Levosimendan Pretreatment Attenuates Mesenteric Artery Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury and Multi-Organ Damage in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
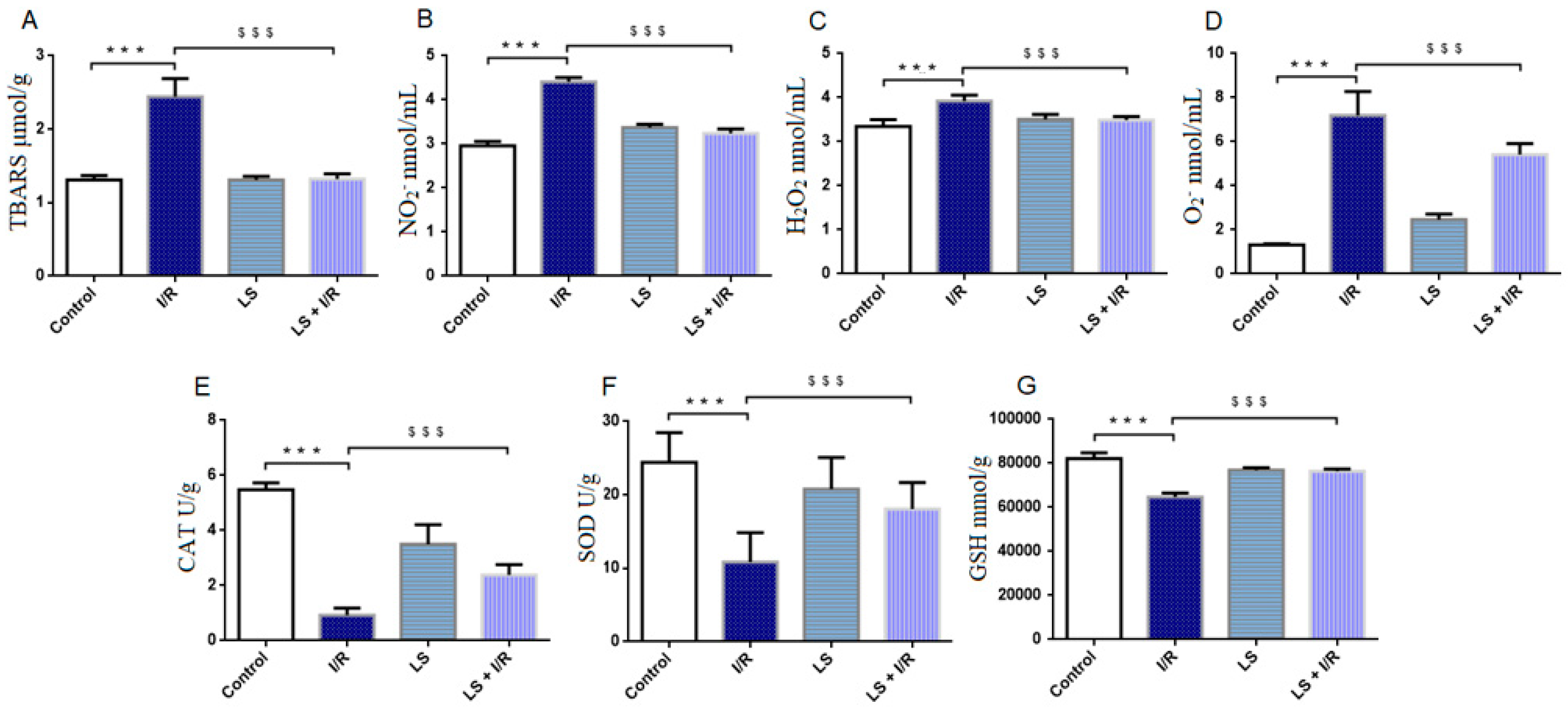
2.1. Levosimendan Attenuates the Effects of Mesenteric I/R Injury on Oxidative Stress Markers in Blood, Intestinal Tissue, and Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid
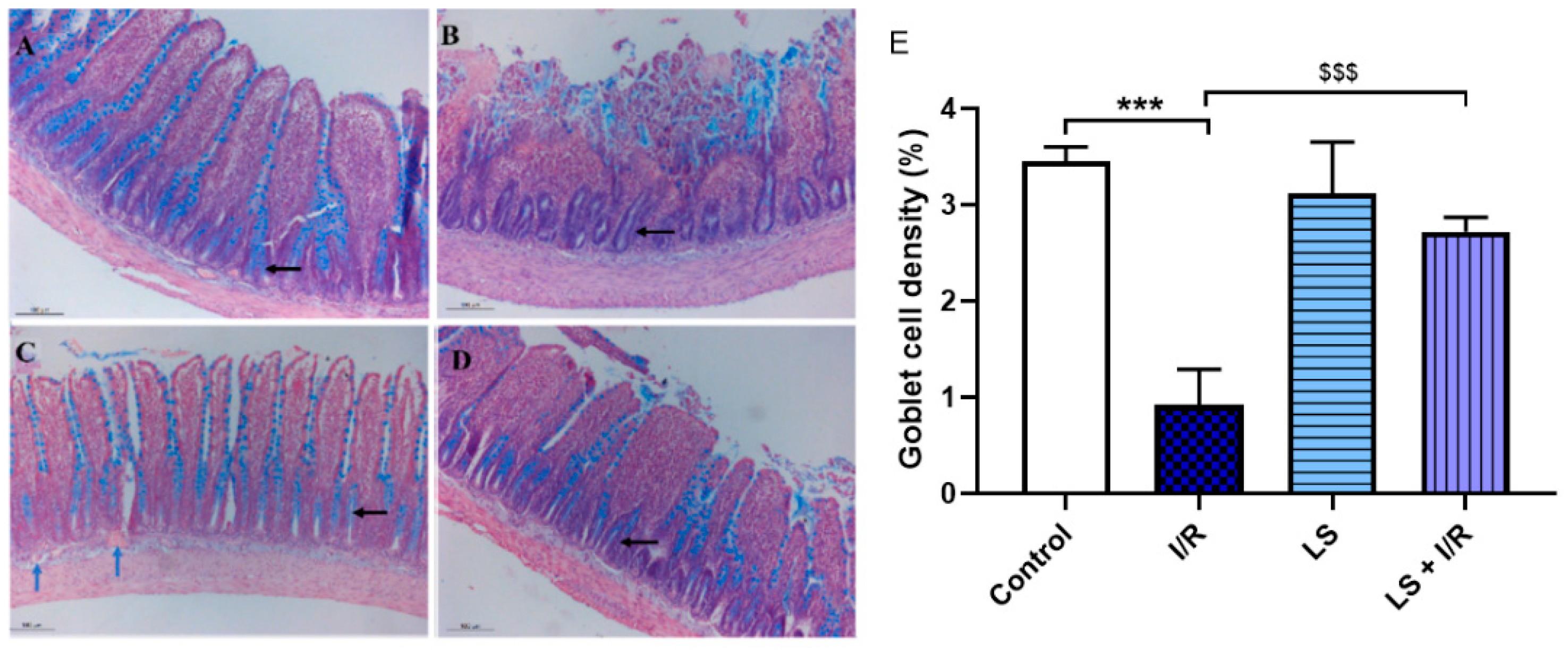
2.2. Protective Effects of Levosimendan on Rat Terminal Ileum Epithelial Cells Induced by I/R Injury
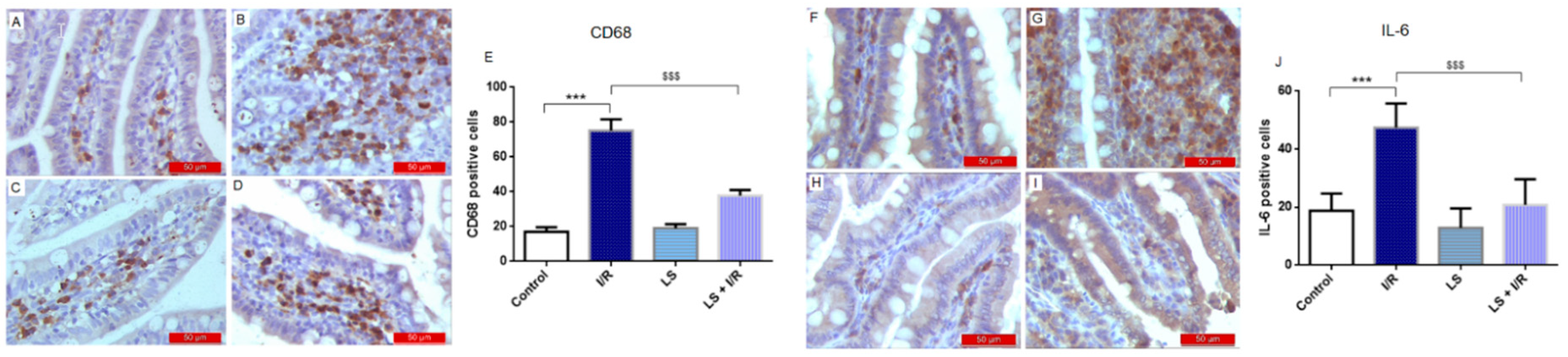
2.3. Effects of Levosimendan on Inflammatory Response of Intestinal Tissue Induced by Mesenteric I/R Injury
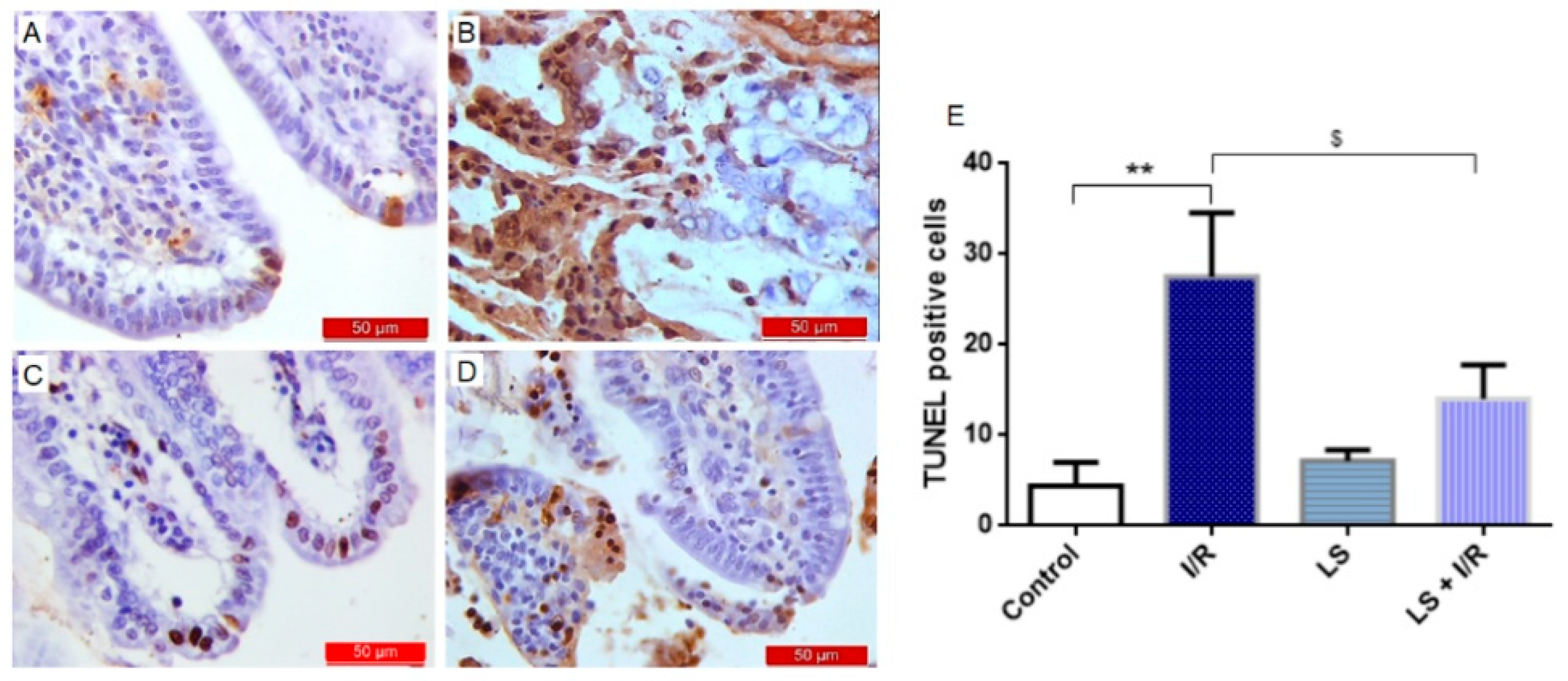
2.4. Levosimendan Attenuated Apoptosis of Intestinal Epithelial Cells Induced by I/R Injury
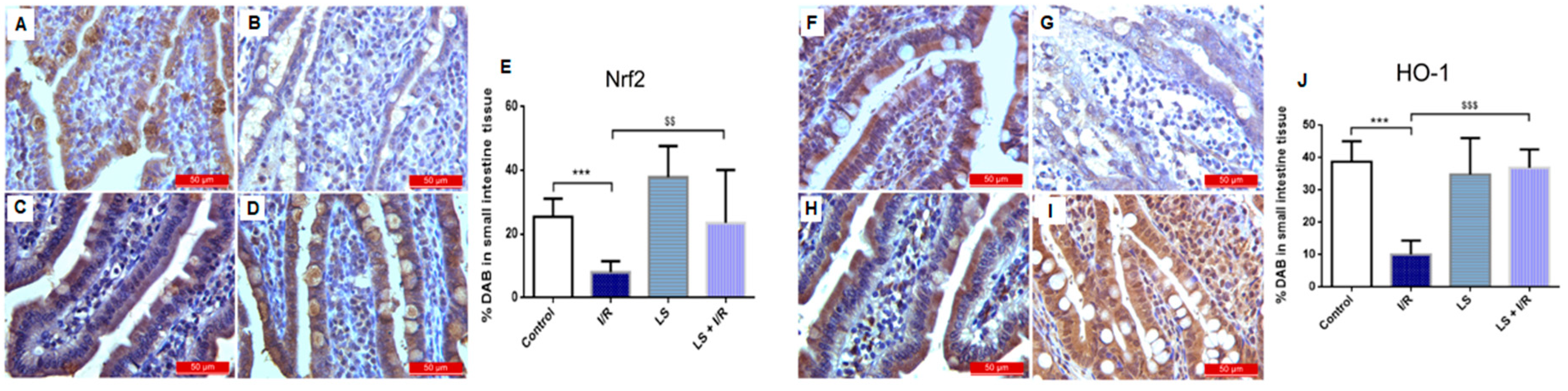
2.5. Levosimendan Pretreatment Induced Upregulation of Nrf2, HO-1, and Nrf2/HO-1 Signalling
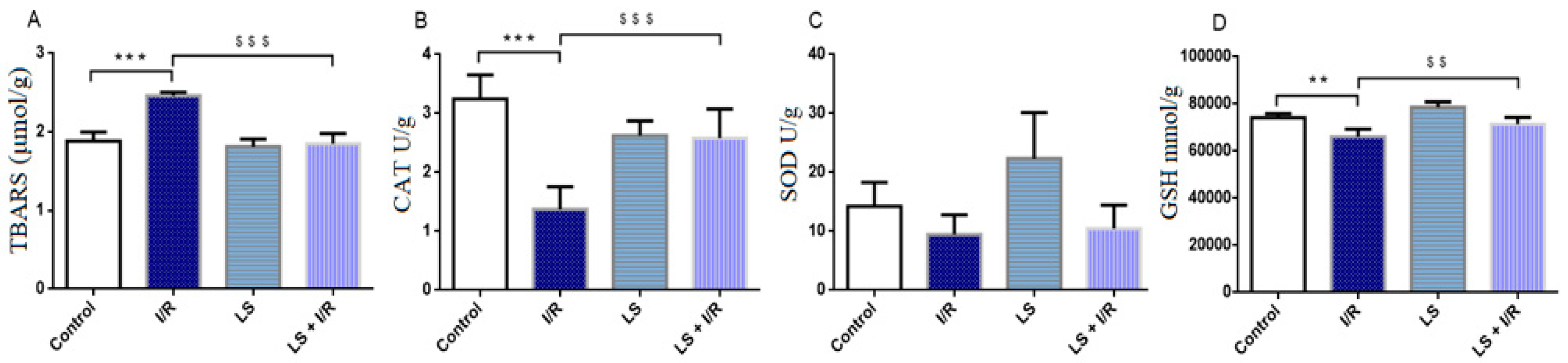
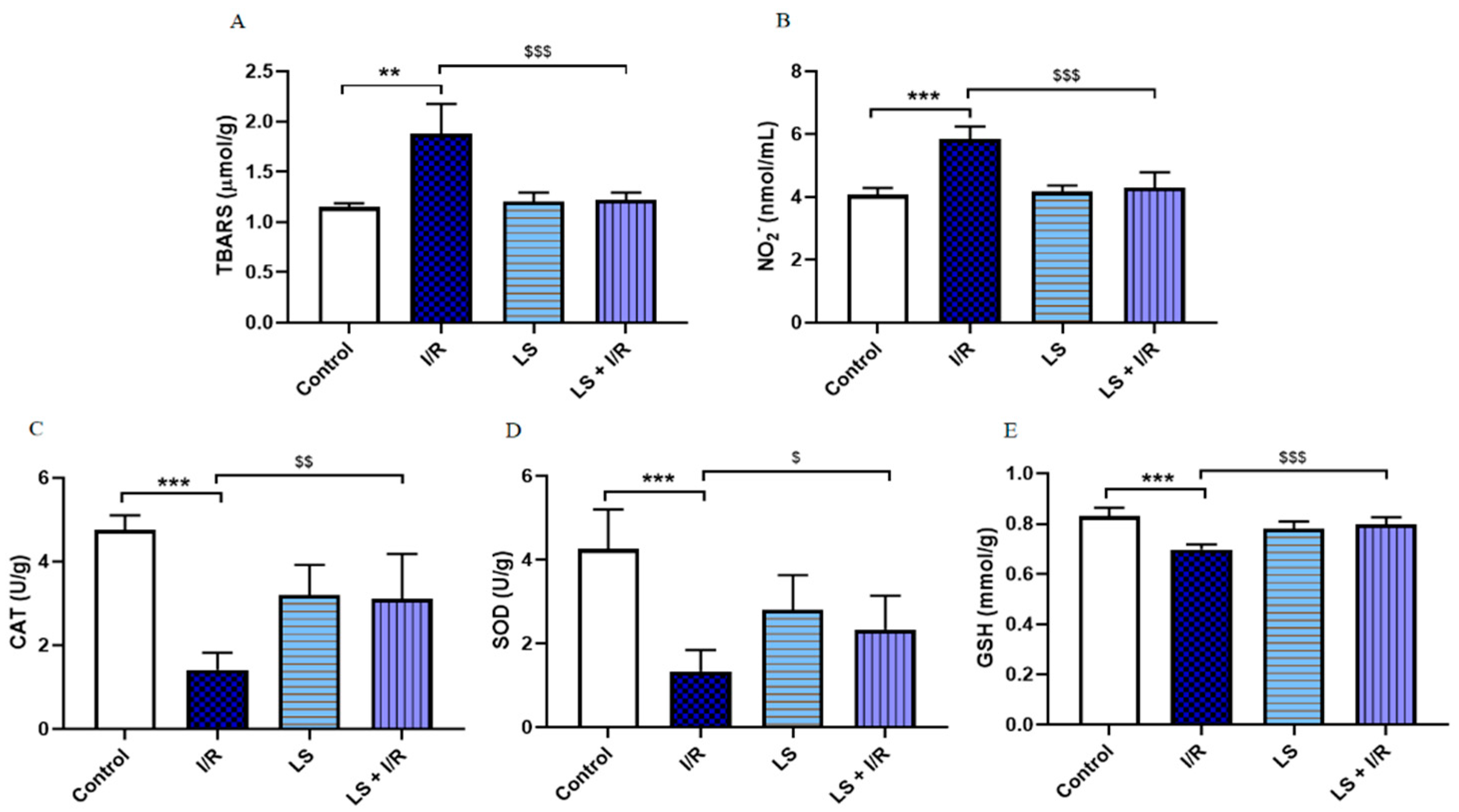
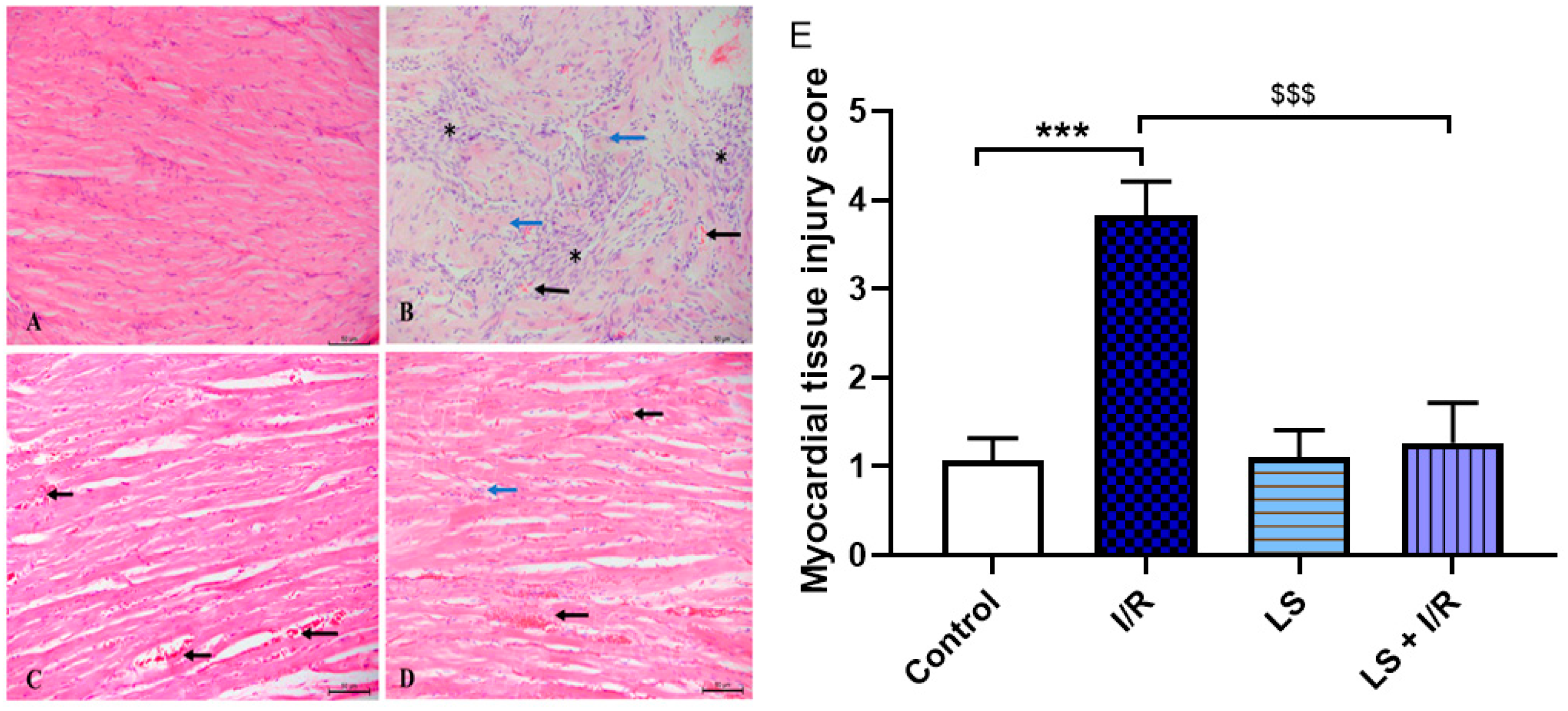
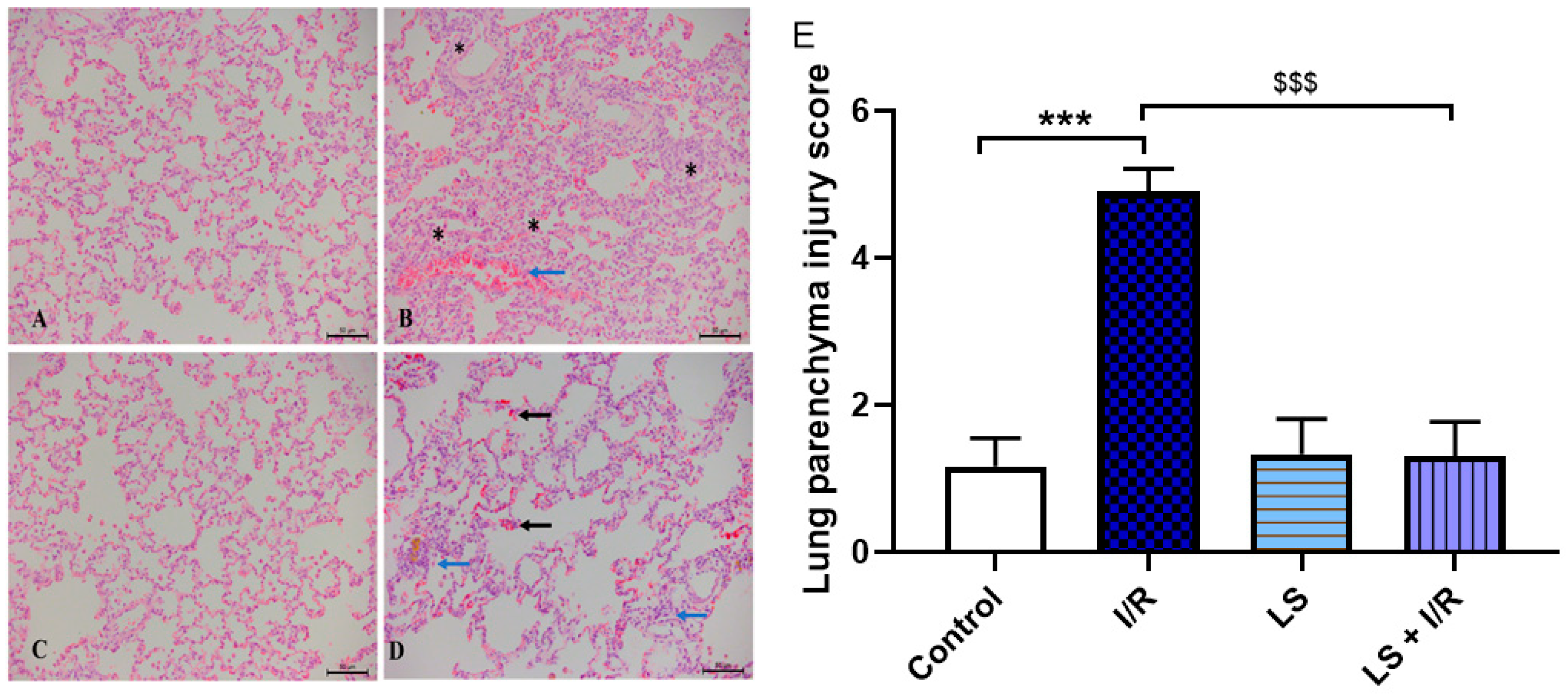
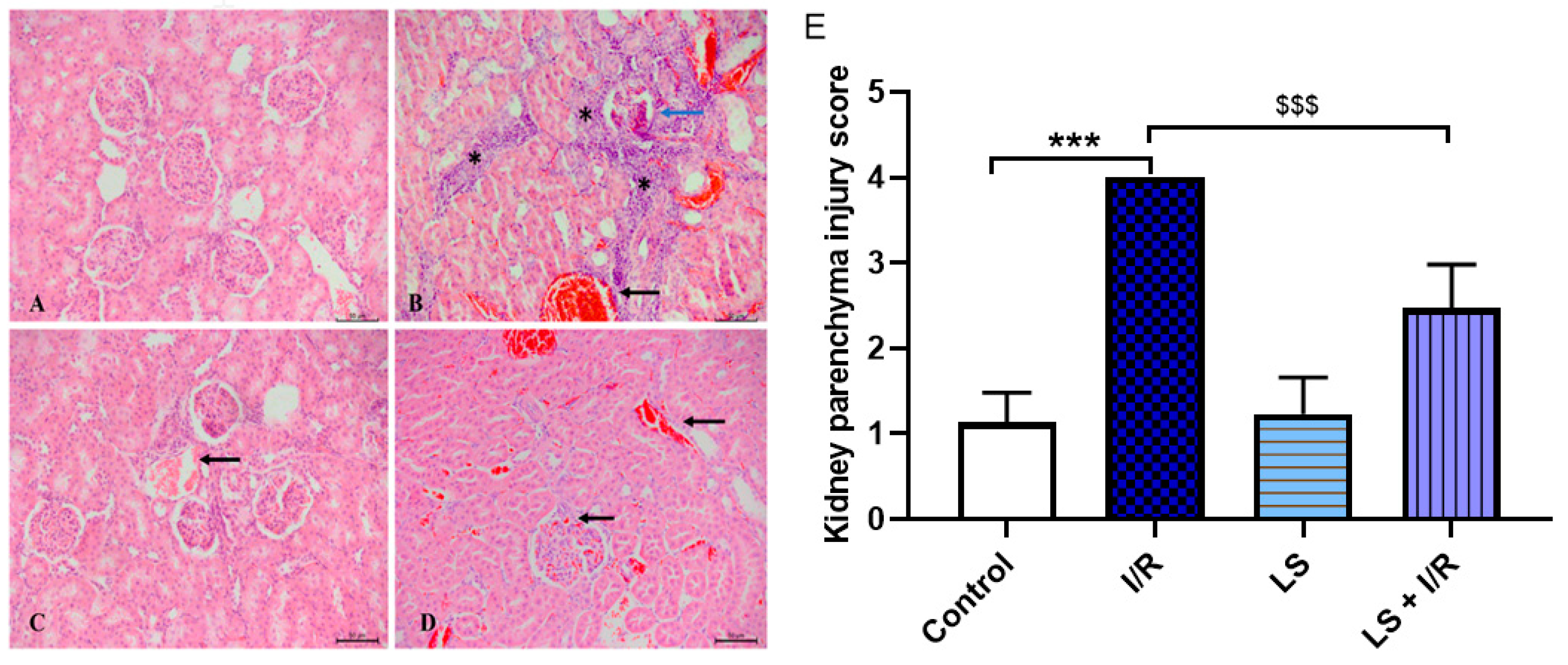
2.6. Protective Effects of Levosimendan on Heart, Lung, and Kidney Induced by Mesenteric Artery I/R Injury
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Principles
4.2. Experimental Animals and Protocols
4.3. Oxidative Stress Markers
4.4. Histopathological Examination and Morphometric Analysis
4.5. Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Limitation of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Apoptotic index |
| AMI | Acute mesenteric ischemia |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BALF | Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| Bcl-2 | B cell lymphoma-2 |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CC3 | Cleaved caspase 3 |
| DAB | 3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| GSH | Reduced glutathione |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| HO-1 | Hem Oxygenase 1 |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| I/R | Ischemia/reperfusion |
| IL-1 | Interleukin-1 |
| Il-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| LS | Levosimendan |
| MODS | Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome |
| NaOH | Sodium hydroxide |
| NF-kB | Nuclear Factor kappa light-chain enhancer of activated B cells |
| NO2 | Nitrogen dioxide |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2- related factor |
| O2− | Super oxide anjon radical |
| OH | Hydroxyl radical |
| ONOO− | Peroxynitrite |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| ROS/RNS | Reactive oxygen/nitrogen species |
References
