Richter Transformation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Current Treatment Challenges and Evolving Therapies
Abstract
1. Introduction
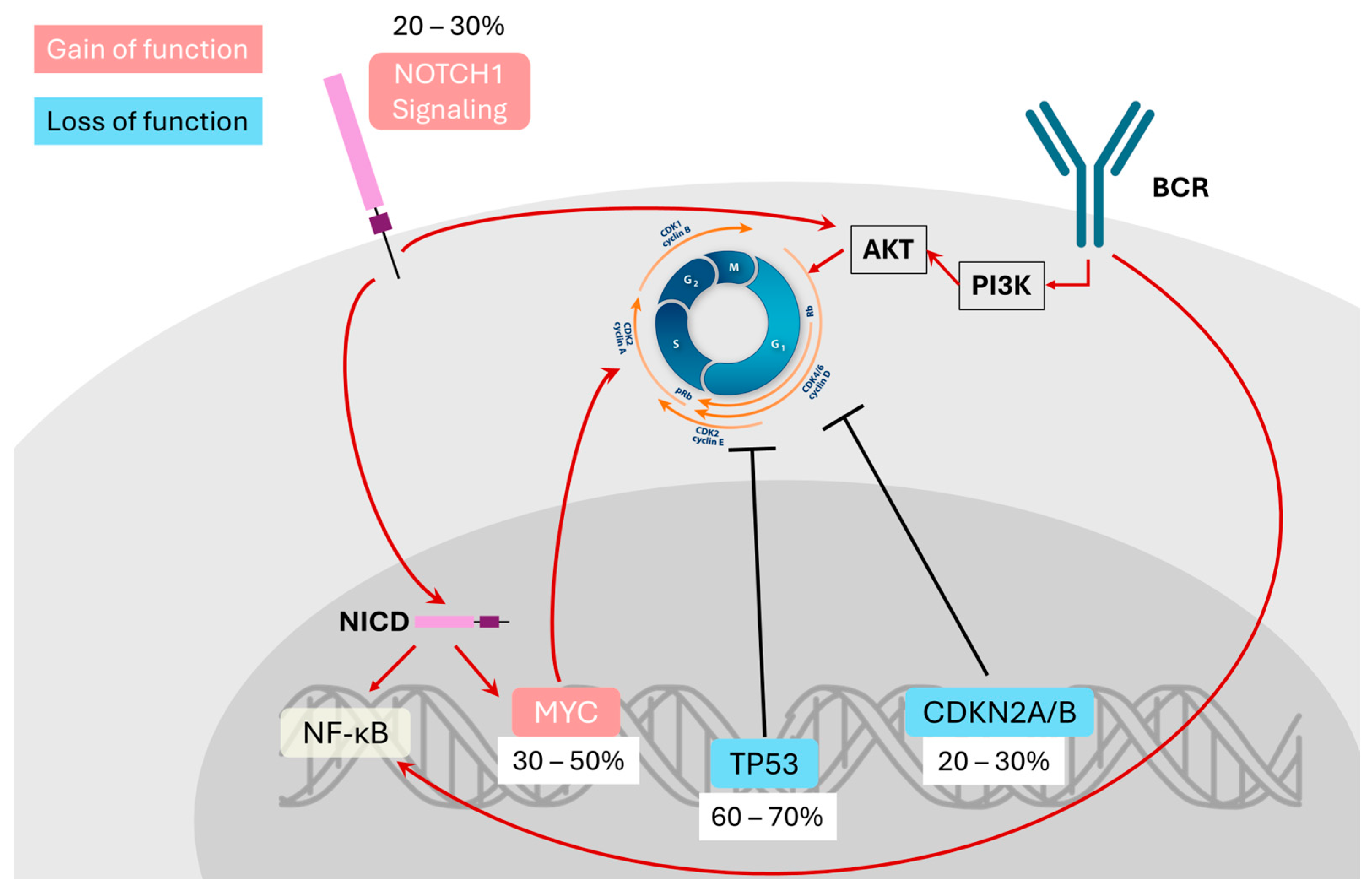
2. Molecular Features and Pathogenesis
3. RT Incidence and Outcomes
4. Treatment Outcomes Across CIT, BTKi, and BCL2 Inhibitor Eras
5. Role of Allo-HSCT
6. CAR T-Cell Therapy in RT
7. Bispecific Antibody Therapies
8. Ongoing and Future Clinical Trials
8.1. Combination Chemo-Immunotherapy Trials
8.2. Checkpoint Inhibitor Combinations
8.3. Triple Targeted Therapy Regimens
8.4. CAR T-Cell Therapy Enhancements
8.5. Bispecific Antibodies and Emerging Immunotherapies
8.6. Targeting ROR1 and Novel Molecular Pathways
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CLL | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
| RT | Richter transformation |
| DLBCL | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| IGHV | Immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region |
| OS | Overall survival |
| allo-HSCT | Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| CAR | Chimeric antigen receptor |
| CIT | Chemoimmunotherapy |
| BTKi | Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| CR | Complete response |
| ORR | Overall response rate |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| MRD | Minimal residual disease |
| TRM | Treatment-related mortality |
| RIC | Reduced-intensity conditioning |
| r/r DLBCL | Relapsed or refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma |
| Liso-cel | Lisocabtagene maraleucel |
| CRS | Cytokine release syndrome |
| ICANS | Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome |
References
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Wen, S.; O’Brien, S.; McLaughlin, P.; Wierda, W.G.; Ferrajoli, A.; Faderl, S.; Manning, J.; Lerner, S.; Mai, C.V.; et al. Assessment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma by absolute lymphocyte counts in 2,126 patients: 20 years of experience at the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4648–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: 2025 Update on the Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Am. J. Hematol. 2025, 100, 450–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, S.A.; Kay, N.E.; Shanafelt, T.D. How we treat Richter syndrome. Blood 2014, 123, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.W.; Davids, M.S.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Puvvada, S.D.; Gerecitano, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Brown, J.R.; Gressick, L.; et al. Targeting BCL2 with Venetoclax in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.N. Generalized Reticular Cell Sarcoma of Lymph Nodes Associated with Lymphatic Leukemia. Am. J. Pathol. 1928, 4, 285–292.7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tschautscher, M.A.; Rabe, K.G.; Call, T.G.; Leis, J.F.; Kenderian, S.S.; Kay, N.E.; Muchtar, E.; Van Dyke, D.L.; Koehler, A.B.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of Richter transformation: Experience of 204 patients from a single center. Haematologica 2020, 105, 765–773. [Google Scholar]
- Pistoia, V.; Roncella, S.; Di Celle, P.F.; Sessarego, M.; Cutrona, G.; Cerruti, G.; Boccaccio, G.P.; Grossi, C.E.; Foà, R.; Ferrarini, M. Emergence of a B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma in a patient with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Evidence for the single-cell origin of the two tumors. Blood 1991, 78, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klener, P.; Fronkova, E.; Berkova, A.; Jaksa, R.; Lhotska, H.; Forsterova, K.; Soukup, J.; Kulvait, V.; Vargova, J.; Fiser, K.; et al. Mantle cell lymphoma-variant Richter syndrome: Detailed molecular-cytogenetic and backtracking analysis reveals slow evolution of a pre-MCL clone in parallel with CLL over several years. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittai, A.S.; Huang, Y.; Miller, S.; Allan, J.N.; Bhat, S.A.; Bond, D.A.; Brander, D.M.; Byrd, J.C.; Chavez, J.C.; Chong, E.; et al. Outcomes of patients with Richter transformation who received no prior chemoimmunotherapy for their CLL. Blood Cancer J. 2025, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, S.A.; Rabe, K.G.; Call, T.G.; Zent, C.S.; Habermann, T.M.; Ding, W.; Leis, J.F.; Schwager, S.M.; Hanson, C.A.; Macon, W.R.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (Richter syndrome) in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL): A cohort study of newly diagnosed patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 162, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Dali, Y.; Hleuhel, M.H.; Andersen, M.A.; Brieghel, C.; Clasen-Linde, E.; Da Cunha-Bang, C.; Niemann, C.U. Risk Factors Associated with Richter’s Transformation in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2018, 132 (Suppl. S1), 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Cerri, M.; Capello, D.; Deambrogi, C.; Rossi, F.M.; Zucchetto, A.; De Paoli, L.; Cresta, S.; Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; et al. Biological and clinical risk factors of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia transformation to Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 142, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Rasi, S.; Fabbri, G.; Spina, V.; Fangazio, M.; Forconi, F.; Marasca, R.; Laurenti, L.; Bruscaggin, A.; Cerri, M.; et al. Mutations of NOTCH1 are an independent predictor of survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; Fangazio, M.; Monti, S.; Greco, M.; Ciardullo, C.; Famà, R.; Cresta, S.; Bruscaggin, A.; et al. Different impact of NOTCH1 and SF3B1 mutations on the risk of chronic lymphocytic leukemia transformation to Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 158, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Cerri, M.; Rasi, S.; Deambrogi, C.; De Paoli, L.; Laurenti, L.; Maffei, R.; Forconi, F.; Bertoni, F.; et al. Stereotyped B-cell receptor is an independent risk factor of chronic lymphocytic leukemia transformation to Richter syndrome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4415–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Deambrogi, C.; Rasi, S.; Laurenti, L.