Integrated miRNA-mRNA Analyses of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in Black and White Patients with or Without Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographics of Patients Included
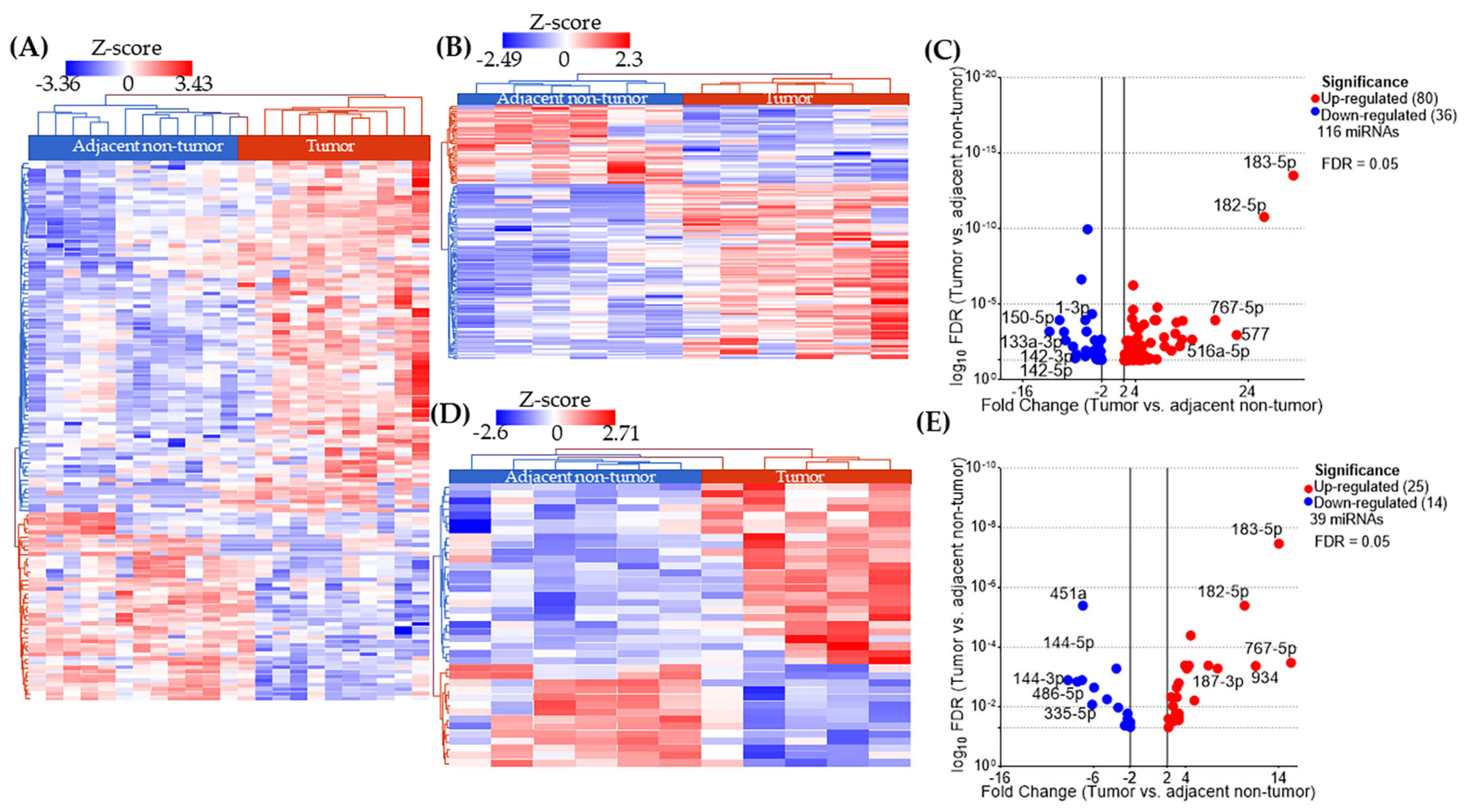
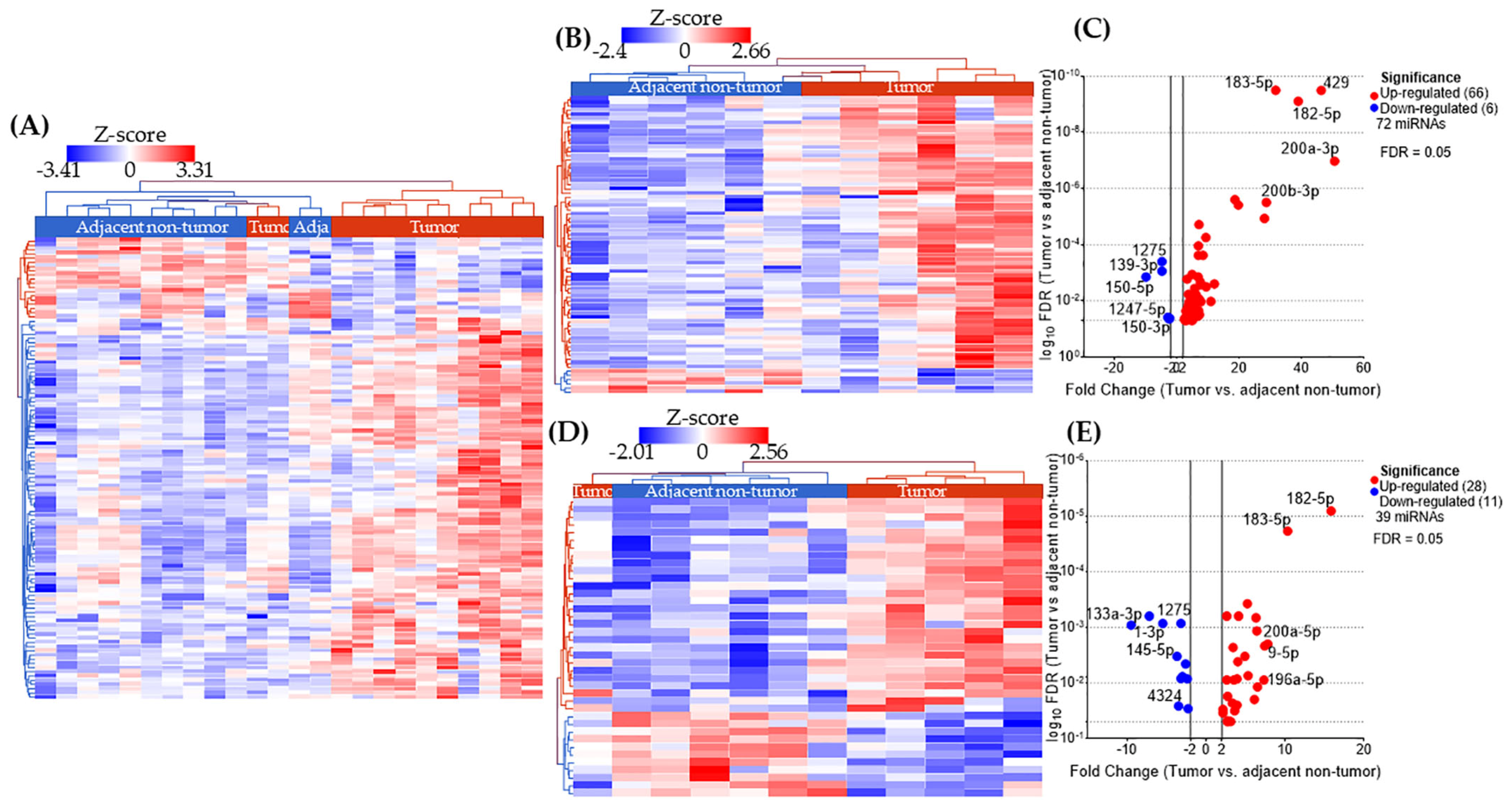
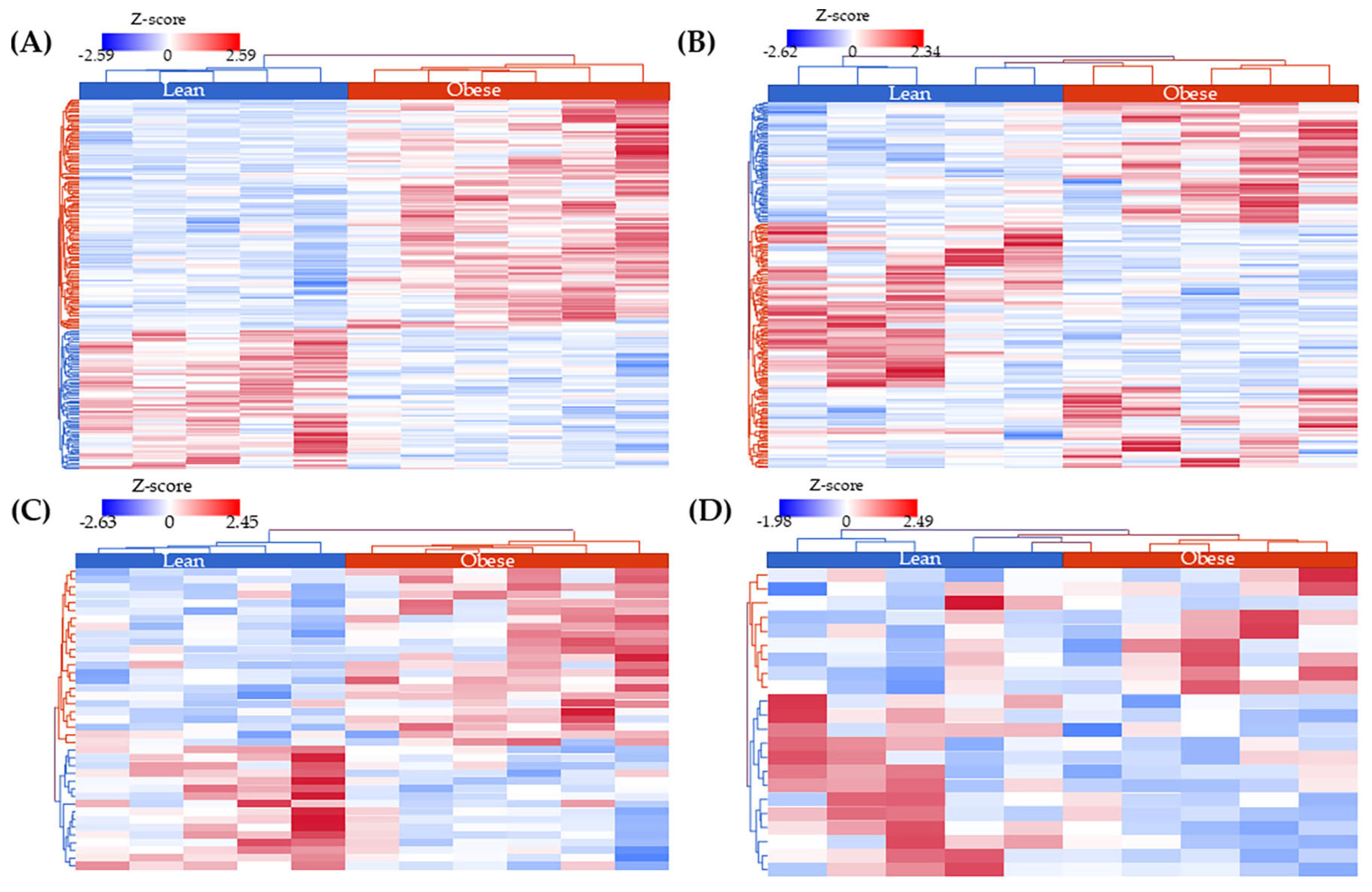
2.2. miRNA Expression Profiles in AA and EA TNBC Patients with or Without Obesity
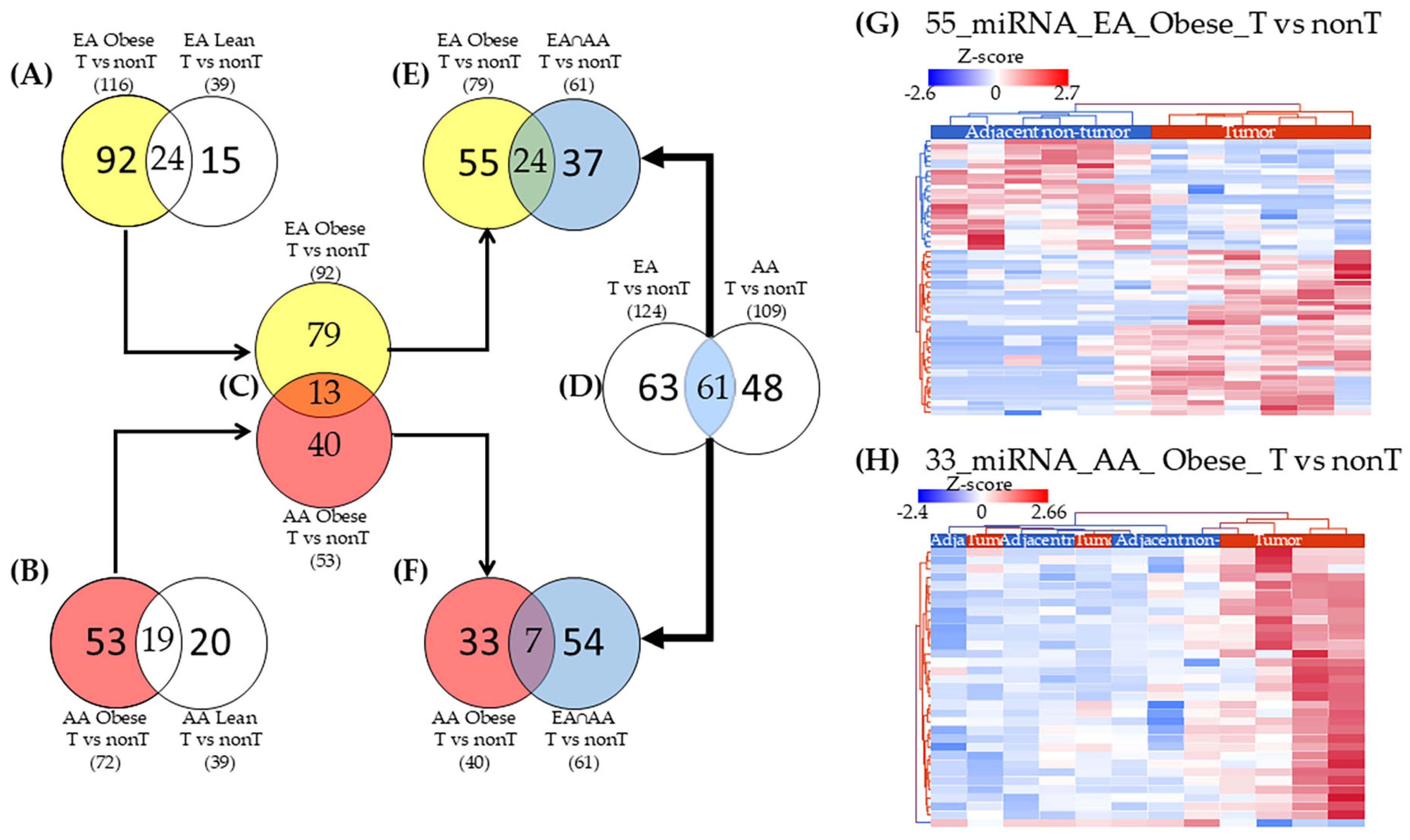
2.3. miRNAs Uniquely Associated with Tumor Tissues in Obese Patients by Racial Group
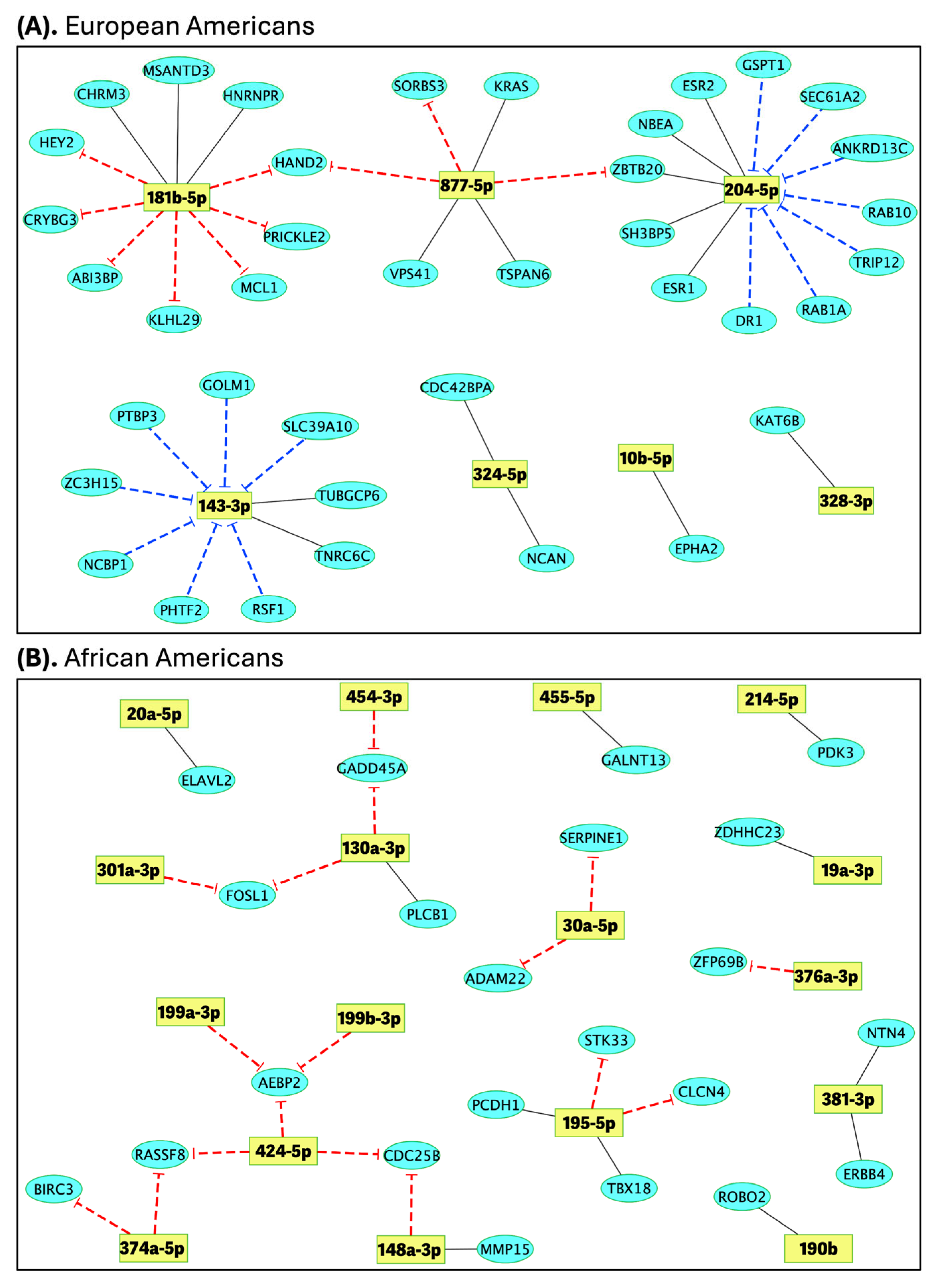
2.4. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) and Correlation with miRNA Expression
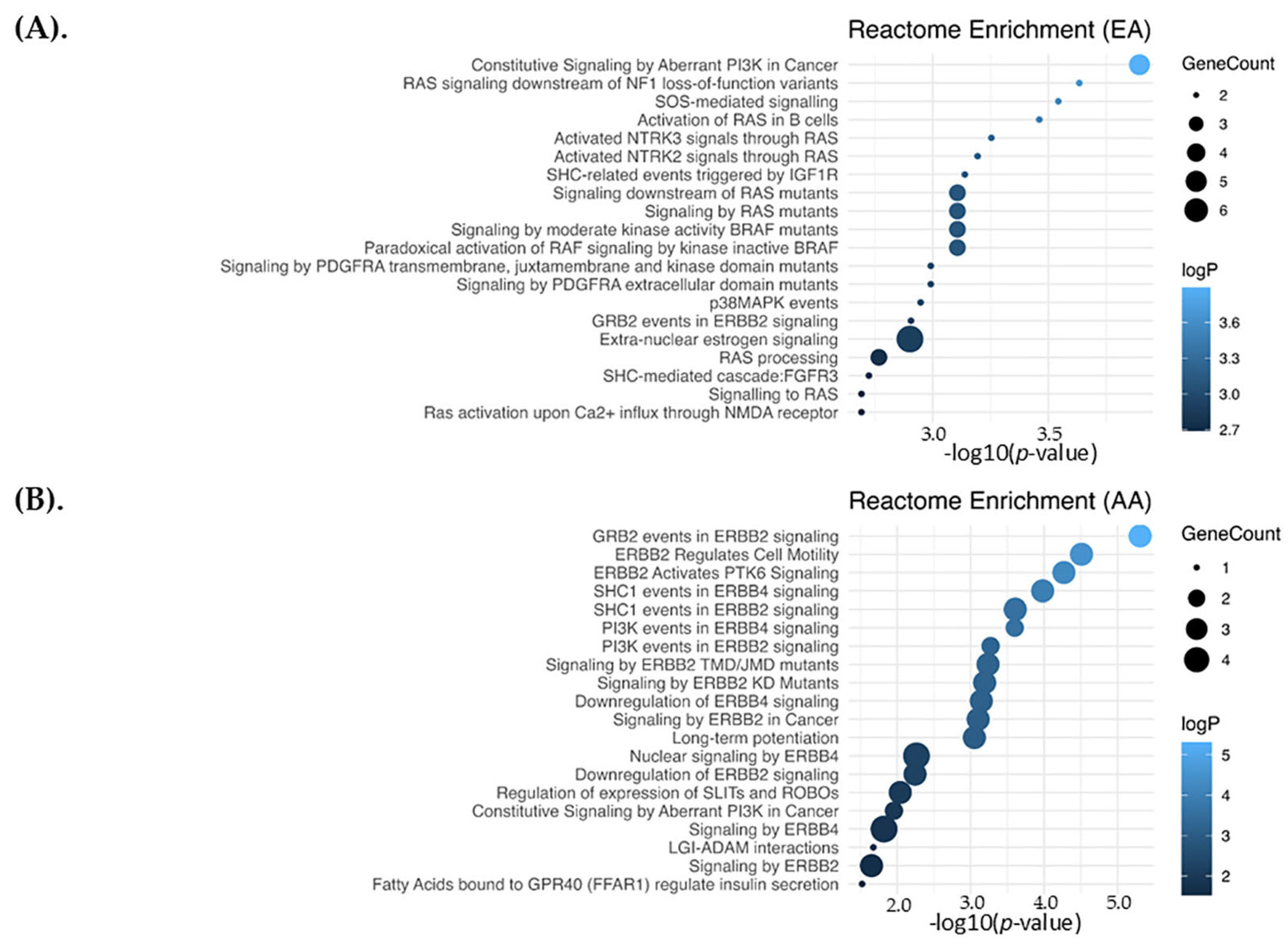
2.5. Pathways Enrichment Analysis
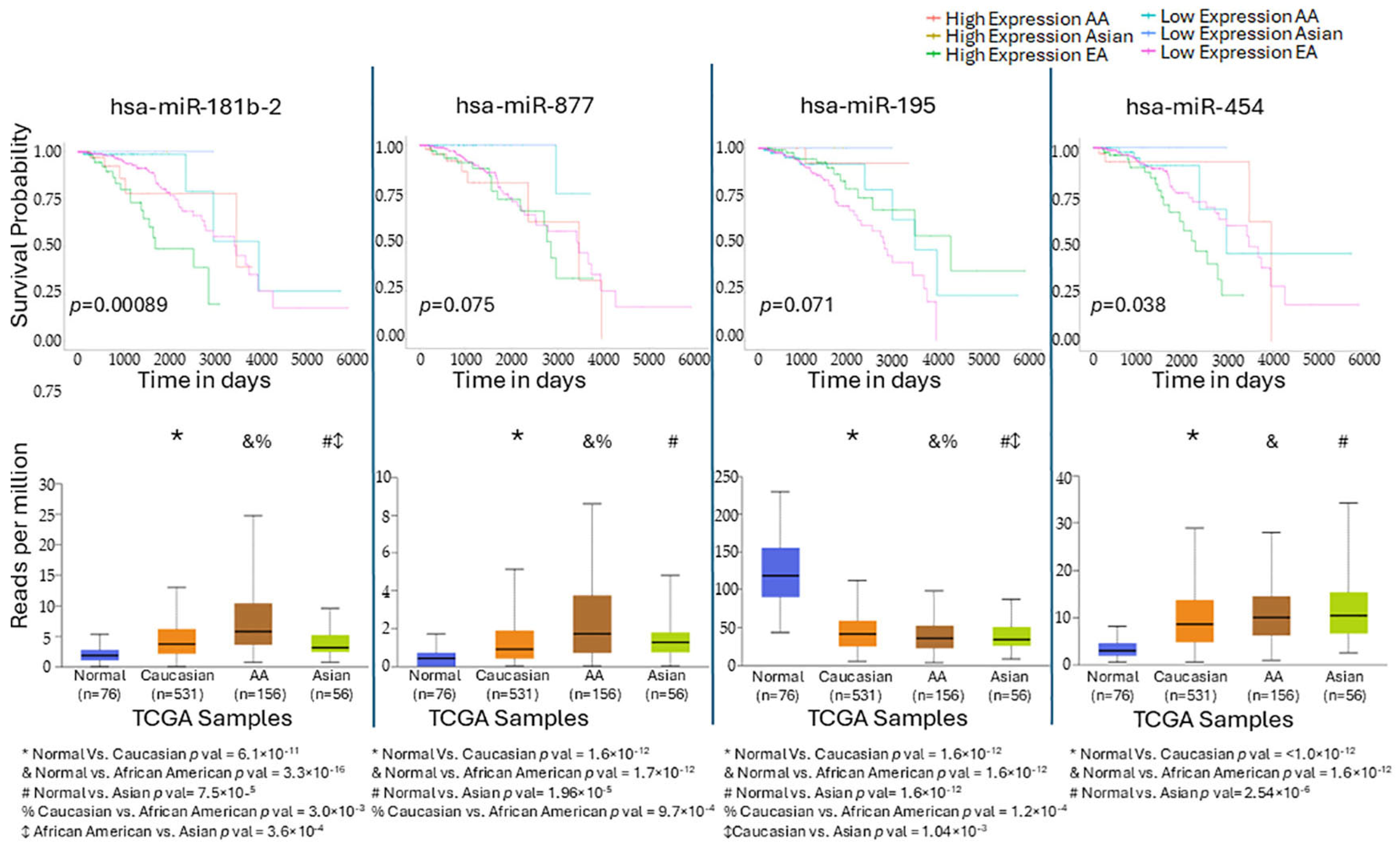
2.6. TCGA External Validation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples Selection and Study Design
4.2. RNA Extraction and Library Preparation
4.3. Sequencing Data Processing
4.4. Strategy for miRNA Selection
4.5. Correlation Analysis
4.6. Pathway Enrichment Analysis and External Validation in TCGA
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| White/EA | European American |
| Black/AA | African American |
| DE | Differentially Expressed |
| DEA | Differential Expression Analysis |
| miRNAs | microRNAs |
| FFPE | Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded |
| TNBC | Triple Negative Breast Cancer |
| BC | Breast Cancer |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| TGC | Translational Genomics Core |
References
- de Ruijter, T.C.; Veeck, J.; de Hoon, J.P.J.; van Engeland, M.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C. Characteristics of triple-negative breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 137, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Castro, A.C.; Lin, N.U.; Polyak, K. Insights into Molecular Classifications of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Improving Patient Selection for Treatment. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 176–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Pietenpol, J.A. Clinical implications of molecular heterogeneity in triple negative breast cancer. Breast 2015, 24, S36–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakha, E.A.; El-Sayed, M.E.; Green, A.R.; Lee, A.H.S.; Robertson, J.F.; Ellis, I.O. Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer 2006, 109, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Y.; Pegram, M. Research advances and new challenges in overcoming triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021, 4, 517–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsamany, S.; Abdullah, S. Triple-negative breast cancer: Future prospects in diagnosis and management. Med Oncol. 