C.A.; Karikari, T.K. Menopausal vasomotor symptoms and plasma Alzheimer disease biomarkers. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2024, 230, 342. e341–342.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangare, S.; Patil, P. Poly(allylamine) coated layer-by-layer assembly decorated 2D carbon backbone for highly sensitive and selective detection of Tau-441 using surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1271, 341474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Z.; Grajales, S.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C.; Nair, M. β-amyloid biomarker detection for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Anal. Test. 2017, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lista, S.; Mapstone, M.; Caraci, F.; Emanuele, E.; López-Ortiz, S.; Martín-Hernández, J.; Triaca, V.; Imbimbo, C.; Gabelle, A.; Mielke, M.M.; et al. A critical appraisal of blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 96, 102290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, S.; Lisi, S.; Ravelet, C.; Peyrin, E.; Minunni, M. Detecting Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers: From antibodies to new bio-mimetic receptors and their application to established and emerging bioanalytical platforms—A critical review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 940, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, C.C.; Antoniolli, G.; Barros, W.P.; Almeida, W.P. Acylhydrazones derived from isonicotinic acid: Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation against Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1313, 138631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Sarkar, B.; Rahman, M.T.; Jin, G.J.; Uddin, M.J.; Bhuiyan, N.H.; Shim, J.S. Development of a highly sensitive CNT-metal graphene hybrid nano-IDA electrochemical biosensor for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomater. Sci. 2024, 12, 5203–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, E.H.; La Joie, R.; Strom, A.; Fonseca, C.; Iaccarino, L.; Wolf, A.; Spina, S.; Allen, I.E.; Cobigo, Y.; Heuer, H.; et al. Plasma phosphorylated tau 217 and phosphorylated tau 181 as biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration: A retrospective diagnostic performance study. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, N.J.; Benedet, A.L.; Pascoal, T.A.; Karikari, T.K.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J. Cerebrospinal fluid p-tau231 as an early indicator of emerging pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. eBioMedicine 2022, 76, 103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnov, D.S.; Ashton, N.J.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, Z.Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, T. Printed biosensors for the detection of Alzheimer’s disease based on blood biomarkers. J. Anal. Test. 2024, 8, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.K.; Lee, J.; Nguyen, A.H.; Sim, S.J. Label-free detection of ApoE4-mediated β-amyloid aggregation on single nanoparticle uncovering Alzheimer’s disease. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 72, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troutwine, B.R.; Hamid, L.; Lysaker, C.R.; Strope, T.A.; Wilkins, H.M. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, C.; Zhang, J. Lactoferrin and its detection methods: A review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouanes, S.; Popp, J. High cortisol and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: A review of the literature. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, B.T.; Phelps, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Bigio, E.H.; Cairns, N.J.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dickson, D.W.; Duyckaerts, C.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; et al. National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2012, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschio, C.; Ni, R. Amyloid and tau positron emission tomography imaging in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 838034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, S.; Jönhagen, M.E.; Cselényi, Z.; Halldin, C.; Julin, P.; Olsson, H.; Freund-Levi, Y.; Andersson, J.; Varnäs, K.; Svensson, S.; et al. Detection of amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease with positron emission tomography using [11 C] AZD2184. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 36, 1859–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.; Philpot, M.P.; Costa, D.C.; Ell, P.J.; Levy, R. The investigation of Alzheimer’s disease with single photon emission tomography. