Impact of Obesity and Ageing on the Expression of Key Mediators of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Human Adipose Tissue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
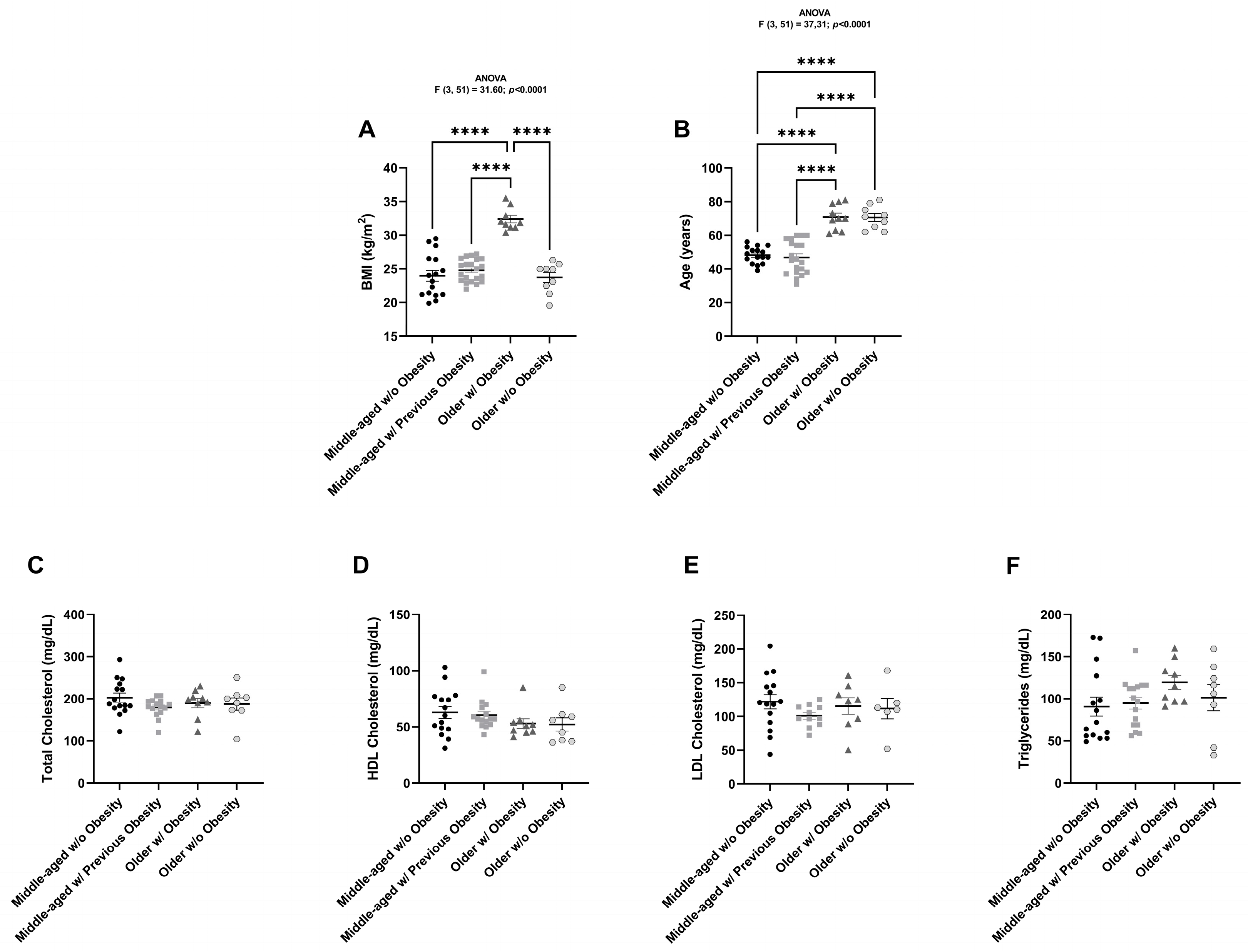
2.1. Anthropometric and Biochemical Characterization of All Individuals
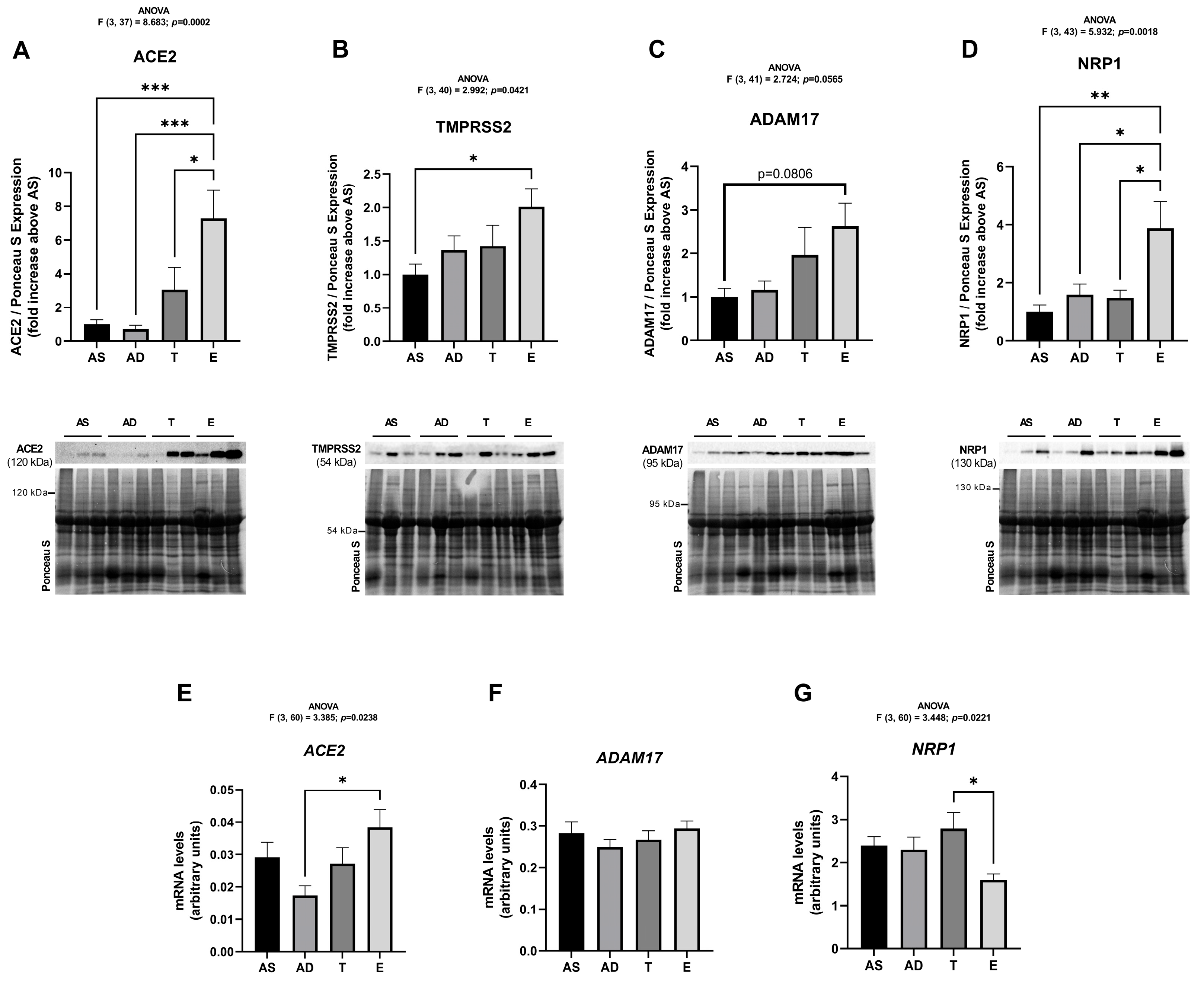
2.2. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Infection Mediators Have Increased Expression in Visceral Adipose Tissue of Middle-Aged Women Without Obesity
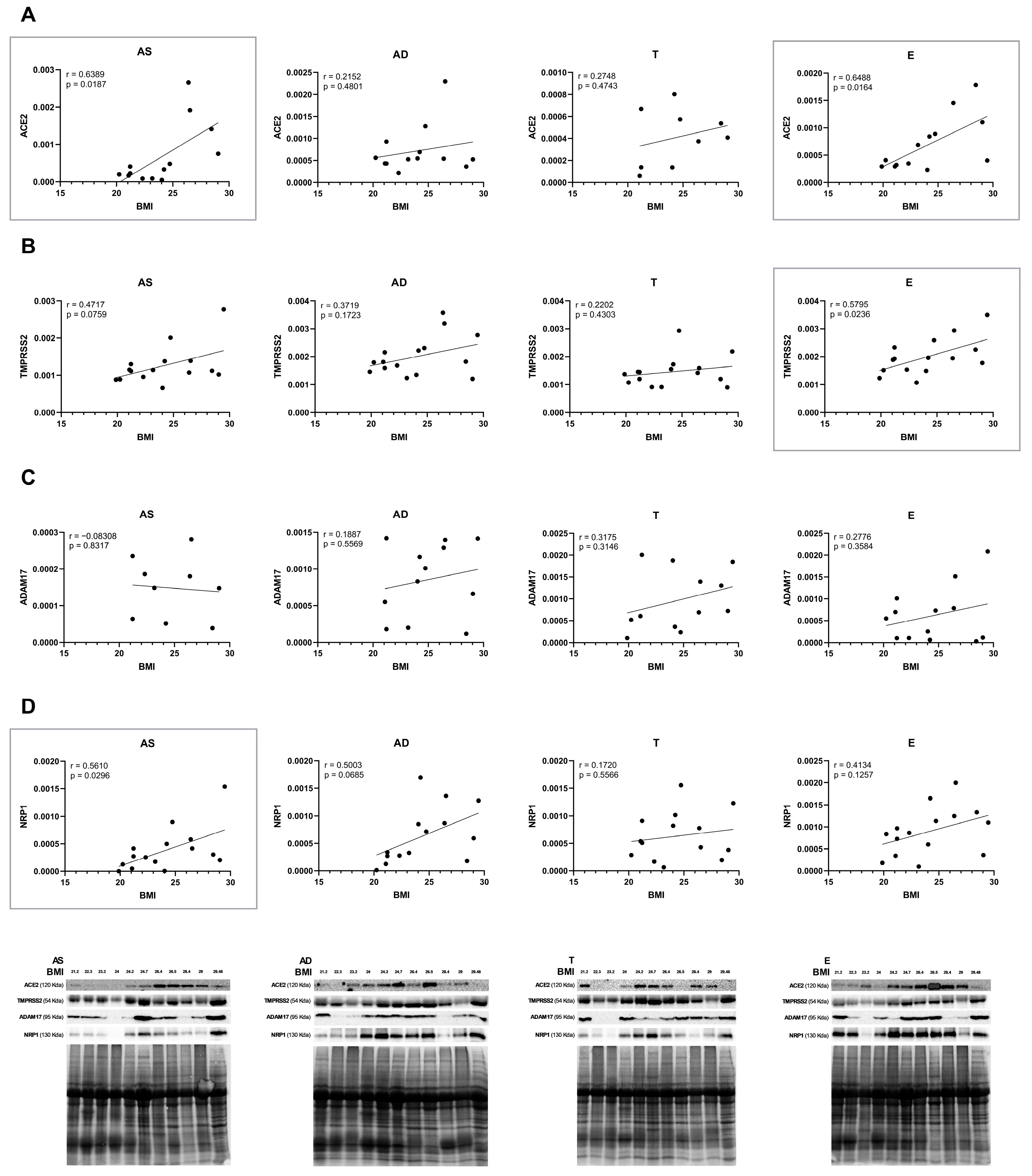
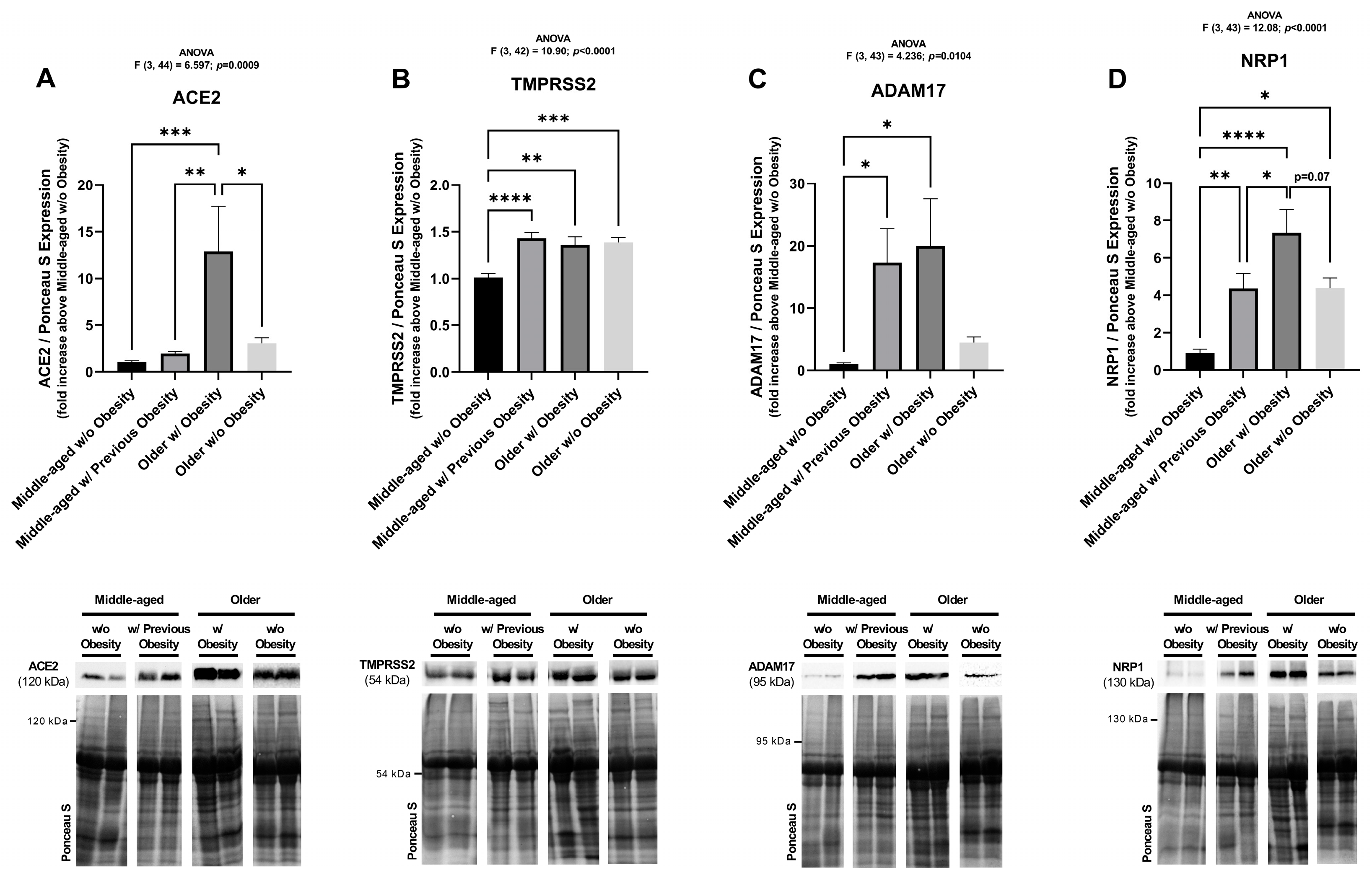
2.3. The Protein Levels of SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Mediators Positively Correlate with BMI
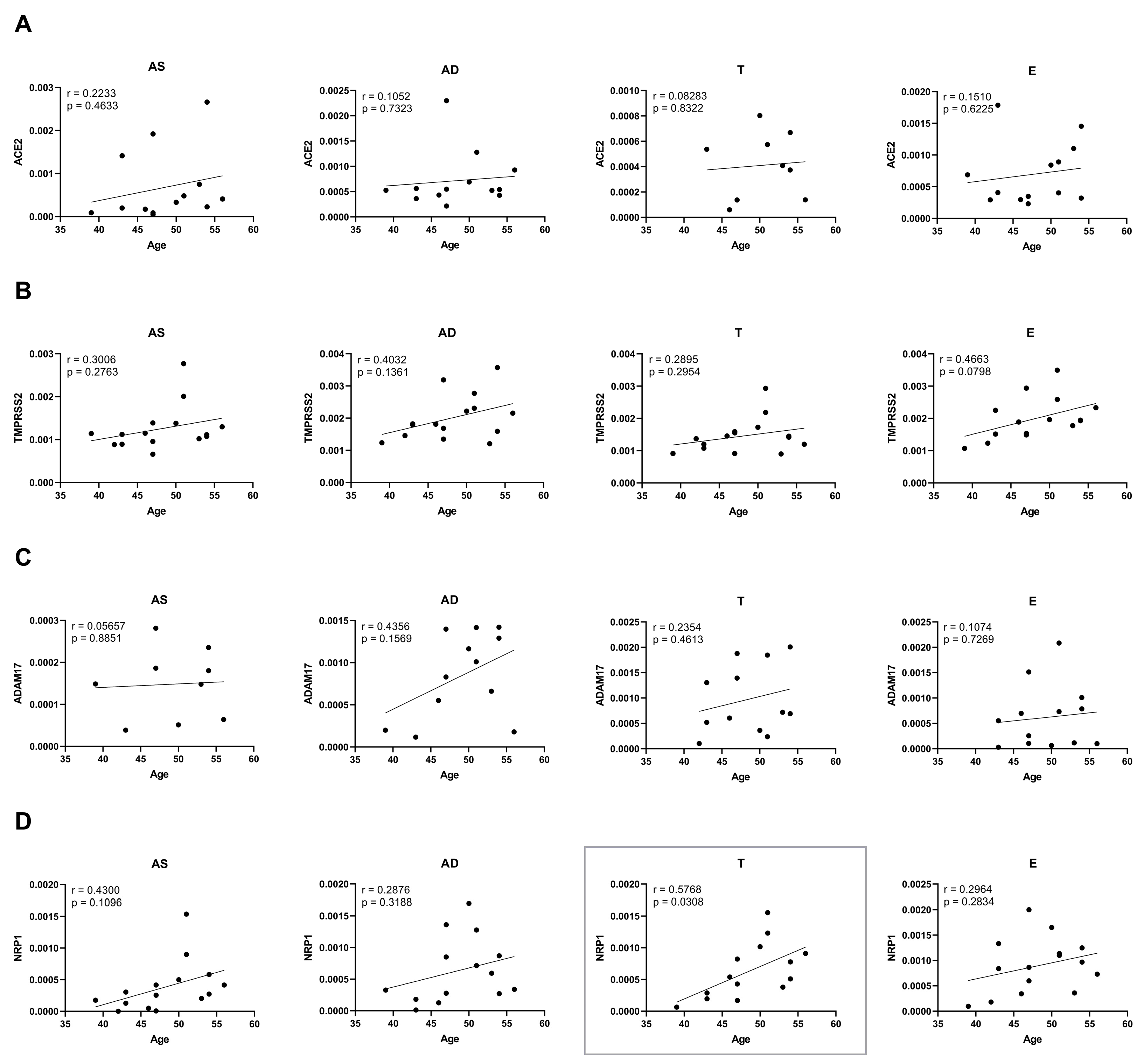
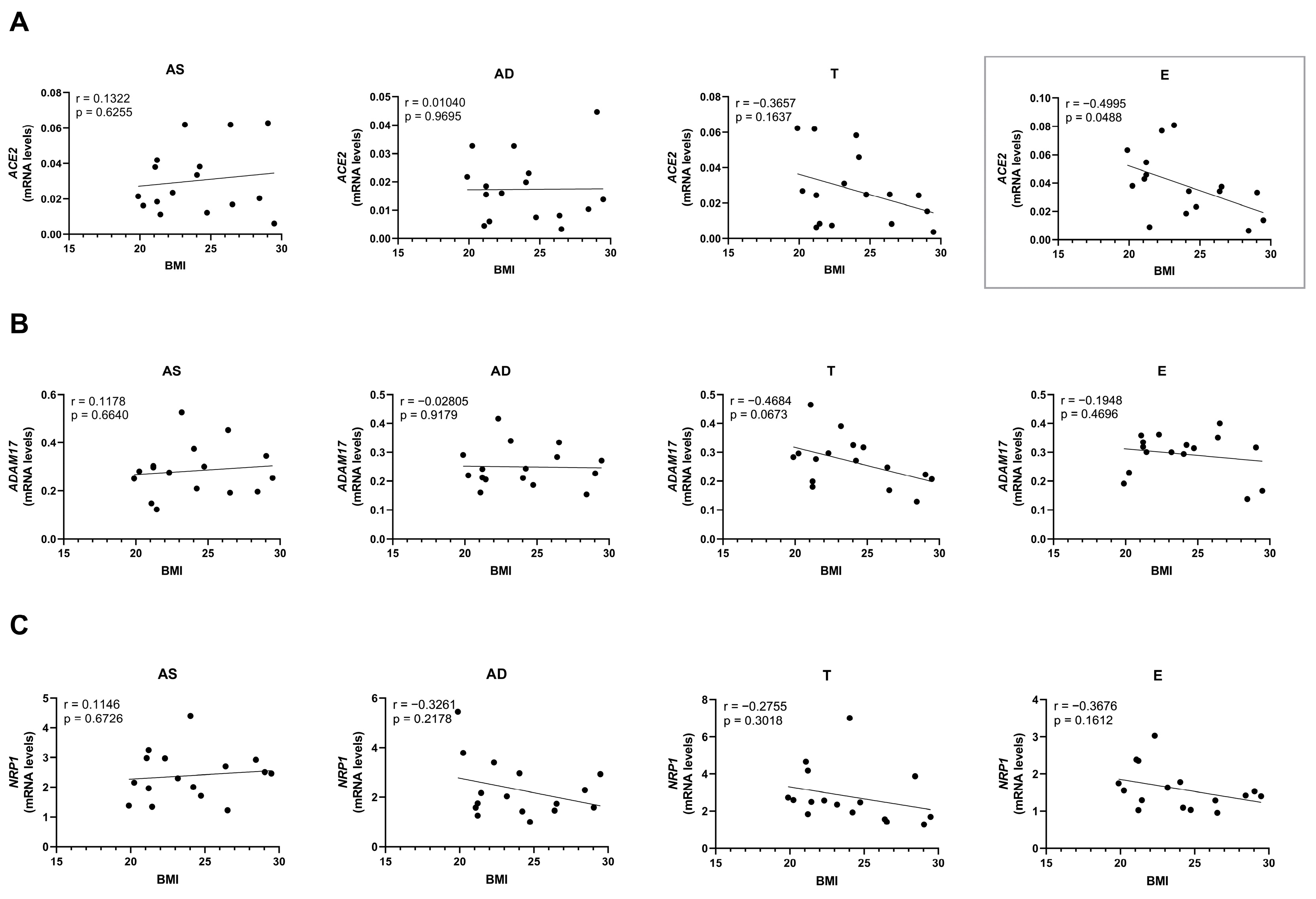
2.4. Ageing and Obesity Differently Influence the Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Factors in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Adipose Tissue Samples
4.2. Real-Time PCR
4.3. Western Blotting
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE2 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| AD | Abdominal deep adipose tissue |
| ADAM17 | Protease A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17 |
| AS | Abdominal superficial adipose tissue |
| AT | Adipose tissue |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CHUSJ | Centro Hospitalar Universitário São João |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| E | Epiploon adipose tissue |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| IPO-Porto | Instituto Português de Oncologia do Porto |
| IPO8 | Importin 8 |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| NRP1 | Neuropilin-1 |
| S | Spike |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| T | Thigh |
| TMPRSS2 | Transmembrane protease serine 2 |
References
- Chen, Y.; Klein, S.L.; Garibaldi, B.T.; Li, H.; Wu, C.; Osevala, N.M.; Li, T.; Margolick, J.B.; Pawelec, G.; Leng, S.X. Aging in COVID-19: Vulnerability, immunity and intervention. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 65, 101205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, M.; Barochiner, J.; Espeche, W.; Ennis, I. COVID-19 and its relationship with hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Hipertens. Riesgo Vasc. 2020, 37, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Baranova, A.; Wei, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, F. Bidirectional causal associations between type 2 diabetes and COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarleri, J.; Delpino, M.V. The interplay of aging, adipose tissue, and COVID-19: A potent alliance with implications for health. Geroscience 2024, 46, 2915–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.R.; Salazar, M.J. and Gouveia, A.M. Obesity and Adipose Tissue Remodeling. In Understanding Obesity: From Its Causes to Impact on Life; Bentham Science: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2020; pp. 55–80. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, E.; Wright, E.; Kushner, B. In Young Adults with COVID-19, Obesity Is Associated with Adverse Outcomes. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 21, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighter, J.; Phillips, M.; Hochman, S.; Sterling, S.; Johnson, D.; Francois, F.; Stachel, A. Obesity in Patients Younger Than 60 Years Is a Risk Factor for COVID-19 Hospital Admission. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 896–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Qi, Y.; Deng, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Meng, Z.; Tang, J.; Dai, Z. Obesity as a Potential Predictor of Disease Severity in Young COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Study. Obesity 2020, 28, 1815–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xiong, Y.; Wei, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Liu, K.; Du, R.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhu, W. Obesity predisposes to the risk of higher mortality in young COVID-19 patients. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2536–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, W.; Santos-Burgoa, C. Obesity and its Implications for COVID-19 Mortality. Obesity 2020, 28, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.S. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Yin, C.; Lu, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Bai, J.; Lu, Y. Two Things about COVID-19 Might Need Attention. Preprints 2020, 2020020315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Benna, S. Association of high level gene expression of ACE2 in adipose tissue with mortality of COVID-19 infection in obese patients. Obes. Med. 2020, 19, 100283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccon, T.D.; Mousovich-Neto, F.; Ludwig, R.G.; Carregari, V.C.; Dos Anjos Souza, A.B.; Dos Passos, A.S.C.; Martini, M.C.; Barbosa, P.P.; de Souza, G.F.; Muraro, S.P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects adipose tissue in a fat depot- and viral lineage-dependent manner. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Colón, G.J.; Ratnasiri, K.; Chen, H.; Jiang, S.; Zanley, E.; Rustagi, A.; Verma, R.; Chen, H.; Andrews, J.R.; Mertz, K.D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection drives an inflammatory response in human adipose tissue through infection of adipocytes and macrophages. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabm9151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basolo, A.; Poma, A.M.; Bonuccelli, D.; Proietti, A.; Macerola, E.; Ugolini, C.; Torregrossa, L.; Giannini, R.; Vignali, P.; Basolo, F.; et al. Adipose tissue in COVID-19: Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in adipocytes and activation of the interferon-alpha response. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2022, 45, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Grass, V.; Tschirner, S.K.; Riepler, L.; Breimann, S.; Kaya, T.; Oelsner, M.; Hamad, M.S.; Hofmann, L.I.; Blobel, C.P.; et al. ADAM10 and ADAM17 promote SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and spike protein-mediated lung cell fusion. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e54305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Sakagami, H.; Miwa, N. ACE2: The key Molecule for Understanding the Pathophysiology of Severe and Critical Conditions of COVID-19: Demon or Angel? Viruses 2020, 12, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D.W.; Yarski, M.; Warner, F.J.; Thornhill, P.; Parkin, E.T.; Smith, A.I.; Hooper, N.M.; Turner, A.J. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha convertase (ADAM17) mediates regulated ectodomain shedding of the severe-acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2). J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30113–30119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurich, A.; Hofmann-Winkler, H.; Gierer, S.; Liepold, T.; Jahn, O.; Pöhlmann, S. TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 cleave ACE2 differentially and only proteolysis by TMPRSS2 augments entry driven by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Ojha, R.; Pedro, L.D.; Djannatian, M.; Franz, J.; Kuivanen, S.; van der Meer, F.; Kallio, K.; Kaya, T.; Anastasina, M.; et al. Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity. Science 2020, 370, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, J.L.; Simonetti, B.; Klein, K.; Chen, K.E.; Williamson, M.K.; Antón-Plágaro, C.; Shoemark, D.K.; Simón-Gracia, L.; Bauer, M.; Hollandi, R.; et al. Neuropilin-1 is a host factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Science 2020, 370, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, M.Y.; Zhang, H.; Tan, P.C.; Zhou, S.B.; Li, Q.F. Adipose tissue aging: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, G.; Legueult, K.; Pradier, C.; Raffaelli, C.; Ichai, C.; Iannelli, A.; Redheuil, A.; Lucidarme, O.; Esnault, V. Visceral fat is associated to the severity of COVID-19. Metabolism 2021, 115, 154440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipeto, D.; Palmeira, J.D.F.; Argañaraz, G.A.; Argañaraz, E.R. ACE2/ADAM17/TMPRSS2 Interplay May Be the Main Risk Factor for COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 576745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, S.; Banerjee, P.; Bhagavatula, S.; Kushwaha, P.P.; Kumar, S. Contributions of human ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in determining host-pathogen interaction of COVID-19. J. Genet. 