An Expendable Player in Positive Vascular Remodeling? ADAMTS13 Deficiency Does Not Affect Arteriogenesis or Angiogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
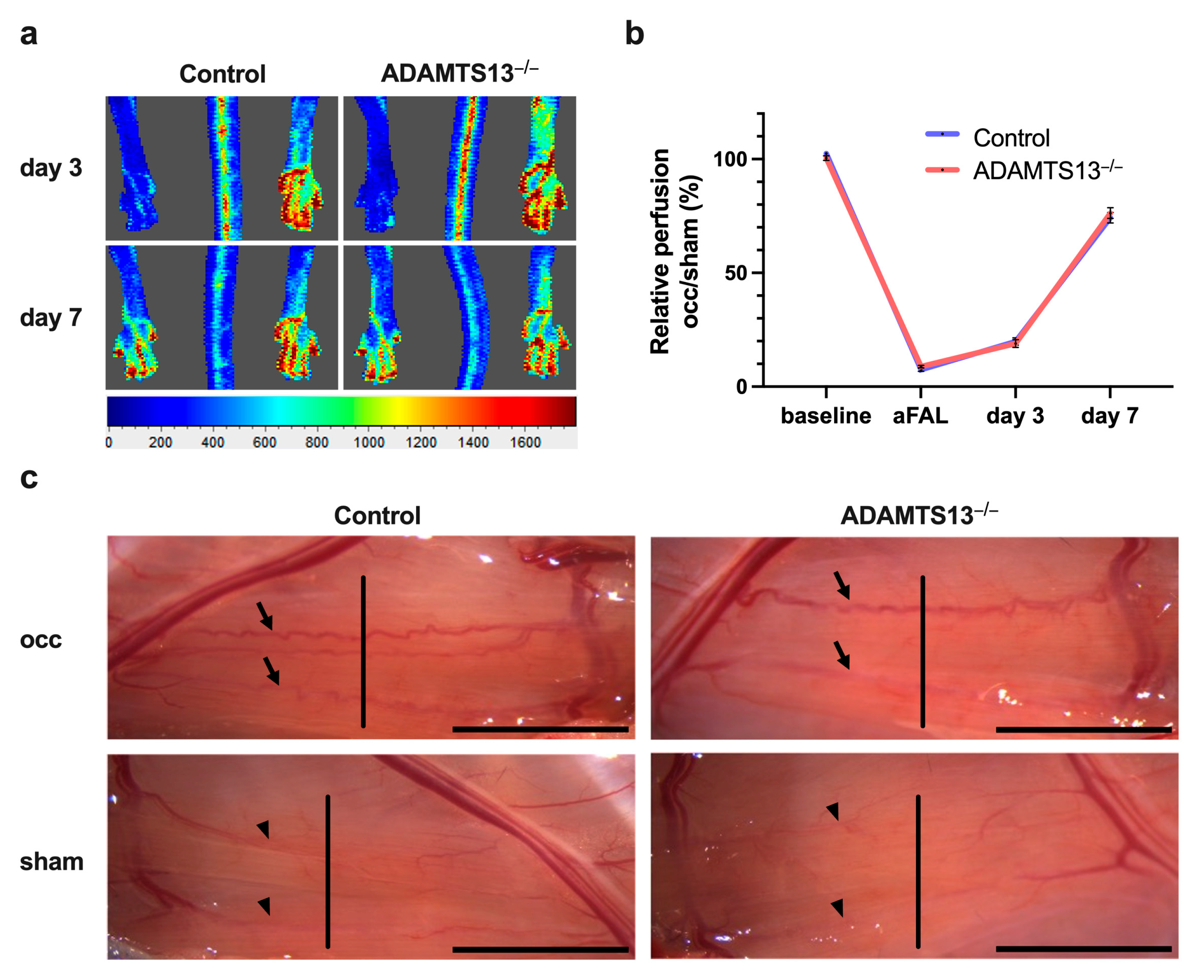
2.1. ADAMTS13 Deficiency Does Not Alter Perfusion Recovery
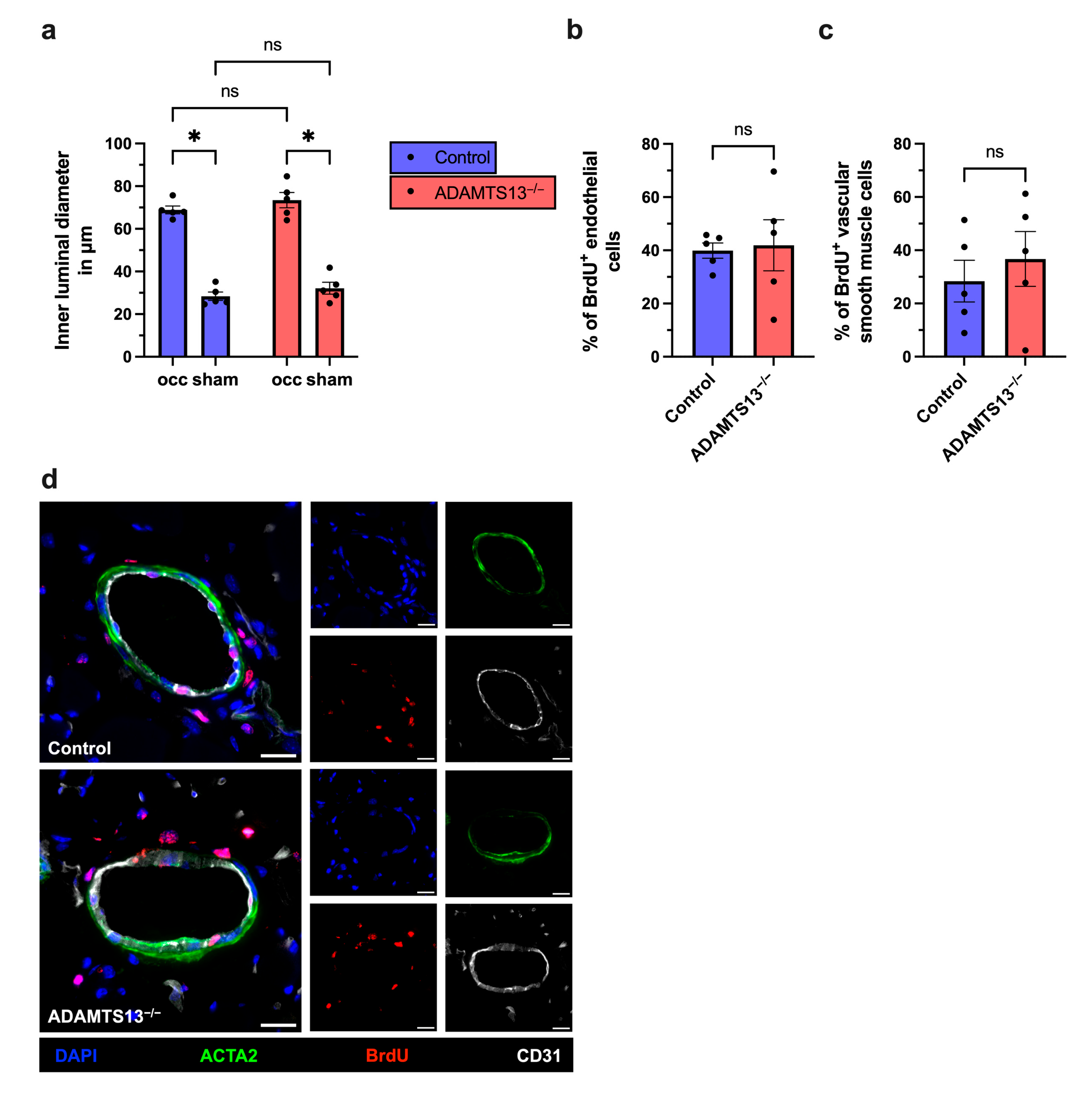
2.2. Collateral Vascular Remodeling Is Preserved in ADAMTS13-Deficient Mice
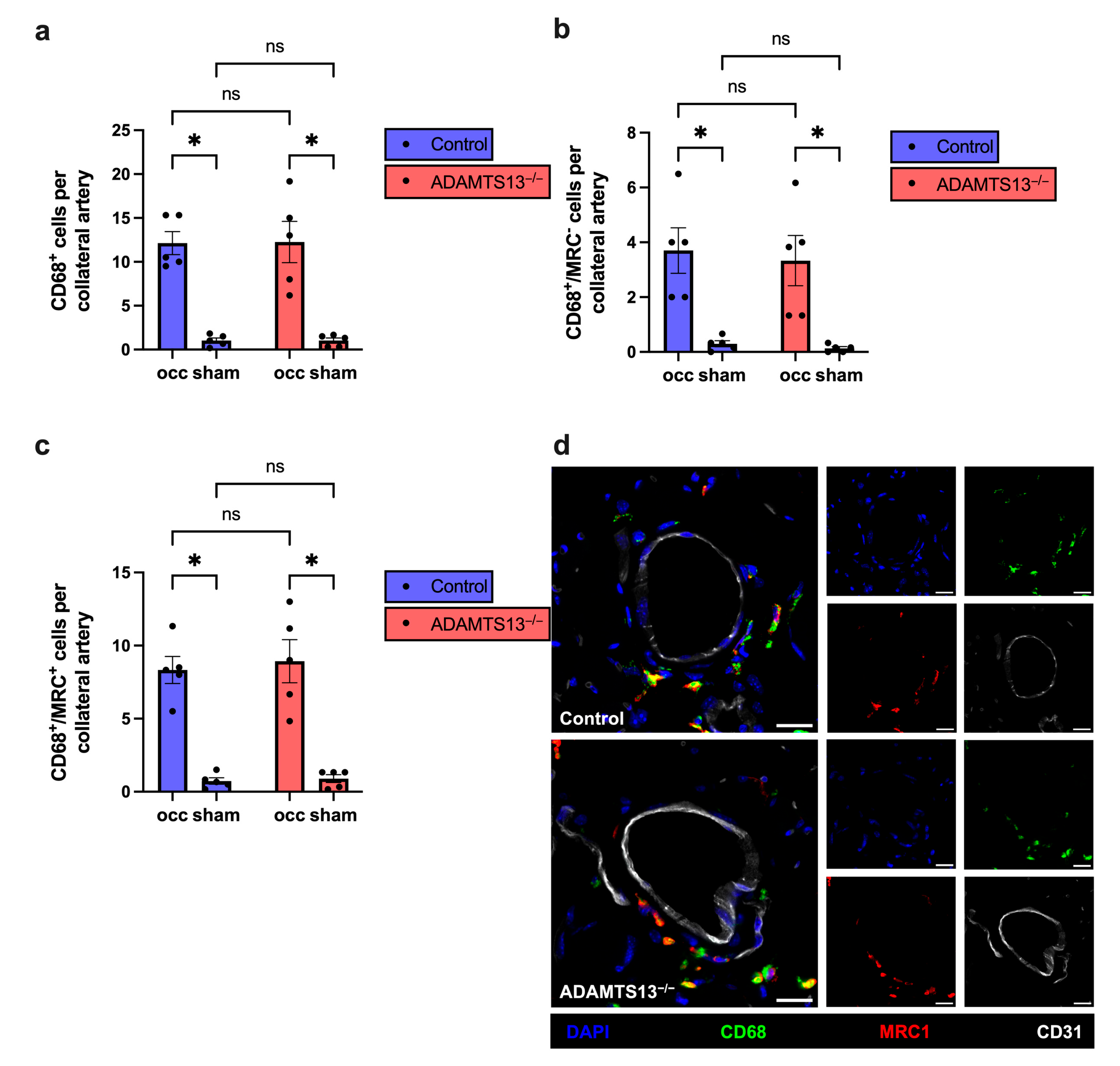
2.3. Macrophage Recruitment and Polarization Are Unaffected by ADAMTS13 Deficiency During Arteriogenesis
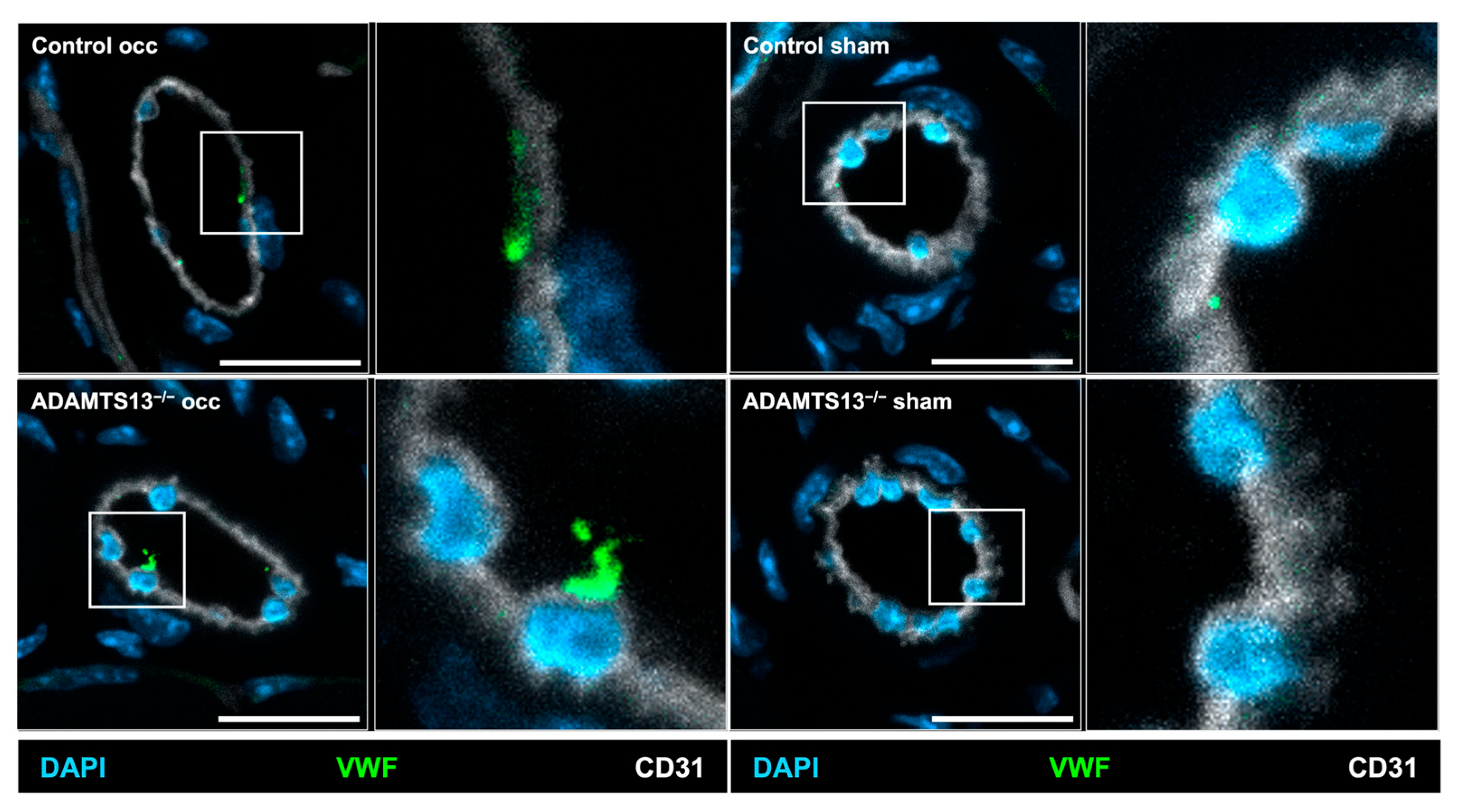
2.4. Endothelial VWF Release Remains Intact in the Absence of ADAMTS13
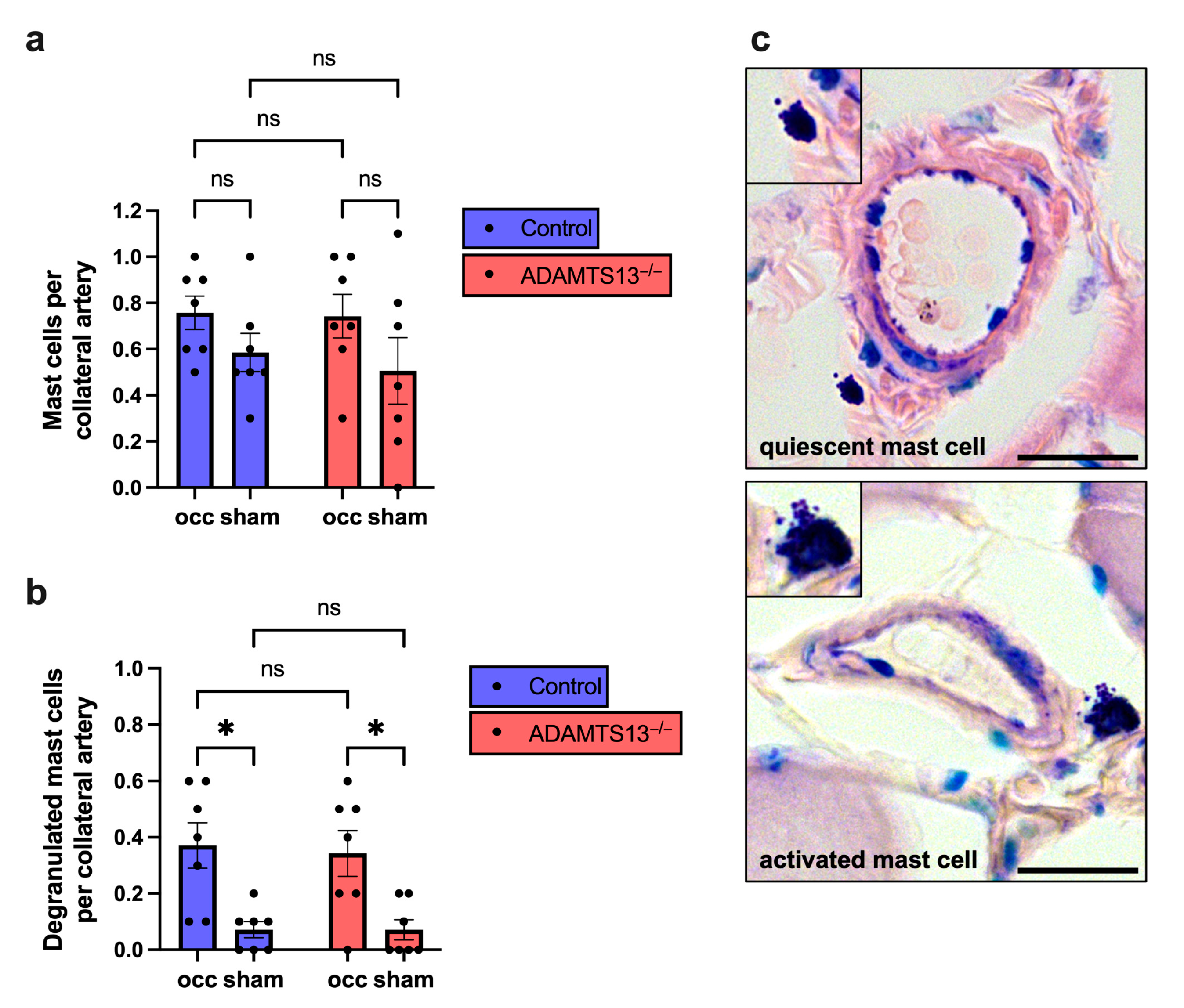
2.5. Platelet-Leukocyte Aggregate Formation and Mast Cell Activation Are Unchanged in ADAMTS13-Deficient Mice
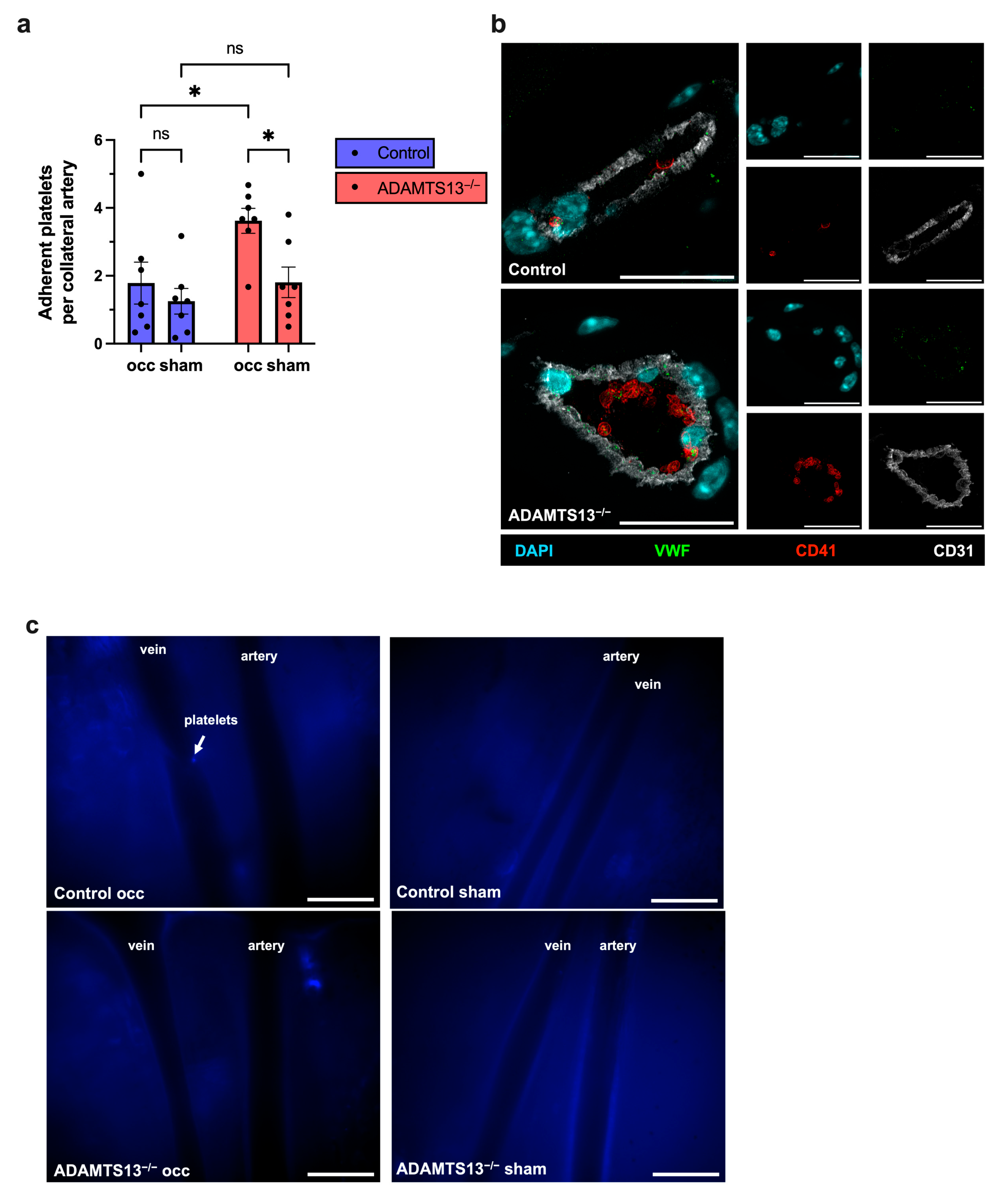
2.6. ADAMTS13 Deficiency Increases Platelet Adhesion Without Thrombus Formation
2.7. Ischemic Injury Extent Is Not Altered by ADAMTS13 Deficiency
2.8. Capillary Density Is Not Altered by ADAMTS13 Deficiency
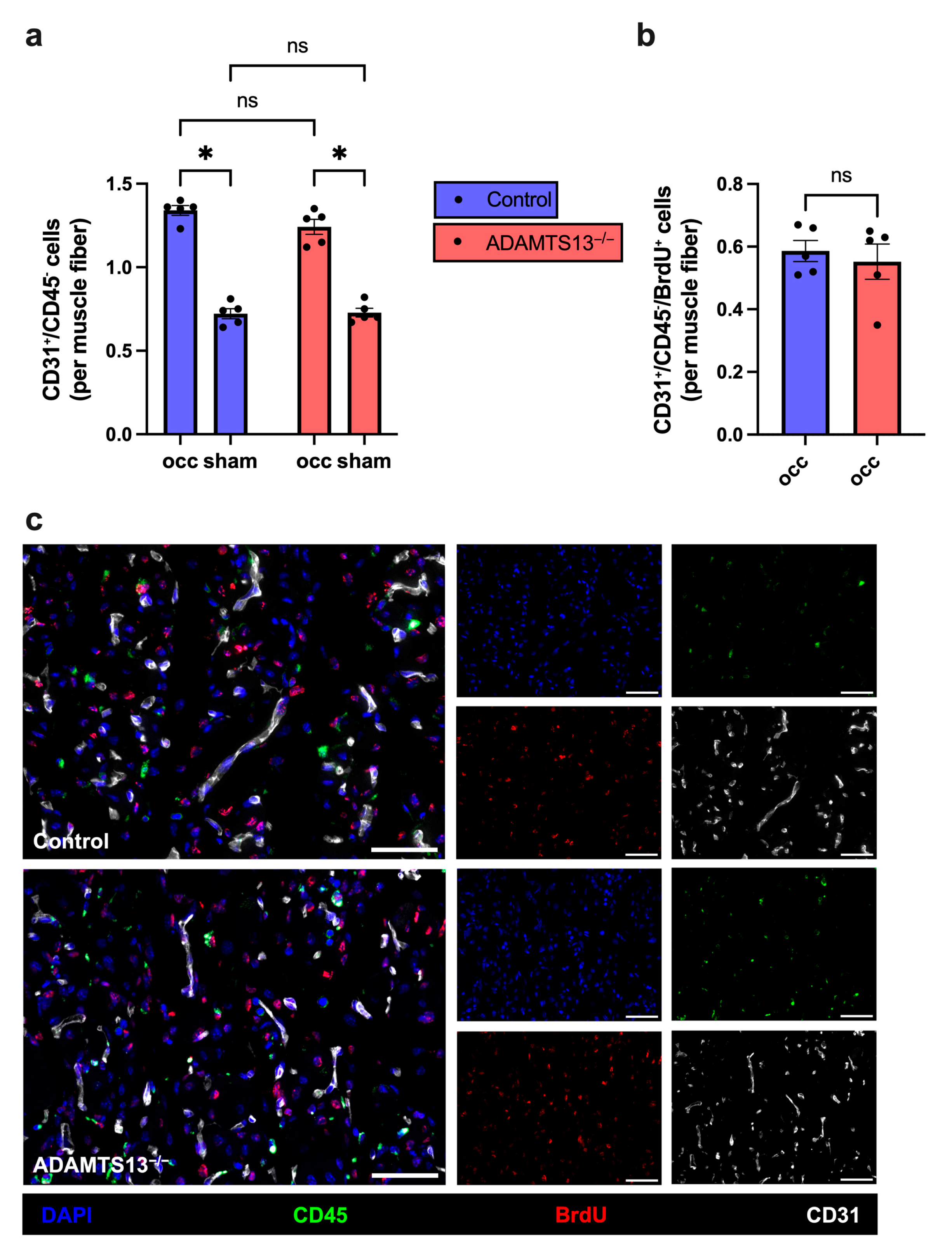
2.9. ADAMTS13 Deficiency Increases Macrophage Recruitment Without Affecting Polarization
2.10. ADAMTS13 Deficiency Does Not Affect Neutrophil Accumulation and NET Formation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Femoral Artery Ligation, Laser-Doppler Perfusion Measurements, and Tissue Sampling
4.3. Histology and Immunohistology
4.4. Intravital Microscopy
4.5. Flow Cytometry
4.6. Genotyping of ADAMTS13−/− Mice
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADAMTS13 | A Disintegrin and Metalloprotease with Thrombospondin type 1 repeats, member 13 |
| BrdU | Bromodeoxyuridine |
| CitH3 | Citrullinated Histone H3 |
| FAL | Femoral Artery Ligation |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| HUVEC | Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells |
| LDI | Laser Doppler imaging |
| MMF | Midazolam, Medetomidine and Fentanyl |
| MRC1 | Mannose Receptor C-type 1 |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| NET | Neutrophil Extracellular Trap |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| ns | not significant |
| occ | occluded |
| PAD | Peripheral Artery Disease |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| PNA | Platelet-Neutrophil Aggregates |
| ROI | Region Of Interest |
| RT | Room Temperature |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| TNFα | Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha |
| TSP1 | Thrombospondin Type 1 |
| TTP | Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura |
| ULVWF | Ultra Large Von Willebrand Factor |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| VWF | Von Willebrand Factor |
References
