Theranostic Radiopharmaceuticals of Somatostatin Receptors for Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors: Agonists Versus Antagonists—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
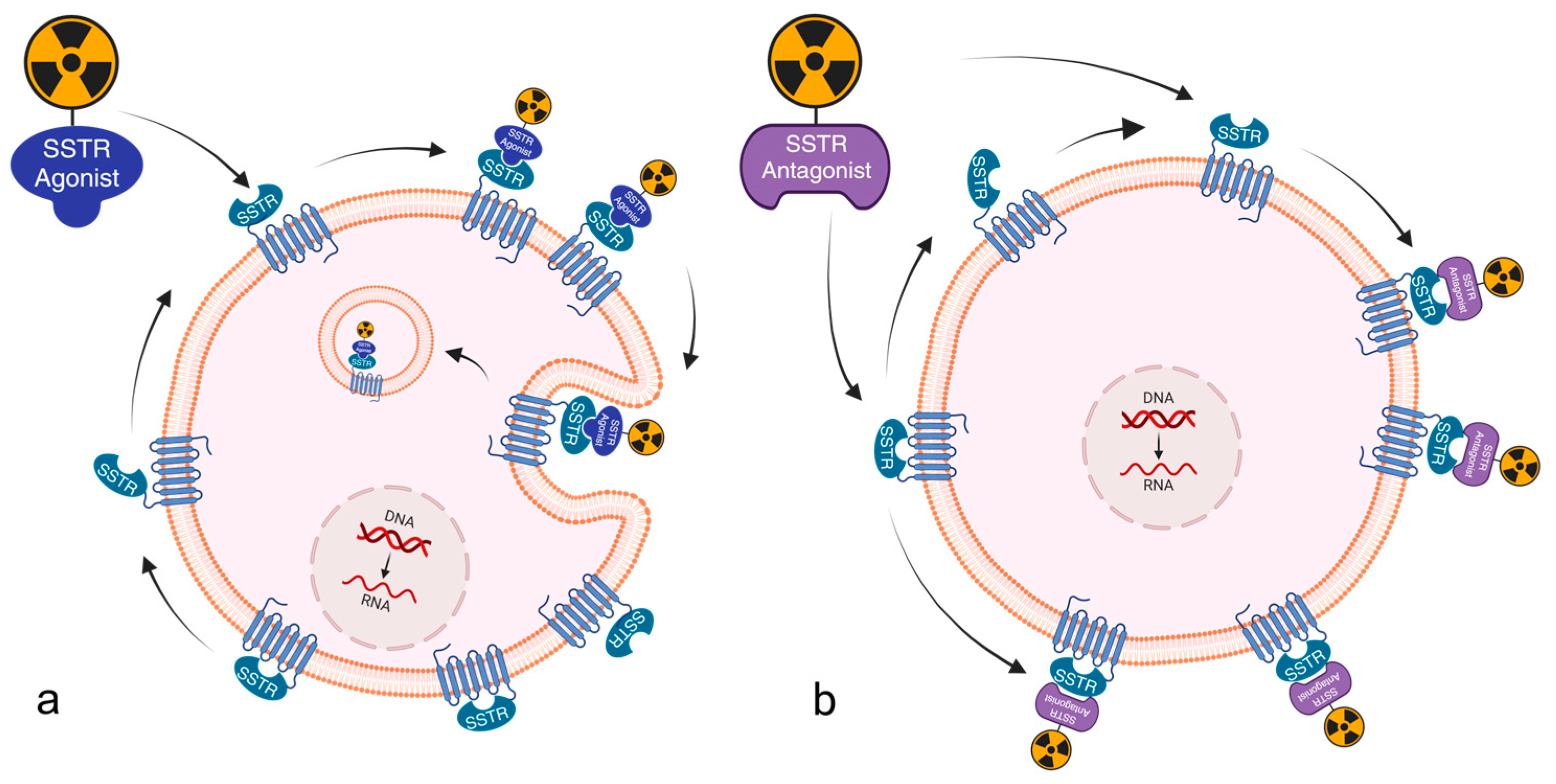
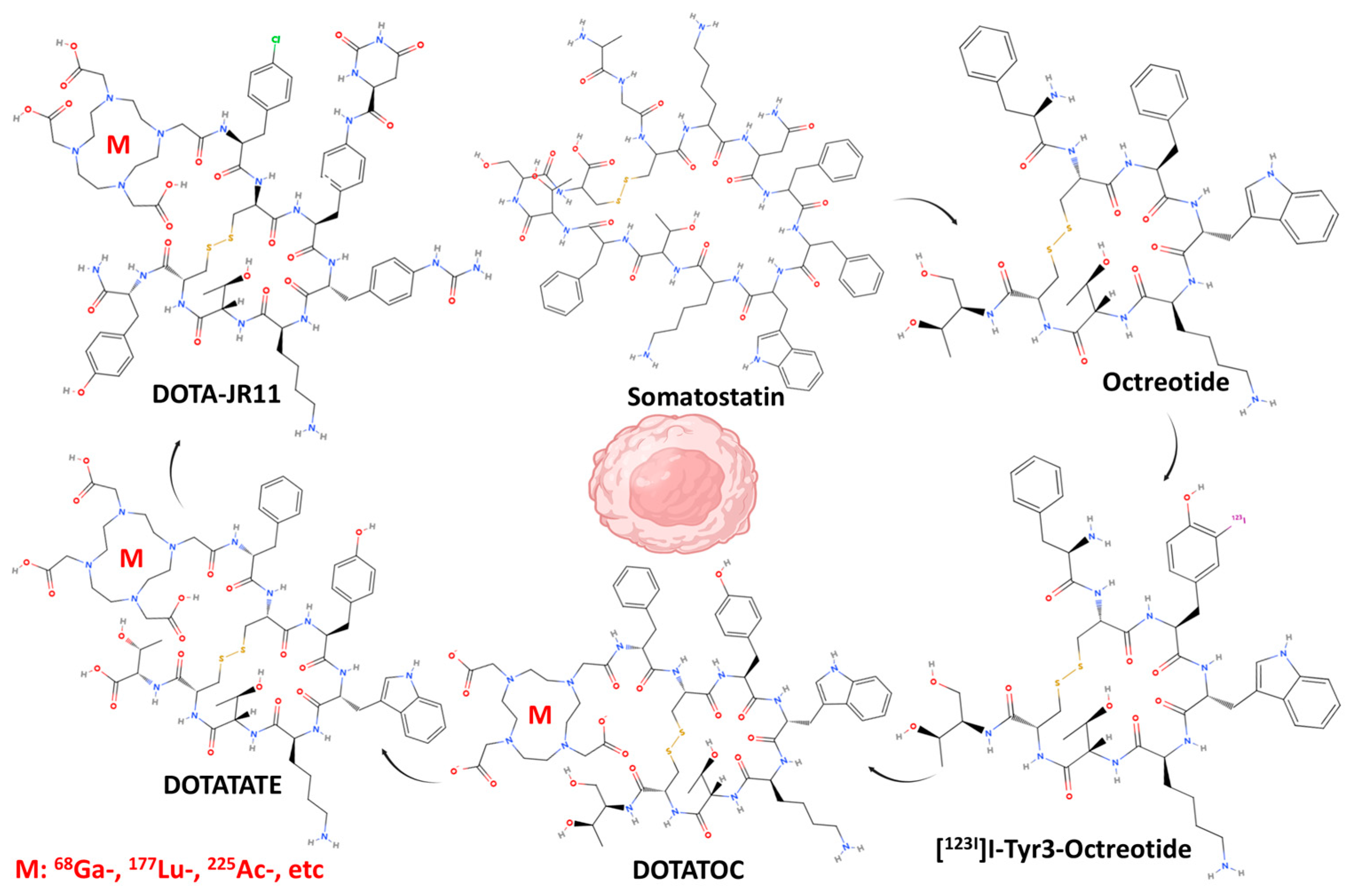
1. Introduction
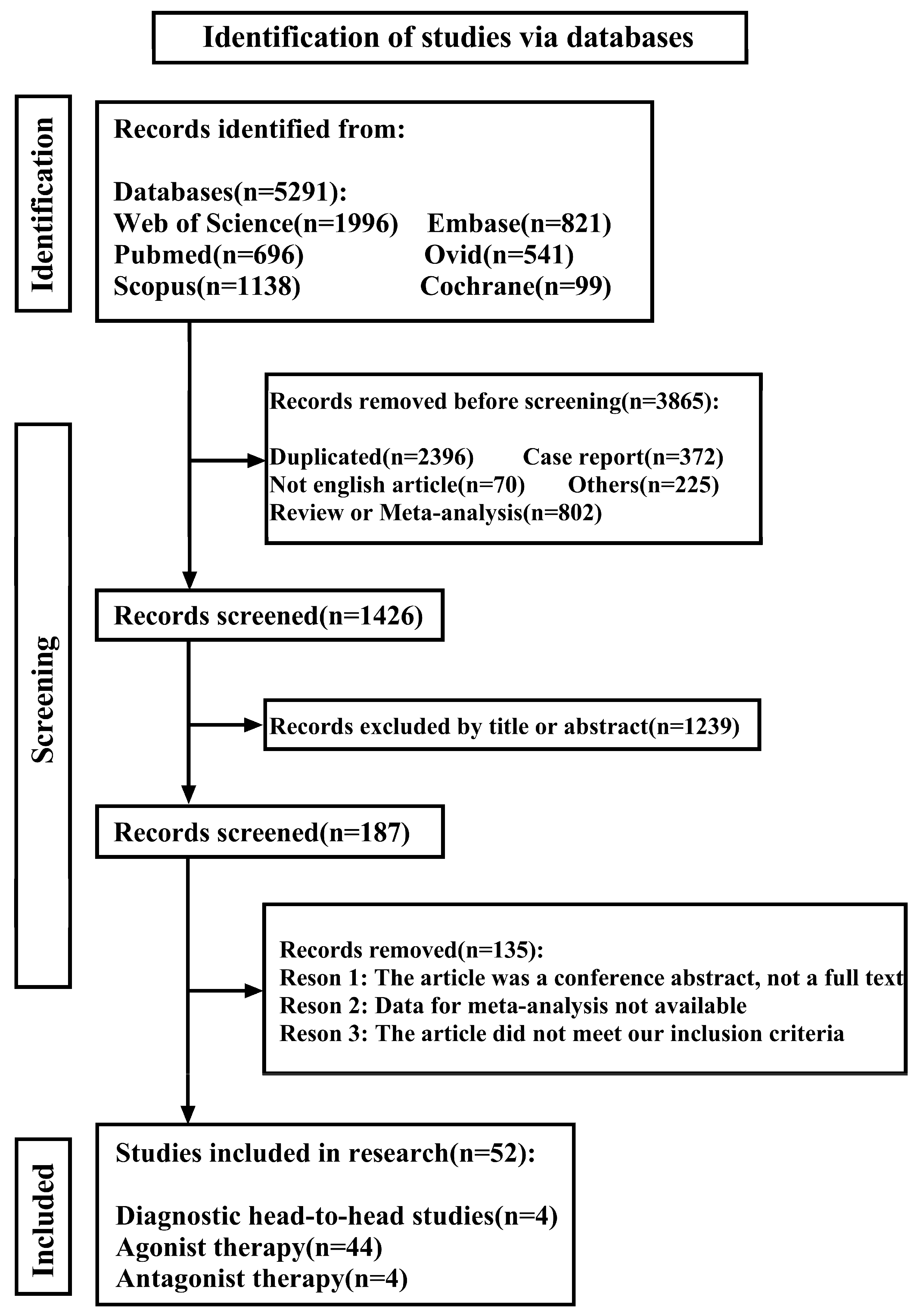
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
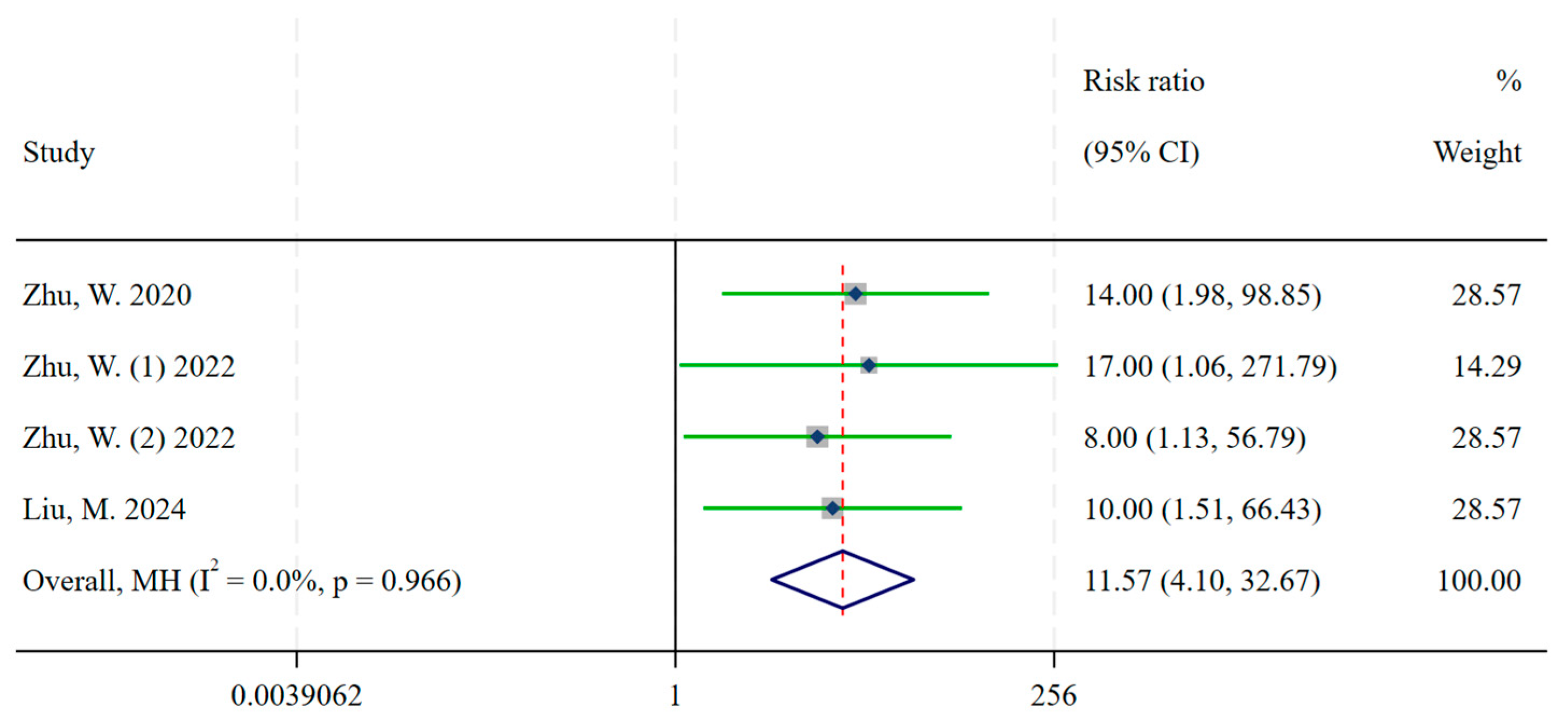
3.1. Diagnosis
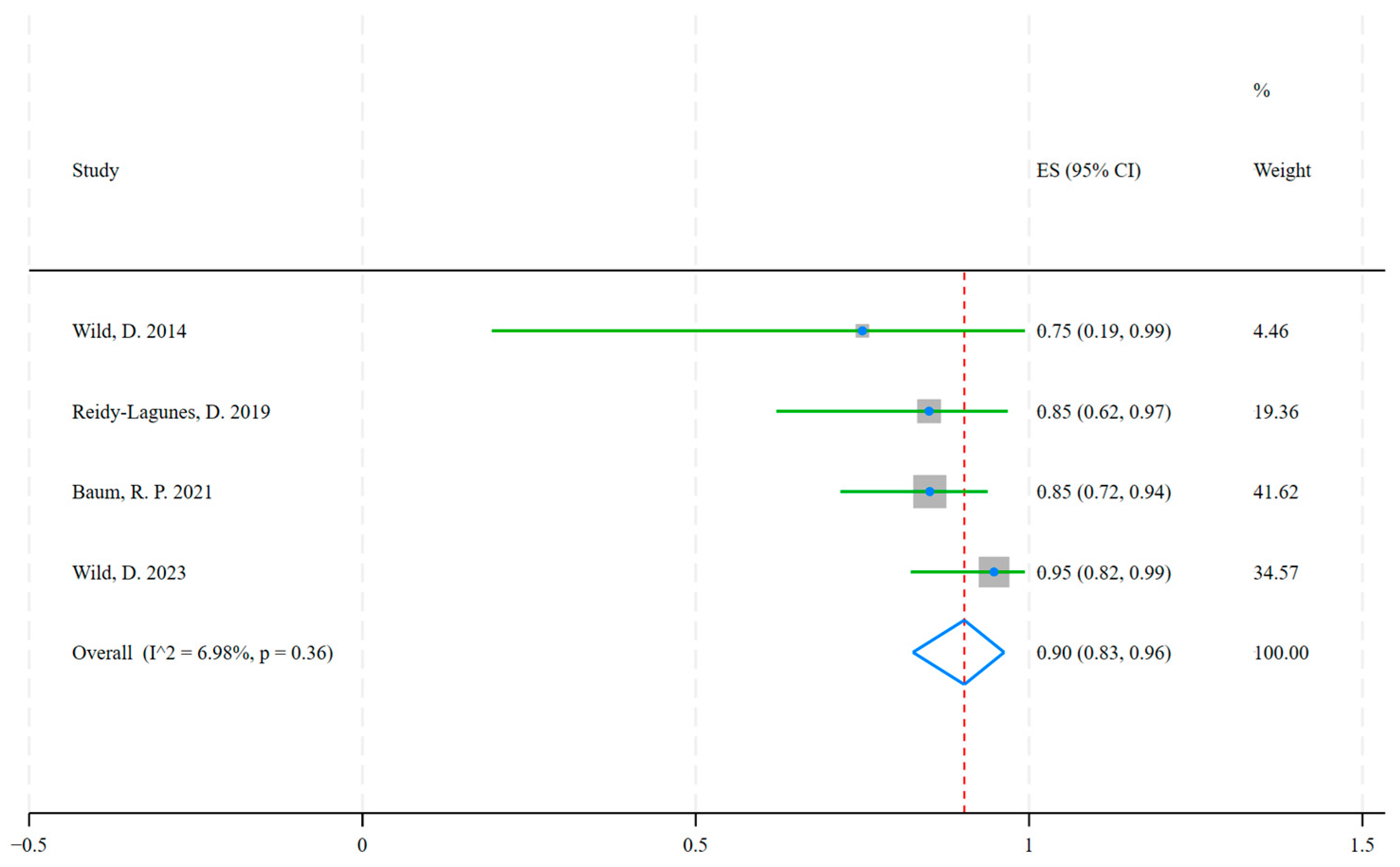
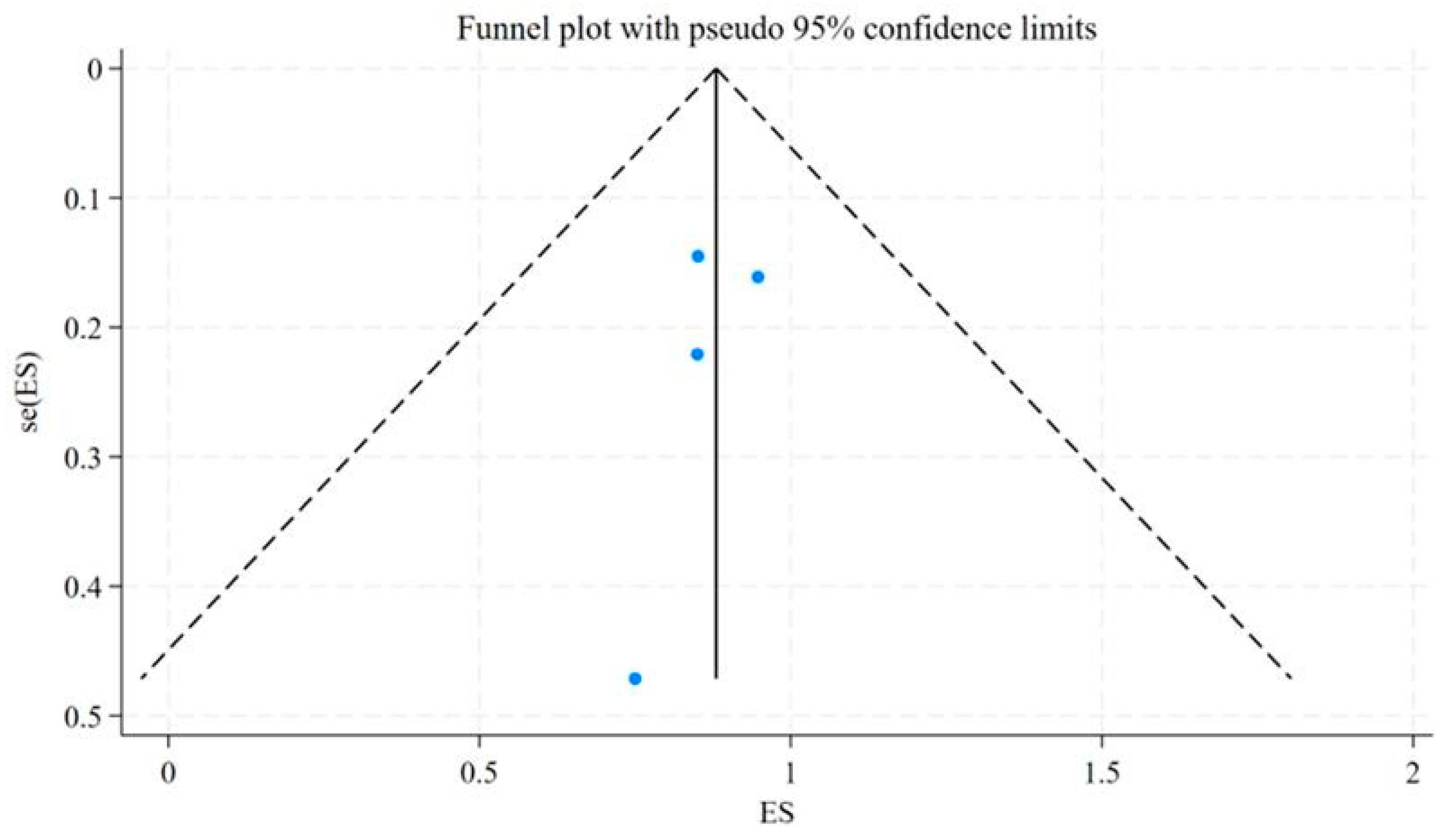
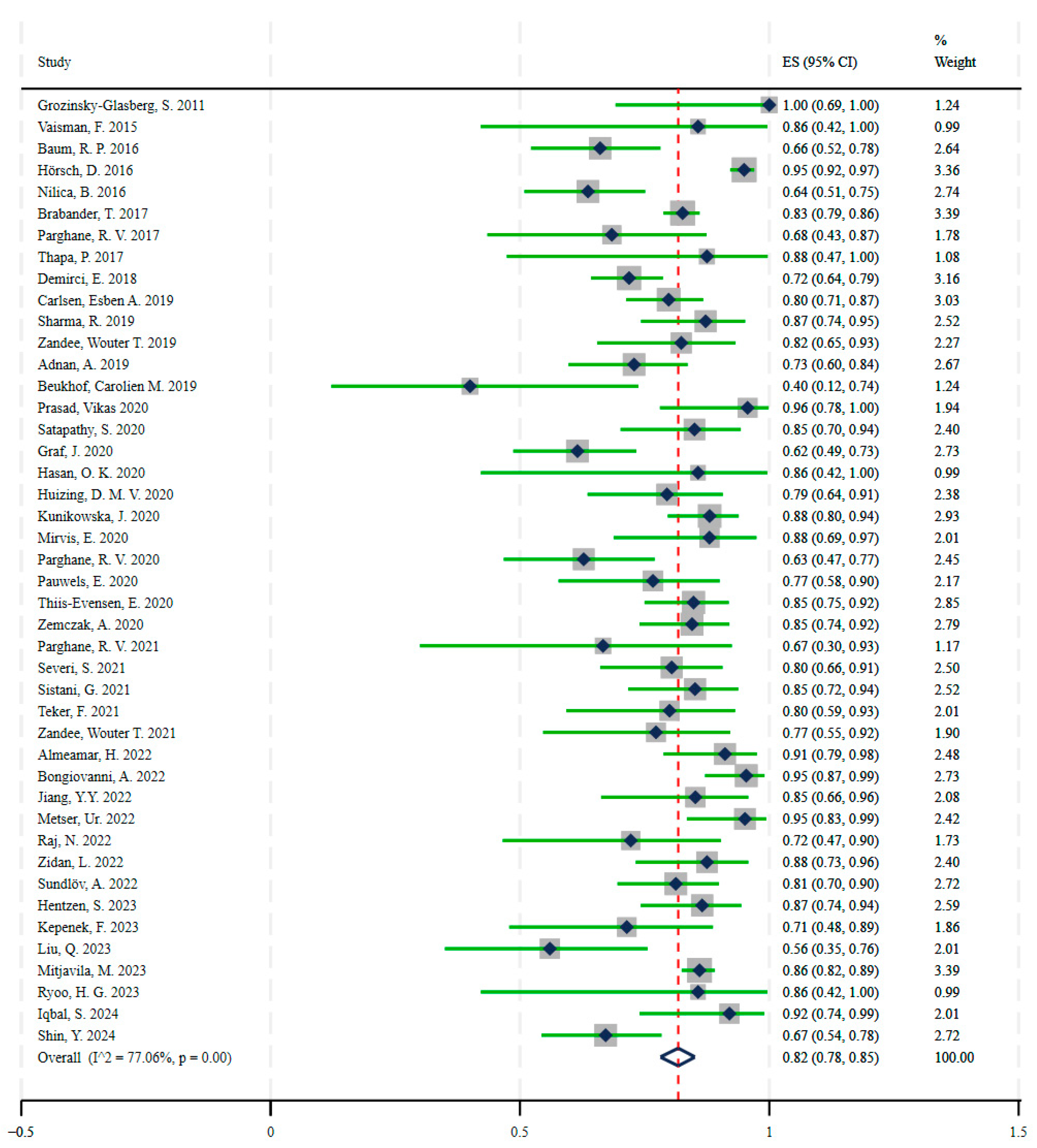
3.2. Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NENs | Neuroendocrine neoplasms |
| NETs | Neuroendocrine tumors |
| NECs | Neuroendocrine carcinomas |
| RR | Risk Ratio |
| ES | Effect Size |
| SSTR | Satostatin Receptor |
| PRRT | Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Evaluations and Meta-Analyses |
| TBR | Tumor-to-Background Ratios |
| SSA | Somatostatin Analogs |
| MR | Minor Response |
| CR | Complete Response |
| PR | Partial Response |
| SD | Stable Disease |
| DCR | Disease Control Rate |
| MH | Mantel-Haenszel model |
Appendix A
| ((((“Neuroendocrine Tumors”[Mesh]) OR (((((Neuroendocrine Tumor[Title/Abstract]) OR (Tumor, Neuroendocrine[Title/Abstract])) OR (Tumors, Neuroendocrine[Title/Abstract])) OR (NETs[Title/Abstract])) OR (NET[Title/Abstract]))) AND ((“Receptors, Somatostatin”[Mesh]) OR ((((((Somatostatin Receptor[Title/Abstract]) OR (Receptor, Somatostatin[Title/Abstract])) OR (Somatostatin Receptors[Title/Abstract])) OR (Receptors, Somatotropin Release Inhibiting Hormone[Title/Abstract])) OR (Receptors, SRIH[Title/Abstract])) OR (SRIH Receptors[Title/Abstract])))) AND ((((((((((“agonists” [Subheading]) OR (“antagonists and inhibitors” [Subheading])) OR (((antagonists[Title/Abstract]AND inhibitors[Title/Abstract]) OR (antagonists[Title/Abstract])) OR (inhibitors[Title/Abstract]))) OR ((“gallium Ga 68 DOTATATE” [Supplementary Concept]) OR ((((((((((((((DOTATATE gallium ga-68[Title/Abstract]) OR (gallium 68 DOTA-octreotide[Title/Abstract])) OR (gallium (68ga) dota-tate[Title/Abstract])) OR (gallium-dota-octreotate, ga-68[Title/Abstract])) OR (gallium DOTATATE, ga-68[Title/Abstract])) OR (gallium 68 DOTATATE[Title/Abstract])) OR (68Ga-DOTATATE[Title/Abstract])) OR (68gallium-DOTA-Tyr(3)-Thr(8)-octreotate[Title/Abstract])) OR (edotreotide gallium ga-68[Title/Abstract])) OR (gallium ga-68 edotreotide[Title/Abstract])) OR (gallium edotreotide ga-68[Title/Abstract])) OR (gallium ga 68-dotatoc[Title/Abstract])) OR (Ga-68 dota0-tyr3-octreotide[Title/Abstract])) OR (gallium Ga 68-edotreotide[Title/Abstract])))) OR ((“68Ga-DOTANOC” [Supplementary Concept]) OR (68Ga-DOTA-NOC[Title/Abstract]))) OR ((“Ga(III)-DOTATOC” [Supplementary Concept]) OR (((67Ga-DOTATOC[Title/Abstract]) OR (gallium-68 DOTATOC[Title/Abstract])) OR (68Ga-DOTATOC[Title/Abstract])))) OR ((“lutetium Lu 177 DOTATATE” [Supplementary Concept]) OR ((((((((177lutetium-DOTA-O-Tyr3-octreotate[Title/Abstract]) OR (lutetium 177Lu oxodotreotide[Title/Abstract])) OR (Lu-177 DOTATE[Title/Abstract])) OR (177Lu-DOTAOTyr3-octreotate[Title/Abstract])) OR (DOTATATE-177Lu[Title/Abstract])) OR (177Lu-DOTATATE[Title/Abstract])) OR (lutetium oxodotreotide Lu-177[Title/Abstract])) OR (Lutathera[Title/Abstract])))) OR ((“177Lu-octreotide, DOTA(0)-Tyr(3)-” [Supplementary Concept]) OR ((177Lu-octreotide, DOTA0, tyrosyl3-[Title/Abstract]) OR (177Lu-DOTATOC[Title/Abstract])))) OR ((((((68Ga-DOTA-JR11[Title/Abstract]) OR (18F-AlF-NOTA-LM3[Title/Abstract])) OR (68Ga-OPS202[Title/Abstract])) OR (68Ga-NODAGA-JR11[Title/Abstract])) OR (111In-DTPA-octreotide[Title/Abstract])) OR (68Ga-DATA(5m)-LM4[Title/Abstract]))) OR (((((177Lu-DOTA-JR11[Title/Abstract]) OR (177Lu-DOTA-LM3[Title/Abstract])) OR (tetulomab tetraxetan lu-177[Title/Abstract])) OR (177LU-DOTA-HH1[Title/Abstract])) OR (177Lu-Satoreotide Tetraxetan[Title/Abstract])))) AND ((((Theranostics[Title/Abstract]) OR (Theranostic[Title/Abstract])) OR ((“Therapeutics”[Mesh]) OR (((((Therapeutic[Title/Abstract]) OR (Therapy[Title/Abstract])) OR (Therapies[Title/Abstract])) OR (Treatment[Title/Abstract])) OR (Treatments[Title/Abstract])))) OR ((“Diagnosis”[Mesh]) OR ((((((((((((((Diagnoses[Title/Abstract]) OR (Diagnose[Title/Abstract])) OR (Diagnoses[Title/Abstract]AND Examinations[Title/Abstract])) OR (Diagnoses[Title/Abstract]AND Examination[Title/Abstract])) OR (Examination[Title/Abstract]AND Diagnoses[Title/Abstract])) OR (Examinations[Title/Abstract]AND Diagnoses[Title/Abstract])) OR (Antemortem Diagnosis[Title/Abstract])) OR (Antemortem Diagnoses[Title/Abstract])) OR (Diagnoses, Antemortem[Title/Abstract])) OR (Diagnosis, Antemortem[Title/Abstract])) OR (Postmortem Diagnosis[Title/Abstract])) OR (Diagnoses, Postmortem[Title/Abstract])) OR (Diagnosis, Postmortem[Title/Abstract])) OR (Postmortem Diagnoses[Title/Abstract])))) |
| Study | Year | Country | Neuroendocrine Tumor Types | Event_Exp 1 | Total_Exp 2 | Radiopharmaceuticals_Exp | Event_Ctrl 3 | Total_Ctrl 4 | Radiopharmaceuticals_Ctrl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhu, W. | 2020 | China | Metastatic, Well-Differentiated NETs | 14 | 26 | [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-JR11 | 1 | 26 | [68Ga]Ga-DOTATATE |
| Zhu, W. (1) | 2022 | China | Well-differentiated NETs | 8 | 16 | [68Ga]Ga-NODAGA-LM3 | 0 | 16 | [68Ga]Ga-DOTATATE |
| Zhu, W. (2) | 2022 | China | Well-differentiated NETs | 8 | 16 | [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-LM3 | 1 | 16 | [68Ga]Ga-DOTATATE |
