Preliminary Evidence on Intra-Articular Autologous Conditioned Serum (ACS) in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMDs): A Systematic Review with a Focus on Mechanisms and Potential Application in Clinical Practice
Abstract
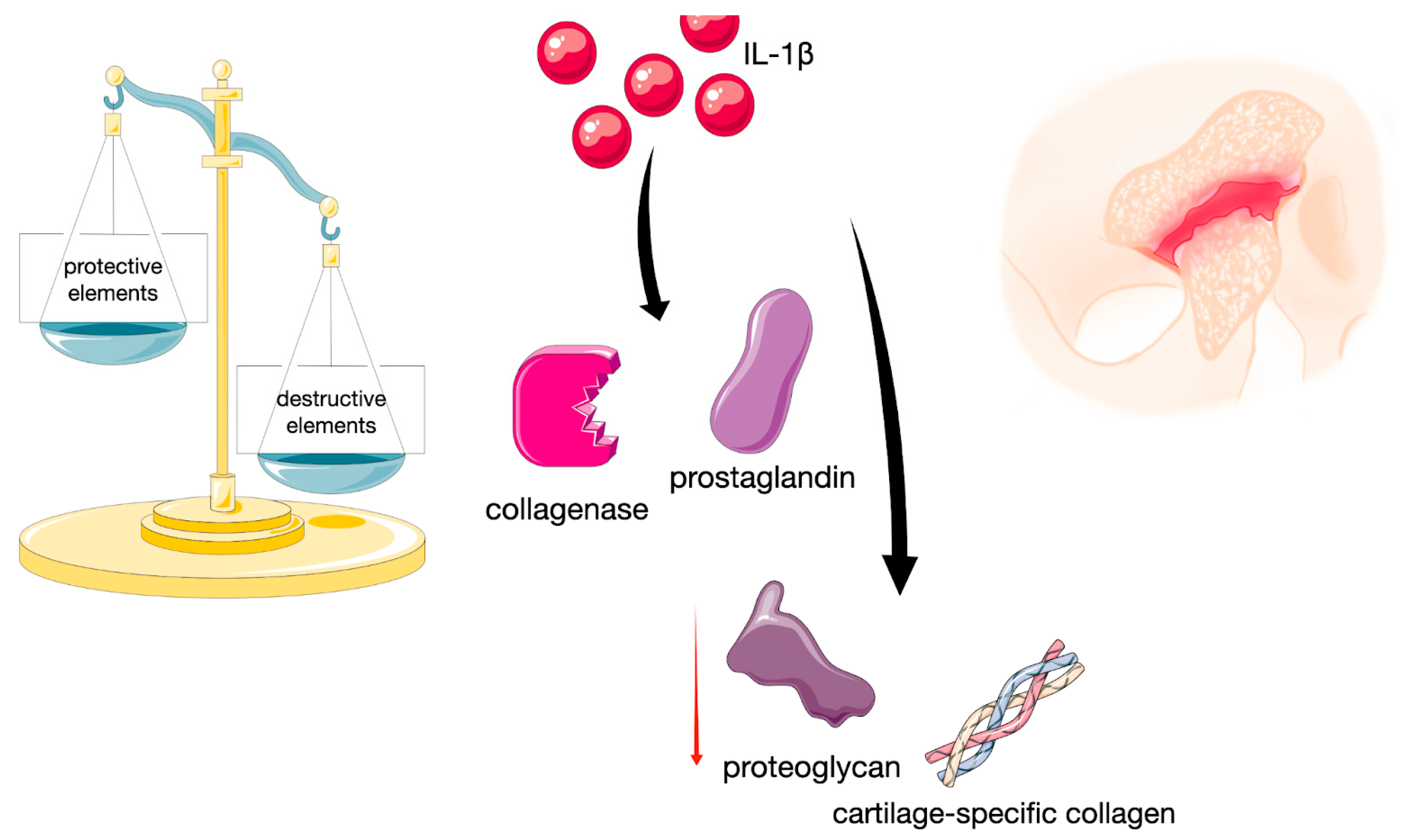
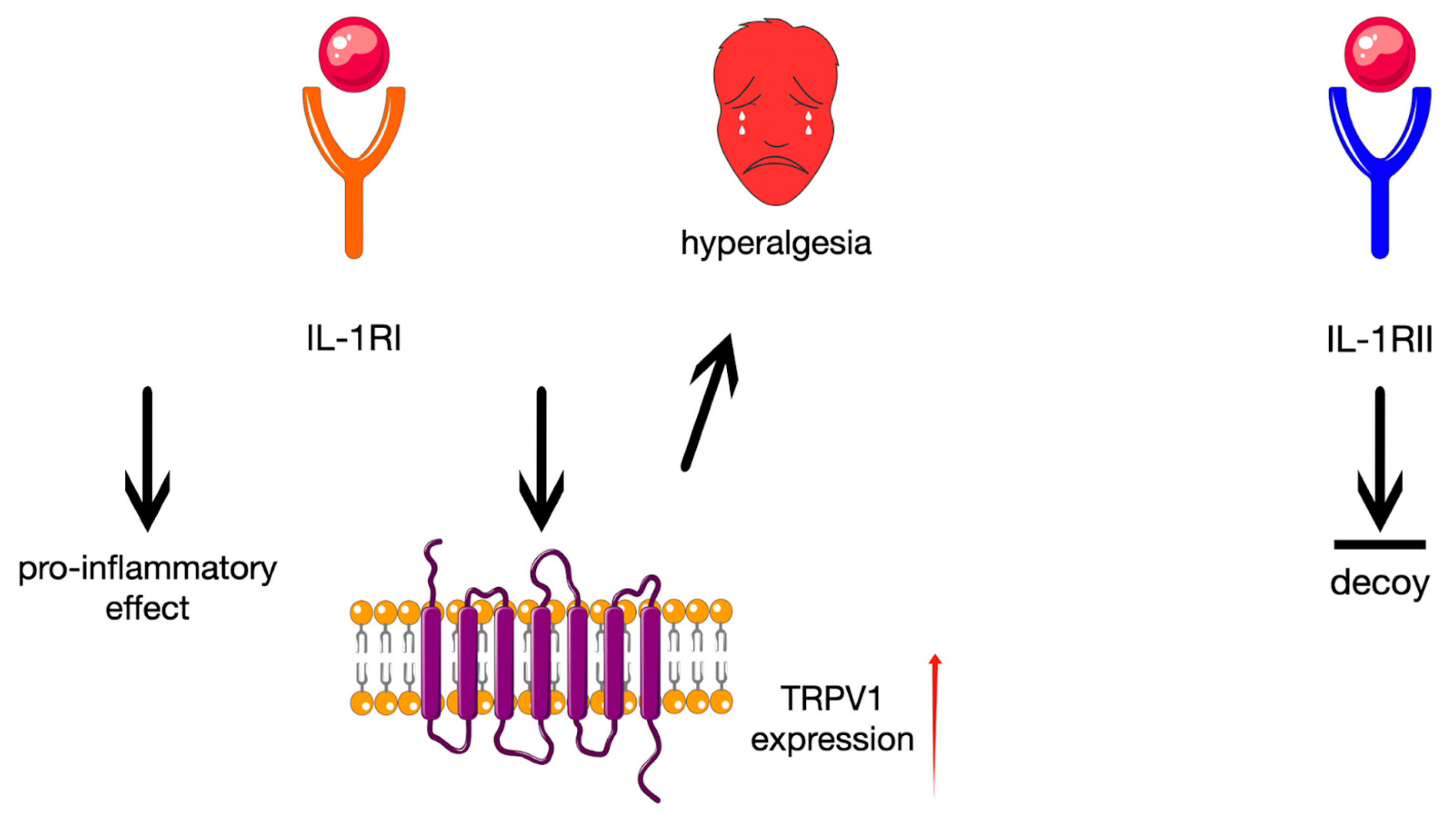
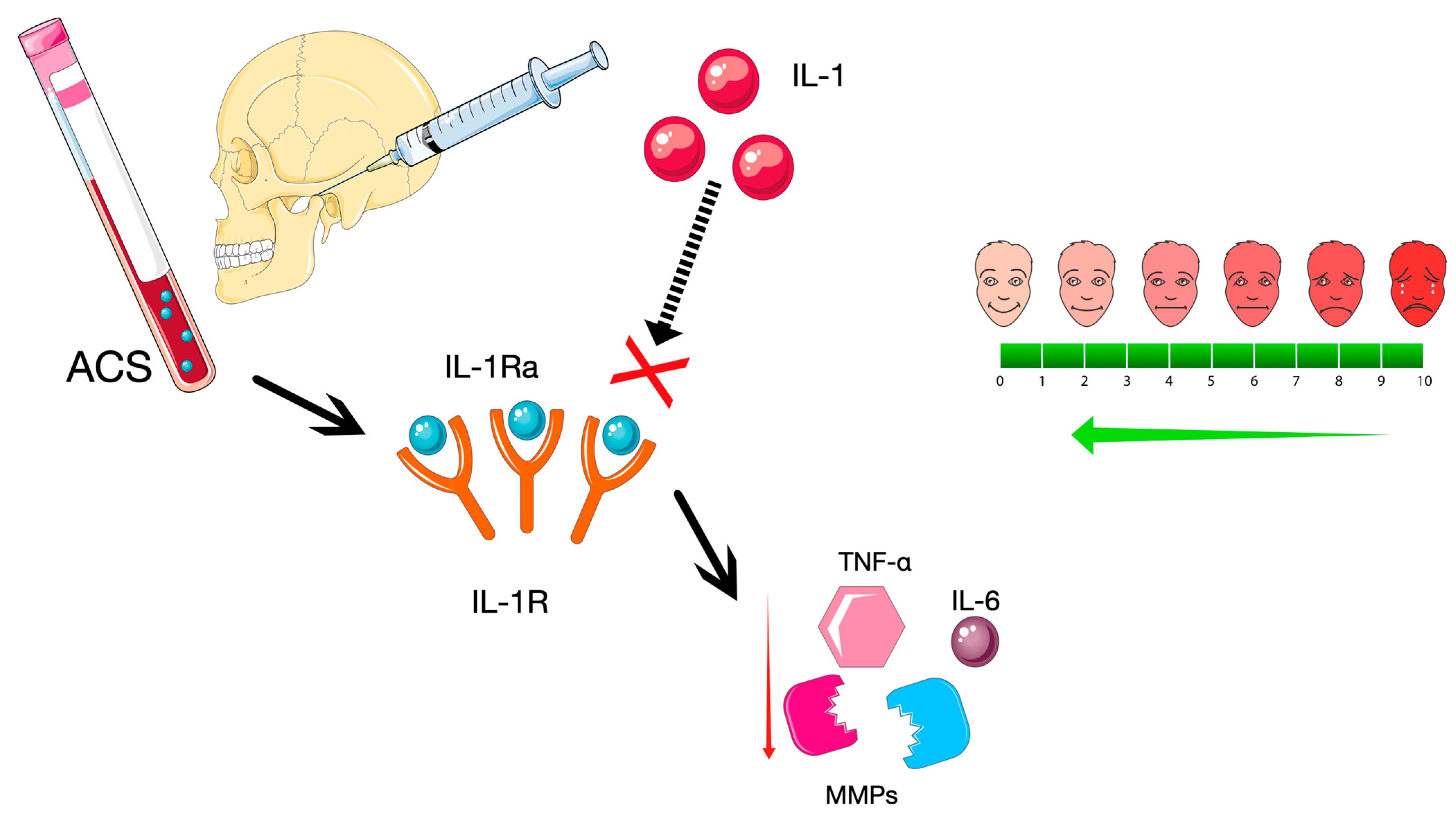
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.3. Selection and Data Processing
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.5. Effect Measures and Synthesis Methods
3. Results
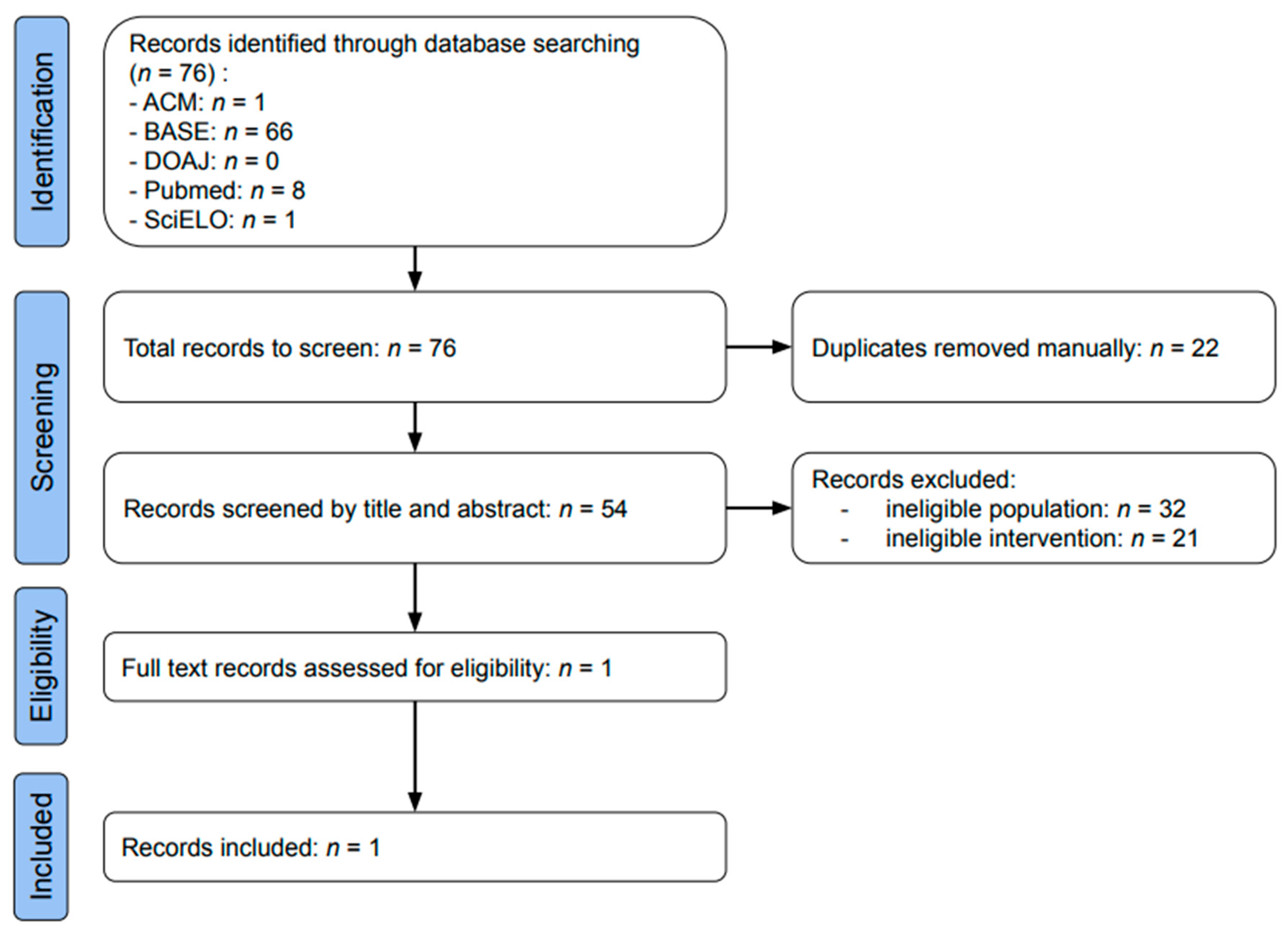
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias in Studies
3.4. Results of Individual Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACS | Autologous Conditioned Serum |
| BFGF | Basic fibroblast growth factor |
| CTGF | Connective tissue growth factor |
| DP | Dextrose prolotherapy |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| FGF | Fibroblast growth factor |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| IGF | Insulin-like growth factor |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-like growth factor-1 |
| IL-1Ra | Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| PDGF | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| PRP | Platelet-rich plasma |
| ROBINS-I | Risk Of Bias In Non-randomized Studies—of Interventions |
| TGF | Transforming growth factor |
| TGF-β1 | Transforming growth factor-β1 |
| TMD | Temporomandibular disorders |
| TMJ | Temporomandibular Joint |
| TMJ-OA | Temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis |
| TNF-β | Tumour necrosis factor beta |
| TRPV 1 | Transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 |
| VAS | Visual Analog Scale |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
Appendix A
| Search Engine | Searched Entries | Identified Items |
