Enhanced Methodology for Peptide Tertiary Structure Prediction Using GRSA and Bio-Inspired Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
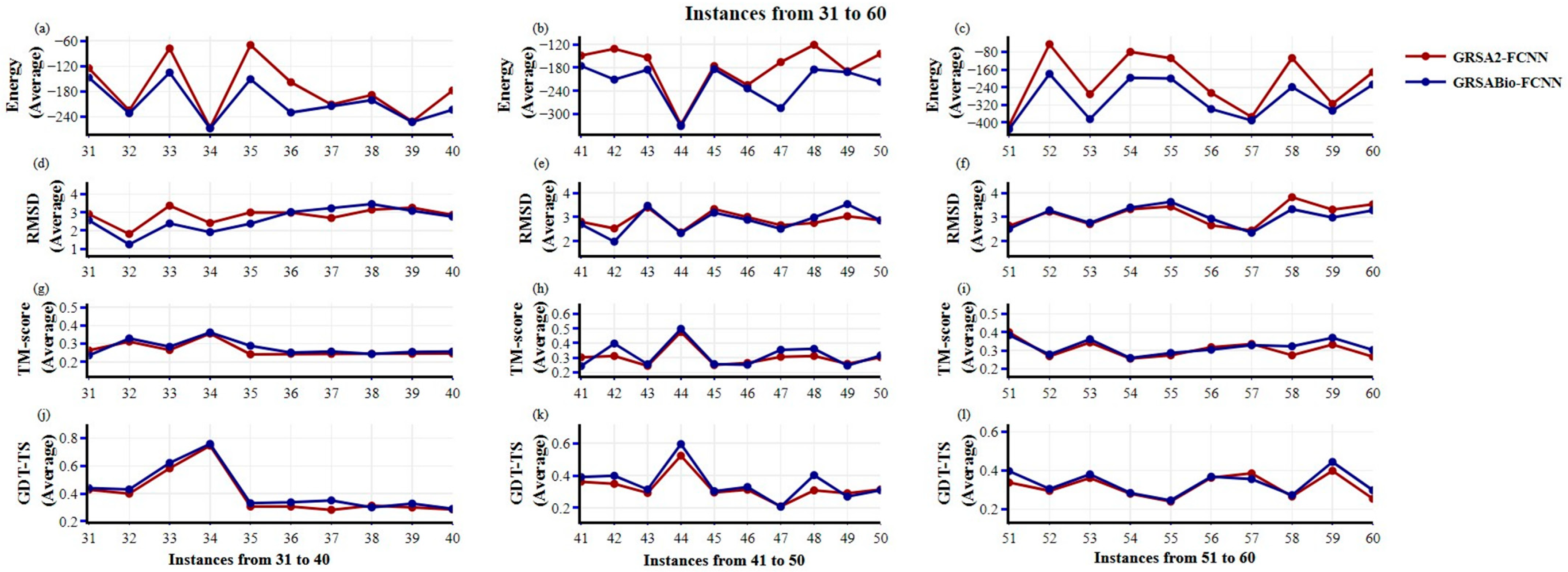
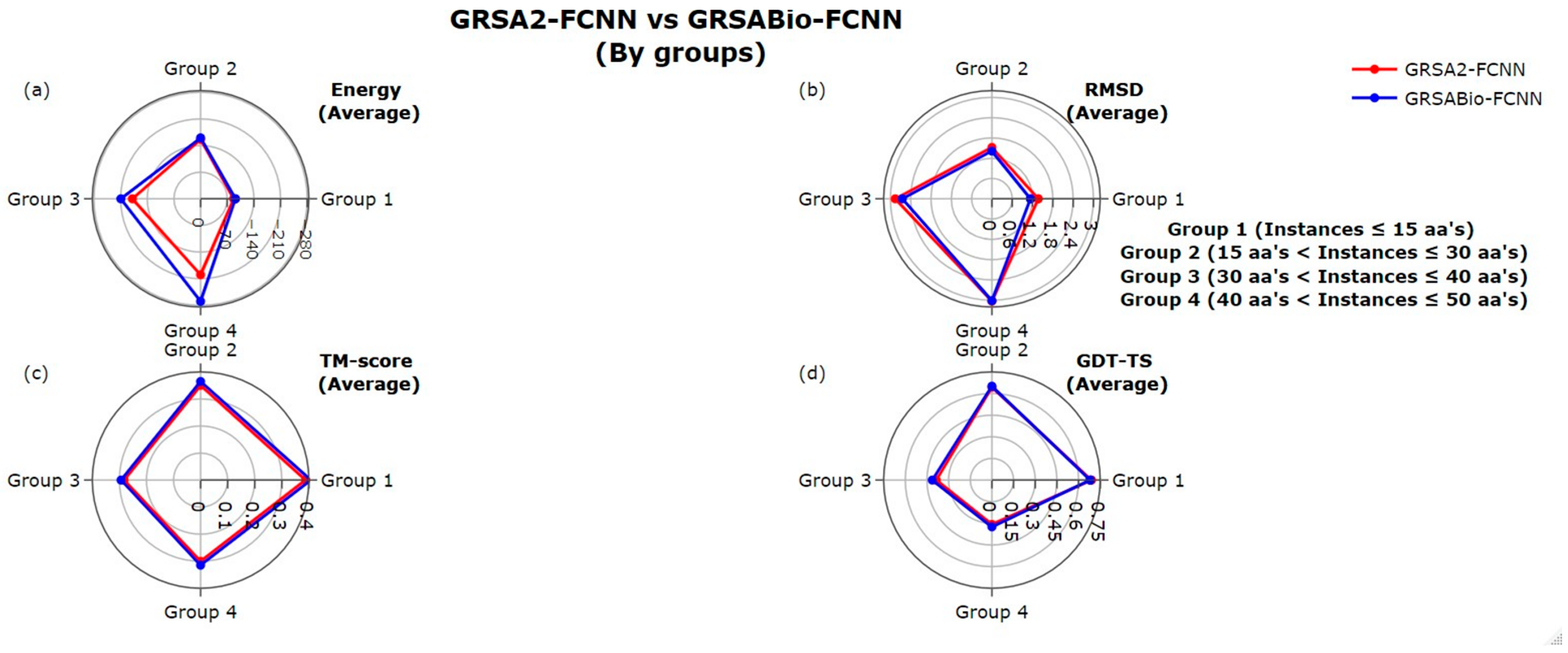
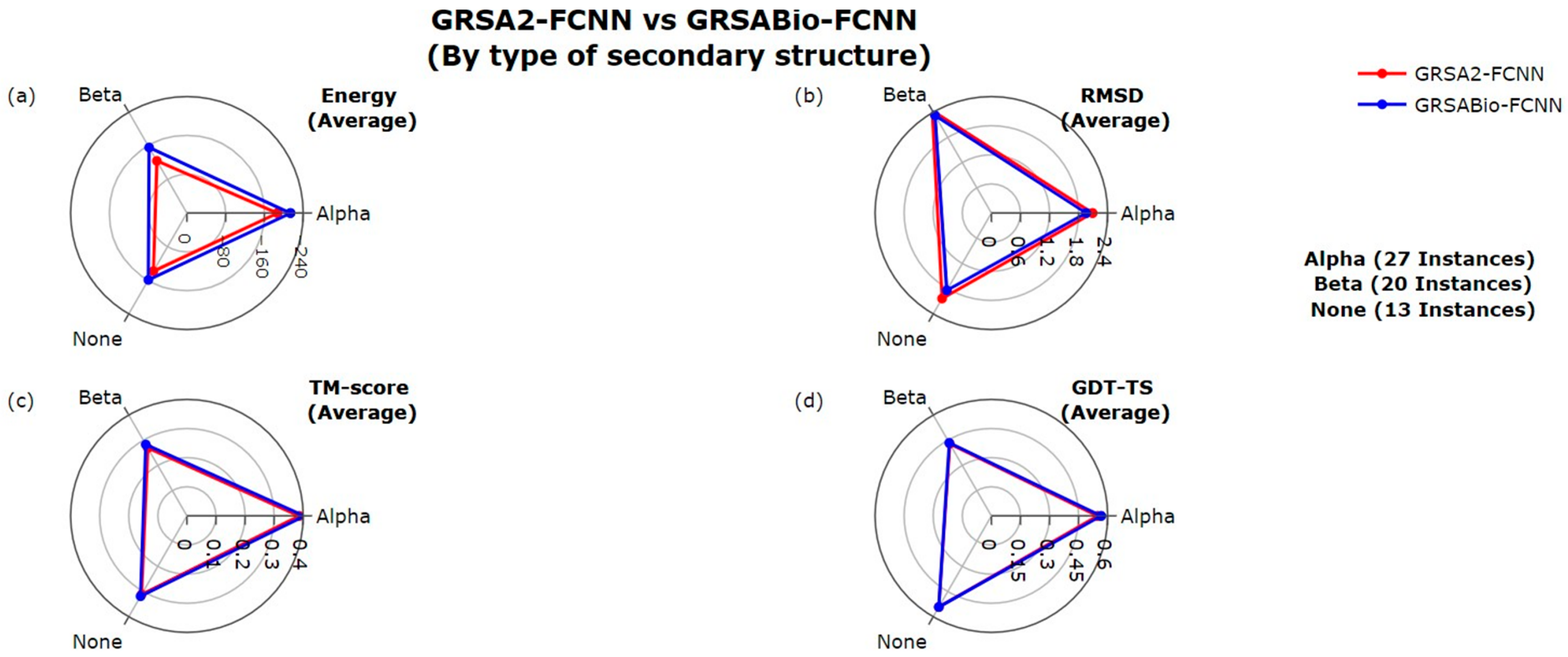
2.1. Evaluation Between GRSA2-FCNN and GRSABio-FCNN
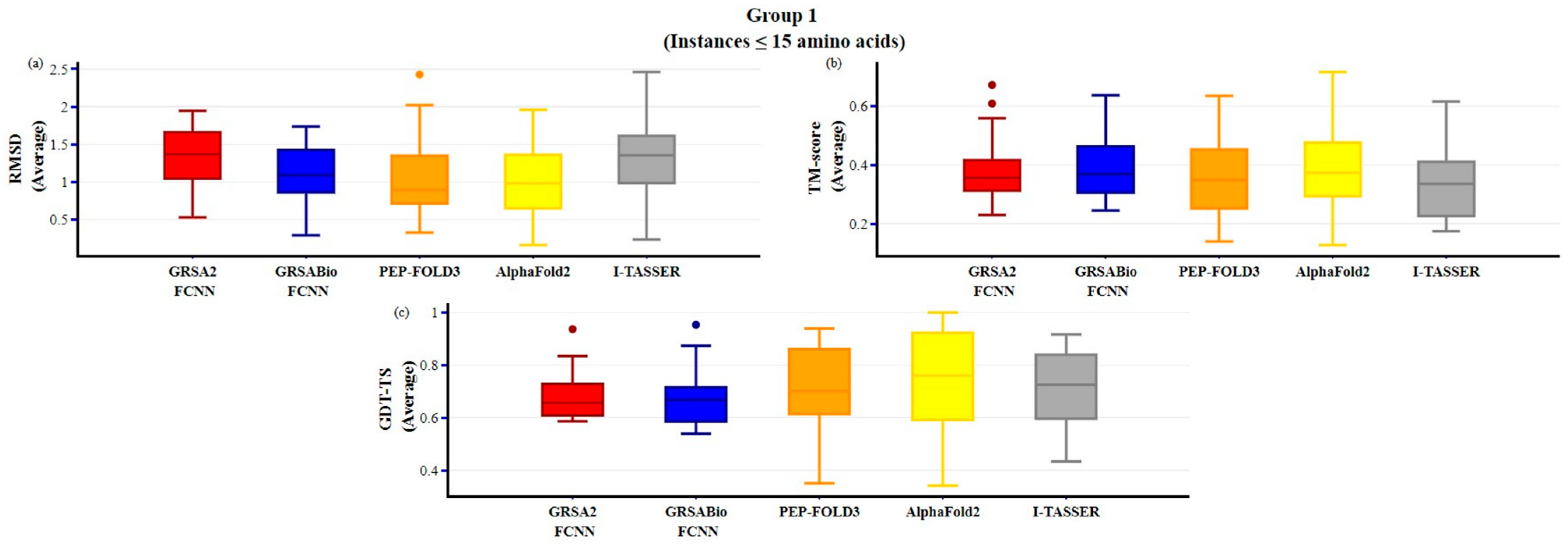
2.2. Evaluation of GRSABio-FCNN and State-of-the-Art Algorithms
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Related Works on Protein Folding Problem (PFP)
- The PFP is recognized as an NP-hard problem, indicating that the computational resources required to solve it increase exponentially with the size of the protein [11].