| Liu, M. | 2024 | China | Well-differentiated NETs | 10 | 12 | [18F]AlF-NOTA-LM3 | 1 | 12 | [68Ga]Ga-DOTATATE |
| Study | Year | Country | Event (DCR = CR + PR + SD) **** | Total | Neuroendocrine Tumor Types | Radiopharmaceuticals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grozinsky-Glasberg, S. | 2011 | Israel | 10 | 10 | Malignant Gastrinomas | [90Y]Y/[177Lu]Lu-DOTATOC |
| Vaisman, F. | 2015 | Brazil | 6 | 7 | Medullary Thyroid Cancer | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Baum, R. P. | 2016 | Germany | 37 | 56 | Gastroenteropancreatic and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATOC |
| Hörsch, D. | 2016 | Germany | 339 | 357 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Bronchial, and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu/[90Y]Y-DOTATOC/DOTATATE |
| Nilica, B. | 2016 | Austria | 42 | 66 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Pulmonary, and other NETs | [90Y]Y-DOTATOC/[177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Brabander, T. ** | 2017 | Netherlands | 366 | 443 | Gastroenteropancreatic and Bronchial NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Parghane, R. V. * | 2017 | India | 13 | 19 | Pulmonary NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Thapa, P. | 2017 | India | 7 | 8 | Thymu, Mediastinum, Ureter, Esophagus, and Sacral NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Demirci, E. | 2018 | Turkey | 115 | 160 | Bronchial, Pancreatic, Nonpancreatic Gastroenteropancreatic-NETs, Pheochromocytoma–Paraganglioma, and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Carlsen, Esben A. | 2019 | Europe | 91 | 114 | Gastroenteropancreatic and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu/[90Y]Y/[111In]In-DOTATOC/DOTATATE |
| Sharma, R. | 2019 | England | 41 | 47 | Gastroenteropancreatic and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Zandee, Wouter T. | 2019 | Netherlands | 28 | 34 | Pancreatic NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Adnan, A. | 2019 | India | 43 | 59 | Gastroenteropancreatic, lung, other, and unknown | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Beukhof, Carolien M. | 2019 | Netherlands | 4 | 10 | Medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) | [177Lu]Lu-octreotate |
| Prasad, Vikas | 2020 | Europe, USA | 22 | 23 | Gastroenteropancreatic and lung-NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE/DOTATOC |
| Satapathy, S. | 2020 | India | 34 | 40 | Gastroenteropancreatic, lung, paraganglioma, MTC, and unknown | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Graf, J. | 2020 | Germany | 40 | 65 | Gastroenteropancreatic, pulmonary, and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATOC/[177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Hasan, O. K. | 2020 | Canada, Australia, Israel | 6 | 7 | Esthesioneuroblastoma | [111In]In/[90Y]Y/[177Lu]Lu-octreotide |
| Huizing, D. M. V. | 2020 | Netherlands | 31 | 39 | Gastroenteropancreatic and Pulmonary NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Kunikowska, J. | 2020 | Poland | 81 | 92 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Pulmonary, and other NETs | [90Y]Y/[177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Mirvis, E. | 2020 | England | 22 | 25 | Bronchial NETs | [90Y]Y/[177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Parghane, R. V. | 2020 | India | 27 | 43 | Medullary thyroid carcinoma | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Pauwels, E. | 2020 | Europe | 23 | 30 | Gastroenteropancreatic and other NETs | [90Y]Y-DOTATOC |
| Thiis-Evensen, E. | 2020 | Norway | 67 | 79 | Gastroenteropancreatic, pulmonary, and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-octreotate |
| Zemczak, A. | 2020 | Poland | 60 | 71 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Pulmonary, and other NETs | [90Y]Y/[177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Parghane, R. V. * | 2021 | India | 6 | 9 | Paraganglioma | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Severi, S. | 2021 | Italy | 37 | 46 | Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma | [90Y]Y-DOTATOC/[177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Sistani, G. | 2021 | Canada | 40 | 47 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Pulmonary, and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Teker, F. | 2021 | Turkey | 20 | 25 | Gastroenteropancreatic NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Zandee, Wouter T. | 2021 | Netherlands | 17 | 22 | Midgut NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Almeamar, H. | 2022 | Ireland, Sweden, England | 41 | 45 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Pulmonary, and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-octreotate |
| Bongiovanni, A. | 2022 | Italy | 62 | 65 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Pulmonary, and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Jiang, Y.Y. | 2022 | China, Singapore | 23 | 27 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Paraganglioma, and otherNETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE PRRT |
