Differential Expression of Galectin-1 and Galectin-9 in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Population
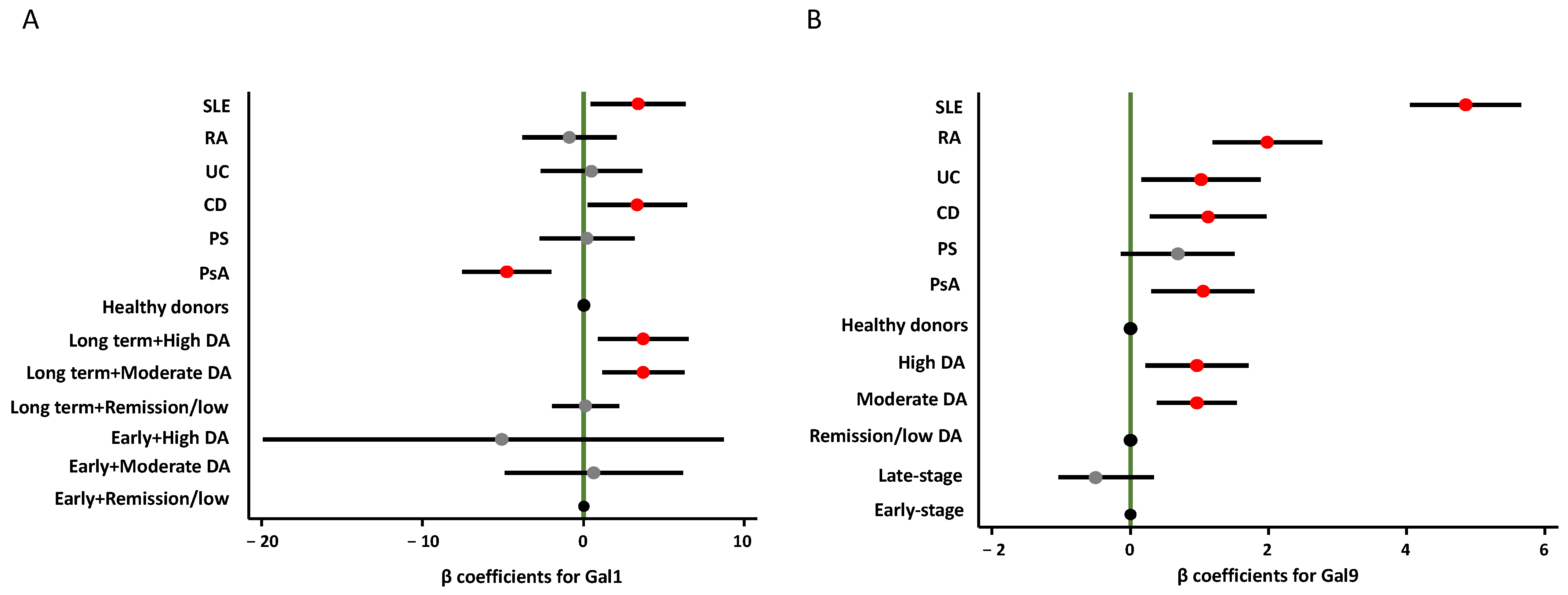
2.2. Gal1 and Gal9 Plasma Levels in Different IMIDs
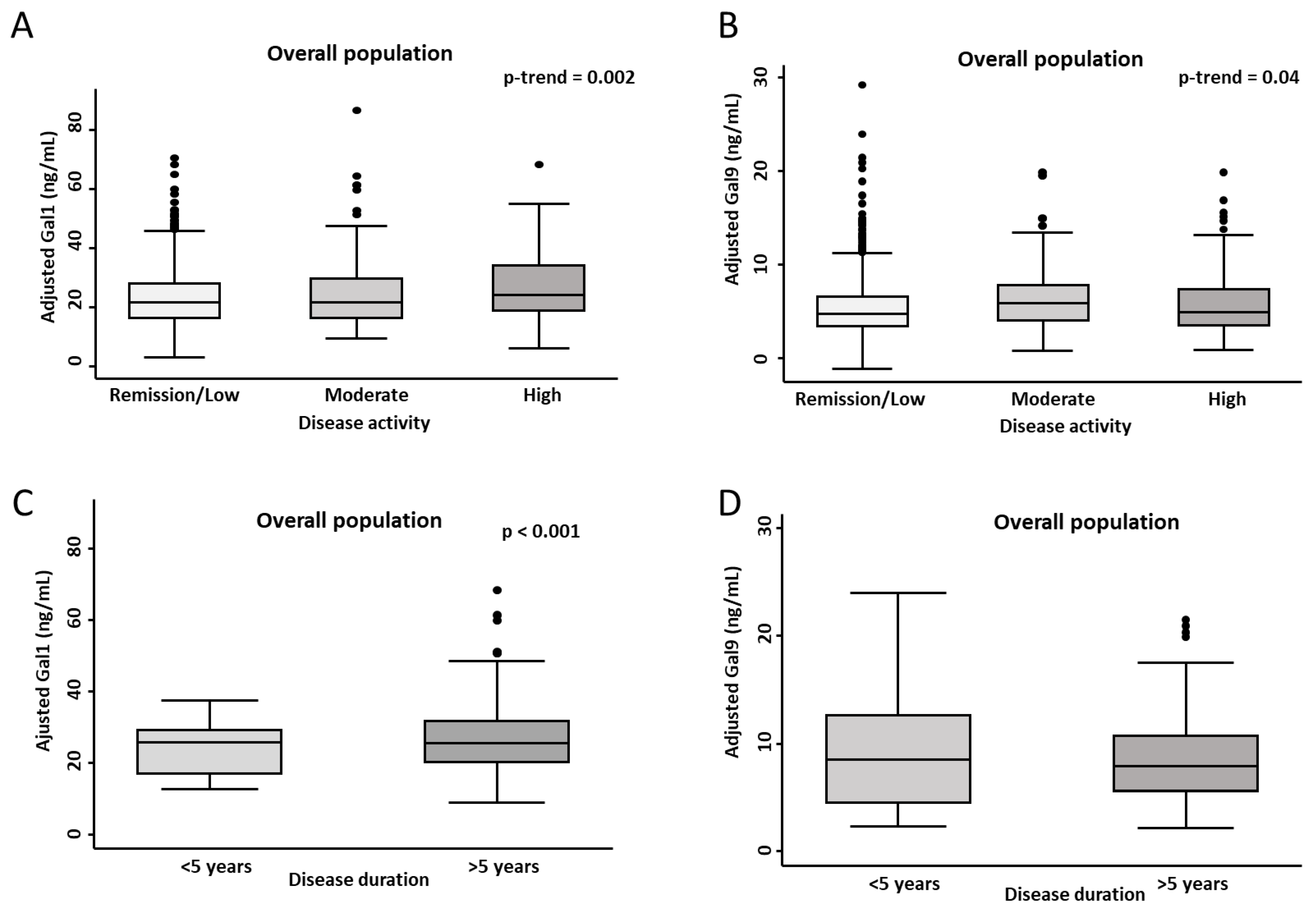
2.3. Association of Gal1 and Gal9 Plasma Levels with Disease Activity and Disease Duration
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Patients and Samples
- RA: American College of Rheumatology (ACR) classification criteria for RA [57].
- PsA: Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) [58].
- PS: diagnosis based on the dermatologist clinical criteria.
- IBD: diagnosed according to the standard Lennard-Jones criteria for CD and UC [59].
- SLE: 1982 revised ACR criteria for SLE classification [60].
