Targeting Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels in Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Insights into 4-Aminopyridine-Induced Cell Death
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Determination of IC50 Values and the Investigation of Cell Death Mechanisms Induced by 4-AP in L929 and MCF-7 Cell Lines
2.2. Assessment of Intracellular Calcium Changes Following Drug Treatments
2.3. Membrane Potential Measurements: Effect of Drug Treatments on Membrane Polarization
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and the Growth Condition
4.2. Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity of 4-AP, Z-VAD-FMK, CHX, 2-APB: Determination of IC50 Values
4.3. Determination of Intracellular Ca2+ Concentration
4.4. Measurement of Transmembrane Potential Using DiBAC4(3)
4.5. Statistical Analyzes
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4-AP | 4-Aminopyridine |
| 2-APB | 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate |
| CHX | Cycloheximide |
| DiBAC4(3) | Bis-(1,3-dibutylbarbituric acid) trimethine oxonol |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| VGKC | Voltage-gated potassium channel |
| VGCC | Voltage-gated calcium channel |
| IP3 | Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| SCI | spinal cord injury |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Orai3 | Orai Calcium Release-Activated Calcium Modulator 3 |
References
- Pardo, L.A.; Stühmer, W. The Roles of K+ Channels in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, A.; Fabian, A.; Hanley, P.J.; Stock, C. Role of Ion Channels and Transporters in Cell Migration. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 1865–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.-H.; Ko, E.A.; Gu, W.; Lim, I.; Bang, H.; Zhou, T. Expression Profiling of Ion Channel Genes Predicts Clinical Outcome in Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaque, N.; Abba, M.L.; Hauser, C.; Patil, N.; Paramasivam, N.; Huebschmann, D.; Leupold, J.H.; Balasubramanian, G.P.; Kleinheinz, K.; Toprak, U.H.