- Although a protein’s three-dimensional native structure is determined by its amino acid sequence, the vast conformational search space complicates accurate predictions.
- The Levinthal Paradox exemplifies this challenge: a protein cannot fold by randomly sampling all possible conformations due to the astronomical number of potential structures [57].
4.1.1. Computational Predictions for PFP
4.1.2. Metaheuristic Algorithms for PFP
Simulated Annealing (SA) Algorithms
4.1.3. Bio-Inspired Algorithms
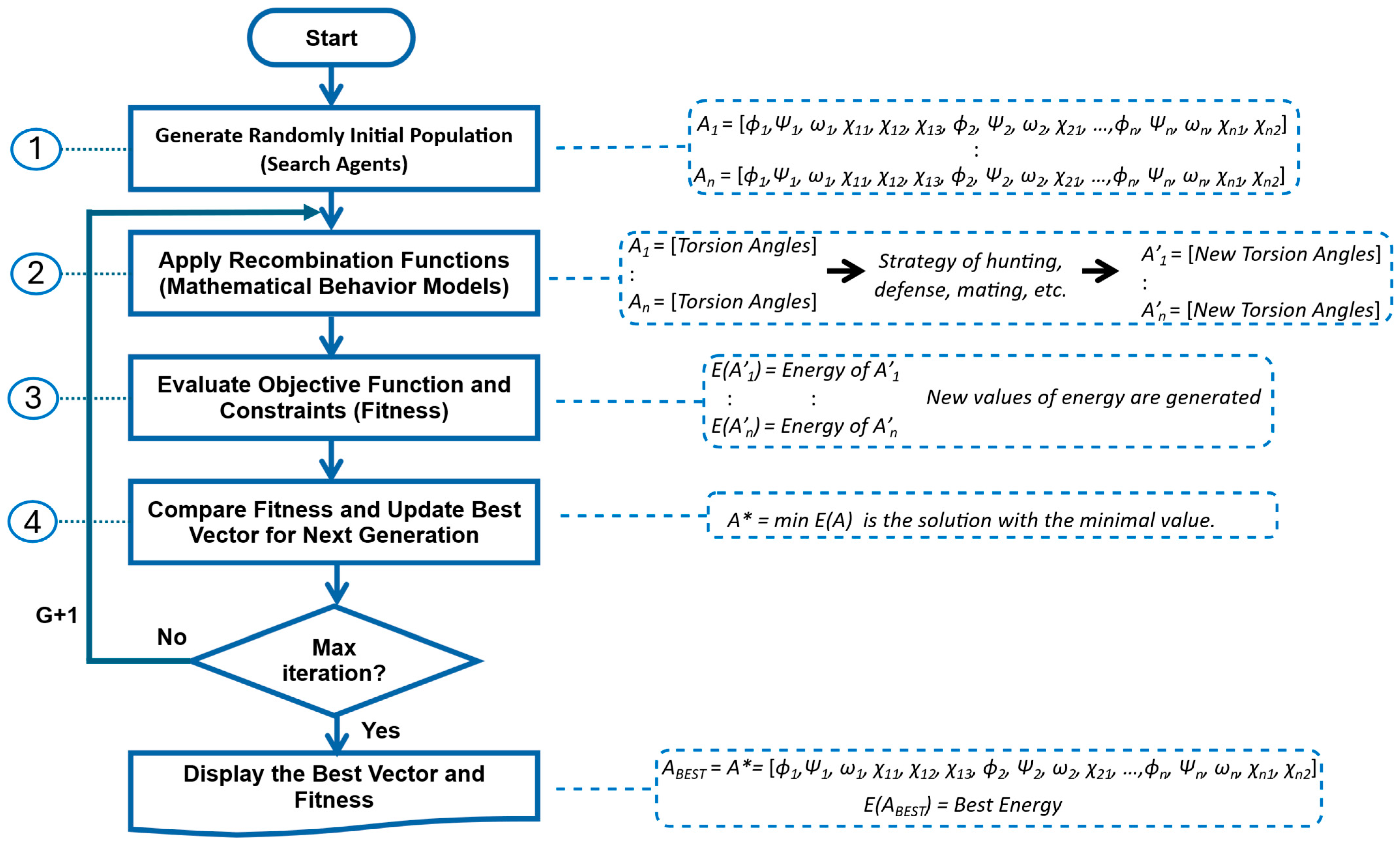
4.2. GRSABio-FCNN Methodology
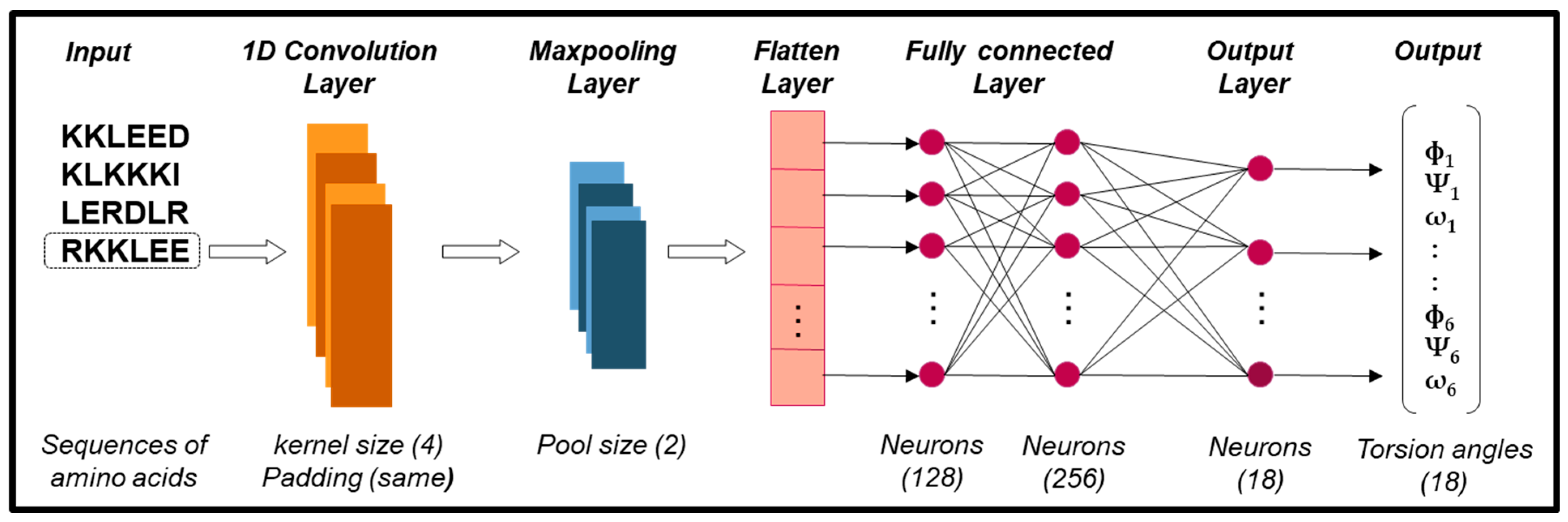
- Amino Acid Sequence (Input) and Fragments Database. The amino acid sequence of the target protein, represented by a single-letter code, serves as the input for our method, while the fragments database contains a collection of fragments categorized based on their predominant secondary structures: alpha-helices, beta-sheets, and loops.
- Fragment Prediction with CNN (Stage 1). The fragment database serves as the input for training a CNN, which predicts fragments (alpha-helices, beta-sheets, and loops) along with their torsion angles—internal angles of the protein backbone, specifically phi (ϕ), psi (ψ), and omega (ω). The input amino acid sequence is segmented into short sequences, or fragments, each consisting of six amino acids, a length chosen to balance prediction accuracy while maintaining low computational requirements. The CNN processes these short sequences and generates their corresponding torsion angles for three-dimensional configuration.
- Assembly of Fragments (Stage 2). The predicted fragments, represented as vectors of torsion angles, are concatenated to construct a preliminary model of the target sequence. In other words, the individual predictions for each segment are combined sequentially to form a complete vector of torsion angles corresponding to the entire protein. During this process, the torsion angles of the fragments are assembled in segments of six amino acids based on the target sequence. If the size of the target sequence is not evenly divisible by the fragment size, resulting in missing angles for the final segment, random values are assigned to fill the gaps, which are refined in the next stage.
- Refinement by GRSABio Algorithm (Stage 3). The complete preliminary model, generated by concatenating the predicted fragments during the assembly phase, is refined using the GRSABio energy minimization process. This refined step optimizes the structure by reducing its energy, resulting in a more accurate and stable conformation.
- Tertiary structure prediction (Output). The outcome of refinement is the final tertiary structure of the target protein.

4.2.1. Prediction and Assembly Fragments
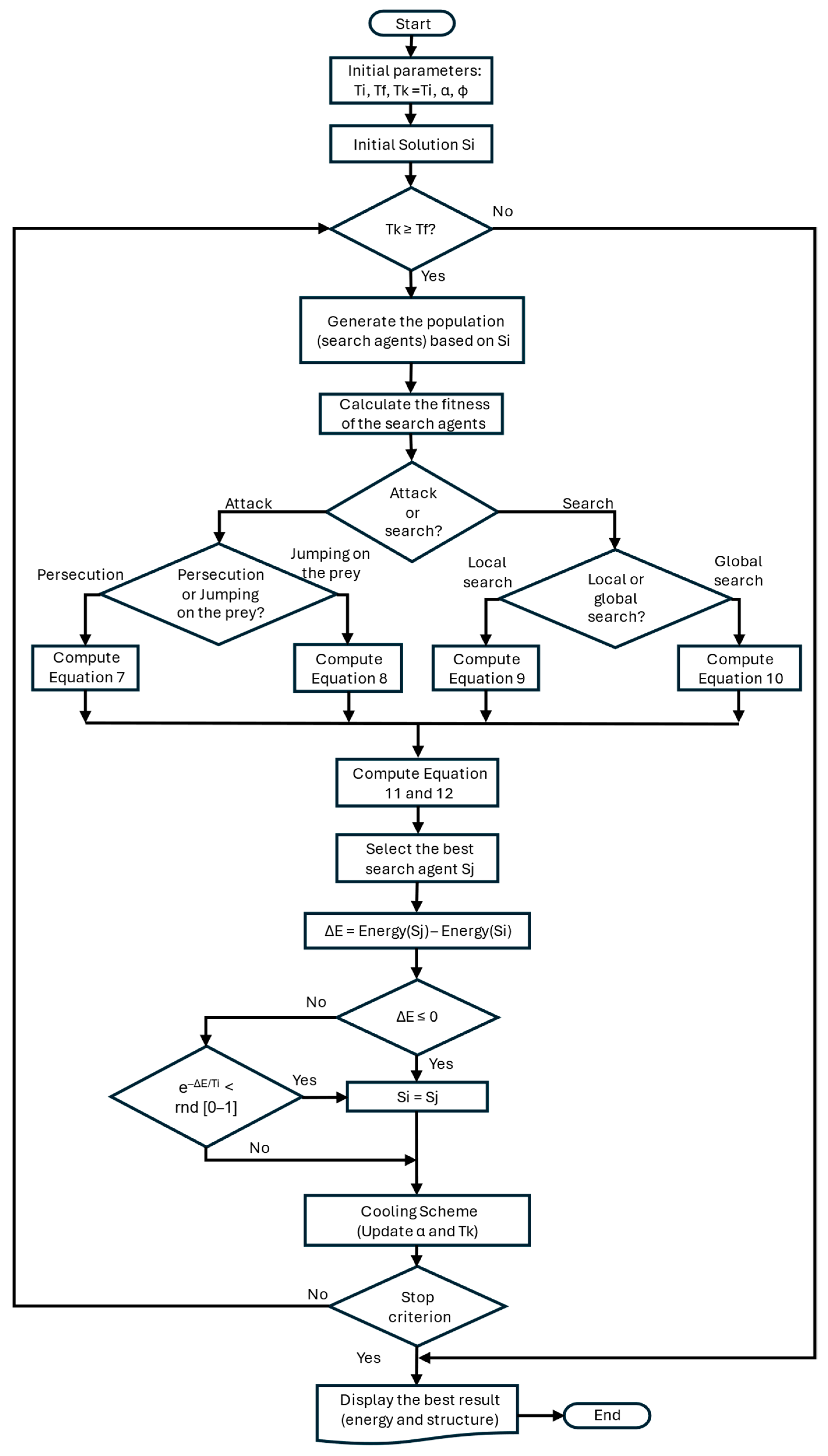
4.2.2. Refinement GRSABio
| Algorithm 1 GRSABio Algorithm |
| 1: Data: Tf, Tfp, Ti, E, S, α 2: α = 0.70; Φ = 0.618 3: Tfp = Ti; Tk = Ti 4: Si = InitialSolution() 5: while Tk ≥ Tf do //Temperature cycle 6: while Metropolis length do //Metropolis cycle 7: Sj = BioperturbationJSOA(Si) 8: ΔE = Energy(Sj) − Energy(Si) 9: if ΔE ≤ 0 then 10: Si = Sj 11: E = Energy(Si) 12: else if e−ΔE/Ti < random [0-1] then 13: Si = Sj 14: E = Energy(Si) 15: end if 16: end while //End Metropolis cycle 17: GRSA_Cooling_Schema(Tfp) 18: GRSA_Stop_Criterion() 19: end while //End Temperature cycle |
| Algorithm 2 BiopertubationJSOA Function |
| 1: BioperturbationJSOA(Si) 2: n=MaxIteration 3: Agents = InitialAgents() 4: while iteration < n do 5: if random < 0.5 then Attack or Search? 6: if random < 0.5 then Strategy 1 7: Attack by persecution, Equation (7) 8: else Strategy 2 9: Attack by jumping on the prey, Equation (8) 10: end if 11: else 12: if random < 0.5 then Strategy 3 Local Search 13: Search for prey by local search, Equation (9) 14: else Strategy 3 Global Search 15: Search for prey by global search, Equation (10) 16: end if 17: end if 18: Update search agents with pheromone by Equations (11) and (12) 19: bestSolution = BestAgent(Si) 20: Iteration = Iteration + 1 21: end while 22: end Function |
| Algorithm 3 Pheromone procedure |
| 1: Pheromone procedure 2: Compute pheromone rate for all spiders (search agents) by Equation (11)) 3: for i = 1 to sizePopulation do 4: if pheromone(i) ≤ 0.3 then 5: search agent update by Equation (12) 6: end if 7: end for 8: return 9: end procedure |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Energy Ave. | RMSD Ave. | TM-Score Ave. | GDT-TS Ave. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instances | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSABio-FCNN | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSABio-FCNN | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSABio-FCNN | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSABio-FCNN |
| 1. 1egs | 1.6866 | −5.7061 | 0.7620 | 0.9120 | 0.3615 | 0.3744 | 0.6556 | 0.6666 |
| 2. 1uao | −51.7199 | −64.1566 | 1.6200 | 0.6020 | 0.3932 | 0.4241 | 0.6900 | 0.6550 |
| 3. 1l3q | −63.0239 | −79.0836 | 1.0740 | 0.9500 | 0.2629 | 03013 | 0.6041 | 0.6667 |
| 4. 2evq | −60.5334 | −76.3770 | 1.9440 | 1.7360 | 0.3182 | 0.3646 | 0.7042 | 0.6958 |
| 5. 1le1 | −69.0947 | −76.8187 | 1.7020 | 1.6680 | 0.3179 | 0.3047 | 0.6250 | 0.5834 |
| 6. 1in3 | −105.5510 | −97.7497 | 1.2140 | 0.7480 | 0.4393 | 0.5034 | 0.5958 | 0.5875 |
| 7. 1eg4 | −99.2259 | −101.5050 | 1.5160 | 1.3840 | 0.3456 | 0.3545 | 0.5962 | 0.5385 |
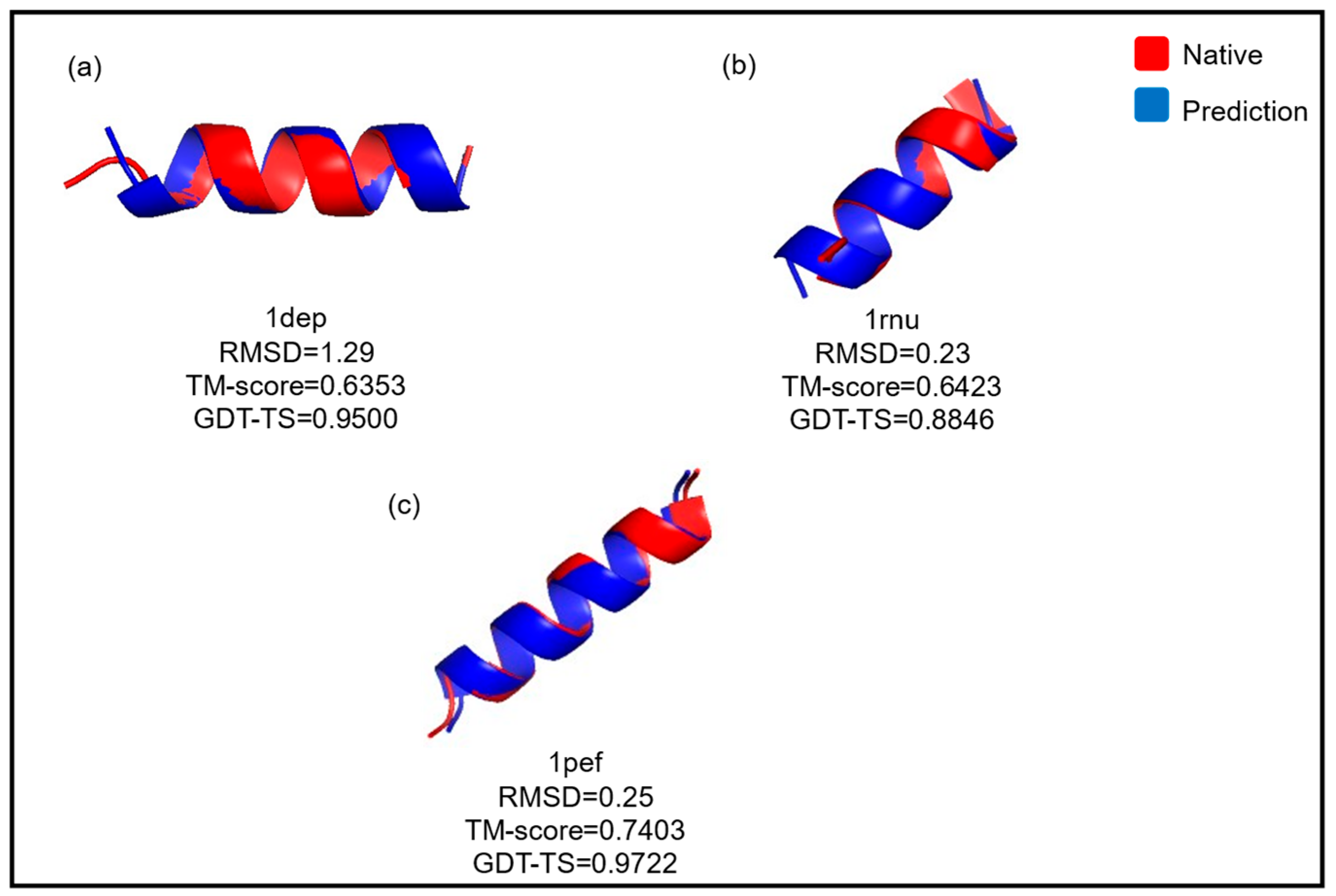
| 8. 1rnu | −108.2189 | −100.2774 | 0.5320 | 0.2940 | 0.6728 | 0.6378 | 0.8346 | 0.8731 |
| 9. 1lcx | −96.6685 | −97.2231 | 1.2500 | 0.8120 | 0.3523 | 0.3529 | 0.7269 | 0.6808 |
| 10. 3bu3 | −101.1031 | −104.0929 | 1.5160 | 1.6700 | 0.3080 | 0.3024 | 0.6467 | 0.6198 |
| 11. 1gjf | −104.9334 | −106.6305 | 1.0220 | 1.3300 | 0.5593 | 0.6295 | 0.7857 | 0.7821 |
| 12. 1k43 | −86.3976 | −88.8112 | 1.7560 | 1.4680 | 0.2822 | 0.2883 | 0.6143 | 0.5821 |
| 13. 1a13 | −40.1823 | −48.5602 | 1.9200 | 1.3460 | 0.3665 | 0.3975 | 0.7286 | 0.7357 |
| 14. 1dep | −140.5410 | −142.4070 | 1.1860 | 1.0420 | 0.6094 | 0.6249 | 0.9367 | 0.9533 |
| 15. 2bta | −180.0959 | −181.545 | 1.4880 | 1.1420 | 0.2301 | 0.2452 | 0.5867 | 0.5733 |
| 16. 1nkf | −89.6251 | −90.9786 | 1.1080 | 0.9380 | 0.3099 | 0.3108 | 0.6750 | 0.6563 |
| 17. 1le3 | −76.2782 | −94.4471 | 2.2440 | 2.2140 | 0.2467 | 0.2513 | 0.5674 | 0.5780 |
| 18. 1pgbF | −96.8106 | −102.0640 | 1.5000 | 1.3280 | 0.2481 | 0.2693 | 0.5705 | 0.6193 |
| 19. 1niz | −86.4210 | −94.8362 | 1.6260 | 1.1780 | 0.2466 | 0.2469 | 0.5214 | 0.4929 |
| 20. 1e0q | −50.4039 | −65.4440 | 1.4460 | 1.9880 | 0.2347 | 0.2149 | 0.5000 | 0.4824 |
| 21. 1wbr | −148.1450 | −152.6280 | 1.6240 | 1.7820 | 0.3127 | 0.3123 | 0.6566 | 0.6558 |
| 22. 1rpv | −306.9186 | −310.1344 | 0.7480 | 0.8240 | 0.4976 | 0.5332 | 0.7412 | 0.8617 |
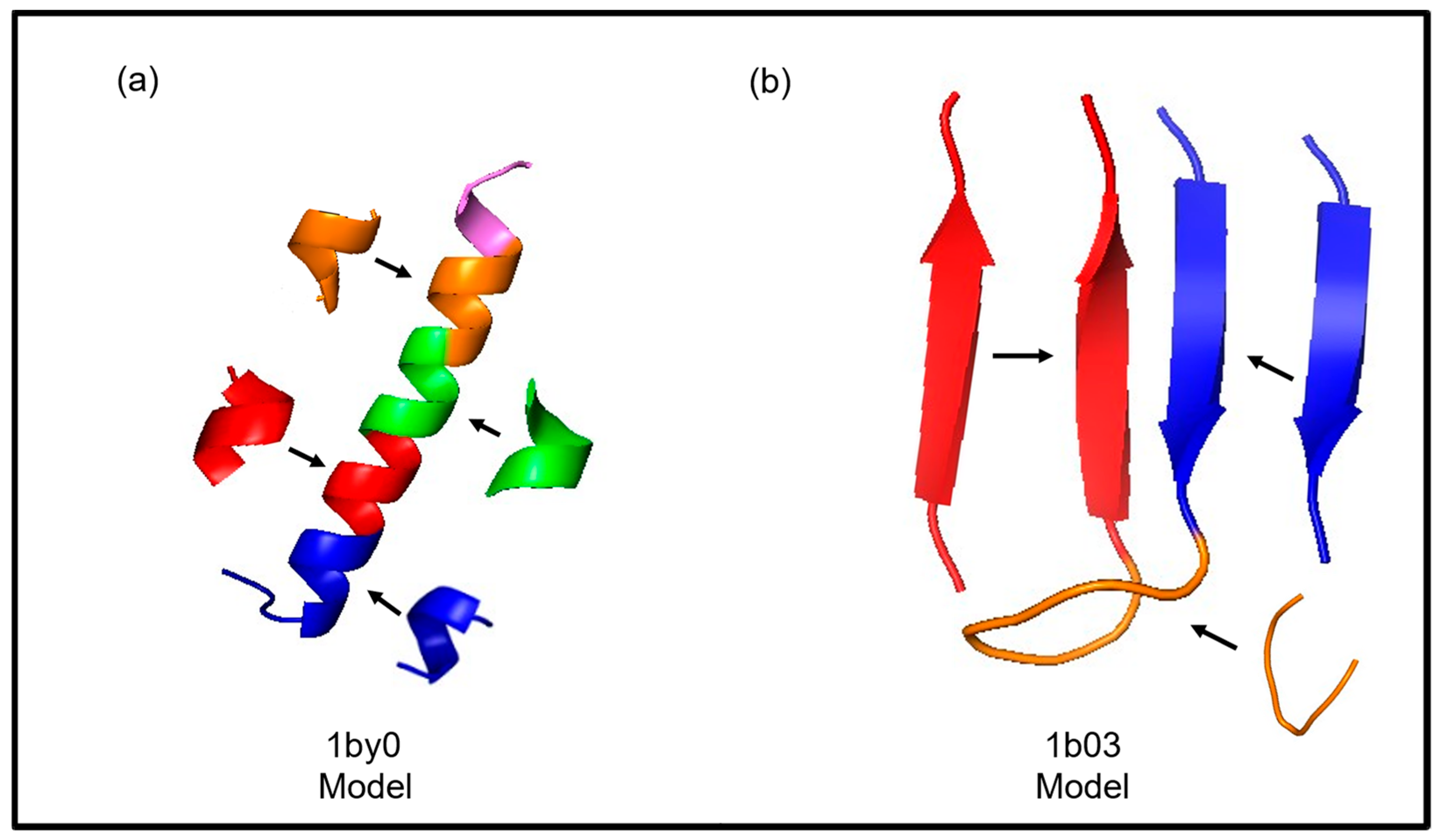
| 23. 1b03 | −119.8978 | −113.3539 | 1.6300 | 1.2060 | 0.2182 | 0.2793 | 0.4472 | 0.4639 |
| 24. 1pef | −127.6188 | −123.9900 | 0.3580 | 0.2920 | 0.7168 | 0.7260 | 0.9722 | 0.9639 |
| 25. 1l2y | −133.7934 | −152.4246 | 2.2340 | 1.6100 | 0.3089 | 0.3486 | 0.6450 | 0.6250 |
