Intermittent Hypoxia Induces Cognitive Dysfunction and Hippocampal Gene Expression Changes in a Mouse Model of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Y-Maze Test and Passive Avoidance Test
2.2. Comparisons of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
2.3. Functional Enrichment Analysis
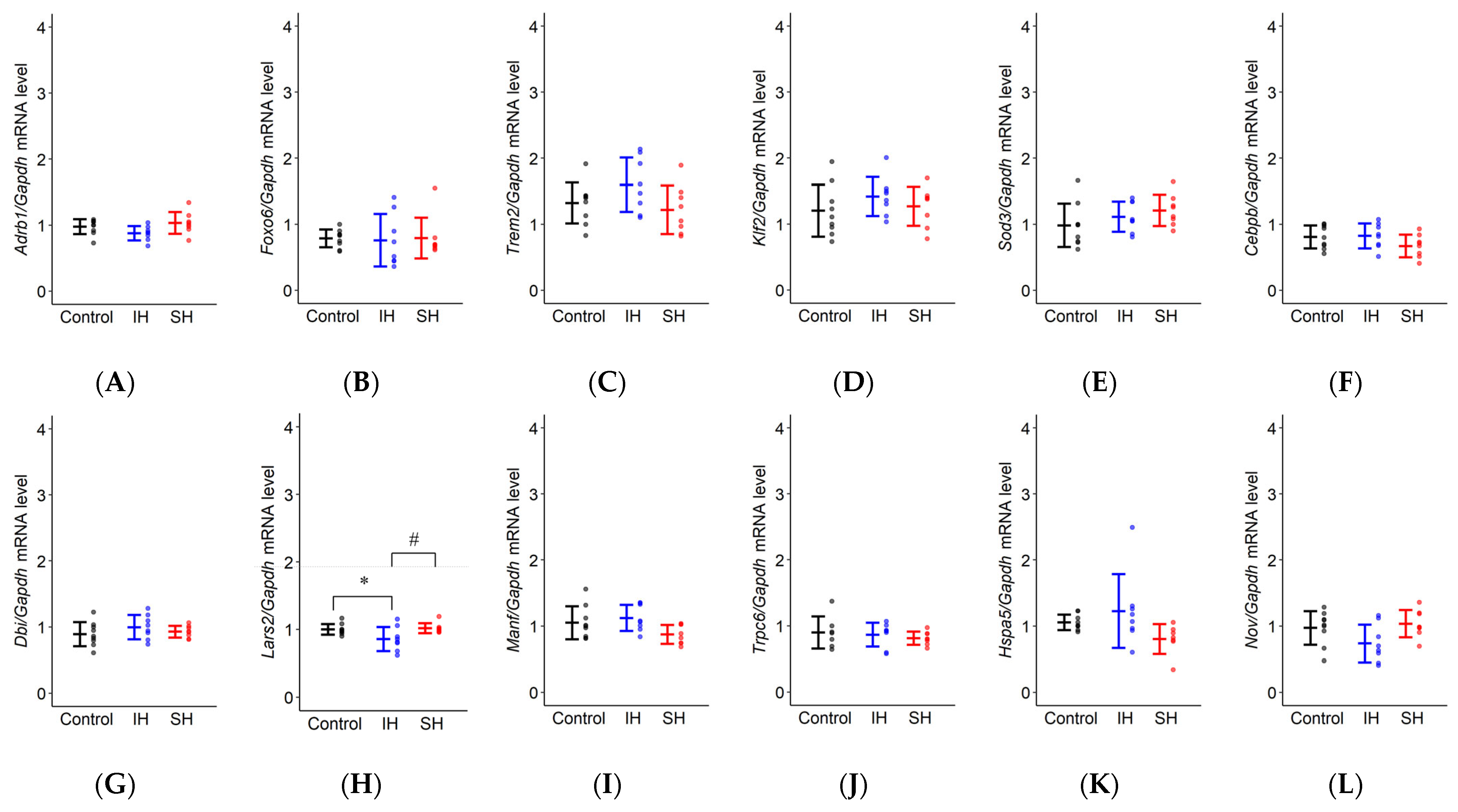
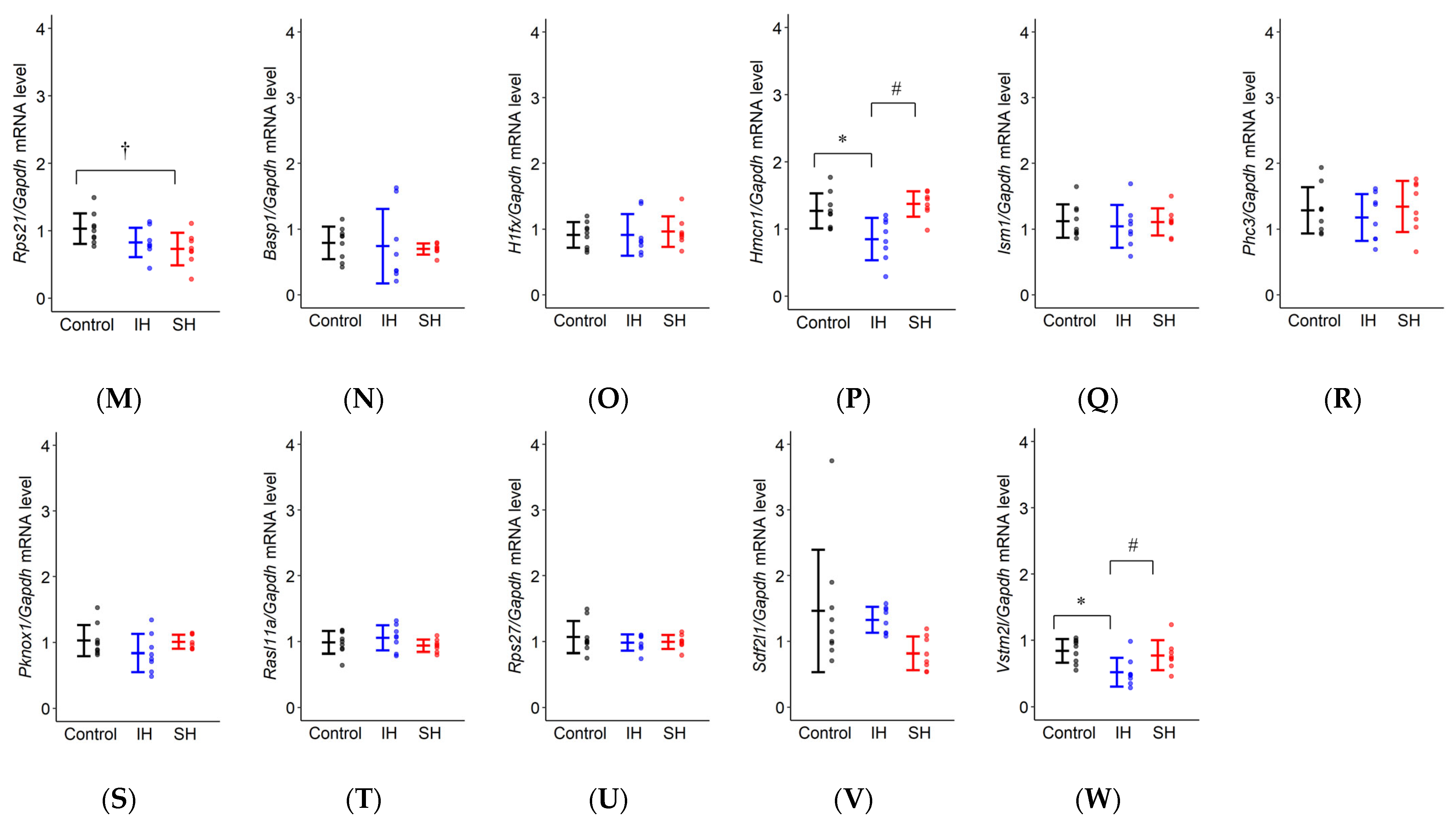
2.4. RT-qPCR
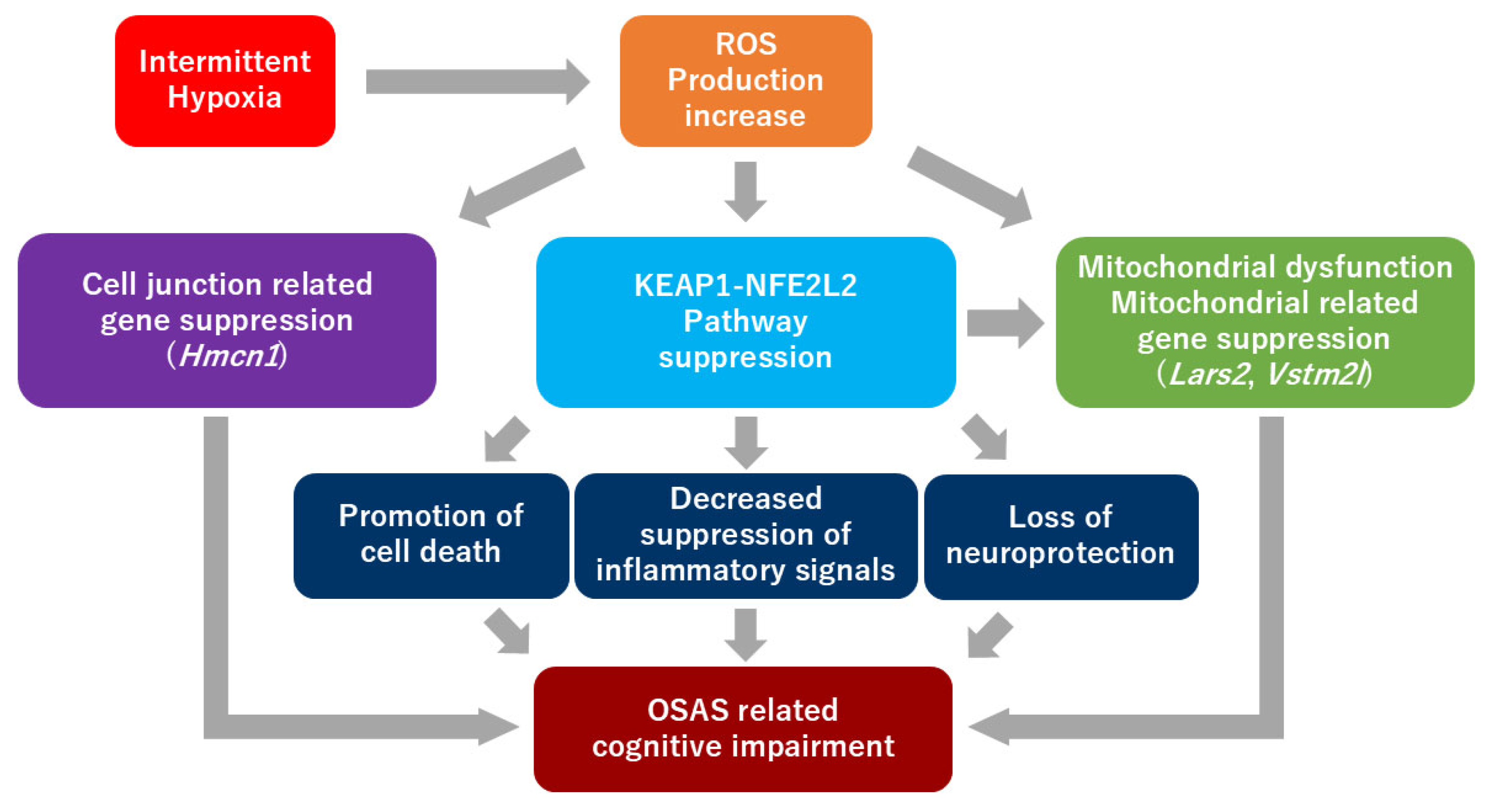
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Experimental Protocol
4.3. Intermittent Hypoxia Exposure, Sustained Hypoxia Exposure
4.4. Y-Maze Test
4.5. Passive Avoidance Test
4.6. RNA Sequencing
4.7. RT-qPCR
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OSAS | Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome |
| IH | Intermittent hypoxia |
| SH | Sustained hypoxia |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RNA-seq | RNA sequencing |
| DEGs | Differentially Expressed Genes |
| FC | Fold change |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| IPA | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis |
References
- Senaratna, C.V.; Perret, J.L.; Lodge, C.J.; Lowe, A.J.; Campbell, B.E.; Matheson, M.C.; Hamilton, G.S.; Dharmage, S.C. Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in the General Population: A Systematic Review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 34, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjafield, A.V.; Ayas, N.T.; Eastwood, P.R.; Heinzer, R.; Ip, M.S.M.; Morrell, M.J.; Nunez, C.M.; Patel, S.R.; Penzel, T.; Pépin, J.L.D.; et al. Estimation of the Global Prevalence and Burden of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: A Literature-Based Analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannella, G.; Pace, A.; Bellizzi, M.G.; Magliulo, G.; Greco, A.; De Virgilio, A.; Croce, E.; Gioacchini, F.M.; Re, M.; Constantino, A.; et al. The Global Burden of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévy, P.; Kohler, M.; McNicholas, W.T.; Barbé, F.; McEvoy, R.D.; Somers, V.K.; Lavie, L.; Pépin, J.L. Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.M.; Agusti, A.; Villar, I.; Forner, M.; Nieto, D.; Carrizo, S.J.; Barbé, F.; Vicente, E.; Wei, Y.; Javier Nieto, F.; et al. Association between Treated and Untreated Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Risk of Hypertension. JAMA 2012, 307, 2169–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reutrakul, S.; Mokhlesi, B. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Diabetes: A State of the Art Review. Chest 2017, 152, 1070–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Adachi, T.; Koshino, Y.; Somers, V.K. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. J. 2009, 73, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucks, R.S.; Olaithe, M.; Eastwood, P. Neurocognitive Function in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: A Meta-Review. Respirology 2013, 18, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beebe, D.W.; Gozal, D. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and the Prefrontal Cortex: Towards a Comprehensive Model Linking Nocturnal Upper Airway Obstruction to Daytime Cognitive and Behavioral Deficits. J. Sleep Res. 2002, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findley, L.J.; Barth, J.T.; Powers, D.C.; Wilhoit, S.C.; Boyd, D.G.; Suratt, P.M. Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Associated Hypoxemia. Chest 1986, 90, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubu, O.M.; Andrade, A.G.; Umasabor-Bubu, O.Q.; Hogan, M.M.; Turner, A.D.; de Leon, M.J.; Ogedegbe, G.; Ayappa, I.; Jean-Louis, G.G.; Jackson, M.L.; et al. Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Cognition and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review Integrating Three Decades of Multidisciplinary Research. Sleep Med. Rev. 2020, 50, 101250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torelli, F.; Moscufo, N.; Garreffa, G.; Placidi, F.; Romigi, A.; Zannino, S.; Bozzali, M.; Fasano, F.; Giulietti, G.; Djonlagic, I.; et al. Cognitive Profile and Brain Morphological Changes in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Cavieres, A.; Fonteh, A.; Castro-Rivera, C.I.; Garcia, A.J. Intermittent Hypoxia Causes Targeted Disruption to NMDA Receptor Dependent Synaptic Plasticity in Area CA1 of the Hippocampus. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 344, 113808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ma, D.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Z. Impact of Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia on Cognitive Function and Hippocampal Neurons in Mice: A Study of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Pathways. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2024, 16, 2029–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Li, D.; Gong, B.; Song, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Y. Sevoflurane Aggravates Cognitive Impairment in OSAS Mice through Tau Phosphorylation and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Exp. Neurol. 2025, 384, 115056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, S.; Guo, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ji, E. Shashen-Maidong Decoction Improved Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Cognitive Impairment through Regulating Glutamatergic Signaling Pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 274, 114040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubrecht, T.G.; Weil, Z.M.; Magalang, U.J.; Nelson, R.J. Dim Light at Night Interacts with Intermittent Hypoxia to Alter Cognitive and Affective Responses. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, L. Oxidative Stress in Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Intermittent Hypoxia-Revisited—The Bad Ugly and Good: Implications to the Heart and Brain. Sleep Med. Rev. 2015, 20, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, N.A.; Nieto, F.J.; Somers, V.K. Intermittent Hypoxemia and OSA: Implications for Comorbidities. Chest 2015, 147, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Cognitive Impairment Associated with Sleep Apnea. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.U.; Luo, L.; Namani, A.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Nrf2 Signaling Pathway: Pivotal Roles in Inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, K.M.; Baird, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hargreaves, I.; Chalasani, A.; Land, J.M.; Stanyer, L.; Yamamoto, M.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Abramov, A.Y. Nrf2 Impacts Cellular Bioenergetics by Controlling Substrate Availability for Mitochondrial Respiration. Biol. Open 2013, 2, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niture, S.K.; Jaiswal, A.K. Nrf2 Protein Up-Regulates Antiapoptotic Protein Bcl-2 and Prevents Cellular Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 9873–9886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; An, C.; Gao, Y.; Leak, R.K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F. Emerging Roles of Nrf2 and Phase II Antioxidant Enzymes in Neuroprotection. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 100, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, T.; Ogawa, S.K.; Roy, D.S.; Okuyama, T.; Morrissey, M.D.; Smith, L.M.; Redondo, R.L.; Tonegawa, S. Engrams and circuits crucial for systems consolidation of a memory. Science 2017, 356, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Feng, X.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, B.; Liu, W.; Zhao, M.; Yao, K.; Ren, C. Inactivation of LARS2, Located at the Commonly Deleted Region 3p21.3, by Both Epigenetic and Genetic Mechanisms in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2009, 41, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyroud, A.S.; Rudinger-Thirion, J.; Frugier, M.; Riley, L.G.; Bidet, M.; Akloul, L.; Simpson, A.; Gilot, D.; Christodoulou, J.; Ravel, C.; et al. LARS2 Variants Can Present as Premature Ovarian Insufficiency in the Absence of Overt Hearing Loss. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 31, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, H.; Kedra, D.; Yang, Y.; Kost-Alimova, M.; Kiss, C.; O’Brien, K.P.; Fransson, I.; Klein, G.; Imreh, S.; Dumanski, J.P. A Novel Gene Containing LIM Domains (LIMD1) Is Located within the Common Eliminated Region 1 (C3CER1) in 3p21.3. Hum. Genet. 1999, 105, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, W. Lin28a Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Human Granulosa Cells via Suppressing LARS2 Expression. Cell. Signal. 2023, 103, 110536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Yuan, L.; Zhuge, W.; Gu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhuge, Q.; Ni, H.; Lv, X. Regulating Lars2 in Mitochondria: A Potential Alzheimer’s Therapy by Inhibiting Tau Phosphorylation. Neurotherapeutics 2024, 21, e00353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Wan, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Tang, M.; Bai, L.; Zhu, Y. LARS2 Regulates Apoptosis via ROS-Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Ovarian Granulosa Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 5501346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Hao, J.L.; Li, L.; Ruan, Y.T.; An, X.N.; Huang, Q.L.; Dong, X.M.; Gao, P. VSTM2L Protects Prostate Cancer Cells against Ferroptosis via Inhibiting VDAC1 Oligomerization and Maintaining Mitochondria Homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, B.E.; Hedgecock, E.M. Hemicentin, a Conserved Extracellular Member of the Immunoglobulin Superfamily, Organizes Epithelial and Other Cell Attachments into Oriented Line-Shaped Junctions. Development 2001, 128, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Tao, Y.; He, Q.; Song, F.; Saffen, D. Functional Enrichment Analysis of Three Alzheimer’s Disease Genome-Wide Association Studies Identities DAB1 as a Novel Candidate Liability/Protective Gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Török, I.; Herrmann-Horle, D.; Kiss, I.; Tick, G.; Speer, G.; Schmitt, R.; Mechler, B.M. Down-Regulation of RpS21, a Putative Translation Initiation Factor Interacting with P40, Produces Viable Minute Imagos and Larval Lethality with Overgrown Hematopoietic Organs and Imaginal Discs. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 2308–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinke, C.; Bevans-Fonti, S.; Drager, L.F.; Shin, M.K.; Polotsky, V.Y. Effects of different acute hypoxic regimens on tissue oxygen profiles and metabolic outcomes. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gileles-Hillel, A.; Almendros, I.; Khalyfa, A.; Nigdelioglu, R.; Qiao, Z.; Hamanaka, R.B.; Mutlu, G.M.; Akbarpour, M.; Gozal, D. Prolonged Exposures to Intermittent Hypoxia Promote Visceral White Adipose Tissue Inflammation in a Murine Model of Severe Sleep Apnea: Effect of Normoxic Recovery. Sleep 2017, 40, zsw074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.B.; Stihl, C.; Schmid, A.; Hirschberger, S.; Mitsigiorgi, R.; Holzer, M.; Patscheider, M.; Weiss, B.G.; Reichel, C.; Hübner, M.; et al. A novel OSA-related model of intermittent hypoxia in endothelial cells under flow reveals pronounced inflammatory pathway activation. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1108966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.S.; Park, K.S.; Jeon, G.S.; Shon, J.; Ahn, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, K.M.; Sung, J.J.; et al. Intermittent Hypoxia Can Aggravate Motor Neuronal Loss and Cognitive Dysfunction in ALS Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Kwon, D.A.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, W.K. Standardized Extract (HemoHIM) Protects against Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia in a Murine Model. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 8884243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape Provides a Biologist-Oriented Resource for the Analysis of Systems-Level Datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.K.; Park, H.H.; Woods, C.E.; Lam, R.K.; Rijsketic, D.R.; Xu, C.; Chu, E.K.; Ciari, P.; Blumenfeld, S.; Vidano, L.M.; et al. Impact of Noradrenergic Inhibition on Neuroinflammation and Pathophysiology in Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salih, D.A.M.; Rashid, A.J.; Colas, D.; de la Torre-Ubieta, L.; Zhu, R.P.; Morgan, A.A.; Santo, E.E.; Ucar, D.; Devarajan, K.; Cole, C.J.; et al. FoxO6 Regulates Memory Consolidation and Synaptic Function. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 2780–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Fan, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, L. Intermittent Hypoxia Training Enhances Aβ Endocytosis by Plaque Associated Microglia via VPS35-Dependent TREM2 Recycling in Murine Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chang, L.; Liu, Z.; Geng, X.; Wang, R.; Yin, X.; Fan, W.; Zhao, B.Q. Neddylation in the Chronically Hypoperfused Corpus Callosum: MLN4924 Reduces Blood-Brain Barrier Injury via ERK5/KLF2 Signaling. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 371, 114587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, T.; Hong, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, J. TFEB-Dependent Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway Is Required for NRF2-Driven Antioxidative Action in Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Induced Neuronal Injury. Cell. Signal. 2025, 128, 111630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Long, C.; Yi, P.; Zhang, G.; Wan, W.; Rao, X.; Ying, J.; Liang, W.; Hua, F. C/EBPβ: A Transcription Factor Associated with the Irreversible Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokce, M.; Velioglu, H.A.; Bektay, M.Y.; Guler, E.M. Evaluating the Clinical Significance of Diazepam Binding Inhibitor in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Comparison with Inflammatory, Oxidative, and Neurodegenerative Biomarkers. Gerontology 2023, 69, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Han, X.; Mu, Q.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Kang, Y.; Liu, Y. Cerebrospinal Fluid Mesencephalic Astrocyte-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Moderating Effect on Sleep Time and Cognitive Function. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2024, 176, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, T.; Xiao, R.; Lv, K.; Wu, C.; Luo, Y.; Cai, Y.; Fan, X. AAV Delivery of ShRNA Against TRPC6 in Mouse Hippocampus Impairs Cognitive Function. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 688655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, G.S.; de Oliveira, R.W.; Perry, J.C.; Tufik, S.; Chagas, J.R. Validation of housekeeping genes in the brains of rats submitted to chronic intermittent hypoxia, a sleep apnea model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julian, G.S.; de Oliveira, R.W.; Tufik, S.; Chagas, J.R. Analysis of the stability of housekeeping gene expression in the left cardiac ventricle of rats submitted to chronic intermittent hypoxia. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2016, 42, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

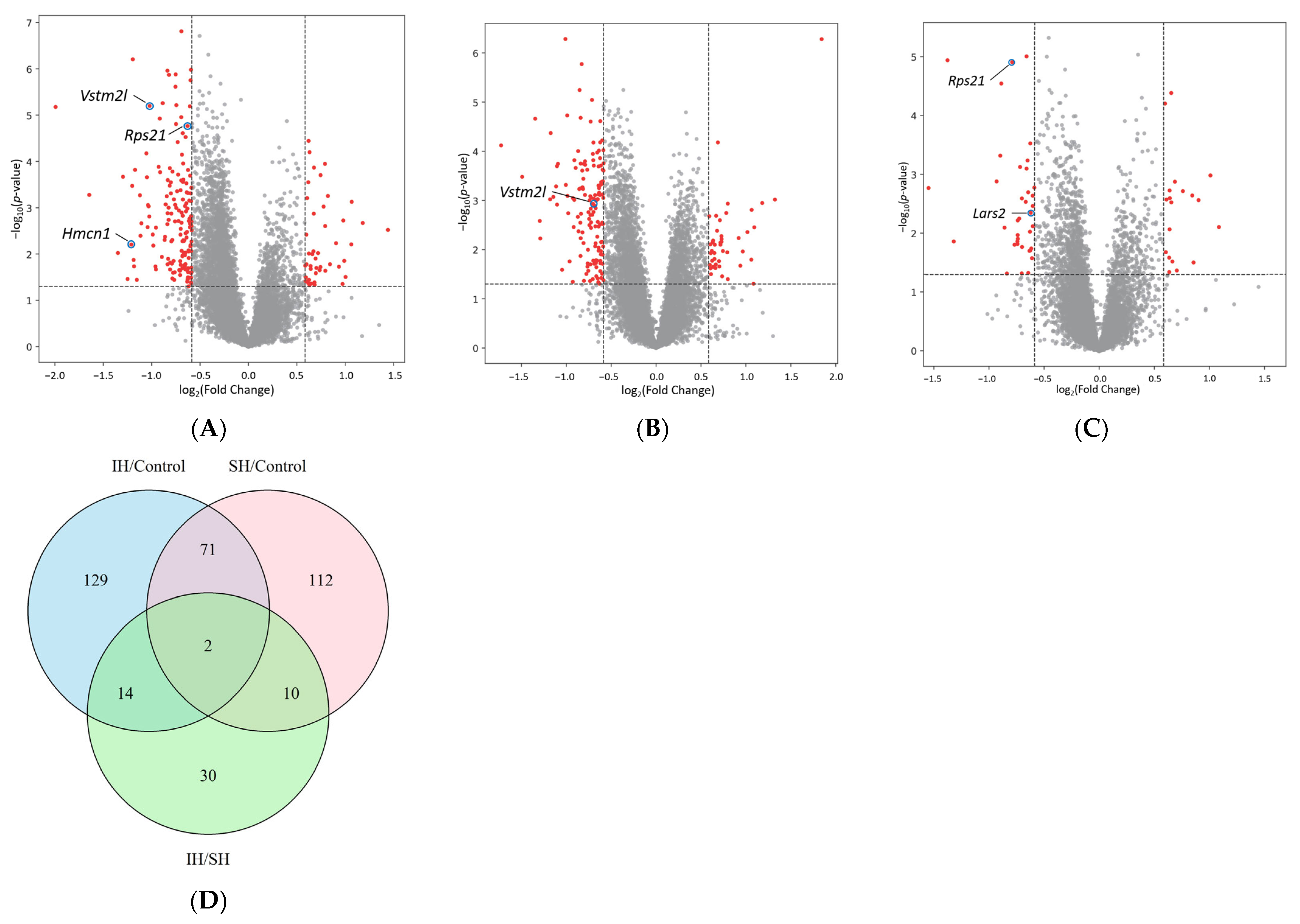

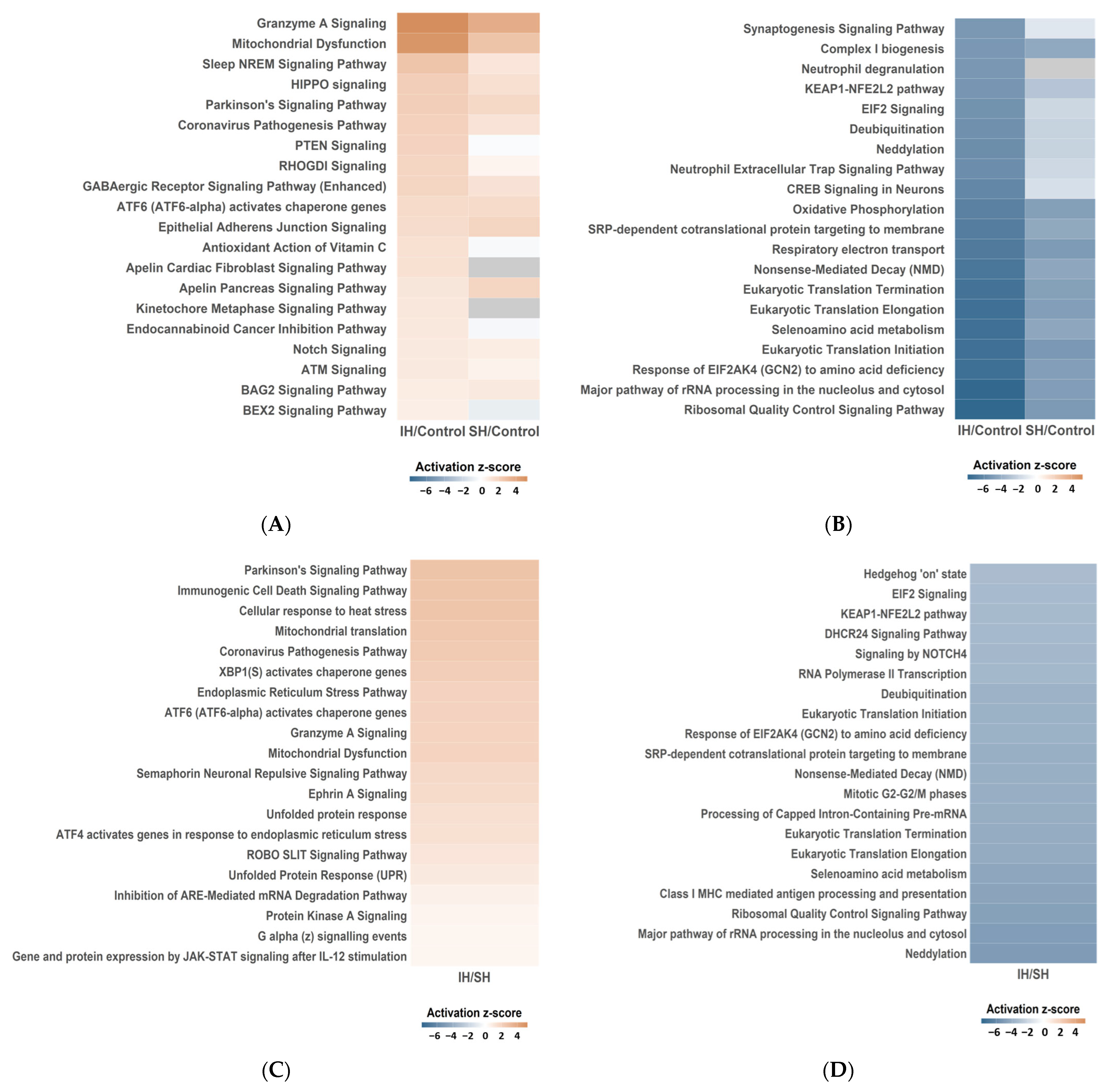
| IH/Control | SH/Control | IH/SH | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | log2FC | p-Value | Gene | log2FC | p-Value | Gene | log2FC | p-Value |
| Cebpb | −1.993 | 6.666 × 10−6 | Phc3 | 1.843 | 5.262 × 10−7 | Phc3 | −1.545 | 1.708 × 10−3 |
| Fos | −1.644 | 5.295 × 10−4 | Gng13 | −1.726 | 7.609 × 10−5 | Cebpb | −1.373 | 1.165 × 10−5 |
| Plin4 | 1.441 | 3.014 × 10−3 | Npas4 | −1.492 | 3.315 × 10−4 | H3c14 | −1.317 | 1.381 × 10−2 |
| Npas4 | −1.349 | 9.500 × 10−3 | Cysrt1 | −1.346 | 2.177 × 10−5 | Map3k6 | 1.086 | 7.855 × 10−3 |
| C2cd4b | −1.296 | 2.150 × 10−4 | Plin4 | 1.323 | 9.619 × 10−4 | Hspb1 | 1.009 | 1.044 × 10−3 |
| Rps27rt | −1.249 | 3.471 × 10−2 | Egr4 | −1.295 | 2.606 × 10−3 | Dynlt1f | −0.929 | 1.321 × 10−3 |
| Hmcn1 | −1.209 | 6.247 × 10−3 | Pcdha11 | −1.290 | 5.937 × 10−3 | Gng13 | 0.901 | 2.744 × 10−3 |
| Cysrt1 | −1.201 | 3.383 × 10−4 | Ankub1 | 1.182 | 1.129 × 10−3 | Rpl17-ps8 | −0.895 | 4.822 × 10−4 |
| H1f10 | −1.195 | 6.248 × 10−7 | C2cd4b | −1.181 | 9.489 × 10−4 | Rpl39 | −0.886 | 2.877 × 10−5 |
| Hbb-bt | −1.187 | 1.340 × 10−2 | Enho | −1.174 | 4.272 × 10−5 | Snurf | −0.857 | 8.045 × 10−3 |
| Arc | −1.181 | 1.848 × 10−2 | Ier2 | −1.145 | 8.485 × 10−4 | Moap1 | 0.856 | 3.136 × 10−2 |
| Pknox1 | 1.181 | 2.139 × 10−3 | Junb | −1.114 | 5.181 × 10−4 | Phospho1 | 0.844 | 2.287 × 10−3 |
| Junb | −1.172 | 1.515 × 10−4 | Fos | −1.104 | 2.005 × 10−4 | Gnpnat1 | −0.836 | 4.827 × 10−2 |
| Egr2 | −1.153 | 3.605 × 10−2 | Gm1673 | −1.103 | 1.217 × 10−3 | Rps21 | −0.788 | 1.248 × 10−5 |
| Btg2 | −1.121 | 5.394 × 10−4 | Slc18a2 | 1.093 | 3.518 × 10−3 | Tnfsf10 | −0.766 | 1.568 × 10−2 |
| Pla2g4e | −1.115 | 4.045 × 10−3 | Btg2 | −1.093 | 1.799 × 10−4 | Hspa1b | 0.759 | 1.929 × 10−3 |
| Egr4 | −1.107 | 2.171 × 10−3 | Zic4 | 1.084 | 4.950 × 10−2 | Gm13304 | −0.740 | 1.380 × 10−2 |
| Sdf2l1 | 1.067 | 7.463 × 10−4 | Inhba | 1.064 | 1.554 × 10−3 | Gm13306 | −0.740 | 1.525 × 10−2 |
| Slc18a2 | 1.062 | 6.197 × 10−3 | Gm44126 | 1.060 | 1.597 × 10−2 | Rpl17 | −0.738 | 1.073 × 10−2 |
| Adrb1 | −1.055 | 6.714 × 10−5 | Arc | −1.047 | 2.575 × 10−2 | Gm10591 | −0.737 | 6.057 × 10−3 |
| Tmem238 | −1.049 | 2.205 × 10−4 | Pknox1 | 1.016 | 4.399 × 10−3 | Ccl21b | −0.736 | 1.243 × 10−2 |
| Ier2 | −1.042 | 2.628 × 10−3 | Mrpl52 | −1.010 | 5.217 × 10−7 | Gm20498 | −0.724 | 5.646 × 10−3 |
| Dusp1 | −1.038 | 8.774 × 10−4 | Rasl11a | −1.005 | 4.835 × 10−4 | Hmgcs2 | −0.716 | 7.510 × 10−4 |
| Rasl11a | −1.031 | 9.329 × 10−4 | Pcsk1n | −0.990 | 1.870 × 10−5 | Rnasek | 0.704 | 4.290 × 10−2 |
| Ism1 | −1.025 | 1.550 × 10−3 | Tmem238 | −0.987 | 8.084 × 10−4 | Dcst1 | −0.701 | 4.809 × 10−2 |
| Vstm2l | −1.021 | 6.329 × 10−6 | Wnt9a | −0.979 | 1.821 × 10−3 | Pcdha3 | −0.699 | 2.567 × 10−3 |
| Ankub1 | 1.004 | 3.126 × 10−2 | Tnfaip6 | 0.965 | 1.090 × 10−2 | U2af1l4 | −0.698 | 1.711 × 10−2 |
| Zfp708 | 0.990 | 1.405 × 10−2 | Oxld1 | −0.963 | 1.739 × 10−2 | Hexim2 | 0.687 | 1.335 × 10−3 |