|---|---|---|
| ACM | 3,910,450 | 1 |
| BASE | 424,706,948 | 66 |
| DOAJ | 11,212,063 | 0 |
| PubMed | Over 38,000,000 | 8 |
| SciELO | 14,407,809 | 1 |
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | Overall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMJ pain (VAS) | Low | Some concerns | Low | Some concerns | Low | Some concerns |
| Mouth opening (mm) | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Deviation (mm) | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Joint sounds | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
References
- Ravikumar, C.; Sasikala, B.; Krishnakumar Raja, V.B.; Elavenil, P. Evaluation of the efficacy of autologous conditioned serum versus dextrose prolotherapy in internal derangement of the TMJ—A pilot study. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 52, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheson, E.M.; Fermo, J.D.; Blackwelder, R.S. Temporomandibular Disorders: Rapid Evidence Review. Am. Fam. Physician 2023, 107, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zieliński, G.; Pająk-Zielińska, B.; Ginszt, M. A Meta-Analysis of the Global Prevalence of Temporomandibular Disorders. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehling, P.; Moser, C.; Frisbie, D.; McIlwraith, C.W.; Kawcak, C.E.; Krauspe, R.; Reinecke, J.A. Autologous Conditioned Serum in the Treatment of Orthopedic Diseases. BioDrugs 2007, 21, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, X.; Wang, J. Neuroimmune interactions in painful TMD: Mechanisms and treatment implications. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 110, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, S.B. Blocking the effects of IL-1 in rheumatoid arthritis protects bone and cartilage. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, D.; Dayer, J.