Abstract
Cadmium (Cd) is a toxic environmental heavy metal that exerts harmful effects on multiple tissues, including the kidney, liver, lung, and bone, and is also associated with the development of anemia. However, the precise molecular mechanisms underlying Cd-induced toxicity remain incompletely understood. In this paper, we review the recent molecular mechanisms of Cd-induced toxicity and its modification, with a particular emphasis on our recent findings. Using a combination of DNA microarray analysis, protein–DNA binding assays, and siRNA-mediated gene silencing, we identified several transcription factors, YY1, FOXF1, ARNT, and MEF2A, as novel molecular targets of Cd. The downregulation of their downstream genes, including UBE2D2, UBE2D4, BIRC3, and SLC2A4, was directly associated with the expression of cytotoxicity. In addition, PPARδ plays a pivotal role in modulating cellular susceptibility to Cd-induced renal toxicity, potentially by regulating apoptosis-related signaling pathways. In addition to apoptosis pathways, Cd toxicity through ROS generation, ferroptosis and pyroptosis were summarized. Furthermore, it has been revealed that Cd suppresses the expression of iron transport-related genes in duodenal epithelial cells leading to impaired intestinal iron absorption as well as decreased hepatic iron levels. These findings provide a mechanistic basis for Cd-induced iron deficiency anemia, implicating disrupted iron homeostasis as a contributing factor.
1. Introduction
Cadmium (Cd) is a heavy metal (atomic weight 112.41, density 8.6 g/cm2) with a melting point of 320.9 °C and boiling point of 767 °C [1]. It was discovered in 1817 by the German mineralogist F. Strohmeyer [2]. In the periodic table, Cd is in group 12 (between zinc and mercury). Cd has been used in pigments, batteries, alloys, and electroplating, as well as in automobile parts, electronic devices, camera components, plastic stabilizers, and nuclear reactor control rods [3,4,5]. In nature, Cd coexists with zinc, copper, lead, and other metals, and is obtained as a byproduct during the mining and smelting of those metals [2,6,7]. Cd, along with arsenic, lead, mercury, and chromium, is a heavy metal lacking any known physiological function and is widely recognized as a toxic environmental contaminant [8,9,10,11,12,13]. Cd is a ubiquitous environmental contaminant found in soil, water, air, and food sources [14,15,16,17,18,19]. Cd enters the human body mainly through dietary intake, smoking, and occupational exposure. Its long biological half-life (>10 years) and accumulation in organs such as the liver, kidney, and pancreas reflect its relevance as a chronic public health hazard [20,21,22,23,24].
As an international standard for the safe intake of Cd, the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) has established a Provisional Tolerable Monthly Intake (PTMI) of 25 μg/kg body weight [25]. In addition, maximum levels for Cd in food, including rice, have been set by the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) of FAO/WHO [26] (see Table 1 for reference values).

Table 1.
Maximum levels for Cd in selected food categories as established by the Codex Alimentarius Commission.
Cd exposure to humans has been associated with damage to tissues including the kidney, bone, lung, reproductive system, and cardiovascular system in cases of occupational exposure (e.g., smelters, battery factories) and environmental contamination via food and water [2,27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. In particular, chronic renal toxicity, characterized by proximal tubular dysfunction, is a major toxic outcome in the safety assessment of Cd [34,35].
In Japan, in addition to occupational Cd poisoning, chronic Cd renal toxicity has occurred in several polluted areas (Fuchu in Toyama, Ikuno in Hyogo, the Kakehashi River basin in Ishikawa, Kosaka in Akita, and Tsushima in Nagasaki) in the past [36]. In 1955, in the Jinzu River basin of Toyama, the prolonged oral intake of rice and drinking water contaminated with Cd led to an outbreak of Itai-itai disease, which was characterized by renal damage and osteomalacia, primarily in older women [1,37]. Itai-itai disease, a pollution-related illness, occurred after the discharge of Cd-containing wastewater from the zinc refinery upstream of the Jinzu River [36,37]. This led to the Cd contamination of drinking water, soil, and agricultural crops, particularly rice, in the downstream area, Fuchu.
In addition to Japan, Cd pollution has also been confirmed in river basins near zinc mines and zinc smelters in Thailand and South Korea in the past, causing health damage to residents in the downstream area [38,39,40]. Furthermore, EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) recommends reducing Cd exposure, as the estimated mean dietary intake among adults in the EU is close to or slightly exceeds the tolerable weekly intake [41].
Recently, Cd poisoning caused by exposure in industrial workplaces or environmental pollution has rarely been observed in Japan. However, trace amounts Cd are present in various foods, including rice, and greater than 40% of the Cd intake by the Japanese population comes from eating rice [36,42]. Thus, Cd is continuously ingested through the diet over a lifetime. Because of its extremely long biological half-life (15–30 years) and tendency to accumulate in the body, there is growing concern about the health effects of long-term and low-level exposure to Cd, particularly among the elderly.
Studies of the mechanisms of Cd toxicity have been carried out for many years by various research groups worldwide. However, the molecular mechanisms of Cd-induced toxicity remain almost unknown. In this article, we review the molecular mechanisms of Cd toxicity and protective factors against it, focusing on the findings from our research.
2. Identification of Target Genes in Cd Renal Toxicity
It has been reported that toxic chemicals trigger cell death through several target genes [43,44,45]. To identify the target genes involved in Cd renal toxicity, we performed a genome-wide DNA microarray analysis of Cd-responsive genes in rat renal proximal tubular (NRK-52E) cells [46]. The exposure of NRK-52E cells to Cd upregulated 73 genes (>2-fold), including stress response genes such as metallothionein 1 (Mt1) and heme oxygenase 1 (Hmox1). In addition, 42 genes were downregulated to less than half their control expression; among these was Ube2d4 (ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 D4), which encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme of the Ube2d family that functions in the ubiquitin-proteasome system for selective protein degradation [46]. Furthermore, to the NRK-52E cell analysis, we have identified numerous Cd-responsive genes in other models, including human proximal tubular (HK-2) cells [47], mouse liver [48], mouse kidney [49], and mouse fetal liver [50].
Prior to the onset of overt cytotoxicity in HK-2 cells, Cd exposure upregulated the expression of 30 genes more than 2.0-fold, including seven genes encoding heat shock proteins. Concurrently, Cd downregulated the expression of 21 genes to less than 50% of control levels, including transcription-related genes such as AP2B1 (adaptor-related protein complex 2 subunit beta 1), HOXA7 (homeobox A7), HOXA9, and TCEB2 (transcription elongation factor B polypeptide 2). Genes involved in defending against Cd toxicity including the zinc transporter ZIP1 (SLC39A1) and the heat shock proteins HSPH1 [heat shock protein family H (Hsp110) member 1] and HSPA8 [heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 8] were among those altered by Cd exposure in HK-2 cells [51,52].
Hepatic transcriptional responses were assessed in mice administered 50 ppm Cd via drinking water for 30 days using DNA microarray analysis [48]. Exposure to Cd resulted in the upregulation of 2 genes and downregulation of 15 genes in the liver, suggesting early molecular alterations might precede the onset of hepatotoxic damage [48]. Mice were fed a control diet or a diet containing 300 ppm Cd for 12 months [49]. Compared with control animals, the hepatic expression levels of 32 genes, including Hmox1 and Mt2, were upregulated more than 2.0-fold, whereas 113 genes, including those involved in transport and ubiquitination, were downregulated less than 0.5-fold [49]. These findings indicate substantial transcriptional reprogramming in response to chronic dietary Cd exposure.
Pregnant mice were administered Cd at a dose of 5 mg/kg, and the fetal liver was collected for transcriptomic analysis using DNA microarrays [50]. Cd exposure during gestation resulted in the upregulation of 1669 genes (≥2.0-fold) and the downregulation of 194 genes (≤0.5-fold) in fetal liver. Differentially expressed genes were classified into functional categories including cell cycle and proliferation, apoptosis, cell growth and differentiation, cellular defense mechanisms, metabolism, transport, transcriptional regulation, signal transduction, metal homeostasis, and the ubiquitin–proteasome system [50]. These findings provide important insights into the molecular mechanisms of transcription pathways underlying fetal toxicity induced by prenatal Cd exposure.
3. Apoptosis-Related Cd Toxicity and Modification
3.1. p53-Dependent Apoptosis via the Suppression of UBE2D Family Genes
As described above, the DNA microarray analysis of NRK-52E cells revealed that Cd treatment reduced the expression of the Ube2d4 gene by approximately half [46]. Moreover, it was found that the expressions of Ube2d4 and other Ube2d family genes (Ube2d1, Ube2d2, and Ube2d3) were markedly suppressed prior to the onset of Cd-induced cytotoxicity [53]. This was accompanied by a notable upregulation of p53, an apoptosis-related protein [53]. It was confirmed that Cd does not lead to an increase in p53 mRNA levels, nor does it exert a direct inhibitory effect on proteasome activity [53]. p53 is a short-lived protein that is normally targeted for ubiquitin-mediated degradation, a process in which Ube2d family ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes are involved [54,55]. Therefore, the Cd-induced overaccumulation of p53 protein is thought to result from the inhibition of p53 degradation related to the downregulation of Ube2d family genes. In addition, Cd treatment increased p53 phosphorylation and observed DNA fragmentation, indicating that Cd induces p53-dependent apoptosis [53]. Using HK-2 cells, it was demonstrated that the double knockdown of UBE2D2 and UBE2D4 resulted in elevated levels of intracellular p53 protein, which is critically involved in Cd-induced apoptosis, and is observed in cells treated with Cd [56].