- Duran, M.; Pohl, E.; Grabitz, K.; Schelzig, H.; Sagban, T.A.; Simon, F. Importance of emergency open surgery in the treatment of acute mesenteric ischemia. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2015, 26, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.W.; Chang, J.B.; Longo, W.E. Update in management of mesenteric ischemia. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 3243–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoots, I.G.; Koffeman, G.I.; Legemate, D.A.; Levi, M.; van Gulik, T.M. Systematic review of survival after acute mesenteric ischaemia according to disease aetiology. Br. J. Surg. 2004, 91, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldenburg, W.A.; Lau, L.L.; Rodenberg, T.J.; Edmonds, H.J.; Burger, C.D. Acute mesenteric ischemia: A clinical review. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khun, F.; Schiergens, T.S.; Klar, E. Acute Mesenteric Ischemia. Visc. Med. 2020, 36, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilsed, J.; Casamassima, A.; Kurihara, H.; Mariani, D.; Martinez, I.; Pereira, J.; Ponchietti, L.; Shamiyeh, A.; al-Ayoubi, F.; Barco, L.A.B.; et al. ESTES guidelines: Acute mesenteric ischaemia. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2016, 42, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeris, T.; Baines, C.P.; Krenz, M.; Korthuis, R.J. Ischemia/reperfusion. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 7, 113–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoni, S.; Ballabeni, V.; Barocelli, E.; Tognolini, M. Mesenteric ischemia-reperfusion: An overview of preclinical drug strategies. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1416–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Deng, Y.Y.; Liu, L.; Tan, Q.H.; Wang, C.H.; Guo, M.M.; Xie, Y.M.; Tang, C.W. Intestinal ischemia-reperfusion of macaques triggers a strong innate immune response. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15327–15334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badripour, A.; Behzadi, M.; Hassanipour, A.; Azar, P.R.S.; Rahbar, A.; Abbaslou, Z.; Ehghaghi, E.; Piranviseh, A.; Khavandi, M.M.; Ahmadi-Tafti, S.M.; et al. Albendazole ameliorates inflammatory response in a rat model of acute mesenteric ischemia reperfusion injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, M.; Catena, F.; Kashuk, J.; De Simone, B.; Gomes, C.A.; Weber, D.; Sartelli, M.; Coccolini, F.; Kluger, Y.; Abu-Zidan, F.M.; et al. Acute mesenteric ischemia: Updated guidelines of the World Society for Emergency Surgery. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2022, 17, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, R.O.S.; Losada, D.M.; Jordani, M.C.; Evora, P.; Castro-E-Silva, O. Ischemia/Reperfusion injury. Revisited an overview of latest Pharmacological Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pataricza, J.; Hohn, J.; Petri, A.; Balogh, A.; Papp, J.G. Comparison of the vasorelaxant effect of cromacalli and a new inodilator, levosimendan, in the isolated human portal vein. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2000, 52, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdei, N.; Papp, Z.; Pollesello, P.; Édes, I.; Bagi, Z. The levosimendan metabolite OR-1896 induces vasodilation by activating K(ATP) and BK(Ca) channels in isolated rat arterioles. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 148, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, B.; Albayrak, A.; Halici, Z.; Karakus, E.; Bayir, Y.; Demirci, E.; Cadirci, E.; Odaci, E.; Yayla, M.; Atamanalp, S.S. The effect of levosimendan in rat mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Investig. Surg. 2013, 26, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aygun, H.; Olguner, C.; Koca, U.; Ergur, B.U.; Sisman, A.R.; Isguven, D.; Girgin, P.; Akkus, M.; Tulgar, S. The effect of postreperfusion levosimendan in an experimental intestinal ischemia-reperfusion model. J. Anesth. Analg. Crit. Care 2022, 2, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenberg, M.H.; Beger, H.G. Reperfusion injury after intestinal ischemia. Crit. Care Med. 1993, 21, 137613–137686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakus, E.; Halici, Z.; Albayrak, A.; Bayir, Y.; Aydin, A.; Unal, D.; Cadirci, E.; Ferah, I.; Odaci, E. Beneficial Pharmacological effects of Levosimendan on Antioxidant status of Acute Inflammation Induced in Paw of rat: Involvement in Inflammatory Mediators. BCPT 2013, 112, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastrelo, M.M.; Dias Ribeiro, C.C.; Duarte, J.W.; Bioago Gollücke, A.P.; Artigiani-Neto, R.; Ribeiro, D.A.; Miszputen, S.J.; Fujiyama Oshima, C.T.; Ribeiro Paiotti, A.P. Effect of Concentrated Apple Extract on Experimental Colitis Induced by Acetic Acid. Int. J. Mol. Cell. Med. 2017, 6, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shi, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhi, H.; An, H.; Hu, Z. Levosimendan protects from sepsis-inducing cardiac dysfunction by suppressing inflammation, oxidative stress and regulating cardiac mitophagy via the PINK-1-Parkin pathway in mice. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Meng, W.; Shu, C.; Gao, H. Levosimendan Ameliorates Hypoxia-Induced Brain Injury in Rats by Modulating PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway-Mediated Ferroptosis. Discov. Med. 2024, 36, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; Wu, B.; Wang, X.; Buchanan, M.E.; Regueiro, M.D.; Hartman, D.J.; Schoen, R.E.