| Metser, Ur. | 2022 | Canada | 39 | 41 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Pulmonary, and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Raj, N. | 2022 | United States | 13 | 18 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Pulmonary, and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Zidan, L. | 2022 | Australia, United States, Israel, England | 35 | 40 | Pulmonary NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Sundlöv, A. | 2022 | Sweden | 52 | 64 | Gastroenteropancreatic and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Hentzen, S. | 2023 | United States | 45 | 52 | Gastroenteropancreatic NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Kepenek, F. | 2023 | Turkey | 15 | 21 | Gastroenteropancreatic NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Liu, Q. | 2023 | Germany, China | 14 | 25 | Medullary thyroid carcinoma | [90Y]Y/[177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE/DOTATOC/DOTANOC |
| Mitjavila, M. | 2023 | Spain | 381 | 443 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Pheochromocytoma, Paraganglioma, Pronchopulmonary, and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Ryoo, H. G. | 2023 | Korea | 6 | 7 | Gastroenteropancreatic NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Iqbal, S. | 2024 | United States | 23 | 25 | Gastroenteropancreatic and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Shin, Y. *** | 2024 | Korea | 43 | 64 | Gastroenteropancreatic NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE |
| Study | Year | Country | Events (DCR = CR + PR + SD) * | Total | Neuroendocrine Tumor Types | Radiopharmaceuticals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wild, D. | 2014 | Switzerland, Germany, United States | 3 | 4 | Bladder, Pulmonary, and Ileum NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-JR11 |
| Reidy-Lagunes, D. | 2019 | United States, Germany | 17 | 20 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Pulmonary, and Kidney NETs | [177Lu]Lu-satoreotide tetraxetan |
| Baum, R. P. | 2021 | Germany, Singapore | 40 | 47 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Pulmonary, and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-LM3 |
| Wild, D. | 2023 | Europe, Canada, Australia | 36 | 38 | Gastroenteropancreatic, Pulmonary, Paraganglioma, Pheochromocytoma and other NETs | [177Lu]Lu-satoreotide tetraxetan |


References
- Fortunati, E.; Bonazzi, N.; Zanoni, L.; Fanti, S.; Ambrosini, V. Molecular imaging Theranostics of Neuroendocrine Tumors. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2023, 53, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.; Barnett, E.; Rodger, E.J.; Chatterjee, A.; Subramaniam, R.M. Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Genetics and Epigenetics. PET Clin. 2023, 18, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, M.; Öberg, K.; Falconi, M.; Krenning, E.P.; Sundin, A.; Perren, A.; Berruti, A. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 844–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.H.; Goldner, W.S.; Benson, A.B.; Bergsland, E.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Brock, P.; Chan, J.; Das, S.; Dickson, P.V.; Fanta, P.; et al. Neuroendocrine and Adrenal Tumors, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc Netw. 2021, 19, 839–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagtegaal, I.D.; Odze, R.D.; Klimstra, D.; Paradis, V.; Rugge, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Washington, K.M.; Carneiro, F.; Cree, I.A. The 2019 WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. Histopathology 2020, 76, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hope, T.A.; Pavel, M.; Bergsland, E.K. Neuroendocrine Tumors and Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy: When Is the Right Time? J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2818–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, V.; Kunikowska, J.; Baudin, E.; Bodei, L.; Bouvier, C.; Capdevila, J.; Cremonesi, M.; de Herder, W.W.; Dromain, C.; Falconi, M.; et al. Consensus on molecular imaging and theranostics in neuroendocrine neoplasms. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 146, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modlin, I.M.; Oberg, K.; Chung, D.C.; Jensen, R.T.; de Herder, W.W.; Thakker, R.V.; Caplin, M.; Delle Fave, G.; Kaltsas, G.A.; Krenning, E.P.; et al. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenstra, M.J.; de Herder, W.W.; Feelders, R.A.; Hofland, L.J. Targeting the somatostatin receptor in pituitary and neuroendocrine tumors. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 1329–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindi, G.; Mete, O.; Uccella, S.; Basturk, O.; La Rosa, S.; Brosens, L.A.A.; Ezzat, S.; de Herder, W.W.; Klimstra, D.S.; Papotti, M.; et al. Overview of the 2022 WHO Classification of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Endocr. Pathol. 2022, 33, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Gervaso, L.; Frigè, G.; Spada, F.; Benini, L.; Cella, C.A.; Mazzarella, L.; Fazio, N. The Role of Liquid Biopsy in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Cancers 2024, 16, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, E.S.; Ziv, E. Neuroendocrine Tumors: Genomics and Molecular Biomarkers with a Focus on Metastatic Disease. Cancers 2023, 15, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, N.; La Salvia, A. Precision medicine in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: Where are we in 2023? Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 37, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.E.; Zhernosekov, K. The evolution of PRRT for the treatment of neuroendocrine tumors; What comes next? Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 941832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grozinsky-Glasberg, S.; Grossman, A.B.; Korbonits, M. The role of somatostatin analogues in the treatment of neuroendocrine tumours. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2008, 286, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reubi, J.C. Peptide receptors as molecular targets for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 389–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benali, N.; Ferjoux, G.; Puente, E.; Buscail, L.; Susini, C. Somatostatin receptors. Digestion 2000, 62 (Suppl. S1), 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maecke, H.R.; Hofmann, M.; Haberkorn, U. (68)Ga-labeled peptides in tumor imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46 (Suppl. S1), 172s–178s. [Google Scholar]
