Mechanical Acupuncture at ST36 Attenuates Inflammatory Pain Involving TRPV1 Signaling in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
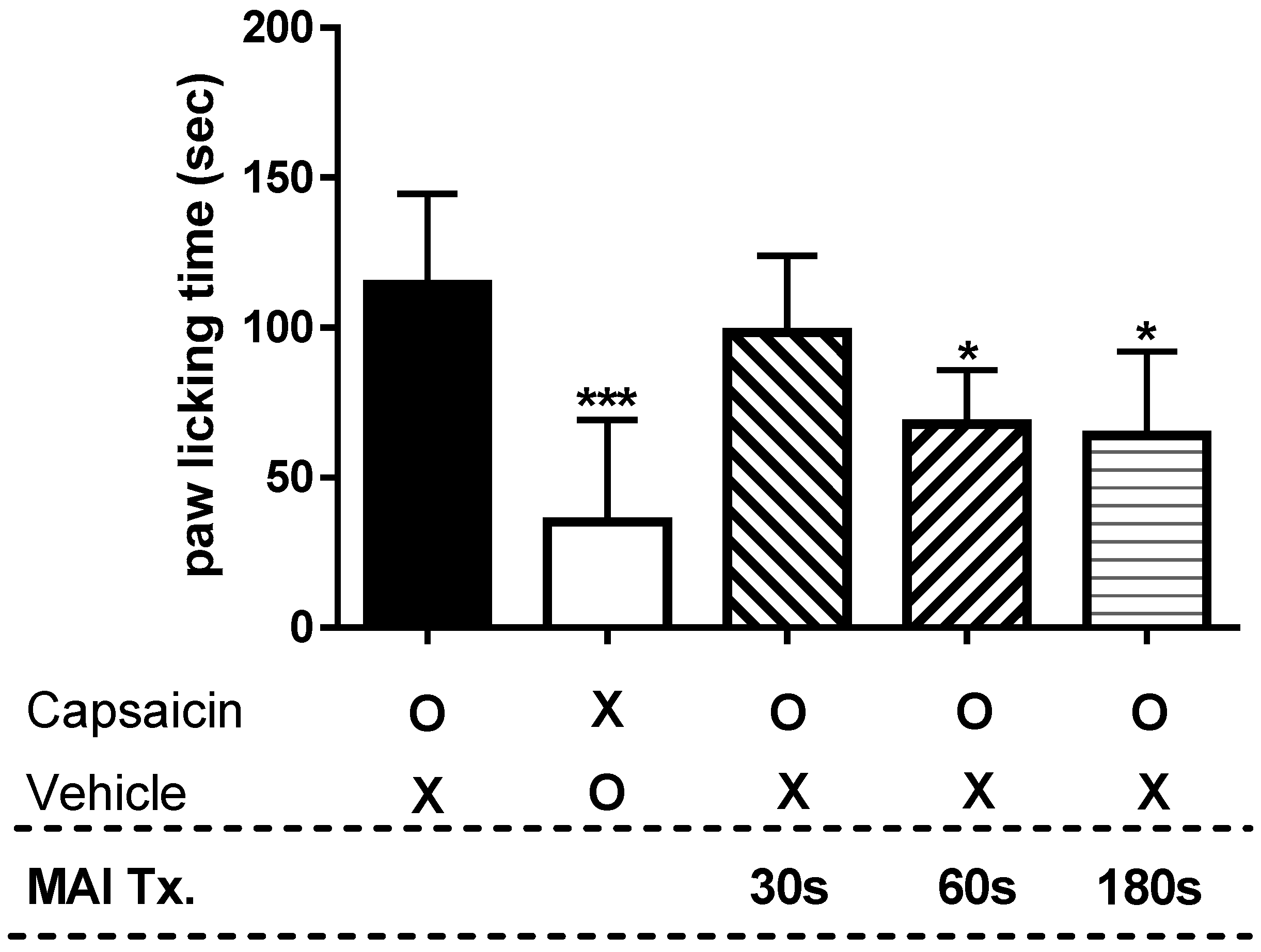
2.1. Anti-Nociceptive Effect of Treating Different Acupuncture Points in Capsaicin-Induced Spontaneous Pain Test
2.2. Time-Dependency of MAI in Capsaicin-Induced Spontaneous Pain Test
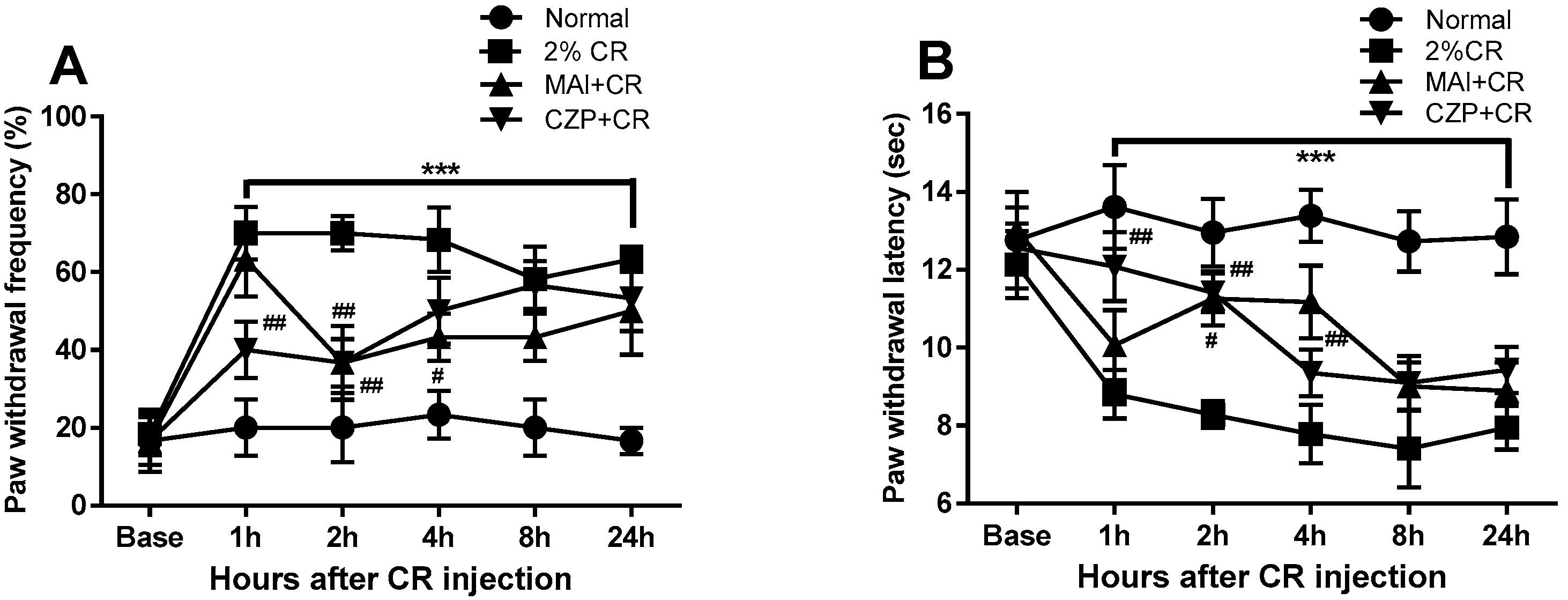
2.3. Anti-Nociceptive Effect of MAI Treatment in Carrageenan-Induced Pain Behavior
2.4. Expression of TRPV1 and Phosphorylated NR2B (pNR2B) in the Spinal Dorsal Horn
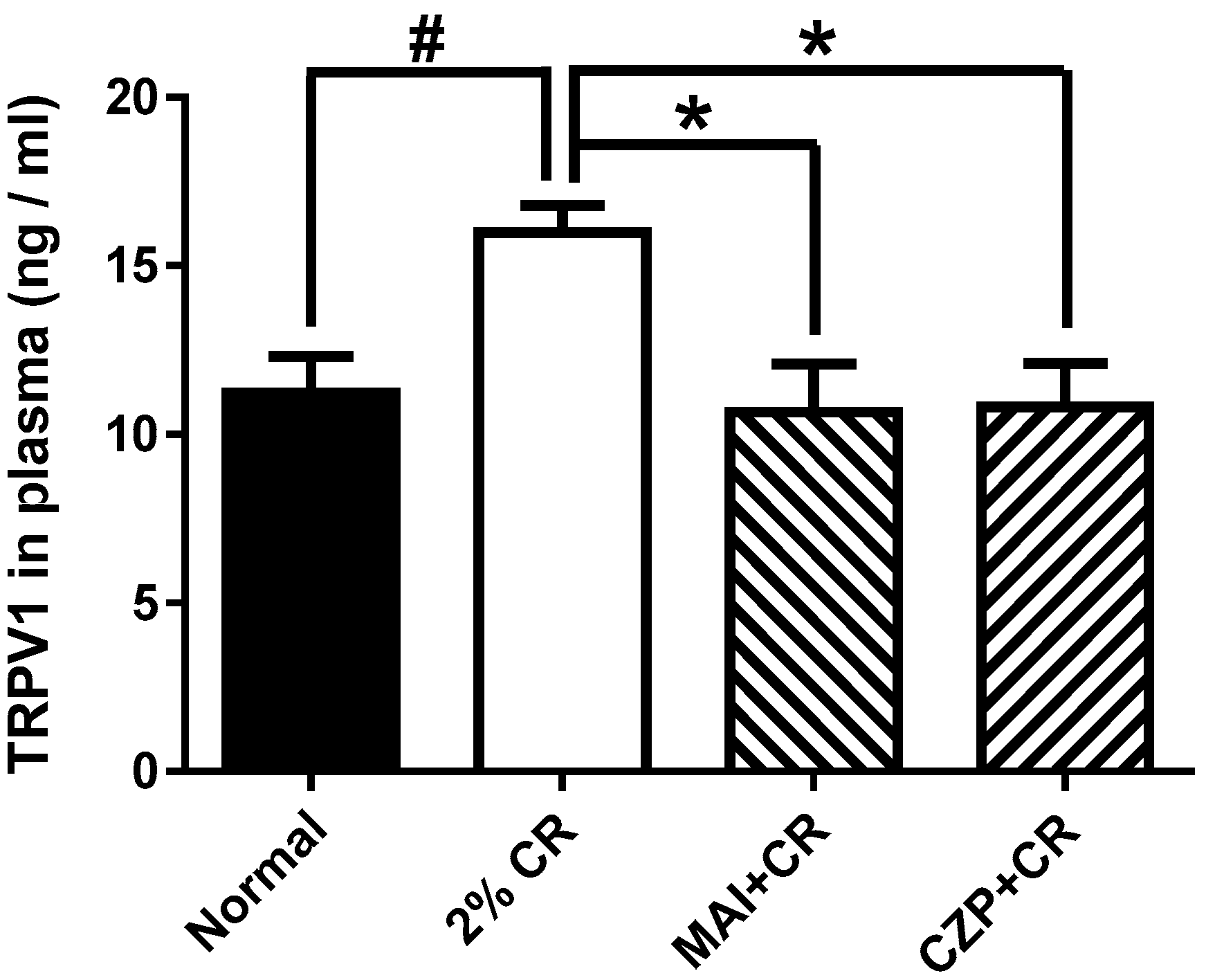
2.5. Effect of MAI Treatment on Plasma TRPV1 Concentration
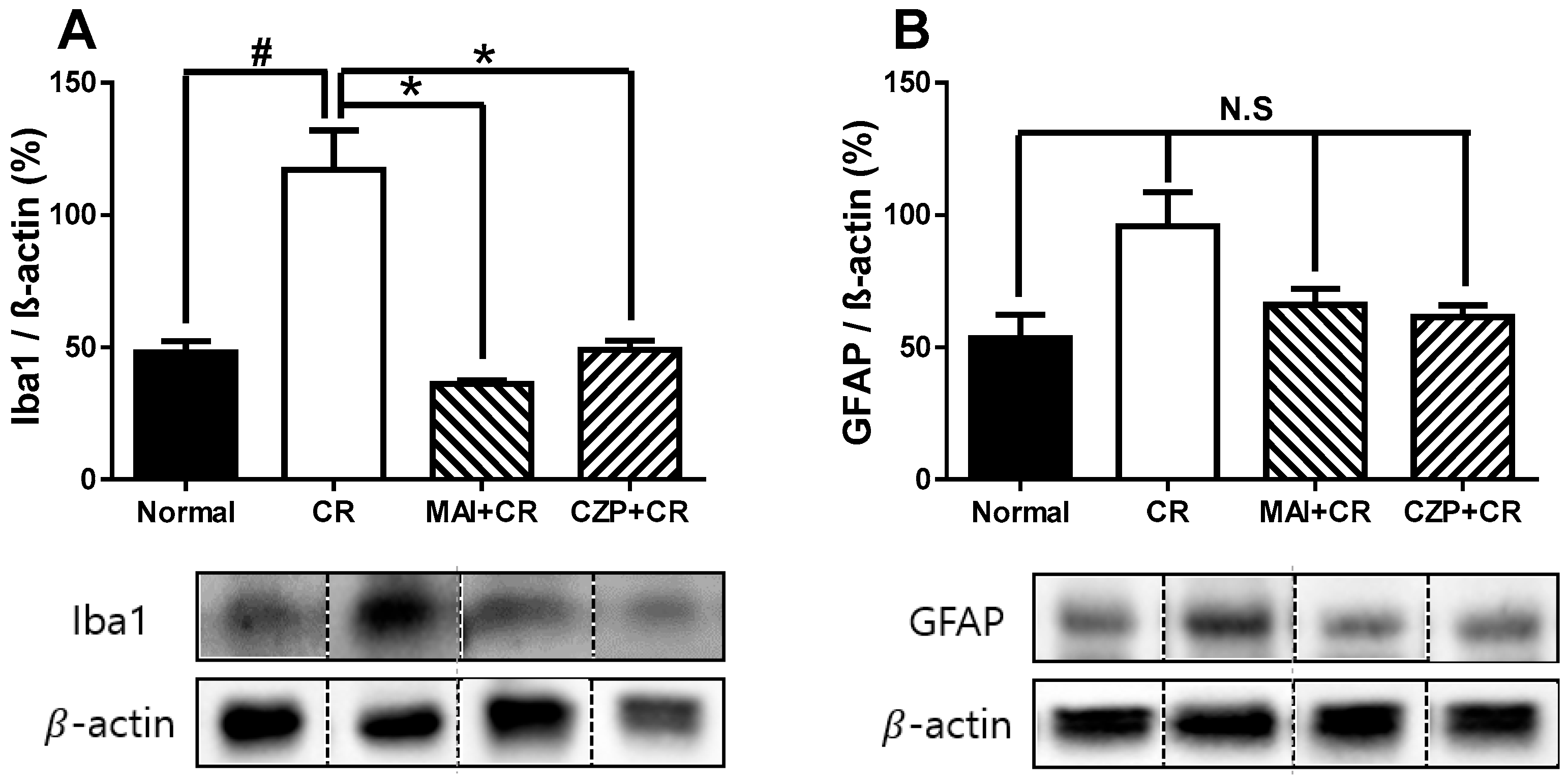
2.6. Iba1 and GFAP Expression in the Spinal Dorsal Horn
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. MAI Treatment
4.3. Capsaicin-Induced Spontaneous Pain Test
4.4. Carrageenan-Induced Inflammatory Pain and Drug Injection
4.5. Evaluation of Pain Behavior
4.6. Plasma TRPV1 Assays
4.7. Western Blotting and Image Analysis
4.8. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gouin, O.; L’Herondelle, K.; Lebonvallet, N.; Le Gall-Ianotto, C.; Sakka, M.; Buhe, V.; Plee-Gautier, E.; Carre, J.L.; Lefeuvre, L.; Misery, L.; et al. TRPV1 and TRPA1 in cutaneous neurogenic and chronic inflammation: Pro-inflammatory response induced by their activation and their sensitization. Protein Cell 2017, 8, 644–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Adamo, D.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q.; Wu, W.; Zheng, Y.L.; Wang, X.Q. Editorial: Inflammatory pain: Mechanisms, assessment, and intervention. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1286215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Li, M.