In Vivo Response of γδ T Cells and Macrophages to Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangements in a Lupus-like Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
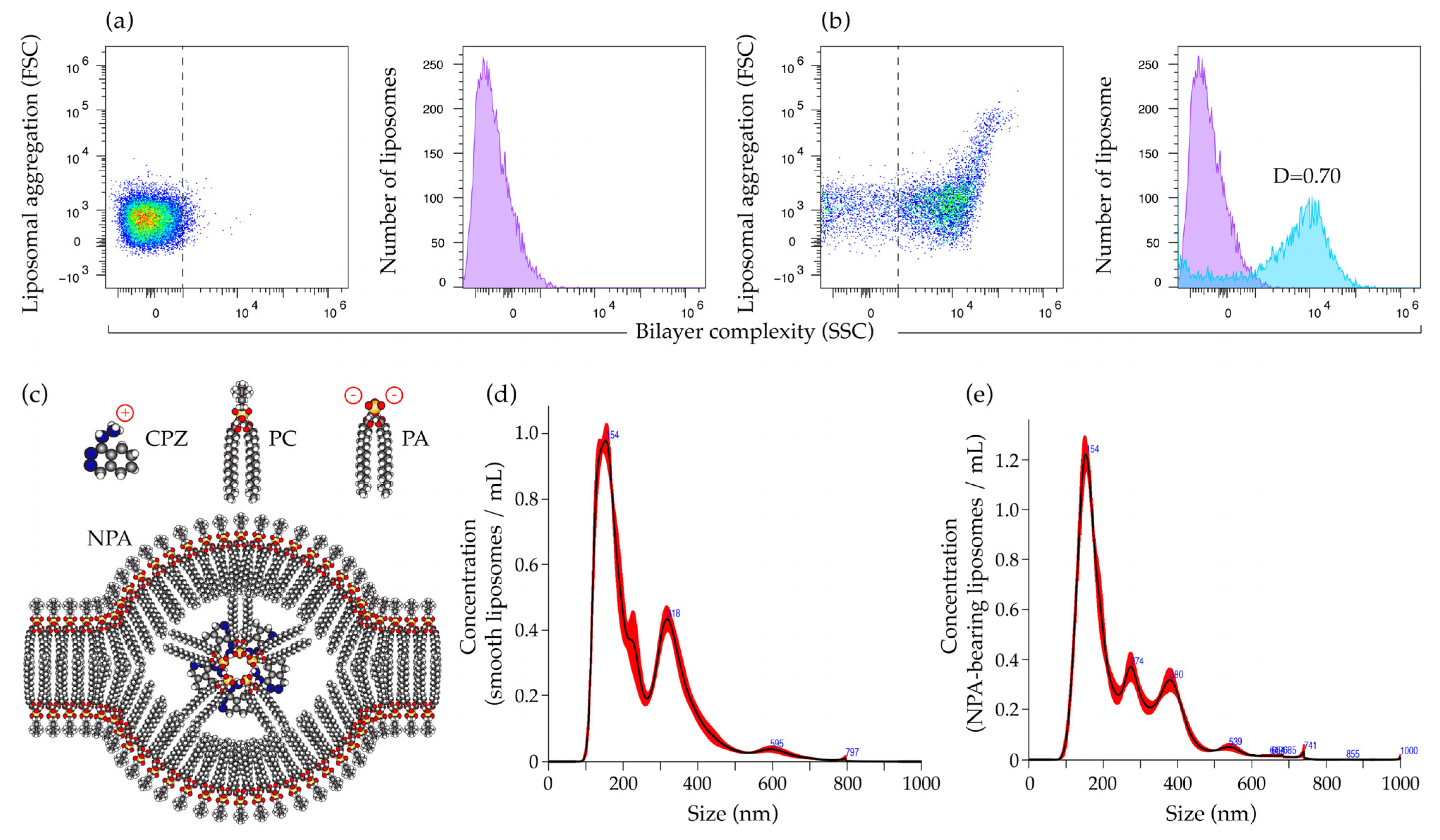
2.1. Characterization of Smooth Liposomes and of Liposomes with Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangements
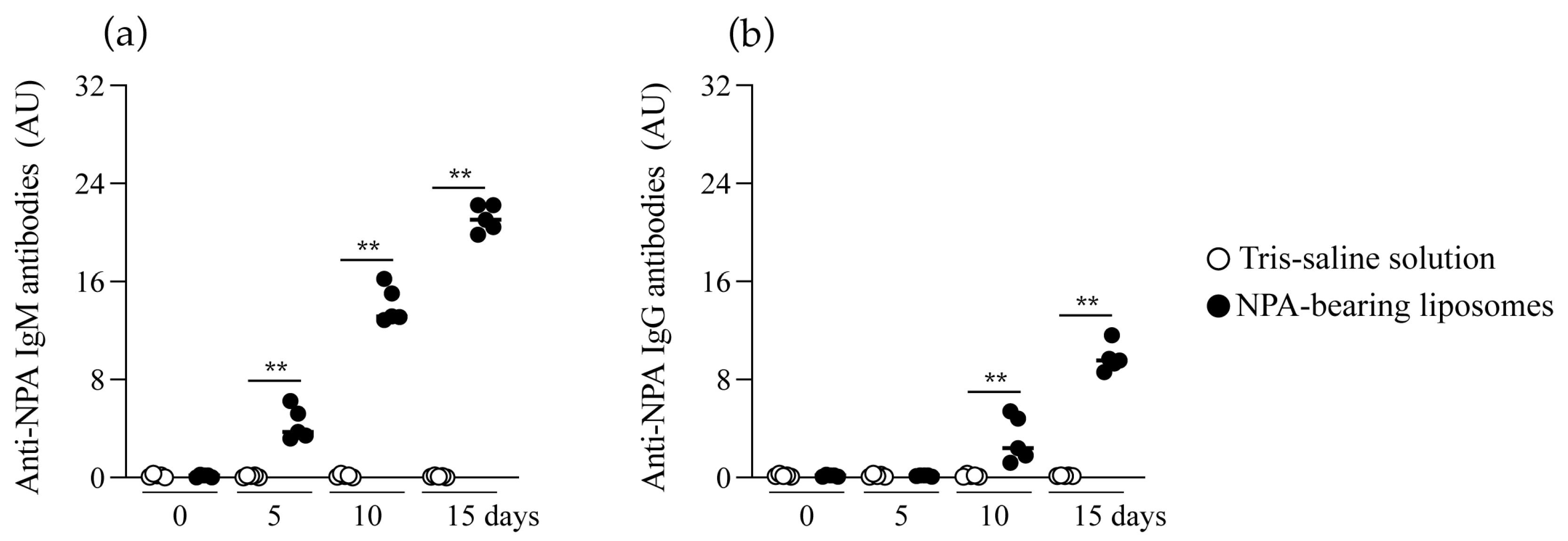
2.2. Mice Produce IgM and IgG Anti-NPA Antibodies in Response to Liposomes Bearing Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangements
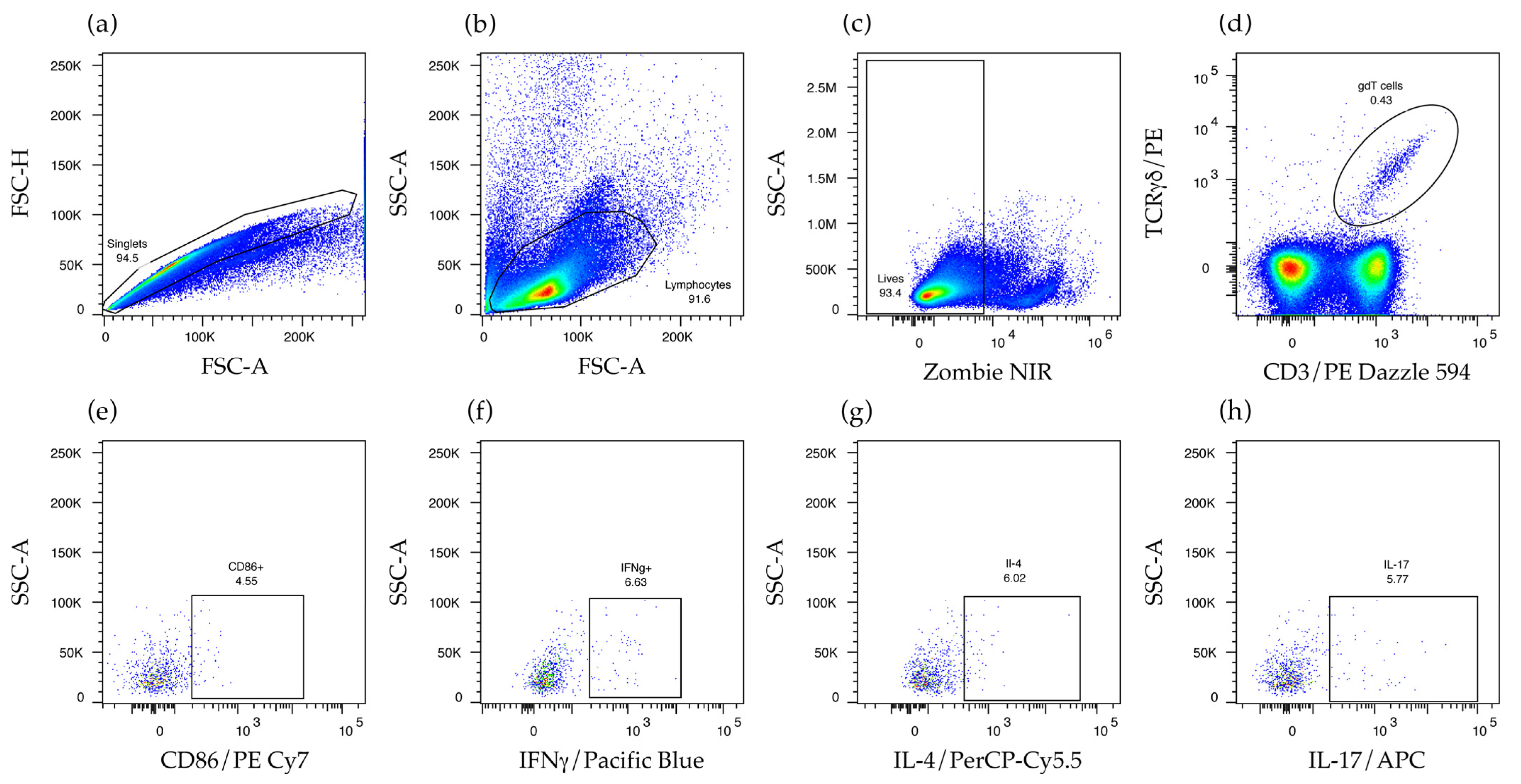
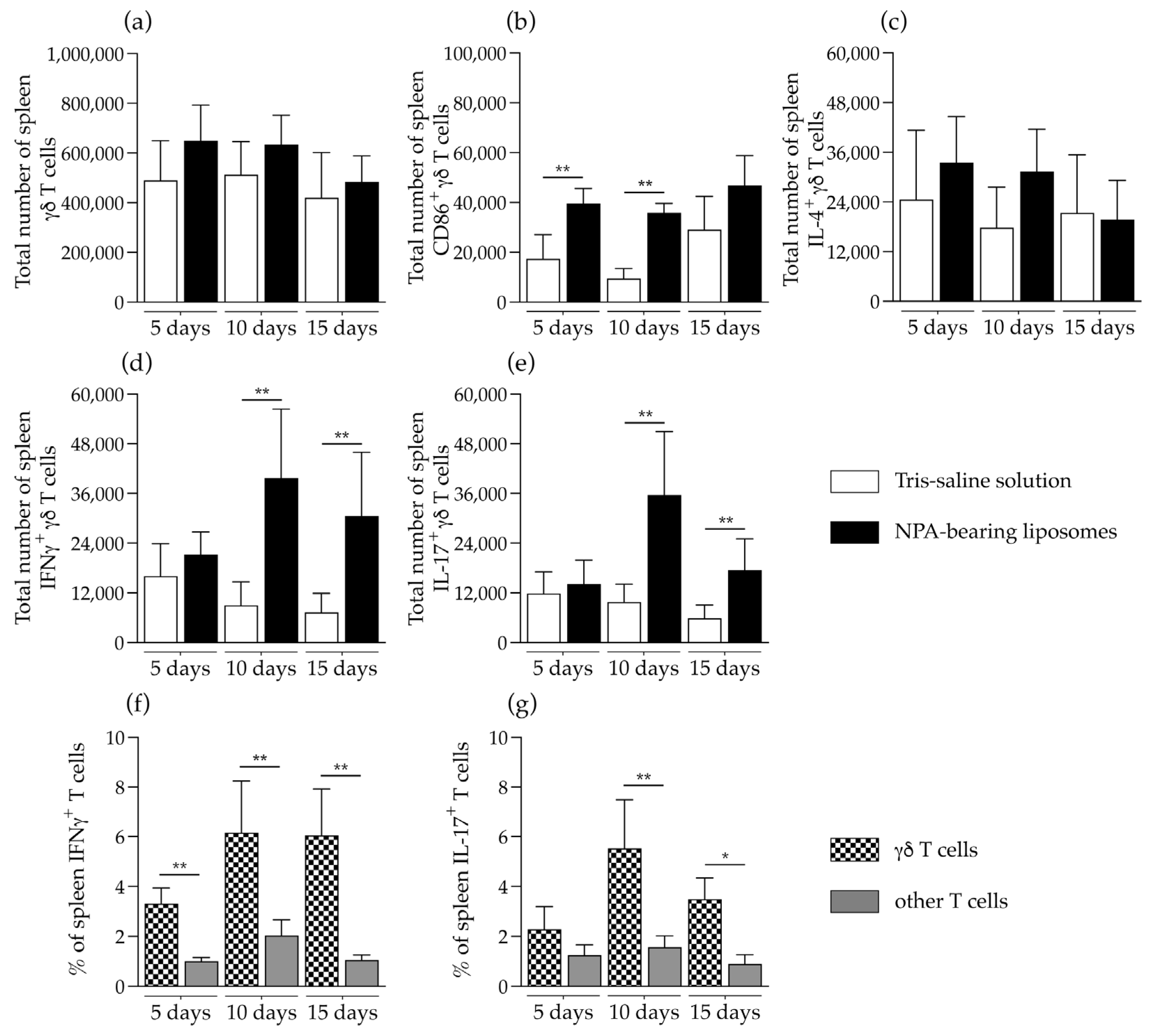
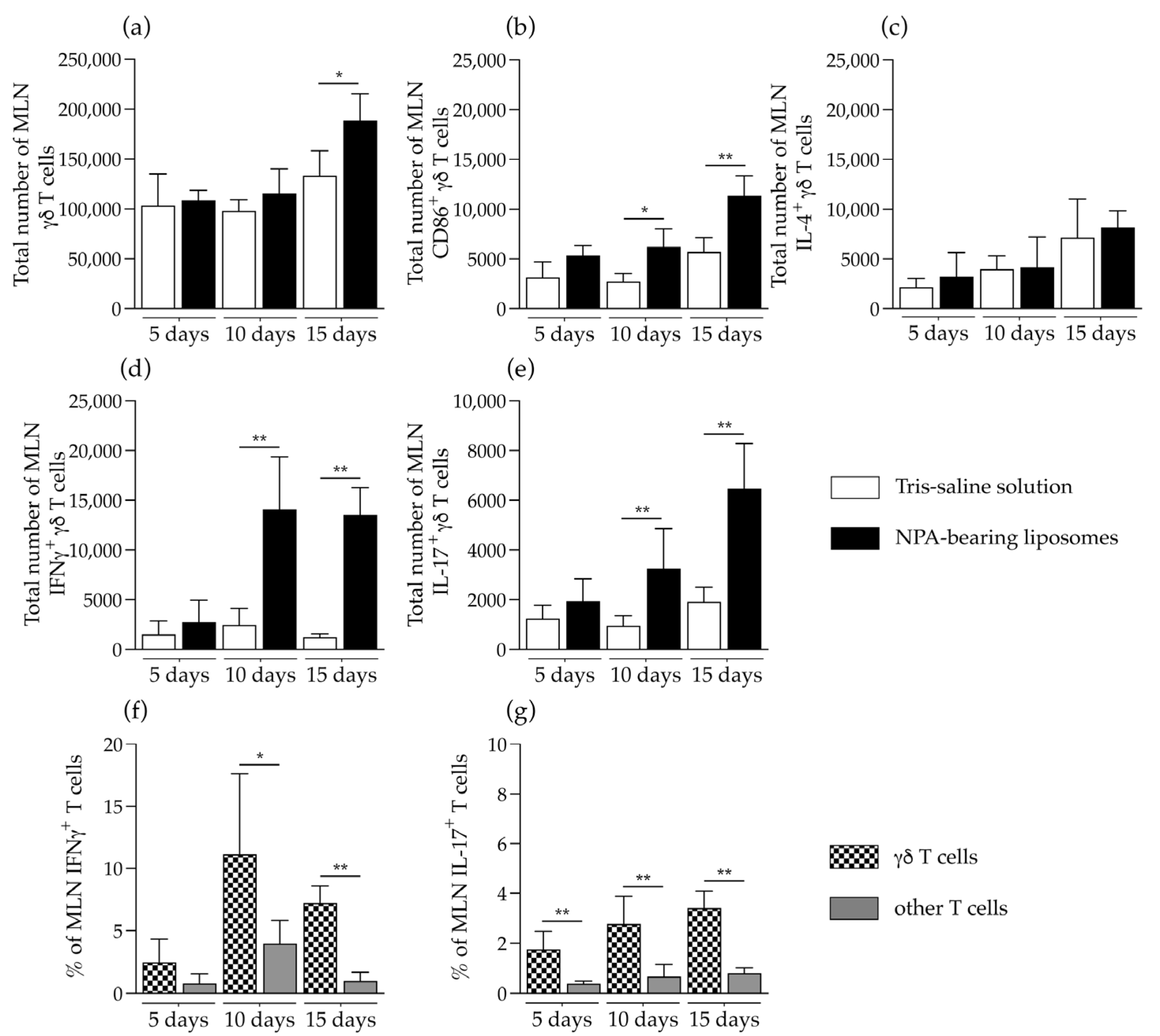
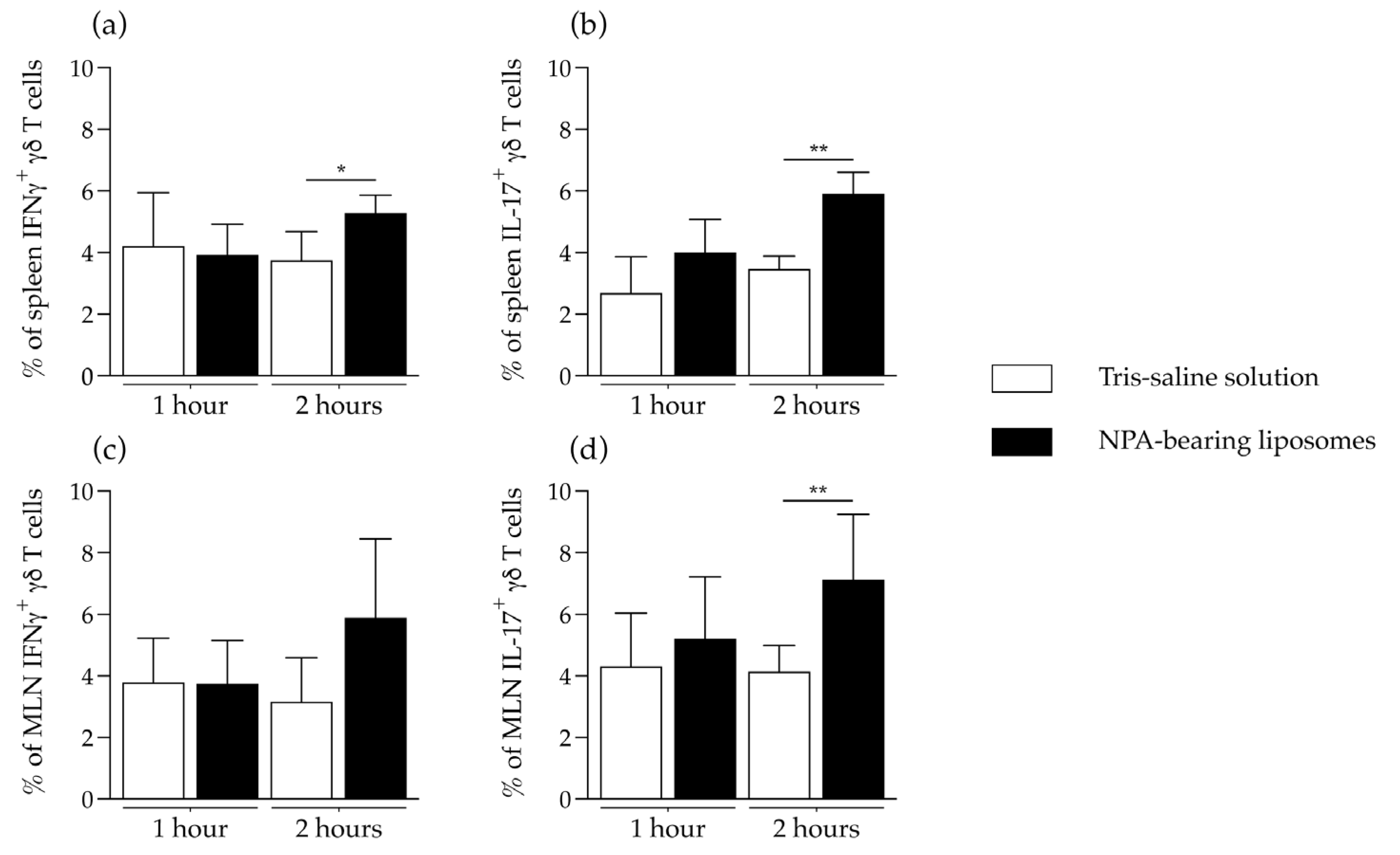
2.3. γδ T Cells Are Activated and Produce IFNγ and IL-17 in the Secondary Lymphoid Organs of Mice That Produce Anti-Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangement Antibodies
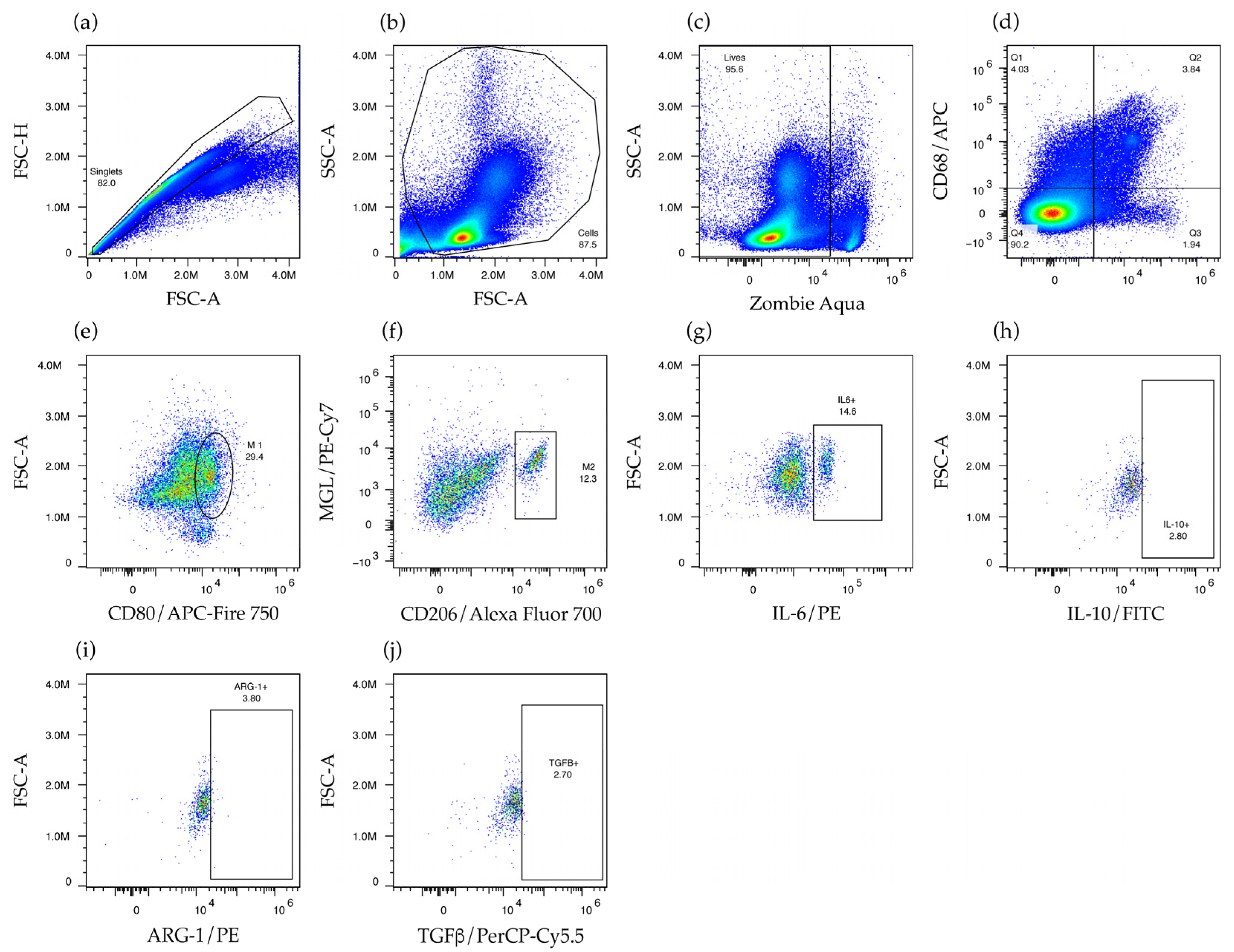
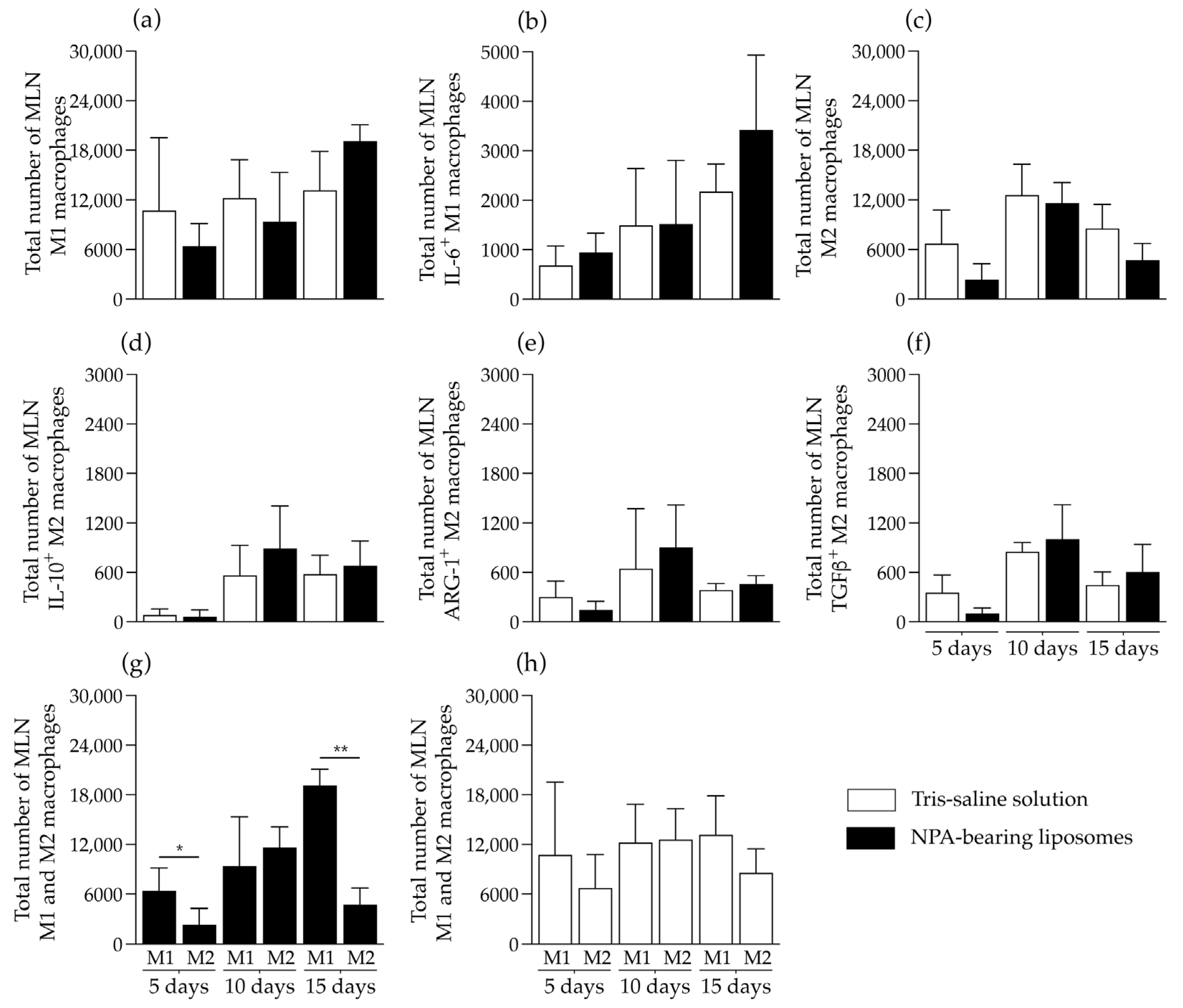
2.4. Liposomes Bearing Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangements Induce M1 Macrophage Polarization in Mice Spleens
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Formation and Characterization of Liposomes Bearing Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangements
4.2. Immunization of Mice with Liposomes Bearing Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangements
4.3. Detection of IgM and IgG Anti-Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangements Antibodies
4.4. Analysis of γδ T Cells
4.5. In Vitro Re-Stimulation of γδ T Cells
4.6. Analysis of M1 and M2 Macrophages
4.7. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| γδ T cells | Gamma delta T cells |
| ARG-1 | Arginase 1 |
| IFNγ | Interferon gamma |
| IL-4 | Interleukin 4 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin 10 |
| IL-17 | Interleukin 17 |
| MGL | Macrophage galactose-type lectin |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| MLN | Mesenteric lymph nodes |
| NPA | Non-bilayer phospholipid arrangements |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| TGFβ | Transforming growth factor beta |
References
