Clinical and Genetic Heterogeneity of Factor XI Deficiency: Insights from a Southern Italian Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Features of Cases with FXI Deficiency
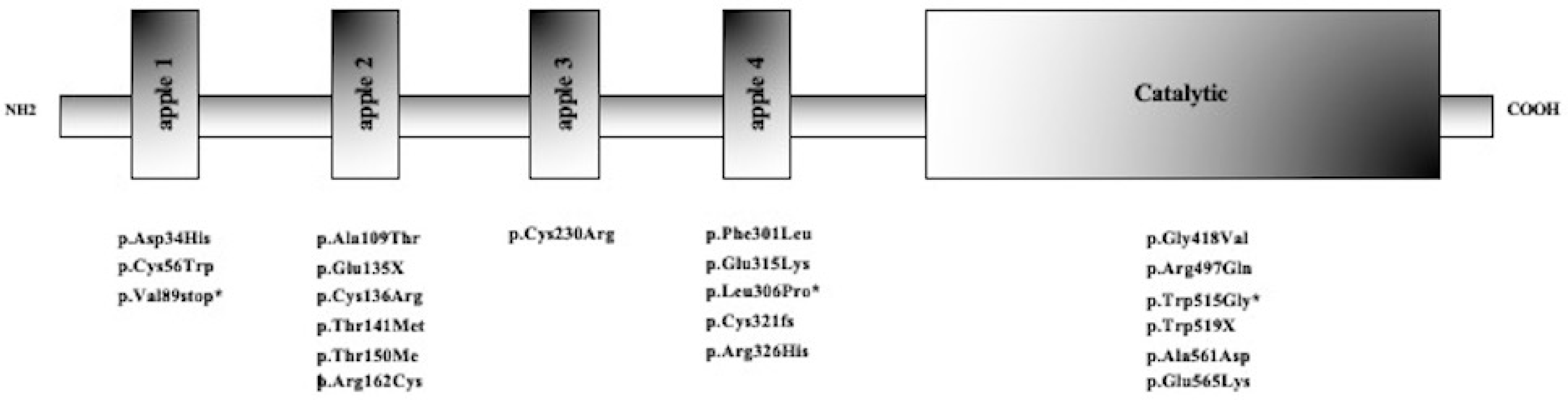
2.2. Molecular Characterization
2.3. FXI Deficiency and Bleeding
3. Discussion
4. Limitations
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Case Index and Relatives
5.2. Coagulation Tests
5.3. Genetic Investigation
5.4. In Silico Analysis of Pathogenicity
5.5. Statistical Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barg, A.A.; Livnat, T.; Kenet, G. Factor XI deficiency: Phenotypic age-related considerations and clinical approach towards bleeding risk assessment. Blood 2024, 143, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakai, R.; Chung, D.W.; Davie, E.W.; Seligsohn, U. Factor XI deficiency in Ashkenazi Jews in Israel. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asselta, R.; Paraboschi, E.M.; Rimoldi, V.; Menegatti, M.; Peyvandi, F.; Salomon, O.; Duga, S. Exploring the global landscape of genetic variation in coagulation factor XI deficiency. Blood 2017, 130, e1–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyvandi, F.; Palla, R.; Menegatti, M.; Siboni, S.M.; Halimeh, S.; Faeser, B.; Pergantou, H.; Platokouki, H.; Giangrande, P.; Peerlinck, K.; et al. European Network of Rare Bleeding Disorders Group. Coagulation factor activity and clinical bleeding severity in rare bleeding disorders: Results from the European Network of Rare Bleeding Disorders. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saes, J.L.; Verhagen, M.J.A.; Meijer, K.; Cnossen, M.H.; Schutgens, R.E.G.; Peters, M.; Nieuwenhuizen, L.; van der Meer, F.J.M.; Kruis, I.C.; van Heerde, W.L.; et al. Bleeding severity in patients with rare bleeding disorders: Real-life data from the RBiN study. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5025–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moellmer, S.A.; Puy, C.; McCarty, O.J.T. Biology of factor XI. Blood 2024, 143, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, R.; Siboni, S.M.; Menegatti, M.; Musallam, K.M.; Peyvandi, F.; European Network of Rare Bleeding Disorders EN-RBD group. European Network of Rare Bleeding Disorders (EN-RBD) group. Establishment of a bleeding score as a diagnostic tool for patients with rare bleeding disorders. Thromb. Res. 2016, 148, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiscia, G.; Favuzzi, G.; Chinni, E.; Colaizzo, D.; Fischetti, L.; Intrieri, M.; Margaglione, M.; Grandone, E. Factor VII deficiency: A novel missense variant and genotype-phenotype correlation in patients from Southern Italy. Hum. Genome Var. 2017, 4, 17048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellona, D.; Favuzzi, G.; Vannini, M.L.; Piras, S.M.; Ruberto, M.F.; Grandone, E.; Marongiu, F. A Sardinian Family with Factor XI Deficiency. Hamostaseologie 2019, 39, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodeghiero, F.; Tosetto, A.; Abshire, T.; Arnold, D.M.; Coller, B.; James, P.; Neunert, C.E.; Lillicrap, D. ISTH/SSC bleeding assessment tool: A standardized questionnaire and a proposal for a new bleeding score for inherited bleeding disorders. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 2063–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, R.E.; McVey, J.H.; Tuddenham, E.G.; Hancock, J.F. Six point mutations that cause factor XI deficiency. Blood 1995, 85, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaman, G.; Giacomelli, S.H.; Dragani, A.; Iuliani, O.; Duga, S.; Rodeghiero, F. Severe factor XI deficiency in the Abruzzo region of Italy is associated to different FXI gene mutations. Haematologica 2008, 93, 957–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Saunders, R.E.; Shiltagh, N.; Gomez, K.; Mellars, G.; Cooper, C.; Perry, D.J.; Tuddenham, E.G.; Perkins, S.J. Structural analysis of eight novel and 112 previously reported missense mutations in the interactive FXI mutation database reveals new insight on FXI deficiency. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, J.; de la Morena-Barrio, M.E.; Salloum-Asfar, S.; Padilla, J.; Miñano, A.; Roldán, V.; Soria, J.M.; Vidal, F.; Corral, J.; Vicente, V. High incidence of FXI deficiency in a Spanish town caused by 11 different mutations and the first duplication of F11: Results from the Yecla study. Haemophilia 2017, 23, e488–e496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guella, I.; Soldà, G.; Spena, S.; Asselta, R.; Ghiotto, R.; Tenchini, M.L.; Castaman, G.; Duga, S. Molecular characterization of two novel mutations causing factor XI deficiency: A splicing defect and a missense mutation responsible for a CRM+ defect. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 99, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbatarny, M.; Mollah, S.; Grabell, J.; Bae, S.; Deforest, M.; Tuttle, A.; Hopman, W.; Clark, D.S.; Mauer, A.C.; Bowman, M.; et al. Normal range of bleeding scores for the ISTH-BAT: Adult and pediatric data from the merging project. Haemophilia 2014, 20, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresele, P.; Orsini, S.; Noris, P.; Falcinelli, E.; Alessi, M.C.; Bury, L.; Borhany, M.; Santoro, C.; Glembotsky, A.C.; Cid, A.R.; et al. Validation of the ISTH/SSC bleeding assessment tool for inherited platelet disorders: A communication from the Platelet Physiology SSC. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.B.; Gailani, D. Update on the physiology and pathology of factor IX activation by factor XIa. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2008, 1, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman Moser, S.; Chodick, G.; Ni, Y.G.; Chalothorn, D.; Wang, M.D.; Shuldiner, A.R.; Morton, L.; Salomon, O.; Jalbert, J.J. The Association between Factor XI Deficiency and the Risk of Bleeding, Cardiovascular, and Venous Thromboembolic Events. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 122, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadra, G.; Asselta, R.; Tenchini, M.L.; Castaman, G.; Seligsohn, U.; Mannucci, P.M.; Duga, S. Simultaneous genotyping of coagulation factor XI type II and type III mutations by multiplex real-time polymerase chain reaction to determine their prevalence in healthy and factor XI-deficient Italians. Haematologica 2008, 93, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaman, G.; Giacomelli, S.H.; Caccia, S.; Riccardi, F.; Rossetti, G.; Dragani, A.; Giuffrida, A.C.; Biasoli, C.; Duga, S. The spectrum of factor XI deficiency in Italy. Haemophilia 2014, 20, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, N.M.; Saunders, R.E.; Lee, C.A.; Perry, D.J.; Perkins, S.J. Structural interpretation of 42 mutations causing factor XI deficiency using homology modeling. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harlow, S.D.; Campbell, O.M. Epidemiology of menstrual disorders in developing countries: A systematic review. BJOG 2004, 111, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, K.J.; Butler, J.; Posada, O.M.; Wilson, C.; Heal, S.; Ali, M.; Hardy, L.; Ahnström, J.; Gailani, D.; Foster, R.; et al. Kallikrein directly interacts with and activates factor IX, resulting in thrombin generation and fibrin formation independent of factor XI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2014810118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duga, S.; Salomon, O. Congenital factor XI deficiency: An update. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2013, 39, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidi, A.; Seligsohn, U.; Jonas, P.; Many, M. Factor XI deficiency: Detection and management during urological surgery. J. Urol. 1978, 119, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, S.; Brady, M.; Buerk, E.; Carlo, W.; Diekema, D.; Freedman, A.; Maxwell, L.; Wegner, S. Male circumcision. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e756–e785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiewel-Verschueren, S.; Arendz, I.J.; Knol, H.M.; Meijer, K. Gynaecological and obstetrical bleeding in women with factor XI deficiency–a systematic review. Haemophilia 2016, 22, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasulo, M.R.; Biguzzi, E.; Abbattista, M.; Stufano, F.; Pagliari, M.T.; Mancini, I.; Gorski, M.M.; Cannavò, A.; Corgiolu, M.; Peyvandi, F.; et al. The ISTH Bleeding Assessment Tool and the risk of future bleeding. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, A.B.; Bucciarelli, P.; Castaman, G.; Mazzucconi, M.G.; Morfini, M.; Rocino, A.; Schiavoni, M.; Peyvandi, F.; Rodeghiero, F.; Mannucci, P.M. The bleeding score predicts clinical outcomes and replacement therapy in adults with von Willebrand disease. Blood 2014, 123, 4037–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, G.; Colaizzo, D.; Vecchione, G.; Grandone, E.; Di Minno, G.; Margaglione, M.; the GLAnzmann’s Thrombasthenia Italian Team (GLATIT). Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia: Identification of 19 new mutations in 30 patients. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 87, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Case Index | Sex | Age at the Presentation | FXI Activity (IU/dL) | Variant 1 | Variant 2 | Symptoms | ISTH-BAT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 21 | 51 | p.Asp34His | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 1-1 | F | 26 | 47 | p.Asp34His | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 1-2 | F | 49 | 55 | p.Asp34His | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 2 | M | 58 | 43 | p.Cys56Trp | Bleeding after surgery | 3 | |
| 2-1 | M | 32 | 38 | p.Cys56Trp | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 2-2 | F | 25 | 38 | p.Cys56Trp | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 3 * | F | 56 | 42 | p.Val89stop | Repeated bleeding after surgery | 4 | |
| 4 | M | 35 | 32 | C.325+1G>A | Epixastis | 2 | |
| 5 (a) | F | 1 | 1 | p.Ala109Thr | C.325+1G>A | Asymptomatic | 0 |
| 5-1 | M | 31 | 48 | C.325+1G>A | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 5-2 | F | 4 | 41 | p.Ala109Thr | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 5-3 | F | 29 | 35 | p.Ala109Thr | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 6 (a) | M | 32 | 39 | p.Glu135X | Epixastis | 2 | |
| 7 (a) | F | 60 | 44 | p.Glu135X | Repeated bleeding after surgery, Menorrhagia | 6 | |
| 8 (a) | F | 26 | 38 | p.Glu135X | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 8-1 | F | 37 | 34 | p.Glu135X | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 9 | M | 16 | 28 | p.Glu135X | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 9-1 | F | 13 | 25 | p.Glu135X | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 9-2 | M | 43 | 48 | p.Glu135X | bleeding after surgery or trauma | 5 | |
| 9-3 | F | 46 | 33 | p.Glu135X | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 10 | F | 7 | 4 | p.Glu135X | p.Cys321fs | Asymptomatic | 0 |
| 10-1 | F | 34 | 69 | p.Cys321fs | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 10-2 | F | 5 | 3 | p.Glu135X | p.Cys321fs | Asymptomatic | 0 |
