Golgi-Cox Staining Protocol for Medium Spiny Neurons in the Striatum of Neonatal and Early Postnatal Mouse Brain Using Cryosections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
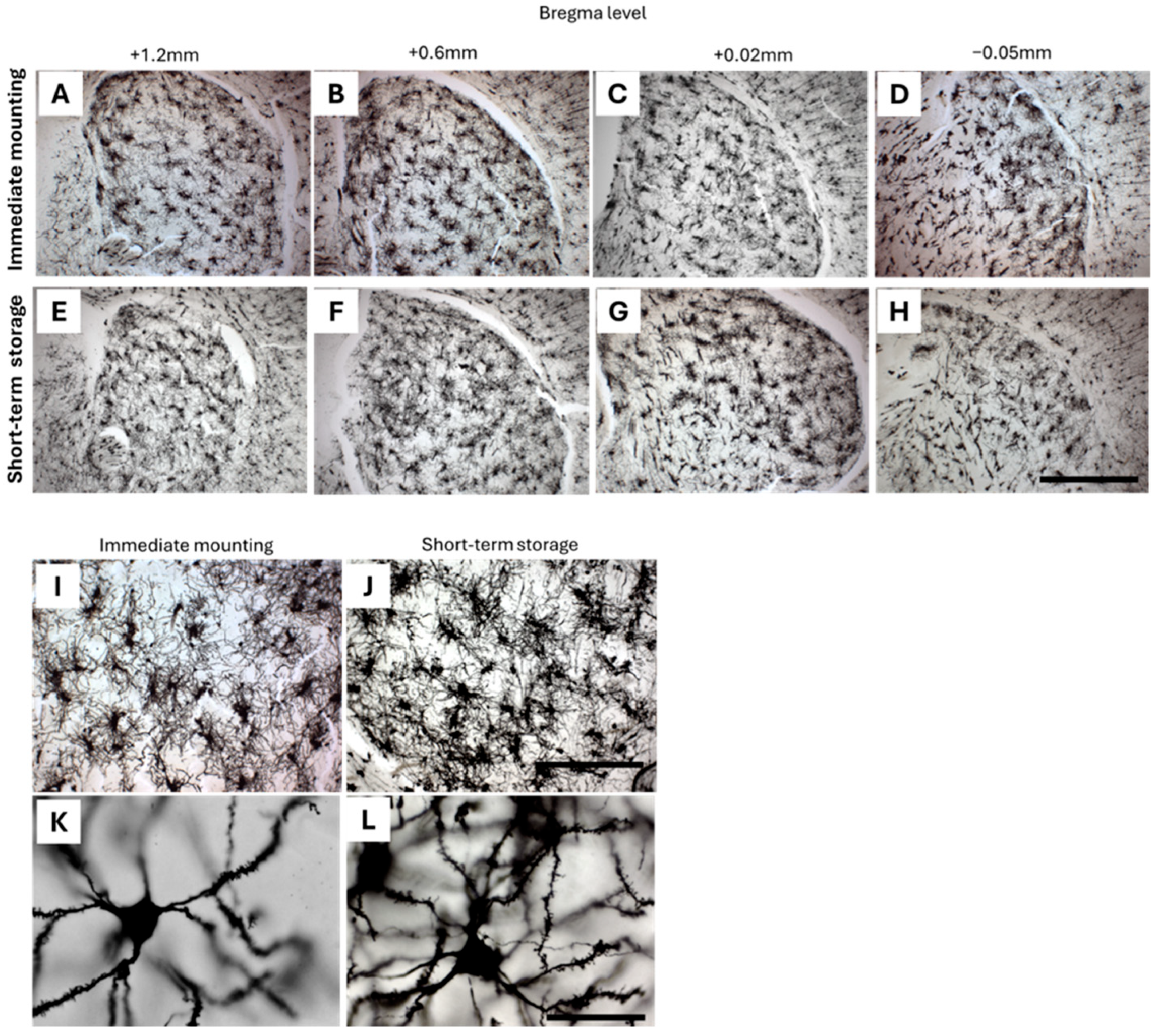
2.1. Optimization of Cryoprotection Step with Golgi-Impregnated Neonatal, Early Postnatal, and Adult Mouse Brain
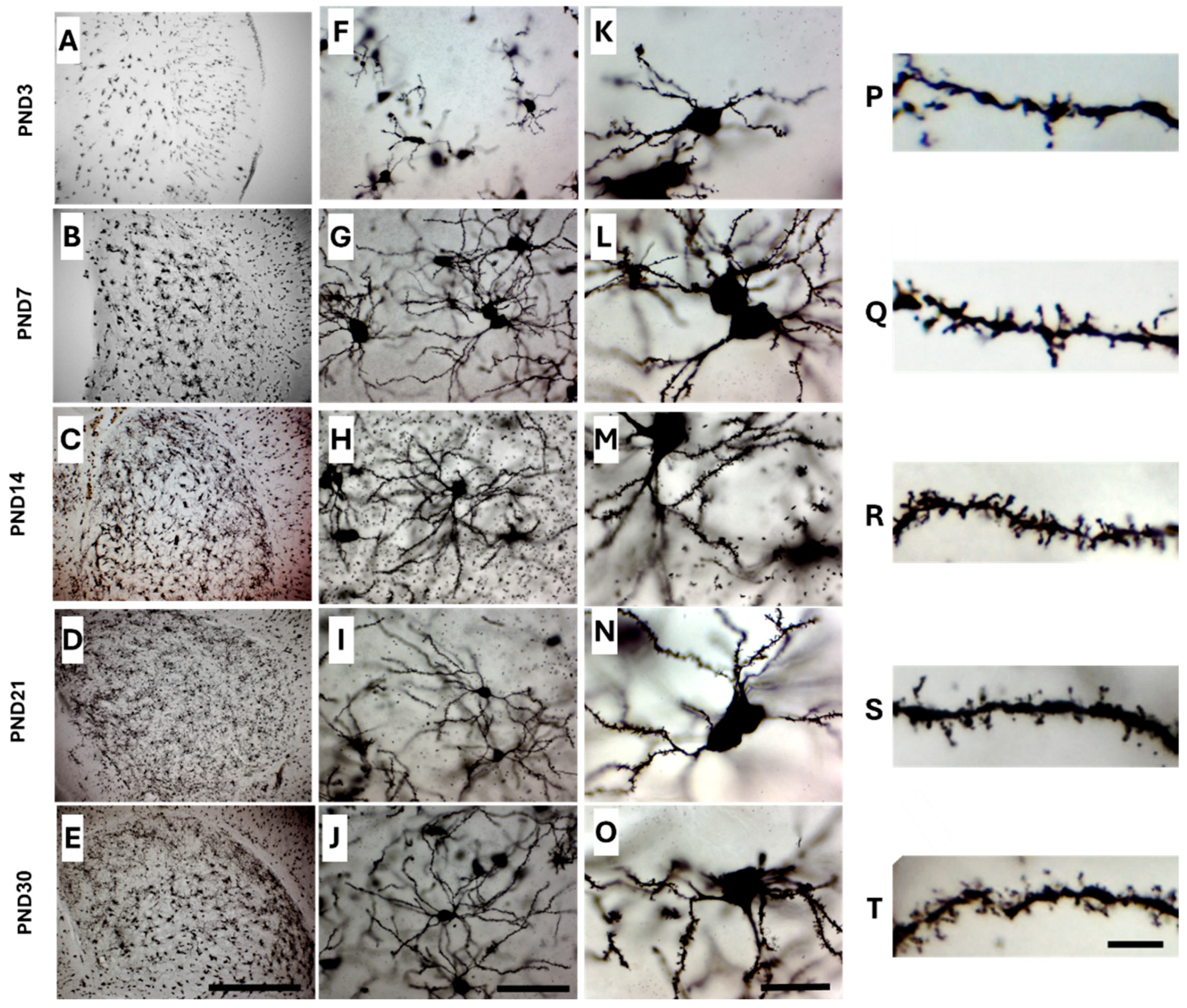
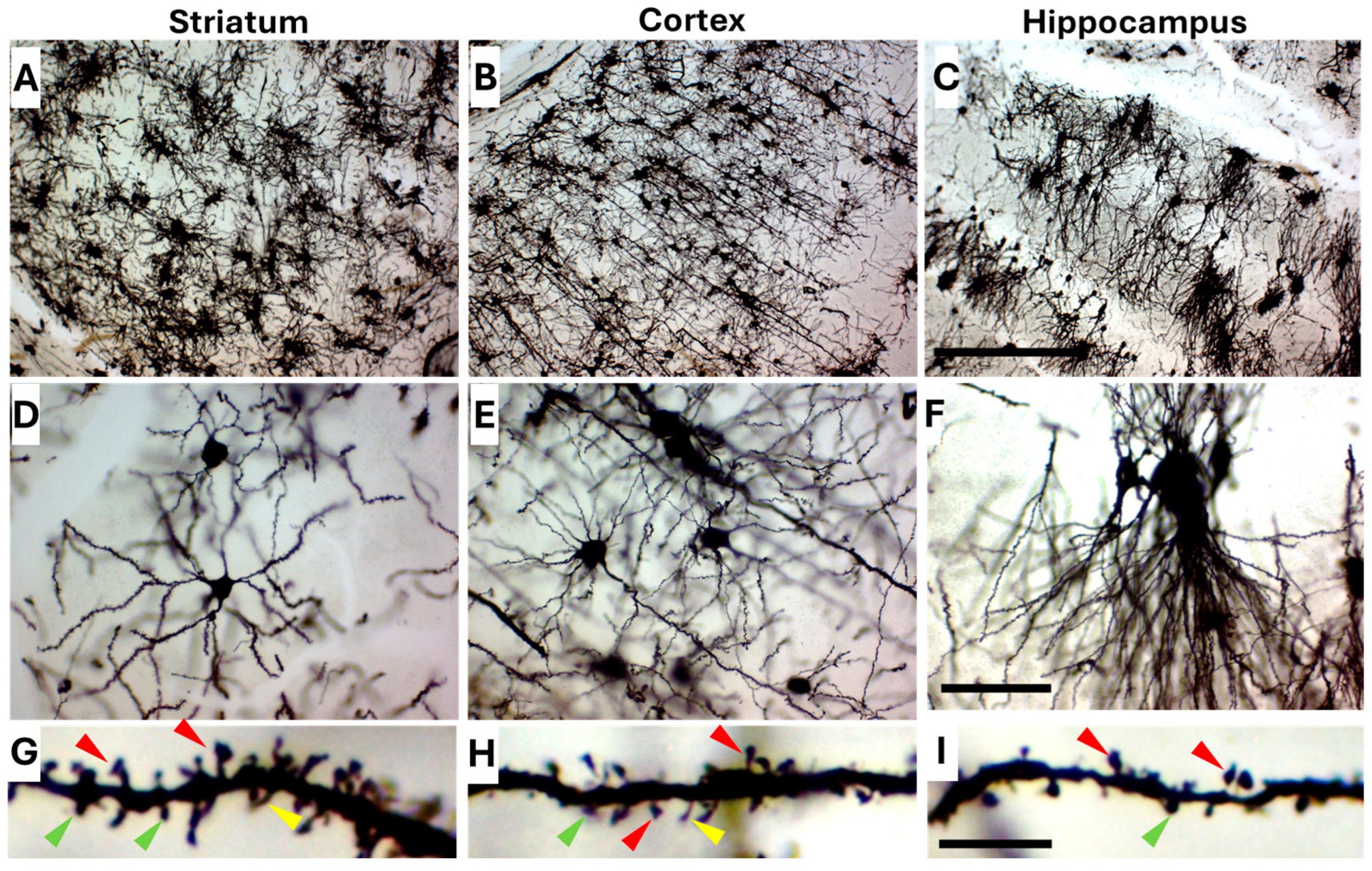
2.2. Golgi-Cox Staining Quality and Tissue Integrity Across All Age Groups
2.3. Optimizing Golgi-Cox Staining for Neonatal Mouse Brain (PND1 and PND3)
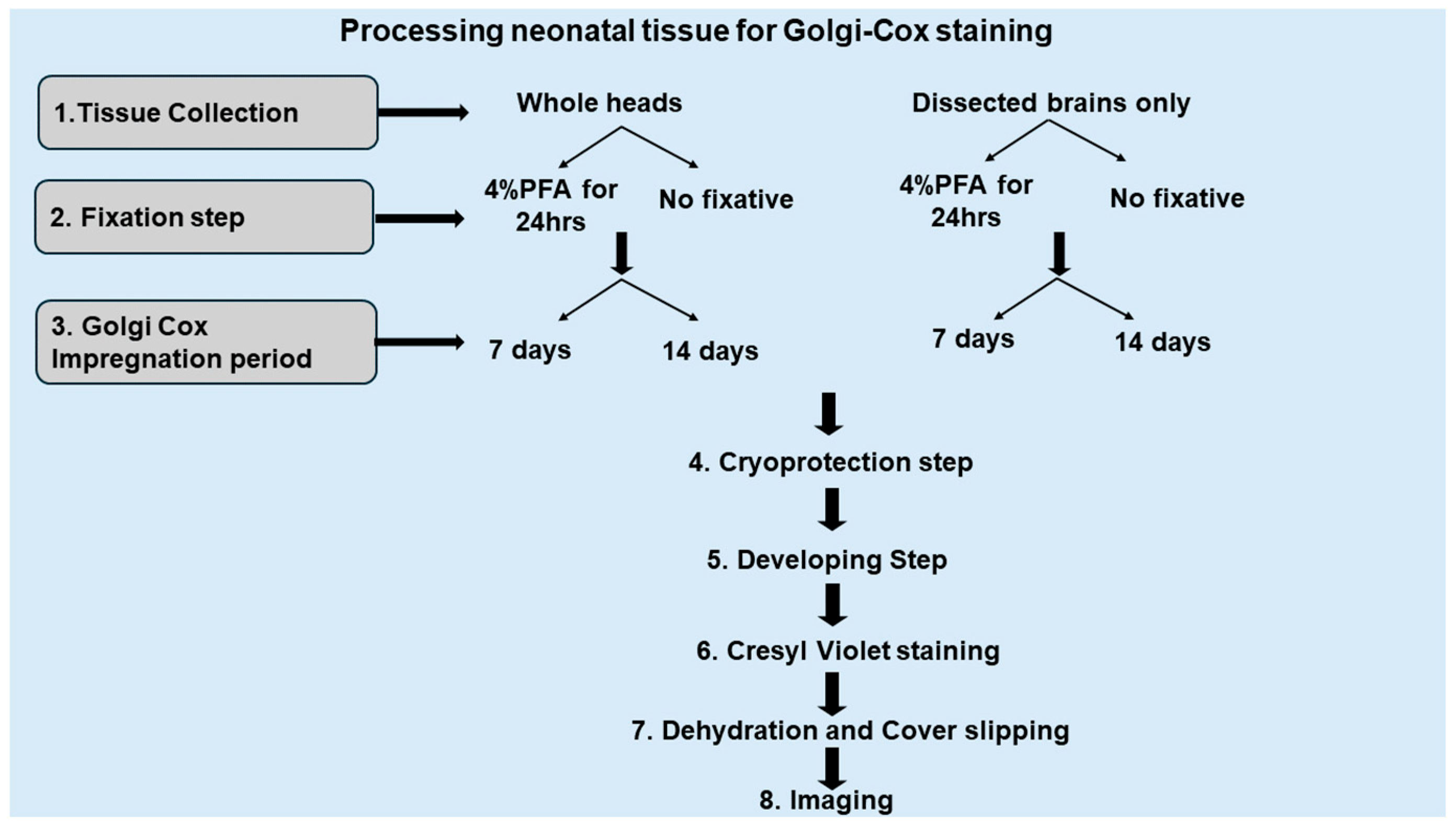
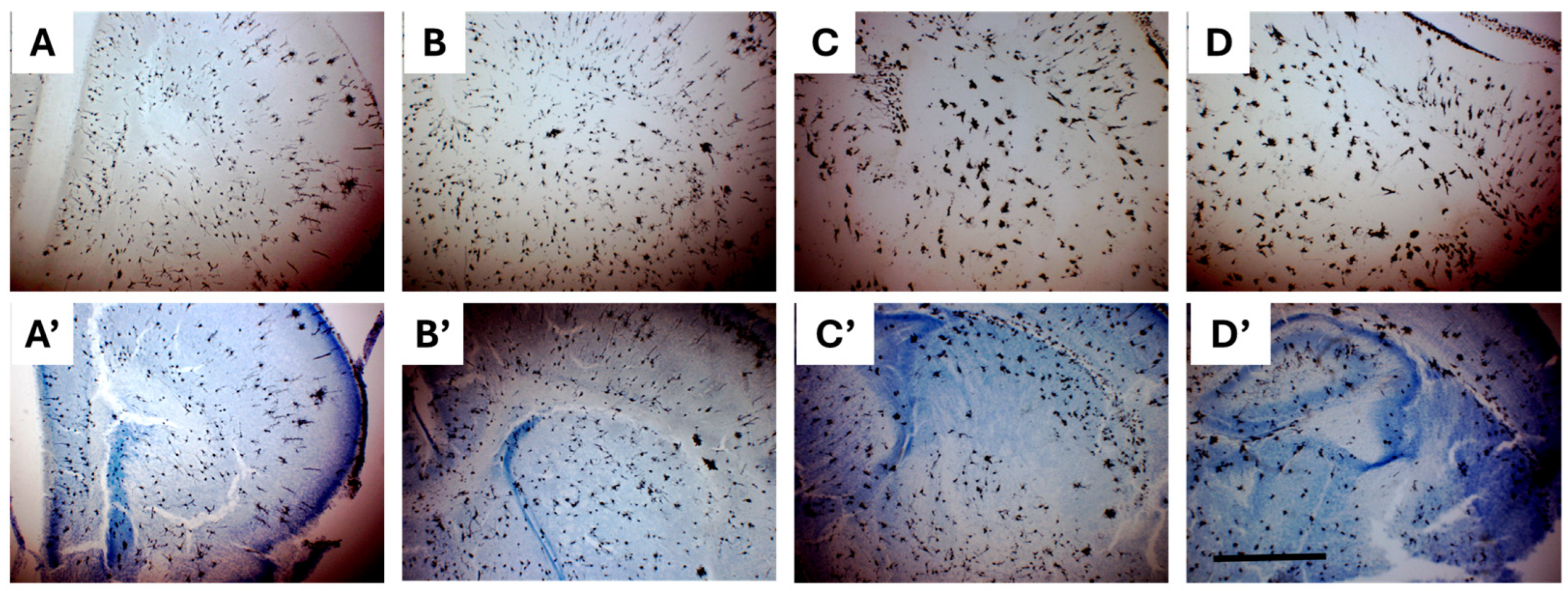
2.3.1. Comparison Between Impregnated Dissected Brains and Whole Heads
2.3.2. Combining Golgi-Cox and Nissl Staining Enhances Demarcation of Striatal Boundaries and Visualization of Individual Neurons in the Neonatal Brain
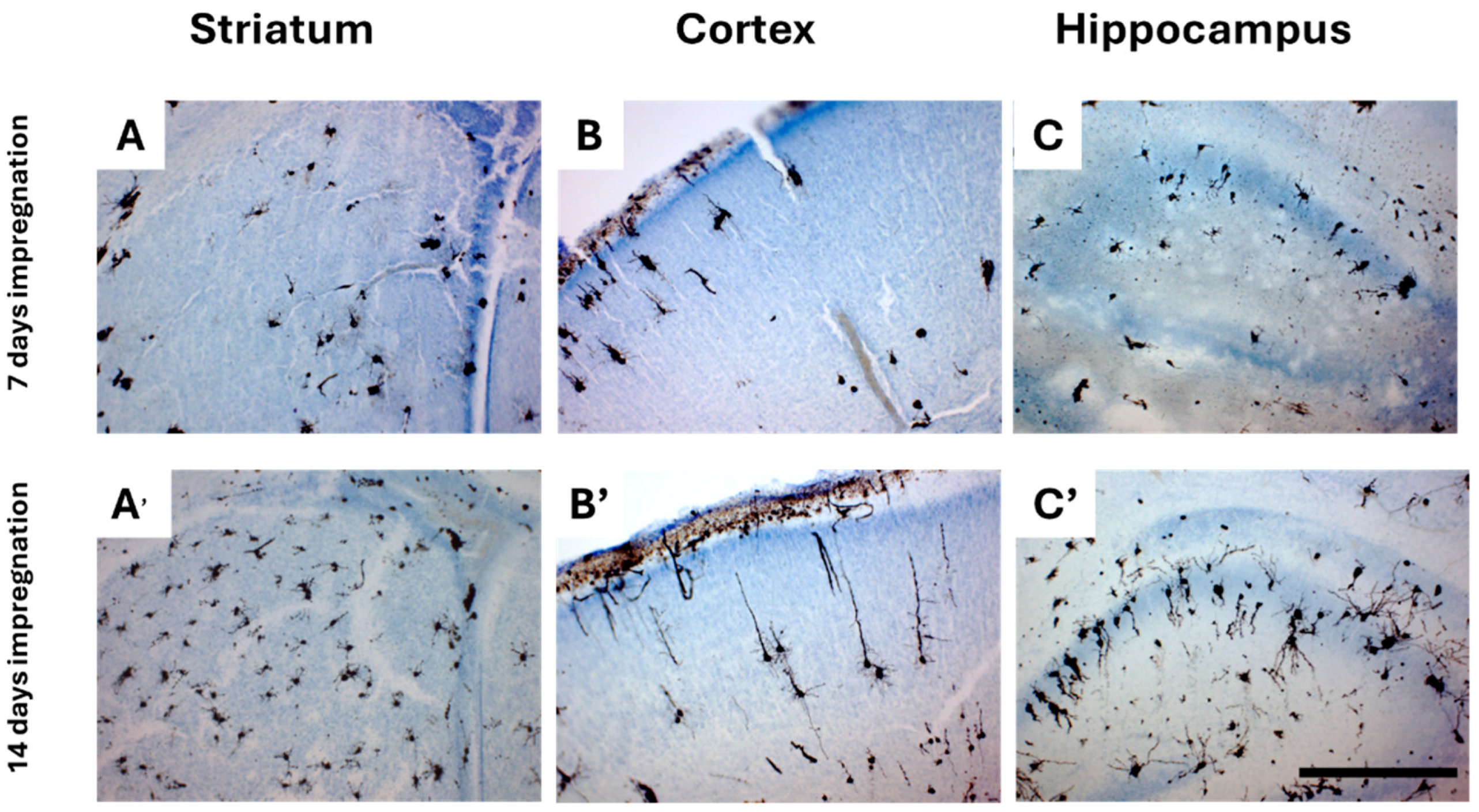
2.3.3. An Impregnation Time of 14 Days Is Required for Both Adult and Neonatal Tissue
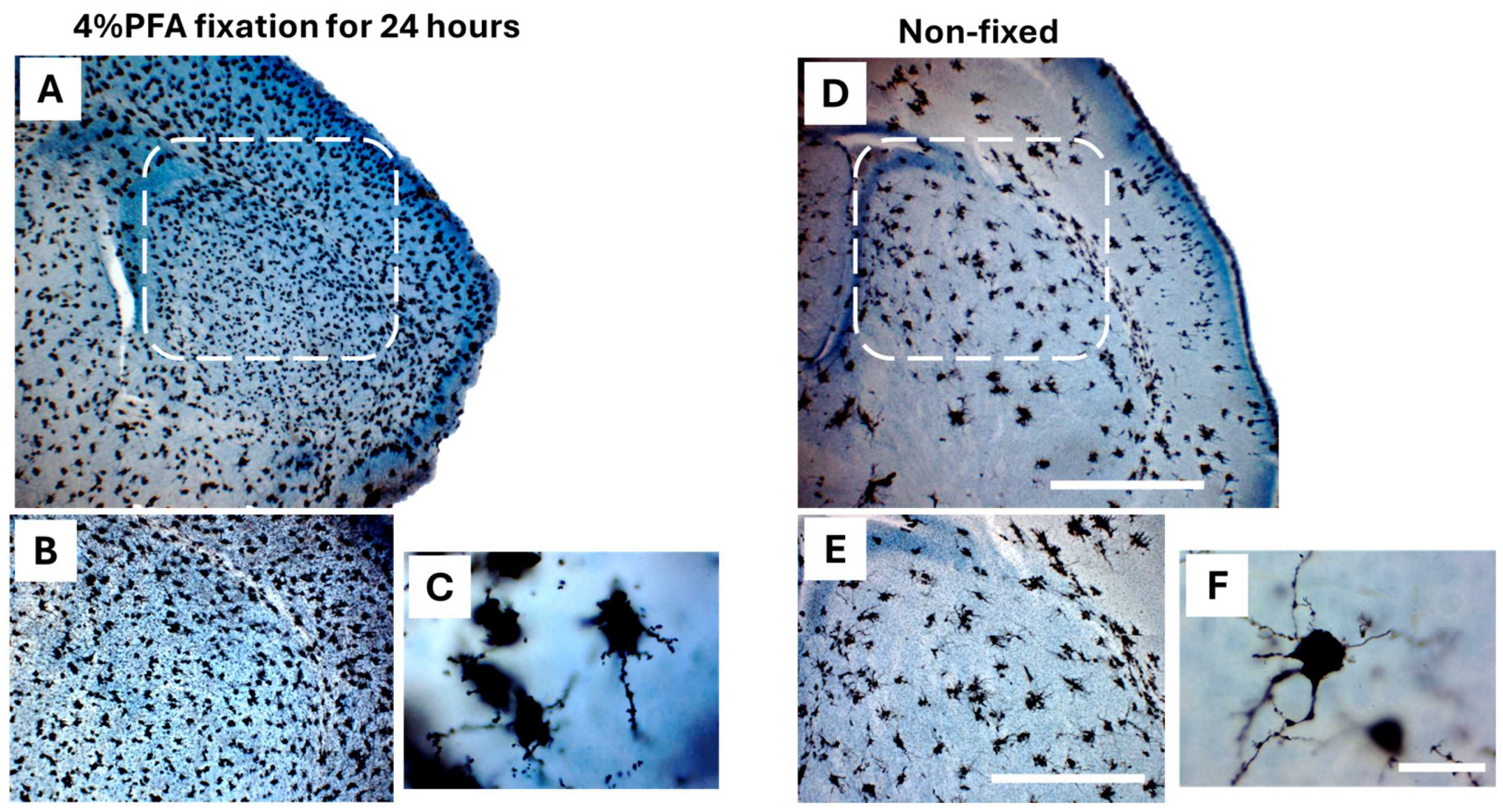
2.3.4. Fixation with 4% Paraformaldehyde (PFA) vs. Non-Fixation
2.4. Golgi-Cox Staining Protocol Is Suitable to Use with Adult Tissue
3. Discussion
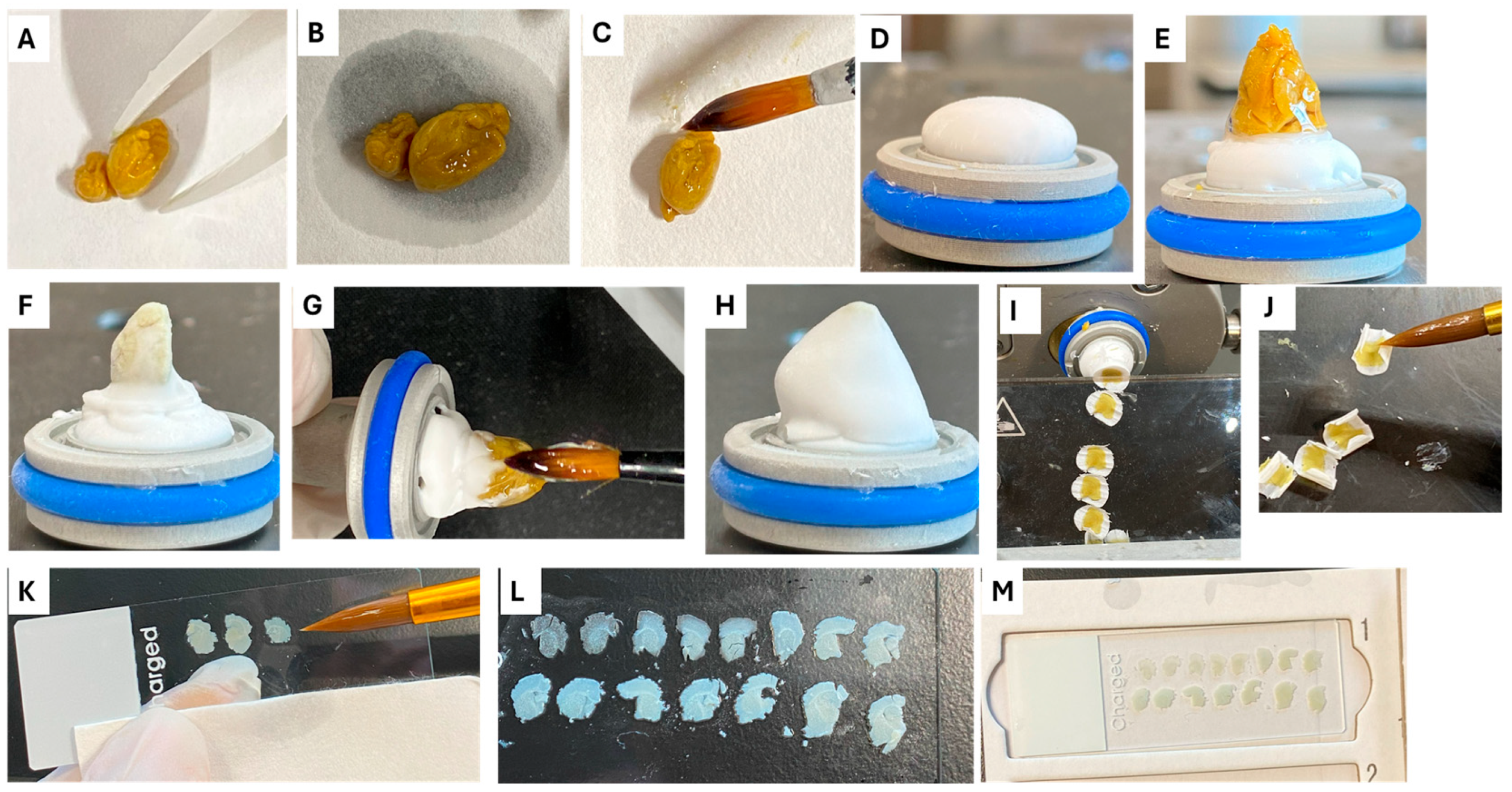
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Solution Preparations
4.1.1. Golgi-Cox Solution Preparation
4.1.2. Cryoprotectant Solution Preparation
4.1.3. PFA Solution (4%) Preparation
4.1.4. Cresyl Violet Solution Preparation
4.1.5. Gelatin-Coated Slide Preparation
4.2. Experimental Animals
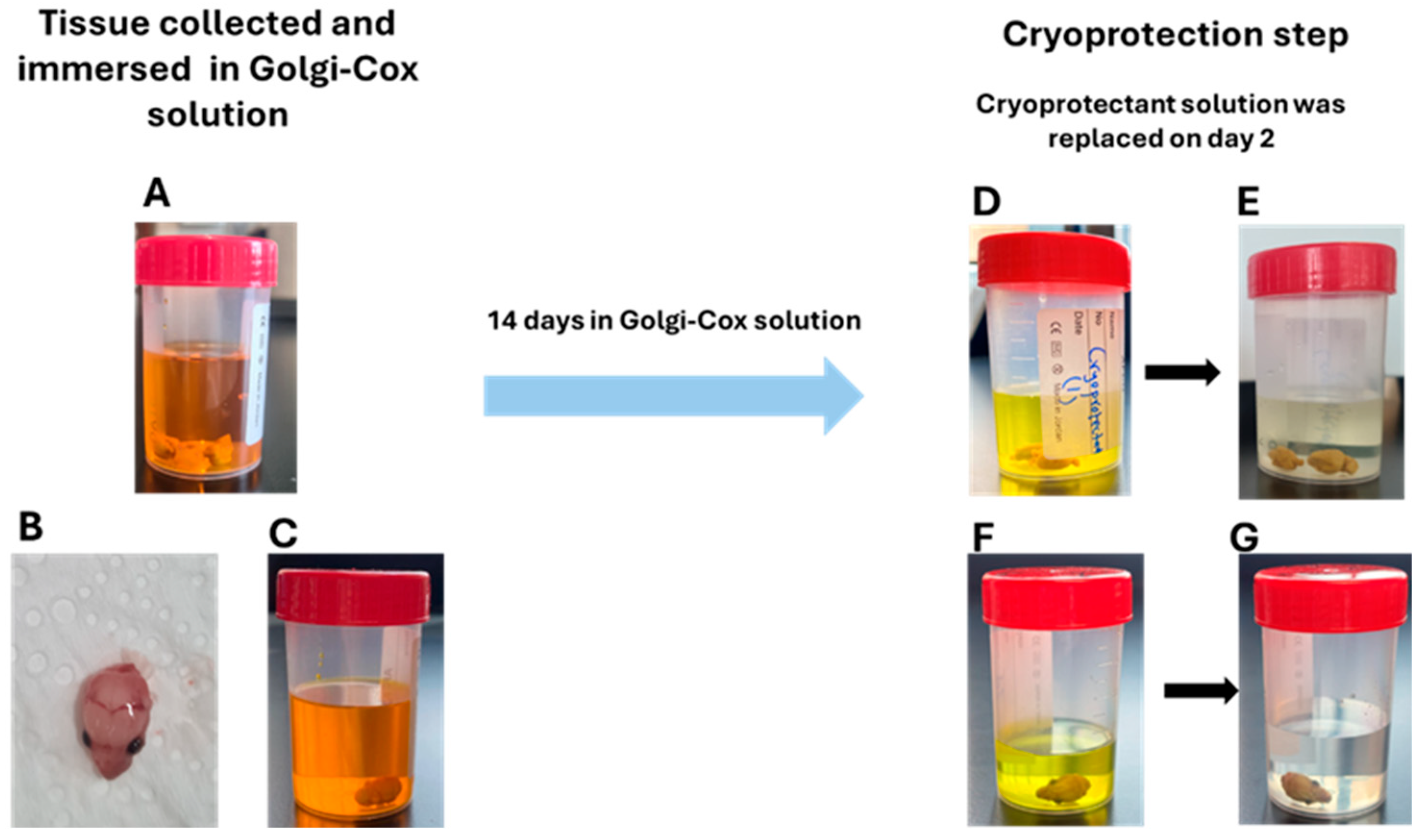
4.3. Collecting Tissue and Cryoprotection
4.4. Cryosectioning Step
4.5. Staining Procedure