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L. PUMA-mediated intestinal epithelial apoptosis contributes to ulcerative colitis in humans and mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Parks, D.A.; Granger, D.N. Contributions of ischemia and reperfusion to mucosal lesion formation. Am. J. Physiol. 1986, 250, G749–G753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolmar, B.; Menger, M.D. Intestinal ishemia/reperfusion: Microcirculatory pathology and functional consequences. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2011, 396, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.Y.; Kuo, W.T.; Tsai, Y.S.; Yu, L.C.; Huang, C.Y. Glucosae- Stimulated mucus secretion by Goblet cells Mitigates Intestinal Barrier dysfunction in a rat model of Mesenteric Ischemia/ reperfusion Injury. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2024, 8, 104431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grootjans, J.; Hundscheid, I.H.; Lenaerts, K.; Boonen, B.; Renes, I.B.; Verheyen, F.K.; Dejong, C.H.; von Meyenfeldt, M.F.; Beets, G.L.; Buurman, W.A. Ischaemia-induced mucus barrier loss and bacterial penetration are rapidly counteracted by increased goblet cell secretory activity in human and rat colon. Gut 2013, 62, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grootjans, J.; Hundscheid, I.H.; Buurman, W.A. Goblet cell compound exocytosis in the defense against bacterial invasion in the colon exposed to ischemia-reperfusion. Gut Microbes 2013, 4, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shimada, M.; Koyama, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Shimada, S. Si-based agent alleviated small bowel ischemia-reperfusion injury through antioxidant effects. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Agoston, D.V. How to translate time? The temporal aspect of human and rodent biology. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.T.; Chen, R.; Chen, C.; Su, K.; Li, W.; Tang, L.H.; Liu, H.M.; Xue, R.; Sun, Q.; Leng, Y.; et al. Transcription factors Nrf2 and NF-κB contribute to inflammation and apoptosis induced by intestinal ischemia-reperfusion in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yilmaz, A.S.; Badak, B.; Erkasap, N.; Ozkurt, M.; Colak, E. The Effect of Antioxidant Astaxanthin on Intestinal Ischemia Reperfusion Damage in Rats. J. Investig. Surg. 2023, 36, 2182930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; He, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Guo, T. Down-regulation of toll-like receptor 4 alleviates intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury and acute lung injury in mice. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13678–13689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tawfik, M.K.; Makary, S.; Keshawy, M.M. Upregulation of antioxidant nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and its dependent genes associated with enhancing renal ischemic preconditioning renoprotection using levosimendan and cilostazol in an ischemia/reperfusion rat model. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 17, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Q.; Yokoo, H.; Takashina, M.; Sakata, K.; Ohashi, W.; Abedelzaher, L.A.; Imaizumi, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Hattori, K.; Matsuda, N.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Profile of Levosimendan in Cecal Ligation-Induced Septic Mice and in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, e508–e520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiermann, P.; Beiras-Fernandez, A.; Mutlak, H.; Weis, F. The protective effects of levosimendan on ischemia/reperfusion injury and apoptosis. Recent Pat. Cardiovasc. Drug Discov. 2011, 6, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, T.; Gok, S.; Nese, N. Levosimendan attenuates reperfusion injury in an isolated perfused rat heart model. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2010, 24, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossini, E.; Pollesello, P.; Bellofatto, K.; Sigaudo, L.; Farruggio, S.; Origlia, V.; Mombello, C.; Mary, D.A.S.G.; Valente, G.; Vacca, G. Protective effects elicited by levosimendan against liver ischemia/reperfusion injury in anesthetized rats. Liver Transplant. 2013, 19, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstgrasser, A.; Melhem, H.; Leonardi, I.; Atrott, K.; Schäfer, M.; Werner, S.; Rogler, G.; Frey-Wagner, I. Cell-specific Activation of the Nrf2 Antioxidant Pathway Increases Mucosal Inflammation in Acute but Not in Chronic Colitis. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodson, M.; de la Vega, M.R.; Cholanians, A.B.; Schmidlin, C.J.; Chapman, E.; Zhang, D.D. Modulating NRF2 in Disease: Timing Is Everything. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 59, 555–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stachel, I.; Geismann, C.; Aden, K.; Deisinger, F.; Rosenstiel, P.; Schreiber, S.; Sebens, S.; Arlt, A.; Schäfer, H. Modulation of nuclear factor E2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) activation by the stress response gene immediate early response-3 (IER3) in colonic epithelial cells: A novel mechanism of cellular adaption to inflammatory stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1917–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Morales, M.; Munné-Bosch, S. Malondialdehyde: Facts and Artifacts. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 1246–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ucar, B.I.; Ucar, G.; Saha, S.; Buttari, B.; Profumo, E.; Saso, L. Pharmacological Protection against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Regulating the Nrf2-Keap1-ARE Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ji, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.D.; Wang, S.F.; Wang, B.T.; Yang, Z.A.; Zhou, X.R.; Lei, N.N.; Yue, W.N. Ischemic preconditioning ameliorates intestinal injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8081–8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- O’Rourke, S.A.; Shanley, L.C.; Dunne, A. The Nrf2-HO-1 system and inflammaging. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1457010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gao, W.; Guo, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, S.; Gong, H.; Zhang, B.K.; Yan, M. Dissecting the Crosstalk Between Nrf2 and NF-κB Response Pathways in Drug-Induced Toxicity. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 9, 809952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, S.; Liao, X.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, R.; Chen, M.; Huang, A.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y. Antioxidant and anti-inflammation effects of dietary phytochemicals: The Nrf2/NF-κB signalling pathway and upstream factors of Nrf2. Phytochemistry 2022, 204, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Luo, L.; Namani, A.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Nrf2 signaling pathway: Pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, V.; Vitale, D.; Tritapepe, L.; Greco, C.; Pietropaoli, P. Use of levosimendan for cardiogenic shock in patients with apical ballooning syndrome. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 149, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieminen, M.S.; Pollesello, P.; Vajda, G.; Papp, Z. Effects of levosimendan on energy balance: Preclinical and clinical evidence. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 53, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Pollesello, P.; Saris, N.E. Levosimendan is an opener of mitochondrial K(ATP) channels. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 428, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.; Meyer, S.; Knors, H.; Klinke, A.; Radunski, U.K.; Rudolph, T.K.; Rudolph, V.; Spin, J.M.; Tsao, P.S.; Costard-Jäckle, A.; et al. Levosimendan shows anti-inflammatory effects and reduces the bioavailability of MPO in patients with severe heart failure. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Su, Q.; Liu, T.; Li, L. Levosimendan pretreatment inhibits myocardial apoptosis in pigs after coronary microembolization. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritapepe, L.; De Santis, V.; Vitale, D.; Guarracino, F.; Pellegrini, F.; Pietropaoli, P.; Singer, M. Pretreatment with levosimendan improves outcomes in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 102, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbüyün, K.; Vatansever, S.; Tok, D.; Ok, G.; Türköz, E.; Aydede, H.; Erhan, Y.; Tekin, İ. Effects of levosimendan and dobutamine on experimental acute lung injury in rats. Acta Histochem. 2009, 111, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasa, H.; Yakut, N.; Emrecan, B.; Ergunes, K.; Ortac, R.; Karahan, N.; Ozbek, C.; Gurbuz, A. Protective effects of levosimendan and iloprost on lung injury induced by limb ischemia-reperfusion: A rabbit model. J. Surg. Res. 2008, 147, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önem, G.; Saçar, M.; Aybek, H.; Kocamaz, E.; Adalı, F.; Saçkan, K.G.; Baltalarlı, A. Protective effects of cilostazol and levosimendan on lung injury induced by lower limb ischemia-reperfusion. Turk. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 20, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedele, F.; Karason, K.; Matskeplishvili, S. Pharmacological approaches to cardio-renal syndrome: The role of the inodilator levosimendan. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2017, 19 (Suppl. SC), C22–C28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zager, R.A.; Johnson, A.C.; Lund, S.; Hanson, S.Y.; Abrass, C.K. Levosimendan protects against experimental endotoxemic acute renal failure. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2006, 290, F1453–F1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pick, E.; Keisari, Y. A simple colorimetric method for the measurement of hydrogen peroxide produced by cells in culture. J. Immunol. Methods 1980, 38, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auclair, C.; Voisin, E. Nitroblue-tetrazolium reduction. In Handbook of Methods for Oxygen Radical Research, 1st ed.; Greenwald, R.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1985; pp. 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutler, E. Red Cell Metabolism: A Manual of Biochemical Methods, 3rd ed.; Grune and Stratton: Orlando, FL, USA; Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1984; pp. 83–85. [Google Scholar]
- Beutler, E. Manual of Biochemical Methods, 2nd ed.; Grune and Stratton: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 105–106. [Google Scholar]