-M.; Palmer, G.; Gabay, C. Is IL-1 a good therapeutic target in the treatment of arthritis? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 20, 879–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colotta, F.; Dower, S.K.; Sims, J.E.; Mantovani, A. The type II ‘decoy’ receptor: A novel regulatory pathway for interleukin 1. Immunol. Today 1994, 15, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisbie, D.; Ghivizzani, S.; Robbins, P.; Evans, C.; McIlwraith, C. Treatment of experimental equine osteoarthritis by in vivo delivery of the equine interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene. Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Honda, K.; Ohshima, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Nakajima, I.; Micke, P.; Otsuka, K. Cytokine profile in synovial fluid from patients with internal derangement of the temporomandibular joint: A preliminary study. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2006, 35, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, J.; Dietrich, D.; Martin, P.; Palmer, G.; Gabay, C. The interleukin (IL)-1 cytokine family—Balance between agonists and antagonists in inflammatory diseases. Cytokine 2015, 76, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorenson, A.; Hresko, K.; Butcher, S.; Pierce, S.; Tramontina, V.; Leonardi, R.; Loreto, C.; Bosio, J.; Almeida, L.E. Expression of Interleukin-1 and temporomandibular disorder: Contemporary review of the literature. CRANIO® 2018, 36, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A. Arthrocentesis of Temporomandibular Joint-Bridging the Gap Between Non-Surgical and Surgical Treatment. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 9, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chęciński, M.; Chęcińska, K.; Turosz, N.; Brzozowska, A.; Chlubek, D.; Sikora, M. Current Clinical Research Directions on Temporomandibular Joint Intra-Articular Injections: A Mapping Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Camino, J.; Vazquez-Delgado, E.; Gay-Escoda, C. Use of autologous conditioned serum (Orthokine) for the treatment of the degenerative osteoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint. Review of the literature. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2013, 18, e433–e438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, H.; Reinecke, J.; Becker, C.; Tholen, G.; Wehling, P. The production of anti-inflammatory cytokines in whole blood by physico-chemical induction. Inflamm. Res. 2003, 52, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.G.A.; Raijmakers, N.J.H.; Van Arkel, E.R.A.; Caron, J.J.; Rijk, P.C.; Willems, W.J.; Zijl, J.A.C.; Verbout, A.J.; Dhert, W.J.A.; Saris, D.B.F. Autologous interleukin-1 receptor antagonist improves function and symptoms in osteoarthritis when compared to placebo in a prospective randomized controlled trial. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutgers, M.; Saris, D.B.; Dhert, W.J.; Creemers, L.B. Cytokine profile of autologous conditioned serum for treatment of osteoarthritis, in vitroeffects on cartilage metabolism and intra-articular levels after injection. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pishgahi, A.; Abolhasan, R.; Shakouri, S.K.; Soltani-Zangbar, M.S.; Dareshiri, S.; Ranjbar Kiyakalayeh, S.; Khoeilar, A.; Zamani, M.; Motavalli Khiavi, F.; Pourabbas Kheiraddin, B.; et al. Effect of Dextrose Prolotherapy, Platelet Rich Plasma and Autologous Conditioned Serum on Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 19, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingender, S.; Dőri, F.; Schmidt, P.; Hermann, P.; Vaszilkó, M.T. Evaluation of the efficiency of hyaluronic acid, PRP and I-PRF intra-articular injections in the treatment of internal derangement of the temporomandibular joint: A prospective study. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 51, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.; Bansal, V.; Dubey, P.; Kapoor, A. A Comparative Analysis of Intra-articular Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Arthrocentesis in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2022, 21, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derwich, M.; Mitus-Kenig, M.; Pawlowska, E. Mechanisms of Action and Efficacy of Hyaluronic Acid, Corticosteroids and Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, D.; Zaror, C.; Iturriaga, V.; Tobias, A.; Brignardello-Petersen, R. Corticosteroids for the Treatment of Internal Temporomandibular Joint Disorders: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Fei, W.; Cen, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, S.; Tang, Y.; Liang, X. Is There a Difference in Intra-Articular Injections of Corticosteroids, Hyaluronate, or Placebo for Temporomandibular Osteoarthritis? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 76, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhao, K.; Ye, G.; Yao, X.; Yu, M.; Ouyang, H. Effectiveness of intra-articular injections of sodium hyaluronate, corticosteroids, platelet-rich plasma on temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Evid.-Based Dent. Pract. 2022, 22, 101720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, L.W. A Treatment for Subluxation of the Temporomandibular Joint. JAMA 1937, 109, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refai, H.; Altahhan, O.; Elsharkawy, R. The Efficacy of Dextrose Prolotherapy for Temporomandibular Joint Hypermobility: A Preliminary Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 2962–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sit, R.W.