4.5.1. Preparation of Development Solution
4.5.2. Dehydration and Mounting Step
4.5.3. Combined Golgi-Cox and Nissl Staining for Neonatal Brains (PND1 and PND3)
4.6. Image Acquisition
4.7. Structural Preservation Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MSNs | Medium Spiny Neurons |
| PND | Postnatal day |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered Saline |
| OCT | Optimal cutting temperature |
| NDDs | Neurodevelopmental disorders |
| dH2O | Distilled water |
References
- Tepper, J.M.; Sharpe, N.A.; Koós, T.Z.; Trent, F. Postnatal development of the rat neostriatum: Electrophysiological, light- and electron-microscopic studies. Dev. Neurosci. 1998, 20, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebouc, M.; Richard, Q.; Garret, M.; Baufreton, J. Striatal circuit development and its alterations in Huntington’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 145, 105076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehorter, N.; Vinay, L.; Hammond, C.; Ben-Ari, Y. Timing of developmental sequences in different brain structures: Physiological and pathological implications. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 1846–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehorter, N.; Michel, F.J.; Marissal, T.; Rotrou, Y.; Matrot, B.; Lopez, C.; Humphries, M.D.; Hammond, C. Onset of pup locomotion coincides with loss of NR2C/D-mediated cortico-striatal EPSCs and dampening of striatal network immature activity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medendorp, W.E.; Petersen, E.D.; Pal, A.; Wagner, L.M.; Myers, A.R.; Hochgeschwender, U.; Jenrow, K.A. Altered Behavior in Mice Socially Isolated During Adolescence Corresponds With Immature Dendritic Spine Morphology and Impaired Plasticity in the Prefrontal Cortex. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, G.W.; Anderson, W.J. Dendritic alterations of cortical pyramidal neurons in postnatally lead-exposed kittens: A Golgi-Cox study. Dev. Neurosci. 1995, 17, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Yang, G.; Kwon, E.; Gan, W.-B. Long-term sensory deprivation prevents dendritic spine loss in primary somatosensory cortex. Nature 2005, 436, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Wang, Y.; Lin, G.; Liao, F.F.; Zhou, F.M. Dopamine-independent development and maintenance of mouse striatal medium spiny neuron dendritic spines. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 181, 106096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, R.T.; Chantranupong, L.; Hakim, R.; Levasseur, J.; Wang, W.; Merchant, T.; Gorman, K.; Budnik, B.; Sabatini, B.L. Abnormal Striatal Development Underlies the Early Onset of Behavioral Deficits in Shank3B−/− Mice. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 2016–2027.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz, B.Y.; Wennagel, D.; Ratié, L.; de Souza, D.A.R.; Deloulme, J.C.; Barbier, E.L.; Buisson, A.; Lanté, F.; Humbert, S. Treating early postnatal circuit defect delays Huntington’s disease onset and pathology in mice. Science 2022, 377, eabq5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tendilla-Beltrán, H.; Antonio Vázquez-Roque, R.; Judith Vázquez-Hernández, A.; Garcés-Ramírez, L.; Flores, G. Exploring the Dendritic Spine Pathology in a Schizophrenia-related Neurodevelopmental Animal Model. Neuroscience 2019, 396, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Yan, S.; Li, S.H.; Li, X.J. Postnatal loss of hap1 reduces hippocampal neurogenesis and causes adult depressive-like behavior in mice. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felbor, U.; Kessler, B.; Mothes, W.; Goebel, H.H.; Ploegh, H.L.; Bronson, R.T.; Olsen, B.R. Neuronal loss and brain atrophy in mice lacking cathepsins B and L. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7883–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golgi, C. Sulla sostanza grigia del cervello. Gazz. Med. Ital. 1873, 33, 244–246. [Google Scholar]
- Kassem, M.S.; Fok, S.Y.Y.; Smith, K.L.; Kuligowski, M.; Balleine, B.W. A novel, modernized Golgi-Cox stain optimized for CLARITY cleared tissue. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 294, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, F.; Liu, L.; Wei, J.-L.; Dai, R.-P. Step by Step Golgi-Cox Staining for Cryosection. Front. Neuroanat. 2019, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayram-Weston, Z.; Olsen, E.; Harrison, D.J.; Dunnett, S.B.; Brooks, S.P. Optimising Golgi-Cox staining for use with perfusion-fixed brain tissue validated in the zQ175 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 265, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vints, K.; Vandael, D.; Baatsen, P.; Pavie, B.; Vernaillen, F.; Corthout, N.; Rybakin, V.; Munck, S.; Gounko, N.V. Modernization of Golgi staining techniques for high-resolution, 3-dimensional imaging of individual neurons. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, B.; Atterton, C.; Whitehead, D.; Thor, S.; Piper, M. A refined Golgi-Cox method for the staining of embryonic neurons in the mouse brain. J. Neurosci. Methods 2025, 418, 110432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, Y.; Tohyama, M. A modified and highly sensitive Golgi-Cox method to enable complete and stable impregnation of embryonic neurons. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 209, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.E.V.; Moore, A.R.; Nam, A.Y.; Saxena, S.; Paradis, S.; Van Hooser, S.D. Experience-Dependent Development of Dendritic Arbors in Mouse Visual Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 6536–6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risher, W.C.; Ustunkaya, T.; Singh Alvarado, J.; Eroglu, C. Rapid Golgi analysis method for efficient and unbiased classification of dendritic spines. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warton, S.S.; Jones, D.G. Postnatal development of the superficial layers in the rat superior colliculus: A study with Golgi-Cox and Klüver-Barrera techniques. Exp. Brain Res. 1985, 58, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budday, S.; Ovaert, T.C.; Holzapfel, G.A.; Steinmann, P.; Kuhl, E. Fifty Shades of Brain: A Review on the Mechanical Testing and Modeling of Brain Tissue. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2020, 27, 1187–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.M.; Zhang, Y.; Kames, C.; Rauscher, A. Myelin water imaging and R2* mapping in neonates: Investigating R2* dependence on myelin and fibre orientation in whole brain white matter. NMR Biomed. 