The gene expressions of Ube2d family members and protein levels of p53 in the kidney of mice chronically exposed to Cd were also investigated. Mice fed a diet containing 300 ppm Cd for 6–12 months developed mild renal toxicity. In these Cd-exposed mice, renal Ube2d1, Ube2d2, and Ube2d3 mRNA levels were significantly decreased, whereas p53 protein levels were significantly increased, consistent with our in vitro findings [53,56]. Furthermore, immunohistochemical analysis revealed that chronic Cd exposure caused a marked accumulation of p53, specifically in the renal proximal tubules, and apoptosis was detected at the same locations [53,56]. This demonstrated that Cd induces p53-dependent apoptosis specifically in proximal tubular cells in vivo [53,56].
In summary, Cd specifically suppresses UBE2D (Ube2d) family gene expressions in cultured proximal tubular cells and in mouse kidney, leading to the overaccumulation of p53 and induction of p53-dependent apoptosis, thereby causing cytotoxicity (Figure 1). On the other hand, inorganic arsenic, but not inorganic mercury, also induced p53-dependent apoptotic pathways through the downregulation of gene expression of Ube2d family in proximal tubular cells [57].
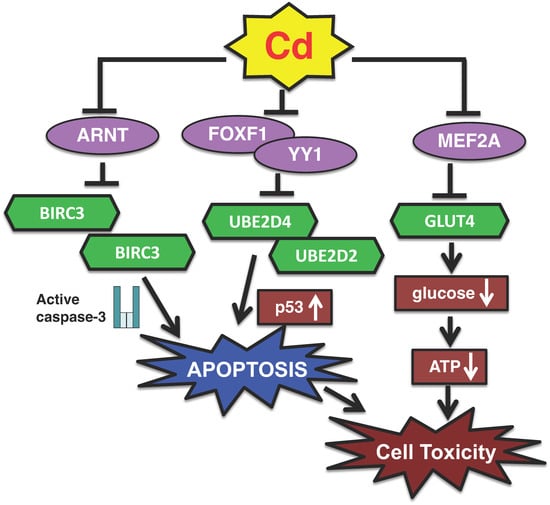
Figure 1.
A new transcription pathway of Cd toxicity in proximal tubular cells. (1) Cd decreases the activities of YY1 and FOXF1 transcription factors and induces p53-dependent apoptosis by suppressing the gene expressions of UBE2D2 and UBE2D4. (2) Cd inactivates the ARNT transcription factor and induces caspase-3-dependent apoptosis by suppressing the expression of BIRC3. (3) Cd suppresses the expression of SLC2A4 coding GLUT4 protein via the inhibition of MEF2A transcriptional activity, resulting in reduced glucose uptake into cells, finally leading to cytotoxicity.
3.2. Identification of Transcription Factors Rgulating UBE2D Family Gene Expression
Gene expression is regulated by transcription factors, and elucidating the mechanisms of transcript regulation is critical for understanding various biological phenomena [58,59]. The suppression of UBE2D family gene expression contributes to Cd-induced toxicity via apoptosis, implying that transcript regulation also underlies Cd toxicity; however, the specific transcription factors targeted by Cd remain largely unidentified. To determine which factors are involved in Cd toxicity, a protein/DNA binding array to identify transcription factors with DNA-binding activity altered by Cd was performed using NRK-52E cells [60]. Of 65 transcription factors examined, this analysis revealed that Cd treatment increased the activity of 6 transcription factors more than 2-fold and decreased the activity of 15 transcription factors less than 0.5-fold. In addition, using HK-2 cells, the protein/DNA binding assay was conducted to screen transcription factors affected by Cd [61]. The analysis revealed that exposure to Cd led to an increase in DNA-binding activity in 20 out of 345 transcription factors, whereas the activity of 28 transcription factors was downregulated [61].
YY1 (Yin-Yang 1) and FOXF1 (forkhead box F1) were among the transcription factors whose activities were decreased by Cd [56,60,61]. Moreover, the UBE2D4 gene was shown to be regulated by FOXF1 [56]. In addition, UBE2D2 gene expression was found to be regulated by YY1 [56]. The knockdown of YY1 and FOXF1 decreased cell viability as well as UBE2D2 and UBE2D4 activity, respectively [56]. Thus, YY1 and FOXF1 were identified as transcription factors that mediated the Cd-induced suppression of UBE2D2 and UBE2D4 gene expressions in HK-2 cells. Putative binding sites for YY1 and FOXF1 were identified in the upstream regulatory regions of UBE2D2 and UBE2D4. However, YY1 specifically regulated the expression of UBE2D2, whereas FOXF1 was involved in the regulation of UBE2D4 expression. These findings suggest that Cd may modulate gene expression via multiple pathways to influence the activity of specific transcription factors. Taken together, these results revealed that the transcription factors YY1 and FOXF1 are involved in the mechanism of Cd toxicity via the suppression of UBE2D family genes (Figure 1).
3.3. Apoptosis Induction via Inhibition of ARNT Transcriptional Activity
Based on the above findings, studies examined whether the silencing of individual transcription factors involved in Cd toxicity would alter cell viability. In HK-2 cells, the siRNA knockdown of ARNT (aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator) significantly reduced cell viability, supporting the involvement of ARNT in Cd toxicity [61]. The mechanism by which Cd inactivates ARNT leading to cell toxicity was investigated. Although Cd treatment did not alter ARNT mRNA levels, it led to a reduction in ARNT protein levels in HK-2 cells. These findings suggest that ARNT is a potential target of Cd-induced renal toxicity at the post-transcriptional level. A microarray analysis of ARNT-knockdown HK-2 cells was performed to identify the downstream factors of ARNT. The results showed that the knockdown of ARNT led to the downregulation of 27 genes, each exhibiting expression levels reduced to less than 0.5-fold compared with control cells.
Among the genes whose activities were decreased by ARNT knockdown, BIRC3 (baculoviral IAP repeat containing 3; also known as cIAP2) was investigated further. BIRC3 is a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) family and suppresses apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-3 activation [62]. ARNT-mediated reduction in intracellular BIRC3 levels significantly decreased cell viability, induced apoptosis, and expressed Cd toxicity in HK-2 cells [61]. Moreover, it was confirmed that Cd inhibited transcriptional activity by reducing intracellular ARNT protein levels [61]. BIRC3 was reported to inhibit apoptosis by suppressing the activity of caspase-3, a key pro-apoptotic effector [62]. Our study revealed that knockdown of the BIRC3 gene activated caspase-3 in HK-2 cells, in a manner comparable with Cd treatment. Furthermore, we examined the kidney of mice with long-term Cd exposure and confirmed a significant decrease in Birc3 mRNA levels [61]. We also found that Cd suppressed intracellular BIRC3 levels by reducing the intracellular levels of the ARNT transcription factor, thereby inhibiting its transcriptional activity, which in turn induced apoptosis. This represents a new apoptotic pathway of Cd toxicity involving ARNT and BIRC3 (Figure 1).
On the other hand, although methylmercury (MeHg) increased cleaved caspase-3 protein levels, mRNA levels of BIRC3 were not changed by MeHg in IMR-32 human neuroblastoma [61]. Inorganic mercury decreased mRNA levels of BIRC3 without cleaved caspase-3 change in HK-2 cells [61]. In mouse hepatic cells (AML-12 cells), arsenic increased the mRNA level of Birc3; however, the protein levels of cleaved caspase-3 were slightly increased by arsenic treatment [61]. Therefore, it is suggested that the activation of caspase-3 through suppression of BIRC3 gene expression by Cd treatment may mainly occur in proximal tubular cells.
3.4. Role of PPARδ as a Modification Factor of Cd Toxicity
To date, metallothionein and glutathione have been identified as key protective factors against Cd toxicity [1,34,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72]; however, other defense mechanisms involved in Cd toxicity remain largely unknown. Recent our findings have demonstrated that Cd increased the activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) in human and rat proximal tubular cells [46,56]. These results suggest that PPARs may be involved in susceptibility to Cd-induced renal toxicity. PPARs are ligand-activated transcription factors classified within the nuclear receptor superfamily and comprise three isoforms in humans: PPARα, PPARδ, and PPARγ [73,74,75,76,77]. Among the PPAR isoforms, only the knockdown of PPARD conferred significant resistance to Cd-induced toxicity in HK-2 cells and PPARδ transcriptional activity was attenuated in HK-2 cells subjected to Cd treatment or PPARD silencing [78]. To elucidate the effect of Cd treatment on PPARD expression in HK-2 cells, PPARD mRNA levels were measured following Cd exposure. Unexpectedly, Cd treatment significantly and dose-dependently increased PPARD mRNA expression [78]. These results suggest that the Cd-induced suppression of PPARδ transcriptional activity is unlikely to be attributable to reduced PPARD gene expression.