-S.; Reeves, K.D.; Zhong, C.C.; Wong, C.H.L.; Wang, B.; Chung, V.C.; Wong, S.Y.; Rabago, D. Efficacy of hypertonic dextrose injection (prolotherapy) in temporomandibular joint dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasheri, A. Glucose: An energy currency and structural precursor in articular cartilage and bone with emerging roles as an extracellular signaling molecule and metabolic regulator. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 29297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahgat, M.M.; Abdel-Hamid, A.M. Is dextrose prolotherapy beneficial in the management of temporomandibular joint internal derangement? A systematic review. CRANIO® 2025, 43, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goiato, M.C.; da Silva, E.V.F.; de Medeiros, R.A.; Túrcio, K.H.L.; Dos Santos, D.M. Are intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid effective for the treatment of temporomandibular disorders? A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, I.; Xu, Y.; Yu, T.; Kang, J.; Wu, F. Does intra-articular injection of PRP help patients with temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis after joint puncture? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Oral Health 2025, 25, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocca, A.D.; McCarthy, M.B.R.; Chowaniec, D.M.; Cote, M.P.; Romeo, A.A.; Bradley, J.P.; Arciero, R.A.; Beitzel, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma Differs According to Preparation Method and Human Variability. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2012, 94, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pufe, T.; Harde, V.; Petersen, W.; Goldring, M.B.; Tillmann, B.; Mentlein, R. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces matrix metalloproteinase expression in immortalized chondrocytes. J. Pathol. 