2020, 33, e4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaqout, S.; Kaindl, A.M. Golgi-Cox Staining Step by Step. Front. Neuroanat. 2016, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Mallick, B.N. A modified method for consistent and reliable Golgi-cox staining in significantly reduced time. Front. Neurol. 2010, 1, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, B.D.; Blomgren, K.; Gimlin, K.; Ferriero, D.M.; Noble-Haeusslein, L.J. Brain development in rodents and humans: Identifying benchmarks of maturation and vulnerability to injury across species. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 106–107, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Tabassum, S.; Jiang, J.X.; Long, C. Optimized Golgi-Cox Staining Validated in the Hippocampus of Spared Nerve Injury Mouse Model. Front. Neuroanat. 2020, 14, 585513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, S.S.; Nikolova, V.D.; Riddick, N.V.; Baker, L.K.; Koller, B.H. Preweaning sensorimotor deficits and adolescent hypersociability in Grin1 knockdown mice. Dev. Neurosci. 2012, 34, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, L.; Sébrié, C.; Laroche, S.; Vaillend, C.; Poirier, R. Delayed postnatal brain development and ontogenesis of behavior and cognition in a mouse model of intellectual disability. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 183, 106163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulianella, A. Cutting Thick Sections Using a Vibratome. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2017, 2017, pdb.prot094011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, R.; Kolb, B. A method for vibratome sectioning of Golgi-Cox stained whole rat brain. J. Neurosci. Methods 1998, 79, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F. Golgi-Cox Staining of Neuronal Dendrites and Dendritic Spines With FD Rapid GolgiStain™ Kit. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2019, 88, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudink, I.; White, T.A.; Ardalan, M.; Mallard, C.; Ballerin, G.; Creed, S.J.; Pham, Y.; Sutherland, A.E.; Castillo-Melendez, M.; Allison, B.J.; et al. An Optimized and Detailed Step-by-Step Protocol for the Analysis of Neuronal Morphology in Golgi-Stained Fetal Sheep Brain. Dev. Neurosci. 2022, 44, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilati, N.; Barker, M.; Panteleimonitis, S.; Donga, R.; Hamann, M. A rapid method combining Golgi and Nissl staining to study neuronal morphology and cytoarchitecture. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2008, 56, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.N.; Bairy, L.K.; Srinivasamurthy, S.K. Determining factors for optimal neuronal and glial Golgi-Cox staining. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 154, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerhoff, J.; Muhie, S.; Chakraborty, N.; Naidu, L.; Sowe, B.; Hammamieh, R.; Jett, M.; Gautam, A. Microdissection of Mouse Brain into Functionally and Anatomically Different Regions. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 168, e61941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Cai, Y.; Wu, X.; Ying, Y.; Tai, Y.; He, M. Transcardiac Perfusion of the Mouse for Brain Tissue Dissection and Fixation. Bio Protoc. 2021, 11, e3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacManus, D.B. Excision of whole intact mouse brain. MethodsX 2023, 10, 102246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozorovitskiy, Y.; Peixoto, R.; Wang, W.; Saunders, A.; Sabatini, B.L. Neuromodulation of excitatory synaptogenesis in striatal development. eLife 2015, 4, e10111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, H.A.; Mahmoud, W.; Alzyoud, J.A.M.; Aolymat, I.; AL-Nassan, S. Golgi-Cox Staining Protocol for Medium Spiny Neurons in the Striatum of Neonatal and Early Postnatal Mouse Brain Using Cryosections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7870. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167870
Ali HA, Mahmoud W, Alzyoud JAM, Aolymat I, AL-Nassan S. Golgi-Cox Staining Protocol for Medium Spiny Neurons in the Striatum of Neonatal and Early Postnatal Mouse Brain Using Cryosections. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7870. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167870
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Heba A., Wafaa Mahmoud, Jihad A. M. Alzyoud, Iman Aolymat, and Saad AL-Nassan. 2025. "Golgi-Cox Staining Protocol for Medium Spiny Neurons in the Striatum of Neonatal and Early Postnatal Mouse Brain Using Cryosections" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7870. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167870
APA StyleAli, H. A., Mahmoud, W., Alzyoud, J. A. M., Aolymat, I., & AL-Nassan, S. (2025). Golgi-Cox Staining Protocol for Medium Spiny Neurons in the Striatum of Neonatal and Early Postnatal Mouse Brain Using Cryosections. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7870. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167870