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing Puts Forward Hypotheses on Metastasis Evolution and Therapy in Colorectal Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.M.; Krishan, A.; Chakarova, C.F.; Moya, L.; Chambers, S.K.; Hollands, M.; Illingworth, J.C.; Williams, S.M.G.; McCabe, H.E.; Shah, A.Z.; et al. MSR1 Repeats Modulate Gene Expression and Affect Risk of Breast and Prostate Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Lin, B.; Chai, X.; Li, R.; Liao, Y.; Deng, X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, W.; Cai, Y.; et al. Phospholipid Phosphatase 4 Promotes Proliferation and Tumorigenesis, and Activates Ca2+-Permeable Cationic Channel in Lung Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zou, L.; Ma, K.; Yu, J.; Wu, H.; Wei, M.; Xiao, Q. Cell-Specific Mechanisms of TMEM16A Ca2+-Activated Chloride Channel in Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; He, Y.; Dubuc, A.M.; Hashizume, R.; Zhang, W.; Reimand, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, T.A.; Stehbens, S.J.; Younger, S.; et al. EAG2 Potassium Channel with Evolutionarily Conserved Function as a Brain Tumor Target. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steudel, F.A.; Mohr, C.J.; Stegen, B.; Nguyen, H.Y.; Barnert, A.; Steinle, M.; Beer-Hammer, S.; Koch, P.; Lo, W.; Schroth, W.; et al. SK4 Channels Modulate Ca2+ Signalling and Cell Cycle Progression in Murine Breast Cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 1172–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallet-Daher, H.; Wiel, C.; Gitenay, D.; Navaratnam, N.; Augert, A.; Le Calvé, B.; Verbeke, S.; Carling, D.; Aubert, S.; Vindrieux, D.; et al. Potassium Channel KCNA1 Modulates Oncogene-Induced Senescence and Transformation. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5253–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, E.-K.; Fukushiro-Lopes, D.; Dalheim, A.; Burnette, M.; Zartman, J.; Kaja, S.; Wells, C.; Campo, L.; Curtis, K.J.; Romero-Moreno, R.; et al. Potassium Channel Activity Controls Breast Cancer Metastasis by Affecting β-Catenin Signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Luo, L.; Lal, B.; Ma, X.; Chen, L.; Hann, C.L.; Fulton, A.M.; Leahy, D.J.; Laterra, J.; Li, M. A Monoclonal Antibody against KCNK9 K+ Channel Extracellular Domain Inhibits Tumour Growth and Metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becchetti, A. Ion Channels and Transporters in Cancer. 