Differential Association of the DISC1 Interactome in Hallucinations and Delusions †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genetic Association with Hallucinations and Delusions at the Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Level
2.2. Genetic Associations with Hallucinations and Delusions at the Gene Level
2.3. Genetic Association with Hallucinations and Delusions at the Gene Set Level
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Genotyping and Quality Control
4.3. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)-Level Association Analysis
4.4. Gene-Level and Gene-Set Enrichment Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| APP | Amyloid Beta Precursor Protein |
| BBS4 | Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 4 |
| BD | Bipolar Disorder |
| CDK5 | Cyclin Dependent Kinase 5 |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CLU | Clusterin |
| DISC1 | Disrupted in Schizophrenia 1 |
| DLG1 | Discs Large Homolog 1 |
| DTNBP1 | Dystrobrevin Binding Protein 1 |
| ERBB4 | Receptor Tyrosine-Protein Kinase ErbB-4 |
| EXOC4 | Exocyst Complex Component 4 |
| EXOC7 | Exocyst Complex Component 7 |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| Freq | Frequency in individuals with psychosis |
| GIGYF2 | Grb-10 Interacting GYF Protein 2 |
| GnomAD | Genome Aggregation Database |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| GRIA1 | Glutamate Ionotropic Receptor AMPA Type Subunit 1 |
| GRIA2 | Glutamate Ionotropic Receptor AMPA Type Subunit 2 |
| GRIA4 | Glutamate Ionotropic Receptor AMPA Type Subunit 4 |
| GSK3B | Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta |
| GWAS | Genome-Wide Association Studies |
| IL6R | Interleukin 6 receptor |
| KCNQ1 | Potassium Voltage-Gated Channel Subfamily Q Member 1 |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| KIF3A | Kinesin Family Member 3A |
| LD | Linkage Disequilibrium |
| lncRNA | Long non-coding RNA |
| MAF | Minor Allele Frequency |
| MxGDAR/ENCODAT | Mexican Genomic Database for Addiction Research |
| NMDAR | N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor |
| NRG1 | Neuregulin 1 |
| NRXN1 | Neurexin 1 |
| NUP210 | Nucleoporin 210 |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PCM1 | Pericentriolar Material 1 |
| PCNT | Pericentrin |
| PDE4D | Phosphodiesterase 4D |
| PPP3CB | Protein Phosphatase 3 Catalytic Subunit Beta |
| QC | Quality Control |
| Ref/alt | Reference and Alternative alleles |
| SANS | Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms |
| SAPS | Scale for the Assessment of Positive Symptoms |
| SLC6A4 | Solute Carrier Family 6 Member 4 |
| SCZ | Schizophrenia |
| SNP | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| TRIO | Trio Rho Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor |
| VEP | Variant Effect Predictor |
| ZNF365 | Zinc Finger Protein 365 |
References
