Modulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels from Sensory Neurons by Isoeugenol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
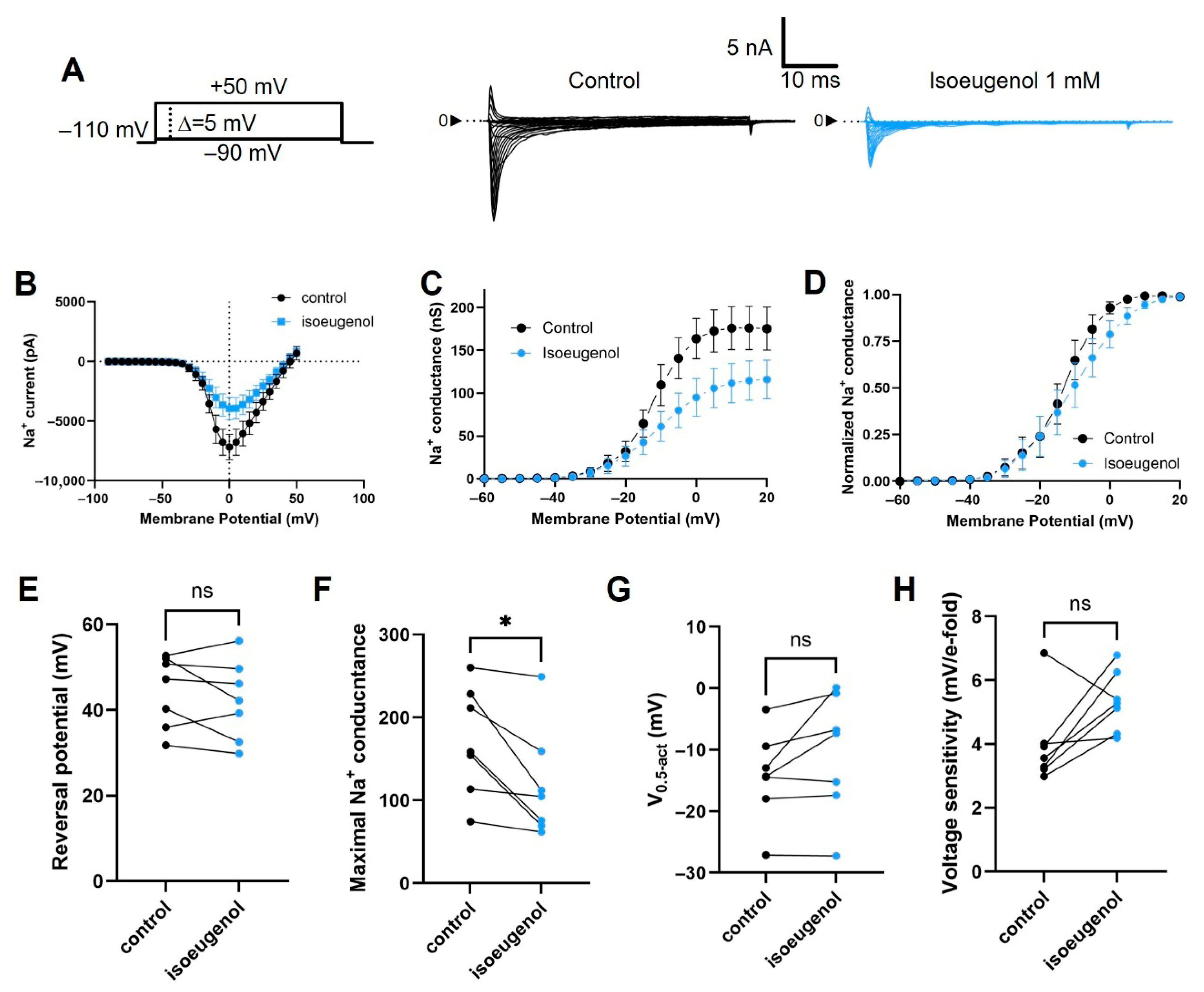
2.1. Isoeugenol Modulates INa in a Dose-Dependent Manner
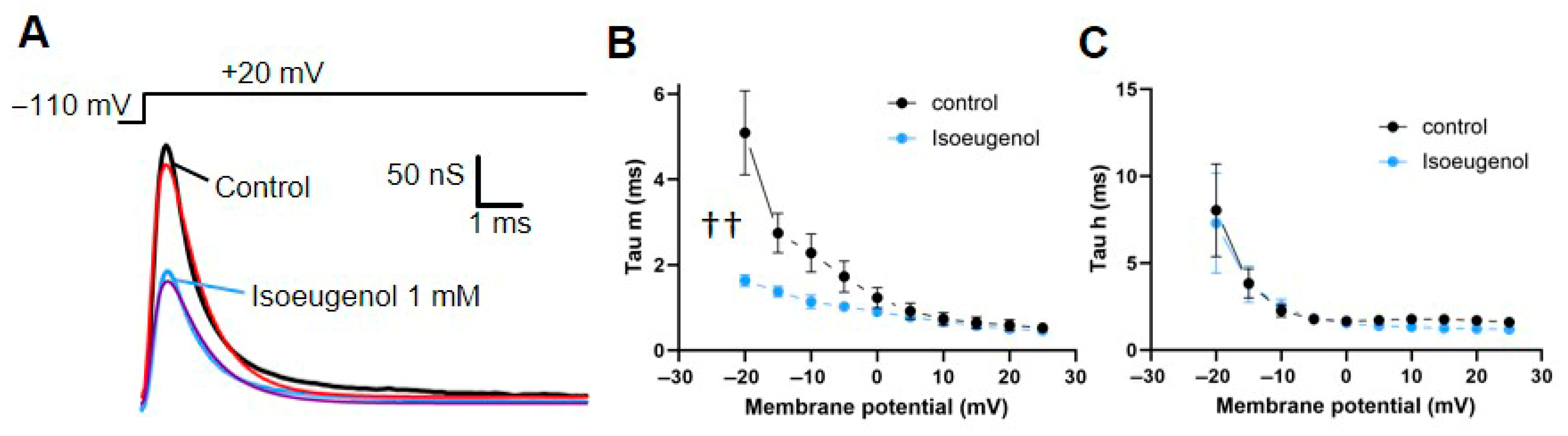
2.2. Isoeugenol Accelerates INa Activation
2.3. Isoeugenol Does Not Affect the Activation of INa by Voltage
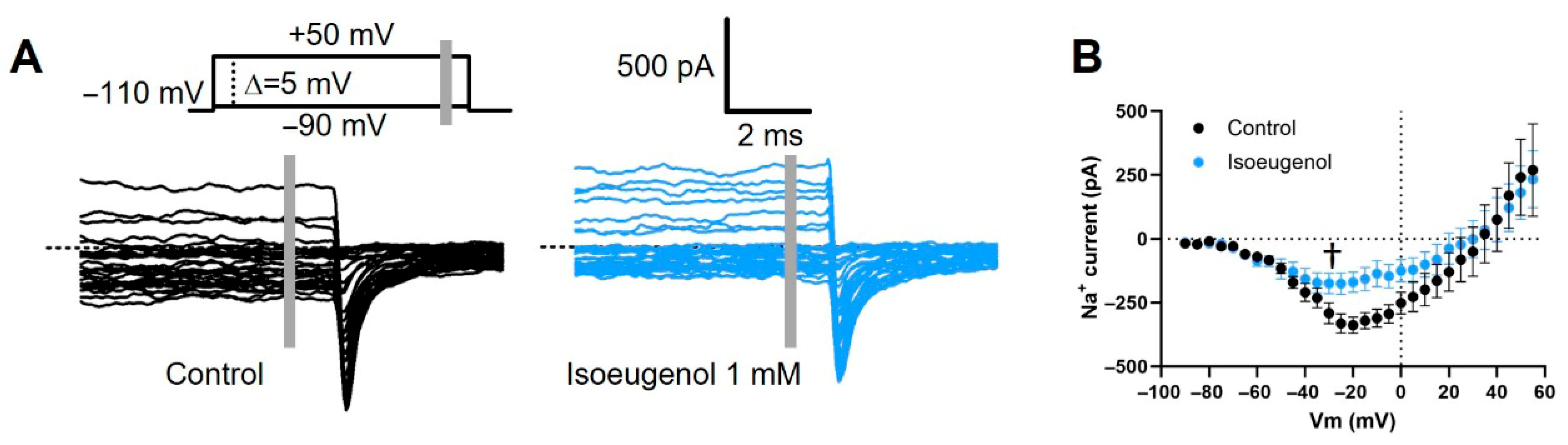
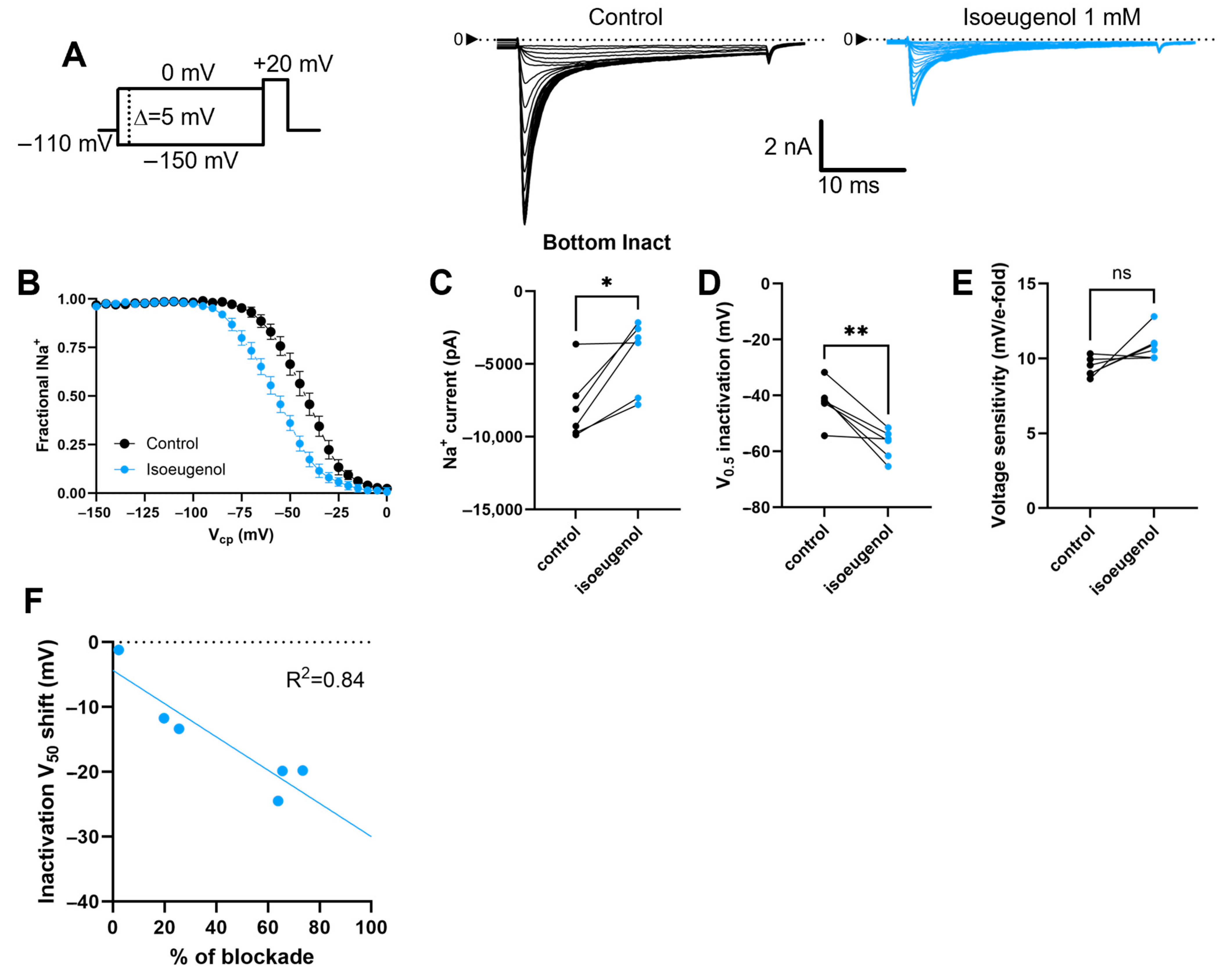
2.4. Isoeugenol Remarkably Affects the Inactivation of INa by Voltage
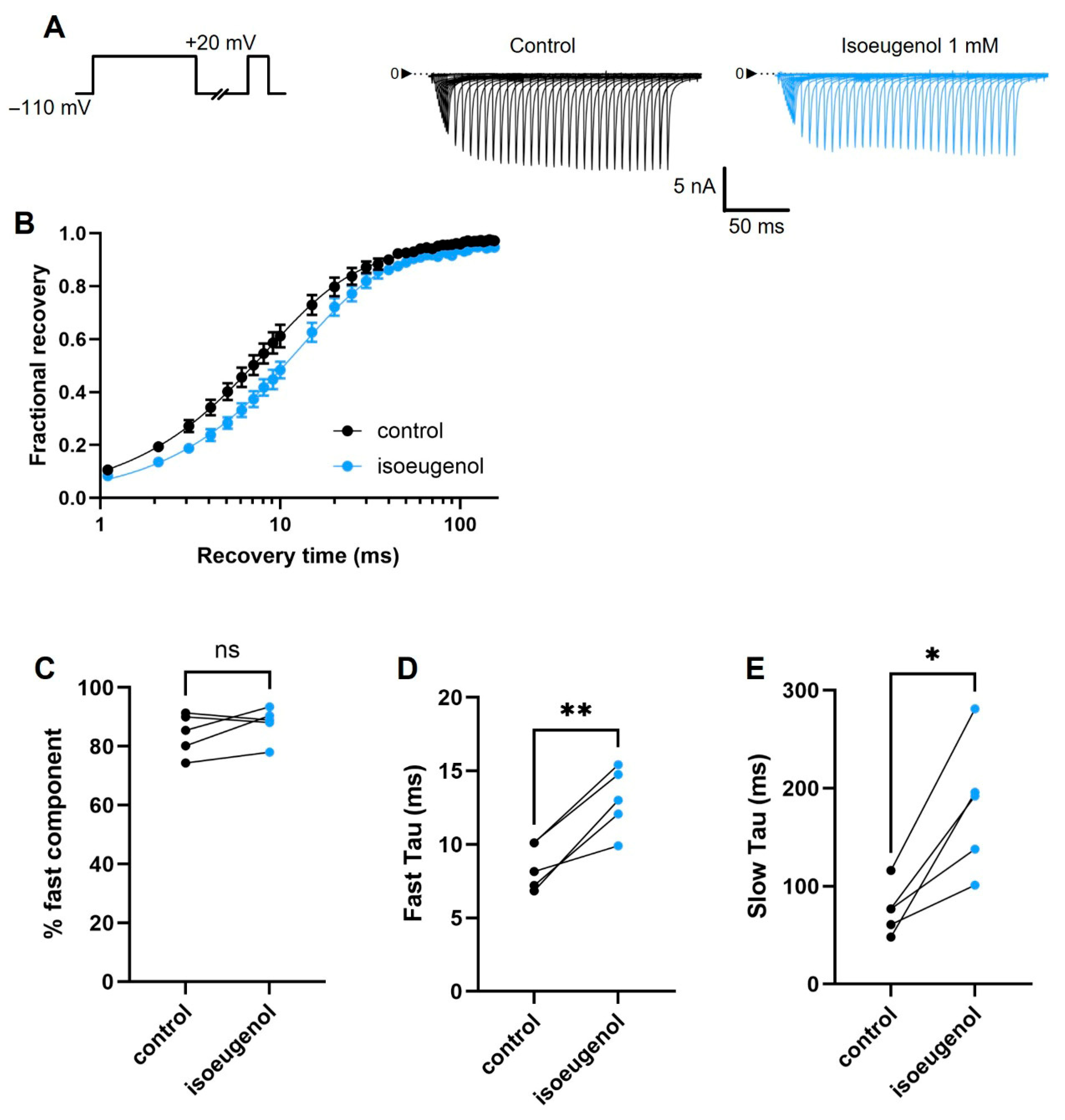
2.5. Isoeugenol Changes the Recovery from Inactivation of INa
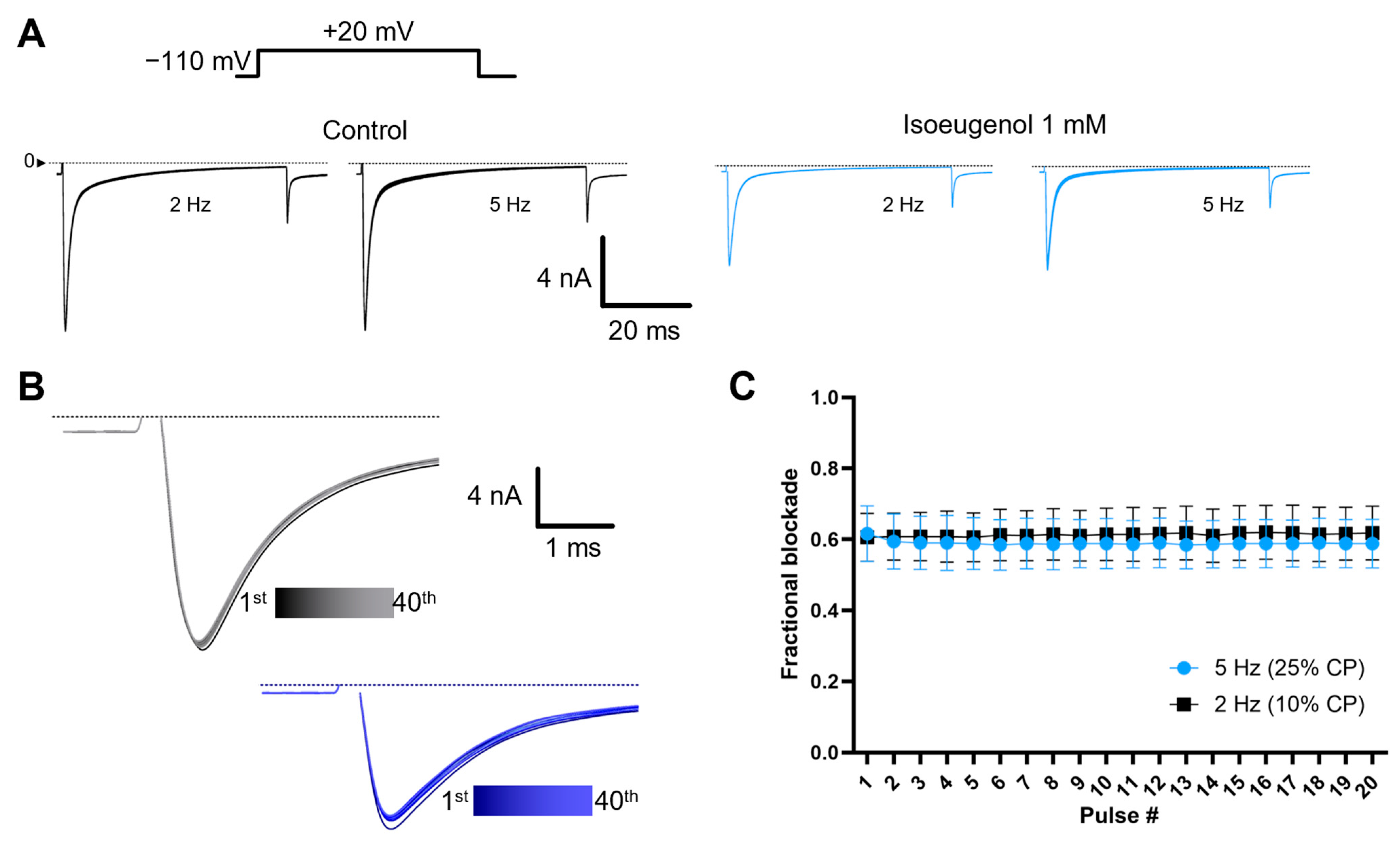
2.6. The Modulation of INa by Isoeugenol Is Not Intensified by High-Frequency Depolarizations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells Preparation
4.2. Isoeugenol Solutions
4.3. Electrophysiology
4.4. Data Analysis and Graphing
4.5. Fitting Models
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hyldgaard, M.; Mygind, T.; Meyer, R.L. Essential oils in food preservation: Mode of action, synergies, and interactions with food matrix components. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.M.; Keresztes, A.; Bui, T.; Hecksel, R.J.; Peña, A.; Lent, B.; Gao, Z.-G.; Gamez-Rivera, M.; Seekins, C.A.; Chou, K.; et al. Terpenes from Cannabis sativa Induce Antinociception in Mouse Chronic Neuropathic Pain via Activation of Spinal Cord Adenosine A2A Receptors. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Elisha, I.L.; van Vuuren, S.; Viljoen, A. Volatile phenolics: A comprehensive review of the anti-infective properties of an important class of essential oil constituents. Phytochemistry 2021, 190, 112864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, H.; Yılmaztekin, M. Natural Vanillin Production from Isoeugenol by Using Pseudomonas putida in Biphasic Bioconversion Medium. J. Agr. Sci. 2022, 28, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeduka, T.; Fridman, E.; Gang, D.R.; Vassão, D.G.; Jackson, B.L.; Kish, C.M.; Orlova, I.; Spassova, S.M.; Lewis, N.G.; Noel, J.P.; et al. Eugenol and isoeugenol, characteristic aromatic constituents of spices, are biosynthesized via reduction of a coniferyl alcohol ester. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10128–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hume, W.R. An analysis of the release and the diffusion through dentin of eugenol from zinc oxide-eugenol mixtures. J. Dent. Res. 1984, 63, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Substances Added to Food (formerly EAFUS). Available online: https://www.hfpappexternal.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/index.cfm?set=FoodSubstances&id=ISOEUGENOL (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Quentin, T.; Franke, H.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Risk Assessment of Isoeugenol in Food Based on Benchmark Dose-Response Modeling. Toxics 2023, 11, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyldgaard, M.; Mygind, T.; Piotrowska, R.; Foss, M.; Meyer, R.L. Isoeugenol has a non-disruptive detergent-like mechanism of action. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Pi, C.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wei, Y. Recent advances of analogues of curcumin for treatment of cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 180, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafie, M.S.; Elghazawy, N.H.; Owf, S.M.; Arafa, K.