Insights into FGFR4 (rs351855 and rs7708357) Gene Variants, Ki-67 and p53 in Pituitary Adenoma Pathophysiology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. By Gender: Females and Males
2.2. Associations of FGFR4 rs351855 and rs7708357 with Pituitary Adenoma’s Tumor Size
2.3. Associations of FGFR4 rs351855 and rs7708357 with Pituitary Adenoma’s Invasiveness
2.4. Associations of FGFR4 rs351855 and rs7708357 with Pituitary Adenomas’ Activity
2.5. Associations of FGFR4 rs351855 and rs7708357 with Pituitary Adenomas’ Recurrence
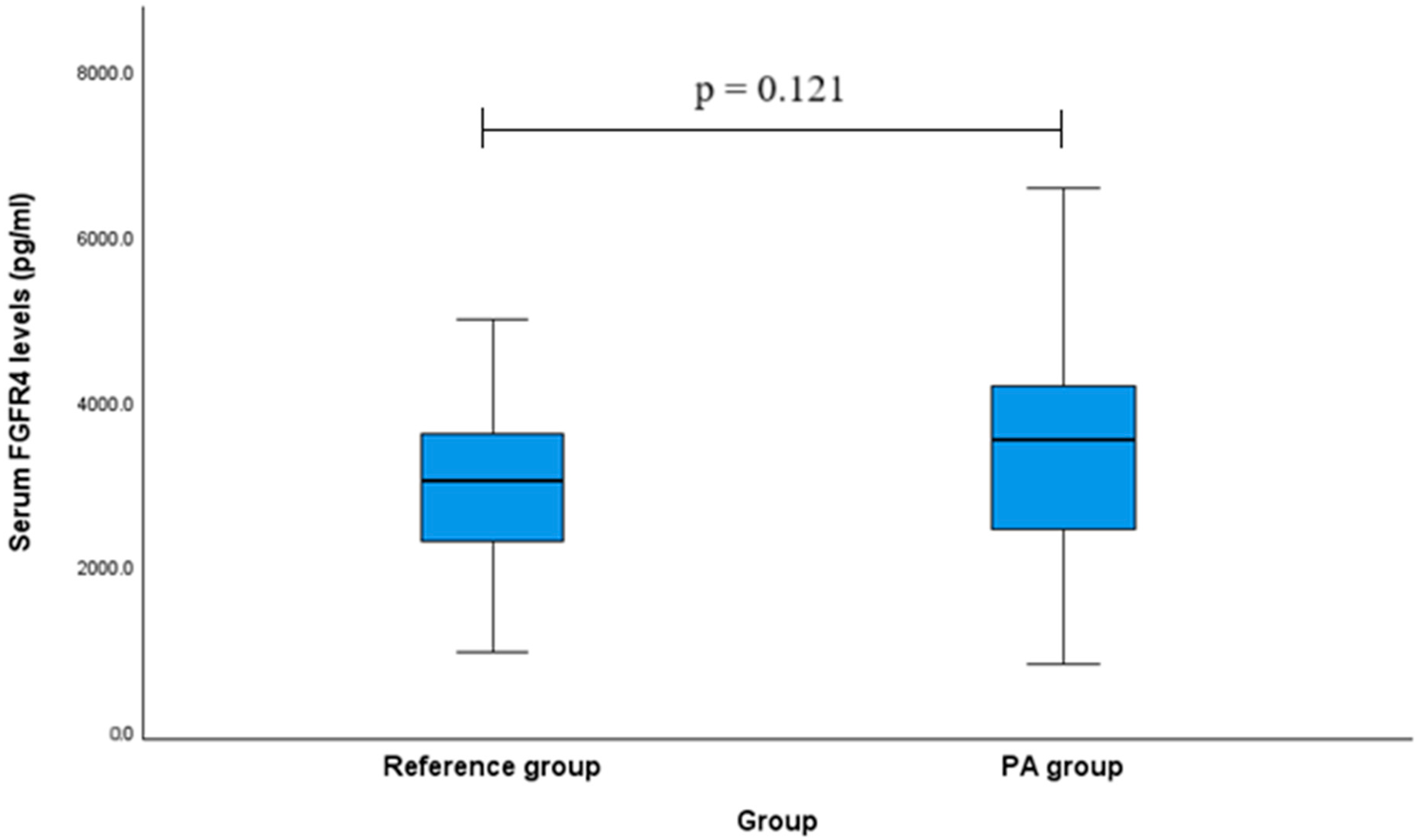
2.6. Serum FGFR4 Levels in Patients with PA and Controls
2.7. Ki-67 Labeling Index
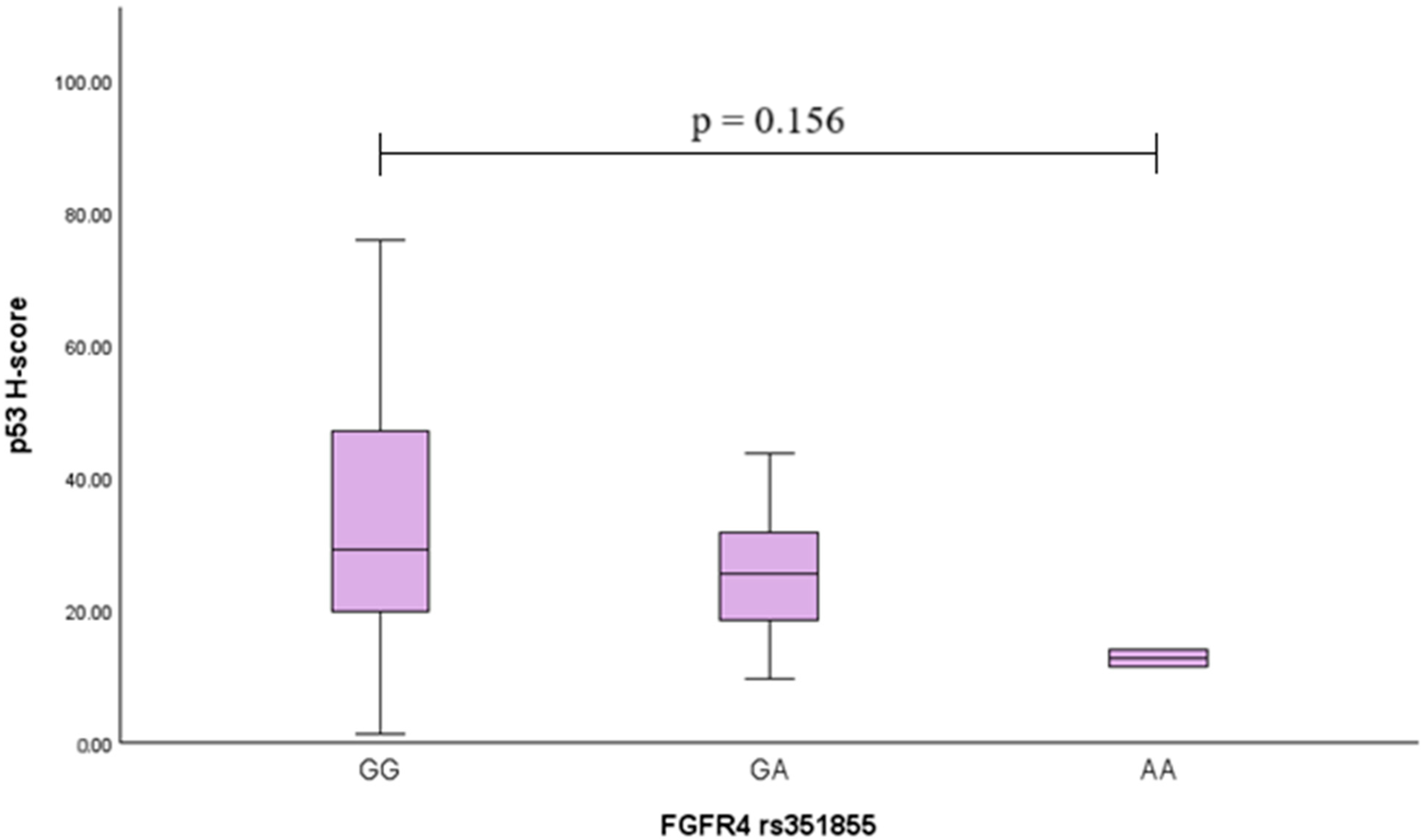
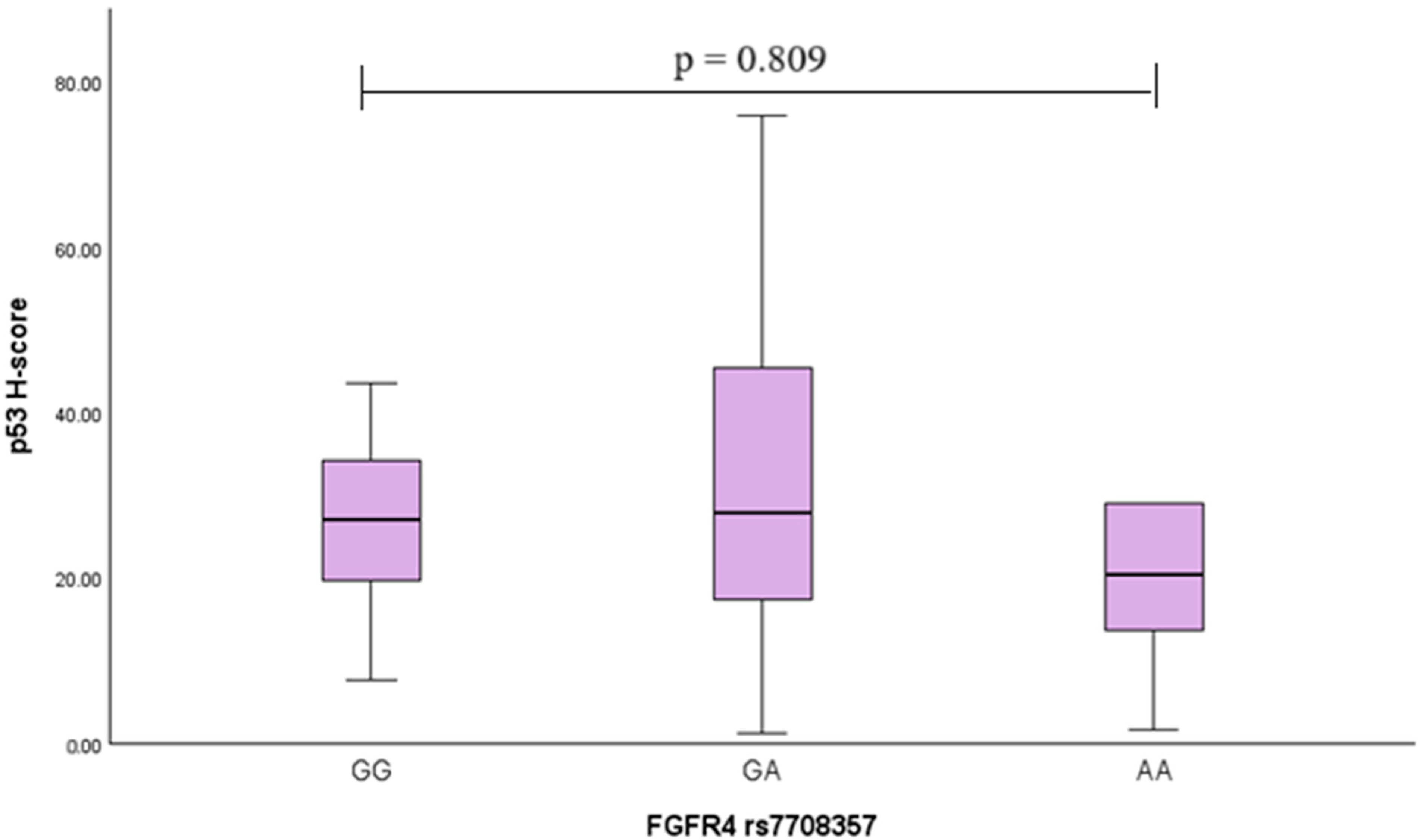
2.8. p53 Analysis in PA Tissues
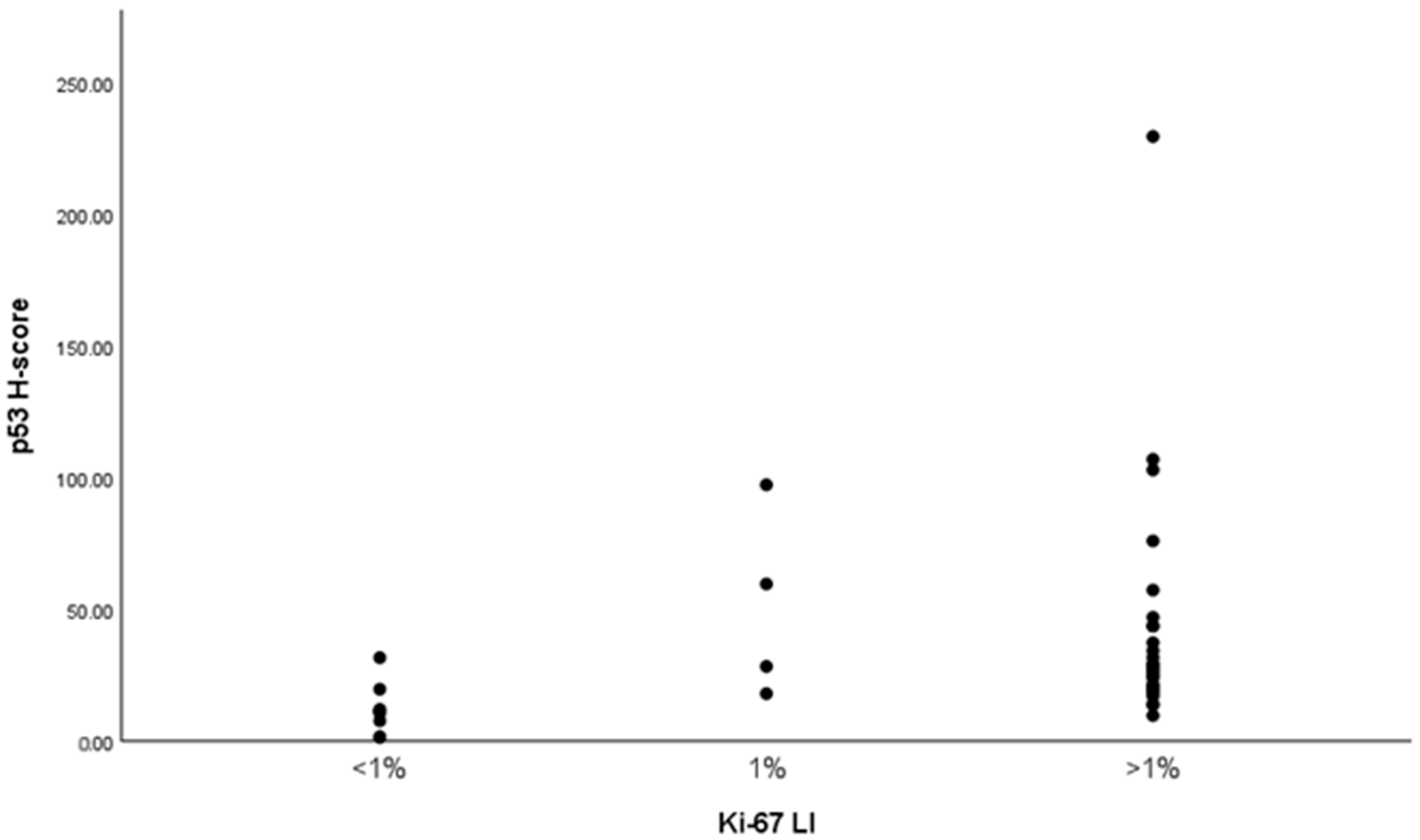
2.9. Correlation Between Ki-67 and p53
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Study Population
4.3. DNA Extraction and Genotyping
4.4. Serum Level’s Measurement
4.5. Evaluation of Ki-67 and p53
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTH | Adrenocorticotropic Hormone |
| APT/PC | Atypical Pituitary Tumor/Pituitary Carcinom |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| FGF | fibroblast growth factor |
| FPA | functional pituitary adenoma |
| FS H/LH | Follicle-Stimulating Hormone/Luteinizing Hormone |
| GH | Growth Hormone |
| GFG | Human Endogenous FGF Antisense Gene |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NFPA | non-functional pituitary adenomas |
| PA | pituitary adenoma |
| RT-PCR | real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| SNV | single-nucleotide variant |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
References
- Ezzat, S.; Asa, S.L.; Couldwell, W.T.; Barr, C.E.; Dodge, W.E.; Vance, M.L.; McCutcheon, I.E. The prevalence of pituitary adenomas: A systematic review. Cancer 2004, 101, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nammour, G.M.; Ybarra, J.; Naheedy, M.H.; Romeo, J.H.; Aron, D.C. Incidental pituitary macroadenoma: A population-based study. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1997, 314, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.; Karavitaki, N.; Wass, J.A. Prevalence of pituitary adenomas: A community-based, cross-sectional study in Banbury (Oxfordshire, UK). Clin. Endocrinol. 2010, 72, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Pang, B.; Liang, Y.; Xu, S.C.; Xin, T.; Fan, H.T.; Yu, Y.-B.; Pang, Q. Overexpression of EpCAM and Trop2 in pituitary adenomas. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 7907–7914. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, X. The molecular pathogenesis of pituitary adenomas: An update. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 28, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Itoh, N.; Ornitz, D.M. Evolution of the Fgf and Fgfr gene families. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzat, S.; Smyth, H.S.; Ramyar, L.; Asa, S.L. Heterogenous in vivo and in vitro expression of basic fibroblast growth factor by human pituitary adenomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Asa, S.L.; Ramyar, L.; Murphy, P.R.; Li, A.W.; Ezzat, S. The endogenous fibroblast growth factor-2 antisense gene product regulates pituitary cell growth and hormone production. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbass, S.A.; Asa, S.L.; Ezzat, S. Altered expression of fibroblast growth factor receptors in human pituitary adenomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Asa, S.L.; Weigel, R.J.; Ezzat, S. Pituitary tumor AP-2α recognizes a cryptic promoter in intron 4 of fibroblast growth factor receptor 4. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 19597–19602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzat, S.; Zheng, L.; Asa, S.L. Pituitary tumor-derived fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 isoform disrupts neural cell-adhesion molecule/N-cadherin signaling to diminish cell adhesiveness: A mechanism underlying pituitary neoplasia. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 2543–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.R.; Sano, T.; Asa, S.L.; Yamada, S.; Horiguchi, H.; Tashiro, T.; Li, C.C.; Hirokawa, M.; Kovacs, K.; Ezzat, S. Cytoplasmic expression of fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 in human pituitary adenomas: Relation to tumor type, size, proliferation, and invasiveness. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 1904–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Jang, H.J.; Park, S.T.; Kim, H.S. FGFR4 Gly388Arg Polymorphism Reveals a Poor Prognosis, Especially in Asian Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 762528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wei, Y.; Guo, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, H. Association between FGFR4 Gly388Arg polymorphism and cancer risk: A meta-analysis of 27 studies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20774. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, S. FGFR4 confers chemotherapy resistance via MAPK/ERK activation and is a potential therapeutic target in cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 633453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, M.; Jiang, X.; Wang, F.; Ling, S.; Niu, C. Prediction of Higher Ki-67 Index in Pituitary Adenomas by Pre- and Intra-Operative Clinical Characteristics. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Joerger, A.C.; Stiewe, T.; Soussi, T. TP53: The unluckiest of genes? Cell Death Differ. 2025, 32, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ho, H.K.; Pok, S.; Streit, S.; Ruhe, J.E.; Hart, S.; Lim, K.S.; Loo, H.L.; Aung, M.O.; Lim, S.G.; Ullrich, A. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 regulates proliferation, anti-apoptosis and alpha-fetoprotein secretion during hepatocellular carcinoma progression and represents a potential target for therapeutic intervention. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahadevan, K.; Darby, S.; Leung, H.Y.; Mathers, M.E.; Robson, C.N.; Gnanapragasam, V.J. Selective over-expression of fibroblast growth factor receptors 1 and 4 in clinical prostate cancer. J. Pathol. 2007, 213, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaakkola, S.; Salmikangas, P.; Nylund, S.; Lehtovirta, P.; Nevanlinna, H.; Partanen, J.; Armstrong, E.; Pyrhönen, S. Amplification of fgfr4 gene in human breast and gynecological cancers. Int. J. Cancer 1993, 54, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bange, J.; Prechtl, D.; Cheburkin, Y.; Specht, K.; Harbeck, N.; Schmitt, M.; Knyazeva, T.; Müller, S.; Gärtner, S.; Sures, I.; et al. Cancer progression and tumor cell motility are associated with the FGFR4 Arg(388) allele. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stadler, C.R.; Knyazev, P.; Bange, J.; Ullrich, A. FGFR4 GLY388 isotype suppresses motility of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells by EDG-2 gene repression. Cell. Signal. 2006, 18, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitzer, N.; Mayr, T.; Streit, S.; Ullrich, A. A single nucleotide change in the mouse genome accelerates breast cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yu, W.; Cai, Y.; Ren, C.; Ittmann, M.M. Altered fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 stability promotes prostate cancer progression. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Varjosalo, M.; Björklund, M.; Cheng, F.; Syvänen, H.; Kivioja, T.; Kilpinen, S.; Sun, Z.; Kallioniemi, O.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; He, W.-W.; et al. Application of active and kinase-deficient kinome collection for identification of kinases regulating hedgehog signaling. Cell 2008, 133, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gospodarowicz, D. Fibroblast growth factor and vertebrate regeneration. Adv. Neurol. 1981, 29, 149–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baird, A.; Bohlen, P.; Esch, F.; Guillemin, R.; Ling, N.; Mormede, P.; Naoto, U.; Ying, S.-Y.; Wehrenberg, W.B. Molecular Characterization of Fibroblast Growth Factor: Distribution and Biological Activities in Various Tissues. In Recent Progress in Hormone Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; Volume 42, pp. 143–205. [Google Scholar]
- Tateno, T.; Asa, S.L.; Zheng, L.; Mayr, T.; Ullrich, A.; Ezzat, S. The FGFR4-G388R polymorphism promotes mitochondrial STAT3 serine phosphorylation to facilitate pituitary growth hormone cell tumorigenesis. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ezzat, S.; Yu, S.; Asa, S.L. Ikaros isoforms in human pituitary tumors: Distinct localization, histone acetylation, and activation of the 5’ fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 promoter. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ramírez, C.; Cheng, S.; Vargas, G.; Asa, S.L.; Ezzat, S.; González, B.; Cabrera, L.; Guinto, G.; Mercado, M. Expression of Ki-67, PTTG1, FGFR4, and SSTR 2, 3, and 5 in nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas: A high throughput TMA, immunohistochemical study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, S.; Monsalves, E.; Tateno, T.; Zadeh, G. Role of mTOR Inhibitors in Growth Hormone-Producing Pituitary Adenomas Harboring Different FGFR4 Genotypes. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 3577–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durcan, E.; Keskin, F.E.; Ozkaya, H.M.; Sirolu, S.; Sahin, S.; Korkmaz, O.P.; Gazioglu, N.; Tanriover, N.; Comunoglu, N.; Oz, B.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-4 Expression in Pituitary Adenomas is Associated with Aggressive Tumor Features. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2022, 130, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, L.P.; Lerário, A.M.; Bronstein, M.D.; Soares, I.C.; Mendonca, B.B.; Fragoso, M.C. Influence of the fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 expression and the G388R functional polymorphism on Cushing’s disease outcome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, E271–E279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glebauskiene, B.; Liutkeviciene, R.; Vilkeviciute, A.; Gudinaviciene, I.; Rocyte, A.; Simonaviciute, D.; Mazetyte, R.; Kriauciuniene, L.; Zaliuniene, D. Association of Ki-67 Labelling Index and IL-17A with Pituitary Adenoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 7490585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Roncaroli, F.; Kovacs, K.; Lloyd, R.V.; Matsuno, A.; Righi, A. Pituitary carcinoma. In WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs; Lloyd, R.V., Osamura, R.Y., Klöpel, G., Rosai, J., Eds.; International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): Lyon, France, 2017; Chapter 1; pp. 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Foltran, R.K.; Amorim, P.V.G.H.; Duarte, F.H.; Grande, I.P.P.; Freire, A.C.T.B.; Frassetto, F.P.; Dettoni, J.; Alves, V.; Castro, I.; Trarbach, E.; et al. Study of major genetic factors involved in pituitary tumorigenesis and their impact on clinical and biological characteristics of sporadic somatotropinomas and non-functioning pituitary adenomas. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, e7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Honegger, J.; Prettin, C.; Feuerhake, F.; Petrick, M.; Schulte-Mönting, J.; Reincke, M. Expression of Ki-67 antigen in nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas: Correlation with growth velocity and invasiveness. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 99, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.F.; Zada, G.; Kim, S.; Lamborn, K.R.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Tyrrell, J.B.; Wilson, C.B.; Kunwar, S. Long-term recurrence and mortality after surgery and adjuvant radiotherapy for nonfunctional pituitary adenomas. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 108, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shraim, M.; Asa, S.L. The 2004 World Health Organization classification of pituitary tumors: What is new? Acta Neuropathol. 2006, 111, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitz, K.; Knosp, E.; Koos, W.T.; Korn, A. Proliferation in pituitary adenomas: Measurement by MAb KI 67. In Processes of the Cranial Midline; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1991; pp. 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastronardi, L.; Guiducci, A.; Spera, C.; Puzzilli, F.; Liberati, F.; Maira, G. Ki-67 labelling index and invasiveness among anterior pituitary adenomas: Analysis of 103 cases using the MIB-1 monoclonal antibody. J. Clin. Pathol. 1999, 52, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thapar, K.; Kovacs, K.