NEDD4L-Mediated Ubiquitination of GPX4 Exacerbates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. DOX-Induced Ferroptosis and Apoptosis in Cardiomyocytes
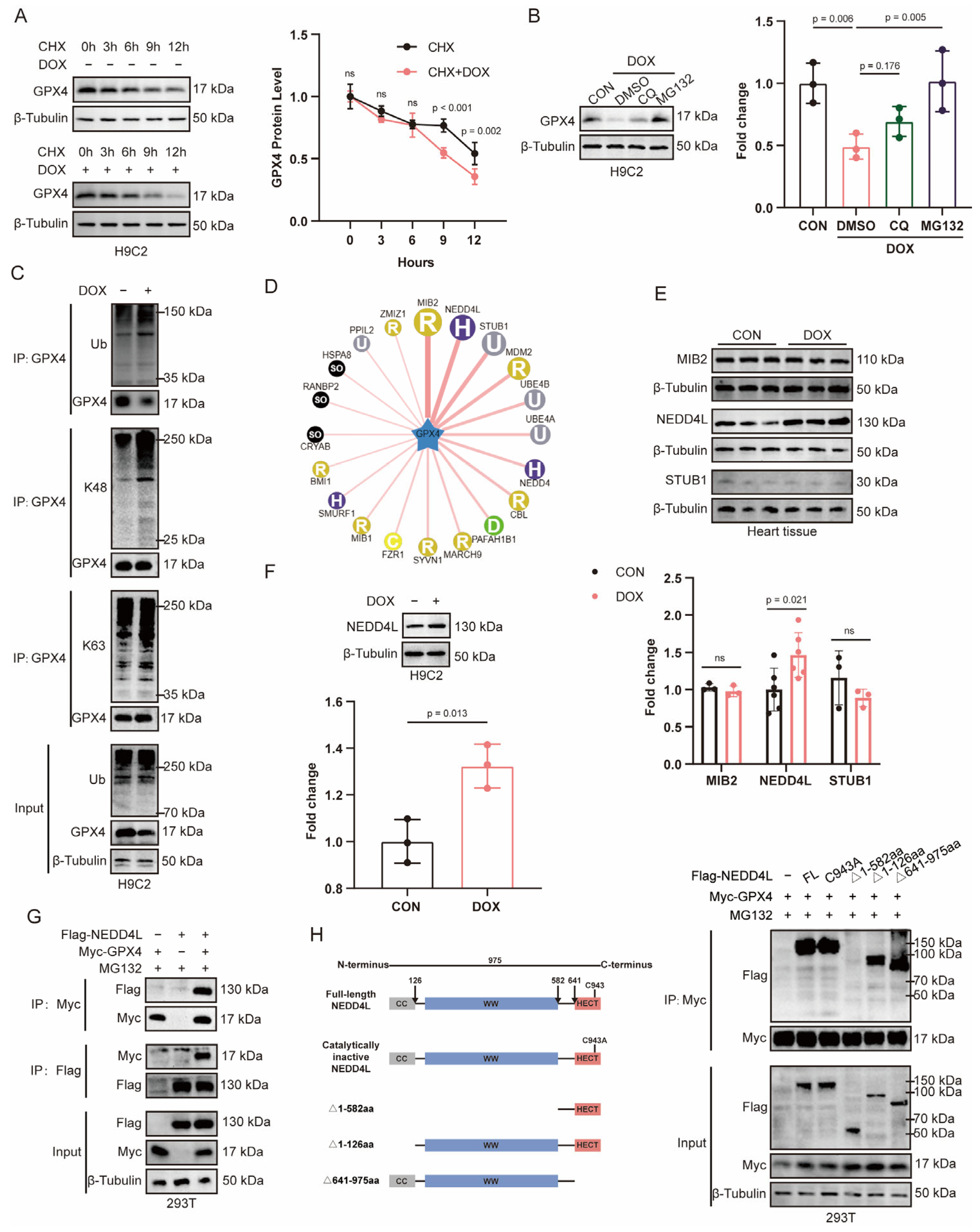
2.2. DOX-Induced Ubiquitin-Mediated Degradation of GPX4
2.3. NEDD4L Was Highly Expressed in DOX-Treated Cardiac Tissue and Cardiomyocytes
2.4. NEDD4L Knockdown Ameliorated Myocardial Dysfunction in DOX-Induced Cardiotoxicity (DIC)
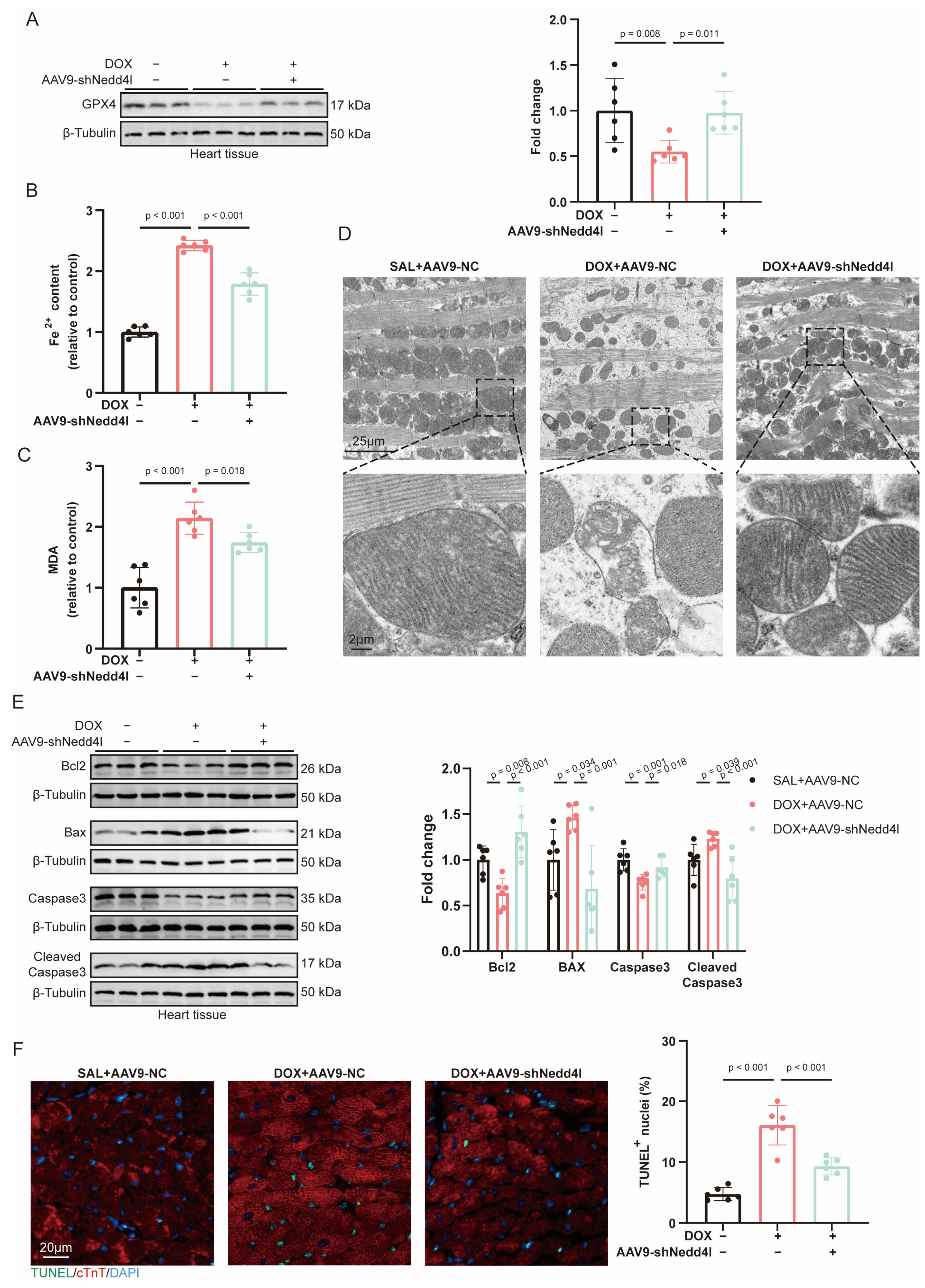
2.5. Knockdown of NEDD4L Suppressed DOX-Induced Ferroptosis and Apoptosis In Vivo
2.6. Knockdown of NEDD4L Alleviated DOX-Induced Ferroptosis and Apoptosis In Vitro
2.7. NEDD4L Promotes Proteasomal Degradation of GPX4 via K48-Linked Polyubiquitination Following DOX Treatment
2.8. NEDD4L Regulates GPX4 to Promote Ferroptosis and Apoptosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Transfection of Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) and Plasmid
4.5. Ferrous Iron, Lipid Peroxidation, and ROS Detection
4.6. Malondialdehyde (MDA) Detection
4.7. Apoptosis Detection
4.8. Animals
4.9. Adenovirus and Adeno-Associated Virus
4.10. Echocardiography
4.11. Histological Analysis
4.12. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.13. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase-Mediated dUTP In Situ Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
4.14. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.15. Iron Measurement
4.16. Serum CK-MB and LDH Measurement
4.17. Immunofluorescence (IF)
4.18. Immunoblots (IBs) and Immunoprecipitation (IP)
4.19. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAV9 | Serotype 9 Adeno-associated Virus |
| CHX | Cycloheximide |
| CQ | Chloroquine |
| DIC | Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity |
| DOX | Doxorubicin |
| Fer-1 | Ferrostatin-1 |
| GPX4 | Glutathione Peroxidase 4 |
| LVEF | Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction |
| FS | Fractional Shortening |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| NEDD4L | Neural Precursor Cell Expressed Developmentally Down-regulated Protein 4-like |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| Ub | Ubiquitin |
References
- Moslehi, J.J. Cardio-Oncology: A New Clinical Frontier and Novel Platform for Cardiovascular Investigation. Circulation 2024, 150, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, A.R.; Dent, S.; Stanway, S.; Earl, H.; Brezden-Masley, C.; Cohen-Solal, A.; Tocchetti, C.G.; Moslehi, J.J.; Groarke, J.D.; Bergler-Klein, J.; et al. Baseline cardiovascular risk assessment in cancer patients scheduled to receive cardiotoxic cancer therapies: A position statement and new risk assessment tools from the Cardio-Oncology Study Group of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology in collaboration with the International Cardio-Oncology Society. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Wang, L.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J. Mitochondrial quality control mechanisms as therapeutic targets in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 44, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.S.; Jaiswal, A.; Khurana, A.; Bhatti, J.S.; Navik, U. Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: An update on the molecular mechanism and novel therapeutic strategies for effective management. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 139, 111708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.Y.; Guo, Z.; Song, P.