Abstract
The potent and selective ‘genetic zipper’ method for insect pest control consists of three essential components: an antisense DNA (the finder), its complementary mature rRNA or pre-rRNA of the pest (the target), and the host’s endogenous DNA-guided rRNase (the degrader). Although this approach has been validated, the spectrum of effective rRNA targets remains insufficiently explored. In this study, we report for the first time the insecticidal efficacy of a novel oligonucleotide insecticide, Eriola-11, which targets the mitochondrial 16S rRNA of the woolly apple aphid Eriosoma lanigerum Hausmann. We hypothesized that the antisense-mediated silencing of mitochondrial rRNA would impair aphid viability and lead to physiological disruptions associated with mitochondrial energy metabolism. Eriola-11 was applied either once or twice (with a 24 h interval) to aphid-infested plants, and aphid mortality was recorded over 14 days. Mitochondrial 16S rRNA expression levels were quantified using molecular assays, and the degradation kinetics of Eriola-11 were assessed in aphid tissue homogenates. Results showed significant insecticidal activity, with 67.55% mortality after a single treatment and 83.35% after two treatments. Treated aphids exhibited the loss of their characteristic white woolly wax covering, and mitochondrial 16S rRNA expression was reduced 0.66-fold relative to the control. Additionally, Eriola-11 was fully degraded by aphid DNases from tissue homogenates within 3 h, highlighting its rapid biodegradability. These findings establish mitochondrial 16S rRNA as a viable target for antisense insecticides and expand the catalogue of potential rRNA-based targets, offering a promising avenue for environmentally sustainable pest control strategies.
1. Introduction
The woolly apple aphid Eriosoma lanigerum Hausmann (Hemiptera: Aphididae) is a well-studied and economically important pest of apple trees, particularly in young orchards. This phloem-feeding insect induces the formation of hypertrophic galls on both the aerial and underground plant parts, leading to structural deformities and physiological stress [1]. Colonies that establish on roots are protected from pesticide applications and environmental fluctuations, thereby serving as reservoirs for above-ground reinfestations in subsequent growing seasons [2,3,4]. Aphid-induced galls impede sap flow and frequently rupture, creating nutrient-rich feeding sites and vulnerable entry points for fungal pathogens, especially since E. lanigerum preferentially settles on damaged tissues [1]. Severe infestations, particularly under organic production systems, can significantly reduce photosynthesis, impair plant health, hinder bud formation, and increase susceptibility to disease [5]. Moreover, the accumulation of honeydew encourages the growth of sooty mould, and the white woolly wax produced by the aphid also contaminates the fruit. Together, these factors reduce marketability and cause overall yield losses [4,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. As a result, E. lanigerum poses a major threat to sustainable apple production [15]. Therefore, efficient aphid control strategies are essential to minimize economic losses and ensure stable crop yields [16,17,18].
Integrated pest management (IPM) strategies in apple orchards increasingly emphasize biological control as an alternative to synthetic insecticides. The reduction in the use of broad-spectrum insecticides, such as carbamates and organophosphates, has facilitated the resurgence of natural enemies, particularly the parasitoid Aphelinus mali, a cornerstone species in biological control programmes targeting E. lanigerum [19,20]. Nevertheless, chemical insecticides remain the primary tool for pest management in many agricultural systems worldwide, including apple orchards [21,22,23]. However, excessive reliance on such chemicals has resulted in undesirable consequences, including pesticide resistance, non-target effects, and environmental pollution [24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. These challenges underscore the need for safer and more targeted pest control alternatives.
Among these emerging alternatives, oligonucleotide insecticides represent a promising and environmentally compatible solution. The ‘genetic zipper’ method based on short contact-unmodified antisense DNA biotechnology (CUADb) has gained attention for its high specificity and minimal off-target effects [32]. This approach utilizes antisense oligonucleotides designed to complement conserved regions of mature rRNA and/or pre-rRNA, thereby inhibiting protein biosynthesis. These oligonucleotide insecticides (referred to as “finders”) bind with high affinity and specificity to the target rRNA (the targets), recruiting DNA-guided rRNases (the degraders), like RNase H1, leading to the degradation of target rRNA in the RNA–DNA duplex. Given that ribosomal RNA (rRNA) constitutes approximately 80% of the total cellular RNA, in contrast to just ~5% for mRNAs [33], rRNA presents a high-yield target with a strong signal-to-noise ratio (~105:1) and considerable variability, reducing the likelihood of off-target effects in non-target organisms [33,34,35]. Moreover, more than 60% of all energy is spent on the production and maintenance of ribosomes [36].
Importantly, research on Sternorrhynchan insects has demonstrated that oligonucleotide insecticides can induce both the upregulation and downregulation of target genes through a mechanism termed DNA containment (DNAc). This mechanism operates in two sequential steps: The first involves the arrest of target mature rRNA and/or pre-rRNA (formation of DNA–rRNA duplex), leading to a functional block of ribosomes and triggering the compensatory overexpression of rRNA via rDNA transcription. The second step of the DNA containment mechanism involves the degradation of the arrested mature rRNA and/or pre-rRNA via DNA-guided rRNase, like RNase H1 [37].