2014, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, K.R.; Brown, M.; Cress, R.D.; Parise, C.A.; Caggiano, V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: A population-based study from the California cancer Registry. Cancer 2007, 109, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahmood, S.; Sapiezynski, J.; Garbuzenko, O.B.; Minko, T. Metastatic and triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and treatment options. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 1483–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plasilova, M.L.; Hayse, B.; Killelea, B.K.; Horowitz, N.R.; Chagpar, A.B.; Lannin, D.R. Features of triple-negative breast cancer. Medicine 2016, 95, e4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W. Impact of tiny miRNAs on cancers. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved Seed Pairing, Often Flanked by Adenosines, Indicates that Thousands of Human Genes are MicroRNA Targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.-H.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, J.; e Silva, B.V.R.; Gao, T.; Xu, Z.; Cui, J. Dynamic and Modularized MicroRNA Regulation and Its Implication in Human Cancers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Storey, K.B. MicroRNA Cues from Nature: A Roadmap to Decipher and Combat Challenges in Human Health and Disease? Cells 2021, 10, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.-M.; Zhu, H.-Y.; Bai, W.-D.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, A.-G.; Jia, L.-T. Epigenetic silencing of miR-375 induces trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer by targeting IGF1R. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleckova, M.; Janikova, M.; Kolar, Z. MicroRNAs in triple-negative breast cancer. Neoplasma 2018, 65, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schooneveld, E.; Wildiers, H.; Vergote, I.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Dirix, L.Y.; Van Laere, S.J. Dysregulation of microRNAs in breast cancer and their potential role as prognostic and predictive biomarkers in patient management. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Ahmad, A.; Sarkar, F.H. The Role of MicroRNAs in Breast Cancer Migration, Invasion and Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 13414–13437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, A.; Jacks, T. MicroRNAs and Cancer: Short RNAs Go a Long Way. Cell 2009, 136, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lim, W.; You, D.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.E.; Shin, T.H.; Lee, G.; Park, S. Chemoresistance in the Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Line MDA-MB-231 Induced by Doxorubicin Gradient Is Associated with Epigenetic Alterations in Histone Deacetylase. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabit, H.; Cevik, E.; Tombuloglu, H.; Abdel-Ghany, S.; Tombuloglu, G.; Esteller, M. Triple negative breast cancer in the era of miRNA. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2021, 157, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Tao, H.; Humphries, B.; Li, A.