| 10-3 | F | 3 | 39 | p.Glu135X | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 11 (b) | F | 47 | 1 | p.Glu135X | p.Glu135X | Repeated bleeding after surgery or trauma | 6 |
| 11-1 | M | 76 | 50 | p.Glu135X | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 11-2 | F | 74 | 76 | p.Glu135X | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 11-3 | M | 45 | 1 | p.Glu135X | p.Glu135X | Repeated bleeding after surgery or trauma | 5 |
| 11-4 | F | 33 | 52 | p.Glu135X | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 11-5 | M | 41 | 2 | p.Glu135X | p.Glu135X | Repeated bleeding after surgery or trauma | 5 |
| 12 (a) | F | 55 | 1 | p.Glu135X | p.Cys136Arg | Asymptomatic | 0 |
| 12-1 | F | 57 | 2 | p.Glu135X | p.Cys136Arg | Asymptomatic | 0 |
| 13 | F | 26 | 40 | p.Glu135X | Menorrhagia | 2 | |
| 14 | F | 41 | 60 | p.Glu135X | Menorrhagia | 3 | |
| 15 | M | 10 | 22 | p-Thr141Met | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 15-1 | M | 54 | 35 | p-Thr141Met | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 16 (a) | M | 7 | 34 | p.Thr150Met | Epistaxis | 2 | |
| 16-1 | M | 38 | 52 | p.Thr150Met | Epistaxis | 1 | |
| 16-2 | M | 46 | 41 | p.Thr150Met | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 16-3 | M | 21 | 34 | p.Thr150Met | Epistaxis | 1 | |
| 17 (a) | F | 6 | 47 | p.Arg162Cys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 17-1 | F | 6 | 43 | p.Arg162Cys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 17-2 | F | 36 | 45 | p.Arg162Cys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 18 (a) | M | 20 | 34 | p.Cys230Arg | Bleeding after surgery | 3 | |
| 18-1 | F | 50 | 34 | p.Cys230Arg | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 19 | M | 41 | 44 | p.Phe301Leu | Repeated bleeding after surgery | 3 | |
| 20 | F | 5 | 46 | p.Phe301Leu | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 21 (a) | F | 8 | 6 | p.Phe301Leu | p.Trp519X | Bleeding after surgery | 4 |
| 21-1 | F | 39 | 40 | p.Phe301Leu | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 22 (a) | F | 14 | 4 | p.Phe301Leu | c.595+3A>G | Asymptomatic | 0 |
| 22-1 | F | 43 | 85 | c.595+3A>G | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 22-2 | M | 49 | 51 | p.Phe301Leu | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 23 * | M | 15 | 40 | p.Leu306Pro | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 23-1 | F | 11 | 45 | p.Leu306Pro | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 23-2 | F | 49 | 38 | p.Leu306Pro | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 24 | F | 3 | 34 | p.Glu315Lys | p.Ala561Asp | Asymptomatic | 0 |
| 24-1 | F | 29 | 36 | p.Glu315Lys | p.Ala561Asp | Asymptomatic | 0 |
| 25 | F | 37 | 28 | p.Glu315Lys | Menorrhagia | 2 | |
| 25-1 | F | 36 | 33 | p.Glu315Lys | Bleeding after surgery | 2 | |
| 25-2 | M | 66 | 18 | p.Glu315Lys | Bleeding after surgery | 3 | |
| 26 (a) | F | 24 | 7 | p.Glu315Lys | p.Trp519X | Menorrhagia | 3 |
| 26-1 | F | 22 | 29 | p.Glu315Lys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 26-2 | M | 60 | 49 | p.Trp519X | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 26-3 | F | 46 | 39 | p.Glu315Lys | Repeated bleeding after trauma | 4 | |
| 27 | M | 16 | 34 | p.Glu315Lys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 27-1 | M | 45 | 27 | p.Glu315Lys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 28 | M | 10 | 31 | p.Glu315Lys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 28-1 | F | 49 | 37 | p.Glu315Lys | Menorrhagia | 2 | |
