CFAP300 Loss-of-Function Mutations with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Evidence from Ex Vivo and ALI Cultures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Characteristics of PCD Patients
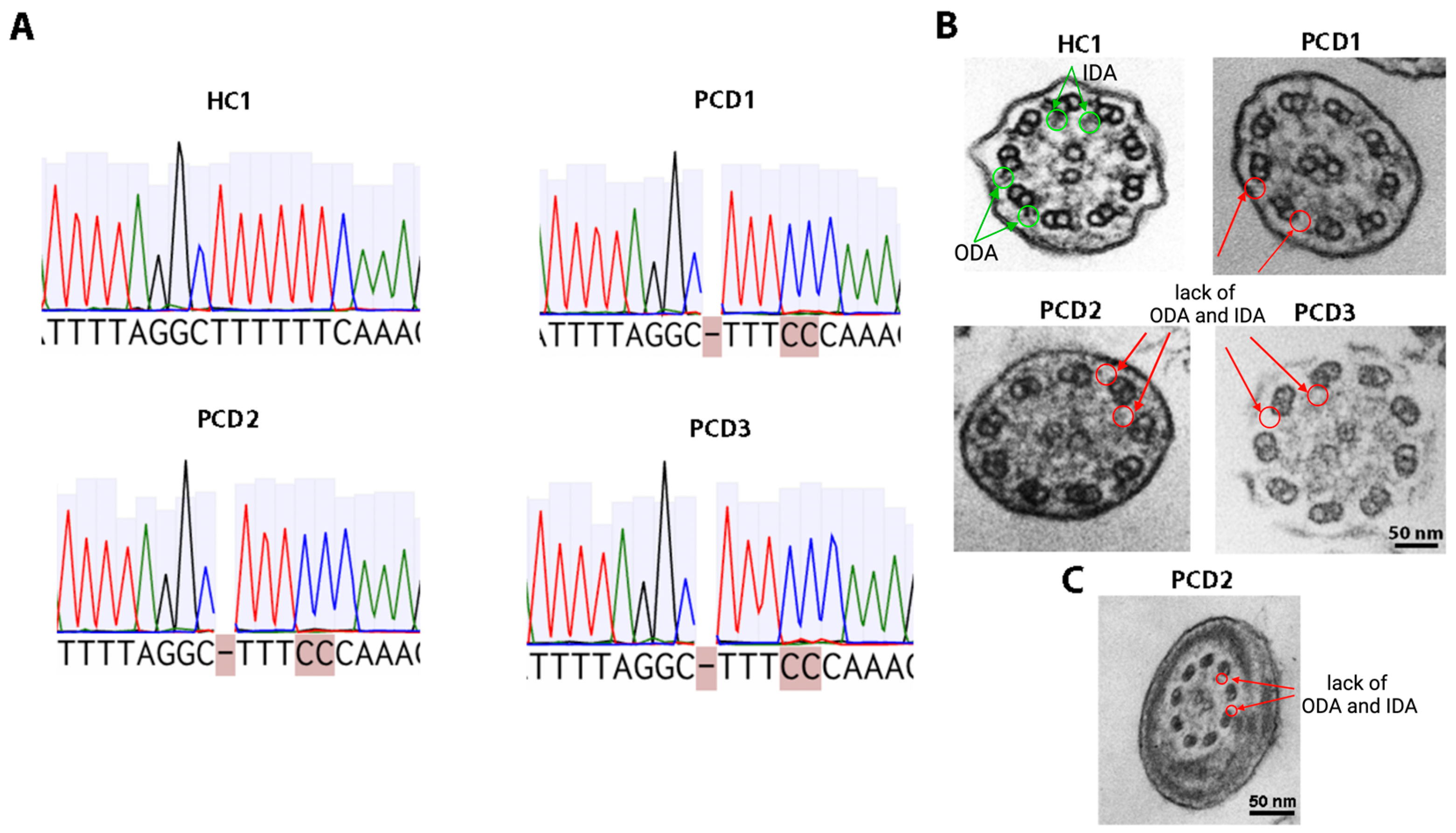
2.2. Characterization of Nasal Epithelium Samples Ex Vivo
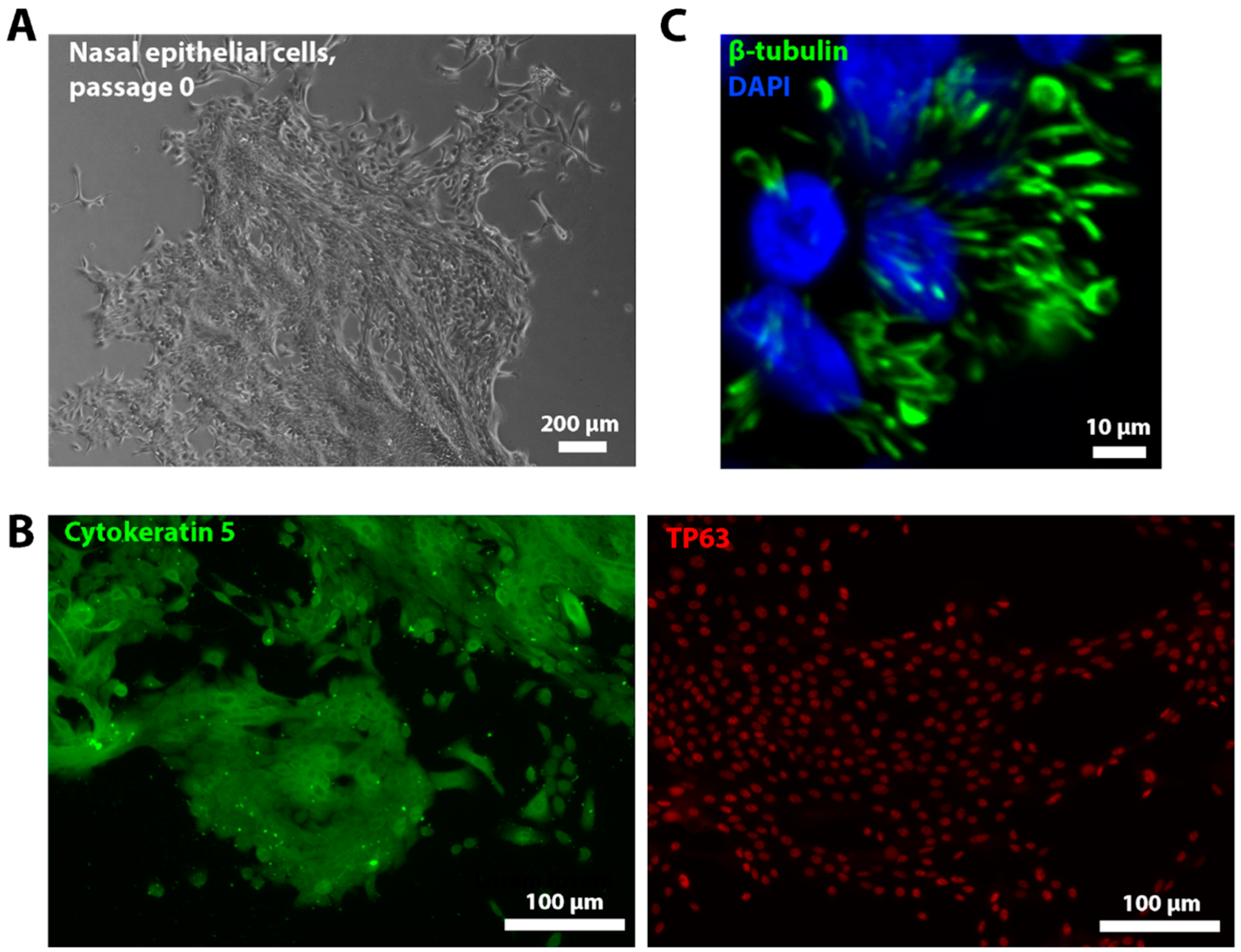
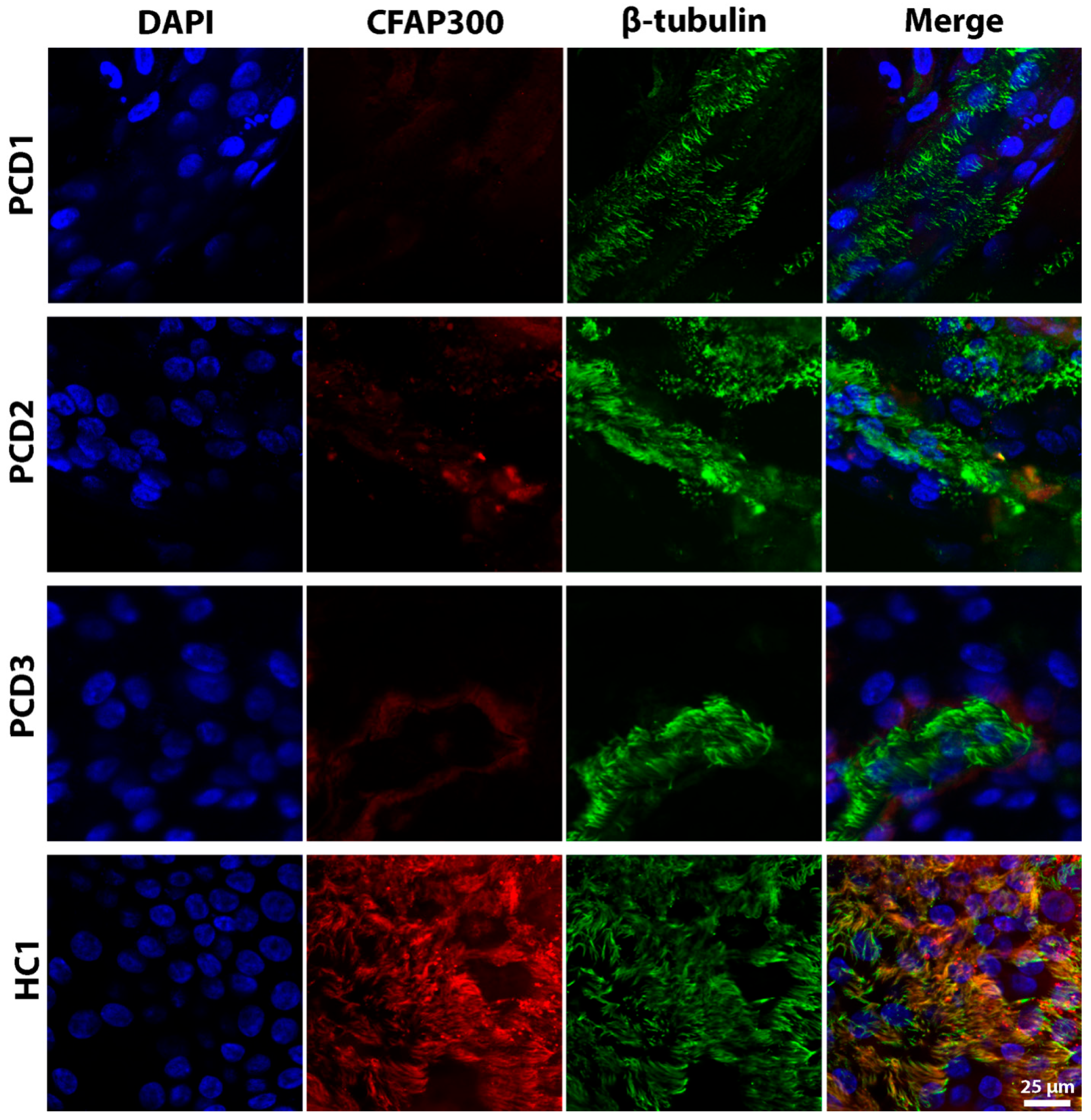
2.3. Characterization of Ciliated Epithelium Samples In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subject
4.2. Nasal Biopsies Collection
4.3. Genetics
4.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.5. Culturing and Ciliogenesis of Nasal Epithelial Cells
4.6. Video Microscopy Analysis
4.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCD | Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia |
| CFAP300 | Cilia and Flagella-Associated Protein 300 |
| ALI | Air–Liquid Interface |
| ODA | Outer Dynein Arm |
| IDA | Inner Dynein Arm |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| CBF | Ciliary Beat Frequency |
| CBP | Ciliary Beat Pattern |
| SCD | Secondary Ciliary Dyskinesia |
| NICU | Neonatal Intensive Care Unit |
| FEV1 | Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 s |
| IVF | In Vitro Fertilization |
| N/A | Not Analyzed |
| RT | Room Temperature |
| fps | Frames Per Second |
References
- Mirra, V.; Werner, C.; Santamaria, F. Primary ciliary dyskinesia: An update on clinical aspects, genetics, diagnosis, and future treatment strategies. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, M.R.; Daniels, L.A.; Davis, S.D.; Zariwala, M.A.; Leigh, M.W. Primary ciliary dyskinesia. Recent advances in diagnostics, genetics, and characterization of clinical disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, W.B.; A Seifert, B.; Truty, R.; A Zariwala, M.; Ameel, K.; Zhao, Y.; Nykamp, K.; Gaston, B. The global prevalence and ethnic heterogeneity of primary ciliary dyskinesia gene variants: A genetic database analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.S.; Davis, S.D.; Omran, H.; Shoemark, A. Primary ciliary dyskinesia in the genomics age. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, R.; Elenius, V.; Fassad, M.R.; Freke, G.; Rogers, A.; Shoemark, A.; Koistinen, T.; Mohamed, M.A.; Lim, J.S.Y.; Mitchison, H.M.; et al. CFAP300 mutation causing primary ciliary dyskinesia in Finland. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 985227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sironen, A.; Shoemark, A.; Patel, M.; Loebinger, M.R.; Mitchison, H.M. Sperm defects in primary ciliary dyskinesia and related causes of male infertility. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 2029–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biebach, L.; Cindrić, S.; Koenig, J.; Aprea, I.; Dougherty, G.W.; Raidt, J.; Bracht, D.; Ruppel, R.; Schreiber, J.; Hjeij, R.; et al. Recessive Mutations in CFAP74 Cause Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia with Normal Ciliary Ultrastructure. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 67, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höben, I.M.; Hjeij, R.; Olbrich, H.; Dougherty, G.W.; Nöthe-Menchen, T.; Aprea, I.; Frank, D.; Pennekamp, P.; Dworniczak, B.; Wallmeier, J.; et al. Mutations in C11ORF70 cause primary ciliary dyskinesia with randomization of left/right body asymmetry due to outer and inner dynein arm defects. bioRxiv 2018, 102, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.L.; Behan, L.; Collins, S.A.; Goggin, P.M.; Adam, E.C.; Coles, J.L.; Evans, H.J.; Harris, A.; Lackie, P.; Packham, S.; et al. Accuracy of diagnostic testing in primary ciliary dyskinesia. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ceuninck van Capelle, C.; Luo, L.; Leitner, A.; Tschanz, S.A.; Latzin, P.; Ott, S.; Herren, T.; Müller, L.; Ishikawa, T. Proteomic and structural comparison between cilia from primary ciliary dyskinesia patients with a DNAH5 defect. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2025, 12, 1593810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.S.; Barbato, A.; Collins, S.A.; Goutaki, M.; Behan, L.; Caudri, D.; Dell, S.; Eber, E.; Escudier, E.; Hirst, R.A.; et al. European Respiratory Society guidelines for the diagnosis of primary ciliary dyskinesia. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.J.; Leigh, M.W. Value of transmission electron microscopy for primary ciliary dyskinesia diagnosis in the era of molecular medicine: Genetic defects with normal and non-diagnostic ciliary ultrastructure. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2017, 41, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olm, M.A.K.; Kögler, J.E.; Macchione, M.; Shoemark, A.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Rodrigues, J.C.; Peabody, J.E.; Shei, R.-J.; Bermingham, B.M.; Phillips, S.E.; et al. Primary ciliary dyskinesia: Evaluation using cilia beat frequency assessment via spectral analysis of digital microscopy images. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, J.L.; Thompson, J.; Horton, K.L.; Hirst, R.A.; Griffin, P.; Williams, G.M.; Goggin, P.; Doherty, R.; Lackie, P.M.; Harris, A.; et al. A revised protocol for culture of airway epithelial cells as a diagnostic tool for primary ciliary dyskinesia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, J.S.; Burgess, A.; Mitchison, H.M.; Moya, E.; Williamson, M.; Hogg, C. Diagnosis and management of primary ciliary dyskinesia. Arch. Dis. Child. 2014, 99, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifferi, M.; Cangiotti, A.M.; Ragazzo, V.; Baldini, G.; Cinti, S.; Boner, A.L. Primary ciliary dyskinesia: Diagnosis in children with inconclusive ultrastructural evaluation. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2001, 12, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirst, R.A.; Jackson, C.L.; Coles, J.L.; Williams, G.; Rutman, A.; Goggin, P.M.; Adam, E.C.; Page, A.; Evans, H.J.; Lackie, P.M.; et al. Culture of primary ciliary dyskinesia epithelial cells at air-liquid interface can alter ciliary phenotype but remains a robust and informative diagnostic aid. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowy-Bieryłło, Z.; Daca-Roszak, P.; Jurczak, J.; Przystałowska-Macioła, H.; Jaksik, R.; Witt, M.; Ziętkiewicz, E. In vitro differentiation of ciliated cells in ALI-cultured human airway epithelium–the framework for functional studies on airway differentiation in ciliopathies. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 101, 151189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifferi, M.; Montemurro, F.; Cangiotti, A.M.; Ragazzo, V.; Di Cicco, M.; Vinci, B.; Vozzi, G.; Macchia, P.; Boner, A.L. Simplified cell culture method for the diagnosis of atypical primary ciliary dyskinesia. Thorax 2009, 64, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marthin, J.K.; Stevens, E.M.; Larsen, L.A.; Christensen, S.T.; Nielsen, K.G. Patient-specific three-dimensional explant spheroids derived from human nasal airway epithelium: A simple methodological approach for ex vivo studies of primary ciliary dyskinesia. Cilia 2017, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van der Vaart, J.; Böttinger, L.; Geurts, M.H.; van de Wetering, W.J.; Knoops, K.; Sachs, N.; Begthel, H.; Korving, J.; Lopez-Iglesias, C.; Peters, P.J.; et al. Modelling of primary ciliary dyskinesia using patient-derived airway organoids. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e52058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesekara, P.; Yadav, P.; Perkins, L.A.; Stolz, D.B.; Franks, J.M.; Watkins, S.C.; Jacome, E.R.; Brody, S.L.; Horani, A.; Xu, J.; et al. Engineering rotating apical-out airway organoid for assessing respiratory cilia motility. iScience 2022, 25, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, A.; Kondo, M.; Honda, N.; Orimo, M.; Miyoshi, A.; Kobayashi, F.; Abe, K.; Akaba, T.; Tsuji, M.; Arimura, K.; et al. Analysis of the diagnosis of Japanese patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia using a conditional reprogramming culture. Respir. Investig. 2022, 60, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietkiewicz, E.; Bukowy-Bieryllo, Z.; Rabiasz, A.; Daca-Roszak, P.; Wojda, A.; Voelkel, K.; Rutkiewicz, E.; Pogorzelski, A.; Rasteiro, M.; Witt, M. CFAP300: Mutations in slavic patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia and a role in ciliary dynein arms trafficking. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 61, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassad, M.R.; Shoemark, A.; le Borgne, P.; Koll, F.; Patel, M.; Dixon, M.; Hayward, J.; Richardson, C.; Frost, E.; Jenkins, L.; et al. C11orf70 mutations disrupting the intraflagellar transport-dependent assembly of multiple axonemal dyneins cause primary ciliary dyskinesia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 956–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbo, B.; Lucas, J.S. Clinical care for primary ciliary dyskinesia: Current challenges and future directions. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchison, H.M.; Valente, E.M. Motile and non-motile cilia in human pathology: From function to phenotypes. J. Pathol. 2017, 241, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Mao, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Cilia-related diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 3974–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemark, A.; Frost, E.; Dixon, M.; Ollosson, S.; Kilpin, K.; Patel, M.; Scully, J.; Rogers, A.V.; Mitchison, H.M.; Bush, A.; et al. Accuracy of immunofluorescence in the diagnosis of primary ciliary dyskinesia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frommer, A.; Hjeij, R.; Loges, N.T.; Edelbusch, C.; Jahnke, C.; Raidt, J.; Werner, C.; Wallmeier, J.; Große-Onnebrink, J.; Olbrich, H.; et al. Immunofluorescence analysis and diagnosis of primary ciliary dyskinesia with radial spoke defects. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 53, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baz-Redón, N.; Rovira-Amigo, S.; Fernández-Cancio, M.; Castillo-Corullón, S.; Cols, M.; Caballero-Rabasco, M.A.; Asensio, Ó.; De Vicente, C.M.; Martínez-Colls, M.D.M.; Torrent-Vernetta, A.; et al. Immunofluorescence analysis as a diagnostic tool in a Spanish cohort of patients with suspected primary ciliary dyskinesia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behan, L.; Dimitrov, B.D.; Kuehni, C.E.; Hogg, C.; Carroll, M.; Evans, H.J.; Goutaki, M.; Harris, A.; Packham, S.; Walker, W.T.; et al. PICADAR: A diagnostic predictive tool for primary ciliary dyskinesia. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyian, T.; Borovikov, A.; Anisimova, I.; Ryzhkova, O.; Bulakh, M.; Bragina, E.; Avakyan, M.; Demchenko, A.; Zabnenkova, V.; Kovalev, V.; et al. Expanding the Genotypic and Phenotypic Spectrum of OFD1-Related Conditions: Three More Cases. Genes 2024, 15, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyian, T.A.; Smirnikhina, S.A.; Demchenko, A.G.; Veiko, R.V.; Kondratyeva, E.I. A new software for automated analysis of respiratory tract ciliary epithelium movement for the diagnosis of primary ciliary dyskinesia. Pulmonologiya 2024, 34, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | PCD1 | PCD2 | PCD3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neonatal period | Unremarkable | Intrauterine hydrocephalus, congenital pneumonia, admitted to NICU on day 1 | Congenital pneumonia |
| Family history of PCD or situs inversus | − | +(grandfather with Kartagener syndrome) | − |
| Situs inversus (Kartagener syndrome) | − | + | + |
| Bronchiectasis | + | + | + |
| PICADAR score | 8 | 12 | 12 |
| FEV1 (% predicted, normal ≥80%) | 99.9% | 66% | 44% |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | − | + | + |
| Chronic rhinosinusitis | + | + | + |
| Nasal polyposis | − | − | + |
| Otitis | − | + | + |
| Hearing loss severity | − | Mild (grade 1) | Moderate (grade 1–2) |
| IV anti-pseudomonal therapy (per year) | − | 2–3 courses | 1–2 courses |
| Inhaled anti-pseudomonal therapy | − | Tobramycin (continuous) | Colistimethate sodium (continuous) |
| Oral antibiotics for exacerbations (per year) | 1–2 courses | 4–5 courses | 4–6 courses |