2004, 202, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisterbach, P.E.; Todorov, A.; Flückiger, R.; Evans, C.H.; Majewski, M. Effect of BMP-12, TGF-β1 and autologous conditioned serum on growth factor expression in Achilles tendon healing. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2012, 20, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadpour, N.; Shooshtari, Z.; Kazemian, M.; Gholami, M.; Vatanparast, N.; Samieirad, S. Combined Platelet-Rich Plasma and Hyaluronic Acid can Reduce Pain in Patients Undergoing Arthrocentesis for Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 80, 1474–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chęciński, M.; Lubecka, K.; Bliźniak, F.; Chlubek, D.; Sikora, M. Hyaluronic Acid/Platelet-Rich Plasma Mixture Improves Temporomandibular Joint Biomechanics: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria | |
|---|---|---|
| Population | TMD patients | Patients with a TMJ prosthesis on a given side |
| Intervention | Intra-TMJ administration of ACS | More invasive co-intervention, e.g., arthroscopy |
| Comparison (applicable to specific analyses only) | Placebo or other intra-articular substance | More invasive comparison, e.g., including arthroscopy |
| Outcomes (applicable to specific analyses only) | Articular pain, mandibular mobility, or health-related quality of life | Results that cannot be quantified |
| Timeframe | Any | Not applicable |
| Study types | Any clinical studies for review inclusion, randomized controlled trials for specific analyses | Not applicable |
| Publication form | English-language scientific articles | Reports without full text access |
| ACS | PRP |
|---|---|
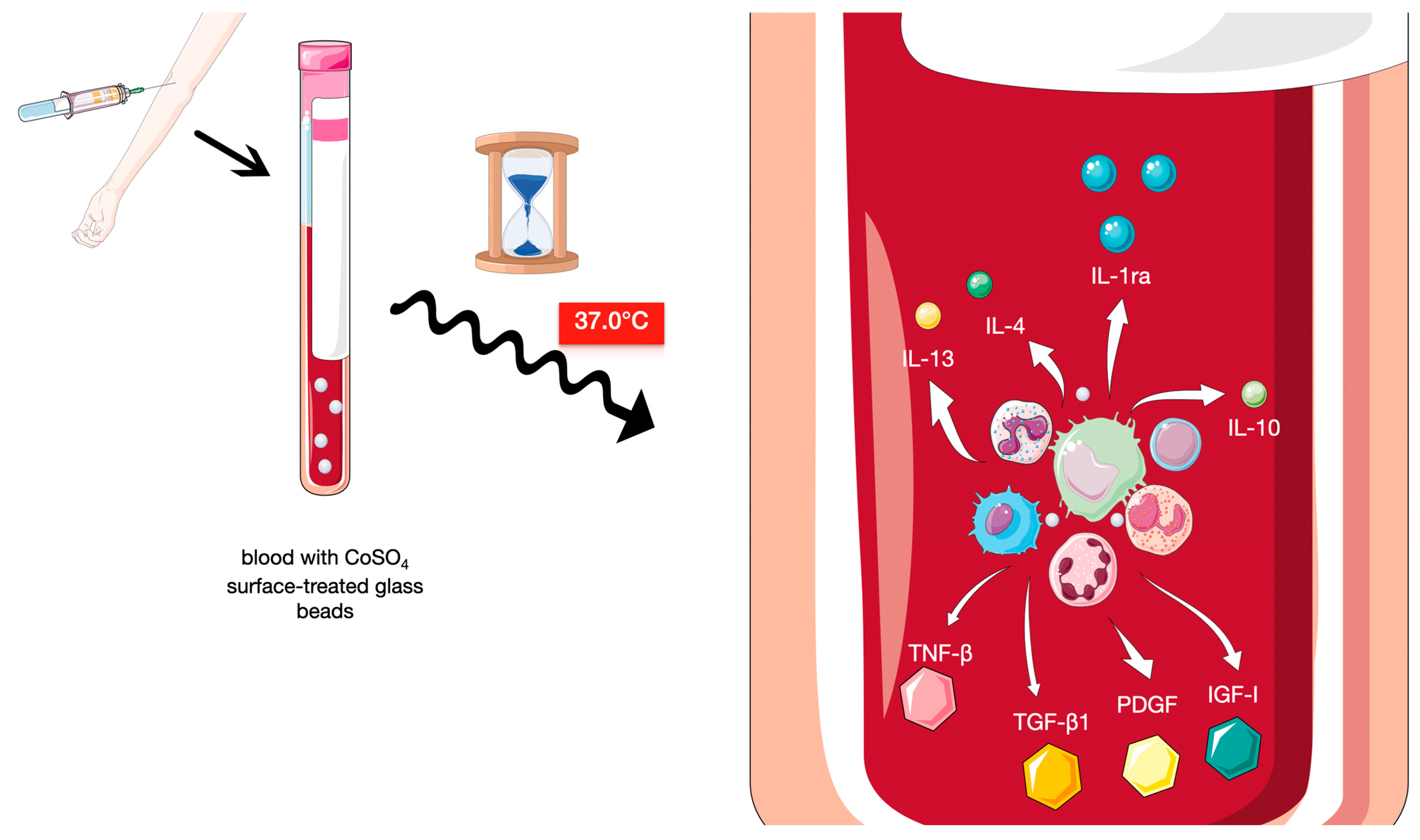