To identify genes regulated by PPARδ, DNA microarray analysis of HK-2 cells following transfection with PPARD siRNA was conducted. PPARD knockdown resulted in the upregulation of 53 genes more than 3-fold [78]. Several of the genes upregulated by PPARD knockdown, including RYR2 (ryanodine receptor 2), ITPK1 (inositol-tetrakisphosphate 1-kinase), PALD1 (phosphatase domain containing paladin 1), ZNF488 (zinc finger protein 488), TFF2 (trefoil factor 2), IL9R (interleukin 9 receptor), PANX2 (pannexin 2), CPA4 (carboxypeptidase A4), CCL19 (CC motif chemokine ligand 19), FSIP1 (fibrous sheath interacting protein 1), and MLXIPL (MLX interacting protein like), are involved in apoptotic pathways. PPARD knockdown led to the downregulation of 39 genes, with expression levels reduced to ≤0.5-fold [78]. Of these downregulated genes, LPAR3 (lysophosphatidic acid receptor 3), GAL3ST1 (galactose-3-O-sulfotransferase 1), PTPN11 (protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 11), and RORA (RAR related orphan receptor A) are involved in apoptotic pathways [78]. Microarray-based transcriptomic profiling indicated that PPARD knockdown altered the expressions of genes associated with apoptotic pathways. Further study demonstrated that Cd exposure increased the mRNA levels of CPA4 and FSIP1, both of which were upregulated by PPARD knockdown [78]. Moreover, the upregulation of CPA4 and FSIP1 attenuated apoptotic signaling, suggesting their potential anti-apoptotic roles [79,80]. These results indicate that apoptosis may be involved in the enhanced resistance to Cd toxicity observed in PPARD knockdown cells.
Therefore, it was investigated whether the resistance to Cd toxicity observed in PPARD knockdown cells was associated with alterations in apoptotic processes. In control cells, Cd treatment significantly induced apoptosis and increased levels of cleaved caspase-3; however, PPARD knockdown attenuated the Cd-induced apoptosis and elevation of cleaved caspase-3 [78]. It is possible that PPARD knockdown altered the intracellular accumulation of Cd in HK-2 cells, which was increased in a dose-dependent manner with increasing Cd-treated concentrations [78]. However, PPARD knockdown had no effect on intracellular Cd levels [78].
This study provides strong evidence that the transcription factor PPARδ modulates cellular susceptibility to Cd toxicity. In HK-2 cells, PPARδ transcriptional activity was suppressed in response to Cd exposure. Of note, this Cd-induced reduction in PPARδ activity was associated with the attenuation of the apoptosis pathway, and PPARD knockdown conferred resistance to Cd toxicity (Figure 2). These findings suggest that the inhibition of PPARδ activity may be an adaptive cellular response to mitigate Cd-induced cytotoxicity. Furthermore, PPARD knockdown did not affect intracellular Cd concentrations, indicating that the observed resistance is not attributable to altered Cd uptake or excretion mechanisms in HK-2 cells [78].
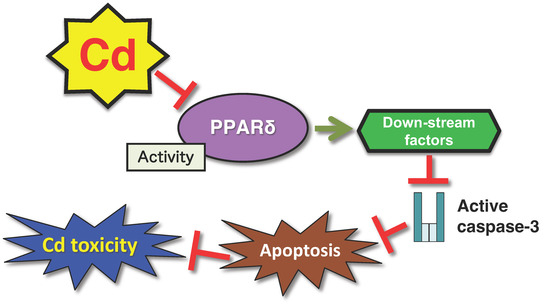
Figure 2.
A defense mechanism against Cd toxicity mediated by the PPARδ transcription factor. Reduction in the activity of the PPARδ transcription factor suppresses Cd-induced apoptosis mediated by cleaved caspase-3.
3.5. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Related Apoptosis Involved in Cd Toxicity
Apoptosis is triggered through ROS generation from mitochondrial malfunction [81]. Occupational exposure to cadmium among workers in battery recycling and welding industries has been shown to result in cadmium accumulation in the lungs, leading to long-term toxic effects [82]. Recent findings have demonstrated that Cd induces cytotoxicity in human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B cells) through mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis and oxidative stress [83]. Exposure to Cd reduced mitochondrial membrane potential, while increasing intracellular ROS and apoptotic cell death [83]. Molecular analysis revealed downregulation of Bcl-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2) and upregulation of Bax (Bcl-2-associated X protein) and cleaved caspase-3, indicating activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway [83]. Additionally, Cd exposure enhanced the phosphorylation of JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase), ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase), and p38, suggesting involvement of the MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) signaling pathways [83]. These results indicate that Cd induces apoptosis in bronchial cells by elevating ROS levels, activating MAPK signaling, and triggering mitochondria-dependent apoptotic mechanisms.
Cd exposure reduces the viability of A549 lung epithelial cells, accompanied by increased ROS, lipid peroxidation, and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) leakage [84]. Antioxidant enzymes SOD (superoxide dismutase) and GSH-Px (glutathione peroxidase) were depleted, indicating oxidative stress [84]. Both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways were activated, as evidenced by upregulation of TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α), caspase-8, and Bax, and downregulation of Bcl-2 [84]. These studies provide mechanistic insight into Cd-induced pulmonary cytotoxicity and contribute to understanding ROS-related apoptosis in Cd-related lung diseases.
3.6. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)-Mediated Apoptosis Involved in Cd Toxicity
Disruption of intracellular calcium (Ca2+) homeostasis has been shown to inhibit autophagy, promote oxidative stress, and subsequently induce apoptotic cell death [85]. Recent studies have demonstrated that activation of the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) mitigates Cd-induced cytotoxicity in mouse renal tubular epithelial cells (mRTECs) by restoring Ca2+ homeostasis in ER [86]. Cd exposure reduced SERCA2 (sarco/ER Ca2+-ATPase 2) expression and phosphorylation of its regulator, phospholamban (p-PLB), both in vitro and in vivo, contributing to ER stress and apoptosis [86]. Overexpression of SERCA2 effectively suppressed ER stress and cell death [86]. Notably, Cd promoted proteasomal degradation of SERCA2, as evidenced by rescue with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 [86]. These findings suggest that ER stress plays a central role in Cd toxicity through apoptosis, and that proteasomal regulation of SERCA2 stability may be suggested a therapeutic target to prevent Cd-induced nephrotoxicity.
Not only in renal tubular cells but also in MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts, Cd induces ER stress in a dose-dependent manner, leading to apoptosis [87]. Cd activated ER stress pathway through the PERK (protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase)–eIF2α (eukaryotic translation initiation factor α)–ATF4 (activating transcription factor 4)–CHOP (C/EBP homologous protein) and suppressed the antioxidant response mediated by Nrf2 (Nuclear Respiratory Factor2)/NQO1 (NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1) [87]. Co-treatment with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and 4-phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) alleviated ER stress and attenuated Cd-induced apoptosis [87]. Furthermore, using the rats, Cd induced oxidative stress, renal tissue damage, and apoptosis by inhibiting the PERK signaling pathway [88]. These findings suggest that targeting oxidative stress and ER stress may provide protective strategies against Cd-induced tissue injuries.
4. Non-Apoptotic Cell Death Pathways Regulating Cd Toxicity
4.1. Suppression of GLUT4 via Inhibition of MEF2A, and Reduction in Intracellular Glucose
It was suggested that Cd may target MEF2A (myocyte enhancer factor 2) transcription factors in the pathway of renal toxicity [61]. MEF2A has been reported to regulate the transcription of SLC2A4, which encodes a glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) [89,90]. We examined the effects of Cd exposure and MEF2A knockdown on SLC2A4 expression and cellular glucose uptake in HK-2 cells [91]. The siRNA-mediated knockdown of MEF2A significantly decreased SLC2A4 gene expression, and similarly, Cd exposure markedly reduced SLC2A4 mRNA levels [91]. Cd also reduced GLUT4 protein levels in HK-2 cells [91]. Furthermore, the knockdown of SLC2A4 itself caused a significant decrease in the viability of HK-2 cells [91]. These results suggest that the Cd-induced inhibition of MEF2A leads to the downregulation of GLUT4, which is involved in Cd cytotoxicity.
GLUT2 is highly expressed in the human kidney [92]; however, the knockdown of SLC2A2 encoding GLUT2 did not affect the viability of HK-2 cells [91]. Notably, MEF2A knockdown specifically suppressed SLC2A4 expression without reducing SLC2A2 mRNA levels [91]. These findings suggest that GLUT4, but not GLUT2, is a key mediator in the Cd toxicity pathway, as a downstream factor of MEF2A inhibition.
Because GLUT4 is a glucose transporter, we measured intracellular glucose levels after Cd exposure and SLC2A4 knockdown. Cd treatment and SLC2A4 siRNA caused a significant decrease in intracellular glucose in HK-2 cells [91] suggesting that the Cd-induced suppression of GLUT4 leads to reduced glucose uptake into cells, contributing to cytotoxicity. Indeed, we found that HK-2 cells cultured in glucose-free medium, which lowers intracellular glucose levels, also reduced cell viability [91]. Intracellular glucose is metabolized to ATP [93]; therefore, changes in intracellular ATP levels were investigated in Cd-treated HK-2 cells and SLC2A4-knockdown cells. A significant reduction in ATP levels was observed following exposure to Cd and in SLC2A4-knockdown cells, indicating a potential link between SLC2A4 expression and cellular energy metabolism. Taken together, our results indicate that Cd inhibits MEF2A, resulting in decreased GLUT4 levels and impaired glucose uptake, which in turn causes cytotoxicity (Figure 1).