4.2. Measurement of Gal1 and Gal9 Plasma Levels in HD and IMID Population
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| DA | disease activity |
| DAS-28 | disease activity score 28 (joints) |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| GLMs | generalized linear models |
| HD | healthy donors |
| IBD | inflammatory bowel disease |
| IMIDs | immune-mediated inflammatory diseases |
| PASI | Psoriasis Area and Severity Index |
| PsA | psoriatic arthritis |
| PS | psoriasis |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| SLE | systemic lupus erythematosus |
| SLEDAI | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index |
| UC | ulcerative colitis |
References
- El-Gabalawy, H.; Guenther, L.C.; Bernstein, C.N. Epidemiology of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: Incidence, prevalence, natural history, and comorbidities. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 2010, 85, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degboe, Y.; Vastert, S.J.; Prakken, B.J.; McInnes, I.B. How does age determine the development of human immune-mediated arthritis? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofilopoulos, A.N.; Kono, D.H.; Baccala, R. The multiple pathways to autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuek, A.; Hazleman, B.L.; Ostör, A.J. Immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and biologic therapy: A medical revolution. Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 83, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffer, M.A.; Schoels, M.M.; Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Breedveld, F.C.; Burmester, G.; Bykerk, V.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P.; Haraoui, B.; et al. Evidence for treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: Results of a systematic literature search. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgers, L.E.; Raza, K.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H. Window of opportunity in rheumatoid arthritis—Definitions and supporting evidence: From old to new perspectives. RMD Open 2019, 5, e000870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, M.; Gallagher, P.; FitzGerald, O. Diagnostic delay of more than 6 months contributes to poor radiographic and functional outcome in psoriatic arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoeck Henkemans, S.V.J.; de Jong, P.H.P.; Luime, J.J.; Kok, M.R.; Tchetverikov, I.; Korswagen, L.A.; van der Kooij, S.M.; van Oosterhout, M.; Baudoin, P.; Bijsterbosch, J.; et al. Window of opportunity in psoriatic arthritis: The earlier the better? RMD Open 2024, 10, e004062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, D.; Forte, G.; Poddubnyy, D.; Ciccia, F. The Role of Early Treatment in the Management of Axial Spondyloarthritis: Challenges and Opportunities. Rheumatol. Ther. 2024, 11, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barondes, S.H.; Cooper, D.N.; Gitt, M.A.; Leffler, H. Galectins. Structure and function of a large family of animal lectins. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 20807–20810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, J.; Kasai, K. The family of metazoan metal-independent beta-galactoside-binding lectins: Structure, function and molecular evolution. Glycobiology 1993, 3, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.A.; Krautter, F.; Zhi, Z.; Iqbal, A.J.; Recio, C. The interplay of galectins-1, -3, and -9 in the immune-inflammatory response underlying cardiovascular and metabolic disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutine, A.M.; Bach, C.A.; Veigas, F.; Merlo, J.P.; Laporte, L.; Manselle Cocco, M.N.; Massaro, M.; Sarbia, N.; Perrotta, R.M.; Mahmoud, Y.D.; et al. Tissue-specific control of galectin-1-driven circuits during inflammatory responses. Glycobiology 2021, 31, 891–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, R.D.; Liu, F.T.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Stowell, S.R.; Vasta, G.R. Galectins. In Essentials of Glycobiology [Internet], 4th ed; Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Stanley, P., Hart, G.W., Aebi, M., Mohnen, D., Kinoshita, T., Packer, N.H., Prestegard, J.H., et al., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2022. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK579987/ (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- He, Y.S.; Hu, Y.Q.; Xiang, K.