| 26. 1du1 | −196.6084 | −198.5546 | 1.4640 | 1.2340 | 0.2958 | 0.3050 | 0.6400 | 0.6025 |
| 27. 1pei | −197.7513 | −198.8485 | 1.0140 | 1.1420 | 0.4075 | 0.4135 | 0.7335 | 0.7443 |
| 28. 1wz4 | −157.5255 | −163.4536 | 2.5540 | 2.5100 | 0.2720 | 0.2849 | 0.5065 | 0.5500 |
| 29. 1yyb | −280.2210 | −266.9556 | 1.8080 | 1.3340 | 0.4495 | 0.4569 | 0.7327 | 0.7327 |
| 30. 1by0 | −274.7173 | −274.8341 | 1.4480 | 1.5940 | 0.4890 | 0.5147 | 0.7426 | 0.7352 |
| Energy Ave. | RMSD Ave. | TM-Score Ave. | GDT-TS Ave. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instances | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSABio-FCNN | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSABio-FCNN | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSABio-FCNN | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSABio-FCNN |
| 31. 1t0c | −124.9148 | −147.2932 | 2.9060 | 2.5640 | 0.2628 | 0.2352 | 0.4290 | 0.4403 |
| 32. 2gdl | −225.0245 | −231.8165 | 1.8120 | 1.2400 | 0.3113 | 0.3287 | 0.4000 | 0.4306 |
| 33. 2l0g | −78.1438 | −135.3045 | 3.3700 | 2.3900 | 0.2650 | 0.2828 | 0.5831 | 0.6221 |
| 34. 2bn6 | −266.2744 | −267.7155 | 2.4160 | 1.9140 | 0.3556 | 0.3617 | 0.7468 | 0.7595 |
| 35. 2kya | −70.0008 | −151.1348 | 2.9960 | 2.3800 | 0.2413 | 0.2882 | 0.3074 | 0.3309 |
| 36. 1wr3 | −158.1745 | −230.0375 | 2.9820 | 3.0180 | 0.2445 | 0.2510 | 0.3069 | 0.3375 |
| 37. 1wr4 | −211.1636 | −214.6153 | 2.6900 | 3.2220 | 0.2439 | 0.2565 | 0.2833 | 0.3514 |
| 38. 1e0m | −188.4646 | −200.8406 | 3.1520 | 3.4580 | 0.2442 | 0.2430 | 0.3135 | 0.3014 |
| 39. 1yiu | −251.4423 | −252.6822 | 3.2560 | 3.0840 | 0.2443 | 0.2547 | 0.3000 | 0.3284 |
| 40. 1e0l | −177.8004 | −223.3877 | 2.8620 | 2.7660 | 0.2457 | 0.2564 | 0.2865 | 0.2906 |
| 41. 1bhi | −148.8985 | −175.5776 | 2.8080 | 2.7040 | 0.3024 | 0.2421 | 0.3619 | 0.3908 |
| 42. 1jrj | −131.3705 | −210.8226 | 2.5320 | 1.9880 | 0.3114 | 0.3972 | 0.3487 | 0.3987 |
| 43. 1i6c | −153.8447 | −185.2439 | 3.3920 | 3.4680 | 0.2439 | 0.2550 | 0.2923 | 0.3141 |
| 44. 1bwx | −326.6206 | −330.6057 | 2.3680 | 2.3360 | 0.4760 | 0.4983 | 0.5231 | 0.5949 |
| 45. 2ysh | −175.8431 | −183.8752 | 3.3320 | 3.1820 | 0.2494 | 0.2558 | 0.2950 | 0.3037 |
| 46. 1wr7 | −224.9640 | −233.5755 | 3.0100 | 2.8900 | 0.2635 | 0.2514 | 0.3122 | 0.3293 |
| 47. 1k1v | −165.7520 | −284.3404 | 2.6640 | 2.5180 | 0.3060 | 0.3542 | 0.2097 | 0.2073 |
| 48. 2hep | −121.0992 | −184.8579 | 2.7580 | 2.9820 | 0.3117 | 0.3608 | 0.3083 | 0.4024 |
| 49. 2dmv | −189.2054 | −191.4439 | 3.0380 | 3.5340 | 0.2575 | 0.2456 | 0.2907 | 0.2698 |
| 50. 1res | −144.2967 | −216.6926 | 2.8700 | 2.8560 | 0.3026 | 0.3156 | 0.3140 | 0.3093 |
| 51. 2p81 | −413.1129 | −430.3809 | 2.6440 | 2.5140 | 0.4001 | 0.3840 | 0.3375 | 0.3966 |
| 52. 1ed7 | −44.4465 | −179.0525 | 3.2240 | 3.2780 | 0.2680 | 0.2774 | 0.2948 | 0.3051 |
| 53. 1f4i | −271.4136 | −384.3786 | 2.7100 | 2.7640 | 0.3436 | 0.3615 | 0.3611 | 0.3800 |
| 54. 2l4j | −79.2959 | −196.8989 | 3.3260 | 3.3940 | 0.2546 | 0.2582 | 0.2800 | 0.2841 |
| 55. 1qhk | −107.7690 | −199.9758 | 3.4340 | 3.6260 | 0.2731 | 0.2861 | 0.2393 | 0.2457 |
| 56. 1dv0 | −265.8274 | −338.6817 | 2.6600 | 2.9340 | 0.3177 | 0.3040 | 0.3622 | 0.3678 |
| 57. 1pgy | −374.6846 | −390.3784 | 2.4480 | 2.3540 | 0.3353 | 0.3283 | 0.3851 | 0.3553 |
| 58. 1e0g | −107.2451 | −238.9335 | 3.8200 | 3.3260 | 0.2731 | 0.3225 | 0.2656 | 0.2729 |
| 59. 1ify | −315.1808 | −346.1995 | 3.3100 | 2.9820 | 0.3319 | 0.3698 | 0.3983 | 0.4438 |
| 60. 1nd9 | −171.3091 | −227.3267 | 3.5260 | 3.2820 | 0.2654 | 0.3022 | 0.2541 | 0.2979 |
| RMSD Ave. | TM-Score Ave. | GDT-TS Ave. | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instances | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSABio-FCNN | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSA2-FCNN | PEP-FOLD3 | AlphaFold2 | I-TASSER | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSABio-FCNN | PEP-FOLD3 | AlphaFold2 | I-TASSER |
| 1. 1egs | 0.7620 | 0.9120 | 0.6600 | 0.6760 | - | 0.3615 | 0.3744 | 0.2629 | 0.2976 | - | 0.6556 | 0.6666 | 0.6722 | 0.5722 | - |
| 2. 1uao | 1.6200 | 0.6020 | 1.2820 | 1.0140 | 1.3200 | 0.3932 | 0.4241 | 0.4565 | 0.4866 | 0.3825 | 0.6900 | 0.6550 | 0.9000 | 0.9300 | 0.8750 |
| 3. 1l3q | 1.0740 | 0.9500 | 2.0200 | 0.1641 | 0.2391 | 0.2629 | 0.3013 | 0.2391 | 0.1275 | 0.1979 | 0.6041 | 0.6667 | 0.6333 | 0.3416 | 0.4333 |
| 4. 2evq | 1.9440 | 1.7360 | 0.8800 | 0.3520 | 1.6120 | 0.3182 | 0.3646 | 0.4503 | 0.7171 | 0.2443 | 0.7042 | 0.6958 | 0.9208 | 1.0000 | 0.6750 |
| 5. 1le1 | 1.7020 | 1.6680 | 1.1360 | 0.6320 | 0.9800 | 0.3179 | 0.3047 | 0.3510 | 0.4673 | 0.3539 | 0.6250 | 0.5834 | 0.8083 | 0.9875 | 0.9167 |
| 6. 1in3 | 1.2140 | 0.7480 | 0.6120 | 1.1920 | 1.0400 | 0.4393 | 0.5034 | 0.4071 | 0.4443 | 0.4201 | 0.5958 | 0.5875 | 0.6667 | 0.6375 | 0.6875 |
| 7. 1eg4 | 1.5160 | 1.3840 | 0.7740 | 1.7320 | 1.6240 | 0.3456 | 0.3545 | 0.2488 | 0.2913 | 0.2137 | 0.5962 | 0.5385 | 0.4731 | 0.7346 | 0.5961 |
| 8. 1rnu | 0.5320 | 0.2940 | 0.8280 | 0.4040 | 0.8900 | 0.6728 | 0.6378 | 0.6355 | 0.5862 | 0.4110 | 0.8346 | 0.8731 | 0.8884 | 0.9231 | 0.7346 |
| 9. 1lcx | 1.2500 | 0.8120 | 1.2580 | 1.5840 | 1.4900 | 0.3523 | 0.3529 | 0.3402 | 0.3644 | 0.3375 | 0.7269 | 0.6808 | 0.7308 | 0.7654 | 0.7308 |
| 10. 3bu3 | 1.5160 | 1.6700 | 1.4100 | 1.9600 | 1.6020 | 0.3080 | 0.3024 | 0.2553 | 0.1982 | 0.2266 | 0.6467 | 0.6198 | 0.5675 | 0.4406 | 0.5037 |
| 11. 1gjf | 1.0220 | 1.3300 | 0.9120 | 0.9580 | 2.0100 | 0.5593 | 0.6295 | 0.6218 | 0.6014 | 0.6169 | 0.7857 | 0.7821 | 0.8214 | 0.8036 | 0.8393 |
| 12. 1k43 | 1.7560 | 1.4680 | 1.5660 | 1.3080 | 0.9875 | 0.2822 | 0.2883 | 0.3652 | 0.3837 | 0.3347 | 0.6143 | 0.5821 | 0.8321 | 0.9215 | 0.7188 |
| 13. 1a13 | 1.9200 | 1.3460 | 1.2900 | 1.4120 | 1.3900 | 0.3665 | 0.3975 | 0.3484 | 0.3019 | 0.3339 | 0.7286 | 0.7357 | 0.7322 | 0.7536 | 0.7500 |
| 14. 1dep | 1.1860 | 1.0420 | 0.8600 | 0.9560 | 1.2800 | 0.6094 | 0.6249 | 0.5444 | 0.4521 | 0.5887 | 0.9367 | 0.9533 | 0.9389 | 0.8233 | 0.9000 |
| 15. 2bta | 1.4880 | 1.1420 | 2.4260 | 1.2100 | 2.4600 | 0.2301 | 0.2452 | 0.1866 | 0.1986 | 0.1750 | 0.5867 | 0.5733 | 0.5933 | 0.6100 | 0.5833 |
| 16. 1nkf | 1.1080 | 0.9380 | 0.6500 | 1.3860 | 1.2680 | 0.3099 | 0.3108 | 0.2612 | 0.2474 | 0.2899 | 0.6750 | 0.6563 | 0.5969 | 0.5688 | 0.7781 |
| 17. 1le3 | 2.2440 | 2.2140 | 2.1460 | 0.9120 | 1.2300 | 0.2467 | 0.2513 | 0.2060 | 0.4101 | 0.3090 | 0.5674 | 0.5780 | 0.4246 | 0.7412 | 0.6313 |
| 18. 1pgbF | 1.5000 | 1.3280 | 1.6900 | 1.1520 | 1.4420 | 0.2481 | 0.2693 | 0.2504 | 0.3418 | 0.3386 | 0.5705 | 0.6193 | 0.5161 | 0.6621 | 0.6918 |
| 19. 1niz | 1.6260 | 1.1780 | 1.3000 | 1.9060 | 1.9420 | 0.2466 | 0.2469 | 0.2867 | 0.1749 | 0.2451 | 0.5214 | 0.4929 | 0.3688 | 0.4464 | 0.4429 |
| 20. 1e0q | 1.4460 | 1.9880 | 1.3300 | 1.5700 | 0.9400 | 0.2347 | 0.2149 | 0.3080 | 0.2530 | 0.3223 | 0.5000 | 0.4824 | 0.8382 | 0.7765 | 0.8971 |
| 21. 1wbr | 1.6240 | 1.7820 | 1.0940 | 1.6520 | 0.8200 | 0.3127 | 0.3123 | 0.2670 | 0.2927 | 0.2835 | 0.6566 | 0.6558 | 0.5503 | 0.5670 | 0.5792 |
| 22. 1rpv | 0.7480 | 0.8240 | 0.9520 | 0.6080 | 1.2600 | 0.4976 | 0.5332 | 0.3826 | 0.4779 | 0.5778 | 0.7412 | 0.8617 | 0.8264 | 0.8588 | 0.8676 |