- Maccauro, M.; Follacchio, G.A.; Spreafico, C.; Coppa, J.; Seregni, E. Safety and Efficacy of Combined Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy and Liver Selective Internal Radiation Therapy in a Patient With Metastatic Neuroendocrine Tumor. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, e286–e288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, V.; Fani, M.; Fanti, S.; Forrer, F.; Maecke, H.R. Radiopeptide imaging and therapy in Europe. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52 (Suppl. S2), 42s–55s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellis, C.; Jacene, H.A. Neuroendocrine Tumors: Diagnostics. PET Clin. 2024, 19, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, G.; Di Santo, G.; Virgolini, I. Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy of Neuroendocrine Tumors: Agonist, Antagonist and Alternatives. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2024, 54, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinova, M.; Mücke, M.; Fischer, F.; Essler, M.; Cuhls, H.; Radbruch, L.; Ghaei, S.; Conrad, R.; Ahmadzadehfar, H. Quality of life in patients with midgut NET following peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2252–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckbecker, G.; Lewis, I.; Albert, R.; Schmid, H.A.; Hoyer, D.; Bruns, C. Correction: Weckbecker et al. Opportunities in somatostatin research: Biological, chemical and therapeutic aspects. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 999–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cescato, R.; Schulz, S.; Waser, B.; Eltschinger, V.; Rivier, J.E.; Wester, H.J.; Culler, M.; Ginj, M.; Liu, Q.; Schonbrunn, A.; et al. Internalization of sst2, sst3, and sst5 receptors: Effects of somatostatin agonists and antagonists. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krebs, S.; O’Donoghue, J.A.; Biegel, E.; Beattie, B.J.; Reidy, D.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; Lewis, J.S.; Bodei, L.; Weber, W.A.; Pandit-Taskar, N. Comparison of (68)Ga-DOTA-JR11 PET/CT with dosimetric (177)Lu-satoreotide tetraxetan ((177)Lu-DOTA-JR11) SPECT/CT in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors undergoing peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 3047–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallak, N.; Yilmaz, B.; Meyer, C.; Winters, C.; Mench, A.; Jha, A.K.; Prasad, V.; Mittra, E. Theranostics in Neuroendocrine Tumors: Updates and Emerging Technologies. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2024, 52, 101129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, D.; Fani, M.; Behe, M.; Brink, I.; Rivier, J.E.; Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, H.R.; Weber, W.A. First clinical evidence that imaging with somatostatin receptor antagonists is feasible. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginj, M.; Zhang, H.; Waser, B.; Cescato, R.; Wild, D.; Wang, X.; Erchegyi, J.; Rivier, J.; Mäcke, H.R.; Reubi, J.C. Radiolabeled somatostatin receptor antagonists are preferable to agonists for in vivo peptide receptor targeting of tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16436–16441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, D.; Fani, M.; Fischer, R.; Del Pozzo, L.; Kaul, F.; Krebs, S.; Fischer, R.; Rivier, J.E.; Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, H.R.; et al. Comparison of somatostatin receptor agonist and antagonist for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy: A pilot study. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Yao, S.; Bai, C.; Zhao, H.; Jia, R.; Xu, J.; Huo, L. Head-to-Head Comparison of (68)Ga-DOTA-JR11 and (68)Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT in Patients with Metastatic, Well-Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Prospective Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Jia, R.; Yang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Bai, C.; Xu, J.; Yao, S.; Huo, L. A prospective randomized, double-blind study to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of (68)Ga-NODAGA-LM3 and (68)Ga-DOTA-LM3 in patients with well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors: Compared with (68)Ga-DOTATATE. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J.; Miao, W.; Yao, S.; Huo, L. Head-to-Head Comparison of (68)Ga-NODAGA-JR11 and (68)Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT in Patients with Metastatic, Well-Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumors: Interim Analysis of a Prospective Bicenter Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 64, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ren, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Jia, R.; Cheng, Y.; Bai, C.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, W.; et al. Evaluation of the safety, biodistribution, dosimetry of [(18)F]AlF-NOTA-LM3 and head-to-head comparison with [(68)Ga]Ga-DOTATATE in patients with well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors: An interim analysis of a prospective trial. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2024, 51, 3719–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grozinsky-Glasberg, S.; Barak, D.; Fraenkel, M.; Walter, M.A.; Müeller-Brand, J.; Eckstein, J.; Applebaum, L.; Shimon, I.; Gross, D.J. Peptide receptor radioligand therapy is an effective treatment for the long-term stabilization of malignant gastrinomas. Cancer 2011, 117, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisman, F.; Rosado de Castro, P.H.; Lopes, F.P.; Kendler, D.B.; Pessoa, C.H.; Bulzico, D.A.; de Carvalho Leal, D.; Vilhena, B.; Vaisman, M.; Carneiro, M.; et al. Is there a role for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in medullary thyroid cancer? Clin. Nucl. Med. 2015, 40, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, R.P.; Kluge, A.W.; Kulkarni, H.; Schorr-Neufing, U.; Niepsch, K.; Bitterlich, N.; van Echteld, C.J. [(177)Lu-DOTA](0)-D-Phe(1)-Tyr(3)-Octreotide ((177)Lu-DOTATOC) For Peptide Receptor Radiotherapy in Patients with Advanced Neuroendocrine Tumours: A Phase-II Study. Theranostics 2016, 6, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hörsch, D.; Ezziddin, S.; Haug, A.; Gratz, K.F.; Dunkelmann, S.; Miederer, M.; Schreckenberger, M.; Krause, B.J.; Bengel, F.M.; Bartenstein, P.; et al. Effectiveness and side-effects of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy for neuroendocrine neoplasms in Germany: A multi-institutional registry study with prospective follow-up. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 58, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilica, B.; Waitz, D.; Stevanovic, V.; Uprimny, C.; Kendler, D.; Buxbaum, S.; Warwitz, B.; Gerardo, L.; Henninger, B.; Virgolini, I.; et al. Direct comparison of (68)Ga-DOTA-TOC and (18)F-FDG PET/CT in the follow-up of patients with neuroendocrine tumour treated with the first full peptide receptor radionuclide therapy cycle. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabander, T.; van der Zwan, W.A.; Teunissen, J.J.M.; Kam, B.L.R.; Feelders, R.A.; de Herder, W.W.; van Eijck, C.H.J.; Franssen, G.J.H.; Krenning, E.P.; Kwekkeboom, D.J. Long-Term Efficacy, Survival, and Safety of [(177)Lu-DOTA(0),Tyr(3)]octreotate in Patients with Gastroenteropancreatic and Bronchial Neuroendocrine Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4617–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parghane, R.V.; Talole, S.; Prabhash, K.; Basu, S. Clinical Response Profile of Metastatic/Advanced Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors to Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy with 177Lu-DOTATATE. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2017, 42, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, P.; Parghane, R.; Basu, S. (177)Lu-DOTATATE Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy in Metastatic or Advanced and Inoperable Primary Neuroendocrine Tumors of Rare Sites. World J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 16, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Demirci, E.; Kabasakal, L.; Toklu, T.; Ocak, M.; Şahin, O.E.; Alan-Selcuk, N.; Araman, A. 177Lu-DOTATATE therapy in patients with neuroendocrine tumours including high-grade (WHO G3) neuroendocrine tumours: Response to treatment and long-term survival update. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2018, 39, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsen, E.A.; Fazio, N.; Granberg, D.; Grozinsky-Glasberg, S.; Ahmadzadehfar, H.; Grana, C.M.; Zandee, W.T.; Cwikla, J.; Walter, M.A.; Oturai, P.S.; et al. Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in gastroenteropancreatic NEN G3: A multicenter cohort study. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Wang, W.M.; Yusuf, S.; Evans, J.; Ramaswami, R.; Wernig, F.; Frilling, A.; Mauri, F.; Al-Nahhas, A.; Aboagye, E.O.; et al. (68)Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT parameters predict response to peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in neuroendocrine tumours. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 141, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandee, W.T.; Brabander, T.; Blažević, A.; Kam, B.L.R.; Teunissen, J.J.M.; Feelders, R.A.; Hofland, J.; de Herder, W.W. Symptomatic and Radiological Response to 177Lu-DOTATATE for the Treatment of Functioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adnan, A.; Sampathirao, N.; Basu, S. Implications of fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in low-intermediate grade metastatic neuroendocrine tumors from peptide receptor radionuclide therapy outcome viewpoint: A semi-quantitative standardized uptake value-based analysis. World J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 18, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beukhof, C.M.; Brabander, T.; van Nederveen, F.H.; van Velthuysen, M.F.; de Rijke, Y.B.; Hofland, L.J.; Franssen, G.J.H.; Fröberg, L.A.C.; Kam, B.L.R.; Visser, W.E.; et al. Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma: Predictors and pitfalls. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, V.; Srirajaskanthan, R.; Toumpanakis, C.; Grana, C.M.; Baldari, S.; Shah, T.; Lamarca, A.; Courbon, F.; Scheidhauer, K.; Baudin, E.; et al. Lessons from a multicentre retrospective study of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy combined with lanreotide for neuroendocrine tumours: A need for standardised practice. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 2358–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satapathy, S.; Mittal, B.R.; Sood, A.; Sood, A.; Kapoor, R.; Gupta, R. Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy as First-Line Systemic Treatment in Advanced Inoperable/Metastatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2020, 45, e393–e399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, J.; Pape, U.F.; Jann, H.; Denecke, T.; Arsenic, R.; Brenner, W.; Pavel, M.; Prasad, V. Prognostic Significance of Somatostatin Receptor Heterogeneity in Progressive Neuroendocrine Tumor Treated with Lu-177 DOTATOC or Lu-177 DOTATATE. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, O.K.; Ravi Kumar, A.S.; Kong, G.; Oleinikov, K.; Ben-Haim, S.; Grozinsky-Glasberg, S.; Hicks, R.J. Efficacy of Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy for Esthesioneuroblastoma. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizing, D.M.V.; Aalbersberg, E.A.; Versleijen, M.W.J.; Tesselaar, M.E.T.; Walraven, I.; Lahaye, M.J.; de Wit-van der Veen, B.J.; Stokkel, M.P.M. Early response assessment and prediction of overall survival after peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunikowska, J.; Zemczak, A.; Kołodziej, M.; Gut, P.; Łoń, I.; Pawlak, D.; Mikołajczak, R.; Kamiński, G.; Ruchała, M.; Kos-Kudła, B.; et al. Tandem peptide receptor radionuclide therapy using (90)Y/(177)Lu-DOTATATE for neuroendocrine tumors efficacy and side-effects—polish multicenter experience. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirvis, E.; Toumpanakis, C.; Mandair, D.; Gnanasegaran, G.; Caplin, M.; Navalkissoor, S. Efficacy and tolerability of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) in advanced metastatic bronchial neuroendocrine tumours (NETs). Lung Cancer 2020, 150, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parghane, R.V.; Naik, C.; Talole, S.; Desmukh, A.; Chaukar, D.; Banerjee, S.; Basu, S. Clinical utility of (177) Lu-DOTATATE PRRT in somatostatin receptor-positive metastatic medullary carcinoma of thyroid patients with assessment of efficacy, survival analysis, prognostic variables, and toxicity. Head Neck 2020, 42, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauwels, E.; Van Binnebeek, S.; Vandecaveye, V.; Baete, K.; Vanbilloen, H.; Koole, M.; Mottaghy, F.M.; Haustermans, K.; Clement, P.M.; Nackaerts, K.; et al. Inflammation-Based Index and (68)Ga-DOTATOC PET-Derived Uptake and Volumetric Parameters Predict Outcome in Neuroendocrine Tumor Patients Treated with (90)Y-DOTATOC. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiis-Evensen, E.; Poole, A.C.; Nguyen, H.T.; Sponheim, J. Achieving objective response in treatment of non-resectable neuroendocrine tumors does not predict longer time to progression compared to achieving stable disease. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemczak, A.; Kołodziej, M.; Gut, P.; Królicki, L.; Kos-Kudła, B.; Kamiński, G.; Ruchała, M.; Pawlak, D.; Kunikowska, J. Effect of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) with tandem isotopes—[90Y]Y/[177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE in patients with disseminated neuroendocrine tumours depending on [18F]FDG PET/CT qualification in Polish multicentre experience—do we need [18F]FDG PET/CT for qualification to PRRT? Endokrynol. Pol. 2020, 71, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parghane, R.V.; Talole, S.; Basu, S. (131)I-MIBG negative progressive symptomatic metastatic paraganglioma: Response and outcome with (177)Lu-DOTATATE peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2021, 35, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severi, S.; Bongiovanni, A.; Ferrara, M.; Nicolini, S.; Di Mauro, F.; Sansovini, M.; Lolli, I.; Tardelli, E.; Cittanti, C.; Di Iorio, V.; et al. Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in patients with metastatic progressive pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: Long-term toxicity, efficacy and prognostic biomarker data of phase II clinical trials. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistani, G.; Sutherland, D.E.K.; Mujoomdar, A.; Wiseman, D.P.; Khatami, A.; Tsvetkova, E.; Reid, R.H.; Laidley, D.T. Efficacy of (177)Lu-Dotatate Induction and Maintenance Therapy of Various Types of Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Phase II Registry Study. Curr. Oncol. 2020, 28, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teker, F.; Elboga, U. Is SUVmax a useful marker for progression-free survival in patients with metastatic GEP-NET receiving (177)Lu-DOTATATE therapy? Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 24, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zandee, W.T.; Brabander, T.; Blažević, A.; Minczeles, N.S.; Feelders, R.A.; de Herder, W.W.; Hofland, J. Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy With 177Lu-DOTATATE for Symptomatic Control of Refractory Carcinoid Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e3665–e3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeamar, H.; Cullen, L.; Murphy, D.J.; Crowley, R.K.; Toumpanakis, C.; Welin, S.; O’Shea, D.; O’Toole, D. Real-world efficacy of lutetium peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in patients with neuroendocrine tumours. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2022, 34, e13138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni, A.; Nicolini, S.; Ibrahim, T.; Foca, F.; Sansovini, M.; Di Paolo, A.; Grassi, I.; Liverani, C.; Calabrese, C.; Ranallo, N.; et al. (177)Lu-DOTATATE Efficacy and Safety in Functioning Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Joint Analysis of Phase II Prospective Clinical Trials. Cancers 2022, 14, 6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, G.; Sui, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, X. Safety and efficacy of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with (177)Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors. Theranostics 2022, 12, 6437–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metser, U.; Eshet, Y.; Ortega, C.; Veit-Haibach, P.; Liu, A.; Rebecca, K.S.W. The association between lesion tracer uptake on 68Ga-DOTATATE PET with morphological response to 177Lu-DOTATATE therapy in patients with progressive metastatic neuroendocrine tumors. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2022, 43, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, N.; Coffman, K.; Le, T.; Do, R.K.G.; Rafailov, J.; Choi, Y.; Chou, J.F.; Capanu, M.; Dunphy, M.; Fox, J.J.; et al. Treatment Response and Clinical Outcomes of Well-Differentiated High-Grade Neuroendocrine Tumors to Lutetium-177-DOTATATE. Neuroendocrinology 2022, 112, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidan, L.; Iravani, A.; Oleinikov, K.; Ben-Haim, S.; Gross, D.J.; Meirovitz, A.; Maimon, O.; Akhurst, T.; Michael, M.; Hicks, R.J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of (177)Lu-DOTATATE in Lung Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Bicenter study. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundlöv, A.; Gleisner, K.S.; Tennvall, J.; Ljungberg, M.; Warfvinge, C.F.; Holgersson, K.; Hallqvist, A.; Bernhardt, P.; Svensson, J. Phase II trial demonstrates the efficacy and safety of individualized, dosimetry-based (177)Lu-DOTATATE treatment of NET patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 3830–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentzen, S.; Mehta, K.; Al-Rajabi, R.M.T.; Saeed, A.; Baranda, J.C.; Williamson, S.K.; Sun, W.; Kasi, A. Real world outcomes in patients with neuroendocrine tumor receiving peptide receptor radionucleotide therapy. Explor. Target. Antitumor Ther. 2023, 4, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepenek, F.; Kömek, H.; Can, C.; Kaplan, İ.; Altindağ, S.; Gündoğan, C. The prognostic role of whole-body volumetric 68 GA-DOTATATE PET/computed tomography parameters in patients with gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor treated with 177 LU-DOTATATE. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2023, 44, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Kulkarni, H.R.; Zhao, T.; Schuchardt, C.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Baum, R.P. Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy in Patients With Advanced Progressive Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Efficacy, Safety, and Survival Predictors. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2023, 48, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitjavila, M.; Jimenez-Fonseca, P.; Belló, P.; Pubul, V.; Percovich, J.C.; Garcia-Burillo, A.; Hernando, J.; Arbizu, J.; Rodeño, E.; Estorch, M.; et al. Efficacy of [(177)Lu]Lu-DOTATATE in metastatic neuroendocrine neoplasms of different locations: Data from the SEPTRALU study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 2486–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, H.G.; Suh, M.; Kang, K.W.; Lee, D.W.; Han, S.W.; Cheon, G.J. Phase 1 Study of No-Carrier Added 177Lu-DOTATATE (SNU-KB-01) in Patients with Somatostatin Receptor-Positive Neuroendocrine Tumors: The First Clinical Trial of Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy in Korea. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 55, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.; Zhuang, E.; Raj, M.; Bahary, N.; Monga, D.K. Long-term clinical outcomes of [(177)Lu]Lu-DOTATATE in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1393317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.; Moon, B.H.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Chang, H.M.; Kim, K.P.; Hong, Y.S.; Kim, T.W.; Ryu, J.S.; Kim, Y.I.; Yoo, C. Efficacy and Safety of Lu-177 DOTATATE Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy in Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic Neuroendocrine Tumors in Korea. Target. Oncol. 2024, 19, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidy-Lagunes, D.; Pandit-Taskar, N.; O’Donoghue, J.A.; Krebs, S.; Staton, K.D.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; Lewis, J.S.; Raj, N.; Gönen, M.; Lohrmann, C.; et al. Phase I Trial of Well-Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumors (NETs) with Radiolabeled Somatostatin Antagonist (177)Lu-Satoreotide Tetraxetan. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6939–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, R.P.; Zhang, J.; Schuchardt, C.; Müller, D.; Mäcke, H. First-in-Humans Study of the SSTR Antagonist (177)Lu-DOTA-LM3 for Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy in Patients with Metastatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Dosimetry, Safety, and Efficacy. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, D.; Grønbæk, H.; Navalkissoor, S.; Haug, A.; Nicolas, G.P.; Pais, B.; Ansquer, C.; Beauregard, J.M.; McEwan, A.; Lassmann, M.; et al. A phase I/II study of the safety and efficacy of [(177)Lu]Lu-satoreotide tetraxetan in advanced somatostatin receptor-positive neuroendocrine tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 51, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Franco, M.; Zanoni, L.; Fortunati, E.; Fanti, S.; Ambrosini, V. Radionuclide Theranostics in Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: An Update. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2024, 26, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, R.; Sheikh, G.T.; Brendel, M.; Ricke, J.; Cyran, C.C. ESR Essentials: Role of PET/CT in neuroendocrine tumors-practice recommendations by the European Society for Hybrid, Molecular and Translational Imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2025, 35, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomykala, K.L.; Hadaschik, B.A.; Sartor, O.; Gillessen, S.; Sweeney, C.J.; Maughan, T.; Hofman, M.S.; Herrmann, K. Next generation radiotheranostics promoting precision medicine. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, M.; Decristoforo, C.; Kendler, D.; Dobrozemsky, G.; Heute, D.; Uprimny, C.; Kovacs, P.; Von Guggenberg, E.; Bale, R.; Virgolini, I.J. 68Ga-DOTA-Tyr3-octreotide PET in neuroendocrine tumors: Comparison with somatostatin receptor scintigraphy and CT. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoropoulou, M.; Stalla, G.K. Somatostatin receptors: From signaling to clinical practice. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2013, 34, 228–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Parihar, A.S.; Bodei, L.; Hope, T.A.; Mallak, N.; Millo, C.; Prasad, K.; Wilson, D.; Zukotynski, K.; Mittra, E. Somatostatin Receptor Imaging and Theranostics: Current Practice and Future Prospects. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binderup, T.; Knigge, U.; Loft, A.; Mortensen, J.; Pfeifer, A.; Federspiel, B.; Hansen, C.P.; Højgaard, L.; Kjaer, A. Functional imaging of neuroendocrine tumors: A head-to-head comparison of somatostatin receptor scintigraphy, 123I-MIBG scintigraphy, and 18F-FDG PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strosberg, J.R.; Caplin, M.E.; Kunz, P.L.; Ruszniewski, P.B.; Bodei, L.; Hendifar, A.; Mittra, E.; Wolin, E.M.; Yao, J.C.; Pavel, M.E.; et al. Correction: Strosberg at al. (177)Lu-Dotatate plus long-acting octreotide versus high-dose long-acting octreotide in patients with midgut neuroendocrine tumours (NETTER-1): Final overall survival and long-term safety results from an open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1752–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikhbahaei, S.; Sadaghiani, M.S.; Rowe, S.P.; Solnes, L.B. Neuroendocrine Tumor Theranostics: An Update and Emerging Applications in Clinical Practice. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 217, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, S.; Alkatheeri, A.; Alomaim, W.; Elliyanti, A. Radiopharmaceutical Treatments for Cancer Therapy, Radionuclides Characteristics, Applications, and Challenges. Molecules 2022, 27, 5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fani, M.; Braun, F.; Waser, B.; Beetschen, K.; Cescato, R.; Erchegyi, J.; Rivier, J.E.; Weber, W.A.; Maecke, H.R.; Reubi, J.C. Unexpected sensitivity of sst2 antagonists to N-terminal radiometal modifications. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodei, L.; Weber, W.A. Somatostatin Receptor Imaging of Neuroendocrine Tumors: From Agonists to Antagonists. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 907–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, S.; Pandit-Taskar, N.; Reidy, D.; Beattie, B.J.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; Lewis, J.S.; Bodei, L.; Weber, W.A.; O’Donoghue, J.A. Biodistribution and radiation dose estimates for (68)Ga-DOTA-JR11 in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, P.L.; Reidy-Lagunes, D.; Anthony, L.B.; Bertino, E.M.; Brendtro, K.; Chan, J.A.; Chen, H.; Jensen, R.T.; Kim, M.K.; Klimstra, D.S.; et al. Consensus guidelines for the management and treatment of neuroendocrine tumors. Pancreas 2013, 42, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frilling, A.; Clift, A.K. Therapeutic strategies for neuroendocrine liver metastases. Cancer 2015, 121, 1172–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Librizzi, D.; Bagheri, S.; Ebrahimifard, A.; Hojjat Shamami, A.; Rinke, A.; Eilsberger, F.; Luster, M.; Hooshyar Yousefi, B. Theranostic Radiopharmaceuticals of Somatostatin Receptors for Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors: Agonists Versus Antagonists—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178539
Wang Q, Librizzi D, Bagheri S, Ebrahimifard A, Hojjat Shamami A, Rinke A, Eilsberger F, Luster M, Hooshyar Yousefi B. Theranostic Radiopharmaceuticals of Somatostatin Receptors for Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors: Agonists Versus Antagonists—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178539
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qi, Damiano Librizzi, Shamim Bagheri, Ali Ebrahimifard, Azimeh Hojjat Shamami, Anja Rinke, Friederike Eilsberger, Markus Luster, and Behrooz Hooshyar Yousefi. 2025. "Theranostic Radiopharmaceuticals of Somatostatin Receptors for Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors: Agonists Versus Antagonists—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178539
APA StyleWang, Q., Librizzi, D., Bagheri, S., Ebrahimifard, A., Hojjat Shamami, A., Rinke, A., Eilsberger, F., Luster, M., & Hooshyar Yousefi, B. (2025). Theranostic Radiopharmaceuticals of Somatostatin Receptors for Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors: Agonists Versus Antagonists—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178539