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, C.; Luo, R.; Wang, Z. Integrin α5 down-regulation by miR-205 suppresses triple negative breast cancer stemness and metastasis by inhibiting the Src/Vav2/Rac1 pathway. Cancer Lett. 2018, 433, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, K.-J.; Jia, Q.-J.; Ding, X.-F. Roles of miRNA and IncRNA in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Zhejiang Univ. B 2020, 21, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volovat, S.R.; Hordila, I.; Hordila, D.-A.; Mirestean, C.C.; Miron, O.T.; Lungulescu, C.; Scripcariu, D.V.; Stolniceanu, C.R.; Konsoulova-Kirova, A.A.; Grigorescu, C.; et al. MiRNA and LncRNA as Potential Biomarkers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Review. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 526850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, K.; Douglas, I.; Forbes, H.; dos-Santos-Silva, I.; Leon, D.A.; Smeeth, L. Body-mass index and risk of 22 specific cancers: A population-based cohort study of 5.24 million UK adults. Lancet 2014, 384, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, A.J.; Allen, N.E.; Appleby, P.N.; Crowe, F.L.; Travis, R.C.; Tipper, S.J.; Overvad, K.; Grønbæk, H.; Tjønneland, A.; Johnsen, N.F.; et al. Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Concentration and Risk of Prostate Cancer: Results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2012, 21, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Tyson, M.; Egger, M.; Heller, R.F.; Zwahlen, M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008, 371, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggio, F.; Blondeaux, E.; Tagliamento, M.; Perachino, M.; Nardin, S.; Conte, B.; Giuliano, M.; Arpino, G.; De Laurentiis, M.; Gravina, A.; et al. Efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy schedules for breast cancer according to body mass index: Results from the phase III GIM2 trial. ESMO Open 2024, 9, 103650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arner, E.; Mejhert, N.; Kulyté, A.; Balwierz, P.J.; Pachkov, M.; Cormont, M.; Lorente-Cebrián, S.; Ehrlund, A.; Laurencikiene, J.; Hedén, P.; et al. Adipose Tissue MicroRNAs as Regulators of CCL2 Production in Human Obesity. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1986–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.-Y.; Wu, H.-L.; Chen, C.-C.; Gamboa, G.M.; Layman, L.C.; Diamond, M.P.; Azziz, R.; Chen, Y.-H. MicroRNA-223 Expression Is Upregulated in Insulin Resistant Human Adipose Tissue. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Shimabukuro, M.; Yagi, S.; Nishimoto, S.; Kozuka, C.; Fukuda, D.; Soeki, T.; Masuzaki, H.; Tsutsui, M.; Sata, M.; et al. MicroRNA-378 Regulates Adiponectin Expression in Adipose Tissue: A New Plausible Mechanism. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerson, A.; Traurig, M.; Ossowski, V.; Fleming, J.M.; Mullins, M.; Baier, L.J. Human adipose microRNA-221 is upregulated in obesity and affects fat metabolism downstream of leptin and TNF-α. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.J.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Pardo, G.; Sabater, M.; Hummel, M.; Ferrer, A.; Rodriguez-Hermosa, J.I.; Ruiz, B.; Ricart, W.; Peral, B.; et al. MiRNA Expression Profile of Human Subcutaneous Adipose and during Adipocyte Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra, P.E.; García-Solís, P.; Solís-Sáinz, J.C.; Cruz-Hernández, A. Expression of miRNA in obesity and insulin resistance: A review. Endokrynol. Polska 2021, 72, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telonis, A.G.; Rigoutsos, I. Race Disparities in the Contribution of miRNA Isoforms and tRNA-Derived Fragments to Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1140–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.-J. Linking altered microRNA expression to racial disparities in uterine serous carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021, 163, 446–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, E.J.; Yoon, H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.T.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, S. MicroRNA Expression Profiles in Serous Ovarian Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2690–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Shirvani-Farsani, Z.; Branicki, W.; Taheri, M. MicroRNA Signature in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, Z.; Mohammadpour-Gharehbagh, A.; Eskandari, M.; Harati-Sadegh, M.; Salimi, S. Genetic polymorphisms of miRNA let7a-2 and pri-mir-34b/c are associated with an increased risk of papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinical/pathological features. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 120, 8640–8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magee, R.G.; Telonis, A.G.; Loher, P.; Londin, E.; Rigoutsos, I. Profiles of miRNA Isoforms and tRNA Fragments in Prostate Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podany, E.L.; Foffano, L.; Gerratana, L.; Medford, A.J.; Clifton, K.; Tapiavala, S.; Velimirovic, M.; Lipsyc-Sharf, M.; Reduzzi, C.; Bubie, A.; et al. Racial Differences in ctDNA Profiles, Targeted Therapy Use, and Outcomes in Metastatic Breast Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e2461899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piasecka, D.; Braun, M.; Kordek, R.; Sadej, R.; Romanska, H. MicroRNAs in regulation of triple-negative breast cancer progression. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, L.; Mao, X.; Shi, P.; He, B.; Xu, K.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J. MicroRNAs in the prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer. Medicine 2017, 96, e7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, T.A.B.d.S.; Passamai, L.d.O.; de Miranda, F.S.; Borin, T.F.; Borges, G.F.; Luiz, W.B.; Campos, L.C.G. The Role of miRNAs in the Prognosis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Dai, M.