Regulation of Cell Cycle-Related Damage/Repair Mechanism and Oxidative Stress Status by Oroxylin A in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
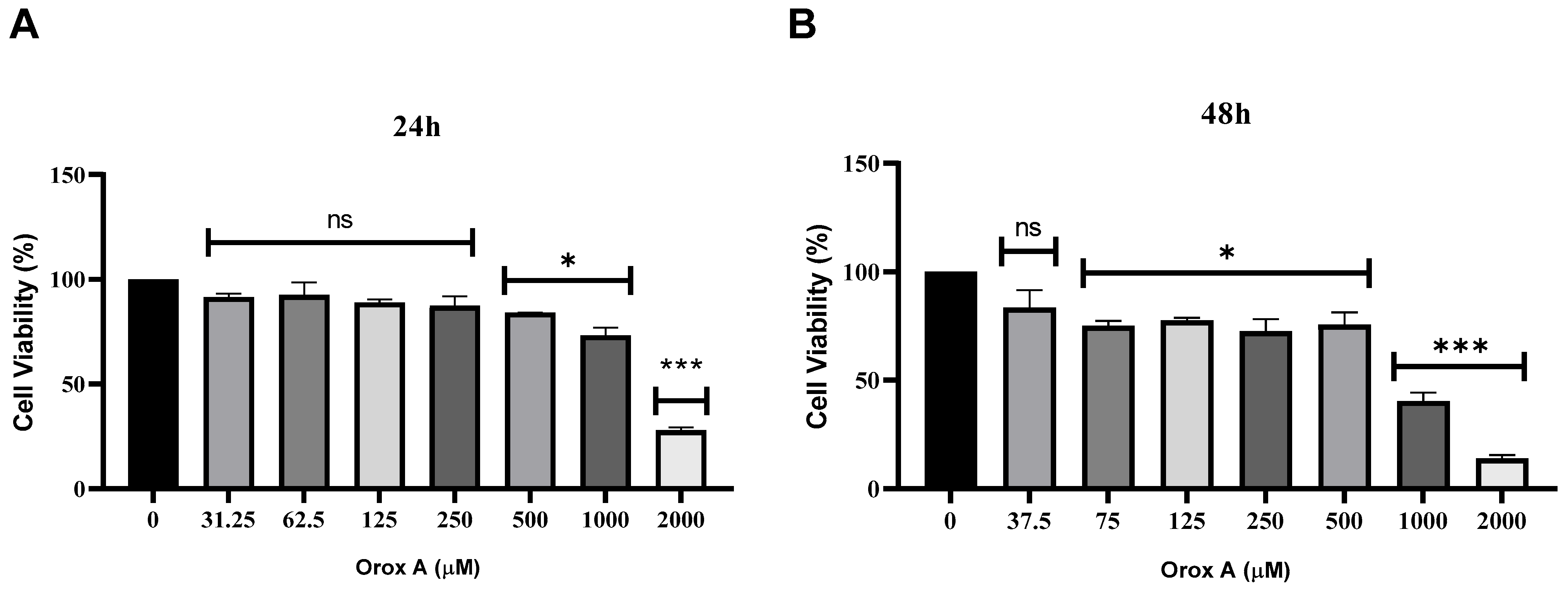
2.1. Orox A Inhibited the Proliferation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
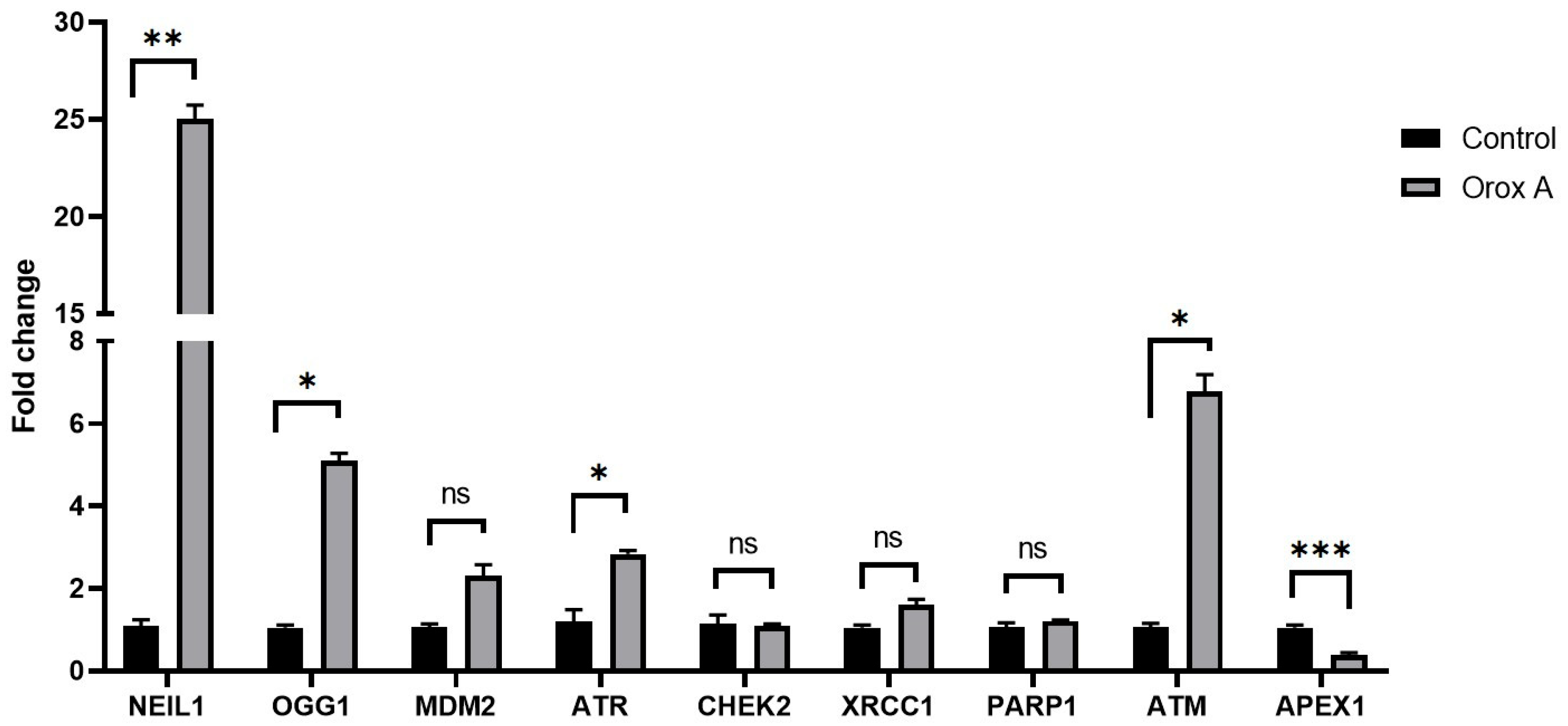
2.2. Orox A Altered the Expression of DNA Damage and Repair Genes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
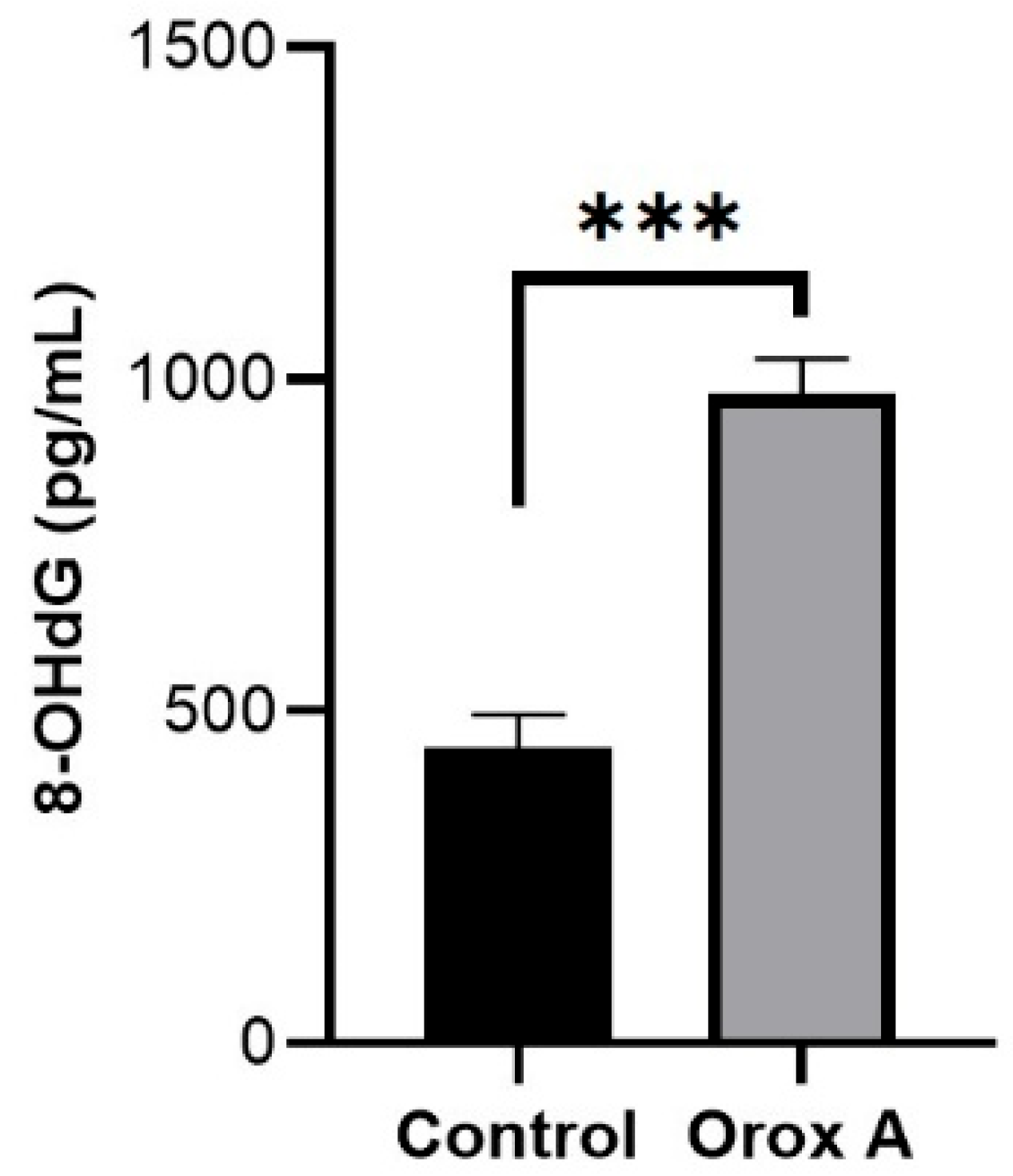
2.3. Orox A Application Increases the Amount of DNA Damage Product 8-OHdG in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
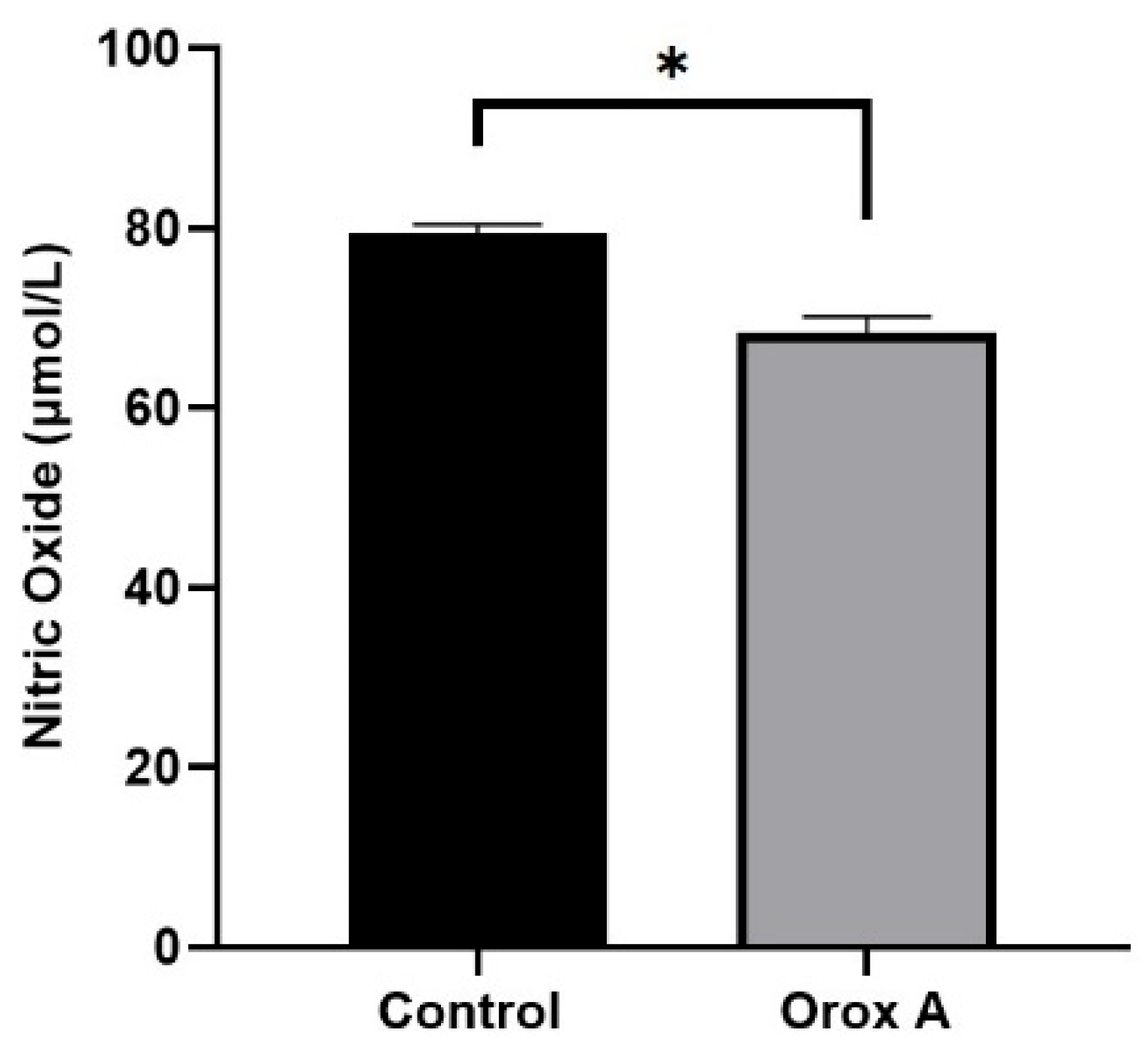
2.4. Orox A Suppressed Nitric Oxide Synthesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
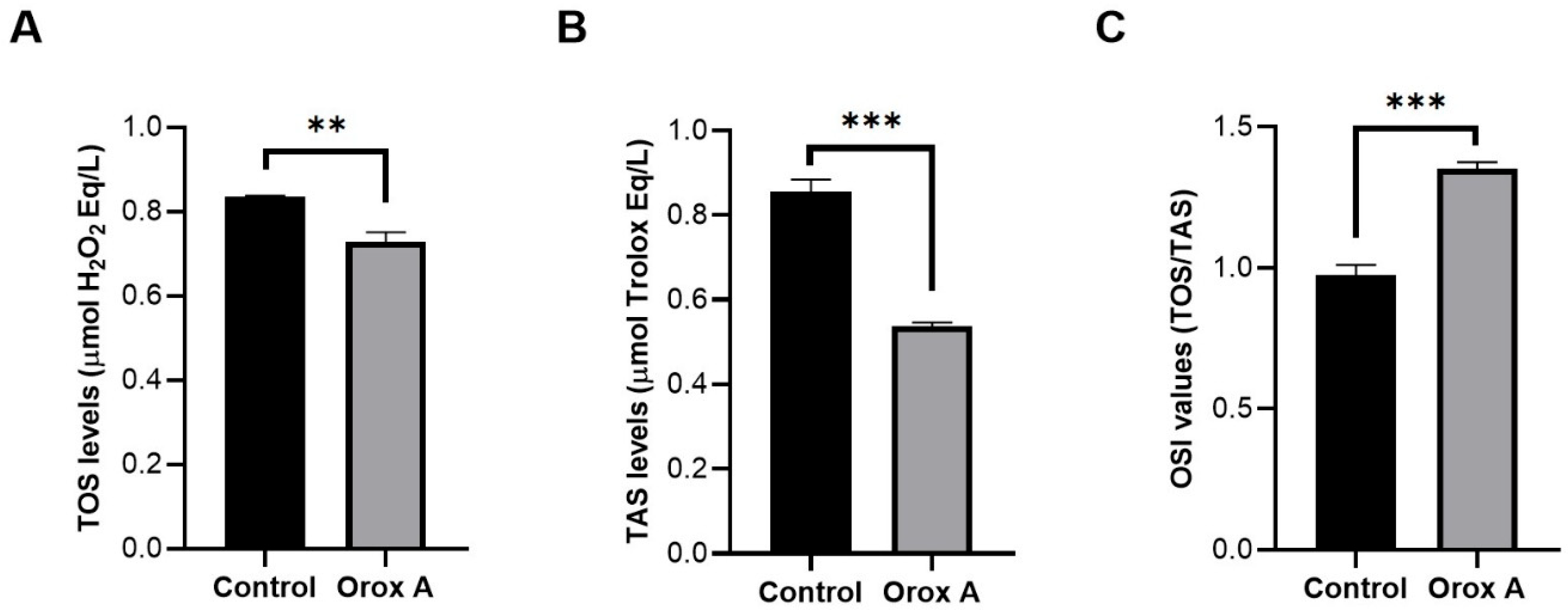
2.5. The Effect of Orox A Treatment on Redox Balance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
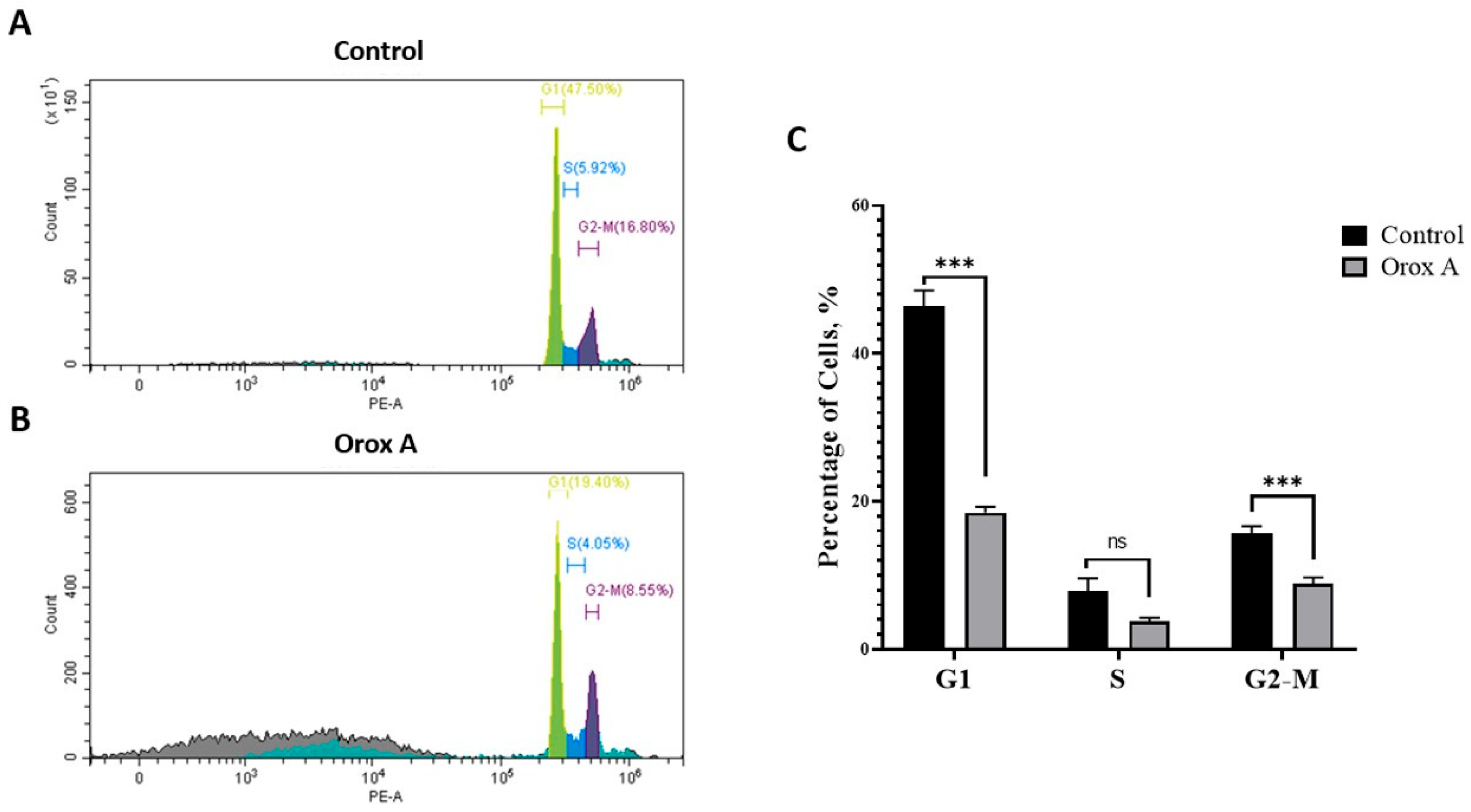
2.6. Orox A Induces Cell Cycle Arrest at the G2/M Phase
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Chemicals
4.2. MTT Assay
4.3. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
4.4. RT-qPCR Analysis
4.5. Measurement of the DNA Damage Product 8-OHdG
4.6. Nitric Oxide (NO) Measurement Using ELISA
4.7. Biochemical Evaluation of Redox Equilibrium
4.8. Determination of Cell Cycle Stage by Flow Cytometry
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhanasekaran, R. Deciphering tumor heterogeneity in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) multi-Omic and singulomic approaches. Semin. Liver Dis. 2021, 41, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoda, M.; Nishiyama, T.; Matsukawa, Y.; Moriyasu, M. Cytotoxic activities of flavonoids from two Scutellaria plants in Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 91, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, N.; Yu, X.; Liu, X.; Hu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, L.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, Q. Oroxylin A, a natural compound, mitigates the negative effects of TNFα-treated acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Dai, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zou, M.; Li, Z.; Lu, N.; Guo, Q. Oroxylin A sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to anoikis via glucose-deprivation-like mechanisms: C-Src and hexokinase II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 3835–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhou, Y.; Qiao, C.; Ni, T.; Li, Z.; You, Q.; Guo, Q.; Lu, N. Oroxylin A inhibits glycolysisdependent proliferation of human breast cancer via promoting SIRT3-mediated SOD2 transcription and HIF1α destabilization. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Lin, J.; Wang, T.; Dong, H.; Li, X.; Yu, D. Oroxin A suppresses non-small cell lung cancer via the HSP90AA1/AKT signaling pathway. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Wei, L.; Dai, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, Q.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Guo, Q.; Lu, N. UCP2-related mitochondrial pathway participates in oroxylin A-induced apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2015, 230, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, R.; Qi, Q.; Gu, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Rong, J.; Liu, W.; Lu, N.; You, Q.; Guo, Q. Involvement of p53 in oroxylin A-induced apoptosis in cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Gu, H.