Comparative Effect of Conventional and Non-Conventional Over-the-Counter Treatments for Male Androgenetic Alopecia: A Network Meta-Analysis Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
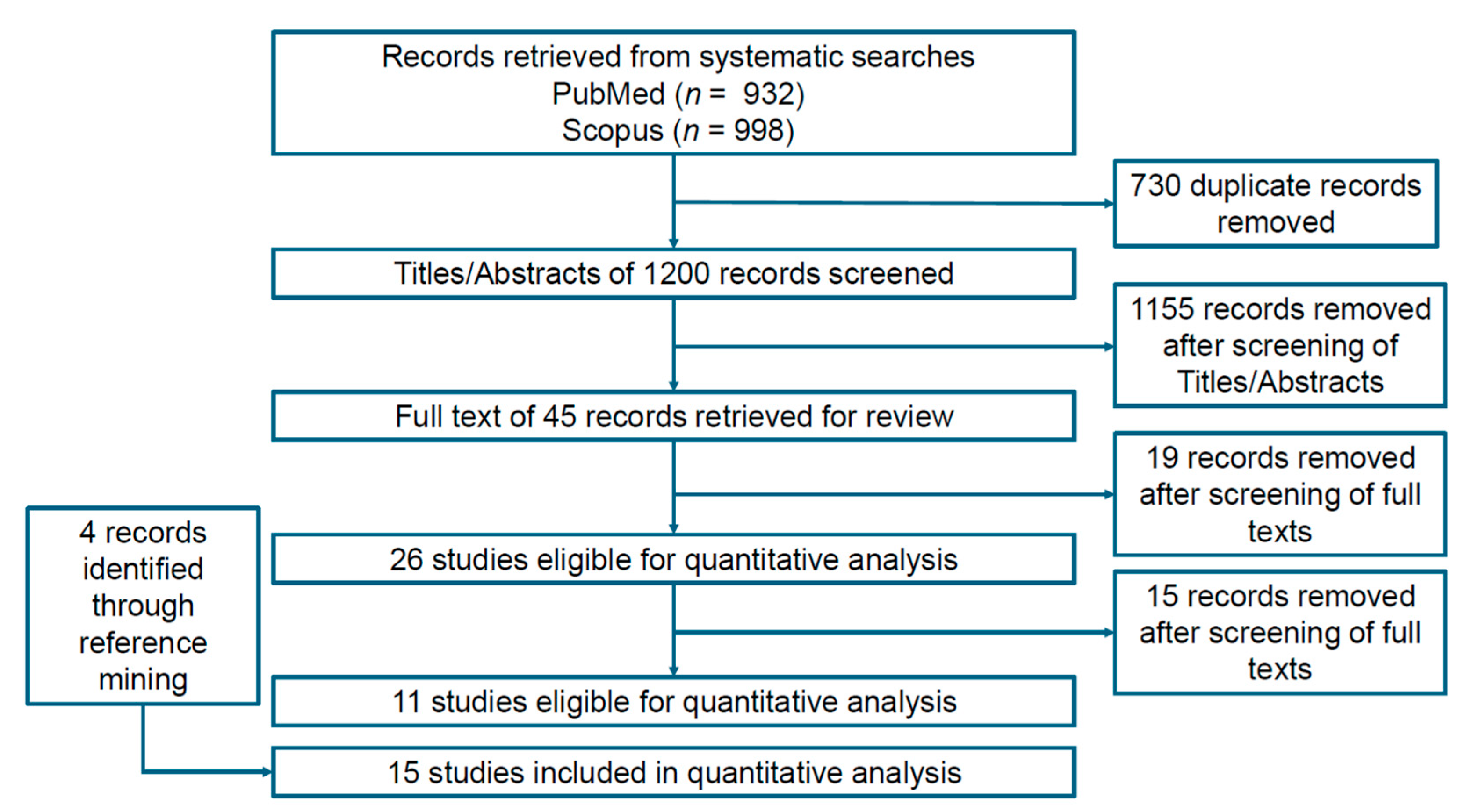
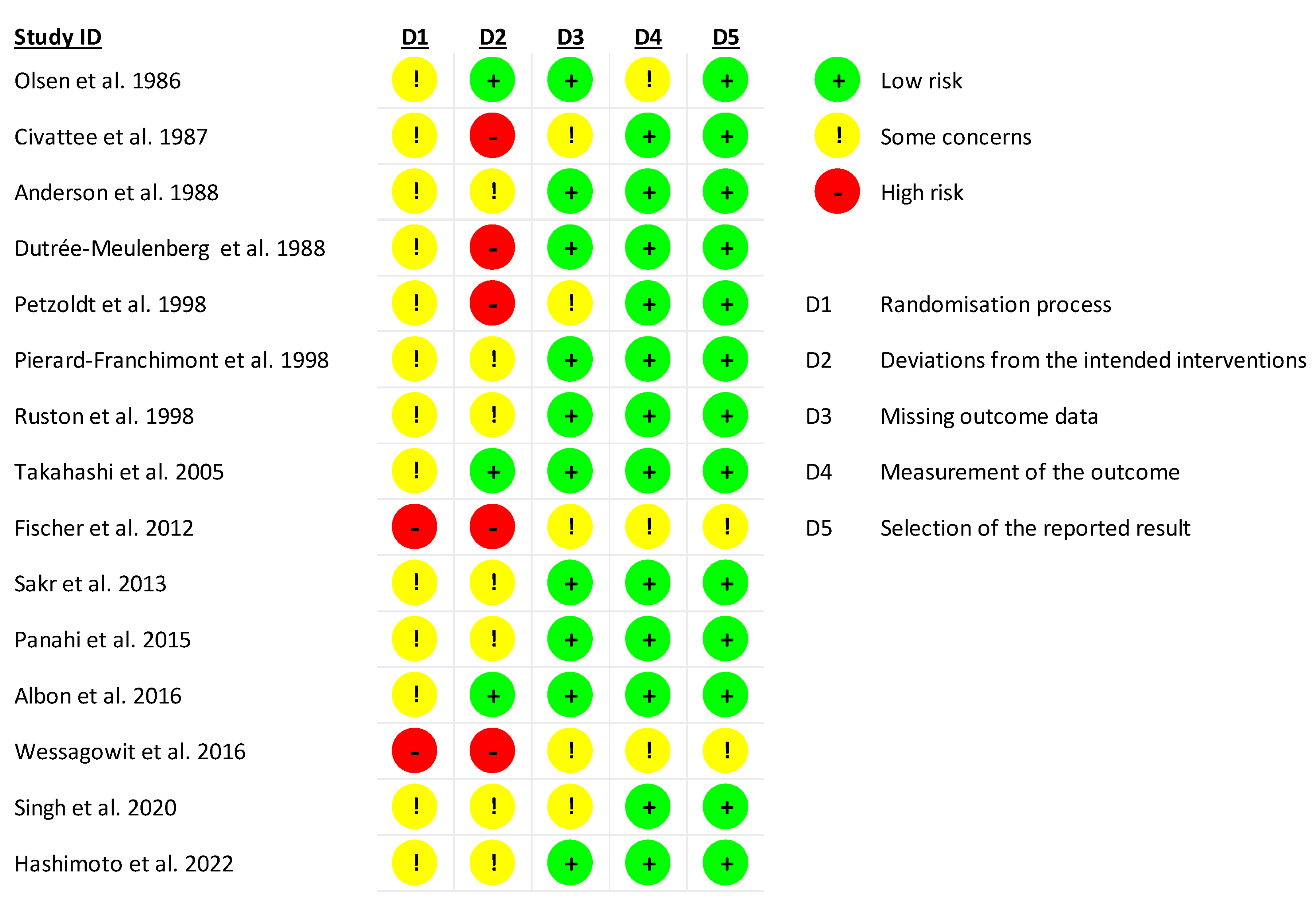
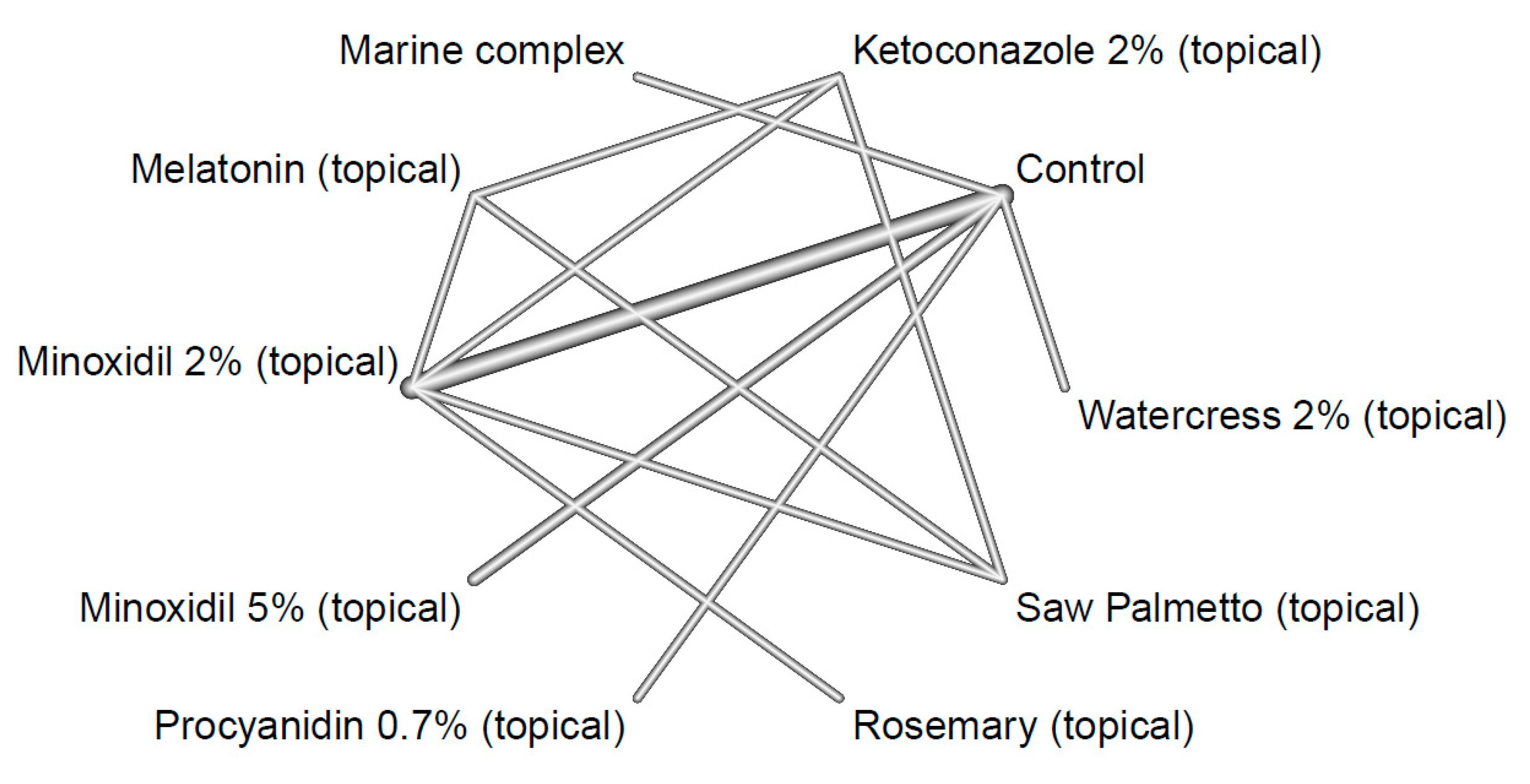
2. Materials and Methods
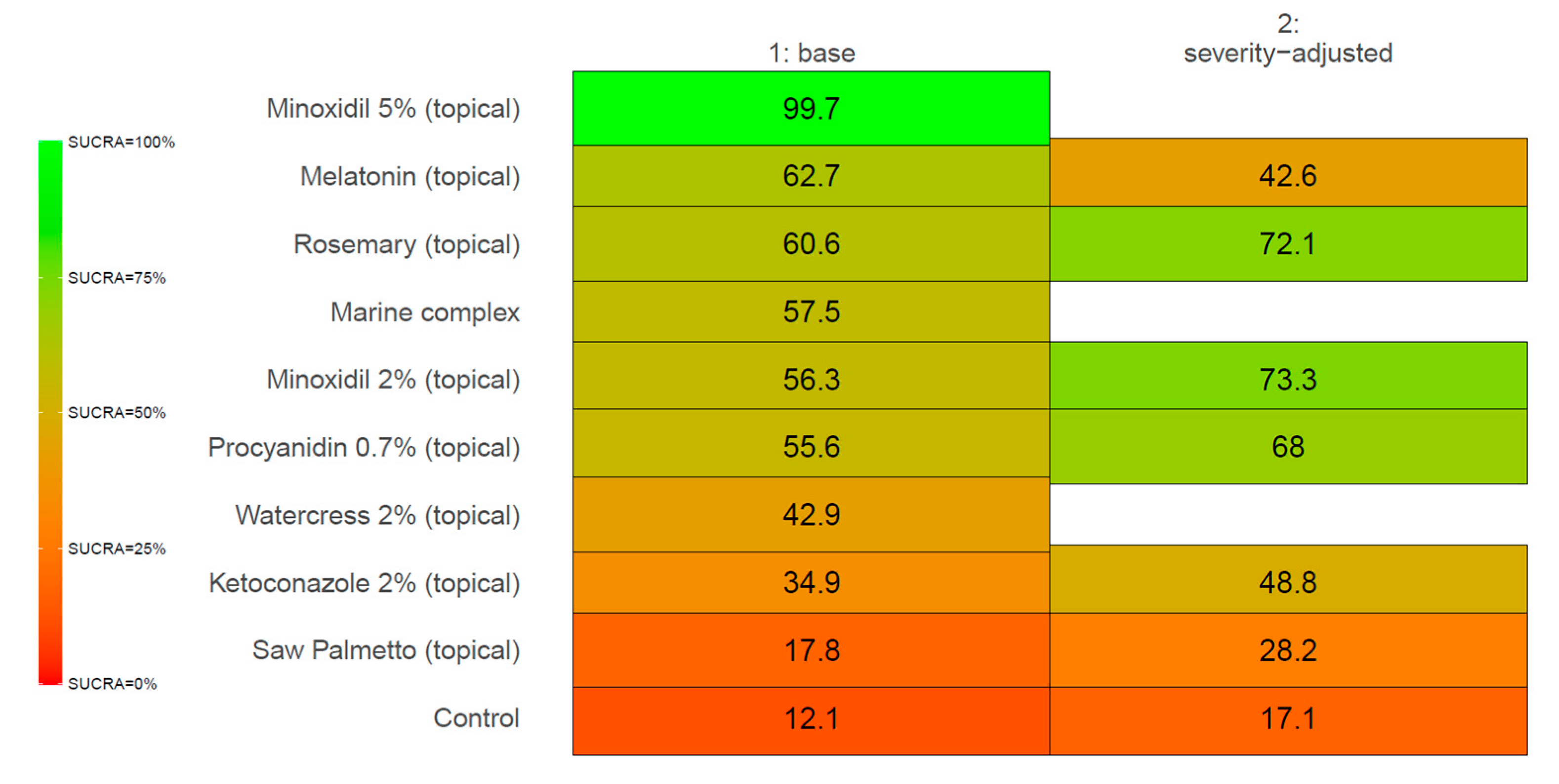
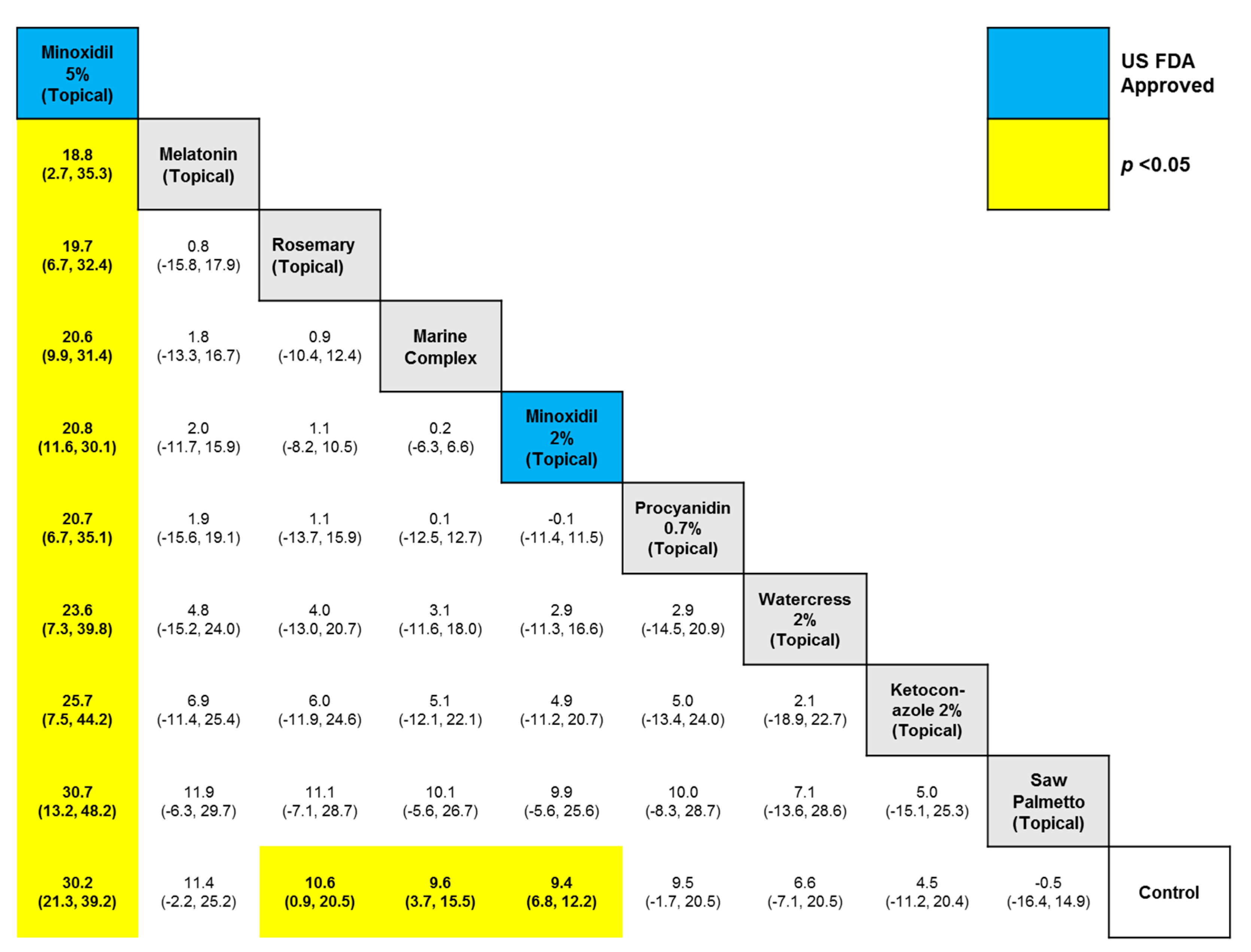
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. SULT1A1 and Minoxidil Response
4.2. Melatonin as an AGA Treatment
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Systematic Review Registration Statement
Appendix A
References
- Tosti, A.; Piraccini, B.M.; Iorizzo, M.; Voudouris, S. The natural history of androgenetic alopecia. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2005, 4, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.B. Male hormone stimulation is prerequisite and an incitant in common baldness. Am. J. Anat. 2005, 71, 451–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirya, C.T.; Wu, W.; Wu, K. Classification of Male-pattern Hair Loss. Int. J. Trichol. 2017, 9, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, E.A. Female pattern hair loss. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, S70–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, Q.Q.; Sinclair, R. Female pattern hair loss: Current treatment concepts. Clin. Interv. Aging 2007, 2, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, E. Classification of the types of androgenetic alopecia (common baldness) occurring in the female sex. Br. J. Dermatol. 1977, 97, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassakis, K. Androgenetic Alopecia from A to Z, 1st ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Seidman, M.; Westfried, M.; Maxey, R.; Rao, T.K.; Friedman, E.A. Reversal of male pattern baldness by minoxidil. A case report. Cutis 1981, 28, 551–553. [Google Scholar]