| 23. 1b03 | 1.6300 | 1.2060 | 1.4900 | 1.9720 | 2.2520 | 0.2182 | 0.2793 | 0.2502 | 0.2733 | 0.1436 | 0.4472 | 0.4639 | 0.4389 | 0.4889 | 0.4000 |
| 24. 1pef | 0.3580 | 0.2920 | 0.5780 | 0.3880 | 0.3400 | 0.7168 | 0.7260 | 0.6805 | 0.7225 | 0.6493 | 0.9722 | 0.9639 | 0.9694 | 0.9778 | 0.9722 |
| 25. 1l2y | 2.2340 | 1.6100 | 2.0280 | 0.7540 | 2.1100 | 0.3089 | 0.3486 | 0.3322 | 0.4751 | 0.1471 | 0.6450 | 0.6250 | 0.7300 | 0.9650 | 0.5175 |
| 26. 1du1 | 1.4640 | 1.2340 | 1.4400 | 1.6800 | 1.6750 | 0.2958 | 0.3050 | 0.2505 | 0.2789 | 0.2704 | 0.6400 | 0.6025 | 0.6575 | 0.6650 | 0.6500 |
| 27. 1pei | 1.0140 | 1.1420 | 1.6120 | 1.1640 | 1.7620 | 0.4075 | 0.4135 | 0.3472 | 0.4180 | 0.3682 | 0.7335 | 0.7443 | 0.7156 | 0.8097 | 0.7522 |
| 28. 1wz4 | 2.5540 | 2.5100 | 1.9960 | 2.8060 | 2.2820 | 0.2720 | 0.2849 | 0.2429 | 0.2596 | 0.2508 | 0.5065 | 0.5500 | 0.5217 | 0.5957 | 0.5587 |
| 29. 1yyb | 1.8080 | 1.3340 | 1.7080 | 1.6460 | 2.1680 | 0.4495 | 0.4569 | 0.3849 | 0.4340 | 0.3779 | 0.7327 | 0.7327 | 0.7148 | 0.7558 | 0.6444 |
| 30. 1by0 | 1.4480 | 1.5940 | 1.5750 | 1.7700 | 1.8200 | 0.4890 | 0.5147 | 0.4682 | 0.4903 | 0.4540 | 0.7426 | 0.7352 | 0.7732 | 0.7871 | 0.8056 |
| RMSD Ave. | TM-Score Ave. | GDT-TS Ave. | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instances | GRSA2 | GRSAB | PEP | Alpha | I-TAS | Ros | Top | GRSA2 | GRSB | PEP | Alpha | I-TAS | Ros | Top | GRSA2-FCNN | GRSABio-FCNN | PEP-FOLD3 | AlphaFold2 | I-TASSER | Rosetta | TopModel |
| 31. 1t0c | 2.9060 | 2.5640 | 2.8160 | 2.8860 | 3.1440 | 2.7017 | 3.0733 | 0.2628 | 0.2352 | 0.2070 | 0.1981 | 0.2260 | 0.3085 | 0.2002 | 0.4290 | 0.4403 | 0.3806 | 0.3000 | 0.4726 | 0.4745 | 0.3199 |
| 32. 2gdl | 1.8120 | 1.2400 | 1.8180 | 2.5920 | 2.3800 | 2.2600 | 1.8120 | 0.3113 | 0.3287 | 0.3246 | 0.3147 | 0.3815 | 0.3151 | 0.3970 | 0.4000 | 0.4306 | 0.4290 | 0.5323 | 0.6145 | 0.3887 | 0.4790 |
| 33. 2l0g | 3.3700 | 2.3900 | 2.2820 | 1.5320 | 1.6880 | 2.1860 | 1.4720 | 0.2650 | 0.2828 | 0.5248 | 0.6485 | 0.5725 | 0.5895 | 0.6568 | 0.5831 | 0.6221 | 0.5856 | 0.7237 | 0.6389 | 0.6579 | 0.7330 |
| 34. 2bn6 | 2.4160 | 1.9140 | 2.0800 | 1.9820 | 1.9525 | 1.8900 | 1.5760 | 0.3556 | 0.3617 | 0.3214 | 0.5445 | 0.3976 | 0.5654 | 0.5337 | 0.7468 | 0.7595 | 0.3928 | 0.5968 | 0.4529 | 0.6248 | 0.5957 |
| 35. 2kya | 2.9960 | 2.3800 | 1.8120 | 2.6440 | 2.8200 | 1.7460 | 1.9260 | 0.2413 | 0.2882 | 0.3127 | 0.2858 | 0.3193 | 0.3586 | 0.5300 | 0.3074 | 0.3309 | 0.3514 | 0.4132 | 0.4250 | 0.4588 | 0.6853 |
| 36. 1wr3 | 2.9820 | 3.0180 | 2.2280 | 1.8440 | 1.7600 | 1.9120 | 1.0240 | 0.2445 | 0.2510 | 0.4618 | 0.7041 | 0.6583 | 0.6228 | 0.7713 | 0.3069 | 0.3375 | 0.6472 | 0.8806 | 0.8472 | 0.8236 | 0.9194 |
| 37. 1wr4 | 2.6900 | 3.2220 | 2.2040 | 1.6440 | 1.5867 | 1.4700 | 1.3840 | 0.2439 | 0.2565 | 0.5142 | 0.7339 | 0.7376 | 0.7226 | 0.7009 | 0.2833 | 0.3514 | 0.6861 | 0.8861 | 0.8819 | 0.8861 | 0.8667 |
| 38. 1e0m | 3.1520 | 3.4580 | 2.0820 | 1.5640 | 1.8900 | 1.9860 | 1.6040 | 0.2442 | 0.2430 | 0.4821 | 0.6956 | 0.6973 | 0.6548 | 0.7173 | 0.3135 | 0.3014 | 0.6446 | 0.8595 | 0.8497 | 0.8257 | 0.8702 |
| 39. 1yiu | 3.2560 | 3.0840 | 2.3620 | 1.5600 | 1.5367 | 1.1460 | 1.3780 | 0.2443 | 0.2547 | 0.4649 | 0.7308 | 0.7188 | 0.7417 | 0.6707 | 0.3000 | 0.3284 | 0.6608 | 0.9000 | 0.8919 | 0.8865 | 0.8486 |
| 40. 1e0l | 2.8620 | 2.7660 | 2.2140 | 1.7660 | 1.7300 | 1.1700 | 1.8060 | 0.2457 | 0.2564 | 0.4943 | 0.7152 | 0.6733 | 0.6734 | 0.6246 | 0.2865 | 0.2906 | 0.6703 | 0.8568 | 0.8216 | 0.8054 | 0.7824 |
| 41. 1bhi | 2.8080 | 2.7040 | 2.7460 | 2.2140 | 2.2680 | 2.1080 | 2.1200 | 0.3024 | 0.2421 | 0.3397 | 0.6673 | 0.6313 | 0.6356 | 0.5986 | 0.3619 | 0.3908 | 0.4553 | 0.8171 | 0.7803 | 0.7908 | 0.7539 |
| 42. 1jrj | 2.5320 | 1.9880 | 2.0360 | 1.8240 | 2.2040 | 2.1200 | 1.8260 | 0.3114 | 0.3972 | 0.4929 | 0.6687 | 0.5390 | 0.5303 | 0.6032 | 0.3487 | 0.3987 | 0.5923 | 0.8192 | 0.6756 | 0.6833 | 0.7475 |
| 43. 1i6c | 3.3920 | 3.4680 | 2.4920 | 2.2940 | 2.5040 | 2.5460 | 2.2760 | 0.2439 | 0.2550 | 0.4219 | 0.5581 | 0.4454 | 0.5625 | 0.5304 | 0.2923 | 0.3141 | 0.5680 | 0.7077 | 0.5769 | 0.7025 | 0.6910 |
| 44. 1bwx | 2.3680 | 2.3360 | 2.2060 | 2.0940 | 1.7100 | 1.8140 | 2.4980 | 0.4760 | 0.4983 | 0.4727 | 0.4979 | 0.5854 | 0.5614 | 0.4965 | 0.5231 | 0.5949 | 0.5539 | 0.5679 | 0.7051 | 0.6833 | 0.5859 |
| 45. 2ysh | 3.3320 | 3.1820 | 2.0500 | 2.3100 | 2.0700 | 2.1960 | 2.2700 | 0.2494 | 0.2558 | 0.4712 | 0.5880 | 0.5651 | 0.5854 | 0.5550 | 0.2950 | 0.3037 | 0.6100 | 0.7287 | 0.7375 | 0.7200 | 0.6988 |
| 46. 1wr7 | 3.0100 | 2.8900 | 2.0700 | 1.4080 | 1.2980 | 1.6080 | 1.3920 | 0.2635 | 0.2514 | 0.5284 | 0.7329 | 0.7387 | 0.6949 | 0.6776 | 0.3122 | 0.3293 | 0.6500 | 0.8439 | 0.8464 | 0.8195 | 0.7890 |
| 47. 1k1v | 2.6640 | 2.5180 | 2.2120 | 0.9500 | 1.3500 | 1.2600 | 1.2220 | 0.3060 | 0.3542 | 0.5101 | 0.8277 | 0.7702 | 0.7452 | 0.7558 | 0.2097 | 0.2073 | 0.2805 | 0.2756 | 0.2805 | 0.2781 | 0.2854 |
| 48. 2hep | 2.7580 | 2.9820 | 2.3020 | 2.0280 | 1.9550 | 1.9360 | 2.2400 | 0.3117 | 0.3608 | 0.5372 | 0.6374 | 0.6421 | 0.6189 | 0.5978 | 0.3083 | 0.4024 | 0.7107 | 0.7940 | 0.7828 | 0.7679 | 0.7619 |
| 49. 2dmv | 3.0380 | 3.5340 | 1.9600 | 1.7580 | 2.1060 | 1.9720 | 1.9260 | 0.2575 | 0.2456 | 0.4756 | 0.6194 | 0.6651 | 0.6509 | 0.5877 | 0.2907 | 0.2698 | 0.6105 | 0.7430 | 0.7919 | 0.7651 | 0.7256 |
| 50. 1res | 2.8700 | 2.8560 | 2.1720 | 1.9760 | 1.7700 | 1.7360 | 1.9520 | 0.3026 | 0.3156 | 0.4512 | 0.6295 | 0.6040 | 0.6192 | 0.6330 | 0.3140 | 0.3093 | 0.5756 | 0.7663 | 0.7442 | 0.7372 | 0.7616 |
| 51. 2p81 | 2.6440 | 2.5140 | 2.4400 | 2.2880 | 2.2420 | 2.0400 | 1.9120 | 0.4001 | 0.3840 | 0.4694 | 0.5795 | 0.5396 | 0.4943 | 0.4925 | 0.3375 | 0.3966 | 0.3137 | 0.3398 | 0.3395 | 0.3398 | 0.3398 |
| 52. 1ed7 | 3.2240 | 3.2780 | 3.4340 | 1.3380 | 1.4267 | 1.5800 | 1.3980 | 0.2680 | 0.2774 | 0.3306 | 0.7957 | 0.7954 | 0.7113 | 0.7680 | 0.2948 | 0.3051 | 0.3689 | 0.8879 | 0.8877 | 0.7938 | 0.7338 |
| 53. 1f4i | 2.7100 | 2.7640 | 2.4500 | 1.5500 | 1.4533 | 1.2820 | 1.4100 | 0.3436 | 0.3615 | 0.4075 | 0.8023 | 0.7849 | 0.8332 | 0.8119 | 0.3611 | 0.3800 | 0.4489 | 0.8956 | 0.8871 | 0.9156 | 0.9044 |
| 54. 2l4j | 3.3260 | 3.3940 | 2.5620 | 2.2180 | 2.4340 | 2.4040 | 2.0200 | 0.2546 | 0.2582 | 0.3802 | 0.5459 | 0.5129 | 0.4988 | 0.5395 | 0.2800 | 0.2841 | 0.3734 | 0.6005 | 0.5642 | 0.5487 | 0.5935 |
| 55. 1qhk | 3.4340 | 3.6260 | 3.2800 | 2.3740 | 2.6660 | 2.4340 | 2.2700 | 0.2731 | 0.2861 | 0.2881 | 0.6122 | 0.4555 | 0.5793 | 0.5707 | 0.2393 | 0.2457 | 0.2957 | 0.2351 | 0.2394 | 0.2319 | 0.2340 |
| 56. 1dv0 | 2.6600 | 2.9340 | 1.9400 | 1.2860 | 1.4600 | 1.6640 | 1.5020 | 0.3177 | 0.3040 | 0.3980 | 0.7689 | 0.7853 | 0.7551 | 0.7608 | 0.3622 | 0.3678 | 0.3734 | 0.5011 | 0.4752 | 0.4734 | 0.5078 |
| 57. 1pgy | 2.4480 | 2.3540 | 2.4000 | 2.3800 | 0.4200 | 2.4000 | 2.5060 | 0.3353 | 0.3283 | 0.5053 | 0.6338 | 0.9662 | 0.6386 | 0.5679 | 0.3851 | 0.3553 | 0.6138 | 0.7575 | 0.9947 | 0.7415 | 0.6979 |
| 58. 1e0g | 3.8200 | 3.3260 | 2.9520 | 1.8240 | 1.8300 | 1.8200 | 3.3580 | 0.2731 | 0.3225 | 0.4487 | 0.7396 | 0.7500 | 0.6981 | 0.2985 | 0.2656 | 0.2729 | 0.5656 | 0.8448 | 0.8594 | 0.8104 | 0.2915 |