| IL-1RA, IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, EGF, FGF, TGF-β, PDGF, IGF, VEGF * | PDGF, TGF, VEGF, IGF, FGF, and EGF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pasternak, M.; Chęciński, M.; Chęcińska, K.; Turosz, N.; Chyży, I.; Kosiński, B.; Kwiatkowska, K.; Romańczyk, K.; Hoppe, A.; Sikora, M. Preliminary Evidence on Intra-Articular Autologous Conditioned Serum (ACS) in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMDs): A Systematic Review with a Focus on Mechanisms and Potential Application in Clinical Practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188798
Pasternak M, Chęciński M, Chęcińska K, Turosz N, Chyży I, Kosiński B, Kwiatkowska K, Romańczyk K, Hoppe A, Sikora M. Preliminary Evidence on Intra-Articular Autologous Conditioned Serum (ACS) in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMDs): A Systematic Review with a Focus on Mechanisms and Potential Application in Clinical Practice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188798
Chicago/Turabian StylePasternak, Marcin, Maciej Chęciński, Kamila Chęcińska, Natalia Turosz, Izabella Chyży, Bartosz Kosiński, Klaudia Kwiatkowska, Kalina Romańczyk, Amelia Hoppe, and Maciej Sikora. 2025. "Preliminary Evidence on Intra-Articular Autologous Conditioned Serum (ACS) in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMDs): A Systematic Review with a Focus on Mechanisms and Potential Application in Clinical Practice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188798
APA StylePasternak, M., Chęciński, M., Chęcińska, K., Turosz, N., Chyży, I., Kosiński, B., Kwiatkowska, K., Romańczyk, K., Hoppe, A., & Sikora, M. (2025). Preliminary Evidence on Intra-Articular Autologous Conditioned Serum (ACS) in Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMDs): A Systematic Review with a Focus on Mechanisms and Potential Application in Clinical Practice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188798