- Calabrò, M.; Porcelli, S.; Crisafulli, C.; Albani, D.; Kasper, S.; Zohar, J.; Souery, D.; Montgomery, S.; Mantovani, V.; Mendlewicz, J.; et al. Genetic variants associated with psychotic symptoms across psychiatric disorders. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 720, 134754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.; Thomson, P.A.; McCarthy, S.; Kramer, M.; Muller, S.; Lihm, J.; Morris, S.; Soares, D.C.; Hennah, W.; Harris, S.; et al. Rare disruptive variants in the DISC1 Interactome and Regulome: Association with cognitive ability and schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, B.; Evgrafov, O.V.; Zheng, D.; Hartel, N.; Knowles, J.A.; Graham, N.A.; Ichida, J.K.; Coba, M.P. Endogenous cell type-specific Disrupted in Schizophrenia 1 interactomes reveal protein networks associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facal, F.; Costas, J. Evidence of association of the DISC1 interactome gene set with schizophrenia from GWAS. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 95, 109729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhar, S.; Johnstone, M.; McKenna, P.J. Schizophrenia. Lancet 2022, 399, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, C.Z.; Ryan, K.A.; Kamali, M.; Marshall, D.F.; Harrington, G.; McInnis, M.G.; Tso, I.F. Psychosis in bipolar disorder: Does it represent a more “severe” illness? Bipolar Disord. 2018, 20, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardno, A.G.; Owen, M.J. Genetic relationships between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and schizoaffective disorder. Schizophr. Bull. 2014, 40, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalin, N.H. Psychotic experiences, cognitive decline, and genetic vulnerabilities in relation to developing psychotic disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2020, 177, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaebel, W.; Zielasek, J. Focus on psychosis. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 17, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, E.A.; Breen, G.; Forstner, A.J.; McQuillin, A.; Ripke, S.; Trubetskoy, V.; Mattheisen, M.; Wang, Y.; Coleman, J.R.; Gaspar, H.A.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 30 loci associated with bipolar disorder. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumette, B.; Sengupta, S.M.; Lepage, M.; Malla, A.; Iyer, S.N.; Kebir, O.; ICAAR study group; Dion, P.A.; Rouleau, G.A.; Krebs, M.-O.; et al. A polymorphism in the glutamate metabotropic receptor 7 is associated with cognitive deficits in the early phases of psychosis. Schizophr. Res. 2022, 249, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Bourgon, J.; Mata, I.; Roiz-Santiáñez, R.; Ayesa-Arriola, R.; Suárez Pinilla, P.; Tordesillas-Gutiérrez, D.; Vazquez-Barquero, J.L.; Crespo-Facorro, B. A Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia 1 gene variant is associated with clinical symptomatology in patients with first-episode psychosis. Psychiatry Investig. 2014, 11, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannath, V.; Gerstenberg, M.; Walitza, S.; Franscini, M.; Heekeren, K.; Rössler, W.; Theodoridou, A.; Grünblatt, E. Neuregulin 1 (NRG1) gene expression predicts functional outcomes in individuals at clinical high-risk for psychosis. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 266, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Lazarovici, P.; Zheng, W. Dysbindin-1 involvement in the etiology of schizophrenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruderfer, D.M.; Ripke, S.; McQuillin, A.; Boocock, J.; Stahl, E.A.; Pavlides, J.M.W.; Mullins, N.; Charney, A.W.; Ori, A.P.; Loohuis, L.M.O.; et al. Genomic dissection of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia, including 28 subphenotypes. Cell 2018, 173, 1705–1715.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Jayathilake, K.; Zhao, Z.; Meltzer, H.Y. Investigating association of four gene regions (GABRB3, MAOB, PAH, and SLC6A4) with five symptoms in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 198, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, O.; Sanjuan, J.; Aguilar, E.J.; Gonzalez, J.C.; Molto, M.D.; de Frutos, R.; Najera, C. Serotonin transporter gene polymorphisms and auditory hallucinations in psychosis. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 50, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Cheah, S.Y.; Lawford, B.R.; Young, R.M.; Morris, C.P.; Voisey, J. Dysbindin (DTNBP1) variants are associated with hallucinations in schizophrenia. Eur. Psychiatry 2015, 30, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy-Jones, S.; Green, M.J.; Scott, R.J.; Tooney, P.A.; Cairns, M.J.; Wu, J.Q.; Oldmeadow, C.; Carr, V. Preliminary evidence of an interaction between the FOXP2 gene and childhood emotional abuse predicting likelihood of auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 50, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoroiu-Serbanescu, M.; Herms, S.; Diaconu, C.C.; Jamra, R.A.; Meier, S.; Bleotu, C.; Neagu, A.I.; Prelipceanu, D.; Sima, D.; Gherghel, M.; et al. Possible association of different G72/G30 SNPs with mood episodes and persecutory delusions in bipolar I Romanian patients. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 34, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colijn, M.A.; Ismail, Z. Presenilin Gene Mutation-associated Psychosis: Phenotypic Characteristics and Clinical Implications. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2024, 38, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.D.; Gill, S.S.; Le-Niculescu, H.; MacKie, O.; Bhagar, R.; Roseberry, K.; Murray, O.K.; Dainton, H.D.; Wolf, S.K.; Shekhar, A.; et al. Precision medicine for psychotic disorders: Objective assessment, risk prediction, and pharmacogenomics. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 1528–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friligkou, E.; Pathak, G.A.; Tylee, D.S.; De Lillo, A.; Koller, D.; Cabrera-Mendoza, B.; Polimanti, R. Characterizing pleiotropy among bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and major depression: A genome-wide cross-disorder meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2025, 55, e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demichele-Sweet, M.A.A.; Klei, L.; Devlin, B.; Ferrell, R.E.; Weamer, E.A.; Emanuel, J.E.; Lopez, O.L.; Sweet, R.A. No association of psychosis in Alzheimer disease with neurodegenerative pathway genes. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 555.e9–555.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadella, R.K.; Pulaparambil, V.; Vemula, A.; Swathi Lakshmi, P.; Saini, J.; Nagaraj, C.; Purushottam, M.; Viswanath, B.; Sullivan, P.F.; Jain, S. Delusions, Hallucinations, and Cognitive Decline in Middle Age: A Case of Dementia, GIGYF2 Gene Mutation, and 22q11 Duplication. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2023, 45, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisafulli, C.; Chiesa, A.; De Ronchi, D.; Han, C.; Lee, S.J.; Park, M.H.; Patkar, A.A.; Pae, C.-U.; Serretti, A. Influence of GRIA1, GRIA2 and GRIA4 polymorphisms on diagnosis and response to antipsychotic treatment in patients with schizophrenia. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 506, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubetskoy, V.; Pardiñas, A.F.; Qi, T.; Panagiotaropoulou, G.; Awasthi, S.; Bigdeli, T.B.; Bryois, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Dennison, C.A.; Hall, L.S.; et al. Mapping genomic loci implicates genes and synaptic biology in schizophrenia. Nature 2022, 604, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhassen, W.; Chen, S.; Vawter, M.; Robbins, B.K.; Nguyen, H.; Myint, T.N.; Saito, Y.; Schulmann, A.; Nauli, S.M.; Civelli, O.; et al. Patterns of cilia gene dysregulations in major psychiatric disorders. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacology Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 109, 110255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeszko, P.R.; Hodgkinson, C.A.; Robinson, D.G.; Derosse, P.; Bilder, R.M.; Lencz, T.; Burdick, K.; Napolitano, B.; Betensky, J.D.; Kane, J.M.; et al. DISC1 is associated with prefrontal cortical gray matter and positive symptoms in schizophrenia. Biol. Psychol 2009, 79, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Aleksic, B.; Ozaki, N. Glia-related genes and their contribution to schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 69, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, A.; Tan, P.L.; Kubo, K.; Engelhard, C.; Ishizuka, K.; Kubo, A.; Tsukita, S.; Pulver, A.E.; Nakajima, K.; Cascella, N.G.; et al. Recruitment of PCM1 to the centrosome by the cooperative action of DISC1 and BBS4. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2008, 65, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, A.; Ng-Cordell, E.; Hanna, N.; Brkic, D.; Baker, K. The neurodevelopmental spectrum of synaptic vesicle cycling disorders. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 208–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, Y. The impact of glycogen synthase kinase 3 β gene on psychotic mania in bipolar disorder patients. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; de Lange, S.C.; Savage, J.E.; Tissink, E.; Qi, T.; Repple, J.; Gruber, M.; Kircher, T.; Dannlowski, U.; Posthuma, D.; et al. Associated Genetics and Connectomic Circuitry in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 94, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhalitskaya, E.V.; Vyalova, N.M.; Ermakov, E.A.; Levchuk, L.A.; Simutkin, G.G.; Bokhan, N.A.; Ivanova, S.A. Association of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Cytokine Genes with Depression, Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder. Genes 2023, 14, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.B.