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y. The dual role of TRPV1 in peripheral neuropathic pain: Pain switches caused by its sensitization or desensitization. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2024, 17, 1400118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Placha, D.; Jampilek, J. Chronic Inflammatory Diseases, Anti-Inflammatory Agents and Their Delivery Nanosystems. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Y.; Ryu, Y. Editorial: Chronic Inflammation and Related Diseases: From Mechanisms to Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Tian, Q.; Deng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Q.; Mei, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. TRPV1 SUMOylation regulates nociceptive signaling in models of inflammatory pain. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1529, Correction in Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Wang, L.; Liao, T.; Li, W.; Zhou, J.; You, Y.; Shi, J. Progress in the development of TRPV1 small-molecule antagonists: Novel Strategies for pain management. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 261, 115806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, P. The role of TRPV1 in RA pathogenesis: Worthy of attention. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1232013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Y.; Seo, S.Y.; Bang, S.K.; Cho, S.J.; Choi, K.H.; Ryu, Y. Inhibition of Spinal TRPV1 Reduces NMDA Receptor 2B Phosphorylation and Produces Anti-Nociceptive Effects in Mice with Inflammatory Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Xing, B. Efficacy and safety of TRPV1-related preparations in the treatment of inflammatory arthralgia. Medicine 2023, 102, e36268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Kang, S.Y.; Choi, J.G.; Kang, D.W.