Whether Slc2a4 gene expression is suppressed following Cd accumulation in the mouse kidney has been investigated. Cd exposure for 6 or 12 months resulted in the accumulation of approximately 200 µg Cd/g kidney [53,56] and chronic Cd exposure led to a marked decrease in renal Slc2a4 mRNA levels [91]. These findings suggest that, consistent with in vitro results, Cd-induced renal toxicity may involve impaired glucose transport in the kidney. This observation has important clinical implications for our understanding of the metabolic consequences of long-term Cd exposure.
4.2. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Necroptotic Cell Death Pathways Involved in Cd Toxicity
Cd is known to exert the cell toxicity through necrosis pathway [94,95,96,97,98]. Necroptosis has recently emerged as a noteworthy form of regulated cell death (RCD) contributing to cytotoxicity. Although necroptosis shares morphological features with necrosis, it is a form of RCD by specific intracellular factors, resembling apoptosis [99,100,101,102,103]. Recent studies have demonstrated that Cd induces necroptotic pathway in several tissues [104,105,106,107]. Cd exposure induces necroptotic cell death in Leydig cells, interstitial cells of the human testis, with significant involvement of the TNF-α/TNFR 1 (tumor necrosis factor receptor 1) signaling pathway and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Co-treatment with Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1), a selective necroptosis inhibitor, effectively suppressed ROS accumulation and TNF-α/TNFR1-mediated necroptosis [107].
In swine small intestine, Cd activated the TNF-α/NF-κB (nuclear factor-kappa B) pathway and upregulated the levels of proinflammatory markers, such as HO-1 (heme oxygenase-1), IL-1β (interleukin 1β), iNOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase), COX2 (cyclooxygenase 2). These changes were alleviated by Nec-1 and N-acetylcysteine (NAC), highlighting the roles of necroptosis and ROS in Cd-induced intestinal toxicity [104]. These results suggest that necroptosis plays a pivotal role in Cd-induced dysfunction in several tissues.
4.3. Induction of Ferroptosis in Cd-Exposed Renal Cells
Ferroptosis is a recently identified form of RCD characterized by iron dependency and triggered by the accumulation of lipid peroxidation products and disturbances in cellular redox homeostasis [108,109,110,111]. A key contributor to this process is the Fenton reaction, wherein ferrous iron (Fe2+) reacts with hydrogen peroxide to generate hydroxyl radicals (·OH), a highly reactive species capable of inflicting severe oxidative damage [108,110,111,112]. Moreover, increasing evidence highlights glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4)—a selenium-containing enzyme—as a critical suppressor of ferroptosis, whose activity is closely linked to intracellular glutathione levels [113].
Recent evidence indicates that chronic low-dose Cd exposure induces ferroptosis and renal dysfunction. In mouse kidney and tubular epithelial cells, Cd exposure disrupted glutathione homeostasis and triggered ferroptotic cell death. It was further identified STEAP3-dependent lysosomal iron overload as a key driver of glutathione redox imbalance and ferroptosis [114]. These findings provide novel insights into the metabolic basis of Cd-induced nephrotoxicity, establishing STEAP3-mediated ferroptosis as a central mechanism.
Cd exposure was shown to downregulate mitochondrial SIRT3 (sirtuin 3), an NAD+-dependent deacetylase critical for mitochondrial protein regulation, in mouse kidney. This downregulation was associated with increased acetylation and decreased expression of mitochondrial GPX4. Particularly, Cd-induced GPX4 acetylation and ferroptotic cell death were further exacerbated in Sirt3 knockout mice. Conversely, pretreatment with nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), a NAD+ precursor, attenuated mitochondrial oxidized lipid accumulation and suppressed GPX4 acetylation and ferroptosis in both HK-2 cells and Cd-exposed mouse kidney [115]. These findings suggest that SIRT3 downregulation promotes mitochondrial GPX4 acetylation, thereby enhancing susceptibility to Cd-induced ferroptosis in renal cells.
4.4. Inflammatory Pyroptosis in Cd Toxicity
Pyroptosis, also known as cell inflammatory necrosis, is a kind of RCD [99,116,117]. It causes cell swelling until the cell membrane ruptures, resulting in the release of cell contents and the activation of a strong inflammatory reaction [30]. Pyroptosis is an important natural immune response of the body, playing a vital role in fighting infection [30].
Recent studies using TM4 Sertoli cells have revealed that Cd significantly increases intracellular ROS, LDH, and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), while impairing mitochondrial function and promoting pyroptosis [118]. Mechanistically, Cd-induced pyroptosis is mediated by gasdermin D (GSDMD), pyroptotic effector protein, activation and inflammasome signaling, particularly through the ROS/NLRP3 (nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing protein 3)/Caspase-1 axis [118]. These findings suggest that Cd induces GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis in Sertoli cells primarily through ROS-dependent inflammasome activation, offering potential targets for mitigating male reproductive toxicity caused by heavy metal exposure.
A recent mouse study demonstrated that intraperitoneal Cd exposure led to reduced testosterone levels, sperm count, and motility, along with increased LDH and IL-1β [119]. Histological and molecular analyses revealed oxidative stress, DNA damage, elevated ROS levels, and increased TUNEL-positive cells in the testis. Transcriptomic profiling indicated activation of inflammatory and chemokine pathways, particularly upregulation of AIM2 (absent in melanoma 2) and downregulation of NLRP3 [119]. Pyroptosis-related proteins, including GSDMD, GSDME, Caspase-1, ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain), and IL-1β, were also elevated [119]. These findings suggest that Cd induces pyroptosis in testicular tissue primarily through AIM2-mediated inflammatory responses triggered by oxidative stress.
4.5. Lysosomal-Irregulated Autophagic Dysfunction in Cd Toxicity
Autophagy is a cellular process that eliminates damaged components via autophagosome–lysosome fusion to maintain homeostasis [120]. In the swine model, Cd exposure upregulated ER stress-related genes and altered calcium signaling in myocardium samples [121]. Particularly, autophagy-related genes, CAMKKII (calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2), ATG5 (Autophagy-related 5), LC3-II (light chain-3-II) were elevated, whereas mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) was suppressed. Notably, Cd impaired lysosomal function by downregulating V-ATPase and cathepsins (CTSB, CTSD) and promoting cathepsin leakage into the cytoplasm. Cd reduced autophagosome–lysosome colocalization, indicating autophagic flux blockage. These findings suggest that lysosomal dysfunction and impaired autophagy contribute to Cd-induced cardiotoxicity in swine.
Recent studies revealed that autophagy-related Cd toxicity is involved in glycolysis enhancing. In A549 human lung cancer cells, PHGDH (phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase) promoted Cd-induced autophagy, as well as Cd increased PHGDH expressions [122]. Furthermore, transfection with siATF4 inhibited Tm (ER stress inducer)-induced PHGDH expression. In summary, ATF4-mediated transcriptional regulation of PHGDH plays a pivotal role in Cd-induced autophagy initiated by ER stress. The ER stress–PHGDH–autophagy axis contributes to Cd-induced cell migration by promoting glycolytic activity. In human lung fibroblast cells, Cd-induced upregulation of mTOR was dependent on autophagy, while autophagy-driven cell growth and glycolysis required mTOR activation [123]. Autophagy activated mTOR-dependent glycolytic pathways, in which increased expression of GLUT1 (glucose transporter 1) facilitated glucose uptake and accelerated cell proliferation.
5. Molecular Mechanism of Cd-Induced Iron Deficiency
Chronic Cd toxicity can cause iron-deficiency anemia in addition to kidney dysfunction [124,125]. Studies in Japan and elsewhere have reported that Cd induced iron-deficiency anemia by reducing iron stores in the body [124,125]. It has been suggested that the intestinal absorption of Cd involves DMT1 (divalent metal transporter 1), an iron transporter [126,127]. However, the mechanism by which Cd causes iron-deficiency anemia remains largely unknown. Recent studies of this mechanism examined the effect of Cd on the expressions of iron transport-related genes in the intestine and on iron storage in the body, using animal and cell culture models [128,129].
Fujiwara et al. investigated the effect of a single oral dose of Cd on iron transporter expression in the duodenum of mice, as well as on serum iron levels. At 3 h after oral Cd administration, the duodenum showed significantly decreased mRNA levels of Dmt1, Cybrd1 (cytochrome b reductase 1, Dcytb), Fpn1 (ferroportin 1), and Heph (hephaestin) compared with controls [128]. Similarly, the mRNA level of Hcp1 (heme carrier protein 1) was markedly reduced at 3 h post-Cd exposure, comparable with non-heme iron transporters [128]. Cd exposure also markedly suppressed Dmt1 and Fpn1 protein expressions in the duodenum [128]. Twenty-four h after Cd administration, the serum iron concentration was significantly lower in Cd-treated mice than in controls [128]. It was investigated the effect of Cd on iron transporter expression in a human intestinal cell model using Caco-2 cells (a human intestinal epithelial cell line). Exposure to 10 μM Cd significantly decreased the mRNA levels of DMT1, CYBRD1, FPN1, and HEPH, and reduced the protein expressions of DMT1 and FPN1 in Caco-2 cells [128]. These findings indicate that in Caco-2 cells, as in the mouse duodenum, Cd suppresses the expressions of DMT1, CYBRD1, FPN1, and HEPH. Thus, at the cellular level, Cd can directly downregulate iron transport molecules, potentially impairing iron uptake.