1. Ion Channels and Cell Proliferation in Cancer. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, C255–C265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringer, B.K.; Cooper, A.G.; Shepard, S.B. Overexpression of the G-Protein Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channel 1 (GIRK1) in Primary Breast Carcinomas Correlates with Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 582–588. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, S.; Bateman, A.; O’Kelly, I. Altered Expression of Two-Pore Domain Potassium (K2P) Channels in Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wu, J.-F.; Wang, D.-M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.-J.; Xue, G. The Correlation and Role Analysis of KCNK2/4/5/15 in Human Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Microenvironment. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 5162–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Tang, L.; Li, X.; Xiong, F.; Mo, Y.; Jiang, X.; Deng, X.; Peng, M.; Wu, P.; Zhao, M.; et al. Potassium Channel Protein KCNK6 Promotes Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 616784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Lan, H.; Jiang, T.; Wan, X.; Cheng, Y. Identification of KCNK1 as a Potential Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target of Breast Cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 241, 154286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonderlin, W.F.; Woodfork, K.A.; Strobl, J.S. Changes in membrane potential during the progression of MCF-7 human mammary tumor cells through the cell cycle. J. Cell Physiol. 1995, 165, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegman, E.A.; Young, J.A.; Cook, D.I. A 23-pS Ca2+-Activated K+ Channel in MCF-7 Human Breast Carcinoma Cells: An Apparent Correlation of Channel Incidence with the Rate of Cell Proliferation. Pflügers Arch. 1991, 417, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimatcheva, E.; Wonderlin, W.F. An ATP-Sensitive K+ Current That Regulates Progression through Early G1 Phase of the Cell Cycle in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Membr. Biol. 1999, 171, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouadid-Ahidouch, H.; Ahidouch, A. K+ Channel Expression in Human Breast Cancer Cells: Involvement in Cell Cycle Regulation and Carcinogenesis. J. Membr. Biol. 2008, 221, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouadid-Ahidouch, H.; Roudbaraki, M.; Delcourt, P.; Ahidouch, A.; Joury, N.; Prevarskaya, N. Functional and Molecular Identification of Intermediate-Conductance Ca2+-Activated K+ Channels in Breast Cancer Cells: Association with Cell Cycle Progression. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2004, 287, C125–C134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Bruggen, M.A.; Huisman, H.B.; Beckerman, H.; Bertelsmann, F.W.; Polman, C.H.; Lankhorst, G.J. Randomized Trial of 4-Aminopyridine in Patients with Chronic Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurol. 2001, 248, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lastraioli, E. Potassium channels in breast cancer. Ann. Breast Cancer 2018, 2, 1006. [Google Scholar]
- Villalonga, N.; Ferreres, J.C.; Argilés, J.M.; Condom, E.; Felipe, A. Potassium Channels Are a New Target Field in Anticancer Drug Design. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2007, 2, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.A.; Kang, Y.S.; Jung, M.W.; Kang, G.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.S. Ca2+ Influx Mediates Apoptosis Induced by 4-Aminopyridine, a K+ Channel Blocker, in HepG2 Human Hepatoblastoma Cells. Pharmacology 2000, 60, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, S.; Dharan, A.; V., J.P.; Pal, S.; Nair, B.G.; Kar, R.; Mishra, N. Paraptosis: A unique cell death mode for targeting cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1159409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Lee, D.M.; Seo, M.J.