- Zappacosta, A.R. Reversal of baldness in patient receiving minoxidil for hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 1980, 303, 1480–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl, A.E.; Waldon, D.J.; Conrad, S.J.; Mulholland, M.J.; Shull, K.L.; Kubicek, M.F.; Johnson, G.A.; Brunden, M.N.; Stefanski, K.J.; Stehle, R.G. Potassium channel conductance: A mechanism affecting hair growth both in vitro and in vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1992, 98, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, A.; Shapiro, J.; Roberts, J.; McCoy, J.; Desai, N.; Zarrab, Z.; Pietrzak, A.; Lotti, T. Clinical utility and validity of minoxidil response testing in androgenetic alopecia. Dermatol. Ther. 2015, 28, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.; Desai, N.; McCoy, J.; Goren, A. Sulfotransferase activity in plucked hair follicles predicts response to topical minoxidil in the treatment of female androgenetic alopecia. Dermatol. Ther. 2014, 27, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.L.; Liu, J.S.; Lin, A.C.; Yang, C.H.; Chung, W.H.; Wu, W.G. Minoxidil may suppress androgen receptor-related functions. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2187–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Talukder, M.; Venkataraman, M.; Bamimore, M.A. Minoxidil: A comprehensive review. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 1896–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presley, C.L.; Kolodziejczyk, T.C.; Pulsipher, K.J.; Maghfour, J.; Militello, M.; Rietcheck, H.R.; Fonseca, A.; Olayinka, T.J.; Rundle, C.W.; Waller, J.D. A Scoping Review of Pharmacotherapy, Complementary, and Alternative Medicine (CAM), and Surgical Therapies for Androgenic Alopecia. Curr. Dermatol. Rep. 2021, 10, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ufomadu, P. Complementary and alternative supplements: A review of dermatologic effectiveness for androgenetic alopecia. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2024, 37, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Rubaian, N.F.; Alzamami, H.F.A.; Amir, B.A. An Overview of Commonly Used Natural Alternatives for the Treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia, with Special Emphasis on Rosemary Oil. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 2495–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Talukder, M.; Bamimore, M.A. Natural products for male androgenetic alopecia. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Talukder, M. Do non-prescription products help in managing androgenic alopecia? Ski. Appendage Disord. 2024, 11, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piquero-Casals, J.; Saceda-Corralo, D.; Aladren, S.; Bustos, J.; Fernandez-Botello, A.; Navasa, A.; Logusso, G.; Jourdan, E.; Mir-Bonafe, J.F.; Morgado-Carrasco, D. Oral Supplementation with l-Cystine, Serenoa repens, Cucurbita pepo, and Pygeum africanum in Chronic Telogen Effluvium and Androgenetic Alopecia: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Clinical Study. Ski. Appendage Disord. 2025, 11, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Biasio, F.; Ielpo, A.; Santarsiere, L.; Ivaldi, L.; Salamone, R.; Gorgoglione, D. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial to evaluate the effect of an Annurca apple supplement formula in androgenic alopecia. J. Appl. Cosmetol. 2023, 41, 28–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergfeld, W.; Washenik, K.; Callender, V.; Zhang, P.; Quiza, C.; Doshi, U.; Blume-Peytavi, U. A Phase III, Multicenter, Parallel-Design Clinical Trial to Compare the Efficacy and Safety of 5% Minoxidil Foam Versus Vehicle in Women With Female Pattern Hair Loss. J. Drugs Dermatol. JDD 2016, 15, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Juni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouse, B.; Chaimani, A.; Li, T. Network meta-analysis: An introduction for clinicians. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2017, 12, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelimi, R.; Metelli, S.; Sbidian, E.; van Zuuren, E.J.; Flohr, C.; Leonardi-Bee, J.; Le Cleach, L. Network meta-analysis: Methodological points for readers, authors and reviewers. Br. J. Dermatol. 