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1989, 52, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buciuc, M.; Botha, H.; Murray, M.E.; Schwarz, C.G.; Senjem, M.L.; Jones, D.T.; Knopman, D.S.; Boeve, B.F.; Petersen, R.C.; Jack, C.R.; et al. Utility of FDG-PET in diagnosis of Alzheimer-related TDP-43 proteinopathy. Neurology 2020, 95, e23–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierenga, C.E.; Bondi, M.W. Use of functional magnetic resonance imaging in the early identification of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2007, 17, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Jobst, K.; Szatmari, M.; Jaskowski, A.; King, E.; Molyneux, A.; Esiri, M.; McDonald, B.; Wald, N. Detection in life of confirmed Alzheimer’s disease using a simple measurement of medial temporal lobe atrophy by computed tomography. Lancet 1992, 340, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R.; Andrews, J.S.; Beach, T.G.; Buracchio, T.; Dunn, B.; Graf, A.; Hansson, O.; Ho, C.; Jagust, W.; McDade, E.; et al. Revised criteria for diagnosis and staging of Alzheimer’s disease: Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 5143–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcolea, D.; Beeri, M.S.; Rojas, J.C.; Gardner, R.C.; Lleó, A. Blood biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases: Implications for the clinical neurologist. Neurology 2023, 101, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.K.; Shepelytskyi, Y.; Grynko, V.; Albert, M.S. Molecular imaging of fluorinated probes for tau protein and amyloid-β detection. Molecules 2020, 25, 3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, P.; Xie, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, K.; Giannetti, A.; et al. Ultrasensitive and Multiple Biomarker Discrimination for Alzheimer’s Disease via Plasmonic & Microfluidic Sensing Technologies. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2308783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yuan, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, W.; Dong, H.; Chu, Z. Freestanding Nanofiber Assembled Aptasensor for Precisely and Ultrafast Electrochemical Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2304355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, P.; Vatankhahan, H.; Zare-Hoseinabadi, A.; Ferdosi, F.; Ehtiati, S.; Heidari, P.; Dorostgou, Z.; Movahedpour, A.; Baktash, A.; Rajabivahid, M.; et al. Electrochemical biosensors for early detection of breast cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2025, 564, 119923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourian, H.; Parrilla, M.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Montiel, N.F.; Barfidokht, A.; Echelpoel, R.V.; Wael, K.D.; Wang, J. Wearable Electrochemical Sensors for the Monitoring and Screening of Drugs. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2679–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, K.Y.; Reddy, K.K.; Khorshed, A.; Kumar, V.S.; Mishra, R.K. Electrochemical diagnostics of infectious viral diseases: Trends and challenges. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 180, 113112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Song, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Yu, J. Robust and Universal SERS Sensing Platform for Multiplexed Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Core Biomarkers Using PAapt-AuNPs Conjugates. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, J.; Jimenez de Aberasturi, D.; Aizpurua, J.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Auguié, B.; Baumberg, J.J.; Bazan, G.C.; Bell, S.E.J.; Boisen, A.; Brolo, A.G.; et al. Present and Future of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 28–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, G.; Pan, J. Detection of Aβ oligomers in early Alzheimer’s disease diagnose by in vivo NIR-II fluorescence imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Fan, J.; Du, J.; Peng, X. Fluorescent Probes for Sensing and Imaging within Specific Cellular Organelles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruedas-Rama, M.J.; Walters, J.D.; Orte, A.; Hall, E.A.H. Fluorescent nanoparticles for intracellular sensing: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 751, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusbu, F.Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, K. Thioflavin T as a fluorescence probe for biosensing applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 109, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederiksen, H.R.; Holst, B.; Mau-Holzmann, U.A.; Freude, K.; Schmid, B. Generation of two isogenic iPSC lines with either a heterozygous or a homozygous E280A mutation in the PSEN1 gene. Stem Cell Res. 2019, 35, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulatsky, M.I.; Stepanenko, O.V.; Stepanenko, O.V.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Turoverov, K.K.; Sulatskaya, A.I. Prediction of the Feasibility of Using the ≪Gold Standard≫ Thioflavin T to Detect Amyloid Fibril in Acidic Media. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 2158–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, H.; Liu, L.; Xu, M. Simple Colorimetric Detection of Amyloid β-peptide (1–40) basedon Aggregation of Gold Nanoparticles in the Presence of Copper Ions. Small 2015, 11, 2144–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putri, L.A.; Prabowo, Y.D.; Dewi, D.M.M.; Mumtazah, Z.; Adila, F.P.; Fadillah, G.; Amrillah, T.; Triyana, K.; Nugroho, F.A.A.; Wasisto, H.S. Review of Noble Metal Nanoparticle-Based Colorimetric Sensors for Food Safety Monitoring. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 19821–19853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandey, K.; Shrivas, K.; Sharma, A.; Kant, T.; Tejwani, A. Nanomaterial-enabled portable paper-based colorimetric and fluorometric devices: Progress in point-of-care diagnosis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 514, 215919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, E.; Pradhan, N. Gold nanoparticles as efficient sensors in colorimetric detection of toxic metal ions: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 888–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezabakhsh, R.; Rahbarghazi, A.; Fathi, F. Surface plasmon resonance biosensors for detection of Alzheimer’s biomarkers; an effective step in early and accurate diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 167, 112511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kashefi-Kheyrabadi, L.; Joung, Y.; Kim, K.; Dang, H.; Chavan, S.G.; Lee, M.H.; Choo, J. Recent advances in sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral flow assay platforms for point-of-care diagnostics of infectious diseases. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; You, M.; Li, S.; Hu, J.; Liu, C.; Gong, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, F. Paper-based point-of-care immunoassays: Recent advances and emerging trends. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 39, 107442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, E.; Bingol, H.; Zor, E. Lateral flow assays for detection of disease biomarkers. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 225, 115206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadır, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Lateral flow assays: Principles, designs and labels. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Fei, R.; Lu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Wu, X.; Dong, J.; Meng, D.; Ge, Q.; Zhao, X. Ultrasensitive detection of multiple Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers by SERS-LFA. Analyst 2022, 147, 4124–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazaca, L.C.; Moreto, J.R.; Martín, A.; Tehrani, F.; Wang, J.; Zucolotto, V. Colorimetric paper-based immunosensor for simultaneous determination of fetuin B and clusterin toward early Alzheimer’s diagnosis. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13325–13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Hang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, K.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, L. Low background self-primer EXPAR coupled with colorimetric and lateral flow assay for rapid and sensitive point-of-care detection of miRNA. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 399, 134856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Song, S.; Park, S.; Joo, C. Recent advances in high-sensitivity detection methods for paper-based lateral-flow assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 152, 112015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltzov, E.; Guttel, S.; Kei, A.L.Y.; Sinawang, P.D.; Ionescu, R.E.; Marks, R.S. Lateral Flow Immunoassays from Paper Strip to Smartphone Technology. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 2116–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, M.; Bond, R.; Robertson, L.J.; Moore, J.; Kowalczyk, A.; Price, R.; Burns, W.; Nesbit, M.A.; McLaughlin, J.; Moore, T. User experience analysis of AbC-19 Rapid Test via lateral flow immunoassays for self-administrated SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, L.; de la Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Pons, J.; Merkoçi, A. Alzheimer disease biomarker detection through electrocatalytic water oxidation induced by iridium oxide nanoparticles. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postigo, A.; Marcuello, C.; Verstraeten, W.; Sarasa, S.; Walther, T.; Lostao, A.; Göpfrich, K.; Del Barrio, J.; Hernández-Ainsa, S. Folding and Functionalizing DNA Origami: A Versatile Approach Using a Reactive Polyamine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 3919–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, J.; Mao, H.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Sun, T.; Hui, J.; Ma, G. AuNP/Magnetic Bead-Enhanced Electrochemical Sensor Toward Dual Saliva Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seufert, B.; Thomas, S.; Takshi, A. String-Shaped Electrodes for Aβ42 Detection Towards Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Sánchez, M.; Miserere, S.; Morales-Narvaez, E.; Merkoçi, A. On-chip magneto-immunoassay for Alzheimer’s biomarker electrochemical detection by using quantum dots as labels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, W.W.W.; Angela, S.; Le, T.N.; Fadhilah, G.; Chiang, W.H.; Chang, H.C. Diagnostics of Alzheimer’s disease using fluorescent nanodiamond-based spin-enhanced lateral flow immunoassay. Microchem. J. 2024, 205, 111315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhou, X.; Shi, G.; Yu, Y. Molybdenum disulfide nanosheets-based fluorescent “off-to-on” problem for targeted monitoring and inhibition of β-amyloid oligomers. Analyst 2020, 145, 6369–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, M.; Gonzalez Orive, A.; Grundmeier, G.; Keller, A. Effect of DNA Origami Nanostructures on hIAPP Aggregation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Luo, Q.; Luo, H. Nanozyme sensor array based on manganese dioxide for the distinction between multiple amyloid β peptides and their dynamic aggregation process. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 199, 113881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordón Pidal, J.M.; Moreno-Guzmán, M.; Montero-Calle, A.; Barderas, R.; López, M.Á.; Escarpa, A. Dual on-the-move electrochemical immunoassays for the simultaneous determination of amyloid-β (1−42) and Tau in Alzheimer’s patient samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 423, 136785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ren, P.; Zhang, F.; Cao, J.; Li, J.; Chai, X.; Ji, J.; Qin, S.; Wang, Q. Peptide-based electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of amyloid-β oligomer with laccase-mimicking nanozyme assemblies as a signal amplifier. Microche. J. 2025, 214, 114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Shu, Q.; Zhang, N.; Yan, C.; Niu, H.; Li, H.; Hu, X. Electrochemical Immunosensor for the Sensitive Detection of Alzheimer’s Biomarker Amyloid-β (1–42) Using the Heme- amyloid-β (1–42) Complex as the Signal Source. Electroanalysis 2022, 34, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, T.T.; Takamura, Y.; Tamiya, E.; Vestergaard, M.D.C. Modified screen printed electrode for development of a highly sensitive label-free impedimetric immunosensor to detect amyloid beta peptides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 892, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Said, W.A.; Abd El-Hameed, K.; Abo El-Maali, N.; Sayyed, H.G. Label-free Electrochemical Sensor for Ex-vivo Monitoring of Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarker. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, T. Integrated Ultrasound-Enrichment and Machine Learning in Colorimetric Lateral Flow Assay for Accurate and Sensitive Clinical Alzheimer’s Biomarker Diagnosis. Adv. Sci 2024, 11, 2406196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Su, Y.; Liang, X.; Cao, K.; Luo, Q.; Luo, H. Ultrasensitive and point-of-care detection of plasma phosphorylated tau in Alzheimer’s disease using colorimetric and surface-enhanced Raman scattering dual-readout lateral flow assay. