The Role of Blood-Based Biomarkers in Transforming Alzheimer’s Disease Research and Clinical Management: A Review
Abstract
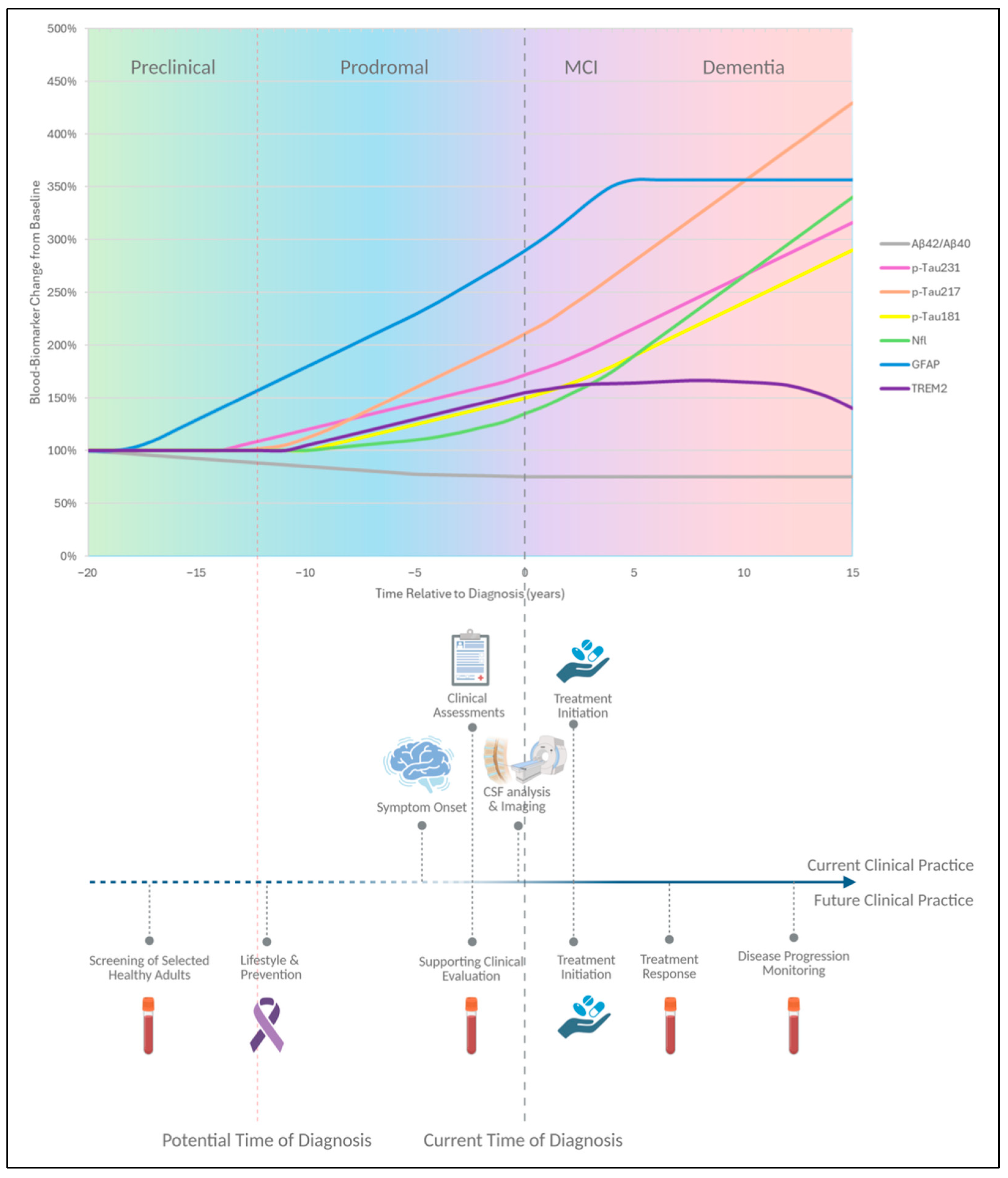
1. Introduction
2. Blood Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease
2.1. Amyloid-β
2.2. Tau Proteins
2.3. Neurofilament Light Chain
2.4. Glial Fibrillary Acid Protein
2.5. Other Inflammatory Biomarkers
2.6. Other Emerging Biomarkers
3. Analytical Techniques
4. Context of Use, Challenges and Limitations of Blood Biomarkers
5. Discussion and Conclusions
6. Search Strategy
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2025 Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 21, 1–148. Available online: https://www.alz.org/getmedia/ef8f48f9-ad36-48ea-87f9-b74034635c1e/alzheimers-facts-and-figures.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Alzheimer’s Disease International. World Alzheimer Report 2025: Journey through the Diagnosis of Dementia; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2025; Available online: https://www.alzint.org/resource/world-alzheimer-report-2024/ (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Roveta, F.; Bonino, L.; Piella, E.M.; Rainero, I.; Rubino, E. Neuroinflammatory Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; El Khoury, J.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blennow, K.; Hampel, H.; Weiner, M.; Zetterberg, H. Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma biomarkers in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Budd Haeberlein, S.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R.; Andrews, J.S.; Beach, T.G.; Buracchio, T.; Dunn, B.; Graf, A.; Hansson, O.; Ho, C.; Jagust, W.; McDade, E.; et al. Revised criteria for diagnosis and staging of Alzheimer’s disease: Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 1234–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Hu, Y.; Cummings, J.; Mattke, S.; Iwatsubo, T.; Nakamura, A.; Vellas, B.; O’Bryant, S.; Shaw, L.M.; Cho, M.; et al. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: Current state and future use in a transformed global healthcare landscape. Neuron 2023, 111, 2781–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.M.; Vanderstichele, H.; Knapik-Czajka, M.; Clark, C.M.; Aisen, P.S.; Petersen, R.C.; Blennow, K.; Soares, H.; Simon, A.; Lewczuk, P.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker signature in Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative subjects. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, N.C.; Leuzy, A.; Janelidze, S.; Palmqvist, S.; Svenningsson, A.L.; Stomrud, E.; Dage, J.L.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Hansson, O. Plasma biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease improve prediction of cognitive decline in cognitively unimpaired elderly populations. Nat. Commun. 2021, 13, 3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, O.; Edelmayer, R.M.; Boxer, A.L.; Carrillo, M.C.; Mielke, M.M.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Salloway, S.; Sperling, R.; Zetterberg, H.; Teunissen, C.E. The Alzheimer’s Association appropriate use recommendations for blood biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 18, 2669–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Bryant, S.E.; Mielke, M.M.; Rissman, R.A.; Lista, S.; Vanderstichele, H.; Zetterberg, H.; Lewczuk, P.; Posner, H.; Hall, J.; Johnson, L.; et al. Blood-based biomarkers in Alzheimer disease: Current state of the science and a novel collaborative paradigm for advancing from discovery to clinic. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therriault, J.; Schindler, S.E.; Salvadó, G.; Pascoal, T.A.; Benedet, A.L.; Ashton, N.J.; Karikari, T.K.; Apostolova, L.; Murray, M.E.; Verberk, I.; et al. Biomarker-based staging of Alzheimer disease: Rationale and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojdała, A.L.; Vanbrabant, J.; Bayoumy, S.; Antwi-Berko, D.; Le Bastard, N.; van der Flier, W.M.; Jeromin, A.; Lambrechts, C.; Van Loo, M.; Vandijck, M.; et al. Analytical and clinical performance of eight Simoa® and Lumipulse® assays for automated measurement of plasma p-tau181 and p-tau217. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevigny, J.; Chiao, P.; Bussière, T.; Weinreb, P.H.; Williams, L.; Maier, M.; Dunstan, R.; Salloway, S.; Chen, T.; Ling, Y.; et al. The antibody aducanumab reduces Aβ plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2016, 537, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Mattsson, N.; Andreasson, U.; Cullen, N.C.; Leuzy, A.; Janelidze, S.; Teunissen, C.E.; Hansson, O.; Salloway, S.; et al. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease-An update. J. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 319, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer’s disease: The amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 1992, 256, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassar, R.; Bennett, B.D.; Babu-Khan, S.; Kahn, S.; Mendiaz, E.A.; Denis, P.; Teplow, D.B.; Ross, S.; Amarante, P.; Loeloff, R.; et al. Beta-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein by the transmembrane aspartic protease BACE. Science 1999, 286, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, W.J.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Knol, D.L.; Tijms, B.M.; Scheltens, P.; Verhey, F.R.J.; Visser, P.J.; Aalten, P.; Aarsland, D.; Alcolea, D.; et al. Prevalence of cerebral amyloid pathology in persons without dementia: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2015, 313, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duits, F.H.; Martinez-Lage, P.; Paquet, C.; Engelborghs, S.; Struyfs, H.; Lleó, A.; Hausner, L.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Stomrud, E.; Farotti, L.; et al. Performance and complications of lumbar puncture in memory clinics: Results of the multicenter lumbar puncture feasibility study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016, 12, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppälä, T.T.; Herukka, S.K.; Hänninen, T.; Tervo, S.; Hallikainen, M.; Soininen, H.; Pirttilä, T. Plasma Abeta42 and Abeta40 as markers of cognitive change in follow-up: A prospective, longitudinal, population-based cohort study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohaupt, P.; Kindermans, J.; Vialaret, J.; Anderl-Straub, S.; Werner, L.; Lehmann, S.; Hirtz, C.; Otto, M.; Oeckl, P. Blood-based biomarkers and plasma Aβ assays in the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and behavioral-variant frontotemporal dementia. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Kaneko, N.; Villemagne, V.L.; Kato, T.; Doecke, J.; Doré, V.; Fowler, C.; Li, Q.-X.; Martins, R.; Rowe, C.; et al. High performance plasma amyloid-β biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2018, 554, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, S.E.; Bollinger, J.G.; Ovod, V.; Mawuenyega, K.G.; Li, Y.; Gordon, B.A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Morris, J.C.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Xiong, C.; et al. High-precision plasma β-amyloid 42/40 predicts current and future brain amyloidosis. Neurology 2019, 93, e1647–e1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verberk, I.M.W.; Slot, R.E.; Verfaillie, S.C.J.; Heijst, H.; Prins, N.D.; van Berckel, B.N.M.; Scheltens, P.; Teunissen, C.E.; van der Flier, W.M. Plasma Amyloid as Prescreener for the Earliest Alzheimer Pathological Changes. Ann Neurol. 2018, 84, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanzad, M.; Karimollah, H.-T. Methods of determining optimal cut-point of diagnostic biomarkers with application of clinical data in ROC analysis: An update review. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2024, 24, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelidze, S.; Stomrud, E.; Palmqvist, S.; Zetterberg, H.; van Westen, D.; Jeromin, A.; Song, L.; Hanlon, D.; Tan Hehir, C.A.; Baker, D.; et al. Plasma β-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular disease. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 26801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Lafferty, T.K.; Sehrawat, A.; Chen, Y.; Ferreira, P.C.L.; Bellaver, B.; Povala, G.; Kamboh, M.I.; Klunk, W.E.; Cohen, A.D.; et al. Multi-analyte proteomic analysis identifies blood-based neuroinflammation, cerebrovascular and synaptic biomarkers in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mandelkow, E. Tau in physiology and pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.; Goedert, M. Tau pathology and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, F.E.; Conti, E.; Remoli, G.; Dell’Orto, N.; Andreoni, S.; Da Re, F.; Sala, G.; Cuffaro, L.; Ferrarese, C.; Appollonio, I.; et al. Core blood biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease: A single-center real-world performance study. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2025, 12, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rumeileh, S.; Scholle, L.; Mensch, A.; Großkopf, H.; Ratti, A.; Kölsch, A.; Stoltenburg-Didinger, G.; Conrad, J.; De Gobbi, A.; Barba, L.; et al. Phosphorylated tau 181 and 217 are elevated in serum and muscle of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M.M.; Hagen, C.E.; Xu, J.; Chai, X.; Vemuri, P.; Lowe, V.J.; Airey, D.C.; Knopman, D.S.; Roberts, R.O.; Machulda, M.M.; et al. Plasma phospho-tau181 increases with Alzheimer’s disease clinical severity and is associated with tau- and amyloid-positron emission tomography. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karikari, T.K.; Pascoal, T.A.; Ashton, N.J.; Janelidze, S.; Benedet, A.L.; Rodriguez, J.L.; Chamoun, M.; Savard, M.; Kang, M.S.; Therriault, J.; et al. Blood phosphorylated tau 181 as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease: A diagnostic performance and prediction modelling study using data from four prospective cohorts. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmqvist, S.; Janelidze, S.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Zetterberg, H.; Lopera, F.; Stomrud, E.; Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Serrano, G.E.; Leuzy, A.; et al. Discriminative Accuracy of Plasma Phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer Disease vs Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. JAMA 2020, 324, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelidze, S.; Mattsson, N.; Palmqvist, S.; Smith, R.; Beach, T.G.; Serrano, G.E.; Chai, X.; Proctor, N.K.; Eichenlaub, U.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Plasma P-tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease: Relationship to other biomarkers, differential diagnosis, neuropathology and longitudinal progression to Alzheimer’s dementia. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarek, D.J.; Mizerka, H.; Nuszkiewicz, J.; Szewczyk-Golec, K. Evaluating p-tau217 and p-tau231 as Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis and Differentiation of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiardi, S.; Quadalti, C.; Mammana, A.; Dellavalle, S.; Zenesini, C.; Sambati, L.; Pantieri, R.; Polischi, B.; Romano, L.; Suffritti, M.; et al. Diagnostic value of plasma p-tau181, NfL, and GFAP in a clinical setting cohort of prevalent neurodegenerative dementias. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmqvist, S.; Tideman, P.; Cullen, N.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Dage, J.L.; Stomrud, E.; Janelidze, S.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Hansson, O.; et al. Prediction of future Alzheimer’s disease dementia using plasma phospho-tau combined with other accessible measures. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milà-Alomà, M.; Ashton, N.J.; Shekari, M.; Salvadó, G.; Ortiz-Romero, P.; Montoliu-Gaya, L.; Benedet, A.L.; Karikari, T.K.; Lantero-Rodríguez, J.; Vanmechelen, E.; et al. Plasma p-tau231 and p-tau217 as state markers of amyloid-β pathology in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1797–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.R.; Zimmer, J.A.; Evans, C.D.; Lu, M.; Ardayfio, P.; Sparks, J.; Wessels, A.M.; Shcherbinin, S.; Wang, H.; Monkul Nery, E.S.; et al. Donanemab in Early Symptomatic Alzheimer Disease: The TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontecorvo, M.J.; Lu, M.; Burnham, S.C.; Schade, A.E.; Dage, J.L.; Shcherbinin, S.; Collins, E.C.; Sims, J.R.; Mintun, M.A. Association of Donanemab Treatment with Exploratory Plasma Biomarkers in Early Symptomatic Alzheimer Disease: A Secondary Analysis of the TRAILBLAZER-ALZ Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, N.J.; Pascoal, T.A.; Karikari, T.K.; Benedet, A.L.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Brinkmalm, G.; Snellman, A.; Schöll, M.; Troakes, C.; Hye, A.; et al. Plasma p-tau231: A new biomarker for incipient Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 141, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedet, A.L.; Brum, W.S.; Hansson, O.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative; Karikari, T.K.; Zimmer, E.R.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Ashton, N.J. The accuracy and robustness of plasma biomarker models for amyloid PET positivity. Alzheimer’s Res Ther. 2022, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, P.F.; Ashton, N.J.; Karikari, T.K.; Strikwerda-Brown, C.; Köbe, T.; Gonneaud, J.; Pichet Binette, A.; Ozlen, H.; Yakoub, Y.; Simrén, J.; et al. Plasma p-tau231, p-tau181, PET Biomarkers, and Cognitive Change in Older Adults. Ann. Neurol. 2022, 91, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, A.J.; Ribaldi, F.; Lathuiliere, A.; Ashton, N.J.; Janelidze, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Scheffler, M.; Assal, F.; Garibotto, V.; Blennow, K.; et al. Head-to-head study of diagnostic accuracy of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid p-tau217 versus p-tau181 and p-tau231 in a memory clinic cohort. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 2053–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelidze, S.; Bali, D.; Ashton, N.J.; Barthélemy, N.R.; Vanbrabant, J.; Stoops, E.; Vanmechelen, E.; He, Y.; Orduña Dolado, A.; Triana-Baltzer, G.; et al. Head-to-head comparison of 10 plasma phospho-tau assays in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2023, 146, 1592–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, A.H.; Dunne, J.; Dolphin, H.; Morrison, L.; O’Connor, A.; Fullam, S.; Kenny, T.; Fallon, A.; O’Dowd, S.; Bourke, N.M.; et al. Clinical performance of the fully automated Lumipulse plasma p-tau217 assay in mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 17, e70080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, G.; Gabelli, C.; Puthenparampil, M.; Cosma, C.; Cagnin, A.; Gallo, P.; Sorarù, G.; Pegoraro, E.; Zaninotto, M.; Antonini, A.; et al. Blood biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease with the Lumipulse automated platform: Age-effect and clinical value interpretation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2025, 565, 120014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Zho, M. Neurofilament Light Chain as a Potential Biomarker in Plasma for Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, L.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P.; Di Filippo, M.; Parnetti, L.; Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in neurological disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiottino, J.; Norgren, N.; Dobson, R.; Topping, J.; Nissim, A.; Malaspina, A.; Bestwick, J.P.; Monsch, A.U.; Regeniter, A.; Lindberg, R.L.; et al. Increased neurofilament light chain blood levels in neurodegenerative neurological diseases. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, N.J.; Janelidze, S.; Al Khleifat, A.; Leuzy, A.; van der Ende, E.; Karikari, T.K.; Benedet, A.L.; Pascoal, T.A.; Lleó, A.; Parnetti, L.; et al. A multicentre validation study of the diagnostic value of plasma neurofilament light. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson, N.; Andreasson, U.; Zetterberg, H.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Association of Plasma Neurofilament Light with Neurodegeneration in Patients With Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, N.J.; Leuzy, A.; Lim, Y.M.; Troakes, C.; Hortobágyi, T.; Höglund, K.; Aarsland, D.; Lovestone, S.; Schöll, M.; Blennow, K.; et al. Increased plasma neurofilament light chain concentration correlates with severity of post-mortem neurofibrillary tangle pathology and neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedet, A.L.; Leuzy, A.; Pascoal, T.A.; Ashton, N.J.; Mathotaarachchi, S.; Savard, M.; Therriault, J.; Kang, M.S.; Chamoun, M.; Schöll, M.; et al. Stage-specific links between plasma neurofilament light and imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2020, 143, 3793–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.; Häsler, L.M.; Lambert, M.; Kaeser, S.A.; Gräber-Sultan, S.; Obermüller, U.; Kuder-Buletta, E.; la Fougere, C.; Laske, C.; Vöglein, J.; et al. Comparative neurofilament light chain trajectories in CSF and plasma in autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Kawarabayashi, T.; Shibata, M.; Kasahara, H.; Makioka, K.; Sugawara, T.; Oka, H.; Ishizawa, K.; Amari, M.; Ueda, T.; et al. High levels of plasma neurofilament light chain correlated with brainstem and peripheral nerve damage. J. Neurol. Sci. 2024, 463, 123137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyck, C.H.; Swanson, C.J.; Aisen, P.; Bateman, R.J.; Chen, C.; Gee, M.; Kanekiyo, M.; Li, D.; Reyderman, L.; Cohen, S.; et al. Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischik, C.M.; Schelter, B.; Penny, L.K.; Miller, S.; Stefanacci, R.; Heslegrave, A.; Zetterberg, H. Significant dose-dependent reduction in neurofilament light chain concentration in plasma with oral tau aggregation inhibitor hydromethylthionine mesylate. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulton, J.B.; He, Y.; Barthélemy, N.R.; Jiang, H.; Holtzman, D.M.; Bateman, R.J. Multi-peptide characterization of plasma neurofilament light chain in preclinical and mild Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcae247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, B.; Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament light chain as neuronal injury marker—What is needed to facilitate implementation in clinical laboratory practice? Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2023, 61, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipp, F.; Vialaret, J.; Mohaupt, P.; Coppens, S.; Jaffuel, A.; Niehoff, A.; Lehmann, S.; Hirtz, C. Glial fibrillary acidic protein in Alzheimer’s disease: A narrative review. Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcae396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, P.; Vermunt, L.; Gordon, B.A.; Pedrini, S.; Boonkamp, L.; Armstrong, N.J.; Xiong, C.; Singh, A.K.; Li, Y.; Sohrabi, H.R.; et al. Plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein in autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease: Associations with Aβ-PET, neurodegeneration, and cognition. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 2790–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, H.; Beyer, L.; Perna, L.; Rujescu, D.; Holleczek, B.; Beyreuther, K.; Stockmann, J.; Schöttker, B.; Gerwert, K.; Brenner, H.; et al. Association of plasma biomarkers, p-tau181, glial fibrillary acidic protein, and neurofilament light, with intermediate and long-term clinical Alzheimer’s disease risk: Results from a prospective cohort followed over 17 years. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.Y.; Shin, K.Y.; Chang, K.A. GFAP as a Potential Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cells 2023, 12, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, V.R.; An, Y.; Kac, P.R.; Bilgel, M.; Moghekar, A.; Loeffler, T.; Amschl, D.; Troncoso, J.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Longitudinal progression of blood biomarkers reveals a key role of astrocyte reactivity in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. medRxiv 2024, 24, 301779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedet, A.L.; Milà-Alomà, M.; Vrillon, A.; Ashton, N.J.; Pascoal, T.A.; Lussier, F.; Karikari, T.K.; Hourregue, C.; Cognat, E.; Dumurgier, J.; et al. Differences Between Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Levels Across the Alzheimer Disease Continuum. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig-Schapiro, R.; Perrin, R.J.; Roe, C.M.; Xiong, C.; Carter, D.; Cairns, N.J.; Minturn, M.A.; Peskind, E.R.; Li, G.; Galasko, D.R.; et al. YKL-40: A novel prognostic fluid biomarker for preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Calvet, M.; Araque Caballero, M.Á.; Kleinberger, G.; Bateman, R.J.; Fagan, A.M.; Morris, J.C.; Levin, J.; Danek, A.; Ewers, M.; Haass, C. Early changes in CSF sTREM2 in dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease occur after amyloid deposition and neuronal injury. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 369ra178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Cao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, H.; McIntyre, R.S.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Zhou, H. Soluble TREM2 changes during the clinical course of Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 686, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhou, X.W.; Wang, J.Z. The dual roles of cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease: Update on interleukins, TNF-α, TGF-β and IFN-γ. Transl. Neurodegener. 2016, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dammer, E.B.; Ping, L.; Duong, D.M.; Modeste, E.S.; Seyfried, N.T.; Lah, J.J.; Levey, A.I.; Johnson, E.C.B. Multi-platform proteomic analysis of Alzheimer’s disease cerebrospinal fluid and plasma reveals network biomarkers associated with proteostasis and the matrisome. Alzheimer’s Res Ther. 2022, 14, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieger, A.; Rocha, A.; Bellaber, B.; Machado, L.; Da Ros, L.; Borelli, W.V.; Therriault, J.; Macedo, A.C.; Pascoal, T.A.; Gauthier, S.; et al. Neuroinflammation Biomarkers in the AT(N) Framework Across the Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2023, 10, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angiulli, F.; Conti, E.; Zoia, C.P.; Da Re, F.; Appollonio, I.; Ferrarese, C.; Tremolizzo, L. Blood-Based Biomarkers of Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Central Role for Periphery? Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Gauthier, S.; Chandekar, S.A.; Hahn-Pedersen, J.H.; Bentsen, M.A.; Zetterberg, H. Neuroinflammatory fluid biomarkers in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic literature review. Mol. Psychiatry 2025, 30, 2783–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roveta, F.; Cermelli, A.; Boschi, S.; Ferrandes, F.; Grassini, A.; Marcinnò, A.; Spina, M.; Rubino, E.; Borsello, T.; Vercelli, A.; et al. Synaptic Proteins as Fluid Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 90, 1381–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, L.; Bellomo, G.; Chiasserini, D.; De Rocker, C.; Goossens, J.; Paolini Paoletti, F.; Vanmechelen, E.; Parnett, L. Influence of co-pathology on CSF and plasma synaptic markers SNAP25 and VAMP2 in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2025, 17, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, H.; Han, J.; Yu, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Lu, Z. Biomarkers of synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2025, 104, 102642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslemnezhad, A.; Mahjoub, S.; Moghadasi, M. Altered plasma marker of oxidative DNA damage and total antioxidant capacity in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 7, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Schrag, M.; Mueller, C.; Zabel, M.; Crofton, A.; Kirsch, W.M.; Ghribi, O.; Squitti, R.; Perry, G. Oxidative stress in blood in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 59, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trares, K.; Chen, L.J.; Schöttker, B. Association of F2-isoprostane levels with Alzheimer’s disease in observational studies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 74, 101552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.; Chu, C.; Qin, Q.; Shen, H.; Wen, L.; Tang, Y.; Qu, M. Lipid metabolism and oxidative stress in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Brain Pathol. 