The CUADb strategy offers several important advantages. Oligonucleotide insecticides (briefly referred to as olinscides or DNA insecticides) degrade naturally in the environment, minimizing the risk of accumulation and resistance development. Current formulations of CUADb-based olinscides have demonstrated promising results, with mortality rates of 80–90% in various pest species within 3–14 days after a single treatment using a 100 ng/μL solution [38]. Previous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of CUADb-based insecticides targeting nuclear rRNAs, such as 28S and 18S rRNA, in multiple Sternorrhyncha pests, including Unaspis euonymi, Dynaspidiotus britannicus, Icerya purchasi, Ceroplastes japonicus, Aonidia lauri, Coccus hesperidum, and Pseudococcus viburni [38,39]. In addition, olinscides targeting internal transcribed spacer (ITS2) regions of pre-rRNA have shown effectiveness against Macrosiphoniella sanborni, Schizolachnus pineti, and Trioza alacris [32,34,40]. Even acaricidal effects have been observed against Tetranychus urticae [41]. Collectively, these findings suggest that CUADb may be applicable to 10–15% of all insect pest species with appropriate target selection and sequence optimization [34].
A promising new direction in this technology is the targeting of mitochondrial rRNAs—16S rRNA (~1140 nt) and 12S rRNA (~600 nt). Mitochondria are essential organelles responsible for adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation recruiting the ATP synthase complex by harnessing the proton gradient created by the electron transport chain, and are central to cellular bioenergetics [42]. While most mitochondrial proteins are encoded by nuclear DNA and synthesized in the cytoplasm, a few subunits of the ATP synthase complex are coded by mitochondrial DNA and synthesized by mitochondrial ribosomes, making rRNA a functionally very important target. Notably, our recent study on differential gene expression (DGE) analysis of C. hesperidum (4th day after contact application of oligonucleotide insecticide Coccus-11 targeting 28S rRNA) showed that during DNAc, most of investigated kinases are downregulated causing ‘kinase disaster’ in insect cells (including mTOR, a serine/threonine protein kinase playing crucial roles in the biogenesis of both cellular and mitochondrial ribosomes through the mTORC1 complex), while proteins from the mitochondrial ATP synthase complex and enzymes of the mitochondrial complex crucial for maintaining cellular energy (phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (mitochondrial form), cytochrome c oxidase, Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone), succinate-CoA ligase, etc.) are upregulated, indicating the deficiency of cellular energy caused by oligonucleotide insecticide Coccus-11 [37,43]. Thus, mitochondrial rRNAs, 16S and 12S, are essential components of the mitochondrial ribosome and are present in high copy numbers, making them attractive and previously untapped targets for CUADb-based insecticides. Targeting mitochondrial rRNA can induce the systemic collapse of energy metabolism, thereby enhancing insecticidal efficacy.
In this study, we explore for the first time the insecticidal efficacy of a CUADb oligonucleotide—Eriola-11, designed to target the mitochondrial 16S rRNA of E. lanigerum. This work expands the utility of CUADb approach to include mitochondrial targets and evaluates the potential of Eriola-11 as a next-generation biotechnological tool for the sustainable management of this economically important pest.
2. Results
2.1. The Olinscide Eriola-11 Shows Pronounced Insecticidal Effects and Changes Morphology of E. lanigerum After Contact Application
The number of E. lanigerum individuals on apple shoots before a single treatment was 41.6 ± 2.8 individuals per 10 cm2 shoot (Figure 1). It was found that on the 3rd, 7th, and 14th days, the mortality of pest individuals after the use of Eriola-11 was 63.57 ± 1.79%, 67.42 ± 1.94%, and 67.55 ± 1.47%, respectively (p < 0.05) (Figure 1A). The characteristic white woolly wax of this species disappeared as a result of treatment with the olinscide Eriola-11, which is an interesting finding (Figure 1B).
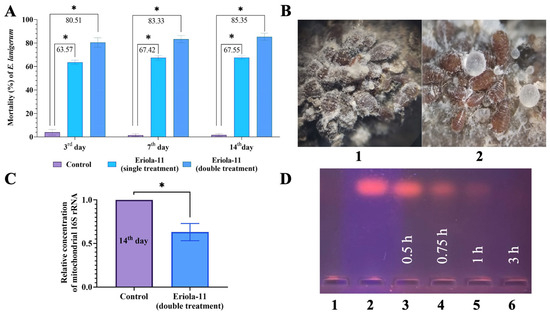
Figure 1.
Experiments with oligonucleotide insecticide Eriola-11 on pest E. lanigerum. (A) Olinscide Eriola-11 shows pronounced insecticidal effect after contact application; Eriola-11—single treatment; Eriola-11—double treatment (with a 24 h interval); * is marked when p < 0.05. (B) Olinscide Eriola-11 changes morphology of E. lanigerum: E. lanigerum on an apple tree shoot (5× magnification) before (1) and after (2) treatment with Eriola-11; (C) Olinscide Eriola-11 significantly decreases the concentration of the mitochondrial 16S rRNA; expression of 16S rRNA was analyzed via RT-PCR; control was taken as 1 (100%); * is marked when p < 0.05. (D) Fast biodegradability of olinscide Eriola-11 via tissue homogenate deoxyribonucleases: 1—pure tissue homogenate of insects; 2—start (pure Eriola-11, 4 μg); 3—0.5 h; 4—0.75; 5—1 h; and 6—3 h.