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y.P.; Teng, T.; Yan, L.; Tang, Q.Z. Underlying the Mechanisms of Doxorubicin-Induced Acute Cardiotoxicity: Oxidative Stress and Cell Death. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Ameri, P.; Cadeddu, C.; Ghigo, A.; Madonna, R.; Marone, G.; Mercurio, V.; Monte, I.; Novo, G.; Parrella, P.; et al. Antineoplastic Drug-Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Redox Perspective. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sowers, J.R.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J. Targeting DNA damage response in cardiovascular diseases: From pathophysiology to therapeutic implications. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 691–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Guo, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, L. Cell death regulation in myocardial toxicity induced by antineoplastic drugs. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1075917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Ren, J. Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targeting of Ferroptosis in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2024, 9, 811–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitakata, H.; Endo, J.; Ikura, H.; Moriyama, H.; Shirakawa, K.; Katsumata, Y.; Sano, M. Therapeutic Targets for DOX-Induced Cardiomyopathy: Role of Apoptosis vs. Ferroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, W. GPX4: The hub of lipid oxidation, ferroptosis, disease and treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 188890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadokoro, T.; Ikeda, M.; Ide, T.; Deguchi, H.; Ikeda, S.; Okabe, K.; Ishikita, A.; Matsushima, S.; Koumura, T.; Yamada, K.I.; et al. Mitochondria-dependent ferroptosis plays a pivotal role in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e169756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Kang, R.; Klionsky, D.J.; Tang, D. GPX4 in cell death, autophagy, and disease. Autophagy 2023, 19, 2621–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangweni, N.F.; Gabuza, K.; Huisamen, B.; Mabasa, L.; van Vuuren, D.; Johnson, R. Molecular insights into the pathophysiology of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: A graphical representation. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Pang, J.; Qin, D.; Li, R.; Zou, D.; Chi, K.; Wu, W.; Rui, H.; Yu, H.; Zhu, W.; et al. Deubiquitinase OTUD5 as a Novel Protector against 4-HNE-Triggered Ferroptosis in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2301852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.K.; Cao, X.; Wan, L.; Diao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Kan, Y.; Ye, L.L.; Mao, Y.M.; Dong, X.Q.; Xiong, Q.W.; et al. Autophagy of OTUD5 destabilizes GPX4 to confer ferroptosis-dependent kidney injury. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Jiang, X.; Hua, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, C.; Hao, X.; Yi, M.; Li, L. NEDD4L facilitates granulosa cell ferroptosis by promoting GPX4 ubiquitination and degradation. Endocr. Connect. 2023, 12, e220459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Dou, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, S.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, H.; Li, J.; Wu, Z. Drug-induced lactate confers ferroptosis resistance via p38-SGK1-NEDD4L-dependent upregulation of GPX4 in NSCLC cells. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, G.; Wang, P.; Wang, W.; Cao, K.; Song, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N. Research progress of Nedd4L in cardiovascular diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, Y.P.; Huang, Y.T.; Zhou, Z.J.; Liu, J.F.; Yu, L.M.; Wang, H.S. Cellular and molecular biology of posttranslational modifications in cardiovascular disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 179, 117374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, M.A.U.; Lin, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, B.; Mao, F. Ferroptosis and the ubiquitin-proteasome system: Exploring treatment targets in cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1383203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kciuk, M.; Gielecińska, A.; Mujwar, S.; Kołat, D.; Kałuzińska-Kołat, Ż.; Celik, I.; Kontek, R. Doxorubicin-an Agent with Multiple Mechanisms of Anticancer Activity. Cells 2023, 12, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Shu, Q.; Zhu, J. Ferroptosis: A novel therapeutic target of natural products against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Xu, T.; Zang, F.; Luo, Y.; Pan, D. Cardiotoxicity of Anticancer Drugs: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Management and Innovative Treatment. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2024, 18, 4089–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y. Iron metabolism in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: From mechanisms to therapies. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2024, 174, 106632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Niu, M.; Hu, X.; He, Y. Targeting mitochondrial dynamics proteins for the treatment of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1241225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Pan, J.; Huang, S.; Chen, X.; Chang, A.C.Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. Hydrogen sulfide protects cardiomyocytes from doxorubicin-induced ferroptosis through the SLC7A11/GSH/GPx4 pathway by Keap1 S-sulfhydration and Nrf2 activation. Redox Biol. 2024, 70, 103066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Guo, Y.; Li, T.; Sun, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Jin, M.; Li, J.; et al. Pharmacological activation of GPX4 ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. Redox Biol. 2024, 70, 103024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Liu, X.; Deng, F.; Wang, P.; Yang, L.; Hu, L.; Huang, K.; He, J. PRMT4 promotes ferroptosis to aggravate doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy via inhibition of the Nrf2/GPX4 pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 1982–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wu, M.; Yu, W.; Xie, D.; Wang, Q.; Chen, B.; Xi, Y.; Yu, L.; Yan, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; et al. High Uric Acid Orchestrates Ferroptosis to Promote Cardiomyopathy Via ROS-GPX4 Signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2024, 41, 1134–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiwe, J.N.; Jaiyeoba-Ojigho, J.E.; Chimezie, J.; Aboribo, P.P.; Fidelis, M.; Obighele, V.R.; Okoh, D.C.; Meseikpe, D.O.; Nwokoro, M.; Ematele, O. Preventive mechanisms of lutein on doxorubicin-induced vasculopathy in male Wistar rat. Clin. Tradit. Med. Pharmacol. 