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Y.T.; Yin, K.J.; Huang, J.X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.D.; Wang, G.H.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Galectin-1 and Galectin-3 in Autoimmune Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Qian, J.; Ding, L.; Yin, S.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S. Galectin-1: A Traditionally Immunosuppressive Protein Displays Context-Dependent Capacities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Stowell, S.R. The role of galectins in immunity and infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, M.; Oomizu, S.; Sakata, K.M.; Sakata, A.; Arikawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Ito, K.; Takeshita, K.; Niki, T.; Saita, N. Galectin-9 suppresses the generation of Th17, promotes the induction of regulatory T cells, and regulates experimental autoimmune arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 127, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossink, E.M.; Coffer, P.J.; Cutilli, A.; Lindemans, C.A. Immunomodulation by galectin-9: Distinct role in T cell populations, current therapeutic avenues and future potential. Cell Immunol. 2025, 407, 104890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Wu, Y.F.; Chou, F.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Yeh, L.T.; Lin, K.I.; Liu, F.T.; Sytwu, H.K. Intracellular Galectin-9 Enhances Proximal TCR Signaling and Potentiates Autoimmune Diseases. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 1158–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.D.; Huang, Q.; Huang, A.F. Emerging role of galectin family in inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triguero-Martínez, A.; de la Fuente, H.; Montes, N.; Ortiz, A.M.; Roy-Vallejo, E.; Castañeda, S.; González-Alvaro, I.; Lamana, A. Validation of galectin-1 as potential diagnostic biomarker of early rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovich, G.A.; Daly, G.; Dreja, H.; Tailor, H.; Riera, C.M.; Hirabayashi, J.; Chernajovsky, Y. Recombinant galectin-1 and its genetic delivery suppress collagen-induced arthritis via T cell apoptosis. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.J.; Shiau, A.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Wang, C.R.; Tsai, C.Y.; Chang, M.Y.; Li, Y.T.; Leu, C.H.; Wu, C.L. Multivalent structure of galectin-1-nanogold complex serves as potential therapeutics for rheumatoid arthritis by enhancing receptor clustering. Eur. Cell Mater. 2012, 23, 170–181; discussion 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, M.; Sakata, K.M.; Oomizu, S.; Arikawa, T.; Sakata, A.; Ueno, M.; Nobumoto, A.; Niki, T.; Saita, N.; Ito, K.; et al. Beneficial effect of galectin 9 on rheumatoid arthritis by induction of apoptosis of synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3968–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Facchinetti, V.; Voynova, E.; Hanabuchi, S.; Karnell, J.L.; Hanna, R.N. Galectin-9 inhibits TLR7-mediated autoimmunity in murine lupus models. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1873–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.B.; Dodd, S.; Yu, L.G.; Subramanian, S. Serum galectins as potential biomarkers of inflammatory bowel diseases. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmed, A.; Al-Rubaee, E. New insight for ulcerative colitis diagnosis via serum netrin-1 and galectin-1 biomarkers. Hum. Antibodies. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowowiejska, J.; Baran, A.; Hermanowicz, J.M.; Sieklucka, B.; Pawlak, D.; Flisiak, I. Evaluation of Plasma Concentrations of Galectins-1, 2 and 12 in Psoriasis and Their Clinical Implications. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Song, L.; Sun, J.; Sui, Y.; Li, D.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Shu, Q. Expression of Galectin-9 and correlation with disease activity and vascular endothelial growth factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, N.; Fujita, Y.; Temmoku, J.; Furuya, M.Y.; Asano, T.; Sato, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Watanabe, H.; Suzuki, E.; et al. Galectin-9 as a biomarker for disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgalil, A.H.; Elsharaby, R.M.; Abd ElGany, S.E.; Ibrahim, W.S. EXPRESS: Assessment of serum level of galectin-9 in systemic lupus erythematosus patients in Tanta university hospitals. J. Investig. Med. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagan-Yasutan, H.; He, N.; Arlud, S.; Fang, J.; Hattori, T. The elevation of plasma galectin-9 levels in patients with psoriasis and its associations with inflammatory and immune checkpoint molecules in skin tissues. Hum. Immunol. 2024, 85, 110741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofal, E.; Eldesoky, F.; Nofal, A.; Abdelshafy, A.; Zedan, A. Serum galectin-9 levels in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis and allergic contact dermatitis: A cross-sectional study. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2019, 85, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibor, D.; Szczeklik, K.; Brzozowski, B.; Mach, T.; Owczarek, D. Serum galectin 3, galectin 9 and galectin 3-binding proteins in patients with active and inactive inflammatory bowel disease. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triguero-Martínez, A.; Roy-Vallejo, E.; Tomero, E.G.; Montes, N.; de la Fuente, H.; Ortiz, A.M.; Castañeda, S.; Lamana, A.; González-Álvaro, I. Galectin-1: A Potential Biomarker Differentiating between Early Rheumatoid Arthritis and Spondyloarthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bably, M.M.; Abdel Aziz, D.M.; Adly, N.N.; Ali, M.A.; Khedr, A.S.; El Leithy, S.A. Galectin-1 in Psoriatic arthritis, Psoriasis, Rheumatoid arthritis and its relation with disease activity and skin lesion. Egypt. J. Immunol. 2023, 30, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessel, C.; Lavric, M.; Weinhage, T.; Brueckner, M.; de Roock, S.; Däbritz, J.; Weber, J.; Vastert, S.J.; Foell, D. Serum biomarkers confirming stable remission in inflammatory bowel disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa Gobbi, R.; De Francesco, N.; Bondar, C.; Muglia, C.; Chirdo, F.; Rumbo, M.; Rocca, A.; Toscano, M.A.; Sambuelli, A.; Rabinovich, G.A.; et al. A galectin-specific signature in the gut delineates Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis from other human inflammatory intestinal disorders. Biofactors 2016, 42, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Huergo, S.P.; Hockl, P.F.; Stupirski, J.C.; Maller, S.M.; Morosi, L.G.; Pinto, N.A.; Berón, A.M.; Musuruana, J.L.; Nasswetter, G.G.; Cavallasca, J.A.; et al. Clinical Relevance of Galectin-1 and Galectin-3 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Differential Regulation and Correlation With Disease Activity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9, 3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Asano, T.; Matsuoka, N.; Temmoku, J.; Sato, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Furuya, M.Y.; Suzuki, E.; Watanabe, H.; Kawakami, A.; et al. A Differential regulation and correlation between galectin-9 and anti-CCP antibody (ACPA) in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ai, X.; Jia, B.; Zhong, X.; Liu, L.; Hu, Q.; Xie, J.; Hong, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, D. Galectin-9 as an indicator of functional limitations and radiographic joint damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1419676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, L.; Li, D.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Shu, Q. Galectin-9 expression correlates with therapeutic effect in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiersma, V.R.; Clarke, A.; Pouwels, S.D.; Perry, E.; Abdullah, T.M.; Kelly, C.; Soyza, A.; Hutchinson, D.; Eggleton, P.; Bremer, E. Galectin-9 Is a Possible Promoter of Immunopathology in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Activation of Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase 4 (PAD-4) in Granulocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.A.; Køster, D.; Mehta, A.Y.; Stengaard-Pedersen, K.; Busson, P.; Junker, P.; Hørslev-Petersen, K.; Hetland, M.L.; Østergaard, M.; Hvid, M.; et al. Increased Galectin-9 Levels Correlate with Disease Activity in Patients with DMARD-Naïve Rheumatoid Arthritis and Modulate the Secretion of MCP-1 and IL-6 from Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells 2023, 12, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Che, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Ren, C.; Wu, Y.; Liang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Knockdown