The number of E. lanigerum individuals (larvae) before the double treatment with Eriola-11 averaged 132.3 ± 5.5 individuals per 10 cm2 shoot (Figure 1(B1)). After the treatment, dead individuals had a changed body colour (became dark grey and black, normally brown or red-brown) and completely lost their species-characteristic white woolly wax (Figure 1(B2)). The effectiveness of the first treatment averaged 66.18 ± 3.87% (p < 0.05). After the double treatment, viable individuals of E. lanigerum were found in areas of bark cracking, as well as under a layer of dead individuals. The effectiveness of the double treatment (with a 24 h interval) of olinscide Eriola-11 was 80.51 ± 4.03%, 83.33 ± 3.02%, and 85.35 ± 3.04% on the 3rd, 7th, and 14th days, respectively. In the water-treated control group, mortality comprised 11.5 ± 4.1%, 11.9 ± 3.9%, and 12.4 ± 3.9 on the 3rd, 7th, and 14th days, respectively (Figure 1A). Thus, double treatment with Eriola-11 (85.35 ± 3.04% mortality) was more efficient than single treatment by 18% (67.55 ± 1.47% mortality) at the end of the experiment (14th day).
2.2. Olinscide Eriola-11 Significantly Decreases the Concentration of the Mitochondrial 16S rRNA
Also, we evaluated the specificity of action of the olinscide Eriola-11 by studying the concentration of the target mitochondrial 16S rRNA. A decrease in the expression of the target gene is the gold standard for proof of the specificity of action for antisense oligonucleotides [44] and is also the characteristic feature of the second step of the DNA containment mechanism [39]. The expression of the mitochondrial 16S rRNA of E. lanigerum was analyzed on the 14th day after double treatment with olinscide Eriola-11. After treatment with the olinscide Eriola-11, the expression of the target mitochondrial 16S rRNA of the woolly apple aphid was significantly reduced 0.66-fold (p < 0.05) relative to the water-treated control group (Figure 1C).
2.3. Fast Biodegradability of Olinscide Eriola-11 via Tissue Homogenate Deoxyribonucleases
An analysis of the nuclease activity of woolly apple aphid tissue homogenates (Figure 1D) showed that within three hours, tissue DNases completely degraded the Eriola-11. The data obtained indicate the high biodegradability potential of such insecticides in ecosystems after their action on pests.
3. Discussion
This study aimed to explore the potential of mitochondrial 16S rRNA as a target for DNA-based insecticides. Our results strongly support the hypothesis that unmodified antisense oligonucleotides can effectively disrupt insect physiology by targeting mitochondrial rRNA. Specifically, we observed that the oligonucleotide insecticide Eriola-11, designed to target mitochondrial 16S rRNA in E. lanigerum, produced a significant insecticidal effect. By day 14, the mortality rate reached 67.55% after a single treatment and increased to 85.32% following a double treatment. These findings align with prior research demonstrating the efficacy of antisense oligonucleotides as insecticides against various pest species, including aphids [32,34,40]. The substantial mortality observed in this study underscores the potential of mitochondrial rRNA as a novel and effective target for pest control.
One of the key findings in this study was the enhanced efficacy of Eriola-11 when applied as a double treatment compared to a single application. The double treatment resulted in a higher mortality rate, which suggests that repeated exposure to the oligonucleotide insecticide enhances its insecticidal effect. This outcome is consistent with previous studies, such as Puzanova et al. [40], which also demonstrated that double treatments with oligonucleotide insecticide Macsan-11 improved the control of chrysanthemum aphid M. sanborni. The increased efficacy observed with double treatments may be attributed to the prolonged interaction of the oligonucleotide with the target rRNA, allowing for the greater disruption of essential mitochondrial processes. Therefore, our results suggest that treatment regimens using oligonucleotide insecticides like Eriola-11 should be optimized, potentially incorporating repeated applications to improve pest control outcomes.
Further supporting the effectiveness of Eriola-11 was the observed reduction in mitochondrial 16S rRNA expression in treated insects. Fourteen days post treatment, the target rRNA was reduced 0.66-fold compared to the water-treated control. This reduction indicates that the oligonucleotide successfully bound to its target rRNA and facilitated its degradation. This finding is consistent with the DNAc mechanism of action of antisense oligonucleotides in insects, which are known to bind to complementary RNA sequences and induce degradation through DNA-guided rRNase activity, including RNase H1 activity [37,39]. Notably, our recent DGE study on C. hesperidum after the application of oligonucleotide insecticide Coccus-11 (targeting 28S rRNA) showed that RNase H1 is also significantly upregulated during DNAc. RNase H1 functions independently of the cell cycle and cleaves RNA in RNA–DNA hybrids, including those formed between DNA and rRNA [37]. Thus, the observed reduction in 16S rRNA confirms the olinscide’s mode of action and its capacity to disrupt mitochondrial protein synthesis, which is essential for insect survival.