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, K.S. Intracellular Ca2+ imbalance critically contributes to paraptosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 607844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, C.; Piao, M.; Liu, M. Oxidative cell death in the central nervous system: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2025, 13, 1562344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gundelach, J.H.; Bram, R.J. Protein synthesis inhibition enhances paraptotic death induced by inhibition of cyclophilins in glioblastoma cells. Cancer Cell Microenviron. 2017, 4, e1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenabeele, P.; Galluzzi, L.; Vanden Berghe, T.; Kroemer, G. Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: An ordered cellular explosion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudelova, J.; Fleischmannova, J.; Adamova, E.; Matalova, E. Pharmacological caspase inhibitors: Research towards therapeutic perspectives. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.J.; Lee, A.R.; Jeong, S.A.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kwon, Y.-J.; Choi, K.S. Release of Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum and its subsequent influx into mitochondria trigger celastrol-induced paraptosis in cancer cells. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 6816–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, S. Intrinsic resistance to chemotherapy in breast cancer. Womens Health 2010, 6, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Fang, H.; Groom, L.; Cheng, A.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, K.; Han, P.; Zheng, M.; et al. Superoxide Flashes in Single Mitochondria. Cell 2008, 134, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, F.; Raimondi, M.; Marzagalli, M.; Di Domizio, A.; Limonta, P. The Emerging Role of Paraptosis in Tumor Cell Biology: Perspectives for Cancer Prevention and Therapy with Natural Compounds. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2020, 1873, 188338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandio, S.; Poksay, K.; de Belle, I.; Lafuente, M.J.; Liu, B.; Nasir, J.; Bredesen, D.E. Paraptosis: Mediation by MAP Kinases and Inhibition by AIP-1/Alix. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, L.E.; Arbiser, J.L. Honokiol, a Multifunctional Antiangiogenic and Antitumor Agent. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2009, 11, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Dai, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, L.; Fu, K.; Ma, C.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Celastrol as an Emerging Anticancer Agent: Current Status, Challenges and Therapeutic Strategies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, X.; Lei, S.; Shao, D.; Jiang, C.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Lei, S.; Sun, H.; et al. Iturin A-like Lipopeptides from Bacillus Subtilis Trigger Apoptosis, Paraptosis, and Autophagy in Caco-2 Cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 6414–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wen, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, L.; Hao, D.; Jiang, X.; He, G. Small-Molecule Compounds Target Paraptosis to Improve Cancer Therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhivotovsky, B.; Orrenius, S. Calcium and Cell Death Mechanisms: A Perspective from the Cell Death Community. Cell Calcium 2011, 50, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motiani, R.K.; Abdullaev, I.F.; Trebak, M. A Novel Native Store-Operated Calcium Channel Encoded by Orai3: Selective Requirement of Orai3 versus Orai1 in Estrogen Receptor-Positive versus Estrogen Receptor-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 19173–19183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHaven, W.I.; Smyth, J.T.; Boyles, R.R.; Bird, G.S.; Putney, J.W. Complex Actions of 2-Aminoethyldiphenyl Borate on Store-Operated Calcium Entry. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 19265–19273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootman, M.D.; Collins, T.J.; Mackenzie, L.; Roderick, H.L.; Berridge, M.J.; Peppiatt, C.M. 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl Borate (2-APB) Is a Reliable Blocker of Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry but an Inconsistent Inhibitor of InsP3-Induced Ca2+ Release. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cüce-Aydoğmuş, E.M.; İnhan-Garip, G.A. Investigation of the Effects of Blocking Potassium Channels with 4-Aminopyridine on Paclitaxel Activity in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Rep. 2024, 7, e70072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