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Stefaneanu, L.; Horvath, E.; Pernicone, P.J.; Murray, D.; Laws, E.R. Proliferative activity and invasiveness among pituitary adenomas and carcinomas: An analysis using the MIB-1 antibody. Neurosurgery 1996, 38, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, A.L.; Morton, J.P.; Manoharan, I.; Nelson, D.M.; Jamieson, N.B.; Pawlikowski, J.S.; McBryan, T.; Doyle, B.; McKay, C.; Oien, K.A.; et al. Activation of the PIK3CA/AKT pathway suppresses senescence induced by an activated RAS oncogene to promote tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rutkowski, M.J.; Alward, R.M.; Chen, R.; Wagner, J.; Jahangiri, A.; Southwell, D.G.; Kunwar, S.; Blevins, L.; Lee, H.; Aghi, M.K. Atypical pituitary adenoma: A clinicopathologic case series. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLellis, R.A.; Heitz, P.U.; Eng, C. Pathology and genetics of tumours of endocrine organs. In World Health Organization Classification of Tumours; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Korbonits, M.; Blair, J.C.; Boguslawska, A.; Caimari, F.; Casar-Borota, O.; Chanson, P.; Chiloiro, S.; Crinò, A.; Daly, A.F.; Di Iorgi, N.; et al. Consensus guideline for the diagnosis and management of pituitary adenomas in childhood and adolescence: Part 1, general recommendations. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Home–SNP–NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Rindi, G.; Mete, O.; Uccella, S.; Basturk, O.; La Rosa, S.; Brosens, L.A.A.; Ezzat, S.; de Herder, W.W.; Klimstra, D.S.; Papotti, M.; et al. Overview of the 2022 WHO Classification of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. In Endocrine Pathology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 33, pp. 115–154. [Google Scholar]
| Characteristics | Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA, n (%) (n = 100) | Control, n (%) (n = 200) | ||
| Age median (IQR) | 51 (21) | 53.5 (40) | 0.655 * |
| Gender, n (%) | 0.294 ** | ||
| Females | 64 (64) | 140 (70) | |
| Males | 36 (36) | 60 (30) | |
| Tumor size, n (%) | - | - | |
| Micro PA | 38 (38) | ||
| Macro PA | 62 (62) | ||
| Hormonal activity, n (%) | - | - | |
| Active | 59 (59) | ||
| Non-active | 41 (41) | ||
| Invasiveness, n (%) | - | - | |
| Invasive | 53 (53) | ||
| Non-invasive | 47 (47) | ||
| Recurrence, n (%) | - | - | |
| PA without recurrence | 77 (77) | ||
| PA with recurrence | 23 (23) | ||
| Gene | Genotype/Allele | PA Group n (%) (n = 100) | Control Group n (%) (n = 200) | p-Value | p-Value HWE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGFR4 (rs351855) | GG | 45 (45) | 95 (47.5) | 0.885 | 0.134 |
| GA | 49 (49) | 92 (46) | |||
| AA | 6 (6) | 13 (6.5) | |||
| In total: | 100 (100) | 200 (100) | |||
| Allele: | 0.800 | ||||
| G | 139 (69.5) | 282 (70.5) | |||
| A | 61 (30.5) | 118 (29.5) | |||
| FGFR4 (rs7708357) | GG | 40 (40) | 86 (43) | 0.755 | 0.791 |
| GA | 49 (49) | 89 (44.5) | |||
| AA | 11 (11) | 25 (12.5) | |||
| In total: | 100 (100) | 200 (100) | |||
| Allele: | 0.855 | ||||
| G | 129 (64.5) | 261 (65.3) | |||
| A | 71 (35.5) | 139 (34.7) |
| Gene | Genotype/Allele | PA Group Females (n = 64) n (%) | Control Group Females (n = 140) n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGFR4 (rs351855) | GG | 27 (42.2) | 69 (49.3) | 0.490 |
| GA | 34 (53.1) | 62 (44.3) | ||
| AA | 3 (4.7) | 9 (6.4) | ||
| In total: | 64 (100) | 140 (100) | ||
| Allele: | 0.581 | |||
| G | 88 (68.75) | 200 (71.4) | ||
| A | 40 (31.25) | 80 (28.6) | ||
| FGFR4 (rs7708357) | GG | 25 (39.1) | 56 (40) | 0.726 |
| GA | 33 (51.6) | 66 (47.1) | ||