Tokumoto et al. investigated the effect of long-term exposure to Cd on iron transporter expression in the duodenum of mice [129]. Although the iron concentration in the liver was markedly decreased by Cd, the serum iron level was not markedly changed. Among the iron-transport-related genes in the proximal duodenum, the gene expressions of Hcp1 and Cybrd1 were significantly decreased by Cd [129]. Long-term exposure to Cd, especially, decreased the mRNA level of hepatic Hamp (hepcidin antimicrobial peptide), which degrades Fpn1 in the intestine [129]. The level of Fpn1 was maintained and this facilitated the transfer of iron from enterocytes to the blood.
Fujiwara et al. demonstrated that the serum iron concentration and total iron-binding capacity (TIBC) were significantly reduced 24 h after a single administration of Cd to mice [128]. In contrast, serum iron levels in mice subjected to long-term Cd exposure remained comparable with control levels, indicating that iron deficiency was not induced under these conditions [129]. However, hepatic iron accumulation was markedly reduced after 12 months of Cd exposure, and the unsaturated iron-binding capacity (UIBC) was significantly increased [129]. Moreover, it was indicated that the TIBC was significantly elevated in mice exposed to Cd for 19 or 21 months. Although serum iron levels appeared unchanged after long-term Cd exposure, hepatic iron concentrations were significantly reduced [129]. Additionally, the UIBC and TIBC were markedly increased following prolonged Cd exposure [129]. These findings suggest that a compensatory biological response to iron deficiency may involve an increased amount of transferrin available for iron binding in the serum.
These results demonstrate that in mice, oral Cd intake rapidly downregulates the expressions of genes that encode duodenal iron transport-related molecules for non-heme and heme iron. On the other hand, in mice chronically exposed to Cd, iron absorption was inhibited and iron was released from the liver into the blood. Consequently, Cd exposure inhibits iron absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, and the resulting lack of iron in the body likely leads to iron-deficiency anemia (Figure 3).
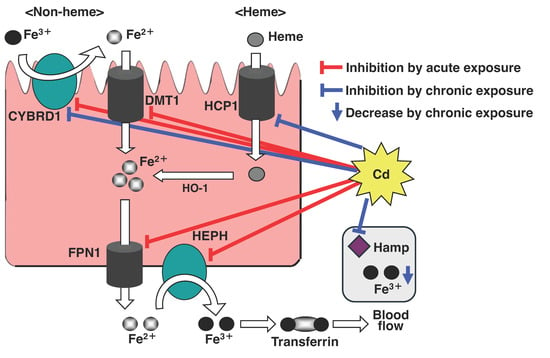
Figure 3.
Scheme of the inhibitory effect of Cd on Fe transport. Cd inhibits iron absorption from duodenal epithelial cells by suppressing expressions of the iron transport-related genes, DMT1, FPN1, DCYTB, HEPH, and HCP1. In particular, the long-term exposure to Cd depletes hepatic iron levels and the expression of Hamp, a regulatory factor of iron homeostasis.
6. Conclusions
Various toxic chemicals induce necrosis and apoptosis, which are the major mechanisms of cell death [96,130,131,132,133]. In particular, toxic heavy metals and metalloids, such as methylmercury, inorganic lead, and inorganic arsenic, induce apoptosis in their respective target tissues [96,130,131,132,134,135]. Apoptosis is a primary toxic mechanism induced by Cd exposure through various pathways [83,118,136,137]. Previous review has summarized the involvement of apoptosis pathway in the Cd-induced renal toxicity: (1) the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-mediated pathway, which involves ER stress and calcium release, subsequently triggering apoptosis via the unfolded protein response (UPR)-dependent and calpain–caspase-dependent mechanisms; and (2) the mitochondria-mediated pathway, in which Cd directly or indirectly induces mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to apoptosis through both caspase-dependent and caspase-independent mechanisms [138]. In this review of our recent studies on Cd toxicity, the transcription factors YY1, FOXF1, and ARNT are introduced as newly proposed regulators of apoptosis (Figure 4).
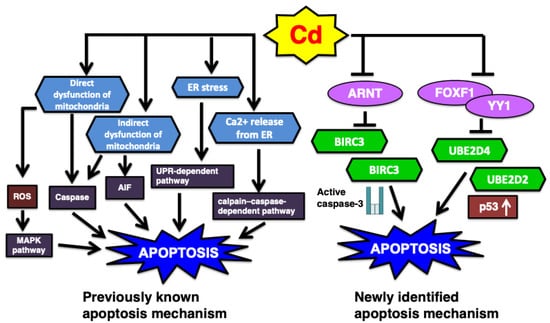
Figure 4.
The summary of previous and newly identified Cd-induced apoptosis pathway. (1) Classically it was demonstrated that ER stress and mitochondria mediated apoptosis are involved in Cd renal toxicity. AIF, apoptosis-inducing factor. (2) Recent studies novelly identified the Cd-induced apoptosis pathways such as UBE2D-regulated p53 and ARNT-modified BIRC3 mechanisms.
In addition, the downstream factor of each transcription factor is summarized. Recent research proposes that regulating the intracellular ATP level is important for cell viability [139,140]. Cd-inhibited MEF2A transcription activity is involved in decreased ATP levels via inhibition of glucose transportation. Moreover, the PPARδ transcription factor is proposed to be a modification factor for Cd toxicity. Genetic polymorphisms in the PPARD gene have been reported [141,142], and alterations in PPARδ expression or activity may contribute to individual variability in susceptibility to Cd-induced renal toxicity.
Finally, we summarized the molecular mechanism of Cd-induced anemia in this review. Anemia remains a significant global public health concern [143,144,145]. Our findings indicate that chronic exposure to Cd may aggravate iron deficiency. Accordingly, it is recommended that individuals at high risk for anemia reduce dietary and lifestyle-related Cd exposure—particularly from sources such as certain foods and tobacco products—and consider iron supplementation as a preventive strategy against anemia and its associated health complications.
A recent study to identify transcription factors involved in Cd toxicity using the liver and kidney of mice exposed to Cd for 3 months showed Cd accumulation in the liver (63.41 ± 5.80 µg/g) and kidney (97.56 ± 9.48 µg/g); however, only minimal hepatic toxicity was observed [146]. Another study reported that 12 months of Cd exposure resulted in a renal Cd concentration of 174.74 µg/g, and that this accumulation induced apoptosis in the mouse kidney [53]. Therefore, transcriptional changes in the kidneys of mice exposed to Cd for 3 months may contribute to the development of Cd-induced renal dysfunction. Research based on altered transcription factors is expected to elucidate the molecular mechanism involved in the early stages of Cd renal toxicity.
Thus, it was found that multiple target molecules, including transcription factors and their downstream genes, are strongly involved in the expression of Cd toxicity. Chronic renal toxicity of Cd induces cell death, such as apoptosis and necrosis, following dysfunction in proximal tubular cells. At these stages, Cd appears to affect multiple target molecules, such as those presented in this review. At present, only a part of the molecular mechanism of Cd toxicity has been elucidated, and the whole picture is not clear. Further research is needed to clarify the whole picture of the molecular mechanisms of Cd toxicity.