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Arcaini, L.; Lucioni, M.; Rocque, G.B.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; et al. The genetics of Richter syndrome reveals disease heterogeneity and predicts survival after transformation. Blood 2011, 117, 3391–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Montserrat, E. New prognostic markers in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Rev. 2008, 22, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliakas, P.; Jeromin, S.; Iskas, M.; Puiggros, A.; Plevova, K.; Nguyen-Khac, F.; Davis, Z.; Rigolin, G.M.; Visentin, A.; Xochelli, A.; et al. Cytogenetic complexity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Definitions, associations, and clinical impact. Blood 2019, 133, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dali, Y.; Hleuhel, M.H.; da Cunha-Bang, C.; Brieghel, C.; Poulsen, C.B.; Clasen-Linde, E.; Bentzen, H.H.N.; Frederiksen, H.; Christiansen, I.; Nielsen, L.H.; et al. Richter’s transformation in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A Nationwide Epidemiological Study. Leuk. Lymphoma 2020, 61, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Raffeld, M.; Richter, M.; Krugmann, J.; Burek, C.; Hartmann, E.; Rudiger, T.; Jaffe, E.S.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; et al. IgVH Mutational Status and Clonality Analysis of Richter’s Transformation: Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma and Hodgkin Lymphoma in Association with B-cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (B-CLL) Represent 2 Different Pathways of Disease Evolution. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, E.M.; ten Hacken, E.; Wu, C.J. Richter syndrome: Novel insights into the biology of transformation. Blood 2023, 142, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, S.; Vitale, C.; Giannarelli, D.; Visentin, A.; Sanna, A.; Frustaci, A.M.; Olivieri, J.; Quaglia, F.M.; Gozzetti, A.; Sportoletti, P.; et al. Richter transformation in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia receiving ibrutinib: Risk factors and outcomes. Leukemia 2025, 39, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeu, F.; Royo, R.; Massoni-Badosa, R.; Playa-Albinyana, H.; Garcia-Torre, B.; Duran-Ferrer, M.; Dawson, K.J.; Kulis, M.; Diaz-Navarro, A.; Villamor, N.; et al. Detection of early seeding of Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J. Molecular Features Accompanying Richter’s Transformation in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Martines, C.; Porro, F.; Fortunati, I.; Bonato, A.; Dimishkovska, M.; Piazza, S.; Yadav, B.S.; Innocenti, I.; Fazio, R.; et al. B-cell receptor signaling and genetic lesions in TP53 and CDKN2A/CDKN2B cooperate in Richter transformation. Blood 2021, 138, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrackova, A.; Turcsanyi, P.; Papajik, T.; Kriegova, E. Revisiting Richter transformation in the era of novel CLL agents. Blood Rev. 2021, 49, 100824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; O’Brien, S.; Khouri, I.; Giles, F.J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Champlin, R.; Wen, S.; Do, K.A.; Smith, S.C.; Lerner, S.; et al. Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors in patients with Richter’s syndrome treated with chemotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy with or without stem-cell transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Robrecht, S.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Cramer, P.; v Tresckow, J.; Lange, E.; Kiehl, M.; Dreyling, M.; Ritgen, M.; et al. Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)-a pooled analysis of German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG) front line treatment trials. Leukemia 2021, 35, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnair, R.; Ellithi, M.; Kallam, A.; Shostrom, V.; Bociek, R.G. Outcomes of Richter’s transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL): An analysis of the SEER database. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 2513–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, T.; Brown, J.R.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Barr, P.M.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Final analysis from RESONATE: Up to six years of follow-up on ibrutinib in patients with previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Barr, P.M.; Robak, T.; Owen, C.; Ghia, P.; Tedeschi, A.; Bairey, O.; Hillmen, P.; Coutre, S.E.; Devereux, S.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of first-line ibrutinib treatment for patients with CLL/SLL: 5 years of follow-up from the phase 3 RESONATE-2 study. Leukemia 2020, 34, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; D’Rozario, J.; Assouline, S.; Owen, C.; Gerecitano, J.; Robak, T.; De la Serna, J.; et al. Venetoclax-Rituximab in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddocks, K.J.; Ruppert, A.S.; Lozanski, G.