2021, 100, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.M.; Shao, Z.; Grenier, V.; Mawambo, G.; Daudelin, J.F.; Dejda, A.; Pilon, F.; Popovic, N.; Boulet, S.; Parinot, C.; et al. Neuropilin-1 expression in adipose tissue macrophages protects against obesity and metabolic syndrome. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaan4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancello, R.; Tordjman, J.; Poitou, C.; Guilhem, G.; Bouillot, J.L.; Hugol, D.; Coussieu, C.; Basdevant, A.; Bar Hen, A.; Bedossa, P.; et al. Increased infiltration of macrophages in omental adipose tissue is associated with marked hepatic lesions in morbid human obesity. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayi, B.S.; Leibowitz, J.A.; Woods, A.T.; Ammon, K.A.; Liu, A.E.; Raja, A. The role of Neuropilin-1 in COVID-19. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emilsson, V.; Gudmundsson, E.F.; Aspelund, T.; Jonsson, B.G.; Gudjonsson, A.; Launer, L.J.; Lamb, J.R.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Jennings, L.L.; Gudnason, V. Serum levels of ACE2 are higher in patients with obesity and diabetes. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2021, 7, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietri, L.; Giorgi, R.; Bégu, A.; Lojou, M.; Koubi, M.; Cauchois, R.; Grangeot, R.; Dubois, N.; Kaplanski, G.; Valéro, R.; et al. Excess body weight is an independent risk factor for severe forms of COVID-19. Metabolism 2021, 117, 154703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saul, H.; Gursul, D.; Piernas, C. People carrying excess weight have an increased risk of severe covid-19. BMJ 2022, 376, o141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.B.; Mori, J.; McLean, B.A.; Basu, R.; Das, S.K.; Ramprasath, T.; Parajuli, N.; Penninger, J.M.; Grant, M.B.; Lopaschuk, G.D.; et al. ACE2 Deficiency Worsens Epicardial Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Cardiac Dysfunction in Response to Diet-Induced Obesity. Diabetes 2016, 65, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couselo-Seijas, M.; Almengló, C.; Agra-Bermejo, R.M.; Luis Fernandez, Á.; Alvarez, E.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; Eiras, S. Higher ACE2 expression levels in epicardial cells than subcutaneous stromal cells from patients with cardiovascular disease: Diabetes and obesity as possible enhancer. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Valentí, V.; Moncada, R.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Becerril, S.; Silva, C.; Portincasa, P.; Escalada, J.; Rodríguez, A. FNDC4 and FNDC5 reduce SARS-CoV-2 entry points and spike glycoprotein S1-induced pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis in human adipocytes. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2457–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenblock, C.; Bechmann, N.; Beuschlein, F.; Wolfrum, C.; Bornstein, S.R. Do adipocytes serve as a reservoir for severe acute respiratory symptom coronavirus-2? J. Endocrinol. 2023, 258, e230027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Heialy, S.; Hachim, M.Y.; Senok, A.; Gaudet, M.; Abou Tayoun, A.; Hamoudi, R.; Alsheikh-Ali, A.; Hamid, Q. Regulation of Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme 2 in Obesity: Implications for COVID-19. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 555039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneera, J.; El-Huneidi, W.; Hamad, M.; Mohammed, A.K.; Elaraby, E.; Hachim, M.Y. Expression Profile of SARS-CoV-2 Host Receptors in Human Pancreatic Islets Revealed Upregulation of ACE2 in Diabetic Donors. Biology 2020, 9, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Eira, D.; Jani, S.; Ceddia, R.B. Obesogenic and Ketogenic Diets Distinctly Regulate the SARS-CoV-2 Entry Proteins ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and the Renin-Angiotensin System in Rat Lung and Heart Tissues. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Spranger, L.; Soll, D.; Beer, F.; Brachs, M.; Spranger, J.; Mai, K. Metabolic impact of weight loss induced reduction of adipose ACE-2—Potential implication in COVID-19 infections? Metabolism 2020, 113, 154401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soll, D.; Beer, F.; Spranger, L.; Li, L.; Spranger, J.; Mai, K. Effects of Weight Loss on Adipose and Muscular Neuropilin 1 mRNA Expression in Obesity: Potential Implication in SARS-CoV-2 Infections? Obes. Facts 2022, 15, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed Moustafa, J.S.; Jackson, A.U.; Brotman, S.M.; Guan, L.; Villicaña, S.; Roberts, A.L.; Zito, A.; Bonnycastle, L.; Erdos, M.R.; Narisu, N.; et al. ACE2 expression in adipose tissue is associated with cardio-metabolic risk factors and cell type composition-implications for COVID-19. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Feher, A.; Davila, A.C.; Romero, M.J.; Patel, V.S.; Kamath, V.M.; Gooz, M.B.; Rudic, R.D.; Lucas, R.; Fulton, D.J.; et al. Role of Adipose Tissue Endothelial ADAM17 in Age-Related Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 1180–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voros, G.; Maquoi, E.; Collen, D.; Lijnen, H.R. Differential expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, TNF-alpha converting enzyme and ADAMTS family members in murine fat territories. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1625, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, M.; Zvibel, I.