-Y.; Lu, N.; Liu, W.; Qi, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.-T.; You, Q.-D.; Guo, Q.-L. Oroxylin A induces G2/M phase cell-cycle arrest via inhibiting Cdk7-mediated expression of Cdc2/p34 in human gastric carcinoma BGC-823 cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 60, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Lu, N.; Li, C.; Li, F.; Zhao, K.; Lin, B.; Guo, Q. Oroxylin A inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 expression and activation by upregulating tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 and suppressing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 209, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.Y.; Xu, S.; Sun, Y.N.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Q.-L.; Wei, L.-B. Novel CDK9 inhibitor oroxylinA promotes wild-type P53 stability and prevents hepatocellularcarcinoma progression by disrupting both MDM2 and SIRT1signaling. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 43, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Guo, Y.; Wei, L. CDK9 inhibition blocks the initiation of PINK1-PRKN-mediated mitophagy by regulating the SIRT1-FOXO3-BNIP3 axis and enhances the therapeutic effects involving mitochondrial dysfunction in hepatocellular carcinoma. Autophagy 2022, 18, 1879–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, T.X.; Wang, X.P.; Yu, Z.; Kong, B.; He, Y.; Guo, Q.L.; Zhang, X.B.; Qiang, L. Oroxylin A inhibits the migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inducing NAG-1 expression. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, M.L.; George, L.K.; Grant, G.D.; Perou, C.M. Common markers of proliferation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, T.; Sicinski, P. Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.E.; Wei, D.; Yang, Y.N.; Chen, S.Q.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.M.; Yu, J. MPTP related mitochondrial pathway in oroxylin A induced-apoptosis in HepG2 cancer cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2016, 9, 11139–11148. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.P.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.S.; Zhu, L.X.; Hu, R.K.; Feng, P.F. Oroxylin A suppressed colorectal cancer metastasis by inhibiting the activation of the TGF-β/SMAD signal pathway. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Lu, N.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H.; Dai, Q.; Wei, L.; Li, Z.; You, Q.; Guo, Q. Activation of the unfolded protein response contributed to the selective cytotoxicity of oroxylin A in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 212, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, M.L.; Hazra, T.K.; Mitra, S. Early steps in the DNA base excision/single-strand interruption repair pathway in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Walker, G.C. Mechanisms of DNA damage, repair and mutagenesis. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 58, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenner, A.; Sartori, A.A. Harnessing DNA double-strand break repair for cancer treatment. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jekimovs, C.; Bolderson, E.; Suraweera, A.; Adams, M.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Chemotherapeutic compounds targeting the DNA double-strand break repair pathways: The good, the bad, and the promising. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumura, D.; Kashiwagi, S.; Jain, R. The role of nitric oxide in tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laura, M. López-Sánchez, Enrique Aranda, Antonio Rodríguez-Ariza, Nitric oxide and tumor metabolic reprogramming. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 176, 113769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaumet-Adkins, A.; Yanez, Y.; Peris-Diaz, M.D.; Calabria, I.; Palanca- Ballester, C.; Sandoval, J. Epigenetics and oxidative stress in aging. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 9175806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Azad, M.B.; Gibson, S.B. Superoxide is the major reactiveoxygen species regulating autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 1040–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, F.S.; Şengül, G.F.; Altveş, S.; Eroğlu Güneş, C. Evaluation of the Apoptotic, Prooxidative and Therapeutic Effects of Odoroside A on Lung Cancer: An In Vitro Study Extended with In Silico Analyses of Human Lung Cancer Datasets. Life 2025, 15, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, M.; Benítez-Buelga, C.; Calvo, P.A.; Hanna, B.M.F.; Mortusewicz, O.; Masuyer, G.; Davies, J.; Wallner, O.; Sanjiv, K.; Albers, J.J.; et