| AA | 6 (9.4) | 18 (12.9) | ||
| In total: | 64 (100) | 140 (100) | ||
| Allele: | 0.803 | |||
| G | 83 (64.8) | 178 (63.6) | ||
| A | 45 (35.2) | 102 (36.4) |
| Gene | Genotype/Allele | PA Group Males (n = 36) n (%) | Control Group Males (n = 60) n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGFR4 (rs351855) | GG | 18 (50) | 26 (43.3) | 0.727 |
| GA | 15 (41.7) | 30 (50) | ||
| AA | 3 (8.3) | 4 (6.7) | ||
| In total: | 36 (100) | 60 (100) | ||
| Allele: | 0.716 | |||
| G | 51 (70.8) | 82 (68.3) | ||
| A | 21 (29.2) | 38 (31.7) | ||
| FGFR4 (rs7708357) | GG | 15 (41.7) | 30 (50) | 0.730 |
| GA | 16 (44.4) | 23 (38.3) | ||
| AA | 5 (13.9) | 7 (11.7) | ||
| In total: | 36 (100) | 60 (100) | ||
| Allele: | 0.450 | |||
| G | 46 (63.9) | 83 (69.2) | ||
| A | 26 (36.1) | 37 (30.8) |
| Gene | Genotype/ Allele | Control Group (n = 200) n (%) | Micro PA (n = 38) n (%) | p-Value | Macro PA (n = 62) n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGFR4 (rs351855) | GG | 95 (47.5) | 15 (39.5) | 0.577 | 30 (48.4) | 0.992 |
| GA | 92 (46) | 21 (55.3) | 28 (45.2) | |||
| AA | 13 (6.5) | 2 (5.3) | 4 (6.5) | |||
| In total: | 200 (100) | 38 (100) | 62 (100) | |||
| Allele: | 0.554 | 0.920 | ||||
| G | 282 (70.5) | 51 (67.1) | 88 (71) | |||
| A | 118 (29.5) | 25 (32.9) | 36 (29) | |||
| FGFR4 (rs7708357) | GG | 86 (43) | 15 (39.5) | 0.836 | 25 (40.3) | 0.494 |
| GA | 89 (44.5) | 17 (44.7) | 32 (51.6) | |||
| AA | 25 (12.5) | 6 (15.8) | 5 (8.1) | |||
| In total: | 200 (100) | 38 (100) | 62 (100) | |||
| Allele: | 0.568 | 0.857 | ||||
| G | 261 (65.3) | 47 (61.8) | 82 (66.1) | |||
| A | 139 (34.7) | 29 (38.2) | 42 (33.9) |
| Gene | Genotype/ Allele | Control Group (n = 200) n (%) | Non-Invasive PA (n = 47) n (%) | p-Value | Invasive PA (n = 53) n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGFR4 (rs351855) | GG | 95 (47.5) | 17 (36.2) | 0.348 | 28 (52.8) | 0.787 |
| GA | 92 (46) | 27 (57.4) | 22 (41.5) | |||
| AA | 13 (6.5) | 3 (6.4) | 3 (5.7) | |||
| In total: | 200 (100) | 47 (100) | 53 (100) | |||
| Allele: | 0.288 | 0.533 | ||||
| G | 282 (70.5) | 61 (64.9) | 78 (73.6) | |||
| A | 118 (29.5) | 33 (35.1) | 28 (26.4) | |||
| FGFR4 (rs7708357) | GG | 86 (43) | 15 (31.9) | 0.353 | 25 (47.2) | 0.367 |
| GA | 89 (44.5) | 24 (51.1) | 25 (47.2) | |||
| AA | 25 (12.5) | 8 (17) | 3 (5.7) | |||
| In total: | 200 (100) | 47 (100) | 53 (100) | |||
| Allele: | 0.156 | 0.286 | ||||
| G | 261 (65.3) | 54 (57.4) | 75 (70.8) | |||
| A | 139 (34.7) | 40 (42.6) | 31 (29.2) |
| Gene | Genotype/ Allele | Control Group (n = 200) n (%) | Non-Active PA (n = 41) n (%) | p-Value | Active PA (n = 59) n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGFR4 (rs351855) | GG | 95 (47.5) | 20 (48.8) | 0.713 | 25 (42.4) | 0.435 |
| GA | 92 (46) | 17 (41.5) | 32 (54.2) | |||
| AA | 13 (6.5) | 4 (9.8) | 2 (3.4) | |||
| In total: | 200 (100) | 41 (100) | 59 (100) | |||
| Allele: | 0.858 | 0.833 | ||||
| G | 282 (70.5) | 57 (69.5) | 82 (69.5) | |||
| A | 118 (29.5) | 25 (30.5) | 36 (30.5) | |||
| FGFR4 (rs7708357) | GG | 86 (43) | 13 (31.7) | 0.360 | 27 (45.8) | 0.866 |
| GA | 89 (44.5) | 23 (56.1) | 26 (44.1) | |||
| AA | 25 (12.5) | 5 (12.2) | 6 (10.2) | |||
| In total: | 200 (100) | 41 (100) | 59 (100) | |||
| Allele: | 0.344 | 0.608 | ||||