Another notable observation was the loss of the characteristic woolly white wax covering of E. lanigerum after treatment with Eriola-11. This change may be linked to the disruptions in mitochondrial biosynthesis, which is essential for the cellular production of energy. We assume that woolly white wax coverings serve as an energy storage substance [45], which may be utilized in response to the energy deficiency caused by mitochondrial dysfunction. The DGE study on C. hesperidum showed that during DNAc enzymes involved in the production of energy from lipids, namely triacylglycerol lipase (PNLIP), lysophospholipase III (LYPLA3), lysosomal acid lipase/cholesteryl ester hydrolase (LIPA), secretory phospholipase A2 (SPLA2), and phospholipase/carboxylesterase (IPR029058), were significantly upregulated. At the same time, crucial glycolytic enzymes were downregulated (pyruvate kinase, aldolase, and phosphofructokinase-1), while none of the glycolytic enzymes was upregulated, indicating a switch in energy synthesis from carbohydrates to lipids [43]. Additionally, some authors suggest that the primary role of secreted wax is to prevent the aphids from becoming contaminated by their own honeydew [46]. Therefore, wax-less aphids may become more vulnerable to honeydew exposure following Eriola-11 treatment. This loss of wax in our study suggests that the mitochondrial dysfunction caused by oligonucleotide targeting may interfere with the biosynthetic processes crucial for protective wax production.
The rapid biodegradation of Eriola-11 was another significant finding of this study. We observed that the oligonucleotide was completely degraded within three hours in the homogenate of E. lanigerum tissues. This degradation rate contrasts sharply with that of conventional chemical insecticides, which can persist in the environment for months or years [47]. The rapid biodegradation of Eriola-11 highlights its environmental safety, as it will be broken down by ubiquitous nucleases in ecosystems. This characteristic is particularly important for sustainable pest control strategies, where long-term environmental contamination by chemical pesticides remains a concern. The observed biodegradability of Eriola-11 is consistent with previous studies on oligonucleotide insecticides, which show faster degradation compared to synthetic chemicals [47]. This makes oligonucleotide insecticides a compelling alternative for environmentally responsible pest control.
In terms of practical application, the use of oligonucleotide insecticides such as Eriola-11 offers several advantages over traditional chemical insecticides. Firstly, oligonucleotide insecticides are highly specific, targeting only the pest species of interest without affecting non-target organisms, including beneficial insects [32]. This specificity minimizes ecological impact, making oligonucleotide insecticides a more environmentally friendly alternative. Additionally, the affordability of DNA insecticide production, facilitated by automatic DNA synthesizers, makes the large-scale production of these insecticides feasible [47]. The potential for the mass production of oligonucleotide insecticides opens up new possibilities for their widespread use in pest management, particularly in the context of IPM strategies [48].
Overall, our study demonstrates that mitochondrial 16S rRNA is a promising target for DNA-based insecticides, and that the oligonucleotide insecticide Eriola-11 shows substantial promise for pest control. Its high efficacy, environmental safety, and specificity highlight its potential as a viable alternative to conventional chemical insecticides. Future research should focus on refining treatment regimens, testing the effectiveness of oligonucleotide insecticides on a broader range of pests, and evaluating their integration into multi-faceted IPM strategies.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect
The aphid E. lanigerum (Hemiptera: Aphididae) was collected from apple trees (Malus domestica L.) in the Nikita Botanical Garden, Crimea (44°30′41.9″ N latitude and 34°13′57.3″ E) between July and October 2024. The degree of harmfulness of the E. lanigerum was determined by examining the bark, branches, petioles, bases of buds, and stems of the apple trees. Aphids were identified based on morphological characteristics; adult individuals (80%) and first instar nymphs (20%) were used directly in all experiments.
4.2. DNA Synthesis and Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Oligonucleotides
Oligonucleotides were synthesized using an automated DNA synthesizer ASM-800ET (BIOSSET, Novosibirsk, Russia) based on standard phosphoramidite chemistry on a universal solid support UnyLinker 500 Å (ChemGenes, Wilmington, MA, USA). Cleavage and deprotection were performed by incubating the oligonucleotides overnight at 55 °C in concentrated ammonia solution. The reaction mixture was subsequently filtered and evaporated using a vacuum rotary evaporator (Heidolph Instruments GmbH & Co. KG, Schwabach, Germany). The resulting residue was dissolved in deionized water (Merck Millipore, Molsheim, France) to the desired concentration, which was determined using the spectrophotometer NanoDrop Lite (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
The molecular mass of the synthesized DNA sequences was determined via MALDI-TOF analysis mass spectrometry. Measurements were conducted in the positive-ion mode using 3-hydroxypicolinic acid as the matrix at a 2:1 matrix-to-analyte ratio on a LaserToF LT2 Plus mass spectrometer (Scientific Analysis Instruments, Manchester, UK). The theoretical m/z values were calculated using ChemDraw 18.0 software [49] (CambridgeSoft, Cambridge, MA, USA). All synthesized oligonucleotides were confirmed to match their expected structures. The measured m/z values differed from the theoretical values by no more than 10 units (Table 1).

