Nido-Carborane Derivatives of (S)-Ornithine and (S)-Lysine as Potential Boron Delivery Agents: Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
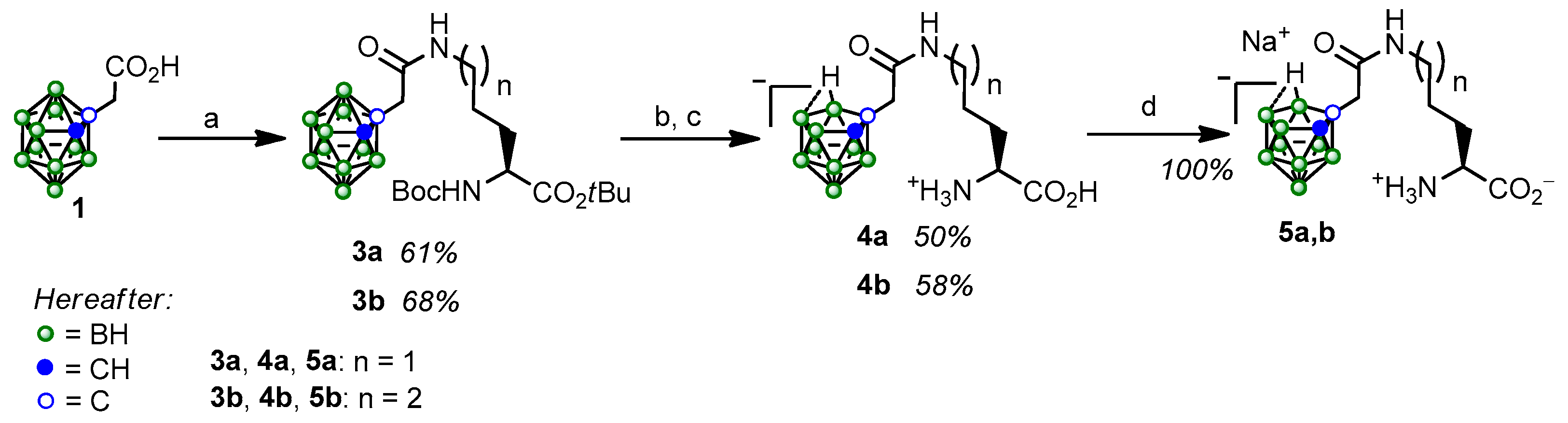
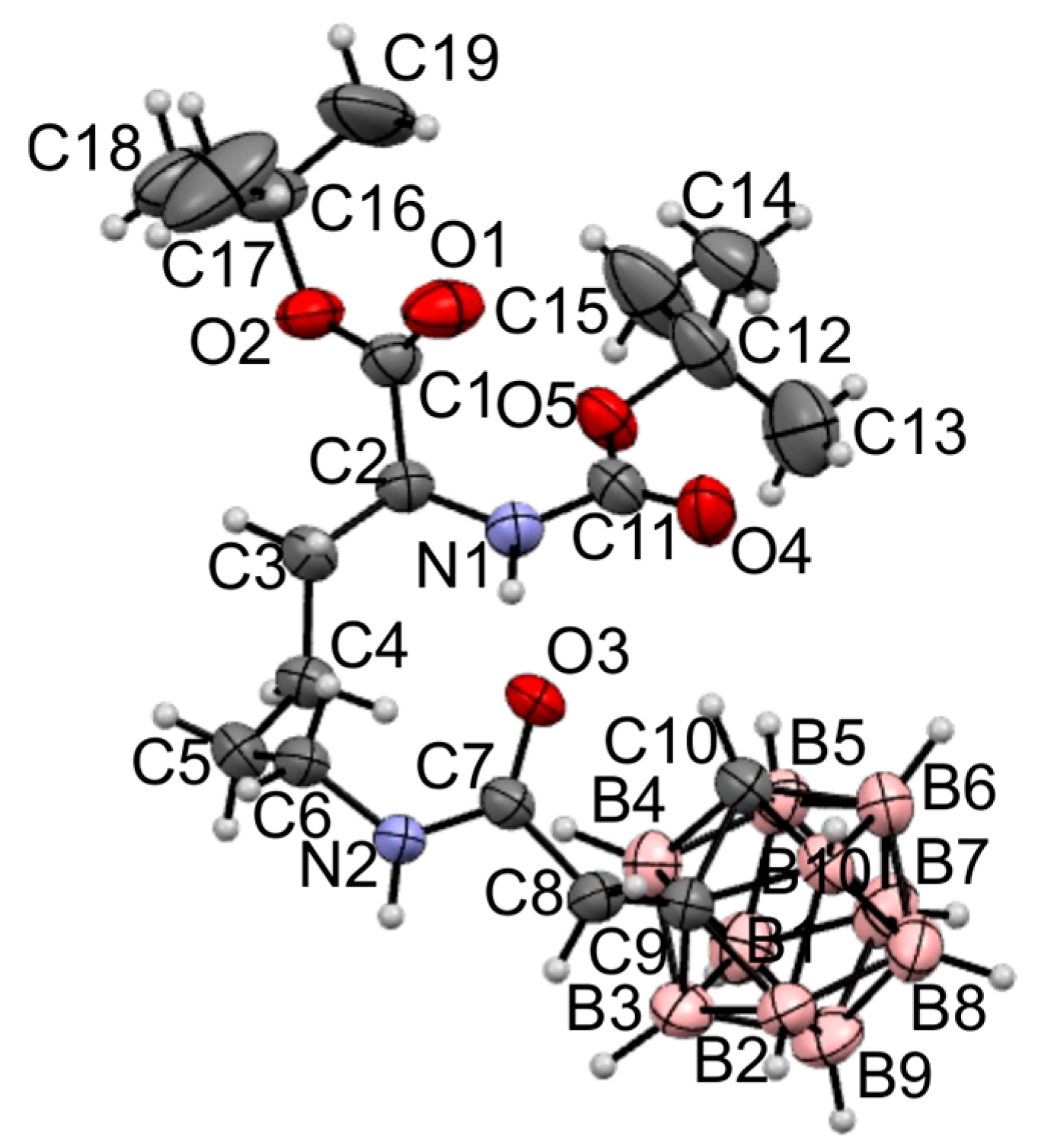
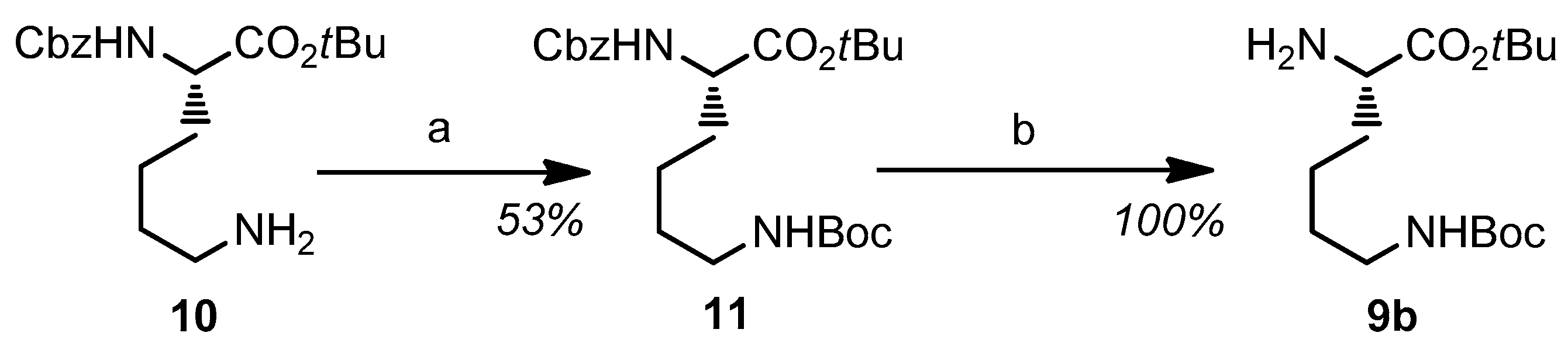
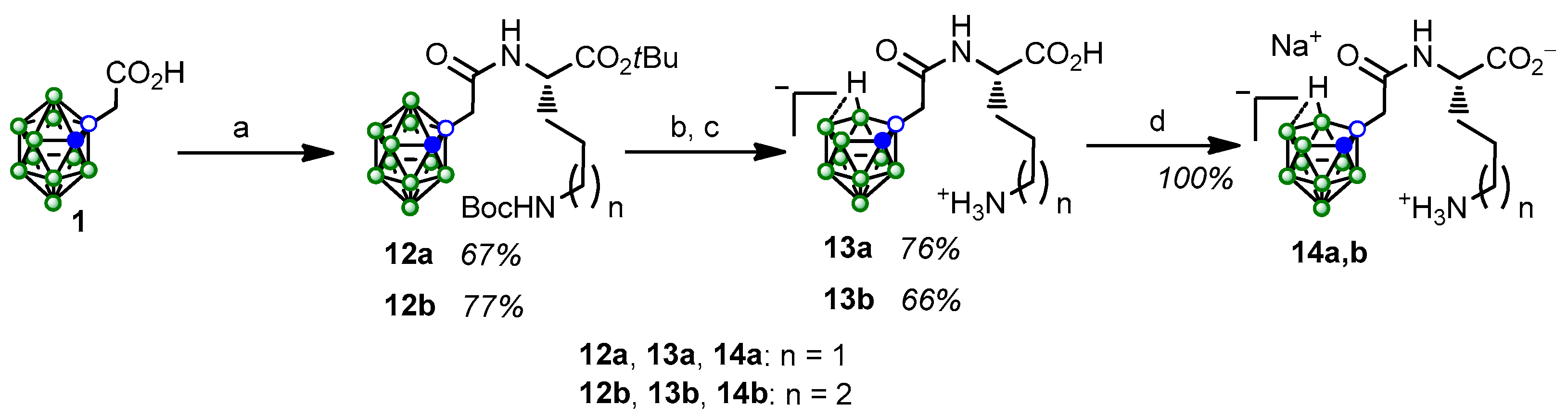
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Obtained Compounds
2.2. In Vitro Evaluation
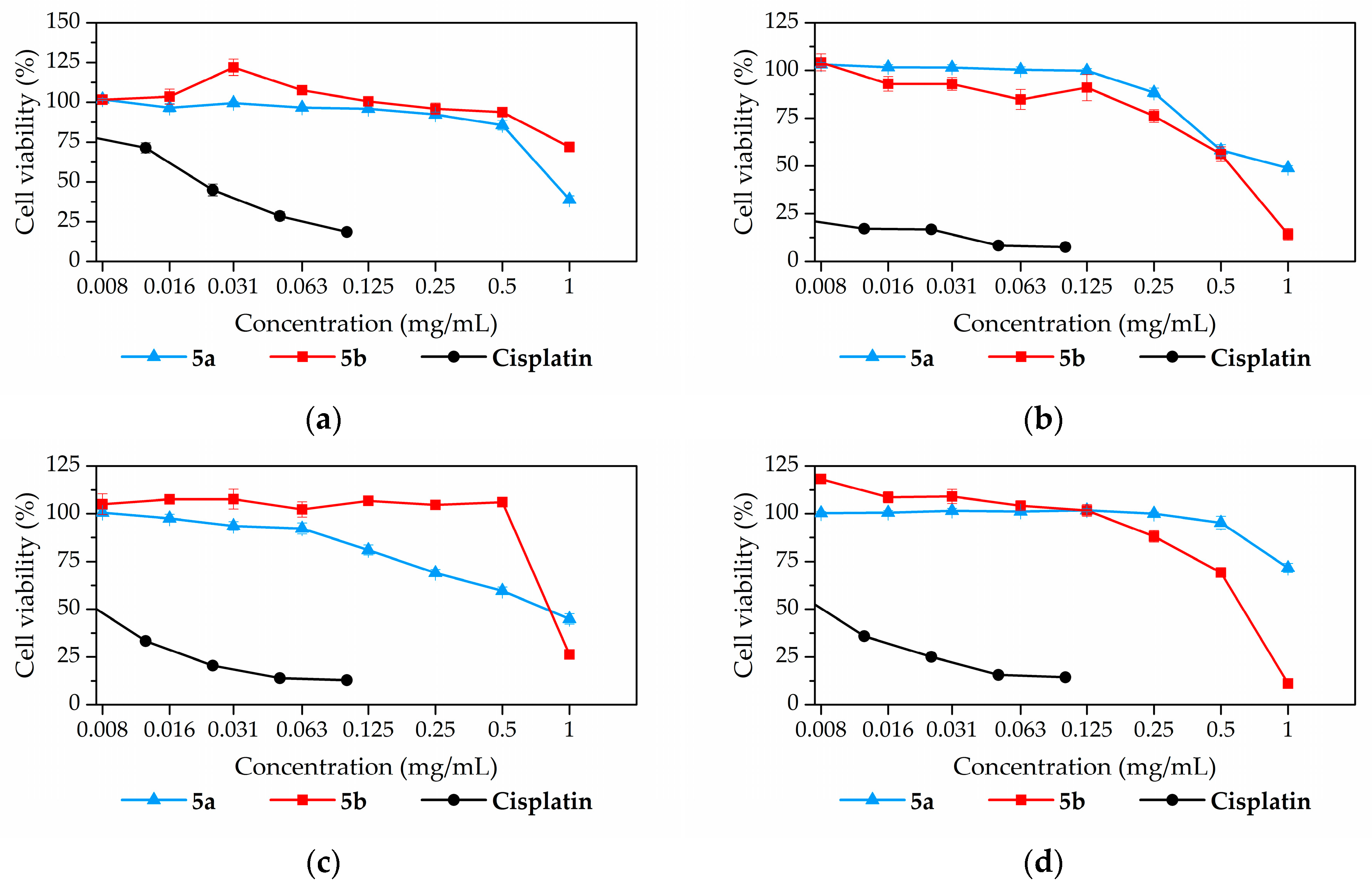
2.2.1. Toxicity Assay
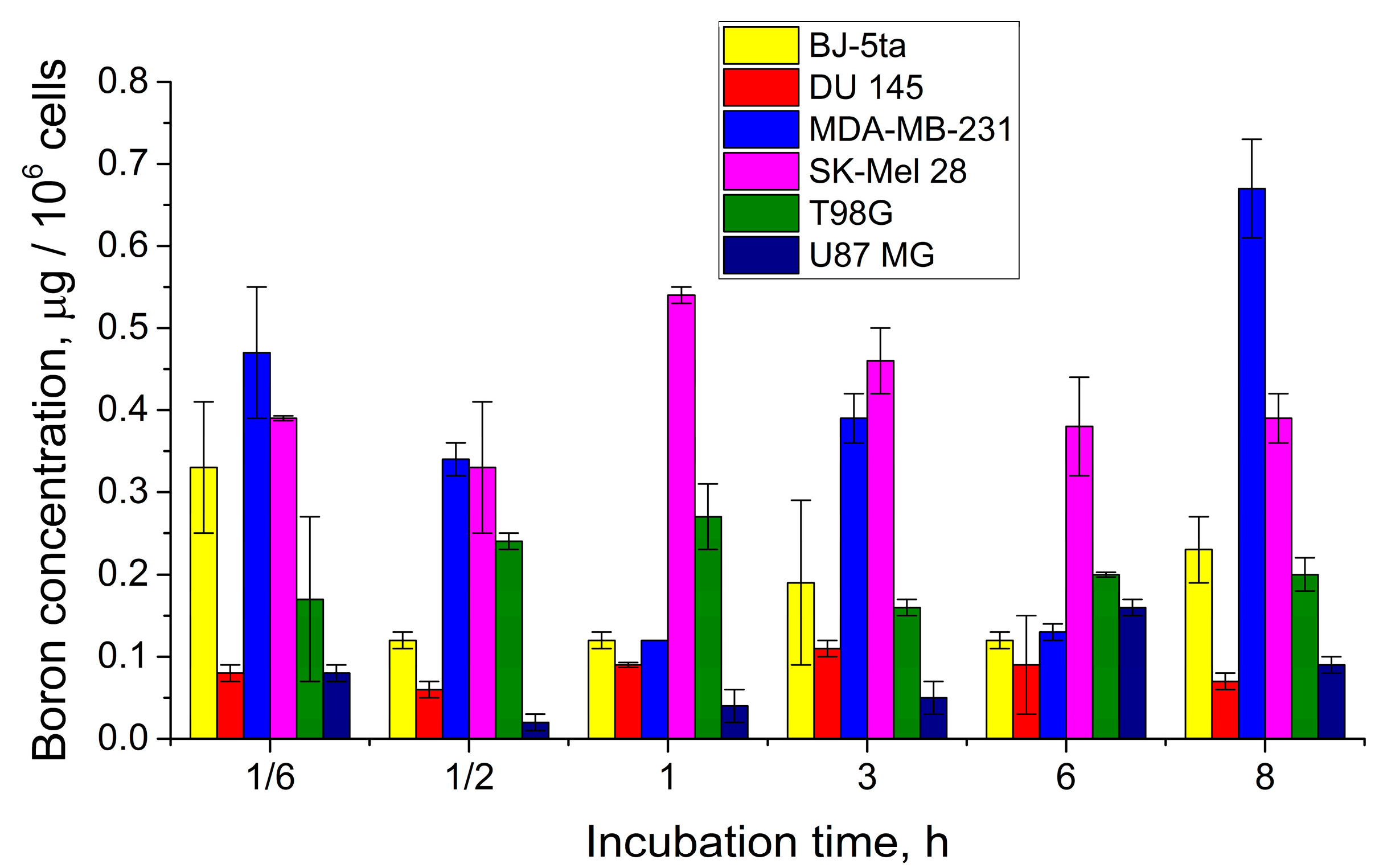
2.2.2. Evaluation of Boron Accumulation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry General Section
3.2. Synthesis
3.3. Cell Lines
3.4. MTT Cytotoxicity Assay
3.5. Boron Uptake and Accumulation Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vig, B.S.; Huttunen, K.M.; Laine, K.; Rautio, J. Amino acids as promoieties in prodrug design and development. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1370–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, N.; Ferreira, A.; Matos, J.; Fresca, P.; Gouveia, M.J. Amino Acids in the Development of Prodrugs. Molecules 2018, 23, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Saklani, S.; Tantra, T.; Thareja, S. Amino Acid Derived Prodrugs: An Approach to Improve the Bioavailability of Clinically Approved Drugs. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 2170–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, J.E. Lisdexamfetamine: A Review in ADHD in Adults. CNS Drugs 2016, 30, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermer, J.C.; Pennick, M.; Frick, G. Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate: Prodrug Delivery, Amphetamine Exposure and Duration of Efficacy. Clin. Drug Investig. 2016, 36, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comiran, E.; Kessler, F.H.; Fröehlich, P.E.; Limberger, R.P. Lisdexamfetamine: A pharmacokinetic review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 89, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanious, A.J.; Asare, A.; Mitchison, D.; James, M.H. Patients perceptions of lisdexamfetamine as a treatment for binge eating disorder: An exploratory qualitative and quantitative analysis. Psychiatry Res. Commun. 2024, 4, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallement, G.; Renault, F.; Baubichon, D.; Peoc’h, M.; Burckhart, M.-F.; Galonnier, M.; Clarençon, D.; Jourdil, N. Compared efficacy of diazepam or avizafone to prevent soman-induced electroencephalographic disturbances and neuropathology in primates: Relationship to plasmatic benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics. Arch. Toxicol. 2000, 74, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbara, C.; Rousseau, J.M.; Turcant, A.; Lallement, G.; Comets, E.; Bardot, I.; Clair, P.; Diquet, B. Bioavailability of diazepam after intramuscular injection of its water-soluble prodrug alone or with atropine–pralidoxime in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.; Winter, T.; Lis, L.; Georg, G.I.; Siegel, R.A. Rapid Delivery of Diazepam from Supersaturated Solutions Prepared Using Prodrug/Enzyme Mixtures: Toward Intranasal Treatment of Seizure Emergencies. AAPS J. 2014, 16, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rautiola, D.; Maglalang, P.D.; Cheryala, N.; Nelson, K.M.; Georg, G.I.; Fine, J.M.; Svitak, A.L.; Faltesek, K.A.; Hanson, L.R.; Mishra, U.; et al. Intranasal co-administration of a diazepam prodrug with a converting enzymes results in rapid absorption of diazepam in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautiola, D.; Updyke, J.L.; Nelson, K.M.; Siegel, R.A. Diazepam Prodrug Stabilizes Human Aminopeptidase B during Lyophilization. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.A.; Kapoor, M.; Cheryala, N.; Georg, G.I.; Cloyd, J.C. Water-soluble benzodiazepine prodrug/enzyme combinations for intranasal rescue therapies. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 49, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.; Cheryala, N.; Rautiola, D.; Georg, G.I.; Cloyd, J.C.; Siegel, R.A. Chirally Pure Prodrugs and Their Converting Enzymes Lead to High Supersaturation and Rapid Transcellular Permeation of Benzodiazepines. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2365–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gynther, M.; Jalkanen, A.; Lehtonen, M.; Forsberg, M.; Laine, K.; Ropponen, J.; Leppänen, J.; Knuuti, J.; Rautio, J. Brain uptake of ketoprofen–lysine prodrug in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 399, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puris, E.; Gynther, M.; Huttunen, J.; Petsalo, A.; Huttunen, K.M. L-type amino acid transporter 1 utilizing prodrugs: How to achieve effective brain delivery and low systemic exposure of drugs. J. Control. Release 2017, 261, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaser, A.; Lehtonen, M.; Gynther, M.; Huttunen, K.M. L-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1-Utilizing Prodrugs of Ketoprofen Can Efficiently Reduce Brain Prostaglandin Levels. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Subudhi, B.B. Development and characterization of lysine-methotrexate conjugate for enhanced brain delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2327–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levit, G.L.; Radina, L.B.; Krasnov, V.P.; Gopko, V.F.; Peretolchina, N.M. Nω-Alkylnitrosocarbamoyl-α,ω-diaminocarboxylic acids. 2. Synthesis and antitumor activity of nitroso derivatives of Nω-(2-chloroethyl)-carbamoyl-α,ω-diaminocarboxylic acids. Pharm. Chem. J. 1996, 30, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levit, G.L.; Radina, L.B.; Krasnov, V.P.; Gopko, V.F.; Nikiforova, N.V.; Peretolchina, N.M. Nω-Alkylnitrosocarbamoyl-α,ω-diaminocarboxylic acids. 3. Synthesis and antitumor activity of Nε-nitroso-Nε-[N’-(2-chloroethyl)carbamoyl]-L-lysine and Nε-[N’-(2-chloroethyl)-N’-nitrosocarbamoyl]-L-lysine. Pharm. Chem. J. 1996, 30, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.R.; Graminski, G.F.; Weeks, R.S.; Chen, Y.; O’Brien, T.G. Lipophilic Lysine–Spermine Conjugates Are Potent Polyamine Transport Inhibitors for Use in Combination with a Polyamine Biosynthesis Inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, N.; Lee, S.; Sampson, N.S.; Hayman, M.J. Selective cancer targeting with prodrugs activated by histone deacetylases and a tumour-associated protease. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, N.; Wang, W.; Swenson, C.; McNaughton, C.; Sampson, N.S.; Hayman, M.J. Synthesis and Preclinical Evaluation of a Highly Improved Anticancer Prodrug Activated by Histone Deacetylases and Cathepsin L. Theranostics 2016, 6, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenora, L.; Alt, J.; Dash, R.P.; Gadiano, A.J.; Novotná, K.; Veeravalli, V.; Lam, J.; Kirkpatrick, Q.R.; Lemberg, K.M.; Majer, P.; et al. Tumor-Targeted Delivery of 6-Diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine (DON) Using Substituted Acetylated Lysine Prodrugs. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 3524–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Qu, K.; Zhao, P.; Yin, X.; Meng, Y.; Herdewijn, P.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Xia, X. Synthesis and anticancer evaluation of acetylated-lysine conjugated gemcitabine prodrugs. RSC Med. Chem. 2023, 14, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Zhanel, G.G.; Schweizer, F. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of amphiphilic lysine-ligated neomycin B conjugates. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwan, S.M.; Abdul-Wahab, A.-H.H. Synthesis of new derivatives of Ceftazidime as possible Prodrugs. Iraqi J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 22, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Domalaon, R.; Yang, X.; Schweizer, F. Amphiphilic lysine conjugated to tobramycin synergizes legacy antibiotics against wild-type and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pept. Sci. 2019, 111, e23091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konai, M.M.; Haldar, J. Lysine-Based Small Molecule Sensitizes Rifampicin and Tetracycline against Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Jiang, X.; Mei, Y.; Sun, J.; Ma, R.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Tian, H.; Sun, X. Role of ornithine decarboxylase in breast cancer. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2008, 40, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I.; Schultz, C.R.; Buras, A.L.; Friedman, E.; Fedorko, A.; Seamon, L.; Chandramouli, G.V.R.; Maxwell, G.L.; Bachmann, A.S.; Risinger, J.I. Ornithine decarboxylase as a therapeutic target for endometrial cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filisola-Villaseñor, J.G.; Arroyo-Sánchez, B.I.; Navarro-González, L.J.; Morales-Ríos, E.; Olin-Sandoval, V. Ornithine decarboxylase and its role in cancer. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2025, 765, 110321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiwata, K.; Abe, Y.; Matsuzawa, T.; Ido, T. Tumor Uptake Studies of D,L-[5-14C]Ornithine and D,L-2-Difluoromethyl[5-14C]Ornithine. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1988, 15, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkman, N.; Gelovani, J.G.; Alauddin, M.M. Radiosynthesis of N5-[18F]fluoroacetylornithine (N5-[18F]FAO) for PET imaging of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) in malignant tumors. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2011, 54, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoGiudice, N.; Le, L.; Abuan, I.; Leizorek, Y.; Roberts, S.C. Alpha-Difluoromethylornithine, an Irreversible Inhibitor of Polyamine Biosynthesis, as a Therapeutic Strategy against Hyperproliferative and Infectious Diseases. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Dong, W.; Yang, L.; Lu, K.; Guo, X.; Liu, H.; Wei, H.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; et al. Radiosynthesis and evaluation of N5-(2-18F-fluoropropanyl) ornithine as a potential agent for tumor PET imaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2021, 94–95, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qin, K.; Shi, D.; Wu, P.; Hao, X.; Liu, H.; Gao, J.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, S. A new 68Ga-labeled ornithine derivative for PET imaging of ornithine metabolism in tumors. Amino Acids 2023, 55, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangella, A.V.; Gajre, A.S.; Chirumamilla, P.C.; Rathhan, P.V. Difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) and Neuroblastoma: A Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e37680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA-Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, R.F.; Soloway, A.H.; Fairchild, R.G. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for Cancer. Sci. Am. 1990, 263, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coderre, J.A.; Turcotte, J.C.; Riley, K.J.; Binns, P.J.; Harling, O.K.; Kiger, W.S., III. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy: Cellular Targeting of High Linear Energy Transfer Radiation. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2003, 2, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozień, D.; Szermer-Olearnik, B.; Rapak, A.; Szczygiel, A.; Anger-Góra, N.; Boratyński, J.; Pajtasz-Piasecka, E.; Bućko, M.M.; Pędzich, Z. Boron-Rich Boron Carbide Nanoparticles as a Carrier in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy: Their Influence on Tumor and Immune Phagocytic Cells. Materials 2021, 14, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneviratne, D.; Advani, P.; Trifiletti, D.M.; Chumsri, S.; Beltran, C.J.; Bush, A.F.; Vallow, L.A. Exploring the Biological and Physical Basis of Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) as a Promising Treatment Frontier in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, L.; Li, Y. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy: Current Status and Challenges. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 788770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.H.; Seldon, C.; Butkus, M.; Sauerwein, W.; Giap, H.B. A Review of Boron Neutron Capture Therapy: Its History and Current Challenges. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2022, 9, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, R.F.; Gupta, N.; Kawabata, S. Evaluation of sodium borocaptate (BSH) and boronophenylalanine (BPA) as boron delivery agents for neutron capture therapy (NCT) of cancer: An update and a guide for the future clinical evaluation of new boron delivery agents for NCT. Cancer Commun. 2024, 44, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdev, D.A.; Levit, G.L.; Krasnov, V.P.; Charushin, V.N. Carborane-containing amino acids and peptides: Synthesis, properties and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 433, 213753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coghi, P.; Li, J.; Hosmane, N.S.; Zhu, Y. Next generation of boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) agents for cancer treatment. Med. Res. Rev. 2023, 43, 1809–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Huang, W.; Chu, F.; Zhu, T.; Feng, B.; Huang, S.; Hou, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, S.; Zeng, W. The Dawn of a New Era: Tumor-Targeting Boron Agents for Neutron Capture Therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 4942–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, J.; Pulkkinen, H.; Rautio, J.; Timonen, J.M. Amino Acid-Based Boron Carriers in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Li, R.; Lin, J.; Gui, L.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Xia, W.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, S.; et al. Novel promising boron agents for boron neutron capture therapy: Current status and outlook on the future. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 511, 215795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, M.; Cerecetto, H. Advancements in the Synthesis and Biological Properties of Carboranes and High-Boron Related Compounds: A Comprehensive Exploration with Emphasis on BNCT Applications. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2024, 35, e-20240109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdev, D.A.; Telegina, A.A.; Levit, G.L.; Solovieva, O.I.; Gusel’nikova, T.Y.; Razumov, I.A.; Krasnov, V.P.; Charushin, V.N. Carborane-Containing Folic Acid bis-Amides: Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Promising Agents for Boron Delivery to Tumour Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zaria, M.E.; Genady, A.R.; Janzen, N.; Petlura, C.I.; Beckford Vera, D.R.; Valliant, J.F. Preparation and evaluation of carborane-derived inhibitors of prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA). Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 4950–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, S.; Kim, K.I.; Ptacek, J.; Ok, K.; Novakova, Z.; Kim, Y.H.; Koo, J.H.; Barinka, C.; Byun, Y. Carborane-containing urea-based inhibitors of glutamate carboxypeptidase II: Synthesis and structural characterization. Bioorga. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5232–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matović, J.; Järvinen, J.; Sokka, I.K.; Imlimthan, S.; Raitanen, J.-E.; Montaser, A.; Maaheimo, H.; Huttunen, K.M.; Peräniemi, S.; Airaksinen, A.J.; et al. Exploring the Biochemical Foundations of a Successful GLUT1-Targeting Strategy to BNCT: Chemical Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of the Entire Positional Isomer Library of ortho-Carboranylmethyl-Bearing Glucoconjugates. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matović, J.; Bahrami, K.; Stockmann, P.; Sokka, I.K.; Khng, Y.C.; Sarparanta, M.; Hey-Hawkins, E.; Rautio, J.; Ekholm, F.S. Sweet Battle of the Epimers—Continued Exploration of Monosaccharide-Derived Delivery Agents for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 3127–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Masunaga, S.-i.; Harada, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Ueda, S.; Okuda, K.; Nagasawa, H. Synthesis and evaluation of cyclic RGD-boron cluster conjugates to develop tumor-selective boron carriers for boron neutron capture therapy. Bioorga. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppenz, P.; Els-Heindl, S.; Kellert, M.; Kuhnert, R.; Saretz, S.; Lerchen, H.-G.; Köbberling, J.; Riedl, B.; Hey-Hawkins, E.; Beck-Sickinger, A. A Selective Carborane-Functionalized Gastrin-Releasing Peptide Receptor Agonist as Boron Delivery Agent for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Cui, L.; Lu, S.; Xu, S. Amino acid metabolism in tumor biology and therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalise, M.; Console, L.; Rovella, F.; Galluccio, M.; Pochini, L.; Indiveri, C. Membrane Transporters for Amino Acids as Players of Cancer Metabolic Rewiring. Cells 2020, 9, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, C.; Thimon, C. Synthesis and Evaluation of Boronated Lysine and Bis(carboranylated) γ-Amino Acids as Monomers for Peptide Assembly. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 2004, 3828–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, V.M.; Frank, R.; Stadlbauer, S.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; Hey-Hawkins, E. Incorporation of ortho-Carbaboranyl-Nε-Modified L-Lysine into Neuropeptide Y Receptor Y1- and Y2-Selective Analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 2368–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, S.; Frank, R.; Hey-Hawkins, E.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; Schmidt, P. Manipulating Y receptor subtype activation of short neuropeptide Y analogs by introducing carbaboranes. Neuropeptides 2013, 47, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrens, V.M.; Frank, R.; Boehnke, S.; Schütz, C.L.; Hampel, G.; Iffland, D.S.; Bings, N.H.; Hey-Hawkins, E.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Receptor-Mediated Uptake of Boron-Rich Neuropeptide Y Analogues for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. ChemMedChem 2015, 10, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R.; Ahrens, V.M.; Boehnke, S.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; Hey-Hawkins, E. Charge-Compensated Metallacarborane Building Blocks for Conjugation with Peptides. ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellert, M.; Worm, D.J.; Hoppenz, P.; Sárosi, M.B.; Lönnecke, P.; Riedl, B.; Koebberling, J.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; Hey-Hawkins, E. Modular triazine-based carborane-containing carboxylic acids—Synthesis and characterization of potential boron neutron capture therapy agents made of readily accessible building blocks. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 10834–10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worm, D.J.; Hoppenz, P.; Els-Heindl, S.; Kellert, M.; Kuhnert, R.; Saretz, S.; Köbberling, J.; Riedl, B.; Hey-Hawkins, E.