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Abruzzo, L.; Lozanski, A.; Davis, M.; Gordon, A.; Smith, L.L.; et al. Etiology of Ibrutinib Therapy Discontinuation and Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Keating, M.; Wierda, W.; Estrov, Z.; Ferrajoli, A.; Jain, N.; George, B.; James, D.; Kantarjian, H.; Burger, J.; et al. Outcomes of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia after discontinuing ibrutinib. Blood 2015, 125, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.S.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, K.A.; Stern, R.; Brown, J.R.; Thompson, P.A.; Brander, D.M.; Danilov, A.V.; Ujjani, C.S.; Parikh, S.A.; et al. Richter’s syndrome (RS) in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) on novel agent therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35 (Suppl. S15), 7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, N.; Eyre, T.A.; Cabes, M.; Jackson, A.; Boucher, R.; Yates, F.; Fox, S.; Rawstron, A.; Hillmen, P.; Schuh, A. The STELLAR trial protocol: A prospective multicentre trial for Richter’s syndrome consisting of a randomised trial investigation CHOP-R with or without acalabrutinib for newly diagnosed RS and a single-arm platform study for evaluation of novel agents in relapsed disease. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 471. [Google Scholar]
- Rawstron, A.C.; Fazi, C.; Agathangelidis, A.; Villamor, N.; Letestu, R.; Nomdedeu, J.; Palacio, C.; Stehlikova, O.; Kreuzer, K.A.; Liptrot, S.; et al. A complementary role of multiparameter flow cytometry and high-throughput sequencing for minimal residual disease detection in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: An European Research Initiative on CLL study. Leukemia 2016, 30, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.A.; Srivastava, J.; Peterson, C.; Strati, P.; Jorgensen, J.L.; Hether, T.; Keating, M.J.; O’Brien, S.M.; Ferrajoli, A.; Burger, J.A.; et al. Minimal residual disease undetectable by next-generation sequencing predicts improved outcome in CLL after chemoimmunotherapy. Blood 2019, 134, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zheng, P.; Liu, H.; Sun, M.; Guo, Y.; Ma, L.; Liu, R.; Fu, Z.; Yang, F.; Ke, X.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy treatment Richter’s transformation. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1591360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coombs, C.C.; Easaw, S.; Grover, N.S.; O’Brien, S.M. Cellular Therapies in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Richter’s Transformation: Recent Developments in Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cells, Natural Killer Cells, and Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant. Cancers 2023, 15, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guièze, R.; Eikema, D.J.; Koster, L.; Schetelig, J.; Sengeloev, H.; Passweg, J.; Finke, J.; Arat, M.; Broers, A.E.C.; Stölzel, F.; et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for patients with Richter transformation: A retrospective study on behalf of the Chronic Malignancies Working Party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2024, 59, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, C.E.; Davids, M.S. Practical Management of Richter Transformation in 2023 and Beyond. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2023, 43, e390804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langerbeins, P.; Busch, R.; Anheier, N.; Dürig, J.; Bergmann, M.; Goebeler, M.E.; Hurtz, H.J.; Stauch, M.B.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Döhner, H.; et al. Poor efficacy and tolerability of R-CHOP in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter transformation. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, E239–E243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durot, E.; Michallet, A.-S.; Leprêtre, S.; Le, Q.-H.; Leblond, V.; Delmer, A. Platinum and high-dose cytarabine-based regimens are efficient in ultra high/high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter’s syndrome: Results of a French retrospective multicenter study. Eur. J. Haematol. 2015, 95, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabaja, B.S.; O’Brien, S.M.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Cortes, J.E.; Thomas, D.A.; Albitar, M.; Schlette, E.S.; Faderl, S.; Sarris, A.; Keating, M.J.; et al. Fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, liposomal daunorubicin (daunoXome), and dexamethasone (hyperCVXD) regimen in Richter’s syndrome. Leuk. Lymphoma 2001, 42, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Cortes, J.; Thomas, D.A.; Faderl, S.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Verstovsek, S.; Ferrajoli, A.; Wierda, W.; Alvarado, Y.; et al. Fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, liposomal daunorubicin, and dexamethasone plus rituximab and granulocyte-macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) alternating with methotrexate and cytarabine plus rituximab and GM-CSF in patients with Richter syndrome or fludarabine-refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 2003, 97, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Wierda, W.G.; Plunkett, W.; Kurzrock, R.; O’Brien, S.; Wen, S.; Ferrajoli, A.; Ravandi-Kashani, F.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Estrov, Z.; et al. Phase I-II study of oxaliplatin, fludarabine, cytarabine, and rituximab combination therapy in patients with Richter’s syndrome or fludarabine-refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, K.A.; Huang, Y.; Ruppert, A.S.; Salem, G.; Stephens, D.M.; Heerema, N.A.; Andritsos, L.A.; Awan, F.T.; Byrd, J.C.; Flynn, J.M.; et al. A single-institution retrospective cohort study of first-line R-EPOCH chemoimmunotherapy for Richter syndrome demonstrating complex chronic lymphocytic leukaemia karyotype as an adverse prognostic factor. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, M.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Call, T.G.; Ding, W.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Leis, J.F.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Bowen, D.; Conte, M.; Schwager, S.M.; et al. The efficacy of ibrutinib in the treatment of Richter syndrome. Blood 2015, 125, 1676–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschalidi, S.; Sepulveda, F.E.; Garrigue, A.; Fischer, A.; de Saint Basile, G. Therapeutic effect of JAK1/2 blockade on the manifestations of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in mice. Blood 2016, 128, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, T.A.; Schuh, A.; Wierda, W.G.; Brown, J.R.; Ghia, P.; Pagel, J.M.; Furman, R.R.; Cheung, J.; Hamdy, A.; Izumi, R.; et al. Acalabrutinib monotherapy for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ACE-CL-001): Analysis of the Richter transformation cohort of an open-label, single-arm, phase 1-2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e912–e921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Ligtvoet, R.; Robrecht, S.; Stumpf, J.; Fink, A.M.; Tausch, E.; Schneider, C.; Boettcher, S.; Mikusko, M.; Ritgen, M.; et al. Tislelizumab plus zanubrutinib for Richter transformation: The phase 2 RT1 trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierda, W.G.; Shah, N.N.; Cheah, C.Y.; Lewis, D.; Hoffmann, M.S.; Coombs, C.C.; Lamanna, N.; Ma, S.; Jagadeesh, D.; Munir, T.; et al. Pirtobrutinib, a highly selective, non-covalent (reversible) BTK inhibitor in patients with B-cell malignancies: Analysis of the Richter transformation subgroup from the multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 BRUIN study. Lancet Haematol. 2024, 11, e682–e692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaizo Moore, V.; Brown, J.R.; Certo, M.; Love, T.M.; Novina, C.D.; Letai, A. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia requires BCL2 to sequester prodeath BIM, explaining sensitivity to BCL2 antagonist ABT-737. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.S.; Roberts, A.W.; Seymour, J.F.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Wierda, W.G.; Puvvada, S.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Salem, A.H.; et al. Phase I First-in-Human Study of Venetoclax in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.S.; Rogers, K.A.; Tyekucheva, S.; Wang, Z.; Pazienza, S.; Renner, S.K.; Montegaard, J.; Ihuoma, U.; Lehmberg, T.Z.; Parry, E.M.; et al. Venetoclax plus dose-adjusted R-EPOCH for Richter syndrome. Blood 2022, 139, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.S.; Rogers, K.A.; Jain, N.; Tyekucheva, S.; Ren, Y.; Carey, C.; Montegaard, J.; Hajdenberg, M.; Ryan, C.E.; Merryman, R.; et al. Initial results of a multicenter phase 2 study of venetoclax in combination with R-CHOP (VR-CHOP) for patients with Richter Syndrome. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. S2), 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, P.J.; Swaminathan, M.; Rogers, K.A.; Parry, E.M.; Burger, J.A.; Davids, M.S.; Ding, W.; Ferrajoli, A.; Hyak, J.M.; Jain, N.; et al. A multicenter study of venetoclax-based treatment for patients with Richter transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 2342–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Ding, W.; Viswanatha, D.S.; Chen, D.; Shi, M.; Van Dyke, D.; Tian, S.; Dao, L.N.; Parikh, S.A.; Shanafelt, T.D.; et al. PD-1 Expression in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and Large B-cell Richter Transformation (DLBCL-RT): A Characteristic Feature of DLBCL-RT and Potential Surrogate Marker for Clonal Relatedness. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frustaci, A.M.; Montillo, M.; Rossi, D.; Zinzani, P.L.; Motta, M.; Gaidano, G.; Quaresmini, G.; Scarfo, L.; Pietrasanta, D.; Coscia, M.; et al. Results of MOLTO, a multicenter, open label, phase II clinical trial evaluating venetoclax, atezolizumab and obinutuzumab combination in Richter syndrome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. S16), 7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannello, A.; Vitale, N.; Coma, S.; Arruga, F.; Chadburn, A.; Di Napoli, A.; Laudanna, C.; Allan, J.N.; Furman, R.R.; Pachter, J.A.; et al. Synergistic efficacy of the dual PI3K-δ/γ inhibitor duvelisib with the Bcl-2 inhibitor venetoclax in Richter syndrome PDX models. Blood 2021, 137, 3378–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crombie, J.L.; Ryan, C.E.; Ren, Y.; Tyekucheva, S.; Carey, C.; Zou, A.; Normilus, S.; Montegaard, J.; Soumerai, J.D.; Bhandari, S.; et al. A Phase 2 Study of Duvelisib and Venetoclax in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory (R/R) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) or Richter’s Syndrome (RS). Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. S1), 4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, T. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Biology and Therapy. In Biology and Treatment of Leukemia and Bone Marrow Neoplasms; Pullarkat, V., Marcucci, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 133–149. [Google Scholar]
- Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A.; Kumar, A.; Stingo, F.E.; Khimani, F.; Hussaini, M.; Ayala, E.; Nishihori, T.; Shah, B.; Locke, F.L.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; et al. Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Richter Syndrome: A Single-Center Experience. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018, 18, e35–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sośnia, O.; Pruszczyk, K.; Danecki, M.; Wąsik-Szczepanek, E.; Tryc-Szponder, J.; Iskierka-Jażdżewska, E.; Majeranowski, A.; Krzemień, H.; Bołkun, Ł.; Paszkiewicz-Kozik, E.; et al. Richter transformation—Retrospective treatment outcomes analysis in Polish Adult Leukemia Study Group. Leuk. Lymphoma 2024, 65, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahoud, O.B.; Devlin, S.M.; Maloy, M.A.; Roeker, L.E.; Dahi, P.B.; Ponce, D.M.; Gyurkocza, B.; Koehne, G.; Young, J.W.; Castro-Malaspina, H.R.; et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter’s transformation. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2879–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhaus, D.; Brauer, D.; Pointner, R.; Bischof, L.; Vucinic, V.; Franke, G.-N.; Niederwieser, D.; Platzbecker, U.; Jentzsch, M.; Schwind, S. A high hematopoietic cell transplantation comorbidity Index (HCT-CI) does not impair outcomes after non-myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia patients 60 years or older. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2023, 58, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janscak, M.; Stelmes, A.; van den Berg, J.; Heim, D.; Halter, J.; Drexler, B.; Arranto, C.; Passweg, J.; Medinger, M. Influence of comorbidities on outcome in 1102 patients with an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2024, 59, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, W.; Han, Y.; Chen, S.; Xue, S.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, H.; Wu, D.; et al. Allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation outcomes of patients aged ≥55 years with acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndromes in China: A retrospective study. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakar, M.S.; Broglie, L.; Logan, B.; Artz, A.; Bunin, N.; Burroughs, L.M.; Fretham, C.; Jacobsohn, D.A.; Loren, A.W.; Kurtzberg, J.; et al. The Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Comorbidity Index predicts survival after allogeneic transplant for nonmalignant diseases. Blood 2019, 133, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, A.F.; Ahn, K.W.; Litovich, C.; Chen, Y.; Assal, A.; Bashir, Q.; Bayer, R.L.; Coleman, M.; DeFilipp, Z.; Farhadfar, N.; et al. Autologous and allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma-type Richter syndrome. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 3528–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puckrin, R.; Owen, C.; Fontaine, A.; Peters, A.; Stewart, D.; Shafey, M. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for Richter transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: An intention-to-transplant analysis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2023, 58, 817–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwynarski, K.; van Biezen, A.; de Wreede, L.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Bunjes, D.; Metzner, B.; Koza, V.; Mohty, M.; Remes, K.; Russell, N.; et al. Autologous and allogeneic stem-cell transplantation for transformed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (Richter’s syndrome): A retrospective analysis from the chronic lymphocytic leukemia subcommittee of the chronic leukemia working party and lymphoma working party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Asmar, J.; Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A. Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Richter Syndrome. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 1938–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouclet, F.; Calleja, A.; Dilhuydy, M.S.; Véronèse, L.; Pereira, B.; Amorim, S.; Cymbalista, F.; Herbaux, C.; de Guibert, S.; Roos-Weil, D.; et al. Real-world outcomes following venetoclax therapy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia or Richter syndrome: A FILO study of the French compassionate use cohort. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Español, I.; Büchler, T.; Ferrá, C.; Gallardo, D.; Reyes, P.; Sarrá, J.; Domingo, A.; Romagosa, V.; Grañena, A. Richter’s syndrome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukaemia successfully treated by withdrawal of immunosuppression, and donor lymphocyte infusion. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2003, 31, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Baker, P.O.; Parry, E.; Davids, M.; Alyea, E.P.; Ho, V.T.; Cutler, C.; Koreth, J.; Gooptu, M.; Romee, R.; et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation outcomes in patients with Richter’s transformation. Haematologica 2021, 106, 3219–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, S.A.; Blättel, J.; Reuß, K.; Maier, C.-P.; Faul, C.; Vogel, W.; Bethge, W.; Lengerke, C. Long-term patient-reported outcomes following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2025, 60, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jäger, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, O.; Fried, S.; Shouval, R.; Flynn, J.R.; Beyar-Katz, O.; Leslie, L.A.; Zucherman, T.; Yerushalmi, R.; Shem-Tov, N.; Palomba, M.L.; et al. Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy has less efficacy in Richter transformation than in de novo large B-cell lymphoma and transformed low-grade B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2024, 109, 3566–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittai, A.S.; Bond, D.; Huang, Y.; Bhat, S.A.; Blyth, E.; Byrd, J.C.; Chavez, J.C.; Davids, M.S.; Cruz, J.P.D.; Dowling, M.R.; et al. Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Richter Transformation: An International, Multicenter, Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 2071–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyar-Katz, O.; Benjamini, O.; Delgado, J.; Ruella, M.; Ram, R.; Grisariu, S.; Visentin, A.; Vandenberghe, E.; Gentile, M.; Avigdor, A.; et al. CD19 CAR-T Cell Therapy Is Effective in Richter Transformation: A Multicenter Retrospective Analysis By the European Research Initiative on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. S1), 4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittai, A.S.; Bond, D.A.; William, B.; Saad, A.; Penza, S.; Efebera, Y.; Larkin, K.; Wall, S.A.; Choe, H.K.; Bhatnagar, B.; et al. Clinical activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in adult patients with Richter syndrome. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 4648–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, J.S.; Palomba, M.L.; Gordon, L.I.; Lunning, M.A.; Wang, M.; Arnason, J.; Mehta, A.; Purev, E.; Maloney, D.G.; Andreadis, C.; et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): A multicentre seamless design study. Lancet 2020, 396, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Breyanzi (Lisocabtagene Maraleucel)—EPAR Product Information. 2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/breyanzi (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Siddiqi, T.; Maloney, D.G.; Kenderian, S.S.; Brander, D.M.; Dorritie, K.; Soumerai, J.; Riedell, P.A.; Shah, N.N.; Nath, R.; Fakhri, B.; et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma (TRANSCEND CLL 004): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 1–2 study. Lancet 2023, 402, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdar, M.; Solomon, S.R.; Arnason, J.; Johnston, P.B.; Glass, B.; Bachanova, V.; Ibrahimi, S.; Mielke, S.; Mutsaers, P.; Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, F.; et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel versus standard of care with salvage chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation as second-line treatment in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (TRANSFORM): Results from an interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 2294–2308, Erratum in Lancet 2022, 400, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Fraietta, J.A.; Lacey, S.F.; Orlando, E.J.; Pruteanu-Malinici, I.; Gohil, M.; Lundh, S.; Boesteanu, A.C.; Wang, Y.; O’Connor, R.S.; Hwang, W.T.; et al. Determinants of response and resistance to CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 561, Erratum in Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Senapati, J.; Thakral, B.; Ferrajoli, A.; Thompson, P.; Burger, J.; Basu, S.; Kadia, T.; Daver, N.; Borthakur, G.; et al. A phase 2 study of nivolumab combined with ibrutinib in patients with diffuse large B-cell Richter transformation of CLL. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 1958–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; LaPlant, B.R.; Call, T.G.; Parikh, S.A.; Leis, J.F.; He, R.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Sinha, S.; Le-Rademacher, J.; Feldman, A.L.; et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with CLL and Richter transformation or with relapsed CLL. Blood 2017, 129, 3419–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, A.; Brody, J.; Carpio, C.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Ben-Yehuda, D.; Ferhanoglu, B.; Nagler, A.; Ozcan, M.; Avivi, I.; Bosch, F.; et al. Safety and activity of ibrutinib in combination with nivolumab in patients with relapsed non-Hodgkin lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A phase 1/2a study. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e67–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadiminti, K.V.; Ahn, K.W.; Patel, D.J.; Lian, Q.; Pasquini, M.C.; Hamadani, M.; Turtle, C.J.; Herrera, A.F.; Shadman, M. CD19-Directed CAR-T Therapy for Richter Transformation: A CIBMTR Analysis. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2025, 31 (Suppl. S2), S207–S208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, A.; Hoogland, A.I.; Kommalapati, A.; Logue, J.; Welniak, T.; Hyland, K.A.; Eisel, S.L.; Small, B.J.; Jayani, R.V.; Booth-Jones, M.; et al. Change in Patients’ Perceived Cognition Following Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Lymphoma. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2022, 28, e1–e401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruark, J.; Mullane, E.; Cleary, N.; Cordeiro, A.; Bezerra, E.D.; Wu, V.; Voutsinas, J.; Shaw, B.E.; Flynn, K.E.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Patient-Reported Neuropsychiatric Outcomes of Long-Term Survivors after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amonoo, H.L.; Johnson, P.C.; Dhawale, T.M.; Traeger, L.; Rice, J.; Lavoie, M.W.; Ufere, N.N.; Longley, R.M.; Harnedy, L.E.; Clay, M.A.; et al. Sharing and caring: The impact of social support on quality of life and health outcomes in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cancer 2021, 127, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Xu, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Cao, J.; Hu, T.; Zhou, F. Quality of life and symptom burden among hematologic malignancy patients undergoing CAR-T therapy: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 17763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, J.S.; Palomba, M.L.; Gordon, L.I.; Lunning, M.; Wang, M.; Arnason, J.; Purev, E.; Maloney, D.G.; Andreadis, C.; Sehgal, A.; et al. Two-year follow-up of lisocabtagene maraleucel in relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma in TRANSCEND NHL 001. Blood 2024, 143, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A single-arm, multicentre, phase 1–2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vom Stein, A.F.; Nguyen, P.H.; Ten Hacken, E. A question of TiME: How microenvironmental interactions shape response to immunotherapy in CLL and Richter Transformation. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1592574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy Yurkovski, I.; Tadmor, T. Accelerated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Richter Transformation in the Era of Novel Agents. Acta Haematol. 2024, 147, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Maldonado, V.; Martínez-Cibrián, N.; Alserawan, L.; Betriu, S.; Triguero, A.; Blum, S.; Faes, M.; Liefaard, M.C.; Pont, M.J.; Spoon, M.; et al. Euplagia-1: A Phase 1/2 Trial of GLPG5201, a Fresh Stem-like Early Memory CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy with a 7-Day Vein-to-Vein Time, in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory CLL and RT. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. S1), 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kater, A.P.; Janssens, A.; Eradat, H.; Offner, F.; Sandoval-Sus, J.D.; Shadman, M.; Bjørn Poulsen, C.; Haaber Christensen, J.; Thompson, M.C.; Rios, M.; et al. CLL-280 Epcoritamab Induces Deep Responses in Patients with Richter Transformation (RT): Primary Results From the EPCORE CLL-1 Trial. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2024, 24, S350–S351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, C.Y.; Assouline, S.; Baker, R.; Bartlett, N.L.; El-Sharkawi, D.; Giri, P.; Ku, M.; Schuster, S.J.; Matasar, M.; Radford, J.; et al. Mosunetuzumab Monotherapy Demonstrates Activity and a Manageable Safety Profile in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Richter’s Transformation. Blood 2023, 142, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guièze, R.; Ysebaert, L.; Roos-Weil, D.; Fornecker, L.-M.; Ferrant, E.; Molina, L.; Aurran, T.; Clavert, A.; de Guibert, S.; Michallet, A.-S.; et al. Blinatumomab after R-CHOP bridging therapy for patients with Richter transformation: A phase 2 multicentre trial. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, A.; Frustaci, A.M.; Condoluci, A.; Coscia, M.; Chiarle, R.; Zinzani, P.L.; Motta, M.; Gaidano, G.; Quaresmini, G.; Scarfò, L.; et al. Atezolizumab, venetoclax, and obinutuzumab combination in Richter transformation diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (MOLTO): A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouse, G.; Chen, C.; Muir, A.; Popplewell, L.; Siddiqi, T.; Zain, J.; Herrera, A.F.; Danilova, O.; Roleder, C.; Wang, L.; et al. Safety and efficacyof the combination of copanlisib and nivolumab in patients with Richter’s transformation or transformed non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Results from a phase I trial. Haematologica 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; LaPlant, B.R.; Parikh, S.A.; Leis, J.F.; Call, T.G.; Shanafelt, T.D.; He, R.; Micallef, I.N.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Habermann, T.M.; et al. Efficacy of pembrolizumab monotherapy and in combination with BCR inhibitors for Richter transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. S16), 7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, S.F.; Schuster, S.J.; Ding, W.; Koehler, A.B.; Brander, D.M.; Rosenthal, A.C.; Leis, J.F.; Tun, H.W.; Moustafa, M.A.; Iqbal, M.; et al. DTRMWXHS-12, a novel Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in combination with everolimus and pomalidomide in patients with relapsed/refractory lymphomas: An open-label, multicenter, phase 1a/1b study. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Study of DTRM-555 in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Hematologic Malignancies. ClinicalTrials.gov, 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04305444?intr=DTRM-555&rank=1 (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Stock, S.; Kluever, A.K.; Endres, S.; Kobold, S. Enhanced Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy through Co-Application of Synergistic Combination Partners. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwstra, R.; van Meerten, T.; Bremer, E. CD47-SIRPα blocking-based immunotherapy: Current and prospective therapeutic strategies. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajwa, A.; Habib, A.; Kittai, A.S. Treatment of Richter’s Transformation with Novel Therapies. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2024, 19, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clubb, J.D.; Gao, T.A.; Chen, Y.Y. Synthetic Biology in the Engineering of CAR-T and CAR-NK Cell Therapies: Facts and Hopes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 1390–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.I.; Vom Stein, A.F.; Hallek, M. Targeting the tumor microenvironment for treating double-refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2024, 144, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Mei, M.; Barr, P.M.; Barrientos, J.; de Vos, S.; Furman, R.; Patel, K.; Thompson, P.A.; Choi, M.; Kallam, A.; et al. Phase 1 Dose Escalation and Cohort Expansion Study of the Anti-ROR1 Antibody-Drug Conjugate Zilovertamab Vedotin (MK-2140) for the Treatment of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2021, 138, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study (Year) | Setting | RT Incidence |
|---|---|---|
| MDACC (1975 to 2005) [27] | CIT era, N = 3986 Retrospective | 5.1% |
| GCLLSG (1999 to 2016) [28] | CIT era, N = 2975 Pooled analysis of trials | 2–10% |
| Nationwide Danish (2008 to 2016) [19] | Retrospective N = 3772 | 2.6% DLBCL-RT |
| SEER registry [29] | Retrospective N = 74,166 | 0.7% |
| RESONATE [30] (2012 to 2018 follow-up) | Phase 3, RCT, r/r CLL Ibrutinib, n = 195 | 5.1% |