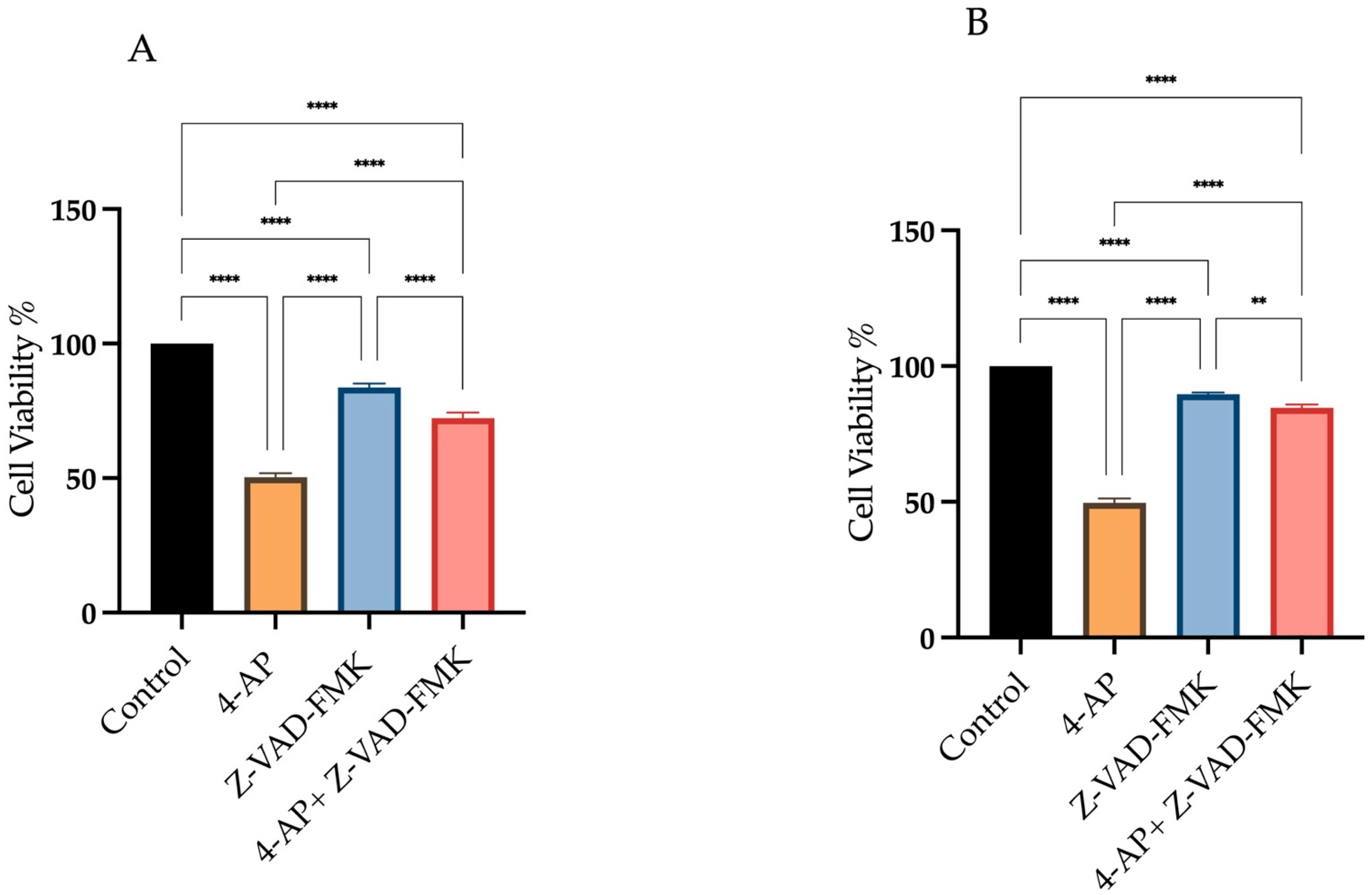
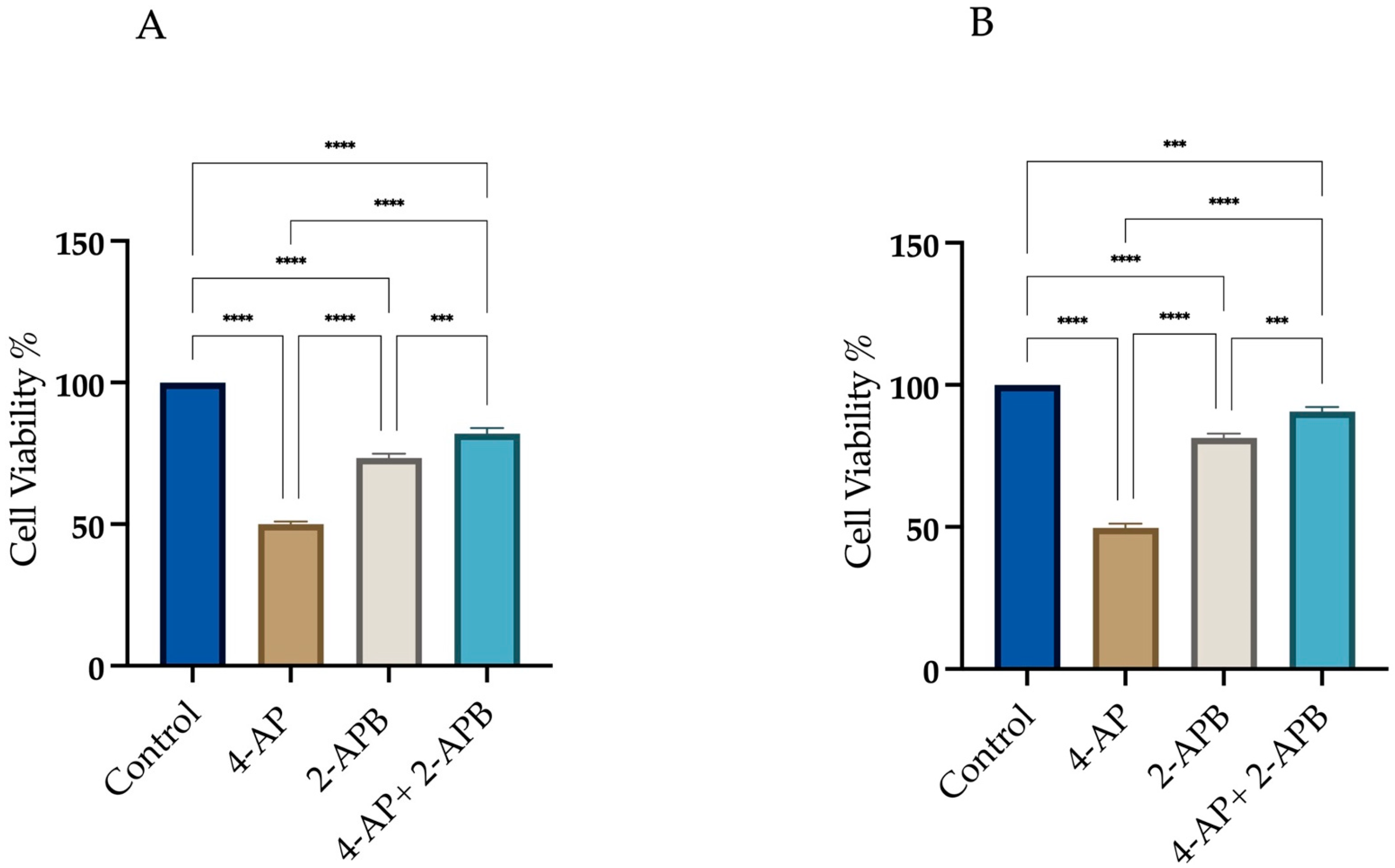
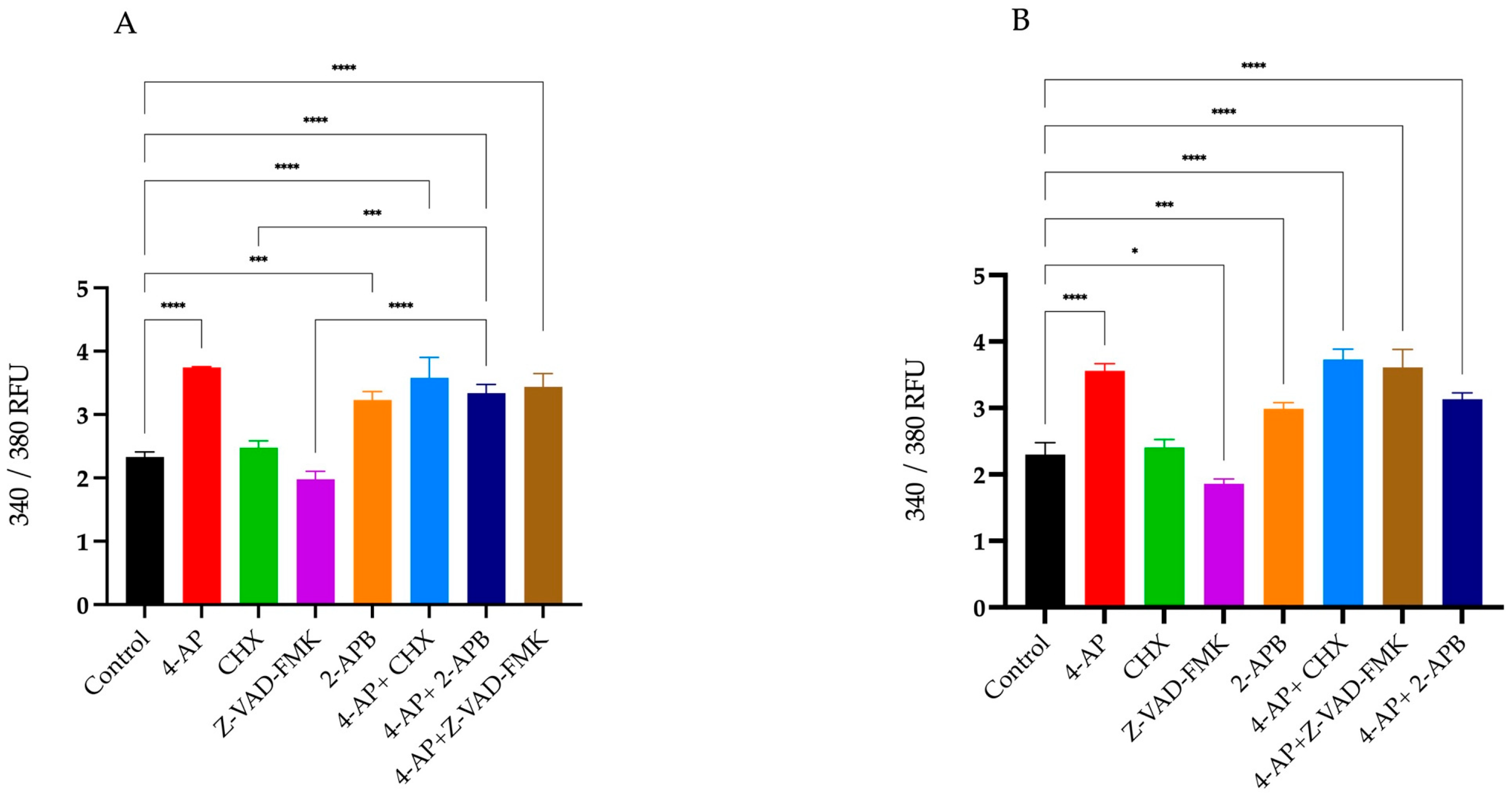
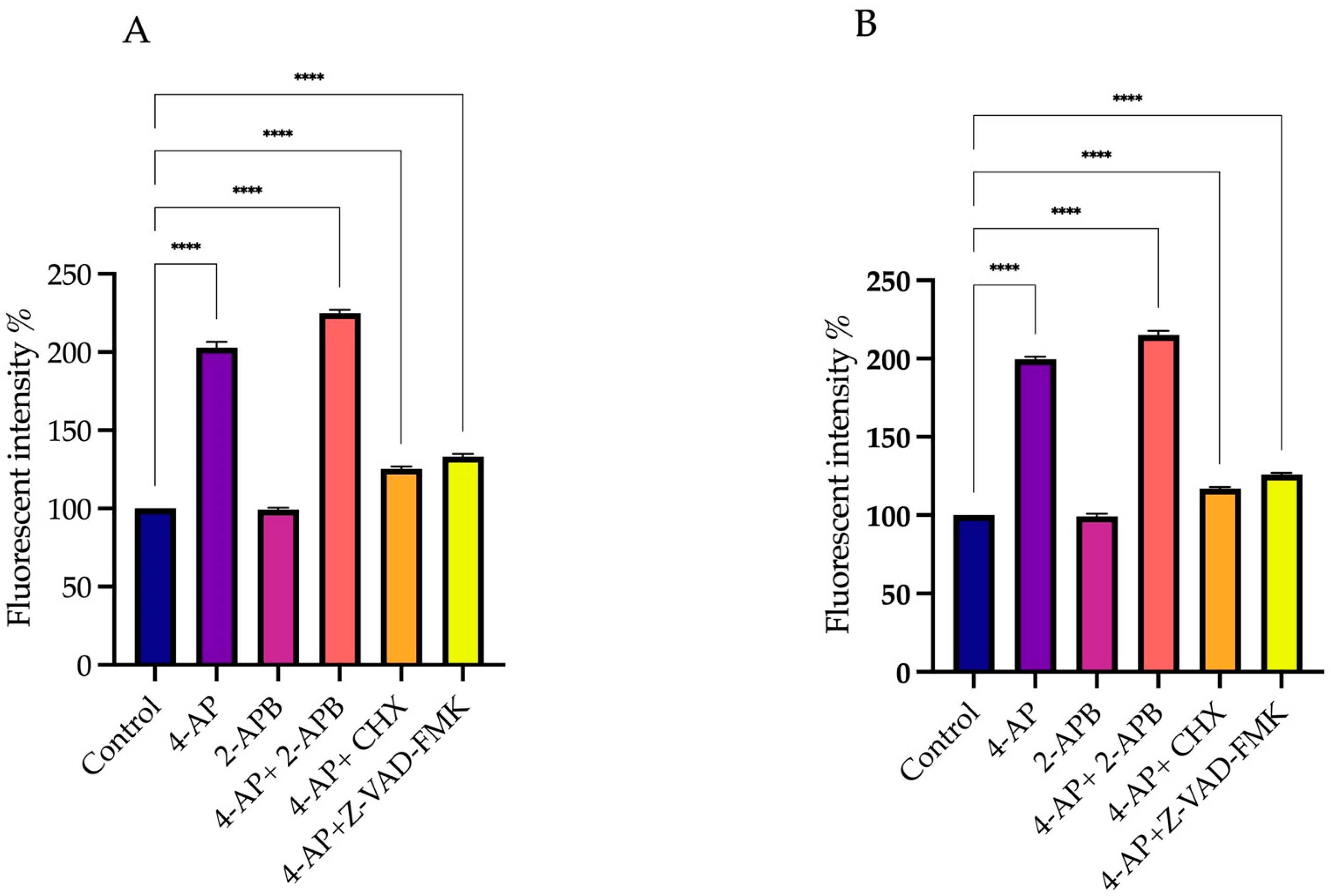

| Treatments | L929 | MCF-7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Viability | The Changes in Intracellular Ca2+ | Cell Viability | The Changes in Intracellular Ca2+ | |
| 4-AP | 50.3% ± 2.3 | 60% ± 0.19 | 49.6% ± 2.9 | 55% ± 0.13 |
| CHX | 61.6% ± 2.4 | 6% ± 0.20 | 77% ± 1.5 | 4% ± 0.11 |
| Z-VAD-FMK | 83.6% ± 1.9 | −16% ± 0.30 | 91% ± 0.9 | −19% ± 0.10 |
| 2-APB | 73.3% ± 1.9 | 38% ± 0.10 | 73% ± 2.1 | 30% ± 0.11 |
| 4-AP+CHX | 78% ± 2.2 | 53% ± 0.37 | 88% ± 1.2 | 62% ± 0.17 |
| 4-AP+Z-VAD-FMK | 72.3% ± 2.4 | 47% ± 0.10 | 85% ± 1.2 | 57% ± 0.26 |
| 4-AP+2-APB | 82% ± 2.5 | 42% ± 0.10 | 92% ± 2.0 | 36% ± 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cüce-Aydoğmuş, E.M.; İyiol, P.; İnhan-Garip, G.A. Targeting Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels in Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Insights into 4-Aminopyridine-Induced Cell Death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167768
Cüce-Aydoğmuş EM, İyiol P, İnhan-Garip GA. Targeting Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels in Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Insights into 4-Aminopyridine-Induced Cell Death. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167768
Chicago/Turabian StyleCüce-Aydoğmuş, Esra Münire, Pınar İyiol, and Günseli Ayşe İnhan-Garip. 2025. "Targeting Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels in Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Insights into 4-Aminopyridine-Induced Cell Death" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167768
APA StyleCüce-Aydoğmuş, E. M., İyiol, P., & İnhan-Garip, G. A. (2025). Targeting Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels in Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Insights into 4-Aminopyridine-Induced Cell Death. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167768