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Selective Neuropeptide Y Conjugates with Maximized Carborane Loading as Promising Boron Delivery Agents for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 2358–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzel, T.; Heß, T.; Waser, B.; Reubi, J.-C.; Roesch, F. closo-Borane Conjugated Regulatory Peptides Retain High Biological Affinity: Synthesis of closo-Borane Conjugated Tyr3-Octreotate Derivatives for BNCT. Bioconju. Chem. 2008, 19, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, S.; Kanoh, D.; Sato, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Nakamura, H. Maleimide-functionalized closo-dodecaborate albumin conjugates (MID-AC): Unique ligation at cysteine and lysine residues enables efficient boron delivery to tumor for neutron capture therapy. J. Control. Release 2016, 237, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worm, D.J.; Els-Heindl, S.; Kellert, M.; Kuhnert, R.; Saretz, S.; Koebberling, J.; Riedl, B.; Hey-Hawkins, E.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. A stable meta-carborane enables the generation of boron-rich peptide agonists targeting the ghrelin receptor. J. Pept. Sci. 2018, 24, e3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadarajan, A.; Hawthorne, M.F. Novel Carboranyl Amino Acids and Peptides: Reagents for Antibody Modification and Subsequent Neutron-Capture Studies. Bioconju. Chem. 1991, 2, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umano, M.; Uechi, K.; Uriuda, T.; Murayama, S.; Azuma, H.; Shinohara, A.; Liu, Y.; Ono, K.; Kirihata, M.; Yanagie, H.; et al. Tumor accumulation of ε-poly-lysines-based polyamines conjugated with boron clusters. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1765–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lützenburg, T.; Neundorf, I.; Scholz, M. Direct carborane-peptide conjugates: Synthesis and evaluation as non-natural lipopeptide mimetics. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2018, 213, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.J.; Khan, A.A.; Goswami, L.N.; Jalisatgi, S.S.; Hawthorne, M.F. A Trimodal Closomer Drug-Delivery System Tailored with Tracing and Targeting Capabilities. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 12715–12723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiue, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Kondo, N.; Kitamatsu, M.; Bin, F.; Nakajima, K.; Hirota, Y.; Kawabata, S.; Nishiki, T.; Ohmori, I.; et al. The acceleration of boron neutron capture therapy using multi-linked mercaptoundecahydrododecaborate (BSH) fused cell-penetrating peptide. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3396–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lützenburg, T.; Burdina, N.; Scholz, M.S.; Neundorf, I. Improving Membrane Activity and Cargo Delivery Efficacy of a Cell-Penetrating Peptide by Loading with Carboranes. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozień, D.; Krygowska, K.; Żeliszewska, P.; Szczygiel, A.; Rudawska, A.; Szermer-Olearnik, B.; Rusiniak, P.; Wątor, K.; Węgierek-Ciura, K.; Jeleń, P.; et al. Surface-Modified Ceramic Boron Carbide as a Platform for Specific Targeting in Tumour Environments. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdev, D.A.; Levit, G.L.; Bazhov, I.V.; Demin, A.M.; Sadretdinova, L.S.; Ol’shevskaya, V.A.; Kalinin, V.N.; Krasnov, V.P.; Chupakhin, O.N. Synthesis of novel carboranyl derivatives of α-amino acids. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2010, 59, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdev, D.A.; Chulakov, E.N.; Levit, G.L.; Krasnov, V.P. Synthesis of purine conjugates with bis-carboranyl derivatives of (S)-lysine or (S)-glutamic acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2023, 127, 154686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdev, D.A.; Vakhrushev, A.V.; Demin, A.M.; Baryshnikova, M.A.; Levit, G.L.; Krasnov, V.P.; Charushin, V.N. Synthesis of closo- and nido-carborane derivatives of the KRGD peptide. J. Organomet. Chem. 2024, 1008, 123052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdev, D.A.; Telegina, A.A.; Ol’shevskaya, V.A.; Andronova, V.L.; Galegov, G.A.; Zarubaev, V.V.; Levit, G.L.; Krasnov, V.P. New nido-carborane-containing conjugates of purine: Synthesis and antiviral activity. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2022, 71, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdev, D.A.; Telegina, A.A.; Chulakov, E.N.; Levit, G.L.; Krasnov, V.P. (7,8-Dicarba-nido-undecaboran-7-yl)acetic acid: Synthesis of individual enantiomers and the first example of the determination of the absolute configuration of chiral monosubstituted nido-carborane. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 17338–17347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdev, D.A.; Levit, G.L.; Olshevskaya, V.A.; Krasnov, V.P. Synthesis of ortho-Carboranyl Derivatives of (S)-Asparagine and (S)-Glutamine. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 53, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdev, D.A.; Telegina, A.A.; Levit, G.L.; Krasnov, V.P. N-Aminoacyl-3-amino-nido-carboranes as a Group of Boron-Containing Derivatives of Natural Amino Acids. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 5437–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musiyak, V.V.; Gruzdev, D.A.; Kravchenko, M.A.; Vakhrusheva, D.V.; Levit, G.L.; Krasnov, V.P.; Charushin, V.N. Synthesis and antimycobacterial activity of purine conjugates with (S)-lysine and (S)-ornithine. Mendeleev Commun. 2019, 29, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, B.; Schnörwangen, E.; Kämpchen, T.; Mordvintcev, P.; Mülsch, A. Synthesis of 15Nω-Hydroxy-L-aginine and ESR and 15N-NMR Studies for the Elucidation of the Molecular Mechanism of Enzymic Nitric Oxide Formation from L-Arginine. Arch. Pharm. 1994, 327, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekner, T.; Li, X.; Lee, M.M.; Chan, M.K. A Pyrrolysine Analogue for Protein Click Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 1633–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, D.; Jeong, J.M.; Ju, C.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, D.S.; Chung, J.-K.; Lee, M.C. Synthesis and evaluation of macrocyclic amino acid derivatives for tumor imaging by gallium-68 positron emission tomography. Bioorga. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 7338–7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, M.A.; Gill, W.R.; Herbertson, P.L.; MacBride, J.A.H.; Wade, K.; Colquhoun, H.M. Deboronation of C-substituted ortho- and meta-closo-carboranes using “wet” fluoride ion solutions. Polyhedron 1996, 15, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Hwang, J.-W.; Do, Y. Facile and Mild Deboronation of o-Carboranes Using Cesium Fluoride. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Zaria, M.E.; Janzen, N.; Valliant, J.F. Room-Temperature Synthesis of Re(I) and Tc(I) Metallocarboranes. Organometallics 2012, 31, 5940–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telegina, A.A.; Gruzdev, D.A.; Levit, G.L.; Krasnov, V.P. Synthesis of a novel planar-chiral nido-carborane amino acid. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2021, 70, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, J.N.; Piwinski, J.J.; Skiles, J.W.; Regan, J.R.; Menard, P.R.; Desai, R.; Golec, F.S.; Reilly, L.W.; Goetzen, T.; Ueng, D.-N.; et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors. 9. Novel [[N-(1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)amino]acyl]glycine Derivatives with Diuretic Activity. J. Med. Chem. 1990, 33, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baut, D.A.; Tanaka, N.; Yokoo, R.; Usuki, T. Preparation of isodesmosine-KLH conjugate for ELISA system. Chirality 2020, 32, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janoušek, Z.; Kaszynski, P. Heterodisubstituted 1,10-dicarba-closo-decaboranes from substituted nido-carborane precursors. Polyhedron 1999, 18, 3517–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tok, O.L.; Holub, J.; Růžička, A.; Růžičková, Z.; Štíbr, B. Direct synthesis of dicarbollides. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 8524–8529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida, O.; Kanai, Y.; Chairoungdua, A.; Kim, D.K.; Segawa, H.; Nii, T.; Cha, S.H.; Matsuo, H.; Fukushima, J.; Fukasawa, Y.; et al. Human L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1): Characterization of function and expression in tumor cell lines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1514, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Ecker, G.F. Insights into the Structure, Function, and Ligand Discovery of the Large Neutral Amino Acid Transporter 1, LAT1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, H.-C.; Colas, C.; Finke, K.; Springer, S.; Stoner, L.; Zur, A.A.; Venteicher, B.; Campbell, J.; Hall, C.; Flint, A.; et al. Reevaluating the Substrate Specificity of the L-Type Amino Acid Transporter (LAT1). J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 7358–7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichert, W. HDAC expression and clinical prognosis in human malignancies. Cancer Lett. 2009, 280, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Wang, F.; Elhassan, R.M.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, X.; Chen, W.; Fang, H.; Hou, X. Targeting histone deacetylases for cancer therapy: Trends and challenges. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2425–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čemažar, M.; Škrk, J.; Mitrovič, B.; Serša, G. Changed delivery of boron to tumours using electroporation for boron neutron capture therapy with BSH. Br. J. Radiol. 