Potential Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in Murine Tear Fluids in the Physiology of Corneal Epithelial Cells In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
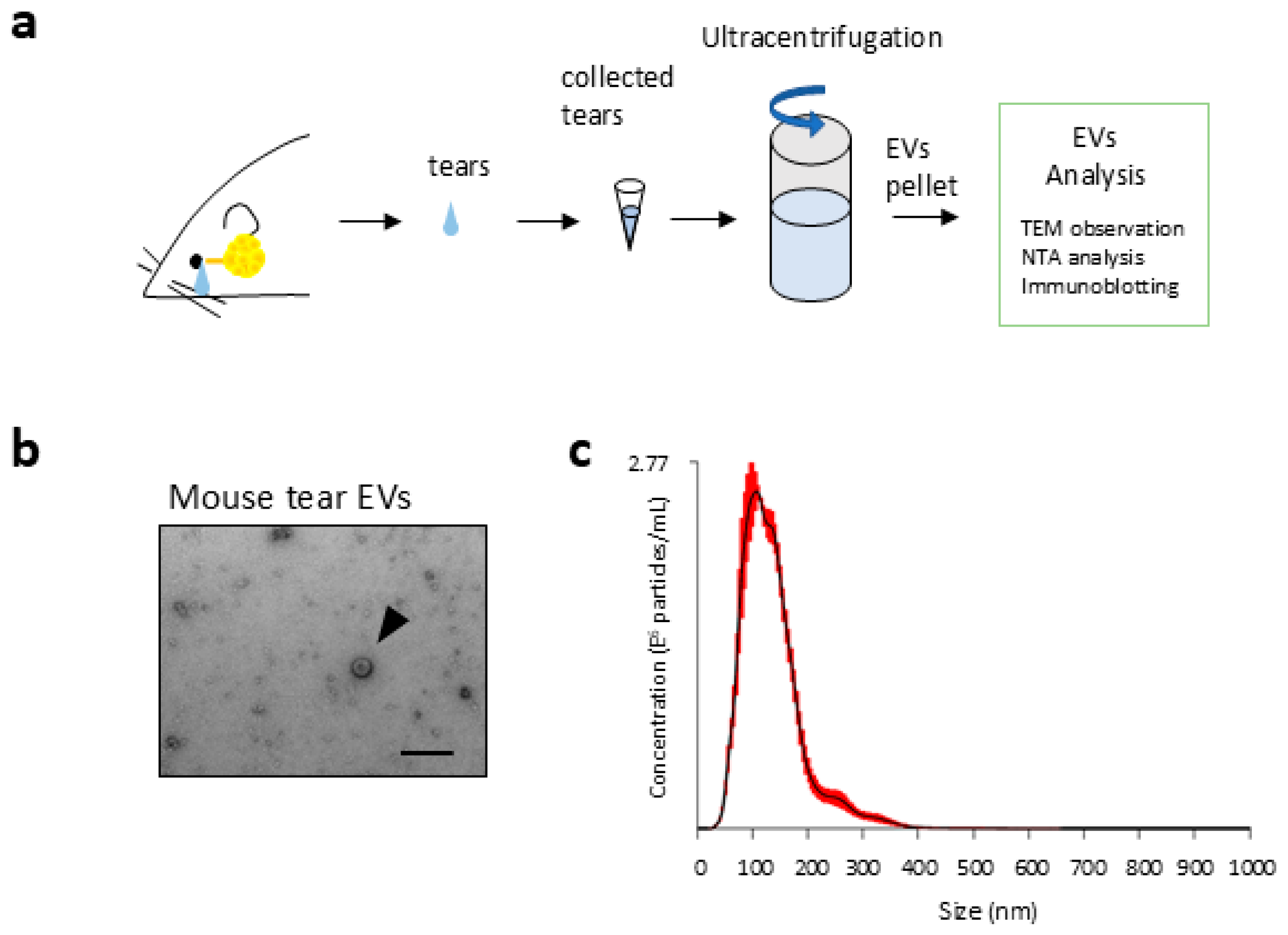
2.1. Morphological Details of EVs in Tear Fluids
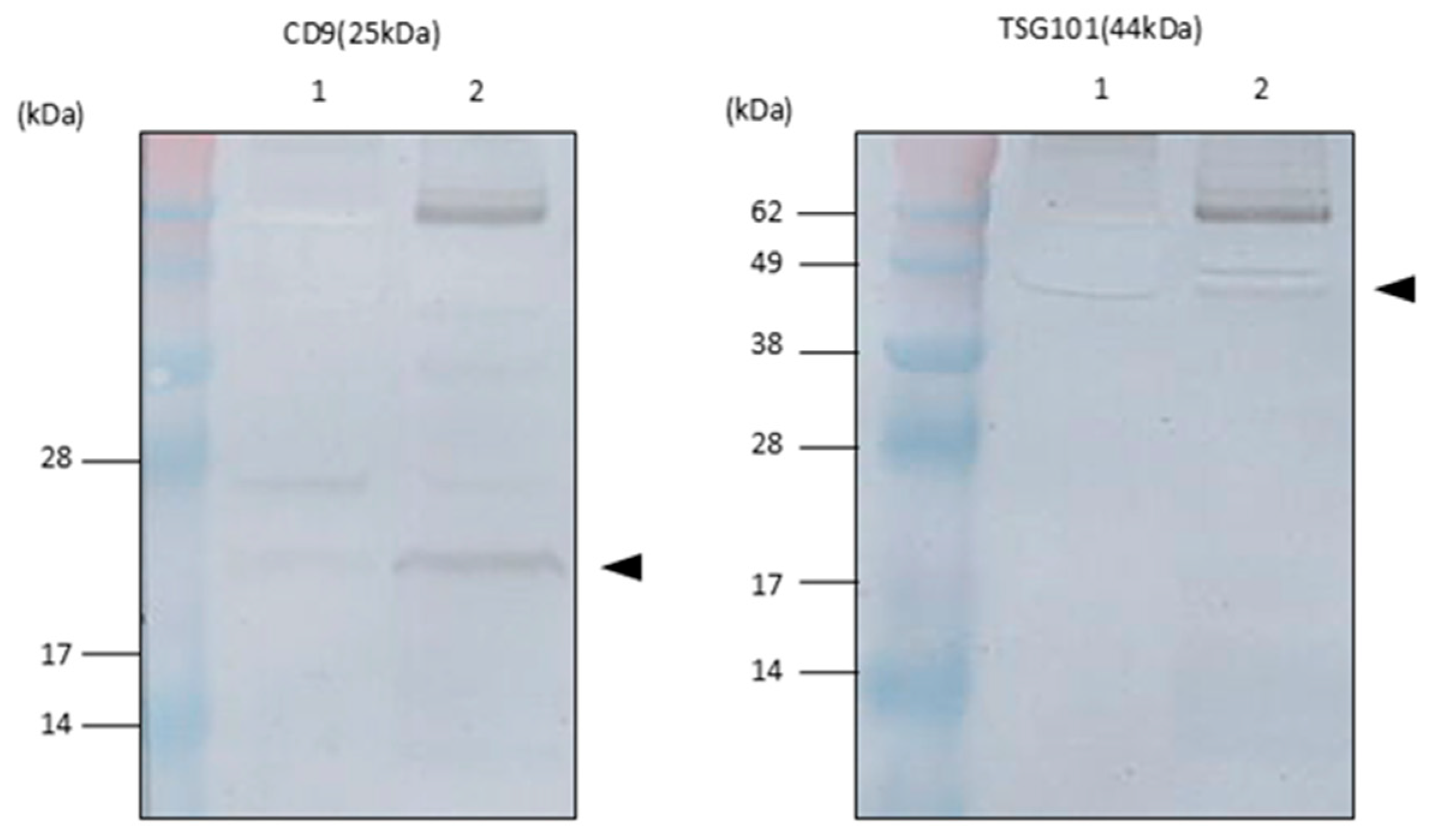
2.2. Exosomal Marker Expression on EVs in Tear Fluids
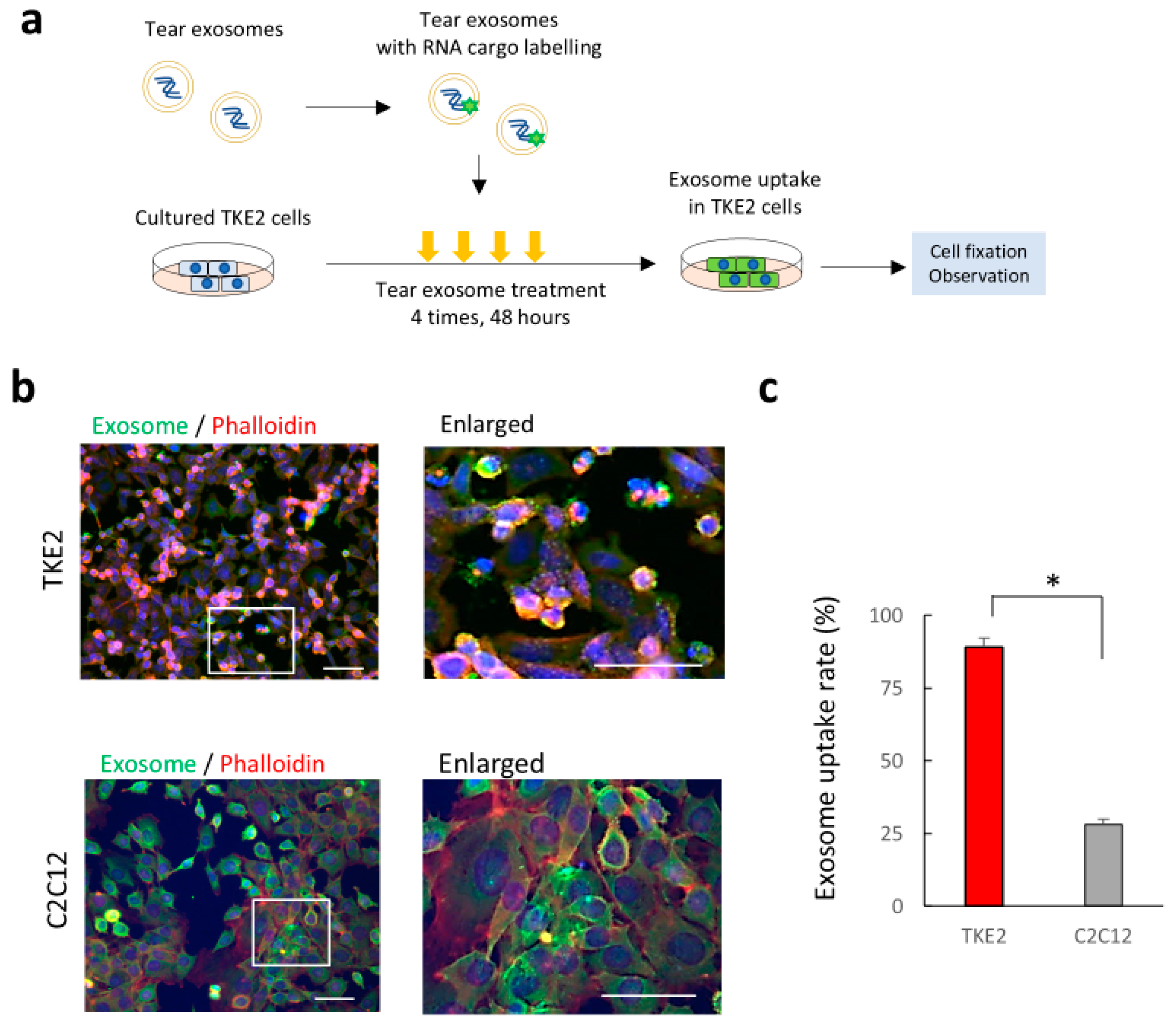
2.3. Uptake of Tear Exosomes in Cultivated Corneal Epithelial Cells In Vitro
2.4. Gene Expression Changes in Corneal Epithelial Cells After the Uptake of Tear Exosomes
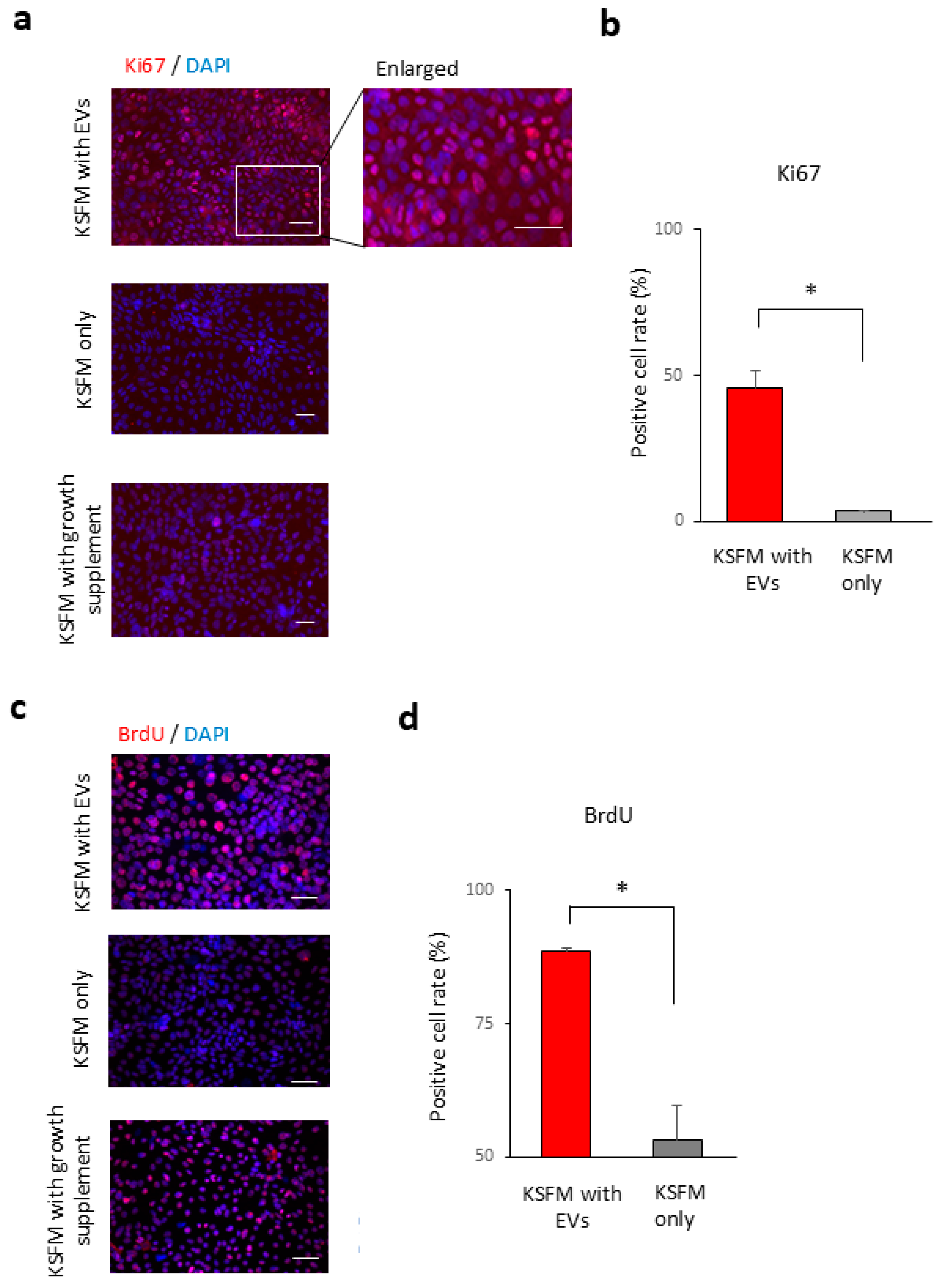
2.5. Tear Exosomes Induce the Proliferation of Cultivated Corneal Epithelial Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Statements
4.2. Tear Fluid Collection
4.3. Isolation of EVs
4.4. Morphological Analysis of Nanoparticles
4.5. Western Blot Immunoblotting
4.6. Cell Culture and Analysis of Exosome Uptake
4.7. BrdU Labelling
4.8. Immunostaining
4.9. Microarray Data Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EVs | Extracellular Vesicles |
| DED | Dry Eye Diseases |
| EDA | Ectodysplasin A |
References
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Hopmans, E.S.; Lindenberg, J.L.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Wurdinger, T.; Middeldorp, J.M. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6328–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Tesic Mark, M.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saman, S.; Kim, W.; Raya, M.; Visnick, Y.; Miro, S.; Jackson, B.; McKee, A.C.; Alvarez, V.E.; Lee, N.C.; Hall, G.F. Exosome-associated tau is secreted in tauopathy models and is selectively phosphorylated in cerebrospinal fluid in early Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 3842–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.T.; Johnstone, R.M. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: Selective externalization of the receptor. Cell 1983, 33, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niel, G.; Porto-Carreiro, I.; Simoes, S.; Raposo, G. Exosomes: A common pathway for a specialized function. J. Biochem. 