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Arafa, R.K. Control of ER-positive breast cancer by ERα expression inhibition, apoptosis induction, cell cycle arrest using semisynthetic isoeugenol derivatives. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 351, 109753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machnik, P.; Biazar, N.; Schuster, S. Recordings in an integrating central neuron reveal the mode of action of isoeugenol. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sensch, O.; Vierling, W.; Brandt, W.; Reiter, M. Effects of inhibition of calcium and potassium currents in guinea-pig cardiac contraction: Comparison of beta-caryophyllene oxide, eugenol, and nifedipine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 131, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.S.; Kim, T.H.; Lim, J.-M.; Song, J.-H. Effects of eugenol on Na+ currents in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Brain Res. 2008, 1243, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Lobo, D.C.A.; Linhares-Siqueira, E.D.; Cruz, G.M.P.; Cruz, J.S.; Carvalho-de-Souza, J.L.; Lahlou, S.; Coelho-de-Souza, A.N.; Barbosa, R.; Magalhães, P.J.C.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H. Eugenol modifies the excitability of rat sciatic nerve and superior cervical ganglion neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 472, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Li, H.Y.; Perez-Reyes, E.; Lee, J.-H. Effects of eugenol on T-type Ca2+ channel isoforms. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 347, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprotosoaie, A.C.; Costache, I.-I.; Miron, A. Anethole and Its Role in Chronic Diseases. In Drug Discovery from Mother Nature, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Gupta, S.C., Prasad, S., Aggarwal, B.B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, S.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Kumar, N.S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Anticholinesterase activity of standardized extract of Illicium verum Hook. f. fruits. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Junior, L.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H.; Cassola, A.C.; Carvalho-de-Souza, J.L. State-Dependent Blockade of Dorsal Root Ganglion Voltage-Gated Na+ Channels by Anethole. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, A.A.; Sorenson, A.L.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H. Effects of essential oil of Croton zehntneri, and of anethole and estragole on skeletal muscles. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1995, 49, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Alves, K.S.; Ferreira-da-Silva, F.W.; Peixoto-Neves, D.; Viana-Cardoso, K.V.; Moreira-Júnior, L.; Oquendo, M.B.; Oliveira-Abreu, K.; Albuquerque, A.A.C.; Coelho-de-Souza, A.N.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H. Estragole blocks neuronal excitability by direct inhibition of Na+ channels. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2013, 46, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Toxicology Program. Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Isoeugenol (CAS No. 97-54-1) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Gavage Studies); U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 1–178.