| Tusc1 | −0.989 | 3.795 × 10−3 | Dnah12 | 0.938 | 2.121 × 10−2 | Gstp-ps | −0.665 | 2.933 × 10−3 |
| Adamts16 | −0.983 | 6.563 × 10−3 | Apold1 | −0.928 | 4.507 × 10−2 | 2300009A05Rik | 0.664 | 3.020 × 10−2 |
| Inhba | 0.980 | 1.889 × 10−3 | Mrpl54 | −0.926 | 8.988 × 10−4 | Itm2a | −0.657 | 9.970 × 10−6 |
| Lamc2 | 0.973 | 4.439 × 10−2 | Prrg1 | 0.919 | 5.807 × 10−3 | Adrb1 | −0.657 | 8.013 × 10−4 |
| Pcdhgb5 | −0.961 | 1.859 × 10−2 | Phospho1 | −0.918 | 3.473 × 10−3 | Lfng | 0.654 | 2.993 × 10−3 |
| Iqschfp | −0.955 | 2.146 × 10−2 | Gm2423 | −0.911 | 9.762 × 10−4 | Dbi | 0.654 | 4.166 × 10−5 |
| Ccl21b | −0.955 | 2.696 × 10−3 | S100a13 | −0.910 | 1.517 × 10−4 | Rps28 | −0.648 | 5.831 × 10−4 |
| Peg10 | 0.935 | 1.883 × 10−2 | Rps29 | −0.896 | 2.184 × 10−4 | Scrg1 | −0.642 | 2.020 × 10−3 |
| Hba-a2 | −0.928 | 1.310 × 10−4 | Ly6h | −0.872 | 2.158 × 10−3 | Adamts16 | −0.642 | 4.729 × 10−2 |
| Gm13889 | −0.916 | 1.187 × 10−5 | Trnp1 | −0.868 | 9.911 × 10−5 | Hspa1a | 0.641 | 2.541 × 10−3 |
| Sap30l | −0.913 | 1.711 × 10−4 | Klf2 | −0.864 | 4.240 × 10−3 | Mrpl54 | 0.639 | 1.883 × 10−3 |
| Plekhg4 | 0.905 | 5.845 × 10−3 | Myl6b | −0.856 | 5.866 × 10−4 | Ptpn6 | 0.639 | 8.596 × 10−3 |
| Gm10591 | −0.894 | 1.155 × 10−2 | Sap30l | −0.852 | 5.689 × 10−6 | Peg10 | 0.636 | 4.555 × 10−2 |
| Fbxl9 | −0.886 | 5.532 × 10−6 | Erf | −0.844 | 5.686 × 10−4 | Rtl3 | 0.635 | 2.598 × 10−2 |
| Wnt9a | −0.866 | 4.959 × 10−3 | Tmem160 | −0.843 | 2.832 × 10−3 | Fancd2 | −0.631 | 1.993 × 10−2 |
| Frat2 | −0.861 | 4.246 × 10−3 | Sox18 | −0.842 | 1.348 × 10−2 | Ror1 | −0.626 | 9.413 × 10−3 |
| Sts | −0.855 | 8.503 × 10−4 | Rpl38 | −0.840 | 2.093 × 10−5 | Otogl | −0.624 | 1.961 × 10−2 |
| Insm1 | −0.844 | 5.657 × 10−4 | Tmem256 | −0.840 | 1.783 × 10−4 | Rpl22l1 | −0.624 | 2.989 × 10−4 |
| Hspb1 | 0.843 | 1.663 × 10−2 | Tead3 | −0.840 | 5.864 × 10−3 | Lars2 | −0.619 | 4.500 × 10−3 |
| Tomm6 | −0.838 | 2.268 × 10−3 | Zfp524 | −0.836 | 1.869 × 10−3 | Nadsyn1 | −0.614 | 1.815 × 10−2 |
| Arf6 | −0.837 | 1.101 × 10−6 | Hcfc1r1 | −0.829 | 1.688 × 10−6 | Cdk2ap2 | 0.611 | 2.685 × 10−3 |
| Pgam2 | −0.836 | 1.671 × 10−2 | Chchd10 | −0.822 | 2.469 × 10−4 | Ppara | −0.608 | 2.653 × 10−2 |
| Gene | F Value | LS Mean | IH vs. Control | SH vs. Control | IH vs. SH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adrb1 | F(2,22) = 2.915, p = 0.075 | Control: 0.977 ± 0.064 IH: 0.877 ± 0.066 SH: 1.033 ± 0.066 | p = 0.277 | p = 0.662 | p = 0.066 |
| Foxo6 | F(2,22) = 0.029, p = 0.971 | Control: 0.786 ± 0.144 IH: 0.758 ± 0.148 SH: 0.791 ± 0.148 | p = 0.979 | p = 0.999 | p = 0.973 |
| Trem2 | F(2,22) = 2.343, p = 0.120 | Control: 1.321 ± 0.176 IH: 1.597 ± 0.181 SH: 1.218 ± 0.181 | p = 0.282 | p = 0.831 | p = 0.116 |
| Klf2 | F(2,22) = 0.899, p = 0.421 | Control: 1.202 ± 0.163 IH: 1.417 ± 0.168 SH: 1.269 ± 0.168 | p = 0.400 | p = 0.912 | p = 0.656 |
| Sod3 | F(2,22) = 1.495, p = 0.246 | Control: 0.984 ± 0.132 IH: 1.114 ± 0.135 SH: 1.209 ± 0.135 | p = 0.588 | p = 0.222 | p = 0.765 |
| Cebpb | F(2,22) = 1.808, p = 0.188 | Control: 0.808 ± 0.087 IH: 0.823 ± 0.089 SH: 0.670 ± 0.089 | p = 0.984 | p = 0.271 | p = 0.223 |
| Dbi | F(2,22) = 0.930, p = 0.409 | Control: 0.892 ± 0.078 IH: 0.997 ± 0.080 SH: 0.928 ± 0.080 | p = 0.384 | p = 0.891 | p = 0.668 |
| Lars2 | F(2,22) = 4.376, * p = 0.025 | Control: 0.999 ± 0.058 IH: 0.857 ± 0.059 SH: 1.016 ± 0.059 | p = 0.056 | p = 0.954 | * p = 0.036 |
| Manf | F(2,22) = 3.191, p = 0.061 | Control: 1.051 ± 0.099 IH: 1.123 ± 0.102 SH: 0.872 ± 0.102 | p = 0.753 | p = 0.194 | p = 0.057 |
| Trpc6 | F(2,20) = 0.452, p = 0.643 | Control: 0.900 ± 0.094 IH: 0.866 ± 0.090 SH: 0.812 ± 0.090 | p = 0.932 | p = 0.624 | p = 0.822 |