2022, 186, 917–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posit Team RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Phillippo, D.M.; Dias, S.; Ades, A.E.; Belger, M.; Brnabic, A.; Schacht, A.; Saure, D.; Kadziola, Z.; Welton, N.J. Multilevel network meta-regression for population-adjusted treatment comparisons. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 2020, 183, 1189–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, E.A.; DeLong, E.R.; Weiner, M.S. Dose-response study of topical minoxidil in male pattern baldness. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1986, 15, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civatte, J.; Laux, B.; Simpson, N.B.; Vickers, C.F. 2% topical minoxidil solution in male-pattern baldness: Preliminary European results. Dermatologica 1987, 175 (Suppl. S2), 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.; Scandinavian and Middle-Eastern Topical Minoxidil Study Group. Topical minoxidil in androgenetic alopecia scandinavian and middle east experience. Int. J. Dermatol. 1988, 27, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutrée-Meulenberg, R.; Nieboer, C.; Koedijk, F.; Stolz, E. Treatment of male pattern alopecia using topical minoxidil in the Netherlands. Int. J. Dermatol. 1988, 27, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzoldt, D.; Group, G.t.M.S. The German double-blind placebo-controlled evaluation of topical minoxidil solution in the treatment of early male pattern baldness. Int. J. Dermatol. 1988, 27, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierard-Franchimont, C.; De Doncker, P.; Cauwenbergh, G.; Pierard, G.E. Ketoconazole shampoo: Effect of long-term use in androgenic alopecia. Dermatology 1998, 196, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, D.H.; Unger, W.P.; Cotterill, P.C.; Kingsley, P.; James, K.C. Quantitative assessment of 2% topical minoxidil in the treatment of male pattern baldness. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1989, 14, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Kamimura, A.; Kagoura, M.; Toyoda, M.; Morohashi, M. Investigation of the topical application of procyanidin oligomers from apples to identify their potential use as a hair-growing agent. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2005, 4, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, T.W.; Trueb, R.M.; Hanggi, G.; Innocenti, M.; Elsner, P. Topical melatonin for treatment of androgenetic alopecia. Int. J. Trichol. 2012, 4, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakr, F.M.; Gado, A.M.; Mohammed, H.R.; Adam, A.N. Preparation and evaluation of a multimodal minoxidil microemulsion versus minoxidil alone in the treatment of androgenic alopecia of mixed etiology: A pilot study. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, Y.; Taghizadeh, M.; Marzony, E.T.; Sahebkar, A. Rosemary oil vs minoxidil 2% for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia: A randomized comparative trial. Skinmed 2015, 13, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ablon, G. A 6-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating the ability of a marine complex supplement to promote hair growth in men with thinning hair. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessagowit, V.; Tangjaturonrusamee, C.; Kootiratrakarn, T.; Bunnag, T.; Pimonrat, T.; Muangdang, N.; Pichai, P. Treatment of male androgenetic alopecia with topical products containing S erenoa repens extract. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2016, 57, e76–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Rai, T. Comparison of efficacy of platelet-rich plasma therapy with or without topical 5% minoxidil in male-type baldness: A randomized, double-blind placebo control trial. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2020, 86, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Kawai, Y.; Masutani, T.; Tanaka, K.; Ito, K.; Iddamalgoda, A. Effects of watercress extract fraction on R-spondin 1-mediated growth of human hair. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2022, 44, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Valkenhoef, G.; Dias, S.; Ades, A.E.; Welton, N.J. Automated generation of node-splitting models for assessment of inconsistency in network meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2016, 7, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phutrakool, P.; Pongpirul, K. Acceptance and use of complementary and alternative medicine among medical specialists: A 15-year systematic review and data synthesis. Syst. Rev. 2022, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangkiatkumjai, M.; Boardman, H.; Walker, D.M. Potential factors that influence usage of complementary and alternative medicine worldwide: A systematic review. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, A.; McCoy, J.; Kovacevic, M.; Situm, M.; Chitalia, J.; Dhurat, R.; Naccarato, T.; Lotti, T. The effect of topical minoxidil treatment on follicular sulfotransferase enzymatic activity. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32, 937–940. [Google Scholar]
- McCoy, J.; Goren, A.; Kovacevic, M.; Shapiro, J. Minoxidil dose response study in female pattern hair loss patients determined to be non-responders to 5% topical minoxidil. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30, 1153–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Slominski, A.; Wortsman, J.; Tobin, D.J. The cutaneous serotoninergic/melatoninergic system: Securing a place under the sun. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author and Year | Study Design | Treatment | Frequency of Use | Sample size at Baseline | Age, Standard Deviation ͳ) | Disease Severity (Mild, Moderate, Severe) † |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olsen 1986 [30] | randomized, double-blind | Minoxidil 2% (topical) | 1 mL twice daily | 19 | 35.4, 4 | 0%, 100%, 0% |
| Control | 19 | 37, 6.3 | 0%, 100%, 0% | |||