- Kirkpatrick, K.V.; Nocton, J.J. Unusual Presentations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 108, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Zhang, D.; Yao, X.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Q. Global epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: A comprehensive systematic analysis and modelling study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, S.; Kahlenberg, J.M. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: New Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches. Annu. Rev. Med. 2023, 74, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhil, A.; Bansal, R.; Anupam, K.; Tandon, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Latest insight into etiopathogenesis. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 43, 1381–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, D.; Sang, A.; Yin, Y.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Morel, L. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 271694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.L.; Gilkeson, G. Mouse models of lupus: What they tell us and what they don’t. Lupus Sci. Med. 2018, 5, e000199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhuang, H.; Arja, R.D.; Reeves, W.H. A novel monocyte differentiation pattern in pristane-induced lupus with diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Elife 2022, 11, e76205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, I.; Leyva, E.; Campos, B.; Lara, M.; Ibanez, M.; Farfan, N.; Orozco, H.; Flores-Romo, L.; Hernandez-Pando, R.; Wong, C. Antibodies to non-bilayer phospholipid arrangements induce a murine autoimmune disease resembling human lupus. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Baeza, C.; Hernandez-Pando, R.; Resendiz, A.; Tescucano, A.; Bustos, I.; Ibanez, M.; Wong, C.; Baeza, I. Molecular organization of the non-bilayer phospholipid arrangements that induce an autoimmune disease resembling human lupus in mice. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2012, 29, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu Ball, W.; Neff, J.K.; Gohil, V.M. The role of nonbilayer phospholipids in mitochondrial structure and function. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Baeza, I.; Nevarez-Lechuga, C.-I.I.; Wong-Baeza, C.; Baeza, I.; Reséndiz Mora, A.; Tescucano, A.; Barrera-Aveleida, G.; Sotelo-Rodríguez, A.; Galarce-Sosa, I. Anti-Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangement Antibodies Trigger an Autoimmune Disease Similar to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Mice. In Systemic Lupus Erythematosus—Pathogenesis and