2000, 73, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpano, M.; Perona, M.; Rodriguez, C.; Nievas, S.; Olivera, M.; Santa Cruz, G.A.; Brandizzi, D.; Cabrini, R.; Pisarev, M.; Juvenal, G.; et al. Experimental studies of boronophenylalanine (10BPA) biodistribution for the individual application of boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) for malignant melanoma treatment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 93, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermawan, A.; Susidatri, R.A.; Ramadani, R.D.; Qodria, L.; Utomo, R.Y.; Ishimura, M.; Hattori, Y.; Ohta, Y.; Kirihata, M.; Meiyanto, E. Cellular uptake evaluation of pentagamaboronon-0 (PGB-0) for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) against breast cancer cells. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 37, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, B.C.; Bode, B.P. Amino acid transporters ASCT2 and LAT1 in cancer: Partners in crime? Semin. Cancer Biol. 2005, 15, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, S.; Nielsen, C.U. Exploring Amino Acid Transporters as Therapeutic Targets for Cancer: An Examination of Inhibitor Structures, Selectivity Issues, and Discovery Approaches. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shennan, D.B.; Thomson, J.; Barber, M.C.; Travers, M.T. Functional and molecular characteristics of system L in human breast cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1611, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liang, Z.; Cho, H.T.; Williams, L.; Zhu, A.; Liang, K.; Huang, K.; Wu, H.; Jiang, C.; Hong, S.; Crowe, R.; et al. Potential Biomarker of L-type Amino Acid Transporter 1 in Breast Cancer Progression. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 45, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geldermalsen, M.; Wang, Q.; Nagarajah, R.; Marshall, A.D.; Thoeng, A.; Gao, D.; Ritchie, W.; Feng, Y.; Bailey, C.G.; Deng, N.; et al. ASCT2/SLC1A5 controls glutamine uptake and tumour growth in triple-negative basal-like breast cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaga, T.; Suehiro, J.; Wada, Y.; Sakurai, H. Induction of CTH expression in response to amino acid starvation confers resistance to anti-LAT1 therapy in MDA-MB-231 cells. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, H.; Han, Y.; Li, X.; Zou, Q.; Yuan, S.; Sun, L. ASCT2 Regulates Fatty Acid Metabolism to Trigger Glutamine Addiction in Basal-like Breast Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, S.; Hanazono, K.; Fu, D.-R.; Endo, Y.; Kadosawa, T.; Iwano, H.; Uchide, T. A new treatment for human malignant melanoma targeting L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1): A pilot study in a canine model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, A.; Kyoichi, K.; Kato, M.; Yasuda, M.; Takahashi, A.; Tominaga, H.; Oriuchi, N.; Nagamori, S.; Kanai, Y.; Oyama, T.; et al. Prognostic significance of L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) expression in cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2015, 25, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisongkram, T.; Weerapreeyakul, N.; Kärkkäinen, J.; Rautio, J. Role of L-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (LAT1) for the Selective Cytotoxicity of Sesamol in Human Melanoma Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Kaneda-Nakashima, K.; Ohgaki, R.; Xu, M.; Okanishi, H.; Endou, H.; Nagamori, S.; Kanai, Y. Inhibition of cancer-type amino acid transporter LAT1 suppresses B16-F10 melanoma metastasis in mouse models. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhirajan, R.K.; Meyer, D.; Sagwal, S.K.; Weltmann, K.-D.; von Woedtke, T.; Bekeschus, S. The amino acid metabolism is essential for evading physical plasma-induced tumour cell death. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coderre, J.A.; Glass, J.D.; Fairchild, R.G.; Roy, U.; Cohen, S.; Fand, I. Selective Targeting of Boronophenylalanine to Melanoma in BALB/c Mice for Neutron Capture Therapy. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 6377–6383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mishima, Y.; Honda, C.; Ichihashi, M.; Obara, H.; Hiratsuka, J.; Fukuda, H.; Karashima, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Kanda, K.; Yoshino, K. Treatment of malignant melanoma by single thermal neutron capture therapy with melanoma-seeking 10B-compound. Lancet 1989, 334, 388–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, H.; Honda, C.; Wadabayashi, N.; Kobayashi, T.; Yoshino, K.; Hiratsuka, J.; Takahashi, J.; Akaizawa, T.; Abe, Y.; Ichihashi, M.