| Civatte 1987 [31] | randomized, double-blind | Minoxidil 2% (topical) | 1 mL twice daily | 125 | 33.4 (18–49) | 0%, 48.15%, 51.85% |
| Control | 122 | 34.8 (20–40) | 0%, 55.29%, 44.71% | |||
| Anderson 1988 [32] | randomized, double-blind | Minoxidil 2% (topical) | 1 mL twice daily | 77 | 32.8 (19–49) | 0%, 100%, 0% |
| Control | 77 | 32.8 (19–49) | 0%, 100%, 0% | |||
| Dutrée-Meulenberg 1988 [33] | randomized, double-blind | Minoxidil 2% (topical) | 1 mL twice daily | 74 | 34.3 (19–49) | |
| Control | 70 | 34.3 (19–49) | ||||
| Petzoldt 1988 [34] | randomized, double-blind | Minoxidil 2% (topical) | 1 mL twice daily | 101 | 32.9 (17–49) | |
| Control | 100 | 32.9 (17–49) | ||||
| Pierard-Franchimont 1998 [35] | prospective cohort | Minoxidil 2% (topical) | 2 to 4 times weekly for 21 months | 4 | 0%, 100%, 0% | |
| Ketoconazole 2% (topical) | 4 | 0%, 100%, 0% | ||||
| Rushton 1998 [36] | randomized, double-blind | Minoxidil 2% (topical) | 1 mL twice daily | 12 | 18–49 | |
| Control | 12 | 18–49 | ||||
| Takahashi 2005 [37] | randomized, double-blind | Procyanidin 0.7% (topical) | 2 mL twice daily | 25 | 47.62%, 52.38%, 0% | |
| Control | 24 | 59.09%, 40.91%, 0% | ||||
| Fischer 2012 [38] | single-arm | Melatonin (topical) | once daily | 35 | 18–41 | 100%, 0%, 0% |
| Sakr 2013 [39] | randomized, double-blind | Minoxidil 5% (topical) | 1 mL twice daily | 11 | 25–30 | |
| Control | 10 | 25–30 | ||||
| Panahi 2015 [40] | randomized, single-blind | Rosemary (topical) | 1 mL twice daily | 50 | 24.78, 3.67 | 74%, 26%, 0% |
| Minoxidil 2% (topical) | 50 | 23.38, 2.5 | 68%, 32%, 0% | |||
| Ablon 2016 [41] | randomized, double-blind | Marine complex (oral) | one capsule per day | 30 | 42.8, 7.7 | |
| Control | 30 | 46.1 | ||||
| Wessagowit 2016 [42] | single-arm | Saw Palmetto (topical) | once daily | 100 | 20–50 | 0%, 70%, 30% |
| Singh 2020 [43] | randomized, double-blind | Minoxidil 5% (topical) | 1 mL twice daily | 20 | 18–60 | |
| Control | 20 | 18–60 | ||||
| Hashimoto 2022 [44] | randomized, double-blind | Watercress 2% (topical) | twice daily | 23 | ||