Management; Lionaki, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza-Ramirez, I. Methods for Diagnostic and/or Treatment of Antiphospholipids Antibodies-Related Diseases, and Devices. US Patent 6777193 B1, 14 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Baeza, C.; Resendiz-Mora, A.; Donis-Maturano, L.; Wong-Baeza, I.; Zarate-Neira, L.; Yam-Puc, J.C.; Calderon-Amador, J.; Medina, Y.; Wong, C.; Baeza, I.; et al. Anti-Lipid IgG Antibodies Are Produced via Germinal Centers in a Murine Model Resembling Human Lupus. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landa-Saldivar, C.; Resendiz-Mora, A.; Sanchez-Barbosa, S.; Sotelo-Rodriguez, A.; Barrera-Aveleida, G.; Nevarez-Lechuga, I.; Galarce-Sosa, I.; Taniguchi-Ponciano, K.; Cruz-Guzman, O.D.R.; Wong-Baeza, I.; et al. Liposomes Bearing Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangements Induce Specific IgG Anti-Lipid Antibodies by Activating NK1.1(+), CD4(+) T Cells in Mice. Membranes 2022, 12, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harly, C.; Robert, J.; Legoux, F.; Lantz, O. gammadelta T, NKT, and MAIT Cells During Evolution: Redundancy or Specialized Functions? J. Immunol. 2022, 209, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayassi, T.; Barreiro, L.B.; Rossjohn, J.; Jabri, B. A multilayered immune system through the lens of unconventional T cells. Nature 2021, 595, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallagi, A.; Girouard, J.; Hamelin-Morrissette, J.; Dadzie, R.; Laurent, L.; Vaillancourt, C.; Lafond, J.; Carrier, C.; Reyes-Moreno, C. The activating effect of IFN-gamma on monocytes/macrophages is regulated by the LIF-trophoblast-IL-10 axis via Stat1 inhibition and Stat3 activation. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.A.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.P.; Gupta, S.; Sarangi, P.P. Monocytes and macrophages: Origin, homing, differentiation, and functionality during inflammation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brailey, P.M.; Evans, L.; Lopez-Rodriguez, J.C.; Sinadinos, A.; Tyrrel, V.; Kelly, G.; O’Donnell, V.; Ghazal, P.; John, S.; Barral, P. CD1d-dependent rewiring of lipid metabolism in macrophages regulates innate immune responses. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougan, S.K.; Kaser, A.; Blumberg, R.S. CD1 expression on antigen-presenting cells. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 314, 113–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, I.T. Proof without prejudice: Use of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for the analysis of histograms from flow systems and other sources. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1977, 25, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zeng, X. Engineering gammadelta T Cells: Recognizing and Activating on Their Own Way. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 889051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biały, S.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. Uncovering the mysteries of human gamma delta T cells: From origins to novel therapeutics. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1543454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russano, A.M.; Bassotti, G.; Agea, E.; Bistoni, O.; Mazzocchi, A.; Morelli, A.; Porcelli, S.A.; Spinozzi, F. CD1-restricted recognition of exogenous and self-lipid antigens by duodenal gammadelta+ T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 3620–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, R.; Durkee, M.S.; Ai, J.; Veselits, M.; Casella, G.; Asano, Y.; Chang, A.; Ko, K.; Oshinsky, C.; Peninger, E.; et al. Specific in situ inflammatory states associate with progression to renal failure in lupus nephritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e155350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, J.L.; Fernandez-Ruiz, R.; Niewold, T.B. T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 47, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Chen, J. The Role of gammadelta T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 2932531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, T.; Ichinose, K.; Kawakami, A.; Tsokos, G.C. Current Insights and Future Prospects for Targeting IL-17 to Treat Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 624971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Fan, X.; Lei, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Xi, X. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals a potential role for CaMK4 in gammadeltaT17 cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients with lupus nephritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.D.; Su, X.; Shin, S.; Li, L.; Youssef, S.; Yamasaki, S.; Steinman, L.; Saito, T.; Locksley, R.M.; Davis, M.M.; et al. Thymic selection determines gammadelta T cell effector fate: Antigen-naive cells make interleukin-17 and antigen-experienced cells make interferon gamma. Immunity 2008, 29, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q.; Guan, Z.; Luo, J.; Cao, G.; Cai, R.