of Galectin-9 alleviates rheumatoid arthritis through suppressing TNF-α-induced activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 220, 115994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Hoogen, L.L.; van Roon, J.A.G.; Mertens, J.S.; Wienke, J.; Lopes, A.P.; de Jager, W.; Rossato, M.; Pandit, A.; Wichers, C.G.K.; van Wijk, F.; et al. Galectin-9 is an easy to measure biomarker for the interferon signature in systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1810–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Singh, P.; Aggarwal, A. Serum and urinary galectin-9 and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10. Lupus 2022, 31, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirioğlu, Ş.; Çinar, S.; Uludağ, Ö.; Gürel, E.; Varelci, S.; Özlük, Y.; Kiliçaslan, I.; Yalçinkaya, Y.; Yazici, H.; Gül, A.; et al. Serum and urine interferon-inducible protein 10, galectin-9, and SIGLEC-1 as biomarkers of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 54, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensous, N.; Vagner, D.; Barnetche, T.; Duffau, P.; Lazaro, E.; Richez, C.; Blanco, P. Galectin 9, CXCL-10 and tumor necrosis factor receptor type II as biomarkers of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Jt. Bone Spine. 2022, 89, 105311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enocsson, H.; Wetterö, J.; Eloranta, M.L.; Gullstrand, B.; Svanberg, C.; Larsson, M.; Bengtsson, A.A.; Rönnblom, L.; Sjöwall, C. Comparison of Surrogate Markers of the Type I Interferon Response and Their Ability to Mirror Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 688753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Zhou, G.; Lin, J.; Li, L.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S. Serum Biomarkers for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.F.; Santos, F.A.; Amorim, L.A.A.; da Silva, A.L.C.; Marques, L.G.A.; Rocha, B.A.M. Galectin-9 is a target for the treatment of cancer: A patent review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, R.H.; Huang, S.S.; Kuo, C.S.; Wang, S.C.; Tsai, Y.L.; Lu, Y.W.; Chang, C.C.; Huang, P.H.; Lin, S.J. Galectin-1 is associated with the severity of coronary artery disease and adverse cardiovascular events in patients undergoing coronary angiography. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Liu, C.; Tang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Mao, X.; Zhong, Y. Serum Galectin-9 Levels Are Associated with Coronary Artery Disease in Chinese Individuals. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 457167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurel Cayir, E.; Demir, L.; Varol, U.; Atahan, M.K.; Salman, T.; Oflazoglu, U.; Yildiz, Y.; Taskaynatan, H.; Saray, S.; Kucukzeybek, Y.; et al. Preliminary study of serum Galectin-1 in breast cancer carcinogenesis [Izmir Oncology Group (IZOG) study]. J. BUON 2020, 25, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arnett, F.C.; Edworthy, S.M.; Bloch, D.A.; McShane, D.J.; Fries, J.F.; Cooper, N.S.; Healey, L.A.; Kaplan, S.R.; Liang, M.H.; Luthra, H.S.; et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 31, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, W.; Gladman, D.; Helliwell, P.; Marchesoni, A.; Mease, P.; Mielants, H.; CASPAR Study Group. Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: Development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2665–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennard-Jones, J.E. Classification of inflammatory bowel disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. Suppl. 1989, 170, 2–6; discussion 16-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.M.; Cohen, A.S.; Fries, J.F.; Masi, A.T.; McShane, D.J.; Rothfield, N.F.; Challer, J.G.; Talal, N.; Winchester, R.J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982, 25, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Riel, P.L.; Renskers, L. The Disease Activity Score (DAS) and the Disease Activity Score using 28 joint counts (DAS28) in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34 (Suppl. 101), S40–S44. [Google Scholar]