2006, 140, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, N.; Avissar, S.; Beit-Yannai, E. Extracellular vesicles mediate signaling between the aqueous humor producing and draining cells in the ocular system. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z. Roles of Exosomes in Ocular Diseases. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 10519–10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaeekia, R.; Rabiee, B.; Putra, I.; Shen, X.; Park, Y.J.; Hematti, P.; Eslani, M.; Djalilian, A.R. Effect of Human Corneal Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-derived Exosomes on Corneal Epithelial Wound Healing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 5194–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingeborn, M.; Dismuke, W.M.; Bowes Rickman, C.; Stamer, W.D. Roles of exosomes in the normal and diseased eye. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2017, 59, 158–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, W.D. Why the eye becomes dry: A cornea and lacrimal gland feedback model. CLAO J. 2000, 26, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doyle, L.M.; Wang, M.Z. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skog, J.; Wurdinger, T.; van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Curry, W.T., Jr.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, T.; Shimmura, S.; Hornia, A.; Higa, K.; Tseng, S.C. Stratified epithelial sheets engineered from a single adult murine corneal/limbal progenitor cell. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Matsuki, Y.; Ochiya, T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17442–17452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene Ontology Consortium. Gene Ontology Consortium: Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D1049–D1056. [CrossRef]
- Tsubota, K.; Satake, Y.; Shimazaki, J. Treatment of severe dry eye. Lancet 1996, 348, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishima, S. Some Physiological Aspects of the Precorneal Tear Film. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1965, 73, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, N.; Uchino, M.; Uchino, Y.; Dogru, M.; Kawashima, M.; Komuro, A.; Sonomura, Y.; Kato, H.; Tsubota, K.; Kinoshita, S. Importance of tear film instability in dry eye disease in office workers using visual display terminals: The Osaka study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 159, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, M.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Michikawa, T.; Shirakawa, K.; Kuwahara, E.; Yamada, M.; Dogru, M.; Schaumberg, D.A.; Kawakita, T.; Takebayashi, T.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors of dry eye disease in Japan: Koumi study. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 2361–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, D.A.; Noecker, R.J.; Kahook, M.Y. Effects of benzalkonium chloride- and polyquad-preserved combination glaucoma medications on cultured human ocular surface cells. Adv. Ther. 2011, 28, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Nijman, H.W.; Stoorvogel, W.; Liejendekker, R.; Harding, C.V.; Melief, C.J.; Geuze, H.J. B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caby, M.P.; Lankar, D.; Vincendeau-Scherrer, C.; Raposo, G.; Bonnerot, C. Exosomal-like vesicles are present in human blood plasma. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisitkun, T.; Shen, R.F.; Knepper, M.A. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13368–13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Kanai-Azuma, M.; Akimoto, Y.; Kawakami, H.; Yanoshita, R. Exosome-like vesicles with dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human saliva. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Izumi, H.; Sekine, K.; Ochiya, T. microRNA as a new immune-regulatory agent in breast milk. Silence 2010, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Street, J.M.; Barran, P.E.; Mackay, C.L.; Weidt, S.; Balmforth, C.; Walsh, T.S.; Chalmers, R.T.; Webb, D.J.; Dear, J.W. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human cerebrospinal fluid. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Lv, W.; Hu, X. Altered microRNA profiles in cerebrospinal fluid exosome in Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37043–37053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madison, M.N.; Roller, R.J.; Okeoma, C.M. Human semen contains exosomes with potent anti-HIV-1 activity. Retrovirology 2014, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runz, S.; Keller, S.; Rupp, C.; Stoeck, A.; Issa, Y.; Koensgen, D.; Mustea, A.; Sehouli, J.; Kristiansen, G.; Altevogt, P. Malignant ascites-derived exosomes of ovarian carcinoma patients contain CD24 and EpCAM. Gynecol. Oncol. 2007, 107, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inubushi, S.; Kawaguchi, H.; Mizumoto, S.; Kunihisa, T.; Baba, M.; Kitayama, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Hoffman, R.M.; Tanino, H.; Sasaki, R. Oncogenic miRNAs Identified in Tear Exosomes From Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 3091–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjordal, O.; Norheim, K.B.; Rodahl, E.; Jonsson, R.; Omdal, R. Primary Sjogren’s syndrome and the eye. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2020, 65, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.T.; Hamar, P.; Guo, C.; Basar, E.; Perdigao-Henriques, R.; Balaj, L.; Lieberman, J. miR-200-containing extracellular vesicles promote breast cancer cell metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 5109–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakkaraju, A.; Rodriguez-Boulan, E. Itinerant exosomes: Emerging roles in cell and tissue polarity. Trends Cell Biol. 2008, 18, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadier, A.; Viriot, L.; Pantalacci, S.; Laudet, V. The ectodysplasin pathway: From diseases to adaptations. Trends Genet. TIG 2014, 30, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, L.A.; Pink, R.C.; Carter, D.R. Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 24641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, K.J.; Christianson, H.C.; Wittrup, A.; Bourseau-Guilmain, E.; Lindqvist, E.; Svensson, L.M.; Morgelin, M.; Belting, M. Exosome uptake depends on ERK1/2-heat shock protein 27 signaling and lipid Raft-mediated endocytosis negatively regulated by caveolin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 17713–17724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkach, M.; Thery, C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell 2016, 164, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, M.; Ogawa, M.; Oshima, M.; Sekine, Y.; Ishida, K.; Yamashita, K.; Ikeda, K.; Shimmura, S.; Kawakita, T.; Tsubota, K.; et al. Functional lacrimal gland regeneration by transplantation of a bioengineered organ germ. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greening, D.W.; Xu, R.; Ji, H.; Tauro, B.J.; Simpson, R.J. A protocol for exosome isolation and characterization: Evaluation of ultracentrifugation, density-gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1295, 179–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| AC1 (Enrichment score: 2.77) | |
| GO Term Biological Process | p-value |
| GO:0007049 cell cycle | 0.007 |
| GO:0051301 cell division | <0.001 |
| GO:0007067 mitotic nuclear division | <0.001 |
| GO:0007059 chromosome segregation | 0.009 |
| GO:0000070 mitotic sister chromatid segregation | <0.001 |
| GO Term Cellular Component | p-value |
| GO:0005694 chromosome | 0.041 |
| GO:0000776 kinetochore | <0.001 |
| GO:0000775 chromosome, centromeric region | 0.002 |
| GO:0000922 spindle pole | 0.001 |
| GO:0000777 condensed chromosome kinetochore | 0.001 |
| GO:0000780 condensed nuclear chromosome | 0.005 |
| AC2 (Enrichment score: 2.27) | |
| GO Term Biological Process | p-value |
| GO:0005886 plasma membrane | 0.015 |
| AC3 (Enrichment score: 1.86) | |
| GO Term Cellular Component | p-value |
| GO:0016020 membrane | 0.015 |
| GO:0016021 integral component of membrane | 0.036 |
| AC5 (Enrichment score: 1.40) | |
| GO Term Biological Process | p-value |
| GO:0007018 microtubule-based movement | 0.073 |