- Fowkes, F.G.; Rudan, D.; Rudan, I.; Aboyans, V.; Denenberg, J.O.; McDermott, M.M.; Norman, P.E.; Sampson, U.K.; Williams, L.J.; Mensah, G.A.; et al. Comparison of global estimates of prevalence and risk factors for peripheral artery disease in 2000 and 2010: A systematic review and analysis. Lancet 2013, 382, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, J.E.; Chilian, W.M.; Deindl, E.; van Royen, N.; Simons, M. A brief etymology of the collateral circulation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1854–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deindl, E.; Schaper, W. The art of arteriogenesis. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 43, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasch, M.; Kleinert, E.C.; Meister, S.; Kumaraswami, K.; Buchheim, J.I.; Grantzow, T.; Lautz, T.; Salpisti, S.; Fischer, S.; Troidl, K.; et al. Extracellular RNA released due to shear stress controls natural bypass growth by mediating mechanotransduction in mice. Blood 2019, 134, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Nishio, M.; Peters, S.C.; Tschernatsch, M.; Walberer, M.; Weidemann, S.; Heidenreich, R.; Couraud, P.O.; Weksler, B.B.; Romero, I.A.; et al. Signaling mechanism of extracellular RNA in endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2100–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.F.; Moake, J.L.; Nolasco, L.; Bernardo, A.; Arceneaux, W.; Shrimpton, C.N.; Schade, A.J.; McIntire, L.V.; Fujikawa, K.; Lopez, J.A. ADAMTS-13 rapidly cleaves newly secreted ultralarge von Willebrand factor multimers on the endothelial surface under flowing conditions. Blood 2002, 100, 4033–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, J.E. Biomedicine. Contact--how platelets touch von Willebrand factor. Science 2002, 297, 1128–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandraratne, S.; von Bruehl, M.L.; Pagel, J.I.; Stark, K.; Kleinert, E.; Konrad, I.; Farschtschi, S.; Coletti, R.; Gartner, F.; Chillo, O.; et al. Critical role of platelet glycoprotein ibalpha in arterial remodeling. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chillo, O.; Kleinert, E.C.; Lautz, T.; Lasch, M.; Pagel, J.I.; Heun, Y.; Troidl, K.; Fischer, S.; Caballero-Martinez, A.; Mauer, A.; et al. Perivascular Mast Cells Govern Shear Stress-Induced Arteriogenesis by Orchestrating Leukocyte Function. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2197–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J. Interferon. Cytokine. Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arras, M.; Ito, W.D.; Scholz, D.; Winkler, B.; Schaper, J.; Schaper, W. Monocyte activation in angiogenesis and collateral growth in the rabbit hindlimb. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deindl, E.; Hoefer, I.E.; Fernandez, B.; Barancik, M.; Heil, M.; Strniskova, M.; Schaper, W. Involvement of the fibroblast growth factor system in adaptive and chemokine-induced arteriogenesis. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoefer, I.E.; van Royen, N.; Rectenwald, J.E.; Bray, E.J.; Abouhamze, Z.; Moldawer, L.L.; Voskuil, M.; Piek, J.J.; Buschmann, I.R.; Ozaki, C.K. Direct evidence for tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling in arteriogenesis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1639–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heil, M.; Ziegelhoeffer, T.; Pipp, F.; Kostin, S.; Martin, S.; Clauss, M.; Schaper, W. Blood monocyte concentration is critical for enhancement of collateral artery growth. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2002, 283, H2411–H2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.A.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troidl, C.; Jung, G.; Troidl, K.; Hoffmann, J.; Mollmann, H.; Nef, H.; Schaper, W.; Hamm, C.W.; Schmitz-Rixen, T. The temporal and spatial distribution of macrophage subpopulations during arteriogenesis. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 11, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, I.; Schaper, W. Arteriogenesis Versus Angiogenesis: Two Mechanisms of Vessel Growth. News Physiol. Sci. 1999, 14, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.H.; Alitalo, K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudry, M.; Bregerie, O.; Andrieu, V.; El Benna, J.; Pocidalo, M.A.; Hakim, J. Intracellular pool of vascular endothelial growth factor in human neutrophils. Blood 1997, 90, 4153–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Neutrophils in tissue injury and repair. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 371, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Cheyne, C.; Tay, H.; De Spiegelaere, W. The complex TIE between macrophages and angiogenesis. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2020, 49, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, G.G.; Nichols, W.C.; Lian, E.C.; Foroud, T.; McClintick, J.N.; McGee, B.M.; Yang, A.Y.; Siemieniak, D.R.; Stark, K.R.; Gruppo, R.; et al. Mutations in a member of the ADAMTS gene family cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nature 2001, 413, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Matsuyama, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Iwamoto, T.A.; Mori, T.; Wanaka, A.; Fukui, H.; et al. Localization of ADAMTS13 to the stellate cells of human liver. Blood 2005, 106, 922–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.; Nolasco, L.; Tao, Z.; Dong, J.F.; Moake, J. Human endothelial cells synthesize and release ADAMTS-13. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockmeyer, C.L.; Forstmeier, V.; Modde, F.; Lovric, S.; Claus, R.A.; Schiffer, M.; Agustian, P.A.; Grothusen, C.; Grote, K.; Birschmann, I.; et al. ADAMTS13—marker of contractile phenotype of arterial smooth muscle cells lost in benign nephrosclerosis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sporn, L.A.; Marder, V.J.; Wagner, D.D. Inducible secretion of large, biologically potent von Willebrand factor multimers. Cell 1986, 46, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, E.M.; Meyer, D.; le Menn, R.; Breton-Gorius, J. Eccentric localization of von Willebrand factor in an internal structure of platelet alpha-granule resembling that of Weibel-Palade bodies. Blood 1985, 66, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmugge, M.; Rand, M.L.; Freedman, J. Platelets and von Willebrand factor. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2003, 28, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.F.; Ginsberg, M.H.; Ruggeri, Z.M.; Batlle, F.J.; Zimmerman, T.S. Multimeric structure of platelet factor VIII/von Willebrand factor: The presence of larger multimers and their reassociation with thrombin-stimulated platelets. Blood 1982, 60, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.W.; Nuschele, S.; Wixforth, A.; Gorzelanny, C.; Alexander-Katz, A.; Netz, R.R.; Schneider, M.F. Shear-induced unfolding triggers adhesion of von Willebrand factor fibers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7899–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, J.T.; de Groot, R.; Xiang, Y.; Luken, B.M.; Lane, D.A. Unraveling the scissile bond: How ADAMTS13 recognizes and cleaves von Willebrand factor. Blood 2011, 118, 3212–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, A.K.; Goerge, T.; Schneider, S.W.; Wagner, D.D. Formation of platelet strings and microthrombi in the presence of ADAMTS-13 inhibitor does not require P-selectin or beta3 integrin. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, K.; Anderson, P.J.; Tuley, E.A.; Wiswall, E.; Sadler, J.E. Platelet-VWF complexes are preferred substrates of ADAMTS13 under fluid shear stress. Blood 2008, 111, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawley, J.T.; Scully, M.A. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: Basic pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2013, 2013, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, A.; Ball, C.; Nolasco, L.; Choi, H.; Moake, J.L.; Dong, J.F. Platelets adhered to endothelial cell-bound ultra-large von Willebrand factor strings support leukocyte tethering and rolling under high shear stress. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.K.; Kisucka, J.; Brill, A.; Walsh, M.T.; Scheiflinger, F.; Wagner, D.D. ADAMTS13: A new link between thrombosis and inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, C.; Khan, M.M.; Lentz, S.R.; Chauhan, A.K. ADAMTS13 reduces vascular inflammation and the development of early atherosclerosis in mice. Blood 2012, 119, 2385–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, S.F.; Savchenko, A.S.; Haas, M.S.; Schatzberg, D.; Carroll, M.C.; Schiviz, A.; Dietrich, B.; Rottensteiner, H.; Scheiflinger, F.; Wagner, D.D. Protective anti-inflammatory effect of ADAMTS13 on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Blood 2012, 120, 5217–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Motto, D.G.; Lentz, S.R.; Chauhan, A.K. ADAMTS13 reduces VWF-mediated acute inflammation following focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, M.; Nakano, T.; Hayakawa, K.; Irie, K.; Akitake, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Mishima, K.; Muroi, C.; Yonekawa, Y.; Banno, F.; et al. ADAMTS13 gene deletion enhances plasma high-mobility group box1 elevation and neuroinflammation in brain ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 33, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, C.; Motto, D.G.; Jensen, M.; Lentz, S.R.; Chauhan, A.K. ADAMTS13 deficiency exacerbates VWF-dependent acute myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Blood 2012, 120, 5224–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu El-Asrar, A.M.; Nawaz, M.I.; Ahmad, A.; Siddiquei, M.; Allegaert, E.; Adyns, L.; Vanbrabant, L.; Gikandi, P.W.; De Hertogh, G.; Struyf, S.; et al. ADAMTS13 Improves Endothelial Function and Reduces Inflammation in Diabetic Retinopathy. Cells 2025, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, D.; Ziegelhoeffer, T.; Helisch, A.; Wagner, S.; Friedrich, C.; Podzuweit, T.; Schaper, W. Contribution of arteriogenesis and angiogenesis to postocclusive hindlimb perfusion in mice. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2002, 34, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluever, A.K.; Braumandl, A.; Fischer, S.; Preissner, K.T.; Deindl, E. The Extraordinary Role of Extracellular RNA in Arteriogenesis, the Growth of Collateral Arteries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.K.; Motto, D.G.; Lamb, C.B.; Bergmeier, W.; Dockal, M.; Plaimauer, B.; Scheiflinger, F.; Ginsburg, D.; Wagner, D.D. Systemic antithrombotic effects of ADAMTS13. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanesha, N.; Doddapattar, P.; Chorawala, M.R.; Nayak, M.K.; Kokame, K.; Staber, J.M.; Lentz, S.R.; Chauhan, A.K. ADAMTS13 Retards Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy by Inhibiting Intrarenal Thrombosis in Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witsch, T.; Martinod, K.; Sorvillo, N.; Portier, I.; De Meyer, S.F.; Wagner, D.D. Recombinant Human ADAMTS13 Treatment Improves Myocardial Remodeling and Functionality After Pressure Overload Injury in Mice. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e007004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, M.A.; de Maat, M.P.; Leebeek, F.W. Von Willebrand factor and ADAMTS13 in arterial thrombosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Rev. 2014, 28, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergouwen, M.D.; Knaup, V.L.; Roelofs, J.J.; de Boer, O.J.; Meijers, J.C. Effect of recombinant ADAMTS-13 on microthrombosis and brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroi, C.; Fujioka, M.; Mishima, K.; Irie, K.; Fujimura, Y.; Nakano, T.; Fandino, J.; Keller, E.; Iwasaki, K.; Fujiwara, M. Effect of ADAMTS-13 on cerebrovascular microthrombosis and neuronal injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, H.M.; Siegerink, B.; Luken, B.M.; Crawley, J.T.; Algra, A.; Lane, D.A.; Rosendaal, F.R. High VWF, low ADAMTS13, and oral contraceptives increase the risk of ischemic stroke and myocardial infarction in young women. Blood 2012, 119, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaikita, K.; Soejima, K.; Matsukawa, M.; Nakagaki, T.; Ogawa, H. Reduced von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13) activity in acute myocardial infarction. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 2490–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawley, J.T.; Lane, D.A.; Woodward, M.; Rumley, A.; Lowe, G.D. Evidence that high von Willebrand factor and low ADAMTS-13 levels independently increase the risk of a non-fatal heart attack. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denorme, F.; Langhauser, F.; Desender, L.; Vandenbulcke, A.; Rottensteiner, H.; Plaimauer, B.; Francois, O.; Andersson, T.; Deckmyn, H.; Scheiflinger, F.; et al. ADAMTS13-mediated thrombolysis of t-PA-resistant occlusions in ischemic stroke in mice. Blood 2016, 127, 2337–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisslthaler, B.; Dimmeler, S.; Hermann, C.; Busse, R.; Fleming, I. Phosphorylation and activation of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase by fluid shear stress. Acta. Physiol. Scand. 2000, 168, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Feil, S.; Wolters, M.; Thunemann, M.; Regler, F.; Schmidt, K.; Friebe, A.; Olbrich, M.; Langer, H.; Gawaz, M.; et al. A shear-dependent NO-cGMP-cGKI cascade in platelets acts as an auto-regulatory brake of thrombosis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancellotti, S.; Basso, M.; De Cristofaro, R. Proteolytic processing of von Willebrand factor by adamts13 and leukocyte proteases. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 5, e2013058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raife, T.J.; Cao, W.; Atkinson, B.S.; Bedell, B.; Montgomery, R.R.; Lentz, S.R.; Johnson, G.F.; Zheng, X.L. Leukocyte proteases cleave von Willebrand factor at or near the ADAMTS13 cleavage site. Blood 2009, 114, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motto, D.G.; Chauhan, A.K.; Zhu, G.; Homeister, J.; Lamb, C.B.; Desch, K.C.; Zhang, W.; Tsai, H.M.; Wagner, D.D.; Ginsburg, D. Shigatoxin triggers thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in genetically susceptible ADAMTS13-deficient mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2752–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Jiang, S.; Guo, J.; Xu, N.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Q.; Fu, X.; Li, L.; et al. ADAMTS13 protects mice against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing inflammation and improving endothelial function. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2019, 316, F134–F145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, S.; Gutch, S.; Fukui, S.; Chu, L.; Wagner, D.D. Anti-inflammatory protective effect of ADAMTS-13 in murine arthritis models. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 2386–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossato, P.; Federti, E.; Matte, A.; Glantschnig, H.; Canneva, F.; Schuster, M.; Coulibaly, S.; Schrenk, G.; Voelkel, D.; Dockal, M.; et al. Evidence of protective effects of recombinant ADAMTS13 in a humanized model of sickle cell disease. Haematologica 2022, 107, 2650–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.Y.; Tohyama, J.; Bauer, R.C.; Cao, N.N.; Rader, D.J.; Zheng, X.L. Genetic ablation of Adamts13 gene dramatically accelerates the formation of early atherosclerosis in a murine model. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1817–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deindl, E.; Ziegelhoffer, T.; Kanse, S.M.; Fernandez, B.; Neubauer, E.; Carmeliet, P.; Preissner, K.T.; Schaper, W. Receptor-independent role of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator during arteriogenesis. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1174–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Rodansky, E.S.; Smith, J.K.; Rodgers, G.M. ADAMTS13 promotes angiogenesis and modulates VEGF-induced angiogenesis. Microvasc. Res. 2012, 84, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Keener, J.; Xiao, J.; Long Zheng, X.; Rodgers, G.M. ADAMTS13 and its variants promote angiogenesis via upregulation of VEGF and VEGFR2. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Lee, M.; Kim, E.H.; Bishop, D.; Rodgers, G.M. siRNA-knockdown of ADAMTS-13 modulates endothelial cell angiogenesis. Microvasc. Res. 2017, 113, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T.N.; de Bruijne, E.L.; Dippel, D.W.; de Jong, A.J.; Deckers, J.W.; Poldermans, D.; de Maat, M.P.; Leebeek, F.W. Lower levels of ADAMTS13 are associated with cardiovascular disease in young patients. Atherosclerosis 2009, 207, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, K.; Mareninov, S.; Diaz, M.F.P.; Yong, W.H. An Introduction to Performing Immunofluorescence Staining. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1897, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Roh, J.; Park, C.S. Immunohistochemistry for Pathologists: Protocols, Pitfalls, and Tips. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2016, 50, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buesa, R.J. Giemsa Staining of Tissue Sections: A New Twist on an Old Technique. J. Histotechnol. 2001, 24, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.H.; Jacobson, K.A.; Rose, J.; Zeller, R. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. CSH Protoc. 2008, 2008, pdb.prot4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasch, M.; Nekolla, K.; Klemm, A.H.; Buchheim, J.I.; Pohl, U.; Dietzel, S.; Deindl, E. Estimating hemodynamic shear stress in murine peripheral collateral arteries by two-photon line scanning. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2019, 453, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baur, C.; Geml, A.; Wimmer, K.-S.; Heim, F.; Holschbach, A.; Elbs, K.; Rohrmoser, M.R.; van den Heuvel, D.; Bauer, A.T.; Schneider, S.W.; et al. An Expendable Player in Positive Vascular Remodeling? ADAMTS13 Deficiency Does Not Affect Arteriogenesis or Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189137
Baur C, Geml A, Wimmer K-S, Heim F, Holschbach A, Elbs K, Rohrmoser MR, van den Heuvel D, Bauer AT, Schneider SW, et al. An Expendable Player in Positive Vascular Remodeling? ADAMTS13 Deficiency Does Not Affect Arteriogenesis or Angiogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):9137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189137
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaur, Carolin, Amanda Geml, Kira-Sofie Wimmer, Franziska Heim, Anja Holschbach, Katharina Elbs, Michael R. Rohrmoser, Dominic van den Heuvel, Alexander T. Bauer, Stefan W. Schneider, and et al. 2025. "An Expendable Player in Positive Vascular Remodeling? ADAMTS13 Deficiency Does Not Affect Arteriogenesis or Angiogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 9137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189137
APA StyleBaur, C., Geml, A., Wimmer, K.-S., Heim, F., Holschbach, A., Elbs, K., Rohrmoser, M. R., van den Heuvel, D., Bauer, A. T., Schneider, S. W., Merkus, D., & Deindl, E. (2025). An Expendable Player in Positive Vascular Remodeling? ADAMTS13 Deficiency Does Not Affect Arteriogenesis or Angiogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 9137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189137