2025, 6, 200211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jin, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Shen, Y.; Zuo, S.; Yu, Y. EP1 activation inhibits doxorubicin-cardiomyocyte ferroptosis via Nrf2. Redox Biol. 2023, 65, 102825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Zhan, S.; Guo, C.; Yin, S.; Zhan, L.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, R.; Yan, H.; Wang, X.; et al. Fucoidan alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting ferroptosis via Nrf2/GPX4 pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 276 Pt 1, 133792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, D.W.; Chen, C. Insights into the post-translational modifications in heart failure. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 100, 102467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; He, F. The role of deubiquitinases in cardiac disease. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2024, 26, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Gong, H.; Huang, H.; Tuerhong, G.; Xia, H. Participation of Mind Bomb-2 in Sevoflurane Anesthesia Induces Cognitive Impairment in Aged Mice via Modulating Ferroptosis. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 2399–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, R.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Shen, N. The E3 ligase TRIM26 suppresses ferroptosis through catalyzing K63-linked ubiquitination of GPX4 in glioma. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Li, X.; Zheng, H.; Si, X.; Li, B.; Wei, G.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liao, W.; et al. Loss of Super-Enhancer-Regulated circRNA Nfix Induces Cardiac Regeneration After Myocardial Infarction in Adult Mice. Circulation 2019, 139, 2857–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, W.; Bai, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Y. microRNA-454-mediated NEDD4-2/TrkA/cAMP axis in heart failure: Mechanisms and cardioprotective implications. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 5082–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Yan, W.; Liu, M. YAP Facilitates NEDD4L-Mediated Ubiquitination and Degradation of ACSL4 to Alleviate Ferroptosis in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Can. J. Cardiol. 2023, 39, 1712–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, T.; Shi, W.; Fang, J.; Deng, H.; Cui, G. Potential targets for intervention against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity based on genetic studies: A systematic review of the literature. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2020, 138, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ke, J.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Liao, C.; Peng, F.; Chai, D.; Lin, J. NEDD4L-Mediated Ubiquitination of GPX4 Exacerbates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178201
Ke J, Li L, Chen S, Liao C, Peng F, Chai D, Lin J. NEDD4L-Mediated Ubiquitination of GPX4 Exacerbates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178201
Chicago/Turabian StyleKe, Jiaxing, Lingjia Li, Shuling Chen, Chenxin Liao, Feng Peng, Dajun Chai, and Jinxiu Lin. 2025. "NEDD4L-Mediated Ubiquitination of GPX4 Exacerbates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178201
APA StyleKe, J., Li, L., Chen, S., Liao, C., Peng, F., Chai, D., & Lin, J. (2025). NEDD4L-Mediated Ubiquitination of GPX4 Exacerbates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178201