| RESONATE-2 [31] (2013 to 2018 follow-up) | Phase 3, RCT, Ibrutinib, n = 136 | 1.5% |
| MURANO [32] (2014 to 2015) | Phase 3, RCT, r/r CLL Venetoclax + Rituximab, n = 194 Bendamustine + Rituximab, n = 195 | V + R, 3.1% B + R, 2.6% |
| Therapy | Pros | Cons | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional standard therapies | |||
| Chemoimmunotherapy | Broad clinical accessibility Induces rapid cytoreduction Established use in standard practice | Low CR rate (~20–30%) Median OS of 6–12 months High frequency of relapse | Historically used as front-line therapy Suboptimal for durable disease control Often serves as induction prior to other approaches |
| Allo-HSCT | Only potentially curative approach Enables long-term remissions (>3 years) Leverages graft-versus-lymphoma effect | High TRM (up to 25%) Restricted to transplant-eligible patients Requires disease CR prior to allo-HSCT | Optimal for younger, fit patients in remission Early referrals Reduced-intensity conditioning expand eligibility |
| Novel approaches | |||
| BTK Inhibitors | Oral administration Active in a subset of RT cases Favorable tolerability | Modest ORR (~38–58%) Short PFS (3–4 months) Common resistance and early relapses | Frequently used as salvage or bridging therapy Combination strategies may enhance efficacy Limited clinical benefit as monotherapy |
| BCL2 Inhibitors | Encouraging in combination regimens ORR up to 90% Chemotherapy-free options | Limited efficacy as monotherapy High relapse rates with single-agent use Potential risk of tumor lysis syndrome | Most effective in combination regimens Commonly utilized as a bridge to allo-HSCT or CAR T-cell therapy |
| CAR T-cell Therapy | High ORR (63–65%) Achieve MRD-negative CR in some cases Demonstrated efficacy in off-label use | Short DOR Limited accessibility T-cell dysfunction and exhaustion Risk of immune-related toxicities | Promising option for chemo-refractory RT Effective as a bridge to transplant in responders Potential for enhanced efficacy in combination strategies |
| Bispecific Antibodies | Off-the-shelf availability Repeat dosing for sustained control ORR of 40–50% reported in RT Manageable toxic profile | Long-term DOR remains uncertain Limited data available Optimal sequencing with CAR T-cell therapy or allo-HSCT is not yet defined | An emerging option, especially for post-CAR T relapses or patients ineligible for cellular therapy Subcutaneous administration enhances accessibility and treatment adherence |
| Considerations | Comments |
|---|---|
| Aggressive Disease | RT often harbors TP53 mutations, complex karyotype, and unmutated IGHV, all of which predict poor outcomes with conventional therapy. |
| Manufacturing Barriers | Rapidly progressing RT necessitates bridging therapy, which may impair CAR T-cell fitness. Lymphodepleting regimens before infusion must be cautiously managed to avoid toxicity. |
| Toxicity | CAR T-cell related adverse events like CRS and ICANS are prominent and more severe in RT patients due to high tumor burden. Infection risk is elevated due to heavy pretreatment and aggressive disease. |
| On-Target, Off-Tumor Toxicity and CD19 Escape | Loss of CD19 antigen expression can lead to CAR T-cell resistance. RT cells may show heterogeneous CD19 expression, complicating targeting. |
| Limited Data | RT patients are often excluded from most pivotal CAR T-cell trials. |
| Patient Factors | RT patients are often older and frailer, with prior toxicities from CLL therapies, limiting eligibility for CAR-T. Functional status and disease kinetics must guide decision-making. |
| Reference | Patient Number | Prior Treatment Lines (Median) | ORR/CR (%) | PFS/OS (mo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benjamini O et al. [81] | 30 (Axi-cel, n = 4; Tisa-cel, n = 7; Liso-cel, n = 3, POC anti-CD19 CAR T, n = 16) | 2 (0–7) | 57/40 | 4.3/9.9 |
| Kittai AS et al. [82] | 69 (Axi-cel, n = 44; Tisa-cel, n = 17, Liso-cel, n = 7; Brexu-cel, n = 1) | 2 (0–7) | 63/46 | 4.7/8.5 |
| Beyar-Katz, O. et al. [83] | 54 (Axi-cel, n = 4; Tisa-cel, n = 20; Liso-cel, n = 1, POC anti-CD19 CAR T, n = 29) | 2 (0–8) | 65/46 | 12-m PFS:41%/14.4 |
| Kittai AS et al. [84] | Axi-cel, n = 8 | 4 | 100/63 | NR/NR |
| Abramson, J.S. et al. [85,86] | Liso-cel, n = 4 | NR | 50/25 | NR/NR |
| Bispecific Antibody | Trial Phase | Patient Numbers | ORR/CR (%) | PFS, Median (mo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epcoritamab [101] | I/II | 35 | 50/35 | 12.8 |
| Mosuntuzumab [102] | I/II | 20 | 40/20 | NR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Z.-C.; Chan, M.-J.; Jaing, T.-H.; Lin, T.-L.; Hung, Y.-S.; Su, Y.-J. Richter Transformation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Current Treatment Challenges and Evolving Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178747
Lin Z-C, Chan M-J, Jaing T-H, Lin T-L, Hung Y-S, Su Y-J. Richter Transformation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Current Treatment Challenges and Evolving Therapies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178747
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Zi-Chi, Ming-Jen Chan, Tang-Her Jaing, Tung-Liang Lin, Yu-Shin Hung, and Yi-Jiun Su. 2025. "Richter Transformation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Current Treatment Challenges and Evolving Therapies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178747
APA StyleLin, Z.-C., Chan, M.-J., Jaing, T.-H., Lin, T.-L., Hung, Y.-S., & Su, Y.-J. (2025). Richter Transformation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Current Treatment Challenges and Evolving Therapies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178747