Author Contributions
J.-Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.T.; writing—review and editing, M.S.; supervision, funding acquisition, and writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partly supported by the Health Effects of Heavy Metals, organized by the Ministry of the Environment, Japan; and partly supported by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sport and Culture, Japan (Grant in Aid for Scientific Research [B], No. 20390175).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nordberg, G.F.; Åkesson, A.; Nogawa, K.; Nordberg, M. Chapter 7—Cadmium. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, 5th ed.; Nordberg Gunnar, F., Max, C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 141–196. [Google Scholar]
- Charkiewicz, A.E.; Omeljaniuk, W.J.; Nowak, K.; Garley, M.; Nikliński, J. Cadmium Toxicity and Health Effects-A Brief Summary. Molecules 2023, 28, 6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaderpoori, M.; Kamarehie, B.; Jafari, A.; Alinejad, A.A.; Hashempour, Y.; Saghi, M.H.; Yousefi, M.; Oliveri Conti, G.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Ghaderpoury, A.; et al. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in cosmetic products sold in Iran: The Monte Carlo simulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 7588–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, F.U.; Liqun, C.; Coulter, J.A.; Cheema, S.A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Wenjun, M.; Farooq, M. Cadmium toxicity in plants: Impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2021, 211, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A. Cadmium pigments in consumer products and their health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, V.; Sharma, S. Sources and Spatial Distribution of Cadmium in the Environment. In Cadmium Toxicity: Challenges and Solutions; Nitish, K., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Teschke, R. Copper, Iron, Cadmium, and Arsenic, All Generated in the Universe: Elucidating Their Environmental Impact Risk on Human Health Including Clinical Liver Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carocci, A.; Catalano, A.; Lauria, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Genchi, G. Lead toxicity, antioxidant defense and environment. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 238, 45–67. [Google Scholar]
- Carocci, A.; Rovito, N.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Genchi, G. Mercury toxicity and neurodegenerative effects. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 229, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Friberg, L.T.; Elinder, G.-G.; Kjellstrom, T.; Nordberg, G.F. Cadmium and Health: A Toxicological and Epidemiological Appraisal: Volume 2: Effects and Response; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 1–110. [Google Scholar]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Carocci, A.; Lauria, G.; Catalano, A. Response to Comment on Giuseppe Genchi et al. Mercury Exposure and Heart Diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinicropi, M.S.; Amantea, D.; Caruso, A.; Saturnino, C. Chemical and biological properties of toxic metals and use of chelating agents for the pharmacological treatment of metal poisoning. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinicropi, M.S.; Caruso, A.; Capasso, A.; Palladino, C.; Panno, A.; Saturnino, C. Heavy metals: Toxicity and carcinogenicity. Pharmacologyonline 2010, 2, 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Makki, A.; DiPette, D.; Whelton, P.K.; Murad, M.H.; Mustafa, R.A.; Acharya, S.; Beheiry, H.M.; Champagne, B.; Connell, K.; Cooney, M.T.; et al. Hypertension Pharmacological Treatment in Adults: A World Health Organization Guideline Executive Summary. Hypertension 2022, 79, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mititelu, M.; Udeanu, D.I.; Docea, A.O.; Tsatsakis, A.; Calina, D.; Arsene, A.L.; Nedelescu, M.; Neacsu, S.M.; Bruno Ștefan, V.; Ghica, M. New method for risk assessment in environmental health: The paradigm of heavy metals in honey. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 115194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciacca, S.; Conti, G.O. Mutagens and carcinogens in drinking water. Mediterr. J. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 2, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbano, T.; Verzelloni, P.; Malavolti, M.; Sucato, S.; Polledri, E.; Agnoli, C.; Sieri, S.; Natalini, N.; Marchesi, C.; Fustinoni, S.; et al. Influence of dietary patterns on urinary excretion of cadmium in an Italian population: A cross-sectional study. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 80, 127298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Sang, P.; Guo, Y.; Jin, P.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Yao, W.; Qian, H. Cadmium in food: Source, distribution and removal. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, S.; Ruan, W.; Hao, M.; Jiang, K.; Guo, H.; Geng, A.; Man, M.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Cadmium exposure and health outcomes:An umbrella review of meta-analyses. Environ. Res. 2025, 276, 121547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, Y.; Nayebi, M.; Mahmoudi, S.; Daraei, M.; Khorsand, S.; Jahazi, M.A.; Farsi, M.Y.; Khalafi, F.; Varseh, M.; Jarrahi, Z.M.; et al. Cadmium exposure and risk of pancreatic cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0319283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.H.; Rubab, S.A.; Abbas, S.R.; Qutaba, S.; Mohd Zahari, M.A.K.; Abdullah, N. Effects of cadmium acetate contaminated drinking water on vital organs: A histopathological and biochemical study. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 37, e23382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli Pirzaman, A.; Ebrahimi, P.; Niknezhad, S.; Vahidi, T.; Hosseinzadeh, D.; Akrami, S.; Ashrafi, A.M.; Moeen Velayatimehr, M.; Hosseinzadeh, R.; Kazemi, S. Toxic mechanisms of cadmium and exposure as a risk factor for oral and gastrointestinal carcinomas. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2023, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Lu, Y.H.; Pi, H.F.; Gao, P.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Pei, L.P.; Mei, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Cadmium Exposure is Associated with the Prevalence of Dyslipidemia. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JECFA. Safety Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants: Prepared by the Seventy-Third Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- CXS 193-1995; General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feed. FAO/WHO: Rome, Italy, 2019.
- Barregard, L.; Sallsten, G.; Lundh, T.; Mölne, J. Low-level exposure to lead, cadmium and mercury, and histopathological findings in kidney biopsies. Environ. Res. 2022, 211, 113119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X.; Liao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, B.; Huang, Y.; Peng, L. Environmental Cadmium Exposure Promotes the Development, Progression and Chemoradioresistance of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 792933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Gu, R.; Ouyang, H.; Wang, L.; Shi, S.; Ji, Y.; Bao, B.; Liao, G.; Xu, B. Cadmium exposure induces osteoporosis through cellular senescence, associated with activation of NF-κB pathway and mitochondrial dysfunction. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Su, Q.; Yue, C.; Zou, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, H.; Song, R.; Liu, Z. The Effect of Oxidative Stress-Induced Autophagy by Cadmium Exposure in Kidney, Liver, and Bone Damage, and Neurotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Wu, M.; He, G. Dose-response evaluation of urinary cadmium and kidney injury biomarkers in Chinese residents and dietary limit standards. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Zheng, W. Cadmium Exposure: Mechanisms and Pathways of Toxicity and Implications for Human Health. Toxics 2024, 12, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeda, T.; Cannon, J.R. Environmental exposures and the etiopathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: The potential role of BACE1 as a critical neurotoxic target. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, M.; Nordberg, G.F. Metallothionein and Cadmium Toxicology-Historical Review and Commentary. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S.; Garrett, S.H.; Sens, M.A.; Sens, D.A. Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshima, K.; Horiguchi, H. Historical Lessons on Cadmium Environmental Pollution Problems in Japan and Current Cadmium Exposure Situation. In Cadmium Toxicity: New Aspects in Human Disease, Rice Contamination, and Cytotoxicity; Seiichiro, H., Keiko, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Aoshima, K. Recent Clinical and Epidemiological Studies of Itai-Itai Disease (Cadmium-Induced Renal Tubular Osteomalacia) and Cadmium Nephropathy in the Jinzu River Basin in Toyama Prefecture, Japan. In Cadmium Toxicity: New Aspects in Human Disease, Rice Contamination, and Cytotoxicity; Seiichiro, H., Keiko, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 23–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, H.; Kim, G.; Chang, J.; Lee, K.; Lee, C.; Lee, B. Chronic Exposure to Lead and Cadmium in Residents Living Near a Zinc Smelter. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Surenbaatar, U.; Lim, H.J.; Kim, B.G.; Eom, S.Y.; Cho, Y.M.; Kim, W.J.; Yu, B.C.; Lee, K.; et al. Association between levels of exposure to heavy metals and renal function indicators of residents in environmentally vulnerable areas. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S.; Vesey, D.A.; Gobe, G.C.; Yimthiang, S.; Buha Đorđević, A. Health Risk in a Geographic Area of Thailand with Endemic Cadmium Contamination: Focus on Albuminuria. Toxics 2023, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoj Tratnik, J.; Kocman, D.; Horvat, M.; Andersson, A.M.; Juul, A.; Jacobsen, E.; Ólafsdóttir, K.; Klanova, J.; Andryskova, L.; Janasik, B.; et al. Cadmium exposure in adults across Europe: Results from the HBM4EU Aligned Studies survey 2014–2020. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 246, 114050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimbo, S.; Zhang, Z.W.; Watanabe, T.; Nakatsuka, H.; Matsuda-Inoguchi, N.; Higashikawa, K.; Ikeda, M. Cadmium and lead contents in rice and other cereal products in Japan in 1998–2000. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 281, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Kumagai, R.; Tanaka, T.; Nakano, T.; Fujie, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Yamamoto, C.; Kaji, T. Lead suppresses perlecan expression via EGFR-ERK1/2-COX-2-PGI2 pathway in cultured bovine vascular endothelial cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2023, 48, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, Y.; Kojima, R.; Ashida, R.; Nada, Y.; Kimura, S.; Sato, E.; Noguchi, T.; Matsuzawa, A. Industrially produced trans-fatty acids are potent promoters of DNA damage-induced apoptosis. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2024, 49, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, Y.; Miki, R.; Fujimura, M.; Oyadomari, S.; Uehara, T. Methylmercury-induced brain neuronal death in CHOP-knockout mice. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2024, 49, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokumoto, M.; Ohtsu, T.; Honda, A.; Fujiwara, Y.; Nagase, H.; Satoh, M. DNA microarray analysis of normal rat kidney epithelial cells treated with cadmium. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 36, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, J.Y.; Tokumoto, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Satoh, M. Gene expression analysis using DNA microarray in HK-2 human proximal tubular cells treated with cadmium. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 38, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumoto, M.; Ohtsu, T.; Imai, S.; Honda, A.; Nagase, H.; Satoh, M. DNA microarray analysis of hepatic gene expression in mice exposed to cadmium for 30 days. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 38, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokumoto, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Satoh, M. DNA microarray expression analysis of mouse kidney following cadmium exposure for 12 months. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 38, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kurita, H.; Nagase, H.; Tokumoto, M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Satoh, M. DNA microarray analysis of fetal liver of C57BL/6J mice exposed to cadmium during gestation. Fundam. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 3, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Tokumoto, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Lee, M.-Y.; Satoh, M. Effects of cadmium on the gene expression of SLC39A1 coding for ZIP1 protein. Fundam. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 1, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Tokumoto, M.; Hwang, G.-W.; Satoh, M. Effect of heat shock protein gene expression on cadmium toxicity in human proximal tubular cells. Fundam. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 5, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumoto, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Shimada, A.; Hasegawa, T.; Seko, Y.; Nagase, H.; Satoh, M. Cadmium toxicity is caused by accumulation of p53 through the down-regulation of Ube2d family genes in vitro and in vivo. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 36, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julier, A.; Radtke, V.; Marx, A.; Scheffner, M. Generation and Characterization of Site-Specifically Mono-Ubiquitylated p53. Chembiochem 2022, 23, e202100659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saville, M.K.; Sparks, A.; Xirodimas, D.P.; Wardrop, J.; Stevenson, L.F.; Bourdon, J.C.; Woods, Y.L.; Lane, D.P. Regulation of p53 by the ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes UbcH5B/C in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 42169–42181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Tokumoto, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Seko, Y.; Shimada, A.; Satoh, M. Accumulation of p53 via down-regulation of UBE2D family genes is a critical pathway for cadmium-induced renal toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumoto, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Uchiyama, M.; Satoh, M. Inorganic arsenic induces apoptosis through downregulation of Ube2d genes and p53 accumulation in rat proximal tubular cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 38, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.; Healy, A.; Zhu, J. Differential regulation of lineage-determining transcription factor expression in innate lymphoid cell and adaptive T helper cell subsets. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1081153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.S.; Li, H.L.; Grierson, D.; Fu, D.Q. NAC Transcription Factor Family Regulation of Fruit Ripening and Quality: A Review. Cells 2022, 11, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumoto, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Satoh, M. Alteration of DNA binding activity of transcription factors in NRK-52E rat proximal tubular cells treated with cadmium. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 39, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, J.Y.; Tokumoto, M.; Hwang, G.W.; Lee, M.Y.; Satoh, M. Identification of ARNT-regulated BIRC3 as the target factor in cadmium renal toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath-Deschner, B.; Nogueira, A.V.B.; Memmert, S.; Nokhbehsaim, M.; Augusto Cirelli, J.; Eick, S.; Miosge, N.; Kirschneck, C.; Kesting, M.; Deschner, J.; et al. Regulation of Anti-Apoptotic SOD2 and BIRC3 in Periodontal Cells and Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Lv, C.; Huang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Shi, P. The involvement of glutathione in cadmium detoxification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2024, 106, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delalande, O.; Desvaux, H.; Godat, E.; Valleix, A.; Junot, C.; Labarre, J.; Boulard, Y. Cadmium-glutathione solution structures provide new insights into heavy metal detoxification. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 5086–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, M.; Duan, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Tao, Z.; Guo, Q. Genome-Wide Identification of Glutathione S-Transferase Family from Dendrobium officinale and the Functional Characterization of DoGST5 in Cadmium Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomova, K.; Alomar, S.Y.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Heavy metals: Toxicity and human health effects. Arch. Toxicol. 2025, 99, 153–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keçecioğlu, C.; Sarıkaya, C.; Aydın, A.; Charehsaz, M.; Efendi, H. Investigation of the Relationship Between Heavy Metals (Cadmium, Arsenic, and Lead) and Metallothionein in Multiple Sclerosis. Cureus 2024, 16, e66754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marikar, F.; Zi-Chun, H. Metal-binding protein: Metallothionein. Int. J. Med. Biochem. 2023, 6, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sabolić, I.; Breljak, D.; Skarica, M.; Herak-Kramberger, C.M. Role of metallothionein in cadmium traffic and toxicity in kidneys and other mammalian organs. Biometals 2010, 23, 897–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Qin, J.; Yuan, H.; Guo, M.; Shang, M.; Niu, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Xue, Y. Recombinant human metallothionein-III alleviates oxidative damage induced by copper and cadmium in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2023, 43, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitelli, V.; Giamborino, A.; Bertolini, A.; Saba, A.; Andreucci, A. Cadmium Stress Signaling Pathways in Plants: Molecular Responses and Mechanisms. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 6052–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Luo, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yue, F.; Xie, B.; Chen, T.; Zou, C. The Next-Generation Probiotic E coli 1917-pSK18a-MT Ameliorates Cadmium-Induced Liver Injury by Surface Display of Metallothionein and Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnuaimi, S.; Reljic, T.; Abdulla, F.S.; Memon, H.; Al-Ali, S.; Smith, T.; Serdarevic, F.; Velija Asimi, Z.; Kumar, A.; Semiz, S. PPAR agonists as add-on treatment with metformin in management of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofides, A.; Konstantinidou, E.; Jani, C.; Boussiotis, V.A. The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) in immune responses. Metabolism 2021, 114, 154338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, C.M.; Gallucci, G.M.; Boyer, J.L.; Assis, D.N.; Ghonem, N.S. PPAR agonists for the treatment of cholestatic liver diseases: Over a decade of clinical progress. Hepatol. Commun. 2025, 9, e0612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Chaudhary, R. Potentials of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) α, β/δ, and γ: An in-depth and comprehensive review of their molecular mechanisms, cellular Signalling, immune responses and therapeutic implications in multiple diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 155, 114616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titus, C.; Hoque, M.T.; Bendayan, R. PPAR agonists for the treatment of neuroinflammatory diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 45, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, C.; Lee, J.-Y.; Tokumoto, M.; Satoh, M. Cadmium Toxicity Is Regulated by Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor δ in Human Proximal Tubular Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Su, L.; Cai, M.; Yao, B.; Xiao, S.; He, Q.; Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhao, C.; Wan, T.; et al. Downregulation of CPA4 inhibits non small-cell lung cancer growth by suppressing the AKT/c-MYC pathway. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 2026–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Zhao, D.; Liu, P.; Yan, M.; Zaidi, N.; Izadmehr, S.; Gupta, A.; Abu-Amer, W.; et al. FSIP1 binds HER2 directly to regulate breast cancer growth and invasiveness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7683–7688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Lu, T.; Zhai, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J. Inhibition of VDAC1 prevents oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by bisphenol A in spermatogonia via AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2023, 48, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloch, S.; Kazi, T.G.; Baig, J.A.; Afridi, H.I.; Arain, M.B. Occupational exposure of lead and cadmium on adolescent and adult workers of battery recycling and welding workshops: Adverse impact on health. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Fu, M.; Bi, R.; Zheng, X.; Fu, B.; Tian, S.; Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, J. Cadmium induced BEAS-2B cells apoptosis and mitochondria damage via MAPK signaling pathway. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran Kumar, K.M.; Naveen Kumar, M.; Patil, R.H.; Nagesh, R.; Hegde, S.M.; Kavya, K.; Babu, R.L.; Ramesh, G.T.; Sharma, S.C. Cadmium induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in lung epithelial cells. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2016, 26, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhou, X.P.; Liu, Z.P.; Song, X.B.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, L. Cadmium disrupts autophagic flux by inhibiting cytosolic Ca2+-dependent autophagosome-lysosome fusion in primary rat proximal tubular cells. Toxicology 2017, 383, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Guo, C.; Ruan, J.; Ning, B.; Wong, C.K.; Shi, H.; Gu, J. Cadmium Disrupted ER Ca2+ Homeostasis by Inhibiting SERCA2 Expression and Activity to Induce Apoptosis in Renal Proximal Tubular Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Ma, T.; Lv, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Chen, H.; Gao, L. Endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated by ROS participates in cadmium exposure-induced MC3T3-E1 cell apoptosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 251, 114517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, K.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Protective effect of quercetin on cadmium-induced kidney apoptosis in rats based on PERK signaling pathway. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 82, 127355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ou, W.C.; Fang, L.; Tian, C.W.; Xiong, Y. Myocyte Enhancer Factor 2A Plays a Central Role in the Regulatory Networks of Cellular Physiopathology. Aging Dis. 2023, 14, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, M.P.; Mullainadhan, V.; Karundevi, B. DEHP and Its Metabolite MEHP Alter the Insr and Glut4 Gene Expression by Blunting the Interaction of Transcription Factors in L6 Myotubes. Int. J. Toxicol. 2025, 44, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Tokumoto, M.; Satoh, M. Cadmium toxicity mediated by the inhibition of SLC2A4 expression in human proximal Tubule cells. Faseb J. 2021, 35, e21236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Chen, H.; Xue, J.; Li, P.; Fu, X. The role of GLUT2 in glucose metabolism in multiple organs and tissues. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 6963–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luengo, A.; Li, Z.; Gui, D.Y.; Sullivan, L.B.; Zagorulya, M.; Do, B.T.; Ferreira, R.; Naamati, A.; Ali, A.; Lewis, C.A.; et al. Increased demand for NAD(+) relative to ATP drives aerobic glycolysis. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 691–707.