- Beutler, E.; Duron, O.; Kelly, B.M. Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1963, 61, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bajic, Z.; Sobot, T.; Amidzic, L.; Vojinovic, N.; Jovicic, S.; Gajic Bojic, M.; Djuric, D.M.; Stojiljkovic, M.P.; Bolevich, S.; Skrbic, R. Liraglutide Protects Cardiomyocytes against Isoprenaline-Induced Apoptosis in Experimental Takotsubo Syndrome. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Trajković, S.; Dobrić, S.; Jaćević, V.; Dragojević-Simić, V.; Milovanović, Z.; Dordević, A. Tissue-protective effects of fullerenol C60(OH)24 and amifostine in irradiated rats. Colloids. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 58, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaćević, V.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuča, K. Acute Toxic Injuries of Rat’s Visceral Tissues Induced by Different Oximes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oltean, M.; Olausson, M. The Chiu/Park scale for grading intestinal ischemia-reperfusion: If it ain’t broke don’t fix it! Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matković, Z.; Gajić Bojić, M.; Maličević, U.; Krivokuća, A.; Mandić-Kovačević, N.; Uletilović, S.; Amidžić, L.; Jovičić, S.; Barudžija, M.; Stojiljković, M.P.; et al. Levosimendan Pretreatment Attenuates Mesenteric Artery Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury and Multi-Organ Damage in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189131
Matković Z, Gajić Bojić M, Maličević U, Krivokuća A, Mandić-Kovačević N, Uletilović S, Amidžić L, Jovičić S, Barudžija M, Stojiljković MP, et al. Levosimendan Pretreatment Attenuates Mesenteric Artery Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury and Multi-Organ Damage in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):9131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189131
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatković, Zoran, Milica Gajić Bojić, Uglješa Maličević, Aleksandra Krivokuća, Nebojša Mandić-Kovačević, Snežana Uletilović, Ljiljana Amidžić, Sanja Jovičić, Maja Barudžija, Miloš P. Stojiljković, and et al. 2025. "Levosimendan Pretreatment Attenuates Mesenteric Artery Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury and Multi-Organ Damage in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 9131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189131
APA StyleMatković, Z., Gajić Bojić, M., Maličević, U., Krivokuća, A., Mandić-Kovačević, N., Uletilović, S., Amidžić, L., Jovičić, S., Barudžija, M., Stojiljković, M. P., Gajanin, R., Bolevich, S., & Škrbić, R. (2025). Levosimendan Pretreatment Attenuates Mesenteric Artery Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury and Multi-Organ Damage in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 9131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189131