- Tsien, R.W.; Rosenberg, E.C. Ion channels and G protein-coupled receptors: Cannabidiol actions on disorders of excitability and synaptic excitatory-inhibitory ratio. Mol. Pharmacol. 2025, 107, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-S.; Mauki, D.H.; Zheng, Y.-X.; Wang, T.-H.; He, X.-Y. Terpenoids: A promising traditional chinese medicine for neuropathic pain relief. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 216, 107789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.L.C. de Análise do efeito inibitório do eugenol sobre canais para Na+ ativados por voltagem em neurônios sensitivos. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Junior, L.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H.; Cassola, A.C.; Carvalho-de-Souza, J.L. Eugenol and lidocaine inhibit voltage-gated Na+ channels from dorsal root ganglion neurons with different mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1354737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berta, T.; Poirot, O.; Pertin, M.; Ji, R.-R.; Kellenberger, S.; Decosterd, I. Transcriptional and functional profiles of voltage-gated Na(+) channels in injured and non-injured DRG neurons in the SNI model of neuropathic pain. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2008, 37, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevrier, P.; Vijayaragavan, K.; Chahine, M. Differential modulation of Nav1.7 and Nav1.8 peripheral nerve sodium channels by the local anesthetic lidocaine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 142, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.; O’Leary, M.E. Single-cell analysis of sodium channel expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2011, 46, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiers, S.; Klein, R.M.; Price, T.J. Quantitative differences in neuronal subpopulations between mouse and human dorsal root ganglia demonstrated with RNAscope in situ hybridization. Pain 2020, 161, 2410–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Matsutomi, T.; Zheng, T.; Nakata, Y.; Wood, J.N.; Ogata, N. Electrophysiological characterization of the tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ channel, Na(v)1.9, in mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons. Pflug. Arch. 2004, 449, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.L.; Clark, A.J.; Huang, J.; Waxman, S.G.; Dib-Hajj, S.D. The Role of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels in Pain Signaling. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1079–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wood, J.N. The roles of sodium channels in nociception: Implications for mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Pain. Med. 2011, 12 (Suppl. 3), S93–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felts, P.A.; Yokoyama, S.; Dib-Hajj, S.; Black, J.A.; Waxman, S.G. Sodium channel alpha-subunit mRNAs I, II, III, NaG, Na6 and hNE (PN1): Different expression patterns in developing rat nervous system. Mol. Brain Res. 1997, 45, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benn, S.C.; Costigan, M.; Tate, S.; Fitzgerald, M.; Woolf, C.J. Developmental expression of the TTX-resistant voltage-gated sodium channels Nav1.8 (SNS) and Nav1.9 (SNS2) in primary sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 6077–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, N.; Tatebayashi, H. Ontogenic development of the TTX-sensitive and TTX-insensitive Na+ channels in neurons of the rat dorsal root ganglia. Dev. Brain Res. 1992, 65, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyuk, P.G.; Veselovsky, N.S.; Tsyndrenko, A.Y. Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons-I. Sodium currents. Neuroscience 1981, 6, 2423–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, H. Hill coefficients, dose–response curves and allosteric mechanisms. J. Chem. Biol. 2009, 3, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindslev, N. Drug-Acceptor Interactions: Modeling Theoretical Tools to Test and Evaluate Experimental Equilibrium Effects; CRC Press: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-1-315-15978-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hille, B. Local anesthetics: Hydrophilic and hydrophobic pathways for the drug-receptor reaction. J. Gen. Physiol. 