al. Small-molecule activation of OGG1 increases oxidative DNA damage repair by gaining a new function. Science 2022, 376, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.; Guillarme, D.; Rudaz, S.; Bonnabry, P.; Fleury-Souverain, S. Simultaneous analysis of various anticancer drugs by supercritical fluid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Part I: Optimization of chromatographic separation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 261, 116838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naser, R.H.; Azeez, Z.F.; Alatawi, Z.; Albalawi, A.; Shamrani, T.; Shahlol, A.M.A.; El-Nablaway, M.; Alahmadi, H.A.; Aloraini, G.S.; Tharwat, N.A.; et al. Oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and apoptosis in multiple cancer cell lines: Novel anticancer properties of marine Aspergillus oryzae NGM91 extract. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 17203–17221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visconti, R.; Della Monica, R.; Grieco, D. Cell cycle checkpoint in cancer: A therapeutically targetable double-edged sword. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali Abdalla, Y.O.; Subramaniam, B.; Nyamathulla, S.; Shamsuddin, N.; Arshad, N.M.; Mun, K.S.; Nagoor, N.H. Natural products for cancer therapy: A review of their mechanism of actions and toxicity in the past decade. J. Trop. Med. 2022, 2022, 5794350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, F.; Burmistrova, O.; Marrero, M.T.; Torres, F.; Hernández, C.; Quintana, J.; Estevez, F. Induction of G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis by the flavonoid tamarixetin on human leukemia cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Alam, W.; Aschner, M.; Alsharif, K.F.; Albrakati, A.; Saso, L.; Khan, H. Natural products targeting the ATR-CHK1 signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, F.S.; Güneş, C.E.; Yavuz, E.; Kurar, E. Apelin triggers macrophage polarization to M2 type in head and neck cancer. Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erel, O. A novel automated direct measurement method for total antioxidant capacity using a new generation, more stable ABTS radical cat ion. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 37, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erel, O. A new automated colorimetric method for measuring total oxidant status. Clin. BioChem. 2005, 38, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Control Group | Orox A-Treated Group | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8-OHdG (pg/mL) | 446 ± 27.75 | 979 ± 29.57 | <0.001 (***) |
| Control Group | Orox A-Treated Group | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO (μmol/L) | 79.37 ± 0.6117 | 68.32 ± 1.0666 | <0.05 (*) |
| Control Group | Orox A-Treated Group | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TAS (μmol Trolox Eq/L) | 0.8567 ± 0.016 | 0.5380 ± 0.005 | <0.001 (***) |
| TOS (μmol H2O2 Eq/L) | 0.8350 ± 0.017 | 0.7280 ± 0.013 | 0.001 (**) |
| OSI (arbitrary unit) | 0.9750 ± 0.021 | 1.353 ± 0.013 | <0.001 (***) |
| Gene | Forward Primer (5′-> 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-> 3′) | PCR (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEIL1 | TCCTGTACCGGCTGAAGAT | TTCTGCAGCTTGGTCCTTATC | 121 |