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.D.; Park, J.B.; Ryu, Y.H.; Kim, H.W. Analgesic effect of electroacupuncture on paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain via spinal opioidergic and adrenergic mechanisms in mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.J.; Lim, J.; Lee, S.; Choi, H.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Oh, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Jung, H.S.; Chae, Y.; et al. Augmented Mechanical Forces of the Surface-Modified Nanoporous Acupuncture Needles Elicit Enhanced Analgesic Effects. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Dou, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Du, S.; Li, J.; Yao, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Gong, Y.; et al. Effects and mechanisms of acupuncture analgesia mediated by afferent nerves in acupoint microenvironments. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1239839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, A.C.M.; Molina Esquivel, N.; Goldschmied Rossel, F.; Benso, B. TRPV1-target drugs for the treatment of orofacial pain. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1568109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anh, D.T.N.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture Mitigates TRPV1 Overexpression in the Central Nervous System Associated with Fibromyalgia in Mice. Life 2024, 14, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.S. Acupuncture and endorphins. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 361, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Q. Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia. Prog. Neurobiol. 2008, 85, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lao, L.; Ren, K.; Berman, B.M. Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain. Anesthesiology 2014, 120, 482–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, M.; Huo, M.; Si, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, D. Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on inflammatory pain. Mol. Pain 2023, 19, 17448069231202882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Dou, B.; Xu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Du, S.; Wang, J.; Fu, J.; Liu, Q.; et al. TRPA1 Ion Channel Mediates the Analgesic Effects of Acupuncture at the ST36 Acupoint in Mice Suffering from Arthritis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 1823–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Tan, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Lai, M.; Luo, W. Research hotspots and trends of acupoint and pain based on PubMed: A bibliometric analysis. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1498576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.A.; Lee, B.H.; Bae, J.H.; Kim, K.J.; Steffensen, S.C.; Ryu, Y.H.; Leem, J.W.; Yang, C.H.; Kim, H.Y. Peripheral afferent mechanisms underlying acupuncture inhibition of cocaine behavioral effects in rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Y.; Bang, S.K.; Kwon, O.S.; Seo, S.Y.; Choi, K.H.; Cho, S.J.; Yoo, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.W.; Ryu, Y. Treatment of electrical wrist stimulation reduces chemotherapy-induced neuropathy and ultrasound vocalization via modulation of spinal NR2B phosphorylation. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 162, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.M.; Wu, T.C.; Hsieh, C.L.; Huang, Y.W.; Lin, Y.W. Distal Electroacupuncture at the LI4 Acupoint Reduces CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain via the Brain TRPV1 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.A.; de Almeida, T.B.; de Oliveira, R.G.; Goncalves, G.M.; de Oliveira, J.M.; Neves Dos Santos, B.B.; Laureano-Melo, R.; Cortes, W.D.S.; Franca, T.D.N.; Vasconcellos, M.; et al. Evaluation of the antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of piperic acid: Involvement of the cholinergic and vanilloid systems. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 834, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Y.; Roh, D.H.; Choi, J.W.; Ryu, Y.; Lee, J.H. Repetitive Treatment with Diluted Bee Venom Attenuates the Induction of Below-Level Neuropathic Pain Behaviors in a Rat Spinal Cord Injury Model. Toxins 2015, 7, 2571–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, S.-Y.; Bang, S.K.; Seo, S.Y.; Cho, S.J.; Choi, K.-H.; Han, S.; Ryu, Y. Mechanical Acupuncture at ST36 Attenuates Inflammatory Pain Involving TRPV1 Signaling in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178534
Kang S-Y, Bang SK, Seo SY, Cho SJ, Choi K-H, Han S, Ryu Y. Mechanical Acupuncture at ST36 Attenuates Inflammatory Pain Involving TRPV1 Signaling in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178534
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Suk-Yun, Se Kyun Bang, Su Yeon Seo, Seong Jin Cho, Kwang-Ho Choi, Sangeun Han, and Yeonhee Ryu. 2025. "Mechanical Acupuncture at ST36 Attenuates Inflammatory Pain Involving TRPV1 Signaling in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178534
APA StyleKang, S.-Y., Bang, S. K., Seo, S. Y., Cho, S. J., Choi, K.-H., Han, S., & Ryu, Y. (2025). Mechanical Acupuncture at ST36 Attenuates Inflammatory Pain Involving TRPV1 Signaling in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178534


_Kim.png)