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of 10B-boronophenylalanine in tumours, skin and blood of melanoma patients: A study of boron neutron capture therapy for malignant melanoma. Melanoma Res. 1999, 9, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiratsuka, J.; Kamitani, N.; Tanaka, R.; Tokiya, R.; Yoden, E.; Sakurai, Y.; Suzuki, M. Long-term outcome of cutaneous melanoma patients treated with boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). J. Radiat. Res. 2020, 61, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, K.-W.; Huang, W.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Hsu, F.-T.; Chien, Y.-C.; Hsiau, Y.-Y.; Wang, T.-W.; Keng, P.Y. In vivo investigation of boron-rich nanodrugs for treating triple-negative breast cancers via boron neutron capture therapy. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 155, 213699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, T.; Maekawa, Y.; Hori, S.; Oguro, A.; Hori, A.; Fujita, I.; Sakurai, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Ito, T.; Yahiro, S.; et al. Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) for left axillary lymph node metastasis of recurrent breast cancer. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2025, 219, 111715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashihara, T.; Nakamura, S.; Yamazaki, N.; Takahashi, A.; Namikawa, K.; Ogata, D.; Nakano, E.; Okuma, K.; Kaneda, T.; Mori, T.; et al. Boron neutron capture therapy for cutaneous angiosarcoma and malignant melanoma: First in-human phase I clinical trial. Radiother. Oncol. 2025, 202, 110607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haushalter, R.C.; Butler, W.M.; Rudolph, R.W. The Preparation and Characterization of Several meso-Tetracarboranylporphyrins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, B.; Balk, S.; Stadlbauer, S.; König, B. Dynamic Interface Imprinting: High-Affinity Peptide Binding Sites Assembled by Analyte-Induced Recruiting of Membrane Receptors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10060–10063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armarego, W.L.F.; Chai, C.L.L. Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 6th ed.; Butterworth Heinemann: Waltham, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Adv. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedatella, S.; Cerchia, C.; Manfra, M.; Cioce, A.; Bolognese, A.; Lavecchia, A. Antitumor agents 7. Synthesis, antiproliferative activity and molecular modeling of new L-lysine-conjugated pyridophenoxazinones as potent DNA-binding ligands and topoisomerase IIα inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 187, 111960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsygankova, A.R.; Kanygin, V.V.; Kasatova, A.I.; Zav’yalov, E.L.; Gusel’nikova, T.Y.; Kichigin, A.I.; Mukhamadiyarov, R.A. Determination of boron by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. Biodistribution of 10B in tumor-bearing mice. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2020, 69, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
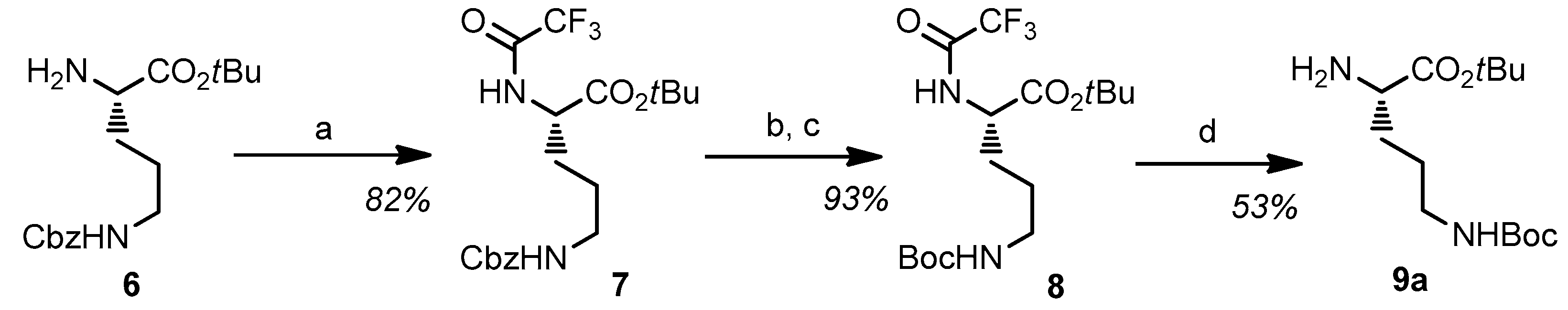
| Compound | Cell Line | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BJ-5ta | DU 145 | MDA-MB-231 | SK-Mel 28 | T98G | U87MG | |
| 5a | 0.82 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 1.76 | n.d. | n.d. |
| 5b | 1.78 | 0.57 | 0.68 | 0.56 | 0.27 | 0.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gruzdev, D.A.; Levit, G.L.; Musiyak, V.V.; Telegina, A.A.; Ganebnykh, I.N.; Ezhikova, M.A.; Kodess, M.I.; Solovieva, O.I.; Gusel’nikova, T.Y.; Razumov, I.A.; et al. Nido-Carborane Derivatives of (S)-Ornithine and (S)-Lysine as Potential Boron Delivery Agents: Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178560
Gruzdev DA, Levit GL, Musiyak VV, Telegina AA, Ganebnykh IN, Ezhikova MA, Kodess MI, Solovieva OI, Gusel’nikova TY, Razumov IA, et al. Nido-Carborane Derivatives of (S)-Ornithine and (S)-Lysine as Potential Boron Delivery Agents: Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178560
Chicago/Turabian StyleGruzdev, Dmitry A., Galina L. Levit, Vera V. Musiyak, Angelina A. Telegina, Ilya N. Ganebnykh, Marina A. Ezhikova, Mikhail I. Kodess, Olga I. Solovieva, Tatiana Y. Gusel’nikova, Ivan A. Razumov, and et al. 2025. "Nido-Carborane Derivatives of (S)-Ornithine and (S)-Lysine as Potential Boron Delivery Agents: Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178560
APA StyleGruzdev, D. A., Levit, G. L., Musiyak, V. V., Telegina, A. A., Ganebnykh, I. N., Ezhikova, M. A., Kodess, M. I., Solovieva, O. I., Gusel’nikova, T. Y., Razumov, I. A., & Krasnov, V. P. (2025). Nido-Carborane Derivatives of (S)-Ornithine and (S)-Lysine as Potential Boron Delivery Agents: Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178560