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhuang, X.H.; Chen, Q.L.; Wu, L.C.; Hu, J.T.; Zhou, H.S.; Xie, W.H.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies TENM4 as a novel candidate gene for schizophrenia in the SCZD2 locus at 11q14-21. Front. Genet. 2019, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, E.; Cho, G.; Hwang, H.; Kim, B.G.; Kim, G.; Joo, Y.Y.; Cha, J. Gene–environment pathways to cognitive intelligence and psychotic-like experiences in children. eLife 2024, 12, RP88117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakoor, S.; Zavos, H.M.; Haworth, C.M.; McGuire, P.; Cardno, A.G.; Freeman, D.; Ronald, A. Association between stressful life events and psychotic experiences in adolescence: Evidence for gene-environment correlations. Br. J. Psychiatry. 2016, 208, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Symptoms | Type of Symptom | SNP (Gene) | Allele | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Gene | Number of SNPs | ZSTAT | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hallucinations | Auditory hallucinations | rs6754640 (NRXN1) | A | 2.27 (1.57–3.29) | 1.48 × 10−5 | NRG1 | 30 | 4.41 | 5.25 × 10−6 |
| PCM1 | 16 | 3.32 | 4.47 × 10−4 | ||||||
| Delusions | Persecutory delusions | rs17039676 (NRXN1) | T | 4.89 (2.27–7.52) | 8.43 × 10−4 | NRG1 | 29 | 3.83 | 6.35 × 10−5 |
| APP | 34 | 3.27 | 5.34 × 10−4 | ||||||
| Delusions of reference | rs6706713 (NRXN1) | G | 3.40 (2.10–5.50) | 6.35 × 10−7 | NRXN1 | 155 | 4.33 | 7.57 × 10−6 | |
| rs11892200 (NRXN1) | C | 3.15 (2.00–4.97) | 7.05 × 10−7 | EXOC4 | 34 | 3.38 | 3.69 × 10−4 | ||
| rs6754640 (NRXN1) | A | 3.33 (2.02–5.40) | 2.54 × 10−6 | NUP210 | 11 | 3.55 | 1.90 × 10−4 | ||
| rs17039676 (NRXN1) | T | 4.13 (2.27–7.52) | 3.52 × 10−6 | APP | 33 | 3.48 | 2.52 × 10−4 | ||
| rs6731061 (NRXN1) | T | 3.05 (1.90–4.89) | 3.95 × 10−6 | ||||||
| rs7578902 (NRXN1) | G | 2.93 (1.85–4.63) | 4.11 × 10−6 | ||||||
| rs10189159 (NRXN1) | C | 3.14 (1.90–5.20) | 7.97 × 10−6 | ||||||
| rs7076156 (ZNF365) | A | 3.48 (2.00–6.08) | 1.13 × 10−5 | ||||||
| rs10263196 (EXOC4) | A | 3.09 (1.86–5.12) | 1.36 × 10−5 | ||||||
| rs10176705 (NRXN1) | T | 3.11 (1.83–5.28) | 2.64 × 10−5 | ||||||
| rs1421579 (NRXN1) | G | 2.52 (1.63–3.88) | 2.83 × 10−5 |
| Position (hg19) | Gene | Consequence | SNP | Ref/alt | Freq | GnomAD | Transcript | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr2:50504180-50504180 | NRXN1 | Downstream gene variant | rs6754640 | G/AT | 0.1593 | 0.3127 | ENST00000331040.9 ENST00000401669.7 | Nonsense-mediated decay Protein coding |
| chr2:50029801-50029801 | NRXN1 | Intron variant | rs17039676 | C/T | 0.0766 | 0.1515 | ENST00000637906.1 ENST00000342183.9 | Nonsense-mediated decay Protein coding |
| chr2:50494373-50494373 | NRXN1 | Intron variant | rs6706713 | A/G | 0.2057 | 0.3929 | ENST00000331040.9 ENST00000401669.7 | Nonsense-mediated decay Protein coding |
| chr2:50480720-50480720 | NRXN1 | Intron variant | rs11892200 | T/C | 0.2233 | 0.4258 | ENST00000331040.9 ENST00000401669.7 | Nonsense-mediated decay Protein coding |
| chr2:50016264-50016264 | NRXN1 | Intron variant | rs6731061 | C/AT | 0.1733 | 0.3410 | ENST00000637906.1 ENST00000342183.9 | Nonsense-mediated decay Protein coding |