| G | 261 (65.3) | 49 (59.8) | 80 (67.8) | |||
| A | 139 (34.7) | 33 (40.2) | 38 (32.2) |
| Gene | Genotype/ Allele |
Control Group (n = 200) n (%) | PA Without Recurrence (n = 77) n (%) | p-Value | PA with Recurrence (n = 23) n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGFR4 (rs351855) | GG | 95 (47.5) | 34 (44.2) | 0.316 | 11 (47.8) | 0.150 |
| GA | 92 (46) | 41 (53.2) | 8 (34.8) | |||
| AA | 13 (6.5) | 2 (2.6) | 4 (17.4) | |||
| In total: | 200 (100) | 77 (100) | 23 (100) | |||
| Allele: | 0.948 | 0.459 | ||||
| G | 282 (70.5) | 109 (70.8) | 30 (65.2) | |||
| A | 118 (29.5) | 45 (29.2) | 16 (34.8) | |||
| FGFR4 (rs7708357) | GG | 86 (43) | 27 (35.1) | 0.465 | 13 (56.5) | 0.339 |
| GA | 89 (44.5) | 40 (51.9) | 9 (39.1) | |||
| AA | 25 (12.5) | 10 (13) | 1 (4.3) | |||
| In total: | 200 (100) | 77 (100) | 23 (100) | |||
| Allele: | 0.354 | 0.140 | ||||
| G | 261 (65.3) | 94 (61) | 35 (76.1) | |||
| A | 139 (34.7) | 60 (39) | 11 (23.9) |
| FGFR4 (rs351855) | |||||
| Model | Genotype/Allele | OR (95% CI) | p-value | AIC | |
| PA without recurrence | |||||
| Codominant | GA vs. GG | 1.245 (0.727–2.131) | 0.424 | 328.894 | |
| AA vs. GG | 0.430 (0.092–2.004) | 0.282 | |||
| Dominant | GA + AA vs. GG | 1.144 (0.675–1.941) | 0.617 | 329.182 | |
| Recessive | AA vs. GG + GA | 0.384 (0.085–1.741) | 0.214 | 327.535 | |
| Overdominant | GA vs. GG + AA | 1.337 (0.789–2.265) | 0.280 | 328.263 | |
| Additive | A | 0.984 (0.631–1.535) | 0.944 | 329.428 | |
| PA with recurrence | |||||
| Model | Genotype/Allele | OR (95% CI) | p-value | AIC | |
| Codominant | GA vs. GG | 0.751 (0.289–1.951) | 0.557 | 148.963 | |
| AA vs. GG | 2.657 (0.737–9.584) | 0.135 | |||
| Dominant | GA + AA vs. GG | 0.987 (0.416–2.342) | 0.976 | 150.038 | |
| Recessive | AA vs. GG + GA | 3.028 (0.898–10.216) | 0.074 | 147.312 | |
| Overdominant | GA vs. GG + AA | 0.626 (0.254–1.543) | 0.309 | 148.969 | |
| Additive | A | 1.298 (0.665–2.537) | 0.445 | 149.464 | |
| FGFR4 (rs7708357) | |||||
| Model | Genotype/Allele | OR (95% CI) | p-value | AIC | |
| PA without recurrence | |||||
| Codominant | GA vs. GG | 1.432 (0.809–2.534) | 0.218 | 329.890 | |
| AA vs. GG | 1.274 (0.544–2.985) | 0.577 | |||
| Dominant | GA + AA vs. GG | 1.397 (0.810–2.410) | 0.230 | 327.967 | |
| Recessive | AA vs. GG + GA | 1.045 (0.476–2.292) | 0.913 | 329.421 | |
| Overdominant | GA vs. GG + AA | 1.348 (0.796–2.284) | 0.266 | 328.195 | |
| Additive | A | 1.201 (0.816–1.769) | 0.353 | 328.571 | |
| PA with recurrence | |||||
| Model | Genotype/Allele | OR (95% CI) | p-value | AIC | |
| Codominant | GA vs. GG | 0.669 (0.272–1.646) | 0.381 | 149.601 | |
| AA vs. GG | 0.265 (0.033–2.123) | 0.211 | |||
| Dominant | GA + AA vs. GG | 0.580 (0.243–1.386) | 0.221 | 148.522 | |
| Recessive | AA vs. GG + GA | 0.318 (0.041–2.465) | 0.273 | 148.379 | |
| Overdominant | GA vs. GG + AA | 0.802 (0.332–1.938) | 0.624 | 149.795 | |
| Additive | A | 0.593 (0.292–1.204) | 0.148 | 147.781 | |
| Ki-67 LI | Tumor Size | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Micro PA (n = 20) (%) | Macro PA (n = 35) (%) | ||
| <1% | 7 (35) | 7 (20) | 0.333 |
| 1% | 1 (5) | 5 (14.3) | |
| >1% | 12 (60) | 23 (65.7) | |
| Ki-67 LI | Invasiveness | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Invasive PA (n = 22) (%) | Invasive PA) (n = 33) (%) | ||