- Llamas-Velasco, M.; de la Cueva, P.; Notario, J.; Martínez-Pilar, L.; Martorell, A.; Moreno-Ramírez, D. Moderate Psoriasis: A Proposed Definition. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017, 108, 911–917, (English, Spanish). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, M.; Bombardieri, S. Assessing remission in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2006, 24 (Suppl. 43), S-99–S-104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Best, W.R. Predicting the Crohn’s disease activity index from the Harvey-Bradshaw Index. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2006, 12, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoepfer, A.M.; Beglinger, C.; Straumann, A.; Safroneeva, E.; Romero, Y.; Armstrong, D.; Schmidt, C.; Trummler, M.; Pittet, V.; Vavricka, S.R. Fecal calprotectin more accurately reflects endoscopic activity of ulcerative colitis than the Lichtiger Index, C-reactive protein, platelets, hemoglobin, and blood leukocytes. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Diagnosis | Total Patients (n = 830) | Age (Median; IQR) | Sex (Female) (n; %) | Duration of Disease (Years; Median: IQR) | Moderate/ High Disease Activity ** (n; %) | csDMARD (n; %) | bDMARD (n; %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD | 150 | 44 (30–75) | 87 (58) | ||||
| Group 1 | 100 | 35 (28–48) | 57 (57) | ||||
| Group 2 | 50 | 48 (44–53) | 30 (60) | ||||
| PsA | 165 | 52.5 (42.5–63) | 85 (51.5) | 10 (5–17) | 42 (25.4) | 92 (55.7) | 41 (24.8) |
| Group 1 | 100 | 50 (42–63) | 50 (50) | 11 (5–17) | 22 (22) | 56 (56) | 31 (31) |
| Group 2 | 65 | 54 (43–61) | 35 (53.8) | 10 (5–16) | 20 (30.7) | 36 (65.4) | 10 (15.3) |
| Psoriasis | 165 | 44.5 (33–59) | 82 (49.6) | 15 (6–25) | 39 (23.6) | 31 (18.2) | 42 (25.4) |
| Group 1 | 100 | 49 (37–60) | 50 (50) | 17.5 (9–27.5) | 24 (24) | 26 (26) | 33 (33) |
| Group 2 | 65 | 40 (28–53) | 32 (49.2) | 11 (4–22) | 15 (23) | 5 (7.6) | 9 (13.8) |
| CD | 100 | 39 (33–49) | 46 (46) | 12 (6–18) | 6 (6) | 79 (79) | 11 (11) |
| Group 1 | 50 | 42 (36–52) | 25 (50) | 16.5 (11–21) | 4 (8) | 38 (76) | 11 (22) |
| Group 2 | 50 | 36 (30–44) | 21 (42) | 7.5 (4–13) | 2 (4) | 41 (82) | 0 (0) |
| UC | 100 | 43.5 (35–57.5) | 51 (51) | 10 (7–16) | 4 (4) | 72 (72) | 7 (7) |
| Group 1 | 50 | 39.5 (32–53) | 25 (50) | 10 (7–14) | 4 (4) | 42 (84) | 3 (6) |
| Group 2 | 50 | 50.5 (39–60) | 26 (52) | 12 (8–17) | 0 (0) | 30 (60) | 4 (8) |
| RA/sero+ * | 150/62 | 63 (54–71) | 90 (60) | 13 (8–19) | 77 (41) | 105 (70) | 73 (48.6) |
| Group 1 | 100 | 62 (54–71) | 50 (50) | 13 (8–18) | 53 (53) | 88 (88) | 63 (63) |
| Group 2 | 50 | 64 (56–72) | 40 (80) | 12.5 (8–23) | 24 (48) | 14 (28) | 10 (20) |
| SLE | 150 | 44 (33–52) | 99 (66) | 14 (8–19) | 23 (15.3) | 97 (64.6) | 4 (4.6) |
| Group 1 | 100 | 42.5 (32–51) | 50 (50) | 13 (7.5–18) | 17 (17) | 62 (62) | 3 (3) |
| Group 2 | 50 | 47 (38–52) | 49 (98) | 15.5 (9–21) | 6 (12) | 35 (70) | 1 (2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valero-Martínez, C.; Pardines-Ortiz, M.; Montes, N.; Dauden, E.; Fernández-Gutierrez, B.; García-Planella, E.; Gomollón García, F.; Gratacós, J.; Pérez-Venegas, J.J.; Julía, A.; et al. Differential Expression of Galectin-1 and Galectin-9 in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189087
Valero-Martínez C, Pardines-Ortiz M, Montes N, Dauden E, Fernández-Gutierrez B, García-Planella E, Gomollón García F, Gratacós J, Pérez-Venegas JJ, Julía A, et al. Differential Expression of Galectin-1 and Galectin-9 in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):9087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189087
Chicago/Turabian StyleValero-Martínez, Cristina, Marisa Pardines-Ortiz, Nuria Montes, Esteban Dauden, Benjamín Fernández-Gutierrez, Esther García-Planella, Fernando Gomollón García, Jordi Gratacós, Jose Javier Pérez-Venegas, Antonio Julía, and et al. 2025. "Differential Expression of Galectin-1 and Galectin-9 in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 9087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189087
APA StyleValero-Martínez, C., Pardines-Ortiz, M., Montes, N., Dauden, E., Fernández-Gutierrez, B., García-Planella, E., Gomollón García, F., Gratacós, J., Pérez-Venegas, J. J., Julía, A., Marsal, S., Lamana, A., García-Vicuña, R., González-Alvaro, I., & Triguero-Martínez, A. (2025). Differential Expression of Galectin-1 and Galectin-9 in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 9087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189087