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Z.; et al. Roles of mTORC1 and mTORC2 in controlling gammadelta T1 and gammadelta T17 differentiation and function. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 2248–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, K.M.; Cauvi, D.M.; Toomey, C.B.; Morris, K.V.; Kono, D.H. Interferon-γ and systemic autoimmunity. Discov. Med. 2013, 16, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Domeier, P.P.; Chodisetti, S.B.; Soni, C.; Schell, S.L.; Elias, M.J.; Wong, E.B.; Cooper, T.K.; Kitamura, D.; Rahman, Z.S. IFN-gamma receptor and STAT1 signaling in B cells are central to spontaneous germinal center formation and autoimmunity. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 715–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.W.; Jacobs, H.M.; Arkatkar, T.; Dam, E.M.; Scharping, N.E.; Kolhatkar, N.S.; Hou, B.; Buckner, J.H.; Rawlings, D.J. B cell IFN-gamma receptor signaling promotes autoimmune germinal centers via cell-intrinsic induction of BCL-6. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, K.; Dalla-Favera, R. Roles of BCL6 in normal and transformed germinal center B cells. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 247, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Maverakis, E.; Eberl, M.; Adamopoulos, I.E. Gammadelta T cells in rheumatic diseases: From fundamental mechanisms to autoimmunity. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papotto, P.H.; Ribot, J.C.; Silva-Santos, B. IL-17(+) gammadelta T cells as kick-starters of inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, A.; Nishizaki, D.; Lippman, S.M.; Kato, S.; Kurzrock, R. Interleukin-17: A pleiotropic cytokine implicated in inflammatory, infectious, and malignant disorders. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2025, 83, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Li, J.; Wang, J.H.; Wu, Q.; Yang, P.; Hsu, H.C.; Smythies, L.E.; Mountz, J.D. IL-17 activates the canonical NF-kappaB signaling pathway in autoimmune B cells of BXD2 mice to upregulate the expression of regulators of G-protein signaling 16. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2289–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X. The function of gammadelta T cells in humoral immune responses. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 72, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarayal, B.; Chauhan, S.K.; Di Zazzo, A.; Dana, R. IL-17 Augments B Cell Activation in Ocular Surface Autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 3464–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsdoerffer, M.; Lee, Y.; Jager, A.; Kim, H.J.; Korn, T.; Kolls, J.K.; Cantor, H.; Bettelli, E.; Kuchroo, V.K. Proinflammatory T helper type 17 cells are effective B-cell helpers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14292–14297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, W.E. History of interleukin-4. Cytokine 2015, 75, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampoldi, F.; Ullrich, L.; Prinz, I. Revisiting the Interaction of gammadelta T-Cells and B-Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, R.M.; Lanser, A.J.; Rubino, S.; Kuhn, C.; Skillin, N.; Moreira, T.G.; Liu, S.; Gabriely, G.; David, B.A.; Menezes, G.B.; et al. gammadelta T cells control humoral immune response by inducing T follicular helper cell differentiation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caccamo, N.; Battistini, L.; Bonneville, M.; Poccia, F.; Fournie, J.J.; Meraviglia, S.; Borsellino, G.; Kroczek, R.A.; La Mendola, C.; Scotet, E.; et al. CXCR5 identifies a subset of Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells which secrete IL-4 and IL-10 and help B cells for antibody production. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 5290–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Mao, Y.; Li, X.; Yue, C.; Zhou, C.; Huang, L.; Mo, W.; Liang, D.; Zhang, J.; He, W.; et al. Hyperactivation and in situ recruitment of inflammatory Vdelta2 T cells contributes to disease pathogenesis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, H.; Su, M.; Wang, Y. Macrophage polarization: An important role in inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1352946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Guo, Y.R.; Zhao, Z.M.; Li, X.Y.; Dai, D.Q.; Zhang, J.K.; Li, Y.S.; Zhang, C.D. Macrophage polarization in cancer and beyond: From inflammatory signaling pathways to potential therapeutic strategies. Cancer Lett. 2025, 625, 217772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, T.S.; Shen, C.Y.; Hsieh, S.C. Systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with impaired autophagic degradation via interleukin-6 in macrophages. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, T.; Bettelli, E.; Oukka, M.; Kuchroo, V.K. IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 485–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccamo, N.; La Mendola, C.; Orlando, V.; Meraviglia, S.; Todaro, M.; Stassi, G.; Sireci, G.; Fournie, J.J.; Dieli, F. Differentiation, phenotype, and function of interleukin-17-producing human Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells. Blood 2011, 118, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.A.; Revez, J.A.; Loh, Z.; Simpson, J.; Zhang, V.; Bain, L.; Varelias, A.; Rose-John, S.; Blumenthal, A.; Smyth, M.J.; et al. Allergen-induced IL-6 trans-signaling activates gammadelta T cells to promote type 2 and type 17 airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamada, M.M.; Jia, Y.; Wu, X. Macrophage Polarization and Plasticity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 734008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labonte, A.C.; Kegerreis, B.; Geraci, N.S.; Bachali, P.; Madamanchi, S.; Robl, R.; Catalina, M.D.; Lipsky, P.E.; Grammer, A.C. Identification of alterations in macrophage activation associated with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, D.; Yang, S.; Zhao, L.; Ren, W.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Yu, T.; Zeng, T.; Zhou, L.; et al. ICAT-Mediated Crosstalk Between Cervical Cancer Cells and Macrophages Promotes M2-Like Macrophage Polarization to Reinforce Tumor Malignant Behaviors. Mol. Carcinog. 2024, 63, 2425–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, C.D.; Kincaid, K.; Alt, J.M.; Heilman, M.J.; Hill, A.M. M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 6166–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shoyaib, A.; Archie, S.R.; Karamyan, V.T. Intraperitoneal Route of Drug Administration: Should it Be Used in Experimental Animal Studies? Pharm. Res. 2019, 37, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.; Pluddemann, A.; Martinez Estrada, F. Macrophage heterogeneity in tissues: Phenotypic diversity and functions. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 262, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, Y.O.; Mueller, S.N. Splenic stromal niches in homeostasis and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, D.A.P.; Liao, S. Lymph Node Subcapsular Sinus Macrophages as the Frontline of Lymphatic Immune Defense. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, E.E.; Cyster, J.G. Lymph node macrophages. J. Innate Immun. 2012, 4, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Baeza, C.; Tescucano, A.; Astudillo, H.; Resendiz, A.; Landa, C.; Espana, L.; Serafin-Lopez, J.; Estrada-Garcia, I.; Estrada-Parra, S.; Flores-Romo, L.; et al. Nonbilayer Phospholipid Arrangements Are Toll-Like Receptor-2/6 and TLR-4 Agonists and Trigger Inflammation in a Mouse Model Resembling Human Lupus. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 369462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (U.S.); Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; Institute for Laboratory Animal Research (U.S.); National Academies Press (U.S.). Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galarce-Sosa, I.; Reséndiz-Mora, A.; Ramos-Monteagudo, R.; Barrera-Aveleida, G.; Rundquist-Sánchez, J.; Gómez-Manzo, S.; Wong-Baeza, I.; Wong-Baeza, C.; Baeza, I. In Vivo Response of γδ T Cells and Macrophages to Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangements in a Lupus-like Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178680
Galarce-Sosa I, Reséndiz-Mora A, Ramos-Monteagudo R, Barrera-Aveleida G, Rundquist-Sánchez J, Gómez-Manzo S, Wong-Baeza I, Wong-Baeza C, Baeza I. In Vivo Response of γδ T Cells and Macrophages to Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangements in a Lupus-like Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178680
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalarce-Sosa, Iván, Albany Reséndiz-Mora, Rodrigo Ramos-Monteagudo, Giovanna Barrera-Aveleida, José Rundquist-Sánchez, Saúl Gómez-Manzo, Isabel Wong-Baeza, Carlos Wong-Baeza, and Isabel Baeza. 2025. "In Vivo Response of γδ T Cells and Macrophages to Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangements in a Lupus-like Mouse Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178680
APA StyleGalarce-Sosa, I., Reséndiz-Mora, A., Ramos-Monteagudo, R., Barrera-Aveleida, G., Rundquist-Sánchez, J., Gómez-Manzo, S., Wong-Baeza, I., Wong-Baeza, C., & Baeza, I. (2025). In Vivo Response of γδ T Cells and Macrophages to Non-Bilayer Phospholipid Arrangements in a Lupus-like Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178680