Table 1.
Results of the analysis of synthesized oligonucleotides using the MALDI-TOF method.
4.3. Application of Eriola-11 as a Contact Insecticide
E. lanigerum was treated using a hand sprayer containing a solution of the oligonucleotide-based insecticide Eriola-11 (5′-AAT-ACT-GCA-GC-3′), which targets mitochondrial 16S rRNA (Figure 2). The solution was prepared in nuclease-free deionized water at a concentration of 100 ng/μL (1 mg per m2 of leaves with the pest). A water-treated group served as the control. A total of 1350 aphids (single and double treatment, 285 aphids and 1065 aphids, respectively), including first instar nymphs and adults, were treated across three independent experimental replicates. Aphid counts were recorded before treatment and on the 3rd, 7th, and 14th days post treatment. Mortality was assessed using a Micromed MS-4-ZOOM LED microscope with 0.75x-5x zoom lens (Micromed, Saint Petersburg, Russia).
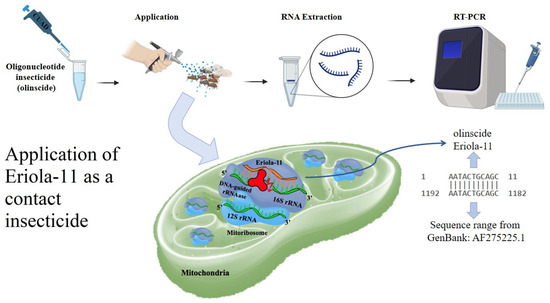
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the application and mode of action of Eriola-11 as a contact insecticide against E. lanigerum. Aphids were treated using a hand sprayer containing Eriola-11 (5′-AAT-ACT-GCA-GC-3′), an oligonucleotide-based insecticide designed to target mitochondrial 16S rRNA through a ‘genetic zipper’ mechanism, in which Eriola-11 serves as the finder strand, 16S rRNA as the target, and DNA-guided rRNase as the degrader. The solution was prepared in nuclease-free deionized water at a concentration of 100 ng/μL. A total of 1350 aphids, including first instar nymphs and adults, were treated across three independent replicates, with water-treated aphids serving as the control. Mortality was assessed on 3rd, 7th, and 14th day post treatment using a Micromed MS-4-ZOOM LED microscope. RNA was extracted from aphid samples, and RT-PCR analysis was conducted to verify the uptake and molecular activity of Eriola-11.
4.4. Reverse Transcription and Real-Time PCR (RT-PCR) for 16S rRNA Quantification
Several studies have determined that ribosomal RNA represents the most stable reference genes, providing an accurate and reproducible real-time PCR assay [50,51,52]. On the 14th day, the total RNA was extracted using 50 E. lanigerum individuals from the experimental group and water-treated control group following treatment using the ExtractRNA reagent [53] (Evrogen, Moscow, Russia). Reverse transcription was performed using the MMLV Reverse Transcriptase kit [54] (Evrogen, Moscow, Russia) with the Eriola-R primer (200 ng per reaction). cDNA synthesis was carried out in a 20 μL reaction volume at 40 °C for 60 min, followed by enzyme inactivation at 70 °C for 10 min, using a LightCycler®96 Real-Time PCR System (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Primer sequences used for real-time PCR amplification of E. lanigerum 16S rRNA.
Real-time PCR was performed using SYBR Green I dye to amplify and quantify cDNA. The reaction mix included 3 μL of cDNA, 5X qPCRmix-HS SYBR master mix (Evrogen, Moscow, Russia), and gene-specific primers (Table 2). Amplification was conducted under the following thermal profile: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 10 min, followed by 45 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 10 s, annealing at 50 °C for 15 s, and elongation at 72 °C for 10 s [55]. All reactions were performed in triplicate. Melt curve analysis was used to confirm the specificity of amplification and absence of the non-specific products.
4.5. Analysis of DNase Activity
DNase activity in E. lanigerum tissue homogenates was analyzed by incubating 5 mg of insect tissue (ca. 5 insect individuals) in 10 μL of Milli-Q deionized water (Millipore, Molsheim, France), followed by the addition of 10 μL of Eriola-11 at a concentration of 400 ng/μL. The homogenate was incubated at 27 °C in a solid-state thermostat for 30, 45, 60, and 180 min. Subsequently, samples were heated at 90 °C for 60 min to denature protein and centrifuged at 12,000× g for 1 min. After that, 10 µL of the homogenate with Eriola-11 was mixed with 3 µL of 4X Gel Loading Dye, Blue (Evrogen, Moscow, Russia) and loaded onto a 1.8% agarose gel prepared with standard TBE buffer and stained with ethidium bromide (EB) (10–15 μL of EB at a concentration of 10 mg/mL per 55 mL of agarose gel). Electrophoresis was carried out at 10 V/cm for 40 min using a BlueMarine electrophoresis system (SERVA Electrophoresis GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany) and Mini-300 power supply (Major Science, Taoyuan City, Taiwan). DNA bands were visualized under a transilluminator (Vilber Lourmat, Marne-la-Vallée, France) [56].