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Qin, S.; Dai, S. Integrated analysis of the potential roles of miRNA-mRNA networks in triple negative breast cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascione, L.; Gasparini, P.; Lovat, F.; Carasi, S.; Pulvirenti, A.; Ferro, A.; Alder, H.; He, G.; Vecchione, A.; Croce, C.M.; et al. Integrated MicroRNA and mRNA Signatures Associated with Survival in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Cao, K.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Han, J. Transcriptome of visceral adipose tissue identifies an inflammation-related ceRNA network that regulates obesity. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2022, 477, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Ji, P.; Wu, H.-L.; He, L.-H.; Jin, M.-L.; Hu, X.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Shao, Z. Integrated analysis reveals the impact of obesity on triple-negative breast cancer. In Proceedings of the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), San Antonio, TX, USA, 5–9 December 2023; Available online: https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/84/9_Supplement/PO1-14-06/744131/Abstract-PO1-14-06 (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Supplitt, S.; Karpinski, P.; Sasiadek, M.; Laczmanski, L.; Kujawa, D.; Matkowski, R.; Kasprzak, P.; Abrahamowska, M.; Maciejczyk, A.; Iwaneczko, E.; et al. The analysis of transcriptomic signature of TNBC—Searching for the potential RNA-based predictive biomarkers to determine the chemotherapy sensitivity. J. Appl. Genet. 2024, 66, 171–182, Correction in J. Appl. Genet. 2025, 66, 249. http://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-024-00902-y. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.N.; Therneau, T.M.; Zhang, Y.; Poland, G.A.; Kocher, J.-P. Calculating Sample Size Estimates for RNA Sequencing Data. J. Comput. Biol. 2013, 20, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröman, G.; Acevedo, F.; Lundahl, P.; Hjertén, S. The glucose transport activity of human erythrocyte membranes. Reconstitution in phospholipid liposomes and fractionation by molecular sieve and ion exchange chromatography. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 1980, 600, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Pan, T.; Deng, J.; Cao, L.; Vicencio, J.M.; Liu, J.; Zhou, G.; Ng, T.; Zhang, J. Exosomal transfer of miR-181b-5p confers senescence-mediated doxorubicin resistance via modulating BCLAF1 in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 128, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, J.; Grinpelc, A.; Farré, P.L.; Duca, R.B.; Lacunza, E.; Graña, K.D.; Scalise, G.D.; Dalton, G.N.; Massillo, C.; Piccioni, F.; et al. miR-877-5p as a Potential Link between Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Development and Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Hu, J.; Song, H.; Xu, H.; Wu, C.; Zhao, B.; Xie, D.; Wu, T.; Zhao, J.; Fang, L. miR-143-3p targeting LIM domain kinase 1 suppresses the progression of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2276–2285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Wei, C.