| Hspa5 | F(2,21) = 2.733, p = 0.088 | Control: 1.057 ± 0.177 IH: 1.226 ± 0.182 SH: 0.802 ± 0.182 | p = 0.591 | p = 0.340 | p = 0.073 |
| Nov | F(2,22) = 2.310, p = 0.123 | Control: 0.973 ± 0.120 IH: 0.738 ± 0.123 SH: 0.954 ± 0.123 | p = 0.145 | p = 0.987 | p = 0.207 |
| Rps21 | F(2,22) = 3.870, * p = 0.036 | Control: 1.029 ± 0.111 IH: 0.826 ± 0.114 SH: 0.729 ± 0.114 | p = 0.182 | * p = 0.033 | p = 0.676 |
| Basp1 | F(2,22) = 0.151, p = 0.861 | Control: 0.792 ± 0.173 IH: 0.741 ± 0.178 SH: 0.697 ± 0.178 | p = 0.953 | p = 0.849 | p = 0.967 |
| H1fx | F(2,22) = 0.110, p = 0.897 | Control: 0.912 ± 0.122 IH: 0.913 ± 0.125 SH: 0.963 ± 0.125 | p = 1.000 | p = 0.909 | p = 0.916 |
| Hmcn1 | F(2,22) = 9.196, * p = 0.001 | Control: 1.271 ± 0.126 IH: 0.849 ± 0.130 SH: 1.373 ± 0.130 | * p = 0.008 | p = 0.703 | * p = 0.002 |
| Ism1 | F(2,22) = 0.204, p = 0.817 | Control: 1.122 ± 0.130 IH: 1.044 ± 0.134 SH: 1.110 ± 0.134 | p = 0.821 | p = 0.995 | p = 0.875 |
| Phc3 | F(2,22) = 0.423, p = 0.660 | Control: 1.286 ± 0.177 IH: 1.179 ± 0.182 SH: 1.344 ± 0.182 | p = 0.819 | p = 0.943 | p = 0.643 |
| Pknox1 | F(2,22) = 1.774, p = 0.193 | Control: 1.030 ± 0.109 IH: 0.840 ± 0.112 SH: 1.010 ± 0.112 | p = 0.212 | p = 0.980 | p = 0.306 |
| Rasl11a | F(2,22) = 1.129, p = 0.342 | Control: 0.988 ± 0.077 IH: 1.057 ± 0.079 SH: 0.938 ± 0.079 | p = 0.652 | p = 0.795 | p = 0.312 |
| Rps27 | F(2,22) = 0.640, p = 0.537 | Control: 1.067 ± 0.084 IH: 0.993 ± 0.086 SH: 0.984 ± 0.086 | p = 0.570 | p = 0.642 | p = 0.993 |
| Sdf2l1 | F(2,22) = 2.764, p = 0.085 | Control: 1.464 ± 0.286 IH: 1.327 ± 0.295 SH: 0.818 ± 0.295 | p = 0.882 | p = 0.084 | p = 0.218 |
| Vstm2l | F(2,22) = 5.509, * p = 0.012 | Control: 0.840 ± 0.100 IH: 0.521 ± 0.103 SH: 0.775 ± 0.103 | * p = 0.012 | p = 0.799 | p = 0.055 |
| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Probe Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adrb1 | 5′-GTTTACTCAAGACCGAAAGCAG-3′ | 5′-CACTCTCCCAACTCCTCCTAA-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/ATGCAAAGC/ZEN/CCACAGATCTATCGAATCA/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Basp1 | 5′-CCTTTGCTGAGCGACCA-3′ | 5′-AGCTTGCCTCCCATCTTG-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/TGAGCGCGG/ZEN/TGCCTCCAA/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Cebpb | 5′-GTTTCGGGACTTGATGCAATC-3′ | 5′-CCGCAGGAACATCTTTAAGTGA-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/ACACGGGAC/ZEN/TGACGCAACACA/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Dbi | 5′-CATCTACAGTCACTTCAAACAAGC-3′ | 5′-ACATAGGTCTTCATGGCACTT-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/ACTCGTGGA/ZEN/ACAAGCTGAAAGGAC/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Foxo6 | 5′-AGGATAAAGCGACAGCAAC-3′ | 5′-CACCATGAACTCTTGCCAGT-3′ | 5’-/56-FAM/AGAACTCCA/ZEN/TTCGGCACAACCTGT/3IABkFQ/-3’ |
| H1fx | 5’-CAGGAAGGTGGCATGGTT-3’ | 5’-TGCAGTAGCGTATCGTTCTG-3’ | 5’-/56-FAM/AGCGCCCGG/ZEN/ATAGAGTACTTGAGG/3IABkFQ/-3’ |
| Hmcn1 | 5’-AGTAAGCACTACAGCCTTCAAG-3’ | 5’-GCACGTCATAGAGGTAGAACTG-3’ | 5’-/56-FAM/CCACCGAAT/ZEN/ATGGACAACGCAATGG/3IABkFQ/-3’ |
| Hspa5 | 5’-AGAGTTCTTCAATGGCAAGGAG-3’ | 5′-ATCAAGCAGTACCAGATCACC-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/ACAGCGGCA/ZEN/CCATAGGCTACAG/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Ism1 | 5′-GATGACAGCAACTTCCTCAGT-3′ | 5′-AGACAGACCAGAGACTCCAAT-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/AGAGCAGCC/ZEN/AGAGTATGATTCCACAGA/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Klf2 | 5′-GCAAGACCTACACCAAGAGC-3′ | 5′-CTTCCAGCCGCATCCTTC-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/TGCGTACAC/ZEN/ACACAGGTGAGAAGC/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Lars2 | 5′-GTTCTATGCACGATTCCTCAGT-3′ | 