| 59. 1ify | 3.3100 | 2.9820 | 2.7800 | 1.5020 | 2.1600 | 1.1520 | 1.7460 | 0.3319 | 0.3698 | 0.3635 | 0.8029 | 0.7123 | 0.8485 | 0.7545 | 0.3983 | 0.4438 | 0.4362 | 0.8799 | 0.8113 | 0.9376 | 0.7209 |
| 60. 1nd9 | 3.5260 | 3.2820 | 3.1580 | 2.7000 | 2.8550 | 2.9820 | 3.2020 | 0.2654 | 0.3022 | 0.4018 | 0.4789 | 0.4628 | 0.2540 | 0.4169 | 0.2541 | 0.2979 | 0.4245 | 0.4827 | 0.4286 | 0.4368 | 0.4225 |
References
- Apostolopoulos, V.; Bojarska, J.; Chai, T.; Elnagdy, S.; Kaczmarek, K.; Matsoukas, J.; New, R.; Parang, K.; Lopez, O.; Parhiz, H.; et al. A global review on short peptides: Frontiers and perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, S.; Belton, O.; Fitzgerald, D. Milk-derived bioactive peptides and their health promoting effects: A potential role in atherosclerosis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.M.; Haratipour, P.; Lingeman, R.G.; Perry, J.J.P.; Gu, L.; Hickey, R.J.; Malkas, L.H. Novel peptide therapeutic approaches for cancer treatment. Cells 2021, 10, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad-Malekshahi, M.; Lempsink, L.; Amidi, M.; Hennink, W.E.; Mastrobattista, E. Biomedical applications of self-assembling peptides. Bioconjugate Chem. 2016, 27, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, P.E.; Xu, X.; Kim, S.; Jon, S. Biomedical applications of a novel class of high-affinity peptides. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 3576–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Adler, J.; Wu, Z.; Green, T.; Zielinski, M.; Zídek, A.; Bridgland, A.; Cowie, A.; Meyer, C.; Laydon, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction for the human proteome. Nature 2021, 596, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauperl, M.; Denny, R.A. AI-based protein structure prediction in drug discovery: Impacts and challenges. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling. 2022, 62, 3142–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høie, M.; Kiehl, E.; Petersen, B.; Nielsen, M.; Winther, O.; Nielsen, H.; Hallgren, J.; Marcatili, P. NetSurfP-3.0: Accurate and fast prediction of protein structural features by protein language models and deep learning. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W510–W515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, S.; Law, E.C.; Shi, J.; Deane, C.M. Sequential search leads to faster, more efficient fragment-based de novo protein structure prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 34, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, A.W.; Evans, R.; Jumper, J.; Kirkpatrick, J.; Sifre, L.; Green, T.; Qin, C.; Žídek, A.; Nelson, A.W.R.; Bridgland, A.; et al. Protein structure prediction using multiple deep neural networks in the 13th Critical Assessment of Protein Structure Prediction (CASP13). Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2019, 87, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, W.E.; Istrail, S. Robust Proofs of NP-Hardness for Protein Folding: General Lattices and Energy Potentials. J. Comput. Biol. 1997, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. Application of nature-inspired computing paradigms in optimal design of structural engineering problems—A review. In Nature-Inspired Computing Paradigms in Systems; Academic Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Lodewijks, G.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, H. Reducing CO2 Emissions of an Airport Baggage Handling Transport System Using a Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 121894–121905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, H.; Iqbal, A.; Joshi, P.; Agrawal, S.; Bakhsh, F.I. (Eds.) Metaheuristic and Evolutionary Computation: Algorithms and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 916. [Google Scholar]
- Calvet, L.; Benito, S.; Juan, A.; Prados, F. On the role of metaheuristic optimization in bioinformatics. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2022, 30, 2909–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouni, S.E.; Menacer, T. Nizar optimization algorithm: A novel metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization and engineering applications. J. Supercomput. 2024, 80, 3229–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Sultan, A.; Sulaiman, M.; Mustapha, A.; Leong, K. Crossover and mutation operators of genetic algorithms. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2017, 7, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Dong, J.S.; Lewis, A.; Sadiq, A.S. Particle Swarm Optimization: Theory, Literature Review, and Application in Airfoil Design. In Nature-Inspired Optimizers: Theories, Literature Reviews and Applications; Mirjalili, S., Song Dong, J., Lewis, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 167–184. [Google Scholar]
- Dorigo, M.; Birattari, M.; Stutzle, T. Ant colony optimization. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2006, 1, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. A Quick Pheromone Matrix Adaptation Ant Colony Optimization for Dynamic Customers in the Vehicle Routing Problem. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peraza-Vázquez, H.; Peña-Delgado, A.F.; Echavarría-Castillo, G.; Morales-Cepeda, A.B.; Velasco-Álvarez, J.; Ruiz-Perez, F. A Bio-Inspired Method for Engineering Design Optimization Inspired by Dingoes Hunting Strategies. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9107547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Delgado, A.F.; Peraza-Vázquez, H.; Almazán-Covarrubias, J.H.; Cruz, N.T.; García-Vite, P.M.; Morales-Cepeda, A.B.; Ramirez-Arredondo, J.M. A novel bio-inspired algorithm applied to selective harmonic elimination in a three-phase eleven-level inverter. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8856040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naruei, I.; Keynia, F. A new optimization method based on COOT bird natural life model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 183, 115352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villuendas-Rey, Y.; Velázquez-Rodríguez, J.; Alanis-Tamez, M.; Moreno-Ibarra, M.-A.; Yáñez-Márquez, C. Mexican Axolotl Optimization: A Novel Bioinspired Heuristic. Mathematics 2021, 9, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peraza-Vázquez, H.; Peña-Delgado, A.; Merino-Treviño, M.; Morales-Cepeda, A.B.; Sinha, N. A novel metaheuristic inspired by horned lizard defense tactics. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Shehab, M.; Alshinwan, M.; Mirjalili, S.; Elaziz, M.A. Ant Lion Optimizer: A Comprehensive Survey of Its Variants and Applications. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 1397–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, S.; Gelatt, C.D.J.; Vecchi, M.P. Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 1983, 220, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabri, N.M.; Puteh, M.; Mahmood, M.R. An overview of Gravitational Search Algorithm utilization in optimization problems. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 3rd International Conference on System Engineering and Technology, Shah Alam, Malaysia, 19–20 August 2013; pp. 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, A.Y.; Li, V.O. Chemical-reaction-inspired metaheuristic for optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2009, 14, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, O.K.; Eksin, I. A new optimization method: Big bang–Big crunch. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2006, 37, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Li, X.; Razmjooy, N.; Ghadimi, N. Breast cancer diagnosis by convolutional neural network and advanced thermal exchange optimization algorithm. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 5595180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatas, B. ACROA: Artificial chemical reaction optimization algorithm for global optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 13170–13180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilagavathi, N.; Amudha, T. Rank based ant algorithm for 2D-HP protein folding. In Computational Intelligence in Data Mining-Volume 3: Proceedings of the International Conference on CIDM, Orlando, FL, USA, 20–21 December 2014; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2014; pp. 441–451. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, D.; Zeng, J.; Shi, Z. Using Gravitropism Artificial Plant Optimization Algorithm to Solve Toy Model of Protein Folding. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2013, 10, 1540–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumedine, N.; Bouroubi, S. Protein folding in 3D lattice HP model using a combining cuckoo search with the Hill-Climbing algorithms. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 119, 108564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frausto, J.; Sánchez, J.P.; Sánchez, M.; García, E.L. Golden Ratio Simulated Annealing for Protein Folding Problem. Int. J. Comput. Methods 2015, 12, 1550037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafarja, M.M.; Mirjalili, S. Hybrid whale optimization algorithm with simulated annealing for feature selection. Neurocomputing 2017, 260, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Sreedevi, I.; Gupta, D. Bio-inspired hybrid optimization algorithms for energy efficient wireless sensor networks: A comprehensive review. Electronics 2022, 11, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdita, M.; Schütze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiranuma, N.; Park, H.; Baek, M.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Baker, D. Improved protein structure refinement guided by deep learning based accuracy estimation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Hernández, J.P.; Frausto-Solís, J.; González-Barbosa, J.J.; Soto-Monterrubio, D.A.; Maldonado-Nava, F.G.; Castilla-Valdez, G. A Peptides Prediction Methodology for Tertiary Structure Based on Simulated Annealing. Math. Comput. Appl. 2021, 26, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Hernández, J.P.; Frausto-Solís, J.; Soto-Monterrubio, D.A.; González-Barbosa, J.J.; Roman-Rangel, E. A peptides prediction methodology with fragments and CNN for tertiary structure based on GRSA2. Axioms 2022, 11, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamiable, A.; Thévenet, P.; Rey, J.; Vavrusa, M.; Derreumaux, P.; Tufféry, P. PEP-FOLD3: Faster de Novo Structure Prediction for Linear Peptides in Solution and in Complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W449–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peraza-Vázquez, H.; Peña-Delgado, A.; Ranjan, P.; Barde, C.; Choubey, A.; Morales-Cepeda, A.B. A bio-inspired method for mathematical optimization inspired by Arachnida salticidade. Mathematics 2021, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortuza, S.M.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Pearce, R.; Zhang, Y. Improving fragment-based ab initio protein structure assembly using low-accuracy contact-map predictions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olechnovič, K.; Monastyrskyy, B.; Kryshtafovych, A.; Venclovas, Č. Comparative analysis of methods for evaluation of protein models against native structures. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frausto, J.; Sánchez, J.P.; Maldonado, F.; González, J.J. GRSA Enhanced for Protein Folding Problem in the Case of Peptides. Axioms 2019, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maupetit, J.; Derreumaux, P.; Tuffery, P. PEP-FOLD: An online resource for de novo peptide structure prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W498–W503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Maupetit, J.; Derreumaux, P.; Tufféry, P. Improved PEP-FOLD approach for peptide and miniprotein structure prediction. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 4745–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, C.; Bell, E.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER gateway: A protein structure and function prediction server powered by XSEDE. In Future Generations Computer Systems: FGCS; ELSEVIER: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 99, pp. 73–85. [Google Scholar]
- Mulnaes, D.; Porta, N.; Clemens, R.; Apanasenko, I.; Reiners, J.; Gremer, L.; Gohlke, H. TopModel: Template-based protein structure prediction at low sequence identity using top-down consensus and deep neural networks. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2020, 16, 1953–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, F.C.; Koetzle, T.F.; Williams, G.J.; Meyer, E.E.J.; Brice, M.D.; Rodgers, J.R.; Kennard, O.; Shimanouchi, T.; Tasumi, M. The Protein Data Bank: A Computer-based Archival File for Macromolecular Structures. J. Mol. Biol. 1977, 112, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Skolnick, J. Scoring function for automated assessment of protein structure template quality. Proteins 2004, 57, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kufareva, I.; Abagyan, R. Methods of protein structure comparison. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 857, 231–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eisenmenger, F.; Hansmann, U.H.; Hayryan, S.; Hu, C.-K. [SMMP] A modern package for simulation of proteins. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2001, 138, 192–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, K.A.; Maccallum, J.L. The Protein-Folding Problem. 50 Years On. Science 2012, 338, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinthal, C. Are There Pathways for Protein Folding. J. Chim. Phys. 1968, 65, 44–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Chialvo, D.R. Critical fluctuations in the native state of proteins. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 088102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, C.M.; Neal, B.L.; Lenhoff, A.M. Van der Waals interactions involving proteins. Biophys. J. 1996, 70, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anfinsen, C.B. Principles that Govern the Folding of Protein Chains. Science 1973, 181, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dill, K.A. Dominant forces in protein folding. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 7133–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponder, J.W.; Case, D.A. Force Fields for Protein Simulations. Accessory Fold. Proteins 2003, 66, 27–85. [Google Scholar]