2024, 34, e13202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, K.; Lim, W.L.F.; Giles, C.; Jayawardana, K.S.; Salim, A.; Mellett, N.A.; Smiith, A.A.T.; Olshansky, G.; Drew, B.G.; Chatterjee, P. Concordant peripheral lipidome signatures in two large clinical studies of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, J.B.; Arnold, M.; Kastenmüller, G.; Chang, R.; Baillie, R.A.; Han, X.; Thambisetty, M.; Tenenbaum, J.D.; Suhre, K.; Thompson, J.W. Metabolic network failures in Alzheimer’s disease: A biochemical road map. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 965–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praticò, D.; Clark, C.M.; Liun, F.; Rokach, J.; Lee, V.Y.-M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Increase of brain oxidative stress in mild cognitive impairment: A possible predictor of Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiandaca, M.S.; Kapogiannis, D.; Mapstone, M.; Boxer, A.; Eitan, E.; Schwartz, J.B.; Abner, E.L.; Petersen, R.C.; Federoff, H.J.; Miller, B.L. Identification of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease by a profile of pathogenic proteins in neurally derived blood exosomes: A case-control study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2015, 11, 600–607.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, C.N.; Goetzl, E.J.; Akers, J.C.; Carter, B.S.; Rockenstein, E.M.; Galasko, D.; Masliah, E.; Rissman, R.A. Prediction of conversion from mild cognitive impairment to dementia with neuronally derived blood exosome protein profile. Alzheimer’s Dementia Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2016, 3, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Yu, J.T.; Tan, L. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Alzheimer’s Disease: Risk, Mechanisms, and Therapy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 1477–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.R.; Sweeney, M.D.; Sagare, A.P.; Zlokovic, B.V. Neurovascular dysfunction and neurodegeneration in dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2016, 1862, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.E.; Zhang, F.; Hall, J.; Brock, C.; Rissman, R.A.; Como, T.; Julovich, D.; Mapstone, M.; Ances, B.M.; Meeker, K. Characterization of plasma AT(N) biomarkers among a racial and ethnically diverse community-based cohort: An HABS-HD study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 1, e70045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, N.C.; Leuzy, A.; Palmqvist, S.; Janelidze, S.; Stomrud, E.; Pesini, P.; Sarasa, L.; Aullé, J.A.; Proctor, N.K.; Zetterberg, H. Individualized prognosis of cognitive decline and dementia in mild cognitive impairment based on plasma biomarker combinations. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orešič, M.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Herukka, S.K.; Sysi-Aho, M.; Mattila, I.; Seppänan-Laakso, T.; Julkunen, V.; Gopalacharyulu, P.V.; Hallikainen, M.; Koikkalainen, J. Metabolome in progression to Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Psychiatry 2011, 1, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Campbell, T.G.; Howes, S.C.; Fournier, D.R.; Song, L.; Piech, T.; Patel, P.P.; Chang, L.; Rivnak, A.J. Single-molecule enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detects serum proteins at subfemtomolar concentrations. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuzy, A.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Palmqvist, S.; Janelidze, S.; Dage, J.L.; Hansson, O. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e14408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilotto, A.; Quaresima, V.; Trasciatti, C.; Tolassi, C.; Bertoli, D.; Mordenti, C.; Galli, A.; Rizzardi, A.; Caratozzolo, S.; Zancanaro, A. Plasma p-tau217 in Alzheimer’s disease: Lumipulse and ALZpath SIMOA head-to-head comparison. Brain 2024, 148, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karikari, T.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, X.; Olvera-Rojas, M.; Sehrawat, A.; Lafferty, T.; Pascoal, T.; Villemagne, V.; Solis-Urra, P.; Trivino-Ibanez, E. A streamlined, resource-efficient immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry method for quantifying plasma amyloid-β biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zeng, X.; Olvera-Rojas, M.; Sehrawat, A.; Lafferty, T.K.; Klunk, W.E.; Ikonomovic, M.D.; Pascoal, T.A.; Erickson, K.I.; Villemagne, V.L. Large-scale validation of an improved and resource-saving immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry assay for plasma amyloid-β biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 20, e092562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Kivisäkk, P.; Fatima, H.A.; Cahoon, D.S.; Otieno, B.; Chacko, L.; Minooei, F.; Demos, C.; Stengelin, M.; Sigal, G.; Wohlstadter, J. Clinical evaluation of a novel plasma pTau217 electrochemiluminescence immunoassay in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmqvist, S.; Janelidze, S.; Stomrud, E.; Zetterberg, H.; Karl, J.; Zink, K.; Bittner, T.; Mattsson, N.; Eichenlaub, U.; Blennow, K. Performance of Fully Automated Plasma Assays as Screening Tests for Alzheimer Disease-Related β-Amyloid Status. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, L.F.; Guerra, A.; Walker, D.G. Amyloid Beta and Tau as Alzheimer’s Disease Blood Biomarkers: Promise from New Technologies. Neurol. Ther. 2017, 6, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelidze, S.; Palmqvist, S.; Leuzy, A.; Stomrud, E.; Verberk, I.M.W.; Zetterberg, H.; Ashton, N.J.; Pesini, P.; Sarasa, L.; Allué, J.A. Detecting amyloid positivity in early Alzheimer’s disease using combinations of plasma Aβ42/Aβ40 and p-tau. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 18, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielke, M.M.; Anderson, M.; Ashford, J.W.; Jeromin, A.; Lin, P.J.; Rosen, A.; Tyrone, J.; VandeVrede, L.; Willis, D.; Hansson, O. Considerations for widespread implementation of blood-based biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 8209–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M.M.; Anderson, M.; Ashford, J.W.; Jeromin, A.; Lin, P.J.; Rosen, A.; Tyrone, J.; Vandevrede, L.; Willis, D.R.; Hansson, O. Recommendations for clinical implementation of blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 8216–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brum, W.S.; Cullen, N.C.; Janelidze, S.; Ashton, N.J.; Zimmer, E.R.; Thierriault, J.; Benedet, A.L.; Rahmouni, N.; Tissot, C.; Stevenson, J. A two-step workflow based on plasma p-tau217 to screen for amyloid β positivity with further confirmatory testing only in uncertain cases. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figdore, D.J.; Griswold, M.; Bornhorst, J.A.; Graff-Radford, J.; Ramanan, V.K.; Vemuri, P.; Lowe, V.J.; Knopman, D.S.; Jack, C.R.; Petersen, R.C. Optimizing cutpoints for clinical interpretation of brain amyloid status using plasma p-tau217 immunoassays. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 6506–6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, S.E.; Galasko, D.; Pereira, A.C.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Salloway, S.; Suárez-Calvet, M.; Khachaturian, A.S.; Mielke, M.M.; Udeh-Momoh, C.; Weiss, J. Acceptable performance of blood biomarker tests of amyloid pathology—Recommendations from the Global CEO Initiative on Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-clears-first-blood-test-used-diagnosing-alzheimers-disease (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- Rajan, K.B.; McAninch, E.A.; Aggarwal, N.T.; Barnes, L.L.; Wilson, R.S.; Weuve, J.; DeCardli, C.S.; Evans, D.A. Longitudinal Changes in Blood Biomarkers of Clinical Alzheimer Disease in a Biracial Population Sample. Neurology 2023, 100, e874–e883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavan, A.; Heslegrave, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Schott, J.M. Stability of blood-based biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease over multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Alzheimer’s Dement (Amst.) 2018, 10, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Z. Blood biomarkers for clinical applications in Alzheimer’s disease: A narrative review. Neuromarkers 2025, 2, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.C.; Schindler, S.E.; McCue, L.M.; Moulder, K.L.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Cruchaga, C.; Fagan, A.M.; Grant, E.; Gordon, B.A.; Holtzman, D.M. Assessment of Racial Disparities in Biomarkers for Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, S.E.; Karikari, T.K.; Ashton, N.J.; Henson, R.L.; Yarasheski, K.E.; West, T.; Meyer, M.R.; Kirmess, K.M.; Li, Y.; Saef, B. Effect of Race on Prediction of Brain Amyloidosis by Plasma Aβ42/Aβ40, Phosphorylated Tau, and Neurofilament Light. Neurology 2022, 99, e245–e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholl, M.; Verberk, I.M.W.; Del Campo, M.; Delaby, C.; Thierriault, J.; Chong, j.r.; Palmqvist, S.; Alcolea, D. Challenges in the practical implementation of blood biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2024, 5, 100630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketchum, F.B. Lessons Learned: Social and Ethical Issues Related to Clinical Implementation of Blood-Based Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 20, e089279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderschaeghe, G.; Dierickx, K.; Vandenberghe, R. Review of the Ethical Issues of a Biomarker-Based Diagnoses in the Early Stage of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Bioethical Inq. 2018, 15, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Lee, G.; Nahed, P.; Kambar, M.E.Z.N.; Zhong, K.; Fonseca, J.; Taghva, K. Alzheimer’s disease drug development pipeline: 2022. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 8, e12295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, O.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Dage, J. Blood biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease in clinical practice and trials. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C.; Lopez, O.; Armstrong, M.J.; Getchius, T.S.D.; Ganguli, M.; Gloss, D.; Gronseth, G.S.; Marson, D.; Pringsheim, T.; Day, G.S. Practice guideline update summary: Mild cognitive impairment [RETIRED]: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2018, 90, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Blood Biomarker | Biological Role | Detection Method | Diagnostic Utility | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aβ42/Aβ40 | Reflects amyloid plaque formation and deposition | Simoa, IP-MS, Lumipulse | Early detection of amyloid pathology; correlates with amyloid PET; useful in preclinical stages | Low plasma abundance; peripheral metabolism confounds levels; assay variability across platforms | [24,70] |
| p-Tau181, p-Tau217, p-Tau231 | Reflect amyloid and tau pathology | Simoa, IP-MS, Lumipulse | Specificity for AD; distinguishes AD from other dementias; early and prodromal stage detection; prognostic for progression | Inter-assay variability; need for standardized cut-offs; emerging data for p-Tau231 | [34,35,71] |
| NfL | Marker of axonal injury and neurodegeneration | Simoa, IP-MS, Lumipulse | Tracks disease progression; prognostic value for cognitive decline | Not specific to AD; elevated in other neurodegenerative diseases and with aging; influenced by comorbidities | [72,73] |
| GFAP | Astrocytic activation and gliosis | Simoa, IP-MS, Lumipulse | Early marker of astroglial activation; correlates with amyloid pathology; predictive of cognitive decline | Elevated in other neurological conditions; assay standardization needed | [74] |
| Biomarker | Biological Role | Detection Method(s) | Current Evidence | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neuro-inflammation YKL-40, sTREM2, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β | Markers of astrocyte and microglial activation; mediators of systemic and central inflammation | ELISA, Simoa Metabolomic platforms (Olink, SomaScan) | Reflect neuroinflammation; correlate with Tau pathology and cognitive decline; track disease progression | Moderate to low specificity; assay variability; influenced by systemic conditions | [70,71] |
| Synaptic Markers Neurogranin, SNAP-25 | Reflect synaptic integrity and dysfunction | ELISA, Simoa | Early indicators of synaptic loss; correlate with cognitive impairment | Limited plasma validation; variable assay sensitivity; less studied in blood | [88] |
| Oxidative Stress Markers 8-OHdG, Malondialdehyde, F2-isoprostanes | Indicators of oxidative DNA and lipid damage | ELISA, Mass Spectrometry | Reflect oxidative stress contributing to AD pathology; may indicate progression | Assay variability; low specificity; influenced by systemic oxidative stress | [82] |
| Metabolomic Markers Phosphatidyl-choline, Sphingomyelin | Reflect lipid metabolism and membrane integrity | Mass Spectrometry, Metabolomic platforms (Olink, SomaScan) | Altered lipid profiles in AD; potential early markers; improve diagnostic panels | High inter-individual variability; best used in multi-marker panels | [94] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pacoova Dal Maschio, V.; Roveta, F.; Bonino, L.; Boschi, S.; Rainero, I.; Rubino, E. The Role of Blood-Based Biomarkers in Transforming Alzheimer’s Disease Research and Clinical Management: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178564
Pacoova Dal Maschio V, Roveta F, Bonino L, Boschi S, Rainero I, Rubino E. The Role of Blood-Based Biomarkers in Transforming Alzheimer’s Disease Research and Clinical Management: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178564
Chicago/Turabian StylePacoova Dal Maschio, Vera, Fausto Roveta, Lucrezia Bonino, Silvia Boschi, Innocenzo Rainero, and Elisa Rubino. 2025. "The Role of Blood-Based Biomarkers in Transforming Alzheimer’s Disease Research and Clinical Management: A Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178564
APA StylePacoova Dal Maschio, V., Roveta, F., Bonino, L., Boschi, S., Rainero, I., & Rubino, E. (2025). The Role of Blood-Based Biomarkers in Transforming Alzheimer’s Disease Research and Clinical Management: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178564