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Song, H.; Li, D.; Fang, L. MicroRNA-195-5p is a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target for breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azoitei, N.; Hoffmann, C.M.; Ellegast, J.M.; Ball, C.R.; Obermayer, K.; Gößele, U.; Koch, B.; Faber, K.; Genze, F.; Schrader, M.; et al. Targeting of KRAS mutant tumors by HSP90 inhibitors involves degradation of STK33. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, G.; Mao, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Owusu, L.; Ren, B.; Tang, Y.; et al. Down-regulation of GADD45A enhances chemosensitivity in melanoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Y.; Lan, J.; Luo, H.; Fu, H.; Xiao, X.; Yang, L. FOS-Mediated PLCB1 Induces Radioresistance and Weakens the Antitumor Effects of CD8+ T Cells in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2024, 64, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deevy, O.; Bracken, A.P. PRC2 functions in development and congenital disorders. Development 2019, 146, dev181354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cong, L.; Xu, D.; Leng, Q.; Shi, M.; Zhou, Y. AC092127.1-miR-451a-AE binding protein 2 Signaling Facilitates Malignant Properties of Breast Cancer. J. Breast Cancer 2021, 24, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.C.-W.; Chen, J.; Cheuk, I.W.-Y.; Siu, M.-T.; Shin, V.Y.; Kwong, A. MicroRNA-199a-3p promotes drug sensitivity in triple negative breast cancer by down-regulation of BRCA1. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 2021–2036. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, M.; Tong, M.; Yang, L.; Pang, L.; Chen, L.; Xu, G.; Chi, X.; Hong, Q.; Ni, Y.; et al. miR-148a is Associated with Obesity and Modulates Adipocyte Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Wnt Signaling. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep09930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lai, Y.; Liu, D. miR-199b-5p inhibits triple negative breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting DDR1. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 4889–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villagrán-Silva, F.; Loren, P.; Sandoval, C.; Lanas, F.; Salazar, L.A. Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: A Narrative Review. Genes 2025, 16, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Chen, D.; Luo, K.; Lu, M.; Gu, Y.; Zeng, S.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, G.; et al. Cip2a/miR-301a feedback loop promotes cell proliferation and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 5964–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Li, H.; Qian, H.; Jiao, X.