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.H.; Lin, H.C.; Chen, S.W.; Tai, Y.T.; Jung, S.M.; Ko, F.H.; Pang, J.S.; Chu, P.H. Cadmium exposure induces histological damage and cytotoxicity in the cardiovascular system of mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 175, 113740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.C.; Hao, W.M.; Chu, P.H. Cadmium and cardiovascular disease: An overview of pathophysiology, epidemiology, therapy, and predictive value. Rev. Port. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 40, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschke, R. Aluminum, Arsenic, Beryllium, Cadmium, Chromium, Cobalt, Copper, Iron, Lead, Mercury, Molybdenum, Nickel, Platinum, Thallium, Titanium, Vanadium, and Zinc: Molecular Aspects in Experimental Liver Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Hou, L.; Cui, Z.; Li, Q.; Huang, H. Selenium alleviates cadmium-induced oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and programmed necrosis in chicken testes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zeng, H.; Guo, C.; Qi, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, W. Cadmium Exposure Induces Apoptosis and Necrosis of Thyroid Cells via the Regulation of miR-494-3p/PTEN Axis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 202, 5061–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertheloot, D.; Latz, E.; Franklin, B.S. Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: An intricate game of cell death. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1106–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketelut-Carneiro, N.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Apoptosis, Pyroptosis, and Necroptosis-Oh My! The Many Ways a Cell Can Die. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, S.; Bridelance, J.; Roelandt, R.; Vandenabeele, P.; Takahashi, N. MLKL in cancer: More than a necroptosis regulator. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1757–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wan, P.; Choksi, S.; Liu, Z.G. Necroptosis and tumor progression. Trends Cancer 2022, 8, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Inuzuka, H.; Wei, W. Necroptosis pathways in tumorigenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Bi, M.; Yang, J.; Cai, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Shi, G.; Zhang, Z. Cadmium exposure triggers oxidative stress, necroptosis, Th1/Th2 imbalance and promotes inflammation through the TNF-α/NF-κB pathway in swine small intestine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalanobish, S.; Saha, S.; Dutta, S.; Ghosh, S.; Sil, P.C. Melatonin counteracts necroptosis and pulmonary edema in cadmium-induced chronic lung injury through the inhibition of angiotensin II. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zec, M.; Srdic-Rajic, T.; Krivokuca, A.; Jankovic, R.; Todorovic, T.; Andelkovic, K.; Radulovic, S. Novel selenosemicarbazone metal complexes exert anti-tumor effect via alternative, caspase-independent necroptotic cell death. Med. Chem. 2014, 10, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Hu, H.; Xu, J.; Dai, Y.; Kanwar, Y.S.; et al. Cadmium exposure induces Leydig cell injury via necroptosis caused by oxidative stress and TNF-α/TNFR1 signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2025, 761, 151717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coradduzza, D.; Congiargiu, A.; Chen, Z.; Zinellu, A.; Carru, C.; Medici, S. Ferroptosis and Senescence: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Minikes, A.M.; Jiang, X. Ferroptosis at the intersection of lipid metabolism and cellular signaling. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, L.; Dogon, G.; Rigal, E.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Lipid Peroxidation and Iron Metabolism: Two Corner Stones in the Homeostasis Control of Ferroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Wang, L.; Tang, H.; Liu, X.; Peng, F.; Peng, C. Ferroptosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Progression and Therapeutic Potential on It. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajarabille, N.; Latunde-Dada, G.O. Programmed Cell-Death by Ferroptosis: Antioxidants as Mitigators. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Kang, R.; Klionsky, D.J.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis: Machinery and regulation. Autophagy 2021, 17, 2054–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Hao, R.; He, M.; Li, M.; Tan, M.; Gao, P.; Wang, L.; Hong, H.; et al. Chronic cadmium exposure triggered ferroptosis by perturbing the STEAP3-mediated glutathione redox balance linked to altered metabolomic signatures in humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Liang, N.N.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, Y.H.; Wu, W.Z.; Liu, Z.B.; He, Y.Z.; Zhang, Y.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Zhang, T.; et al. Mitochondrial GPX4 acetylation is involved in cadmium-induced renal cell ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2024, 73, 103179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, C. Pyroptosis and Its Role in the Modulation of Cancer Progression and Antitumor Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H. The Role of Autophagy and Pyroptosis in Liver Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W.; Su, P. Cadmium exposure induces pyroptosis of TM4 cells through oxidative stress damage and inflammasome activation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 270, 115930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Jia, Y.; Wu, L.; Su, P. Cadmium exposure induces pyroptosis in testicular tissue by increasing oxidative stress and activating the AIM2 inflammasome pathway. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, M.S. Autophagy—A key player in cellular and body metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shi, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, S. Autophagy flux inhibition mediated by lysosomal dysfunction participates in the cadmium exposure-induced cardiotoxicity in swine. Biofactors 2022, 48, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J. ATF4/PHGDH mediates the effects of ER stress on cadmium-induced autophagy and glycolysis. Toxicology 2024, 509, 153976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Zhang, C.; Luo, S.; Jiang, L.; Li, Q.; Kong, Y.; Cao, J. Autophagy induces mTOR-dependent glucose uptake and mTOR-independent lactate utilization in cadmium-treated A549 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2023, 86, 105513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.L.; Valberg, L.S. Relationship between cadmium and iron absorption. Am. J. Physiol. 1974, 227, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiguchi, H. Anemia induced by cadmium intoxication. Jpn. J. Hyg. 2007, 62, 888–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widhalm, R.; Ellinger, I.; Granitzer, S.; Forsthuber, M.; Bajtela, R.; Gelles, K.; Hartig, P.Y.; Hengstschläger, M.; Zeisler, H.; Salzer, H.; et al. Human placental cell line HTR-8/SVneo accumulates cadmium by divalent metal transporters DMT1 and ZIP14. Metallomics 2020, 12, 1822–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.T.; Zhen, J.; Leng, J.Y.; Cai, L.; Ji, H.L.; Keller, B.B. Zinc as a countermeasure for cadmium toxicity. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Banno, H.; Imai, S.; Tokumoto, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Seko, Y.; Nagase, H.; Satoh, M. Cadmium induces iron deficiency anemia through the suppression of iron transport in the duodenum. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 332, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumoto, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Satoh, M. Long-Term Exposure to Cadmium Causes Hepatic Iron Deficiency through the Suppression of Iron-Transport-Related Gene Expression in the Proximal Duodenum. Toxics 2023, 11, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.-J.; Lin, K.-L.; Lee, J.-H.; Luo, K.-H.; Chen, T.-H.; Yang, C.-C.; Chuang, H.-Y. Interaction between Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNP) of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-α) Gene and Plasma Arsenic and the Effect on Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, L.; Wei, Y.; Pan, J.; Li, X.; Xu, B.; Deng, Y.; Yang, T.; Liu, W. Shedding new light on methylmercury-induced neurotoxicity through the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Toxicol. Lett. 2022, 359, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyama, T.; Xu, S.; Kanemitsu, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Noguchi, T.; Lee, J.Y.; Matsuzawa, A.; Naganuma, A.; Hwang, G.W. Methylmercury directly modifies the 105th cysteine residue in oncostatin M to promote binding to tumor necrosis factor receptor 3 and inhibit cell growth. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, J.; Li, K.; Xu, S.; Yin, H.; Li, S.; Gao, X.J. Trimethyltin chloride exposure induces apoptosis and necrosis and impairs islet function through autophagic interference. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renu, K.; Chakraborty, R.; Myakala, H.; Koti, R.; Famurewa, A.C.; Madhyastha, H.; Vellingiri, B.; George, A.; Valsala Gopalakrishnan, A. Molecular mechanism of heavy metals (Lead, Chromium, Arsenic, Mercury, Nickel and Cadmium)—induced hepatotoxicity—A review. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-Z.; Lan, Y.-Y.; Chu, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-K.; Lee, Y.-P.; Chang, H.-Y.; Huang, B.-M. Arsenic compounds induce apoptosis by activating the MAPK and caspase pathways in FaDu oral squamous carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 60, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenod, F.; Lee, W.K. Cadmium and cellular signaling cascades: Interactions between cell death and survival pathways. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1743–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuffour, A.; Adebayiga Kosiba, A.; Addai Peprah, F.; Gu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, H. Cadmium-induced stress: A close look at the relationship between autophagy and apoptosis. Toxicol. Sci. 2023, 194, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Tokumoto, M.; Satoh, M. Cadmium renal toxicity via apoptotic pathways. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Chen, G.; Jin, W.; Mao, K.; Wan, H.; He, Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Parthanatos and Its Role in Diverse Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, S.; Xie, R.; Liu, J. Extracellular ATP accelerates cell death and decreases tight junction protein ZO-1 in hypoxic cochlear strial marginal cells in neonatal rats. Cell Signal. 2023, 108, 110732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailén, M.; Tabone, M.; Bressa, C.; Lominchar, M.G.M.; Larrosa, M.; González-Soltero, R. Unraveling Gut Microbiota Signatures Associated with PPARD and PARGC1A Genetic Polymorphisms in a Healthy Population. Genes 2022, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hishida, A.; Wakai, K.; Naito, M.; Tamura, T.; Kawai, S.; Hamajima, N.; Oze, I.; Imaizumi, T.; Turin, T.C.; Suzuki, S.; et al. Polymorphisms in PPAR Genes (PPARD, PPARG, and PPARGC1A) and the Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease in Japanese: Cross-Sectional Data from the J-MICC Study. PPAR Res. 2013, 2013, 980471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.K.C.; Lam, J.M.; Wong, A.H.C.; Hon, K.L.; Li, X. Iron Deficiency Anemia: An Updated Review. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2024, 20, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Accelerating Anaemia Reduction: A Comprehensive Framework for Action; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh, M.F.; Yano, A.S.; Shaffer, N.E. Anemia in Infants and Children: Evaluation and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2024, 110, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Mori, C.; Tokumoto, M.; Satoh, M. Changes in DNA-binding activity of transcription factors in the kidney of mice exposed to cadmium. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 46, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).