4.6. Statistical Analyses
The mean and standard error of the mean (SE) were calculated using Student’s t-test. Control was taken as 1 (100%) for gene expression analysis. The graph shows the mean values and standard errors for the three replicates compared to the water-treated control group (Figure 1A,C). All above-mentioned calculations were performed using GraphPad Prism 9 software [57] (GraphPad Software Inc., Boston, MA, USA).
5. Conclusions
The CUADb-based ‘genetic zipper’ method offers a simple and efficient approach for pest control, requiring the synthesis of a complementary DNA strand (oligonucleotide insecticide) targeting mature rRNA and/or pre-rRNA, such as mitochondrial 16S rRNA. These insecticides can be applied topically, and the method is highly adaptable through tools like the DNAInsector web application (dnainsector.com). This study demonstrates that the Eriola-11 oligonucleotide insecticide effectively targets E. lanigerum, causing significant insect mortality and the loss of its protective waxy covering (possible compensation of decrease in ATP production via mitochondria through consumption of waxes as energy storage substances). The insecticide biodegrades completely within three hours in insect tissue homogenates, highlighting its rapid environmental degradation. The affordability of DNA insecticide production and their scalability through automatic DNA synthesizers and liquid phase synthesis make CUADb-based oligonucleotide insecticides promising for large-scale pest control. These DNA-based solutions offer a competitive alternative to traditional chemical insecticides, with the potential to address microevolution in pests. Moreover, the biodegradation of these insecticides is much faster than with conventional chemicals, posing a lower environmental risk. CUADb shows promise for creating a sustainable, xenobiotic-free future in agriculture, positioning oligonucleotide pesticides as prospective pest control agents.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.O.; methodology, O.A., A.D., T.R. and N.G.; software, N.G. and A.D.; validation, V.O.; formal analysis, V.O. and N.G.; investigation, V.O., O.A., A.D., T.R. and N.G.; resources, V.O.; data curation, V.O.; writing—original draft preparation, V.O., K.L., O.A., A.D., T.R., J.A. and N.G.; writing—review and editing, V.O., K.L., O.A., A.D., T.R., J.A. and N.G.; visualization, J.A. and N.G.; supervision, V.O. and N.G.; project administration, V.O. and N.G.; funding acquisition, V.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research obtained funding from the Russian Science Foundation No. 25-16-20070, https://rscf.ru/project/25-16-20070/ (accessed on 27 June 2025).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We thank our many colleagues, too numerous to name, for the technical advances and lively discussions that have prompted us to write this article. We apologize to the many colleagues whose work has not been cited. Experiments were carried out at the Molecular Genetics and Biotechnologies Lab created within the framework of a state assignment V.I. Vernadsky Crimean Federal University for 2024 and the planning period of 2024–2026 No. FZEG-2024–0001. We are very much indebted to all anonymous reviewers and our colleagues from the Lab for DNA technologies, PCR analysis, and the creation of DNA insecticides (V.I. Vernadsky Crimean Federal University, Institute of Biochemical Technologies, Ecology and Pharmacy, Department of General Biology and Genetics), and OLINSCIDE BIOTECH LLC. for the valuable comments on our manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Damavandian, M.R.; Pringle, K.L. The field biology of subterranean populations of the woolly apple aphid, Eriosoma lanigerum (Hausmann) (Hemiptera: Aphididae), in South African apple orchards. Afr. Entomol. 2007, 15, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Chandel, R.S.; Sharma, P.L. Spatial distribution and interaction of Eriosoma lanigerum and Aphelinus mali on apple under dry- temperate conditions of India. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 88, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.M.; Yang, Z.S.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Q.M.; Zhou, H.X. Resistance performance of four principal apple cultivars to woolly apple aphid, Eriosoma lanigerum (Hemiptera: Pemphigidae), by simulated seasonal temperature in northern China. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2021, 15, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayimov, N.; Anorbayev, A.; Bababekov, K. Biological properties and influencing factors of woolly apple aphid (Eriosoma lanigerum Hausm) in the condition of orchard agrobiocenosis. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 244, 02009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Kundoo, A.A.; Nissar, M.; Mushtaq, M. Sucking Pests of Temperate Fruits. In Sucking Pests of Crops; Omkar, Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokwe, N.F.; Malan, A.P. Laboratory bioassays to determine susceptibility of woolly apple aphid, Eriosoma lanigerum (Hausmann) (Hemiptera: Aphididae), to entomopathogenic nematodes. Afr. Entomol. 2017, 25, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, A.H.; Spooner-Hart, R.N.; Vickers, R.A. Abundance and natural control of the woolly aphid Eriosoma lanigerum in an Australian apple orchard IPM program. BioControl 2005, 50, 271–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokwe, N.F.; Malan, A.P. Woolly apple aphid, Eriosoma lanigerum (Hausmann), in South Africa: Biology and management practices, with focus on the potential use of entomopathogenic nematodes and fungi. Afr. Entomol. 2016, 24, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovičić, I. Eriosoma lanigerum (Woolly Aphid); CABI Compendium: Oxford, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Emden, H.F.; Harrington, R. Aphids as Crop Pests; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J. The Peach Potato Aphid (Myzus persicae): Ecology and Management, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; p. 