- Lois, G.; Blawzdziewicz, J.; O’Hern, C.S. Protein folding on rugged energy landscapes: Conformational diffusion on fractal networks. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 051907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, H.; Qian, W.; Li, H. Protein structure optimization using improved simulated annealing algorithm on a three-dimensional AB off-lattice model. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2020, 85, 107237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, A. Bio inspired computing—A review of algorithms and scope of applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 59, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, S.H.; Shi, J.; Deane, C.M. Building a better fragment library for de novo protein structure prediction. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, E.E.; Sasiharan, Y.; Elias, D.O.; Mhatre, N. Jump takeoff in a small jumping spider. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2021, 207, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frausto, J.; Sanvicente, H.; Imperial, F. ANDYMARK: An analytical method to establish dynamically the length of the markov chain in simulated annealing for the satisfiability problem. In Asia-Pacific Conference on Simulated Evolution and Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Zemla, A.; Venclovas, C.; Moult, J.; Fidelis, K. Processing and analysis of casp3 protein structure predictions. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 1999, 3, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.B. Simulated Annealing. In Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Technical Reports; Syracuse University: Syracuse, NY, USA, 1992; Volume 170. [Google Scholar]

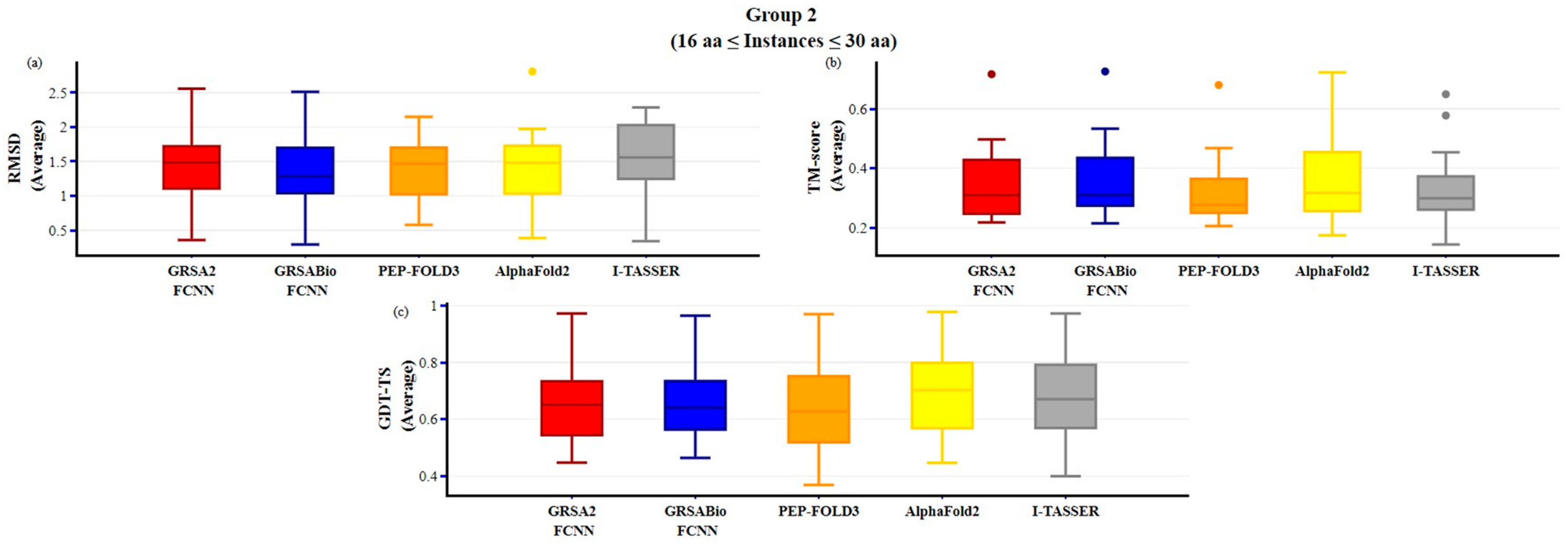
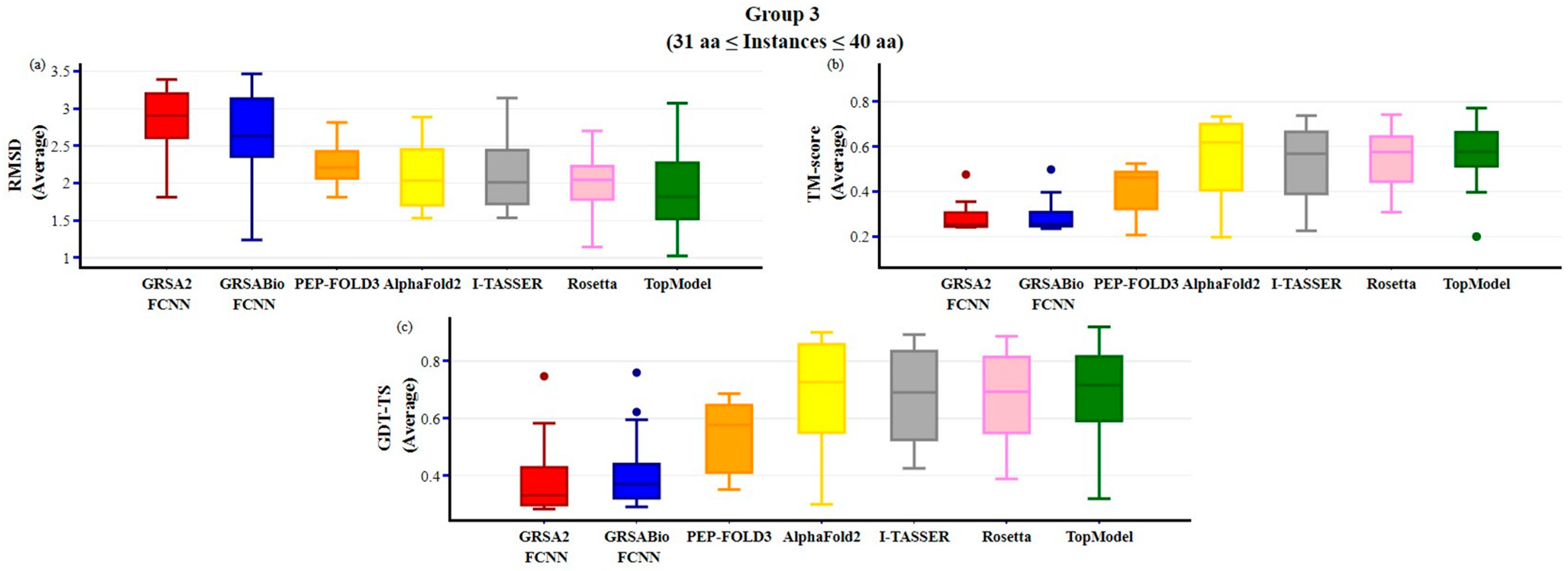
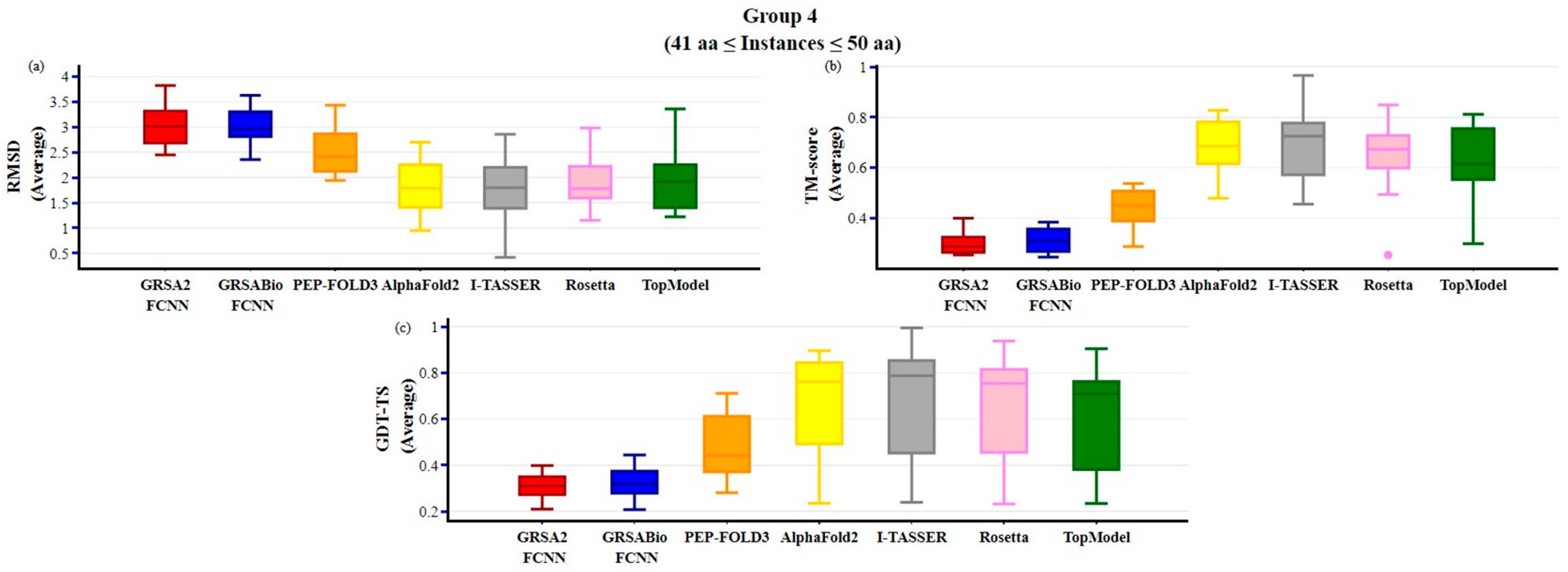

| Method | Type SS | Variables | Aa | PDB-Code | No | Method | Type SS | Variables | Aa | PDB-Code | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMR | N | 163 | 31 | 1t0c | 31 | NMR | N | 49 | 9 | 1egs | 1 |
| NMR | A | 201 | 31 | 2gdl | 32 | NMR | B | 47 | 10 | 1uao | 2 |
| NMR | A | 183 | 32 | 2l0g | 33 | NMR | N | 62 | 12 | 1l3q | 3 |
| NMR | A | 200 | 33 | 2bn6 | 34 | NMR | B | 66 | 12 | 2evq | 4 |
| NMR | A | 210 | 34 | 2kya | 35 | NMR | B | 69 | 12 | 1le1 | 5 |
| NMR | B | 197 | 36 | 1wr3 | 36 | NMR | A | 74 | 12 | 1in3 | 6 |
| NMR | B | 206 | 36 | 1wr4 | 37 | X-ray | N | 61 | 13 | 1eg4 | 7 |
| NMR | B | 206 | 37 | 1e0m | 38 | X-ray | A | 81 | 13 | 1rnu | 8 |
| NMR | B | 212 | 37 | 1yiu | 39 | NMR | N | 81 | 13 | 1lcx | 9 |
| NMR | B | 221 | 37 | 1e0l | 40 | X-ray | N | 74 | 14 | 3bu3 | 10 |
| NMR | N | 216 | 38 | 1bhi | 41 | NMR | A | 79 | 14 | 1gjf | 11 |
| NMR | B | 208 | 39 | 1jrj | 42 | NMR | B | 84 | 14 | 1k43 | 12 |
| NMR | A | 218 | 39 | 1i6c | 43 | NMR | N | 85 | 14 | 1a13 | 13 |
| NMR | A | 242 | 39 | 1bwx | 44 | NMR | A | 94 | 15 | 1dep | 14 |
| NMR | B | 213 | 40 | 2ysh | 45 | NMR | N | 100 | 15 | 2bta | 15 |
| NMR | B | 222 | 41 | 1wr7 | 46 | NMR | A | 86 | 16 | 1nkf | 16 |
| NMR | A | 279 | 41 | 1k1v | 47 | NMR | B | 91 | 16 | 1le3 | 17 |
| NMR | A | 268 | 42 | 2hep | 48 | X-ray | B | 93 | 16 | 1pgbF | 18 |
| NMR | A | 229 | 43 | 2dmv | 49 | NMR | B | 97 | 16 | 1niz | 19 |
| NMR | B | 268 | 43 | 1res | 50 | NMR | B | 109 | 17 | 1e0q | 20 |
| NMR | A | 295 | 44 | 2p81 | 51 | NMR | N | 120 | 17 | 1wbr | 21 |
| NMR | B | 247 | 45 | 1ed7 | 52 | NMR | A | 124 | 17 | 1rpv | 22 |
| NMR | A | 276 | 45 | 1f4i | 53 | NMR | B | 109 | 18 | 1b03 | 23 |
| NMR | B | 250 | 46 | 2l4j | 54 | X-ray | A | 124 | 18 | 1pef | 24 |
| NMR | A | 272 | 47 | 1qhk | 55 | NMR | A | 100 | 20 | 1l2y | 25 |
| NMR | A | 279 | 47 | 1dv0 | 56 | NMR | A | 134 | 20 | 1du1 | 26 |
| NMR | N | 304 | 47 | 1pgy | 57 | NMR | A | 143 | 22 | 1pei | 27 |
| NMR | N | 294 | 48 | 1e0g | 58 | NMR | A | 123 | 23 | 1wz4 | 28 |
| NMR | N | 290 | 49 | 1ify | 59 | NMR | A | 160 | 27 | 1yyb | 29 |
| NMR | A | 303 | 49 | 1nd9 | 60 | NMR | A | 193 | 27 | 1by0 | 30 |
| Approach | Parameter | Typical Value/Description |
|---|---|---|
| GRSA2-FCNN | A | [0.70, 0.95] |
| Φ | 0.618 | |
| Fragment length (residues) | 6 | |
| GRSABio-FCNN | A | [0.70, 0.95] |
| Φ | 0.618 | |
| Fragment length (residues) | 6 | |
| Number of agents | 10 | |
| Maximum Iterations | 20 | |
| PEP-FOLD3 | Number of simulations | 100 |
| Fragment library | Precomputed structural motifs from known peptides | |
| AlphaFold2 | Number of recycles | 3 |
| MSA * depth | ~512 | |
| Structure module iterations | Typically, 3–8 | |
| Model confidence score | pLDDT (0–100) | |
| I-TASSER | Number of threading templates | Top 10 from LOMETS |
| Number of Monte Carlo simulations | 20 models | |
| Clustering method | SPICKER | |
| Rosetta | Fragment length (residues) | (3–9) |
| Number of decoys | (1000–10,000) | |
| Energy function | Rosetta score12 | |
| TopModel | Scoring model | Deep neural network scoring |
| Instances | Energy GRSABio-FCNN vs. GRSA2-FCNN | RMSD GRSABio-FCNN vs. GRSA2-FCNN | TM-score GRSABio-FCNN vs. GRSA2-FCNN | GDT-TS GRSABio-FCNN vs. GRSA2-FCNN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| From 1 to 30 | (+/=/−) 25/0/5 p-value: 5.00 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 22/0/8 p-value: 8.73 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 25/1/4 p-value: 4.41 × 10−4 | (+/=/−) 11/1/18 p-value: 4.96 × 10−1 |
| From 31 to 60 | (+/=/−) 30/0/0 p-value: 2.00 × 10−6 | (+/=/−) 19/0/11 p-value: 7.86 × 10−2 | (+/=/−) 22/0/8 p-value: 2.06 × 10−2 | (+/=/−) 25/0/5 p-value: 8.73 × 10−3 |
| From 1 to 60 | (+/=/−) 55/0/5 p-value: 6.31 × 10−9 | (+/=/−) 41/0/19 p-value: 2.60 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 47/1/12 p-value: 4.20 × 10−5 | (+/=/−) 36/1/23 p-value: 3.86 × 10−2 |
| Algorithms | RMSD | TM-Score | GDT-TS |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. GRSA2-FCNN | (+/=/−) 12/0/3 p-value: 1.67 × 10−2 | (+/=/−) 12/1/2 p-value: 1.85x10−2 | (+/=/−) 5/0/10 p-value: 2.80x10−1 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. PEP-FOLD3 | (+/=/−) 6/0/9 p-value: 9.54 × 10−1 | (+/=/−) 11/0/4 p-value: 9.95 × 10−2 | (+/=/−) 5/0/10 p-value: 7.82 × 10−2 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. AlphaFold2 | (+/=/−) 8/0/7 p-value: 7.76 × 10−1 | (+/=/−) 10/0/5 p-value: 3.34 × 10−1 | (+/=/−) 4/0/11 p-value: 1.91 × 10−1 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. I-TASSER * | (+/=/−) 9/0/5 p-value: 2.71 × 10−1 | (+/=/−) 12/0/2 p-value: 9.18 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 5/0/9 p-value: 4.70 × 10−1 |
