rs2231142 (421 C>A, Q141K) Is More Functionally Influential than rs2231137 (34 G>A, V12M) on Anticancer Drug Resistance Mediated by the ABCG2 Haplotype In Vitro
Abstract
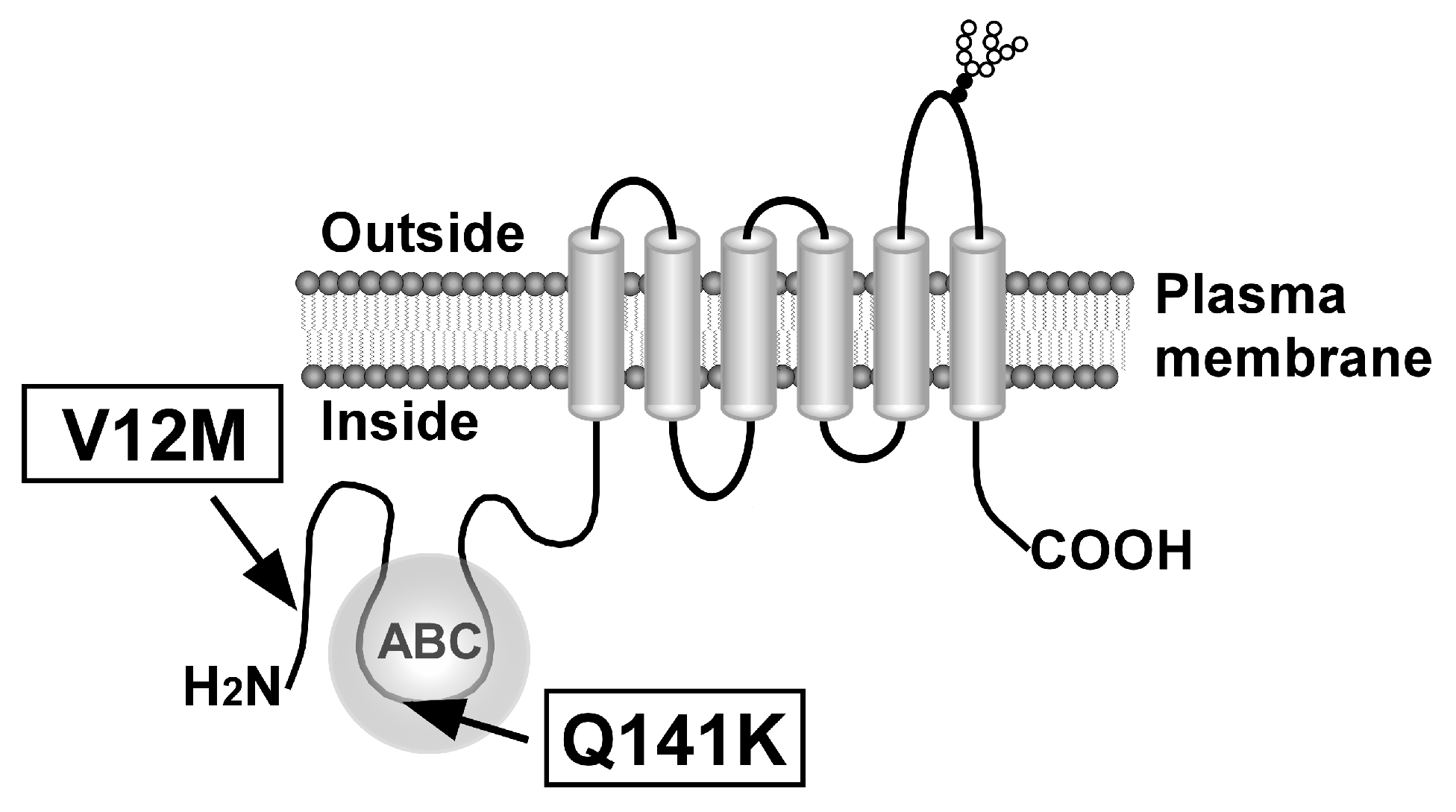
1. Introduction
2. Results
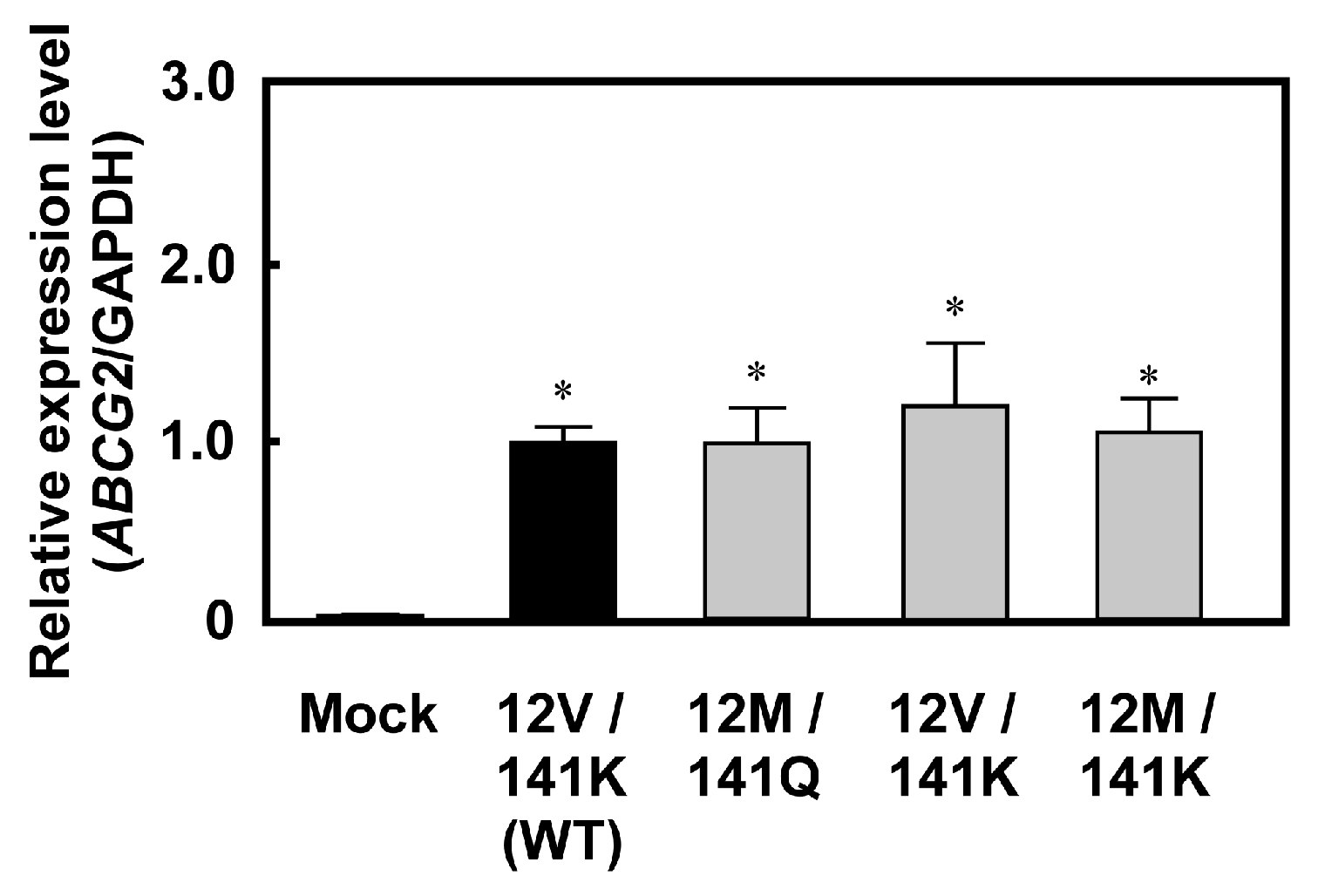
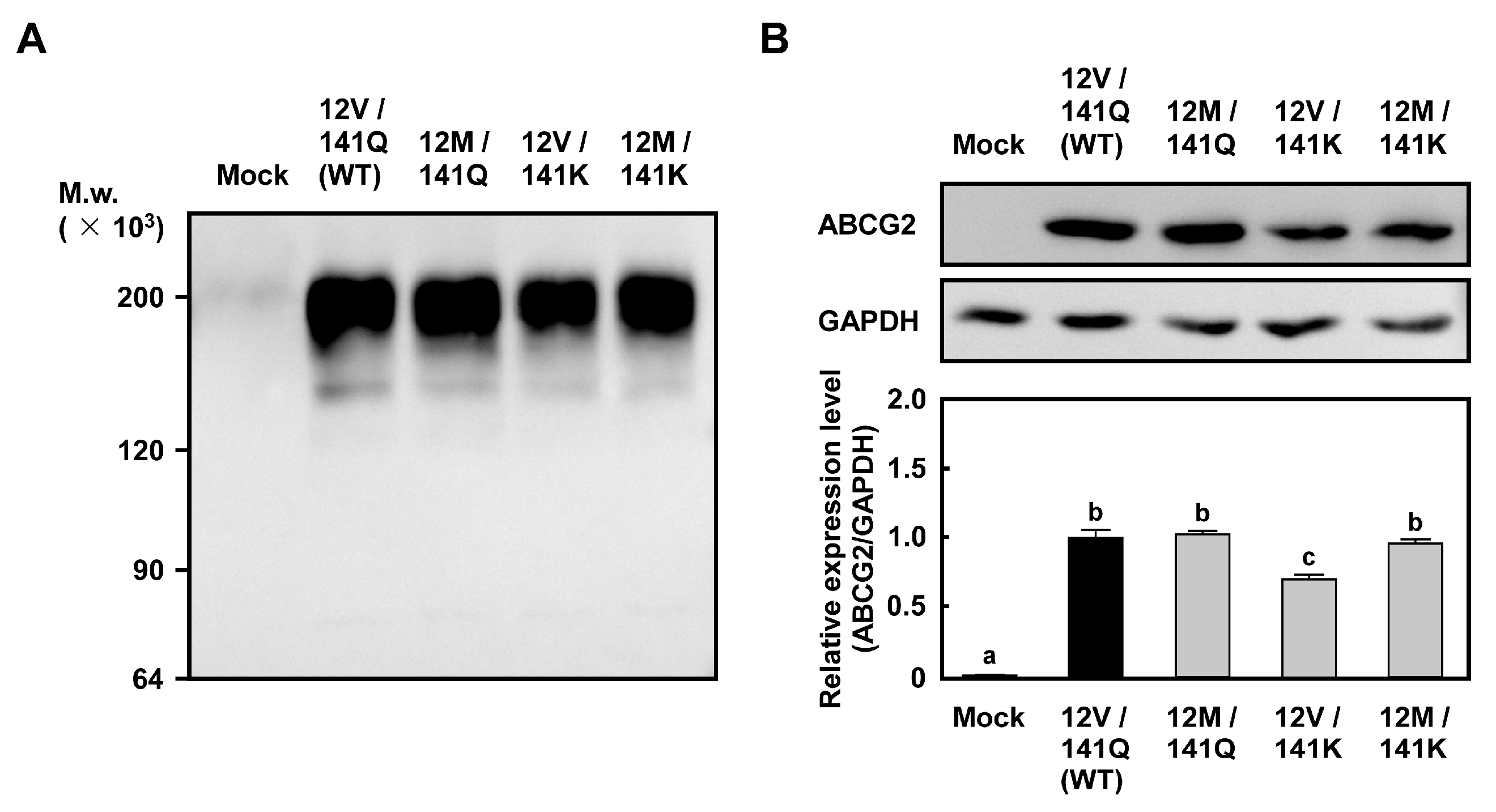
2.1. Levels of ABCG2 mRNA and Protein in Cells Expressing ABCG2 (12M/141K)
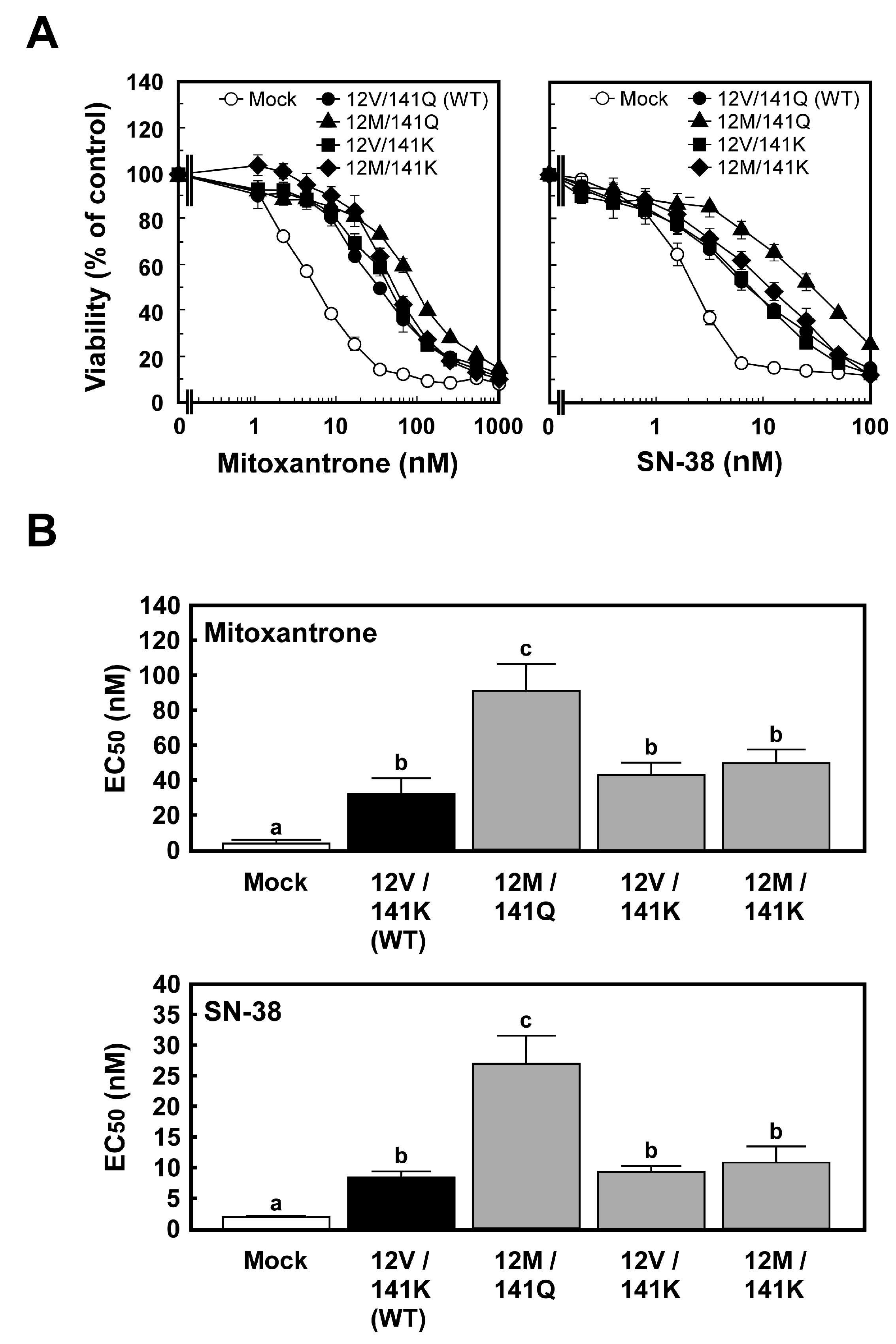
2.2. Anticancer Drug Resistance of Cells Expressing ABCG2 (12M/141K)
3. Discussion
3.1. Establishment of Human ABCG2 (12M/141K)-Expressing Cells Using the Flp-In™ System
3.2. Anticancer Drug Resistance of Flp-In-293/ABCG2 (12M/141K) Cells
3.3. Comparison of Haplotype-Specific Effects of ABCG2 (12M/141Q) and ABCG2 (12V/141K) on Cellular Resistance to Anticancer Drugs
3.4. Haplotype-Specific Effects of ABCG2 (12M/141K) on Cellular Resistance to Anticancer Drugs
3.5. Future Perspectives
4. Materials and Methods
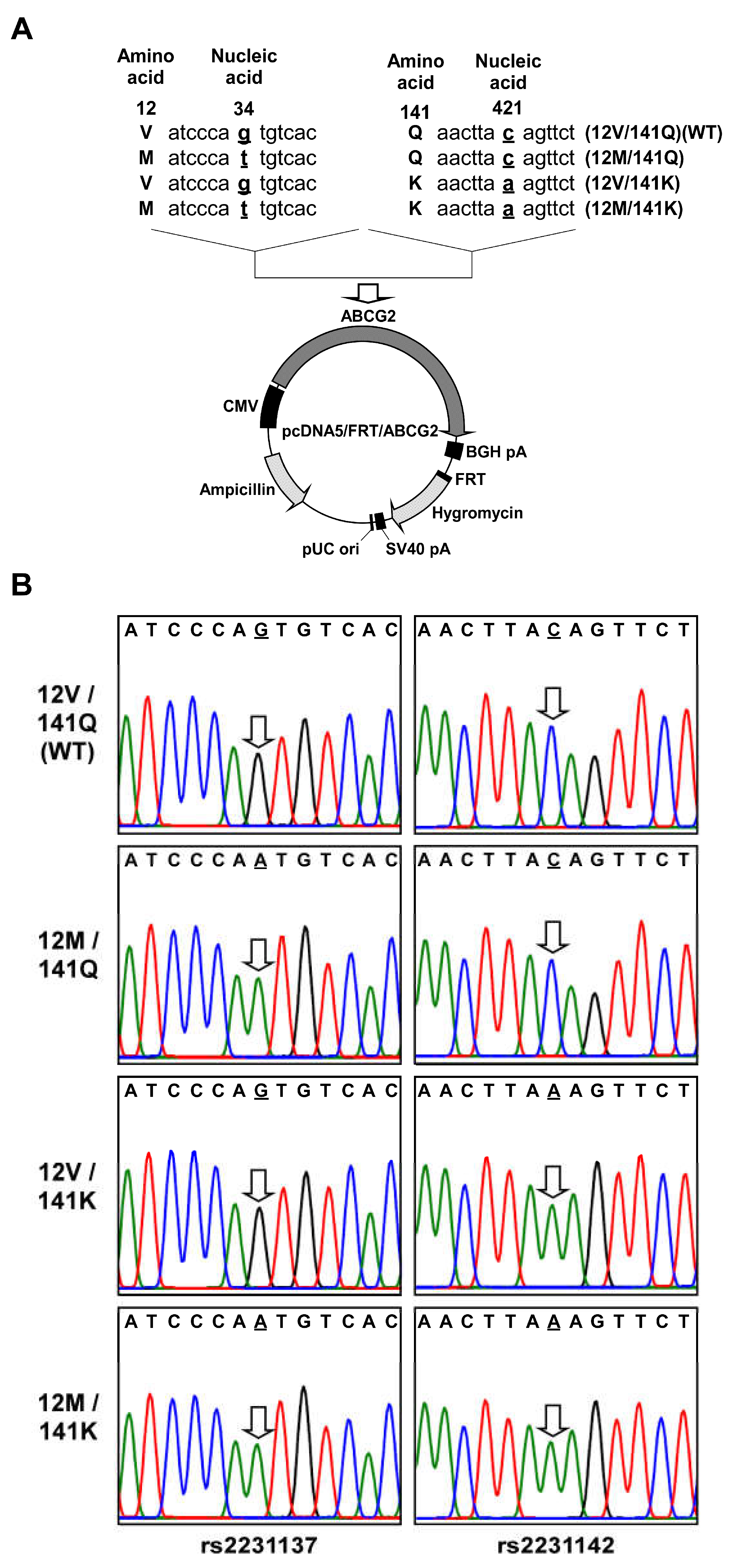
4.1. Preparation of pcDNA5/FRT Containing ABCG2 (12M/141K) Variant cDNA
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Generation of Cells Expressing ABCG2 (12M/141K) Variant
4.4. Total RNA Preparation and First-Strand cDNA Synthesis
4.5. Quantitative Evaluation of ABCG2 mRNA
4.6. MTT Assay
4.7. Cell Lysate Preparation for SDS-PAGE
4.8. Evaluation of Expression Status and Levels of ABCG2
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | ATP-binding cassette |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BCRP | Breast cancer resistance protein |
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| FRT | Flp recombination target |
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| HRP | horseradish peroxidase |
| HSD | Honestly Significant Difference |
| MTT | 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| MXR | Mitoxantrone resistance-associated protein |
| PBS(–) | phosphate-buffered saline without calcium and magnesium |
| qPCR | quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate -Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| TBS | Tris-buffered saline |
| TBST | TBS with 0.05% (v/v) Tween 20 |
| WT | Wild-Type |
References