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, K.M.; Clavijo McCormick, A.; Jones, T.; Garbuz, S.; Minor, M. Honeydew deposition by the giant willow aphid (Tuberolachnus salignus) affects soil biota and soil biochemical properties. Insects 2020, 11, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, P. Observation on the Influence of Apple Woolly Aphid (Eriosoma lanigerum Hausm.) on Vegetative Parameters of Grafted Plants in Container Production. Proc. Bulg. Acad. Sci. 2024, 77, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ali, J.; Ahmad, B.; Yang, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, J.; Alam, A.; Khan, K.; Ghramh, H.; Rahman, N.; et al. Garlic as a companion plant for suppressing Myzus persicae infestation in Brassica rapa. Crop Prot. 2025, 187, 106970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alins, G.; Lordan, J.; Rodríguez-Gasol, N.; Arnó, J.; Peñalver-Cruz, A. Earwig Releases Provide Accumulative Biological Control of the Woolly Apple Aphid over the Years. Insects 2023, 14, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, W.H.; Akhter, M.S.; Nakahara, K.; Maruthi, M.N. Effect of aphid biology and morphology on plant virus transmission. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, B.; Nagy, C.; Fountain, M.T. Organic Control Strategies for Use in IPM of Invertebrate Pests in Apple and Pear Orchards. Insects 2021, 12, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šarac, V.; Narandžić, T.; Rodić, V.; Popović, B.M.; Uka, D.; Tomaš Simin, M.; Ljubojević, M. Harnessing Koelreuteria paniculata Seed Extracts and Oil for Sustainable Woolly Apple Aphid Control. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, J.; Alegre, S.; Gatius, F.; Sarasúa, M.J.; Alins, G. Woolly apple aphid Eriosoma lanigerum Hausmann ecology and its relationship with climatic variables and natural enemies in Mediterranean areas. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2015, 105, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangels, E.; Alhmedi, A.; Akkermans, W.; Bylemans, D.; Belien, T. Towards a Knowledge-Based Decision Support System for Integrated Control of Woolly Apple Aphid, Eriosoma lanigerum, with Maximal Biological Suppression by the Parasitoid Aphelinus mali. Insects 2021, 12, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stehle, S.; Schulz, R. Agricultural insecticides threaten surface waters at the global scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5750–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, J.R.; Dachbrodt-Saaydeh, S.; Kudsk, P.; Messéan, A. Toward a reduced reliance on conventional pesticides in European agriculture. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryalls, J.M.W.; Garratt, M.P.D.; Spadaro, D.; Mauchline, A.L. The benefits of integrated pest management for apple depend on pest type and production metrics. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1321067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, I.; El-Kady, M.M.; Arora, C.; Sundararajan, M.; Maiti, D.; Khan, A. A review on the fatal impact of pesticide toxicity on environment and human health. In Global Climate Change; Singh, S., Singh, P., Rangabhashiyam, S., Srivastava, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 361–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punniyakotti, P.; Vinayagam, S.; Rajamohan, R.; Priya, S.D.; Moovendhan, M.; Sundaram, T. Environmental Fate and Ecotoxicological Behaviour of Pesticides and Insecticides in Non-Target Environments: Nanotechnology-Based Mitigation Strategies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffia, A.; Marra, F.; Canino, F.; Battaglia, S.; Mallamaci, C.; Oliva, M.; Muscolo, A. Humic Substances from Waste-Based Fertilizers for Improved Soil Fertility. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.F.; Ahmad, F.A.; Alsayegh, A.A.; Zeyaullah, M.; AlShahrani, A.M.; Muzammil, K.; Saati, A.A.; Wahab, S.; Elbendary, E.Y.; Kambal, N.; et al. Pesticides impacts on human health and the environment with their mechanisms of action and possible countermeasures. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktar, M.W.; Sengupta, D.; Chowdhury, A. Impact of pesticides use in agriculture: Their benefits and hazards. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Sohail, M.; Hussain Rind, K.; Habib, S.S. Agrochemical contamination and fish health: Eco-toxicological impacts and mitigation strategies. Chem. Ecol. 2025, 41, 959–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khursheed, A.; Rather, M.A.; Jain, V.; Rasool, S.; Nazir, R.; Malik, N.A.; Majid, S.A. Plant based natural products as potential ecofriendly and safer biopesticides: A comprehensive overview of their advantages over conventional pesticides, limitations and regulatory aspects. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 173 Pt A, 105854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarević-Pašti, T.; Milanković, V.; Tasić, T.; Petrović, S.; Leskovac, A. With or Without You?—A Critical Review on Pesticides in Food. Foods 2025, 14, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberemok, V.V.; Novikov, I.A.; Yatskova, E.V.; Bilyk, A.I.; Sharmagiy, A.K.; Gal’chinsky, N.V. Potent and selective ‘genetic zipper’ method for DNA-programmable plant protection: Innovative oligonucleotide insecticides against Trioza alacris Flor. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, A.F.; Lee, E.S. Non-coding RNA: What is functional and what is junk? Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberemok, V.V.; Puzanova, Y.V.; Gal’chinsky, N.V. The ‘genetic zipper’ method offers a cost-effective solution for aphid control. Front. Insect Sci. 2024, 4, 1467221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.L.; Münch, P.C.; Mreches, R.; McHardy, A.C. Rapid and accurate identification of ribosomal RNA sequences via deep learning. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szaflarski, W.; Leśniczak-Staszak, M.; Sowiński, M.; Ojha, S.; Aulas, A.; Dave, D.; Malla, S.; Anderson, P.; Ivanov, P.; Lyons, S.M. Early rRNA processing is a stress-dependent regulatory event whose inhibition maintains nucleolar integrity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 1033–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Gal’chinsky, N.; Sweta, V.; Negi, N.; Filatov, R.; Chandel, A.; Ali, J.; Oberemok, V.; Laikova, K. Perspectives of RNAi, CUADb and CRISPR/Cas as Innovative Antisense Technologies for Insect Pest Control: From Discovery to Practice. Insects 2025, 16, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberemok, V.V.; Laikova, K.V.; Gal’chinsky, N.V. Contact unmodified antisense DNA (CUAD) biotechnology: List of pest species successfully targeted by oligonucleotide insecticides. Front. Agron. 2024, 6, 1415314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal’chinsky, N.V.; Yatskova, E.V.; Novikov, I.A.; Sharmagiy, A.K.; Plugatar, Y.V.; Oberemok, V.V. Mixed insect pest populations of Diaspididae species under control of oligonucleotide insecticides: 3′-end nucleotide matters. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 200, 105838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puzanova, Y.V.; Novikov, I.A.; Bilyk, A.I.; Sharmagiy, A.K.; Plugatar, Y.V.; Oberemok, V.V. Perfect complementarity mechanism for aphid control: Oligonucleotide insecticide macsan-11 selectively causes high mortality rate for Macrosiphoniella sanborni Gillette. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrilova, D.; Grizanova, E.; Novikov, I.; Laikova, E.; Zenkova, A.; Oberemok, V.; Dubosvkiy, I. Antisense DNA acaricide targeting pre-rRNA of two-spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae as efficacy-enhancing agent of fungus Metarhizium robertsii. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2025, 211, 108297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, G.M. Mitochondria. In The Cell: A Molecular Approach, 2nd ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2000. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9896/ (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Oberemok, V.V.; Gal’chinsky, N.V.; Novikov, I.A.; Sharmagiy, A.K.; Yatskova, E.V.; Laikova, E.V.; Plugatar, Y. rRNA-specific antisense DNA and dsDNA trigger rRNA biogenesis and cause potent insecticidal effect on insect pest C. hesperidum L. bioRxiv 2024, 10, 618468. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, N.; Stein, C.A. Antisense oligonucleotides: Basic concepts and mechanisms. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 347–355. [Google Scholar]
- Britannica. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/lipid/Waxes (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Moss, R.; Jackson, R.R.; Pollard, S.D. Mask of wax: Secretions of wax conceal aphids from detection by spider’s eyes. N. Z. J. Zool. 2006, 33, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberemok, V.V.; Laikova, K.V.; Andreeva, O.A.; Gal’chinsky, N.V. Biodegradation of insecticides: Oligonucleotide insecticides and double-stranded RNA biocontrols paving the way for eco-innovation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1430170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.; Jangra, S.; Ghosh, A. Advances in Antisense Oligo Technology for Sustainable Crop Protection. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2024, 43, 405–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, N.M.; Yoder, R.J.; Callam, C.S. Incorporating Chemical Structure Drawing Software throughout the Organic Laboratory Curriculum. J. Chem. Educ. 2019, 96, 2638–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Rao, M.; Sheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Du, W.; Hao, H.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Z.; et al. Identification of Valid Housekeeping Genes for Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analysis of Collapsed Lung Tissues of Neonatal Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer-Derived Cattle. Cell Reprogram. 2015, 17, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebouças, E.D.L.; Costa, J.J.D.N.; Passos, M.J.; Passos, J.R.D.S.; Hurk, R.V.D.; Silva, J.R.V. Real time PCR and importance of housekeepings genes for normalization and quantification of mRNA expression in different tissues. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2013, 56, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paule, M.R.; White, R.J. Transcription by RNA polymerases I and III. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 1283–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, D.C.; Ares, M., Jr.; Hannon, G.J.; Nilsen, T.W. Purification of RNA using TRIzol (TRI reagent). Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2010, 2010, pdb.prot5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arezi, B.; Hogrefe, H. Novel mutations in Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus reverse transcriptase increase thermostability through tighter binding to template-primer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khehra, N.; Padda, I.S.; Swift, C.J. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) [Updated 6 March 2023]. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK589663/ (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Smith, D.R. Agarose gel electrophoresis. Methods Mol. Biol. 1993, 18, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appling, D.R. Prism 4 GraphPad Software, Inc. 5755 Oberlin Drive, #110, San Diego, CA, 92121. www.graphpad.com. See web site for pricing information. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 10482. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).