| Patients with PCD | Genotype | TEM | CBP Ex Vivo | CBF Ex Vivo (Median (Q1–Q3)), Hz | p-Value (vs. HC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCD1 | CFAP300 c.198_200delinsCC homo/hemizygous | Complete lack of ODA and IDA | Immotile cilia | 1.25 (0.3–1.9) | p < 0.0001 |
| PCD2 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||
| PCD3 | Immotile cilia | 0.9 (0.5–1.0) | p < 0.0001 |
| CBP In Vitro | CBF In Vitro (Median (Q1–Q3)), Hz | p-Value (vs. HC) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with PCD | |||
| PCD1 | Almost immotile cilia, only minimal residual ciliary movements | 1.5 (1.4–1.8) | p = 0.0008 |
| PCD2 | Immotile cilia | 1.3 (1.1–1.6) | |
| PCD3 | Immotile cilia | 1.6 (0.5–3.1) | |
| Healthy donors | |||
| HC1 | Regular ciliary beating | 8.0 (7.7–8.9) | |
| HC2 | 6.6 (5.6–7) | ||
| HC3 | 6.9 (6.3–7.2) | ||
| Patients | Gender | Age |
|---|---|---|
| Patients with PCD | ||
| PCD1 | F | 23 |
| PCD2 | M | 28 |
| PCD3 | F | 35 |
| Healthy donors | ||
| HC1 | F | 31 |
| HC2 | M | 26 |
| HC3 | F | 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demchenko, A.G.; Kyian, T.A.; Kondratyeva, E.I.; Bragina, E.E.; Ryzhkova, O.P.; Veiko, R.V.; Nazarova, A.G.; Chernykh, V.B.; Smirnikhina, S.A.; Kutsev, S.I. CFAP300 Loss-of-Function Mutations with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Evidence from Ex Vivo and ALI Cultures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157655
Demchenko AG, Kyian TA, Kondratyeva EI, Bragina EE, Ryzhkova OP, Veiko RV, Nazarova AG, Chernykh VB, Smirnikhina SA, Kutsev SI. CFAP300 Loss-of-Function Mutations with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Evidence from Ex Vivo and ALI Cultures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157655
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemchenko, Anna G., Tatiana A. Kyian, Elena I. Kondratyeva, Elizaveta E. Bragina, Oksana P. Ryzhkova, Roman V. Veiko, Aleksandra G. Nazarova, Vyacheslav B. Chernykh, Svetlana A. Smirnikhina, and Sergey I. Kutsev. 2025. "CFAP300 Loss-of-Function Mutations with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Evidence from Ex Vivo and ALI Cultures" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157655
APA StyleDemchenko, A. G., Kyian, T. A., Kondratyeva, E. I., Bragina, E. E., Ryzhkova, O. P., Veiko, R. V., Nazarova, A. G., Chernykh, V. B., Smirnikhina, S. A., & Kutsev, S. I. (2025). CFAP300 Loss-of-Function Mutations with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Evidence from Ex Vivo and ALI Cultures. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157655