| Control | 23 |
| Agent | Mechanism of action |
|---|---|
| Minoxidil | Vasodilator Reduce inflammation Activate Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway |
| Melatonin | Activate Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway Antioxidant Anti-inflammatory properties Anti-androgen properties |
| Rosemary | Antioxidant Antibacterial Antifungal Anti-inflammatory properties |
| Marine complex | Stimulate proliferation of dermal papilla cells |
| Procyanidin | Reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation Encourage growth of hair epithelial cells |
| Watercress | Modulate key signaling pathways (notably Wnt/β-catenin via RSPO1 and DKK1) Activating growth-promoting kinases Antioxidant property |
| Ketoconazole | Anti-inflammatory Anti-androgen properties |
| Saw Palmetto | Inhibition of 5-α-reductase enzyme |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gupta, A.K.; Talukder, M.; Keene, S.; Williams, G.; Bamimore, M.A. Comparative Effect of Conventional and Non-Conventional Over-the-Counter Treatments for Male Androgenetic Alopecia: A Network Meta-Analysis Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167920
Gupta AK, Talukder M, Keene S, Williams G, Bamimore MA. Comparative Effect of Conventional and Non-Conventional Over-the-Counter Treatments for Male Androgenetic Alopecia: A Network Meta-Analysis Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167920
Chicago/Turabian StyleGupta, Aditya K., Mesbah Talukder, Sharon Keene, Greg Williams, and Mary A. Bamimore. 2025. "Comparative Effect of Conventional and Non-Conventional Over-the-Counter Treatments for Male Androgenetic Alopecia: A Network Meta-Analysis Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167920
APA StyleGupta, A. K., Talukder, M., Keene, S., Williams, G., & Bamimore, M. A. (2025). Comparative Effect of Conventional and Non-Conventional Over-the-Counter Treatments for Male Androgenetic Alopecia: A Network Meta-Analysis Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167920