5′-ATGGAAGGCGGAATGTCTG-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/AAGGTTCCC/ZEN/TGTGCTTCACCATCTT/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Manf | 5′-TCACATTTTCACCAGCCACTA-3′ | 5′-CTTCGACACCTCATTGATGATCT-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/ACCGATTCT/ZEN/CTTTGCCTCTTGCTTCA/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Nov | 5′-AGATGAGACCCTGTGACCAG-3′ | 5′-AAATGACCCCATCGAACACA-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/CGCAGACCC/ZEN/CAACAACCAGACT/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Phc3 | 5′-GCCTTCATCCATTCTTTGCC-3′ | 5′-GCTTCATGTTCATTGCACTCAT-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/CCCTGAACT/ZEN/CATCTGCAACGTCCTG/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Pknox1 | 5′-CTGTTCTTAGATGTTTGCTCGTC-3′ | 5′-GTCCACTTCAGACATCAGATCA-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/TGCACGGCT/ZEN/CTGTTCTTCCAGG/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Rasl11a | 5′-CGACTACGAACCCAACACAG-3′ | 5′-AGAGAATCCACCATTTGACTGAG-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/ATAGCTGGT/ZEN/CCCCCTCCACATAGA/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Rps21 | 5′-GAACGTGGCCGAGGTTG-3′ | 5′-AGACAATTCCATCAGCCTTAGC-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/TCATCTGAC/ZEN/TCGCCCATCCTGC/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Rps27 | 5′-AGTTCTCCTCGCTCGCA-3′ | 5′-CCGTGGTGATTTATAGCATCC-3′ | 5′-/56-FAM/CCAGGCGCT/ZEN/TTTTCTTGTGTTTCCT/3IABkFQ/-3′ |
| Sdf2l1 | 5’-TCGCCGCTATCCAACAAC-3’ | 5’-CCCAGAACATCGGACTGTC-3’ | 5’-/56-FAM/TCATCACCC/ZEN/TCACCGTCTTCCC/3IABkFQ/-3’ |
| Sod3 | 5’-GGCAACTCAGAGGCTCTTC-3’ | 5’-GTAGCAAGCCGTAGAACAAGA-3’ | 5’-/56-FAM/TTTCCCTCT/ZEN/GGTGAAGTTCAGGCC/3IABkFQ/-3’ |
| Trem2 | 5’-GACCTCTCCACCAGTTTCTC-3’ | 5’-GCTTCAAGGCGTCATAAGTACA-3’ | 5’-/56-FAM/TCCCAAGCC/ZEN/CTCAACACCACG/3IABkFQ/-3’ |
| Trpc6 | 5’-CTGGCTCTCATATACTGGTGTG-3’ | 5’-TCAGCTGCATTCATGACGAG-3’ | 5’-/56-FAM/AGGAGGCTG/ZEN/CGTGTGCTACAAA/3IABkFQ/-3’ |
| Vstm2l | 5’-ACTACCTGGCACTTTTCCTG-3’ | 5’-ATCTCTACATCCTCGCCTGT-3’ | 5’-/56-FAM/CCGGACACG/ZEN/CACTCTTCACAGA/3IABkFQ/-3’ |
| Gapdh | 5’-AATGGTGAAGGTCGGTGTG-3’ | 5’-GTGGAGTCATACTGGAACATGTAG-3’ | 5’-/56-FAM/TGCAAATGG/ZEN/CAGCCCTGGTG/3IABkFQ/-3’ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyo, K.; Uchida, Y.; Nakano, R.; Kamijo, S.; Hosonuma, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Isobe, H.; Ishikawa, F.; Onimaru, H.; Yoshikawa, A.; et al. Intermittent Hypoxia Induces Cognitive Dysfunction and Hippocampal Gene Expression Changes in a Mouse Model of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157495
Miyo K, Uchida Y, Nakano R, Kamijo S, Hosonuma M, Yamazaki Y, Isobe H, Ishikawa F, Onimaru H, Yoshikawa A, et al. Intermittent Hypoxia Induces Cognitive Dysfunction and Hippocampal Gene Expression Changes in a Mouse Model of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157495
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyo, Kenta, Yuki Uchida, Ryota Nakano, Shotaro Kamijo, Masahiro Hosonuma, Yoshitaka Yamazaki, Hikaru Isobe, Fumihiro Ishikawa, Hiroshi Onimaru, Akira Yoshikawa, and et al. 2025. "Intermittent Hypoxia Induces Cognitive Dysfunction and Hippocampal Gene Expression Changes in a Mouse Model of Obstructive Sleep Apnea" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157495
APA StyleMiyo, K., Uchida, Y., Nakano, R., Kamijo, S., Hosonuma, M., Yamazaki, Y., Isobe, H., Ishikawa, F., Onimaru, H., Yoshikawa, A., Sakakibara, S.-I., Oguchi, T., Yokoe, T., & Izumizaki, M. (2025). Intermittent Hypoxia Induces Cognitive Dysfunction and Hippocampal Gene Expression Changes in a Mouse Model of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157495