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 7459–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Shi, L.; Zhu, X.; Tang, Q.; Wu, M.; Li, B.; Liu, W.; Jin, Y. Entropy-driven catalysis-based lateral flow assay for sensitive detection of Alzheimer’s-associated MicroRNA. Talanta 2024, 271, 125656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalirirad, S.; Steckl, A.J. Lateral flow assay using aptamer-based sensing for on-site detection of dopamine in urine. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 596, 113637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q.; Xu, T. VG@nAu-based fluorescent biosensor for grading Alzheimer’s disease by detecting P-tau181 protein in clinical samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1340, 343654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.-F.; Chen, B.-C.; Chen, B.; Li, X.-J.; Liao, H.-L.; Huang, H.-M.; Guo, Z.-J.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Wu, L. Detection of Aβ oligomers based on magnetic-field-assisted separation of aptamer-functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and BaYF5:Yb, Er nanoparticles as upconversion fluorescence labels. Talanta 2017, 170, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, L.M.T.; Cho, S. Fluorescent aptasensor and colorimetric aptablot for p-tau231 detection: Toward early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shi, J.; Zhai, W.; Jiang, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Wu, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Construction of a bifunctional near-infrared fluorescent probe for visualization of copper (II) ions and amyloid-β aggregates in Alzheimer’s disease. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 423, 136767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.F.; Bao, G.-M.; Qiu, M.; Xia, Y.-F.; Li, W.; Tao, Y.-Q.; Liu, S.-Y.; Li, S.-H.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Highly selective and sensitive fluorescent biosensor for the detection of serotonin and its metabolite by Eu3+ Doped Metal-Organic framework. Chem. Eng. 2022, 442, 136272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chang, Y.; Yu, J.; Jiang, M.; Xia, N. Two-in-one polydopamine nanospheres for fluorescent determination of beta-amyloid oligomers and inhibitionof beta-amyloid aggregation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 251, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, A.; Tamer, U.; Caykara, T.A. SERS-based sandwich assay for ultrasensitive and selective detection of Alzheimer’s tau protein. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3001–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Ma, S.; Chang, M.; Zhang, X. Ultra-sensitive SERS detection of Aβ 1-42 for Alzheimer’s disease using graphene oxide/gold nanohybrids. Vib. Spectrosc. 2023, 129, 103614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.K.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhorabe, F.; Yan, J.; Gu, Y.; Wang, S.; Yi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M. A buoyant plasmonic microbubble-based SERS sensing platform for amyloid-beta protein detection in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2025, 13, 8883–8896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, N.; Yang, X.; Ling, G.; Zhang, P. The roles of gold nanoparticles in the detection of amyloid-β peptide for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Colloid Interface Sci 2022, 46, 100579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Jeon, C.S.; Kim, K.B.; Kim, H.J.; Pyun, S.H.; Park, Y.M. Quantitative detection of dopamine in human serum with surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) of constrained vibrational mode. Talanta 2023, 260, 124590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Xie, D.; Cheng, L.; Wang, P.; Zeng, Q.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y. In situ monitoring the aggregation dynamics of amyloid-β protein Aβ42 in physiological media via a Raman-based frequency shift method. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremina, O.E.; Yarenkov, N.R.; Bikbaeva, G.I.; Kapitanova, O.O.; Samodelova, M.V.; Shekhovtsova, T.N.; Kolesnikov, I.E.; Syuy, A.V.; Arsenin, A.V.; Volkov, V.S.; et al. Silver nanoparticle-based SERS sensors for sensitive detection of amyloid-βaggregates in biological fluids. Talanta 2024, 266, 124970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Liu, W.; Herrmann, A.K.; Haubold, D.; Holzschuh, M.; Simon, F.; Eychmüller, A. Simple and sensitive colorimetric detection of dopamine based on assembly of cyclodextrin-modified Au nanoparticles. Small 2016, 12, 2439–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.T.; Correia, B.P.; Sousa, M.P.; Sales, G.F. Colorimetric cellulose-based test-strip for rapid detection of amyloid β-42. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, F.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R.; Mahmoudi, M. Label-free detection of β-amyloid peptides (Aβ40 and Aβ42): A colorimetric sensor array for plasma monitoring of Alzheimer’s disease. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 6361–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, W.; Tian, Y.; He, S.; Zheng, W.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, X. A highly sensitive gold-nanoparticle-based assay for acetylcholinesterase in cerebrospinal fluid of transgenic mice with Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria-Lopez, J.A.; González, H.M.; Léger, G.C. Chapter 13-Alzheimer’s disease. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 3rd ed.; DeKosky, S.T., Asthana, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 167, pp. 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-González, D.; Merkoçi, A. Nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Carvalho, L.F.d.C.e.S.d.; Casey, A.; Nogueira, M.S.; Byrne, H.J. Surface-Enhanced Raman Analysis of Uric Acid and Hypoxanthine Analysis in Fractionated Bodily Fluids. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Harten, A.C.; Wiste, H.J.; Weigand, S.D.; Mielke, M.M.; Kremers, W.K.; Eichenlaub, U.; Dyer, R.B.; Algeciras-Schimnich, A.; Knopman, D.S.; Jack, C.R., Jr. Detection of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid beta 1-42, p-tau, and t-tau assays. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 18, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, S.; Delaby, C.; Boursier, G.; Catteau, C.; Ginestet, N.; Tiers, L.; Maceski, A.; Navucet, S.; Paquet, C.; Dumurgier, J. Relevance of Aβ42/40 ratio for detection of Alzheimer disease pathology in clinical routine: The PLMR scale. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmant, L.; Boyer, E.; Gerard, T.; Sleegers, K.; Lhommel, R.; Ivanoiu, A.; Lefèvre, P.; Kienlen-Campard, P.; Hanseeuw, B. Definition of a threshold for the plasma Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio measured by single-molecule array to predict the amyloid status of individuals without dementia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K.; Shaw, L.M.; Stomrud, E.; Mattsson, N.; Toledo, J.B.; Buck, K.; Wahl, S.; Eichenlaub, U.; Lifke, V.; Simon, M. Predicting clinical decline and conversion to Alzheimer’s disease or dementia using novel Elecsys Aβ (1–42), pTau and tTau CSF immunoassays. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, C.I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A. Recent progress in biosensors for environmental monitoring: A review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Neuta, I.; Neumann, F.; Brightmeyer, J.; Ba Tis, T.; Madaboosi, N.; Wei, Q.; Ozcan, A.; Nilsson, M. Smartphone-based clinical diagnostics: Towards democratization of evidence-based health care. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 285, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, E.; Vos, T. Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e105–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaran, K.; Singh, M. Nanomedicine for neurodegenerative disorders: Focus on Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, I.U.; Park, J.S.; Choe, K.; Park, H.Y.; Park, T.J.; Kim, M.O. Overview of a novel osmotin abolishes abnormal metabolic-associated adiponectin mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease: Peripheral and CNS insights. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 100, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrico, A.; Cumba, L.R.; Medina, M.; Engel, T.; Forster, R.J. Ultrasensitive, label-free, electrochemical detection of miRNA-206 in human plasma: A potential biomarker associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Electrochem. Commun. 2024, 162, 107704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Muhammad, M.; Algethami, J.S.; Al-Saidi, H.M.; Almahri, A.; Hassanian, A.A. Synthesis, Characterization and Applications of Schiff Base Chemosensor for Determination of Cr(III) Ions. J. Fluoresc. 2022, 32, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 367–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaire, B.P.; Koronyo, Y.; Fuchs, D.-T.; Shi, H.; Rentsendorj, A.; Danziger, R.; Vit, J.-P.; Mirzaei, N.; Doustar, J.; Sheyn, J.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology in the Retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2024, 101, 101273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Day, C.M.; Abdella, S.; Garg, S. Alzheimer’s disease current therapies, novel drug delivery systems and future directions for better disease management. J. Control Release 2024, 367, 402–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurd, M.D.; Martorell, P.; Delavande, A.; Mullen, K.J.; Langa, K.M. Monetary Costs of Dementia in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Dementia in Australia 2012; AIHW: Bruce, Australia, 2012.