| OGG1 * | GGCTCAACTGTATCACCACTGG | GGCGATGTTGTTGTTGGAGGAAC | 143 |
| MDM2 | CCTACTGATGGTGCTGTAACC | TGTGCACCAACAGACTTTAATAAC | 107 |
| ATR * | GGAGATTTCCTGAGCATGTTCGG | GGCTTCTTTACTCCAGACCAATC | 100 |
| CHEK2 | GCGCCTGAAGTTCTTGTTTC | GGATACCCACTAAGGCAGATAAA | 101 |
| XRCC1 * | CGGATGAGAACACGGACAGTGA | GAAGGCTGTGACGTATCGGATG | 152 |
| PARP1 * | CCAAGCCAGTTCAGGACCTCAT | GGATCTGCCTTTTGCTCAGCTTC | 123 |
| ATM | GCCGTCAACTAGAACATGATAGA | CCTTGTTTGGAATCTGAATGCC | 121 |
| APEX1 * | CTGCTCTTGGAATGTGGATGGG | TCCAGGCAGCTCCTGAAGTTCA | 148 |
| ACTB | TGGCTGGGGTGTTGAAGGTCT | AGCACGGCATCGTCACCAACT | 179 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seçer Çelik, F.; Altveş, S.; Eroğlu Güneş, C. Regulation of Cell Cycle-Related Damage/Repair Mechanism and Oxidative Stress Status by Oroxylin A in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188942
Seçer Çelik F, Altveş S, Eroğlu Güneş C. Regulation of Cell Cycle-Related Damage/Repair Mechanism and Oxidative Stress Status by Oroxylin A in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188942
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeçer Çelik, Fatma, Safaa Altveş, and Canan Eroğlu Güneş. 2025. "Regulation of Cell Cycle-Related Damage/Repair Mechanism and Oxidative Stress Status by Oroxylin A in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188942
APA StyleSeçer Çelik, F., Altveş, S., & Eroğlu Güneş, C. (2025). Regulation of Cell Cycle-Related Damage/Repair Mechanism and Oxidative Stress Status by Oroxylin A in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188942