| Algorithms | RMSD | TM-Score | GDT-TS |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. GRSA2-FCNN | (+/=/−) 10/0/5 p-value: 1.72 × 10−1 | (+/=/−) 13/0/2 p-value: 6.39 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 6/0/8 p-value: 9.24 × 10−1 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. PEP-FOLD3 | (+/=/−) 9/0/6 p-value: 6.90 × 10−1 | (+/=/−) 13/0/2 p-value: 1.70 × 10−2 | (+/=/−) 10/0/5 p-value: 3.06 × 10−1 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. AlphaFold2 | (+/=/−) 9/0/6 p-value: 6.49 × 10−1 | (+/=/−) 10/0/5 p-value: 6.90 × 10−1 | (+/=/−) 4/0/11 p-value: 9.95 × 10−2 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. I-TASSER | (+/=/−) 11/0/4 p-value: 3.63 × 10−1 | (+/=/−) 11/0/4 p-value: 1.91 × 10−1 | (+/=/−) 5/0/10 p-value: 5.70 × 10−1 |
| Algorithms | RMSD | TM-Score | GDT-TS |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. GRSA2-FCNN | (+/=/−) 11/0/4 p-value: 4.08 × 10−2 | (+/=/−) 12/0/3 p-value: 6.91 × 10−2 | (+/=/−) 14/0/1 p-value: 1.46 × 10−3 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. PEP-FOLD3 | (+/=/−) 5/0/10 p-value: 3.56 × 10−2 | (+/=/−) 4/0/11 p-value: 7.59 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 5/0/10 p-value: 6.08 × 10−2 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. AlphaFold2 | (+/=/−) 4/0/11 p-value: 3.08 × 10−2 | (+/=/−) 4/0/11 p-value: 4.51 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 3/0/12 p-value: 6.40 × 10−3 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. I-TASSER | (+/=/−) 5/0/10 p-value: 3.56 × 10−2 | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 8.05 × 10−4 | (+/=/−) 1/0/14 p-value: 3.14 × 10−3 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. Rosetta | (+/=/−) 3/0/12 p-value: 1.05 × 10−2 | (+/=/−) 1/0/14 p-value: 8.05 × 10−4 | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 3.77 × 10−3 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. Top-Model | (+/=/−) 3/0/12 p-value: 4.92 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 1.20 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 3/0/12 p-value: 4.51 × 10−3 |
| Algorithms | RMSD | TM-Score | GDT-TS |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. GRSA2-FCNN | (+/=/−) 8/0/7 p-value: 7.76 × 10−1 | (+/=/−) 8/0/7 p-value: 3.06 × 10−1 | (+/=/−) 11/0/4 p-value: 4.68 × 10−2 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. PEP-FOLD3 | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 1.78 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 5/0/10 p-value: 1.39 × 10−1 | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 3.77 × 10−3 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. AlphaFold2 | (+/=/−) 1/0/14 p-value: 8.05 × 10−4 | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 1.20 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 1.20 × 10−3 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. I-TASSER | (+/=/−) 0/0/15 p-value: 6.53 × 10−4 | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 1.47 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 1.20 × 10−3 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. Rosetta | (+/=/−) 1/0/14 p-value: 8.05 × 10−4 | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 4.51 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 1.20 × 10−3 |
| GRSABio-FCNN vs. TopModel | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 1.47 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 2.61 × 10−3 | (+/=/−) 2/0/13 p-value: 1.47 × 10−3 |
| Algorithms | RMSD | TM-Score | GDT-TS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean of Ranks | Overall of Ranks | Mean of Ranks | Overall of Ranks | Mean of Ranks | Overall of Ranks | |
| GRSA2-FCNN | 3.48 | 4 | 2.95 | 3 | 3.34 | 4 |
| GRSABio-FCNN | 2.45 | 1 | 1.91 | 1 | 3.53 | 5 |
| PEP-FOLD3 | 2.59 | 2 | 3.55 | 4 | 3.22 | 3 |
| AlphaFold2 | 2.97 | 3 | 2.76 | 2 | 2.07 | 1 |
| I-TASSER | 3.52 | 5 | 3.83 | 5 | 2.83 | 2 |
| Algorithms | RMSD | TM-Score | GDT-TS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean of Ranks | Overall of Ranks | Mean of Ranks | Overall of Ranks | Mean of Ranks | Overall of Ranks | |
| GRSA2-FCNN | 6.32 | 7 | 6.47 | 7 | 6.33 | 7 |
| GRSABio-FCNN | 5.50 | 6 | 5.77 | 6 | 5.37 | 6 |
| PEP-FOLD3 | 4.52 | 5 | 5.03 | 5 | 4.98 | 5 |
| AlphaFold2 | 2.87 | 3 | 2.28 | 1 | 2.37 | 1 |
| I-TASSER | 3.30 | 4 | 2.53 | 2 | 2.65 | 2 |
| Rosetta | 2.72 | 1 | 2.77 | 3 | 3.02 | 3 |
| TopModel | 2.78 | 2 | 3.15 | 4 | 3.28 | 4 |
| Approach | Features | Advantages | Disadvantages | Constraints |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEP-FOLD3 | Specialized in de novo prediction of short peptides (up to 50 amino acids). | Fast and easy to use; good for small peptides | Not suitable for large proteins; limited structural accuracy for complex folds. | Limited to peptides; does not handle large or multi-domain proteins. |
| AlphaFold2 | Deep learning-based, uses evolutionary, structural, and physical data. | State-of-the-art accuracy; predicts full atom-level protein structures. | Computationally intensive; model architecture is complex. | Requires multiple sequence alignment (MSA) and significant computing resources; not ideal for short peptides. |
| I-TASSER | Threading-based with ab initio modeling; ranks models using clustering (from 10 to 1500 amino acids). | Good for proteins with known homologs; provides function prediction. | Less accurate for proteins without templates; longer computation times. | Dependent on structural templates; less effective for novel folds. |
| Rosetta | Uses fragment assembly and energy minimization; highly customizable suitable for sequences starting from 27 amino acids | Versatile for structure, docking, and design; proven across many scenarios. | High complexity; steep learning curve; requires fine-tuning. | Demands significant CPU/GPU time and technical knowledge to set up properly |
| TopModel | Combines deep learning with consensus scoring; designed for model quality assessment, applicable from sequences as short as 30 amino acids. | Enhances reliability of predicted structures by model quality evaluation. | Not a structure predictor itself; relies on input from other predictors. | Works as a complementary tool; does not generate initial models. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soto-Monterrubio, D.A.; Peraza-Vázquez, H.; Peña-Delgado, A.F.; González-Hernández, J.G. Enhanced Methodology for Peptide Tertiary Structure Prediction Using GRSA and Bio-Inspired Algorithm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157484
Soto-Monterrubio DA, Peraza-Vázquez H, Peña-Delgado AF, González-Hernández JG. Enhanced Methodology for Peptide Tertiary Structure Prediction Using GRSA and Bio-Inspired Algorithm. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157484
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoto-Monterrubio, Diego A., Hernán Peraza-Vázquez, Adrián F. Peña-Delgado, and José G. González-Hernández. 2025. "Enhanced Methodology for Peptide Tertiary Structure Prediction Using GRSA and Bio-Inspired Algorithm" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157484
APA StyleSoto-Monterrubio, D. A., Peraza-Vázquez, H., Peña-Delgado, A. F., & González-Hernández, J. G. (2025). Enhanced Methodology for Peptide Tertiary Structure Prediction Using GRSA and Bio-Inspired Algorithm. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157484