| <1% | 7 (31.8) | 7 (21.2) | 0.666 |
| 1% | 2 (9.1) | 4 (12.1) | |
| >1% | 13 (59.1) | 22 (66.7) | |
| Ki-67 LI | Activeness | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Active PA (n = 24) (%) | Active PA (n = 31) (%) | ||
| <1% | 5 (20.8) | 9 (29) | 0.224 |
| 1% | 1 (4.2) | 5 (16.1) | |
| >1% | 18 (75) | 17 (54.8) | |
| Ki-67 LI | Recurrence | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA Without Recurrence (n = 37) (%) | PA with Recurrence (n = 18) (%) | ||
| <1% | 9 (24.3) | 5 (27.8) | 0.671 |
| 1% | 5 (13.5) | 1 (5.6) | |
| >1% | 23 (62.2) | 12 (66.7) | |
| Gene, SNV | Genotype/Allele | Ki-67 LI | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1% | 1% | >1% | |||
| FGFR4 rs351855 | GG | 7 (50) | 4 (66.7) | 14 (40) | 0.754 |
| GA | 6 (42.9) | 2 (33.3) | 19 (54.3) | ||
| AA | 1 (7.1) | 0 (0) | 2 (5.7) | ||
| In total: | 14 (100) | 6 (100) | 35 (100) | ||
| Allele: | 0.518 | ||||
| G | 20 (71.4) | 10 (83.3) | 47 (67.1) | ||
| A | 8 (28.6) | 2 (16.7) | 23 (32.9) | ||
| FGFR4 rs7708357 | GG | 8 (57.1) | 2 (33.3) | 16 (45.7) | 0.885 |
| GA | 5 (35.7) | 3 (50) | 15 (42.9) | ||
| AA | 1 (7.1) | 1 (16.7) | 4 (11.4) | ||
| In total: | 14 (100) | 6 (100) | 35 (100) | ||
| Allele: | 0.556 | ||||
| G | 21 (75) | 7 (58.3) | 47 (67.1) | ||
| A | 7 (25) | 5 (41.7) | 23 (32.9) | ||
| PA Subgroups | p53 H Score Median (IQR) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|
| Micro PA | 18.34 (17.65) | 0.005 |
| Macro PA | 30.33 (28.68) | |
| Non-invasive PA | 21.32 (17.65) | 0.324 |
| Invasive PA | 27.5 (26.25) | |
| Non-active PA | 21.02 (17.65) | 0.068 |
| Active PA | 28.33 (49.5) | |
| PA without recurrence | 28.66 (25.41) | 0.360 |
| PA with recurrence | 21.02 (14.65) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juskiene, M.; Duseikaite, M.; Vilkeviciute, A.; Karinauske, E.; Baikstiene, I.; Makstiene, J.; Poskiene, L.; Tamasauskas, A.; Liutkeviciene, R.; Verkauskiene, R.; et al. Insights into FGFR4 (rs351855 and rs7708357) Gene Variants, Ki-67 and p53 in Pituitary Adenoma Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157565
Juskiene M, Duseikaite M, Vilkeviciute A, Karinauske E, Baikstiene I, Makstiene J, Poskiene L, Tamasauskas A, Liutkeviciene R, Verkauskiene R, et al. Insights into FGFR4 (rs351855 and rs7708357) Gene Variants, Ki-67 and p53 in Pituitary Adenoma Pathophysiology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157565
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuskiene, Martyna, Monika Duseikaite, Alvita Vilkeviciute, Egle Karinauske, Ieva Baikstiene, Jurgita Makstiene, Lina Poskiene, Arimantas Tamasauskas, Rasa Liutkeviciene, Rasa Verkauskiene, and et al. 2025. "Insights into FGFR4 (rs351855 and rs7708357) Gene Variants, Ki-67 and p53 in Pituitary Adenoma Pathophysiology" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157565
APA StyleJuskiene, M., Duseikaite, M., Vilkeviciute, A., Karinauske, E., Baikstiene, I., Makstiene, J., Poskiene, L., Tamasauskas, A., Liutkeviciene, R., Verkauskiene, R., & Zilaitiene, B. (2025). Insights into FGFR4 (rs351855 and rs7708357) Gene Variants, Ki-67 and p53 in Pituitary Adenoma Pathophysiology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157565