1977, 69, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, C.M. Na channel inactivation from open and closed states. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17991–17996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheets, M.F.; Hanck, D.A. Molecular action of lidocaine on the voltage sensors of sodium channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2003, 121, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanck, D.A.; Nikitina, E.; McNulty, M.M.; Fozzard, H.A.; Lipkind, G.M.; Sheets, M.F. Using lidocaine and benzocaine to link sodium channel molecular conformations to state-dependent antiarrhythmic drug affinity. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawali, V.S.; Lukacs, P.; Cervenka, R.; Koenig, X.; Rubi, L.; Hilber, K.; Sandtner, W.; Todt, H. Mechanism of Modification, by Lidocaine, of Fast and Slow Recovery from Inactivation of Voltage-Gated Na+ Channels. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 88, 866–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.S.Y.; Kayani, K.; Whyte-Oshodi, D.; Whyte-Oshodi, A.; Nachiappan, N.; Gnanarajah, S.; Mohammed, R. Voltage gated sodium channels as therapeutic targets for chronic pain. J. Pain. Res. 2019, 12, 2709–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK54050/ (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Horishita, T.; Harris, R.A. n-Alcohols inhibit voltage-gated Na+ channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 326, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.V.; Kendig, J.J. Differential sensitivities of TTX-resistant and TTX-sensitive sodium channels to anesthetic concentrations of ethanol in rat sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 1998, 54, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezanilla, F.; Armstrong, C. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J. Gen. Physiol. 1977, 70, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Activation (n = 7) | Inactivation (n = 6) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Isoeugenol 1 mM | Control | Isoeugenol 1 mM | |
| Vr shift (mV) | 44.4 ± 3.18 | 42.3 ± 3.53 ns | N/A | N/A |
| Gmax (nS) | 171.7 ± 24.88 | 119.0 ± 25.09 * | 180.9 ± 21.88 | 100.75 ± 22.98 * |
| V0.5 (mV) | −14.2 ± 2.76 | −10.7 ± 3.72 ns | −42.3 ± 2.95 | −57.3 ± 2.11 ** |
| Paired delta V0.5 (mV) | 3.56 ± 1.86 | −15.1 ± 3.37 ** | ||
| Voltage sensitivity (mV/e-fold) | 4.0 ± 0.50 | 5.34 ± 0.36 ns | 9.4 ± 0.26 | 10.9 ± 0.42 ns |
| Recovery from Inactivation (n = 5) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Control | Isoeugenol 1 mM | |
| % fast component | 84.3 ± 3.15 | 87.8 ± 2.60 ns |
| Fast component tau (ms) | 8.5 ± 0.70 | 13.0 ± 0.98 ** |
| Slow component tau (ms) | 75.9 ± 11.40 | 181.6 ± 30.51 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghim, D.; Dib, J.; Moreira-Junior, L.; Carvalho-de-Souza, J. Modulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels from Sensory Neurons by Isoeugenol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167734
Ghim D, Dib J, Moreira-Junior L, Carvalho-de-Souza J. Modulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels from Sensory Neurons by Isoeugenol. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167734
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhim, David, Jehan Dib, Luiz Moreira-Junior, and Joao Carvalho-de-Souza. 2025. "Modulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels from Sensory Neurons by Isoeugenol" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167734
APA StyleGhim, D., Dib, J., Moreira-Junior, L., & Carvalho-de-Souza, J. (2025). Modulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels from Sensory Neurons by Isoeugenol. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167734