- Juliano, R.L.; Ling, V. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 455, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, K.; Cornwell, M.M.; Gottesman, M.M.; Pastan, I.; Roninson, I.B.; Ling, V.; Riordan, J.R. The mdr1 gene, responsible for multidrug-resistance, codes for P-glycoprotein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 141, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, S.P.; Bhardwaj, G.; Gerlach, J.H.; Mackie, J.E.; Grant, C.E.; Almquist, K.C.; Stewart, A.J.; Kurz, E.U.; Duncan, A.M.; Deeley, R.G. Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung cancer cell line. Science 1992, 258, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.A.; Yang, W.; Abruzzo, L.V.; Krogmann, T.; Gao, Y.; Rishi, A.K.; Ross, D.D. A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15665–15670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allikmets, R.; Schriml, L.M.; Hutchinson, A.; Romano-Spica, V.; Dean, M. A human placenta-specific ATP-binding cassette gene (ABCP) on chromosome 4q22 that is involved in multidrug resistance. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 5337–5339. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, K.; Mickley, L.; Litman, T.; Zhan, Z.; Robey, R.; Cristensen, B.; Brangi, M.; Greenberger, L.; Dean, M.; Fojo, T.; et al. Molecular cloning of cDNAs which are highly overexpressed in mitoxantrone-resistant cells: Demonstration of homology to ABC transport genes. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maliepaard, M.; van Gastelen, M.A.; de Jong, L.A.; Pluim, D.; van Waardenburg, R.C.; Ruevekamp-Helmers, M.C.; Floot, B.G.; Schellens, J.H. Overexpression of the BCRP/MXR/ABCP gene in a topotecan-selected ovarian tumor cell line. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4559–4563. [Google Scholar]
- Kage, K.; Tsukahara, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Asada, S.; Ishikawa, E.; Tsuruo, T.; Sugimoto, Y. Dominant-negative inhibition of breast cancer resistance protein as drug efflux pump through the inhibition of S-S dependent homodimerization. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 97, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, C.; Suzuki, H.; Itoda, M.; Ozawa, S.; Sawada, J.; Kobayashi, D.; Ieiri, I.; Mine, K.; Ohtsubo, K.; Sugiyama, Y. Functional analysis of SNPs variants of BCRP/ABCG2. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Suzuki, H.; Sugimoto, Y.; Sugiyama, Y. ABCG2 transports sulfated conjugates of steroids and xenobiotics. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 22644–22649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan-Garcia, A.; Alvarez-Fernandez, L.; Blanco-Paniagua, E.; Alvarez, A.I.; Merino, G. The ABCG2 Transporter Affects Plasma Levels, Tissue Distribution and Milk Secretion of Lumichrome, a Natural Derivative of Riboflavin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, A.; Watanabe, M.; Saito, H.; Nakagawa, H.; Kamachi, T.; Okura, I.; Ishikawa, T. Functional validation of the genetic polymorphisms of human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter ABCG2: Identification of alleles that are defective in porphyrin transport. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zong, Y.; Ney, P.A.; Nair, G.; Stewart, C.F.; Sorrentino, B.P. Increased expression of the Abcg2 transporter during erythroid maturation plays a role in decreasing cellular protoporphyrin IX levels. Blood 2005, 105, 2571–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zattoni, I.F.; Kronenberger, T.; Kita, D.H.; Guanaes, L.D.; Guimaraes, M.M.; de Oliveira Prado, L.; Ziasch, M.; Vesga, L.C.; Gomes de Moraes Rego, F.; Picheth, G.; et al. A new porphyrin as selective substrate-based inhibitor of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2). Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 351, 109718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, O.M.; Kottgen, A.; Coresh, J.; Boerwinkle, E.; Guggino, W.B.; Kottgen, M. Identification of a urate transporter, ABCG2, with a common functional polymorphism causing gout. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10338–10342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brangi, M.; Litman, T.; Ciotti, M.; Nishiyama, K.; Kohlhagen, G.; Takimoto, C.; Robey, R.; Pommier, Y.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S.E. Camptothecin resistance: Role of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC), mitoxantrone-resistance half-transporter (MXR), and potential for glucuronidation in MXR-expressing cells. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5938–5946. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, S.; Oka, M.; Shiozawa, K.; Tsukamoto, K.; Nakatomi, K.; Soda, H.; Fukuda, M.; Ikegami, Y.; Sugahara, K.; Yamada, Y.; et al. Breast cancer resistance protein directly confers SN-38 resistance of lung cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Nakane, M.; Kage, K.; Tsukahara, S.; Ishikawa, E.; Tsuruo, T.; Miki, Y.; Sugimoto, Y. C421A polymorphism in the human breast cancer resistance protein gene is associated with low expression of Q141K protein and low-level drug resistance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 611–616. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuarai, S.; Aozasa, N.; Kotani, H. Single nucleotide polymorphisms result in impaired membrane localization and reduced ATPase activity in multidrug transporter ABCG2. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, A.; Wakabayashi, K.; Onishi, Y.; Takeda, M.; Ikegami, Y.; Sawada, S.; Tsuji, M.; Matsuda, Y.; Ishikawa, T. Re-evaluation and functional classification of non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms of the human ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, H.; van Tol, H.; Boersma, A.W.; Brok, M.; Wiemer, E.A.; Stoter, G.; Nooter, K. Imatinib mesylate (STI571) is a substrate for the breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP)/ABCG2 drug pump. Blood 2004, 104, 2940–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breedveld, P.; Pluim, D.; Cipriani, G.; Wielinga, P.; van Tellingen, O.; Schinkel, A.H.; Schellens, J.H. The effect of Bcrp1 (Abcg2) on the in vivo pharmacokinetics and brain penetration of imatinib mesylate (Gleevec): Implications for the use of breast cancer resistance protein and P-glycoprotein inhibitors to enable the brain penetration of imatinib in patients. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2577–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitomo, H.; Kato, R.; Ito, A.; Kasamatsu, S.; Ikegami, Y.; Kii, I.; Kudo, A.; Kobatake, E.; Sumino, Y.; Ishikawa, T. A functional study on polymorphism of the ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2: Critical role of arginine-482 in methotrexate transport. Biochem. J. 2003, 373, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Adachi, T.; Kii, I.; Kobatake, E.; Kudo, A.; Ishikawa, T. Identification of cysteine residues critically involved in homodimer formation and protein expression of human ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2: A new approach using the flp recombinase system. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2006, 5, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Volk, E.L.; Farley, K.M.; Wu, Y.; Li, F.; Robey, R.W.; Schneider, E. Overexpression of wild-type breast cancer resistance protein mediates methotrexate resistance. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5035–5040. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.S.; Robey, R.W.; Belinsky, M.G.; Shchaveleva, I.; Ren, X.Q.; Sugimoto, Y.; Ross, D.D.; Bates, S.E.; Kruh, G.D. Transport of methotrexate, methotrexate polyglutamates, and 17beta-estradiol 17-(beta-D-glucuronide) by ABCG2: Effects of acquired mutations at R482 on methotrexate transport. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4048–4054. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, H.; Xiao, Q.; Yao, W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, E.; Wei, M. Genetic Variations in ABCG2 Gene Predict Breast Carcinoma Susceptibility and Clinical Outcomes after Treatment with Anthracycline-Based Chemotherapy. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 279109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao Ing, Y.; Md Salleh, M.S.; Yahya, M.M.; Ankathil, R.; Abdul Aziz, A.A. Association of ABCG2 Polymorphisms on Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Susceptibility Risk. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2023, 24, 3891–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguz, M.; Tarle, M.; Muller, D.; Tomasovic-Loncaric, C.; Chudy, H.; Marinovic, T.; Chudy, D. ABCG2 Expression as a Potential Survival Predictor in Human Gliomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.H.; Yu, J.; Chu, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Yeh, C.T. Child-Pugh Score and ABCG2-rs2231142 Genotype Independently Predict Survival in Advanced Hepatoma Patients Treated with Sorafenib. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, D.; Butterbach, K.; Slager, S.L.; Skibola, C.F.; de Sanjose, S.; Benavente, Y.; Becker, N.; Foretova, L.; Maynadie, M.; Cocco, P.; et al. A comprehensive study of polymorphisms in the ABCB1, ABCC2, ABCG2, NR1I2 genes and lymphoma risk. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.L.; Wang, X.X.; Chen, X.; Chang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Jiang, W.; Zhuang, S.M. BCRP gene polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility and survival of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 1740–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korenaga, Y.; Naito, K.; Okayama, N.; Hirata, H.; Suehiro, Y.; Hamanaka, Y.; Matsuyama, H.; Hinoda, Y. Association of the BCRP C421A polymorphism with nonpapillary renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 117, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, C.; Li, X.; Mao, C.; Qian, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Li, Q.; Bai, C.; Han, B.; et al. A pharmacogenetics study of platinum-based chemotherapy in lung cancer: ABCG2 polymorphism and its genetic interaction with SLC31A1 are associated with response and survival. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 1270–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, T.; Tamura, A.; Saito, H.; Wakabayashi, K.; Nakagawa, H. Pharmacogenomics of the human ABC transporter ABCG2: From functional evaluation to drug molecular design. Naturwissenschaften 2005, 92, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, A.; Wakabayashi, K.; Onishi, Y.; Nakagawa, H.; Tsuji, M.; Matsuda, Y.; Ishikawa, T. Genetic polymorphisms of human ABC transporter ABCG2: Development of the standard method for functional validation of SNPs by using the Flp recombinase system. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2006, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.; Dhotre, K.; Shyamveer; Choudhari, R.; Verma, A.; Mahajan, S.D.; Ali, N. ABCG2 polymorphisms and susceptibility to ARV-associated hepatotoxicity. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2024, 12, e2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gu, X.; Wang, H.; Luo, X.; Zhang, J.; Zou, H.; Guan, M. Functional polymorphisms of the ABCG2 gene are associated with gout disease in the Chinese Han male population. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 9149–9159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, H.; Tamura, A.; Wakabayashi, K.; Hoshijima, K.; Komada, M.; Yoshida, T.; Kometani, S.; Matsubara, T.; Mikuriya, K.; Ishikawa, T. Ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation of non-synonymous SNP variants of human ABC transporter ABCG2. Biochem. J. 2008, 411, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, K.M.; Dixon, E.E.; Lewis, R.M.; Allan, J.; Gamble, G.D.; Phipps-Green, A.J.; Halperin Kuhns, V.L.; Horne, A.M.; Stamp, L.K.; Merriman, T.R.; et al. The ABCG2 Q141K hyperuricemia and gout associated variant illuminates the physiology of human urate excretion. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Chiang, H.Y.; Chang, D.R.; Cheng, C.F.; Wang, C.C.N.; Lu, T.P.; Lee, C.Y.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Lin, Y.T.; Lin, C.C.; et al. Discovery and prioritization of genetic determinants of kidney function in 297,355 individuals from Taiwan and Japan. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimian, M.; Shabani, M.; Nikzad, H. Association of Functional Genetic Variations in Uric Acid Transporters with the Risk of Idiopathic Male Infertility: A Genetic Association Study and Bioinformatic Analysis. Biochem. Genet. 2024, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.; Geng, M.; Zhang, R.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; et al. Value of ABCG2 Q141K and Q126X genotyping in predicting risk of preeclampsia in Chinese Han women population. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2019, 17, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, E.; Kulin, A.; Mozner, O.; Koranyi, L.; Literati-Nagy, B.; Vitai, M.; Cserepes, J.; Sarkadi, B.; Varady, G. Potential role of the ABCG2-Q141K polymorphism in type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, D.; Hauser, H. Flp-mediated integration of expression cassettes into FRT-tagged chromosomal loci in mammalian cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2004, 267, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Wakabayashi-Nakao, K.; Nakagawa, H. Methods to examine the impact of nonsynonymous SNPs on protein degradation and function of human ABC transporter. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1015, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosztyu, P.; Dolezel, P.; Mlejnek, P. Can P-glycoprotein mediate resistance to nilotinib in human leukaemia cells? Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 67, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosztyu, P.; Bukvova, R.; Dolezel, P.; Mlejnek, P. Resistance to daunorubicin, imatinib, or nilotinib depends on expression levels of ABCB1 and ABCG2 in human leukemia cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 219, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cell Type | EC50 (nM) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitoxantrone | SN-38 | |||||
| Mock | 4.67 | ± | 1.27 | 1.97 | ± | 0.105 |
| ABCG2 (12V/141Q)(WT) | 32.9 | ± | 7.75 * | 8.71 | ± | 0.613 * |
| ABCG2 (12M/141Q) | 91.3 | ± | 14.2 *, ** | 25.8 | ± | 3.63 *, ** |
| ABCG2 (12V/141K) | 43.2 | ± | 6.07 * | 9.20 | ± | 0.572 * |
| ABCG2 (12M/141K) | 49.8 | ± | 7.27 * | 11.8 | ± | 1.78 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamashita, M.; Tsukamoto, M.; Imai, R.; Muramatsu, H.; Nakagawa, H. rs2231142 (421 C>A, Q141K) Is More Functionally Influential than rs2231137 (34 G>A, V12M) on Anticancer Drug Resistance Mediated by the ABCG2 Haplotype In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157428
Yamashita M, Tsukamoto M, Imai R, Muramatsu H, Nakagawa H. rs2231142 (421 C>A, Q141K) Is More Functionally Influential than rs2231137 (34 G>A, V12M) on Anticancer Drug Resistance Mediated by the ABCG2 Haplotype In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157428
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamashita, Miho, Megumi Tsukamoto, Ritsuko Imai, Himari Muramatsu, and Hiroshi Nakagawa. 2025. "rs2231142 (421 C>A, Q141K) Is More Functionally Influential than rs2231137 (34 G>A, V12M) on Anticancer Drug Resistance Mediated by the ABCG2 Haplotype In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157428
APA StyleYamashita, M., Tsukamoto, M., Imai, R., Muramatsu, H., & Nakagawa, H. (2025). rs2231142 (421 C>A, Q141K) Is More Functionally Influential than rs2231137 (34 G>A, V12M) on Anticancer Drug Resistance Mediated by the ABCG2 Haplotype In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157428