- Jia, L.; Du, Y.; Chu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, F.; Lyu, D.; Zhu, M.; Jiao, H.; Song, Y.; Shi, Y.; et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: A cross-sectional study. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e661–e671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, D.; Cai, Y.; Li, A.; Lan, G.; Sun, P.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Pathophysiology characterization of Alzheimer’s disease in South China’s aging population: For the Greater-Bay-Area Healthy Aging Brain Study (GHABS). Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Kolster, R.; Triana-Baltzer, G.; Janelidze, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Kolb, H.C. Plasma p-tau immunoassays in clinical research for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 21, e14397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Verberk, I.M.; Thijssen, E.H.; Vermunt, L.; Hansson, O.; Zetterberg, H.; van der Flier, W.M.; Mielke, M.M.; Del Campo, M. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: Towards clinical implementation. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthélemy, N.R.; Horie, K.; Sato, C.; Bateman, R.J. Blood plasma phosphorylated-tau isoforms track CNS change in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20200861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.G.; Das, D.; Barman, U.; Saikia, M.J. Early Alzheimer’s disease detection: A review of machine learning techniques for forecasting transition from mild cognitive impairment. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouchehrinia, A.; Piehl, F.; Hillert, J.; Kuhle, J.; Alfredsson, L.; Olsson, T.; Kockum, I. Confounding effect of blood volume and body mass index on blood neurofilament light chain levels. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.A.; Wijesekara, N.; Fraser, P.E.; De Felice, F.G. The link between tau and insulin signaling: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrahatis, A.G.; Skolariki, K.; Krokidis, M.G.; Lazaros, K.; Exarchos, T.P.; Vlamos, P. Revolutionizing the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease through non-invasive biomarkers: The role of artificial intelligence and deep learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Ferrari, M.; Qin, L. Point-of-care technologies for molecular diagnostics using a drop of blood. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, G.H.; Crowe, C.L.; Kothari, M.; Kwon, D.; Manly, J.J.; Turney, I.C.; Valeri, L.; Belsky, D.W. Testing Black-White disparities in biological aging among older adults in the United States: Analysis of DNA-methylation and blood-chemistry methods. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2022, 191, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorito, G.; Pedron, S.; Ochoa-Rosales, C.; McCrory, C.; Polidoro, S.; Zhang, Y.; Dugué, P.-A.; Ratliff, S.; Zhao, W.N.; McKay, G.J. The role of epigenetic clocks in explaining educational inequalities in mortality: A multicohort study and meta-analysis. J. Gerontol. A 2022, 77, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, M.P.; Klopack, E.T.; Crimmins, E.M. Using machine-learning to identify differences in the association between blood-based biomarkers and later life health across race and ethnicity. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2025, 80, glaf153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaštelan, S.; Gverović Antunica, A.; Puzović, V.; Didović Pavičić, A.; Čanović, S.; Kovačević, P.; Vučemilović, P.A.F.; Konjevoda, S. Non-Invasive Retinal Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtis, L.C.; Regele, O.B.; Wright, J.M.; Jones, G.B. Digital biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: The mobile/wearable devices opportunity. npj Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, K.; Kageyama, I.; Kobayashi, Y.; Lim, Y.; Sengoku, S.; Kodama, K. Leveraging mHealth wearables for managing patients with Alzheimer’s disease: A scoping review. Drug Discov. Today 2025, 30, 104363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhauria, M.; Mondal, R.; Deb, S.; Shome, G.; Chowdhury, D.; Sarkar, S.; Benito-León, J. Blood-based biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease: Advancing non-invasive diagnostics and prognostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, S.; Hou, X. Visual biosensing with specific liquid-based interface behaviors. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 7327–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinthal, A.; Aizenberg, J. Mobile interfaces: Liquids as a perfect structural material for multifunctional, antifouling surfaces. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satya, A.; Missaoui, T.; Hegde, G.; Bhattacharjee, A. Liquid Crystal as a Potential Biosensing Material. In Soft Materials-Based Biosensing Medical Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 81–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
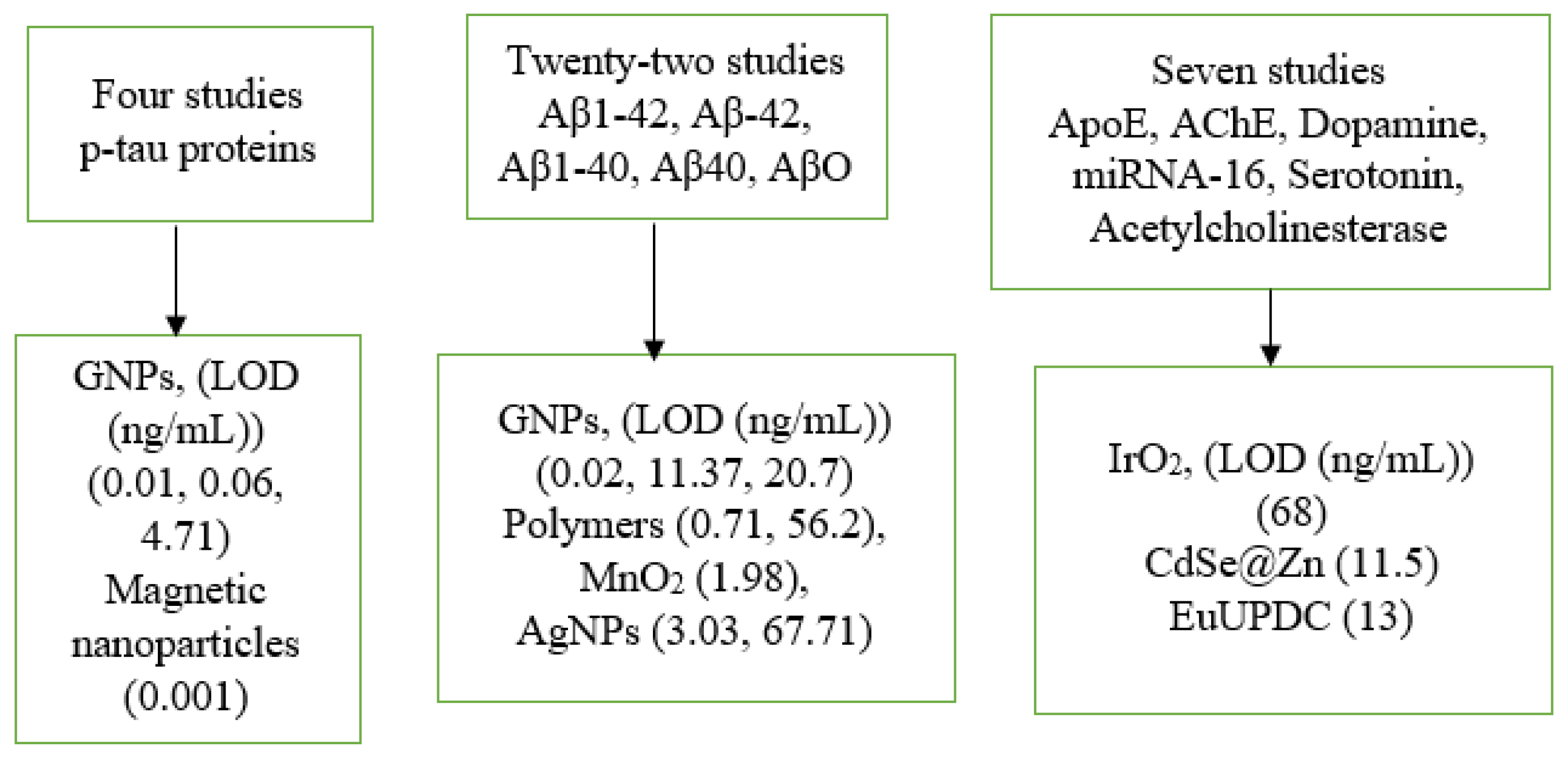

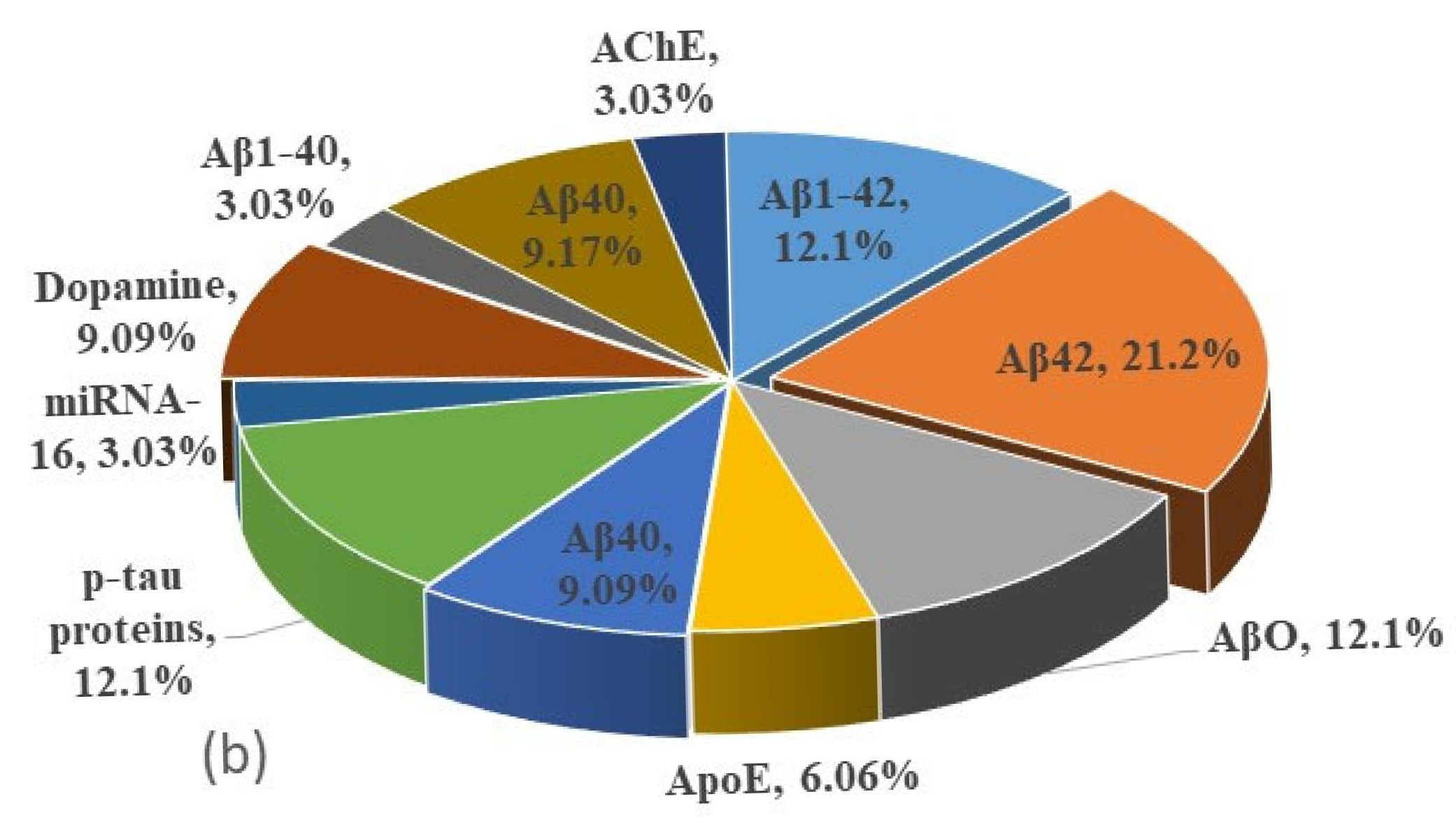

| Techniques | Biomarkers | Biore- Cognition Element | Particles | Size nm | LOD ng/mL | Country of Authors | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. Sensor | Aβ1-42 | Antibody | GNPs | - | 0.0001 | China | 2025 | [79] |
| Aβ42 | Antibody | GNPs | - | 0.00836 | USA | 2025 | [80] | |
| Aβ42 | Antibody | pyrrole | - | 0.04 | Spain | 2025 | [86] | |
| AβO | Antibody | CH-Cu-NAs | - | 0.96 | China | 2025 | [87] | |
| Aβ42 | Antibody | GNPspoly | 45 | 11.37 | China | 2022 | [88] | |
| ApoE | Protein | CdSe@Zn | 13.5 | 11.5 | Spain | 2014 | [81] | |
| Aβ1-42 | Antibody | GNPs | 45 | 11.93 | Japan | 2015 | [89] | |
| Aβ40 | Antibody | GNPs | - | 20.7 | Egypt | 2017 | [90] | |
| ApoE | Protein | IrO2 | 12.5 | 68 | Spain | 2014 | [77] | |
| LFA | p-tau proteins | Antibody | Carbon | 120 | 0.007 | Taiwan | 2024 | [82] |
| tau proteins | Antibody | GNPs | 37.3 | 0.01 | China | 2024 | [91] | |
| p-tau proteins | Antibody | GNPs | 35 | 0.06 | China | 2023 | [92] | |
| miRNA-16 | N. Tides | GNPs | 15 | 14.2 | China | 2024 | [93] | |
| Dopamine | N. Transm. | GNPs | - | 50 | USA | 2020 | [94] | |
| F. Sensor | p-tau 181 | Antibody | GNPs | - | 0.00082 | China | 2025 | [95] |
| AβO | Antibody | Magnetic | 30 | 3.6 | China | 2017 | [96] | |
| p-tau proteins | Antibody | GNPs | 4 | 4.71 | South Korea | 2022 | [97] | |
| Aβ42 | Antibody | LDMD-N | - | 10.86 | China | 2025 | [98] | |
| Serotonin | N. Transm. | EuUPDC | - | 13 | China | 2022 | [99] | |
| AβO | Antibody | MoS2 | 200 | 14 | China | 2020 | [83] | |
| AβO | Antibody | Polymer | 80 | 56.2 | China | 2017 | [100] | |
| SERS | p-ta protein | Antibody | Magnetic | - | 0.001 | Turkey | 2013 | [101] |
| Aβ1-42 | Antibody | GNPs | - | 0.02 | China | 2023 | [102] | |
| Aβ42 | - | GNPs | - | 0.1 | China | 2025 | [103] | |
| Aβ1-40 | - | GNPs | 0.1 | China | 2022 | [104] | ||
| Dopamine | N. Transm. | Ag | 0.15 | South Korea | 2023 | [105] | ||
| Aβ42 | Antibody | Ag | - | 4.5 | China | 2018 | [106] | |
| Aβ42 | Antibody | Ag | 61 | 67.71 | Russia | 2024 | [107] | |
| C. Sensor | Dopamine | N. Transm. | GNPs | 5.7 | 0.3 | Germany | 2016 | [108] |
| Aβ40 | Antibody | Polymer | - | 0.71 | Portugal | 2021 | [109] | |
| Aβ1-42 | Antibody | MnO2 | 220 | 1.98 | China | 2022 | [85] | |
| Aβ40 | Antibody | Ag | 15 | 3.03 | USA | 2018 | [110] | |
| AChE | N. Transm. | GNPs | 13 | 32 | China | 2012 | [111] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zia Ul Haq, M.; Zhao, X.; Obeng Apori, S.; Singh, B.; Tian, F. Molecular Biomarkers for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease and the Complementary Role of Engineered Nanomaterials: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199282
Zia Ul Haq M, Zhao X, Obeng Apori S, Singh B, Tian F. Molecular Biomarkers for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease and the Complementary Role of Engineered Nanomaterials: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199282
Chicago/Turabian StyleZia Ul Haq, Muhammad, Xinyi Zhao, Samuel Obeng Apori, Baljit Singh, and Furong Tian. 2025. "Molecular Biomarkers for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease and the Complementary Role of Engineered Nanomaterials: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199282
APA StyleZia Ul Haq, M., Zhao, X., Obeng Apori, S., Singh, B., & Tian, F. (2025). Molecular Biomarkers for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease and the Complementary Role of Engineered Nanomaterials: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199282