| chr2:50480256-50480256 | NRXN1 | Intron variant | rs7578902 | A/CGT | 0.2173 | 0.4152 | ENST00000331040.9 ENST00000401669.7 | Nonsense-mediated decay Protein coding |
| chr2:50487433-50487433 | NRXN1 | Intron variant | rs10189159 | T/C | 0.1537 | 0.3058 | ENST00000331040.9 ENST00000401669.7 | Nonsense-mediated decay Protein coding |
| chr10:62655424-62655424 | ZNF365 | Non-coding transcript exon variant | rs7076156 | A/CGT | 0.1002 | 0.8516 | ENST00000344640.7 | lncRNA |
| chr7:133271427-133271427 | EXOC4 | Intron variant | rs10263196 | G/A | 0.1332 | 0.2391 | ENST00000253861.5 | Protein coding |
| chr2:50517636-50517636 | NRXN1 | Intron variant | rs10176705 | C/T | 0.1394 | 0.2706 | ENST00000331040.9 ENST00000401669.7 | Nonsense-mediated decay Protein coding |
| chr2:50005007-50005007 | NRXN1 | Intron variant | rs1421579 | G/AT | 0.3110 | 0.4547 | ENST00000637906.1 ENST00000342183.9 | Nonsense-mediated decay Protein coding |
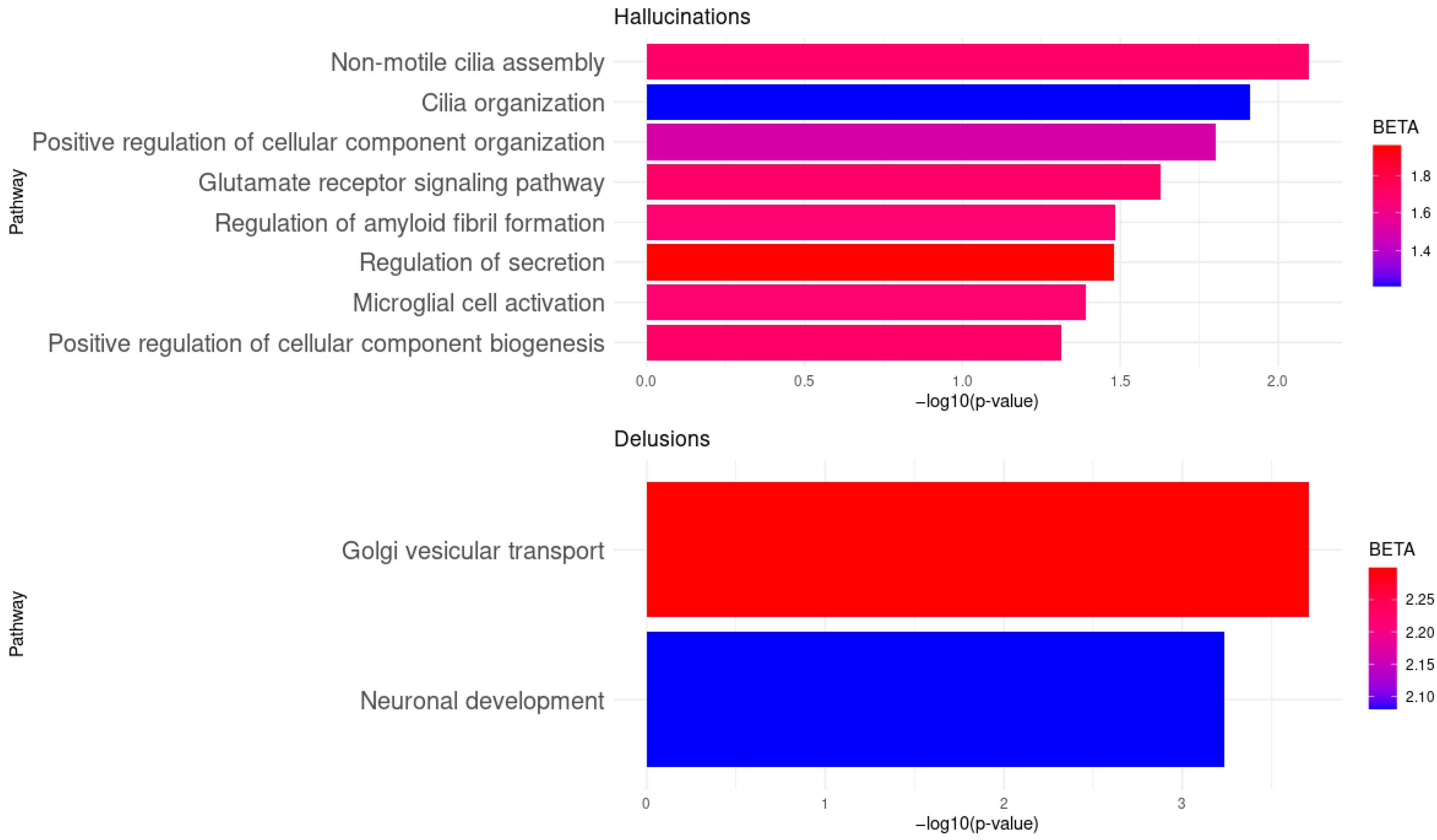
| Symptoms | Type of Symptom | Biological Pathway | Gene | BETA | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hallucinations | Auditory hallucinations | Non-motile cilia assembly | PCM1. DISC1, BBS4 | 1.7 | 8.01 × 10−3 |
| Cilia organization | PCM1, DISC1, BBS4, EXOC7, KIF3A PCNT | 1.21 | 1.23 × 10−2 | ||
| Positive regulation of cellular component organization | GSK3B, NRXN1, NRG1, CLU | 1.5 | 1.58 × 10−2 | ||
| Glutamate receptor signaling pathway | APP, GRIA2 | 1.72 | 2.36 × 10−2 | ||
| Regulation of amyloid fibril formation | APP, CLU | 1.67 | 3.29 × 10−2 | ||
| Regulation of secretion | KCNQ1, NRG1 | 1.96 | 3.30 × 10−2 | ||
| Microglial cell activation | APP, CLU | 1.67 | 4.06 × 10−2 | ||
| Delusions | Persecutory delusions | Golgi vesicular transport | APP, EXOC4, DTNBP1 | 2.3 | 1.96 × 10−4 |
| Neuronal development | APP, GSK3B, CDK5, DTNBP1 | 2.08 | 5.86 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, A.; Genis-Mendoza, A.D.; Villatoro-Velázquez, J.A.; Medina-Mora, M.E.; Nicolini, H. Differential Association of the DISC1 Interactome in Hallucinations and Delusions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8738. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178738
Gutiérrez-Rodríguez A, Genis-Mendoza AD, Villatoro-Velázquez JA, Medina-Mora ME, Nicolini H. Differential Association of the DISC1 Interactome in Hallucinations and Delusions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8738. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178738
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez-Rodríguez, Araceli, Alma Delia Genis-Mendoza, Jorge Ameth Villatoro-Velázquez, María Elena Medina-Mora, and Humberto Nicolini. 2025. "Differential Association of the DISC1 Interactome in Hallucinations and Delusions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8738. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178738
APA StyleGutiérrez-Rodríguez, A., Genis-Mendoza, A. D., Villatoro-Velázquez, J. A., Medina-Mora, M. E., & Nicolini, H. (2025). Differential Association of the DISC1 Interactome in Hallucinations and Delusions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8738. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178738