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, X.; Dai, G.; Huang, J. Upregulation of miR-301a correlates with poor prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Med Oncol. 2014, 31, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Meng, X.; Pang, R.; Li, J. MicroRNA-454 may function as an oncogene via targeting AKT in triple negative breast cancer. J. Biol. Res. 2017, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Zheng, X.; Li, C.; Han, Z. miR-376a inhibits breast cancer cell progression by targeting neuropilin-1 NR. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 5293–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCuaig, W.M.; Thomas, A.; Claros-Sorto, J.C.; Gomez-Gutierrez, J.G.; Alexander, A.C.; Wellberg, E.A.; Grizzle, W.E.; McNally, L.R. Differential expression of microRNA between triple negative breast cancer patients of African American and European American descent. Biotech. Histochem. 2022, 97, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Balasubramanian, A.; Asirvatham, J.R.; Chatterjee, M.; Piyarathna, B.; Kaur, J.; Mohamed, N.; Wu, L.; Wang, S.; Pourfarrokh, N.; et al. Integrative spatial omics reveals distinct tumor-promoting multicellular niches and immunosuppressive mechanisms in Black American and White American patients with TNBC. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, R.; Monteiro, C.; Catalán, V.; Hu, P.; Cunha, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Fraga, A.; Príncipe, P.; Lobato, C.; et al. Obesity and prostate cancer: Gene expression signature of human periprostatic adipose tissue. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-H.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Ann, D.K.; Chen, J.L.-Y.; Kuo, C.-Y. Obesity promotes radioresistance through SERPINE1-mediated aggressiveness and DNA repair of triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.-N.; Ha, H.; Lee, Z.H. cAMP-response-element-binding protein positively regulates breast cancer metastasis and subsequent bone destruction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Xu, X.; Wan, L.; Lv, F.; Wei, W.; Xu, X.; Li, W.; Huang, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, F. RUNX2 facilitates aggressiveness and chemoresistance of triple negative breast cancer cells via activating MMP1. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 996080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.H.; Hoefer, R.A.; Guye, M.L.; Bear, H.D. Persistent EGFR/K-RAS/SIAH pathway activation drives chemo-resistance and early tumor relapse in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022, 5, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, S.; Dushyanthen, S.; Beavis, P.A.; Salgado, R.; Denkert, C.; Savas, P.; Combs, S.; Rimm, D.L.; Giltnane, J.M.; Estrada, M.V.; et al. RAS/MAPK Activation Is Associated with Reduced Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Therapeutic Cooperation Between MEK and PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1499–1509, Correction in Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1437. http://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.S.Y.; Tatevossian, R.; Li, Y.; Ellison, D.W.; Wu, G.; Zhang, J.; Easton, J.B. Optimization of library and enrichment procedures for RNASeq using RNA from formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue. In Proceedings of the AACR Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 1–5 April 2017; Available online: https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/77/13_Supplement/5352/621118/Abstract-5352-Optimization-of-library-and (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All | AA | EA | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All, n (%) | 24 (100.0) | 12 (100.0) | 12 (100.0) | |
| Age at diagnosis in years, mean (std) | 61.4 (13.0) | 65.0 (14.0) | 57.7 (10.8) | 0.1474 # |
| BMI at diagnosis, n (%) | 1 | |||
| Lean | 12 (50.0) | 6 (50.0) | 6 (50.0) | |
| Obese | 12 (50.0) | 6 (50.0) | 6 (50.0) | |
| Tumor stage (SEER), n (%) | 1 | |||
| Localized | 5 (20.8) | 3 (25.0) | 2 (16.7) | |
| Regional | 18 (75.0) | 9 (75.0) | 9 (75.0) | |
| Distant | 1 (4.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (8.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hossain, F.; Gonzalez-Ramirez, M.I.; Garai, J.; Polania-Villanueva, D.; Li, L.; Nafees, F.; Manirujjaman, M.; Liu, B.; Majumder, S.; Wu, X.-C.; et al. Integrated miRNA-mRNA Analyses of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in Black and White Patients with or Without Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189101
Hossain F, Gonzalez-Ramirez MI, Garai J, Polania-Villanueva D, Li L, Nafees F, Manirujjaman M, Liu B, Majumder S, Wu X-C, et al. Integrated miRNA-mRNA Analyses of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in Black and White Patients with or Without Obesity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):9101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189101
Chicago/Turabian StyleHossain, Fokhrul, Martha I. Gonzalez-Ramirez, Jone Garai, Diana Polania-Villanueva, Li Li, Farzeen Nafees, Md Manirujjaman, Bolin Liu, Samarpan Majumder, Xiao-Cheng Wu, and et al. 2025. "Integrated miRNA-mRNA Analyses of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in Black and White Patients with or Without Obesity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 9101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189101
APA StyleHossain, F., Gonzalez-Ramirez, M. I., Garai, J., Polania-Villanueva, D., Li, L., Nafees, F., Manirujjaman, M., Liu, B., Majumder, S., Wu, X.-C., Hicks, C., Del Valle, L., Danos, D., Ochoa, A., Miele, L., & Zabaleta, J. (2025). Integrated miRNA-mRNA Analyses of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in Black and White Patients with or Without Obesity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 9101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189101