| 29 | M | 4 | p.Glu315Lys | p.Glu315Lys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 30 | F | 15 | 36 | p.Glu315Lys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 30-1 | M | 38 | 28 | p.Glu315Lys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 31 | M | 6 | 41 | p.Glu315Lys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 31-1 | M | 40 | 40 | p.Glu315Lys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 32 (a) | F | 18 | 38 | p.Arg326His | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 32-2 | F | 44 | 62 | p.Arg326His | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 33 (a) | F | 29 | 43 | p.Gly418Val | Spontaneous ecchymoses | 3 | |
| 33-1 | F | 52 | 45 | p.Gly418Val | Repeated bleeding after trauma | 3 | |
| 34 | M | 10 | 21 | p.Arg497Gln | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 35 (a) * | F | 40 | 14 | p.Trp515Gly | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 35-1 | M | 17 | 30 | p.Trp515Gly | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 35-2 | F | 15 | 44 | p.Trp515Gly | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 35-3 | F | 43 | 27 | p.Trp515Gly | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 35-4 | M | 46 | 36 | p.Trp515Gly | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 35-6 | F | 69 | 36 | p.Trp515Gly | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 36 | F | 82 | 40 | P.Glu565Lys | Repeated bleeding after surgery | 3 | |
| 37 | F | 18 | 29 | P.Glu565Lys | Spontaneous ecchymoses | 3 | |
| 37-1 | M | 57 | 50 | P.Glu565Lys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 38 | M | 10 | 30 | P.Glu565Lys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 38-1 | M | 6 | 28 | P.Glu565Lys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 38-2 | M | 36 | 28 | P.Glu565Lys | Repeated bleeding after surgery—Epistaxis | 5 | |
| 38-3 | F | 63 | 39 | P.Glu565Lys | Asymptomatic | 0 | |
| 39 | M | 21 | 48 | c.1717-2A>G | Epistaxis | 2 | |
| 39-1 | F | 24 | 42 | c.1717-2A>G | Asymptomatic | 0 |
| GENE | Protein Variation | Frequencies | ClinVar | DyneMut2_ (ΔΔGStability) | Predicted Stability Change | Effect on Protein Structure | ACMG | ACMG Supporting Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FXI | p.Leu306Pro | Exomes: Not found Genomes: Not found | No data available | −0.32 kcal/mol | Destabilizing | Disallowed phi/psi | VUS | PM2, PP3, PP2 |
| FXI | p.Trp515Gly | Exomes: Not found Genomes: Not found (cov: 31.9) | No data available | −2.94 kcal/mol | Destabilizing |
Disrupts all H-bonds
Expansion of cavity | VUS | PM2, PP3, PP2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santacroce, R.; D’Andrea, G.; Tiscia, G.L.; Lassandro, G.; d’Apolito, M.; Barcellona, D.; De Bonis, P.; Marongiu, F.; Giordano, P.; Grandone, E.; et al. Clinical and Genetic Heterogeneity of Factor XI Deficiency: Insights from a Southern Italian Cohort. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188807
Santacroce R, D’Andrea G, Tiscia GL, Lassandro G, d’Apolito M, Barcellona D, De Bonis P, Marongiu F, Giordano P, Grandone E, et al. Clinical and Genetic Heterogeneity of Factor XI Deficiency: Insights from a Southern Italian Cohort. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188807
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantacroce, Rosa, Giovanna D’Andrea, Giovanni Luca Tiscia, Giuseppe Lassandro, Maria d’Apolito, Doris Barcellona, Patrizia De Bonis, Francesco Marongiu, Paola Giordano, Elvira Grandone, and et al. 2025. "Clinical and Genetic Heterogeneity of Factor XI Deficiency: Insights from a Southern Italian Cohort" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188807
APA StyleSantacroce, R., D’Andrea, G., Tiscia, G. L., Lassandro, G., d’Apolito, M., Barcellona, D., De Bonis, P., Marongiu, F., Giordano, P., Grandone, E., & Margaglione, M. (2025). Clinical and Genetic Heterogeneity of Factor XI Deficiency: Insights from a Southern Italian Cohort. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188807