| GO:0007080~mitotic metaphase plate congression | 0.031 |
| GO Term Cellular Component | p-value |
| GO:0005819 spindle | 0.028 |
| GO:0005871 kinesin complex | 0.019 |
| GO:0005876 spindle microtubule | 0.044 |
| GO Term Molecular Function | p-value |
| GO:0008017 microtubule binding | 0.022 |
| GO:0008574 ATP-dependent microtubule motor activity | 0.028 |
| Pathway | p-Value (Comparison) |
|---|---|
| Mm_EDA_Signalling_in_Hair_Follicle_Development_WP3652_97556 | 0.007748972 |
| Mm_Steroid_Biosynthesis_WP55_89970 | 0.027217017 |
| Mm_Glutathione_metabolism_WP164_85644 | 0.057912603 |
| Mm_Kit_Receptor_Signaling_Pathway_WP407_69079 | 0.058914933 |
| Mm_Statin_Pathway_WP1_73346 | 0.06381421 |
| Mm_Metapathway_biotransformation_WP1251_94721 | 0.07834384 |
| Mm_Notch_Signaling_Pathway_WP29_79679 | 0.079050094 |
| Mm_Hedgehog_Signaling_Pathway_WP116_69142 | 0.08262755 |
| Mm_Chemokine_signaling_pathway_WP2292_97515 | 0.098608024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oya, S.; Higa, K.; Yasutake, T.; Yamazaki-Hokama, R.; Hirayama, M. Potential Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in Murine Tear Fluids in the Physiology of Corneal Epithelial Cells In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157559
Oya S, Higa K, Yasutake T, Yamazaki-Hokama R, Hirayama M. Potential Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in Murine Tear Fluids in the Physiology of Corneal Epithelial Cells In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157559
Chicago/Turabian StyleOya, Saya, Kazunari Higa, Tomohiro Yasutake, Risa Yamazaki-Hokama, and Masatoshi Hirayama. 2025. "Potential Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in Murine Tear Fluids in the Physiology of Corneal Epithelial Cells In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157559
APA StyleOya, S., Higa, K., Yasutake, T., Yamazaki-Hokama, R., & Hirayama, M. (2025). Potential Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in Murine Tear Fluids in the Physiology of Corneal Epithelial Cells In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157559