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Varol, C.; Lahat, G.; Abu-Abeid, S.; Klausner, J.M.; Halpern, Z.; Fishman, S. Discriminatory metabolic and inflammatory parameters in serum and omental adipose tissue of obese patients with different insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2014, 1, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matsui, Y.; Tomaru, U.; Miyoshi, A.; Ito, T.; Fukaya, S.; Miyoshi, H.; Atsumi, T.; Ishizu, A. Overexpression of TNF-α converting enzyme promotes adipose tissue inflammation and fibrosis induced by high fat diet. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2014, 97, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.B.; Song, Y.; Kim, Y.H. Visceral adipose tissue macrophage-targeted TACE silencing to treat obesity-induced type 2 diabetes. Biomaterials 2017, 148, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, C.B.; Shreves, A.H.; Shanahan, M.R.; Guard, H.E.; Nhliziyo, M.V.; Pernar, C.H.; Penney, K.L.; Lotan, T.L.; Fiorentino, M.; Mucci, L.A.; et al. Etiology of prostate cancer with the TMPRSS2:ERG fusion: A systematic review of risk factors. Int. J. Cancer 2024, 156, 1898–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, N.; Rose-John, S. ADAM17 orchestrates Interleukin-6, TNFα and EGF-R signaling in inflammation and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancello, R.; Zulian, A.; Gentilini, D.; Mencarelli, M.; Della Barba, A.; Maffei, M.; Vitti, P.; Invitti, C.; Liuzzi, A.; Di Blasio, A.M. Permanence of molecular features of obesity in subcutaneous adipose tissue of ex-obese subjects. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristem, L.; Recamonde-Mendoza, M.; Cigerza, G.C.; Khoraki, J.; Campos, G.M.; Mazzini, G.S. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Downregulates Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) Gene Expression in Subcutaneous White Adipose Tissue: A Putative Protective Mechanism Against Severe COVID-19. Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 2831–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauwenberghs, N.; Prunicki, M.; Sabovčik, F.; Perelman, D.; Contrepois, K.; Li, X.; Snyder, M.P.; Nadeau, K.C.; Kuznetsova, T.; Haddad, F.; et al. Temporal changes in soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 associated with metabolic health, body composition, and proteome dynamics during a weight loss diet intervention: A randomized trial with implications for the COVID-19 pandemic. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Zhang, M.; Chang, T.L. ACE2-Independent Alternative Receptors for SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2022, 14, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipoor, S.D.; Mirsaeidi, M. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry beyond the ACE2 receptor. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 10715–10727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyrou, M.; Pitsillou, E.; Hung, A.; El-Osta, A.; Karagiannis, T.C. Insights into the pathogenic mechanisms associated with the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. J. Struct. Biol. 2025, 217, 108229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melano, I.; Cheng, W.C.; Kuo, L.L.; Liu, Y.M.; Chou, Y.C.; Hung, M.C.; Lai, M.M.C.; Sher, Y.P.; Su, W.C. A disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain 9 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells with low ACE2 expression. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0385422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, M.; Kiarie, I.W.; Mótyán, J.A.; Hoffka, G.; Al-Muffti, A.S.; Tóth, A.; Tőzsér, J. Receptor Binding for the Entry Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2: Insights from the Original Strain and Emerging Variants. Viruses 2025, 17, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Decker, K.E.; Schulz, S.R.; Kempf, A.; Nehlmeier, I.; Moldenhauer, A.S.; Dopfer-Jablonka, A.; Behrens, G.M.N.; Stankov, M.V.; Manthey, L.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Host Cell Entry Efficiency and Neutralization Sensitivity of Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Lineages KP.2, KP.2.3, KP.3, and LB.1. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Xilifu, N.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zang, S.; Jiang, G.; Liu, J. Metabolic memory in gestational diabetes enhances SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility in postpartum women: A prospective cohort study integrated with longitudinal metabolomics. Endocr. Connect. 2025, 14, e240681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinte, L.C.; Castellano-Castillo, D.; Ghosh, A.; Melrose, K.; Gasser, E.; Noé, F.; Massier, L.; Dong, H.; Sun, W.; Hoffmann, A.; et al. Adipose tissue retains an epigenetic memory of obesity after weight loss. Nature 2024, 636, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, W.; Huang, L.; Xiao, J.; Li, F.; Qin, S.; Song, X.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; et al. A comprehensive investigation of the mRNA and protein level of ACE2, the putative receptor of SARS-CoV-2, in human tissues and blood cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Ren, H.; Li, L.; Zheng, X.; Wang, H.; Han, Z. RNA binding protein PUM2 promotes the stemness of breast cancer cells via competitively binding to neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) mRNA with miR-376a. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, H.; Liu, H. RNA binding protein Lin28B confers gastric cancer cells stemness via directly binding to NRP-1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, L.; Khan, A.A.; Li, B.; Gu, B.; Lin, F.; Su, X.; Yan, J. miRNA-124-3p/neuropilin-1(NRP-1) axis plays an important role in mediating glioblastoma growth and angiogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Zheng, X.; Li, C.; Han, Z. miR-376a inhibits breast cancer cell progression by targeting neuropilin-1 NR. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 5293–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Beyer, A.; Aebersold, R. On the Dependency of Cellular Protein Levels on mRNA Abundance. Cell 2016, 165, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Enríquez, M.M.; Lopez-León, S.; Carlos-Escalante, J.A.; Aponte-Torres, Z.; Cuapio, A.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T. ACE2: The molecular doorway to SARS-CoV-2. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Eales, J.M.; Scannali, D.; Nazgiewicz, A.; Prestes, P.; Maier, M.; Denniff, M.; Xu, X.; Saluja, S.; Cano-Gamez, E.; et al. Hypertension and renin-angiotensin system blockers are not associated with expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in the kidney. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 4580–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Qin, J.J.; Cheng, X.; Shen, L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Yuan, Y.; Lei, F.; Chen, M.M.; Yang, H.; Bai, L.; et al. In-Hospital Use of Statins Is Associated with a Reduced Risk of Mortality among Individuals with COVID-19. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 176–187.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.H.; Smith, A.M.; Jonsson, C.B. The Intersection of SARS-CoV-2 and Diabetes. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Awasthi, K.; Usman, K.; Banerjee, M. Role of renin-angiotensin system/angiotensin converting enzyme-2 mechanism and enhanced COVID-19 susceptibility in type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 606–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; El Kholy, A.A.; El-Khateeb, E.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; Elekhnawy, E.; Alsubaie, N.; Hamad, R.S.; Batiha, G.E. The potential therapeutic effect of metformin in type 2 diabetic patients with severe COVID-19. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 11445–11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, B.; Morén, B.; Fryklund, C.; Vliex, L.; Wasserstrom, S.; Albinsson, S.; Berger, K.; Stenkula, K.G. Adipose cell size changes are associated with a drastic actin remodeling. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Guo, X.; Thein, S.; Xu, F.; Sugii, S.; Baas, P.W.; Radda, G.K.; Han, W. Regulation of adipogenesis by cytoskeleton remodelling is facilitated by acetyltransferase MEC-17-dependent acetylation of α-tubulin. Biochem. J. 2013, 449, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, H.; Wallace, S.; Plouse, R.; Tiwari, S.; Gomes, A.V. Ponceau S waste: Ponceau S staining for total protein normalization. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 575, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salazar, M.; Ferreira, M.; Oliveira, S.M.; Saraiva, F.; Pinho, C.; Jarnalo, M.; Correia-Sá, I.; Falcão-Pires, I.; Leite-Moreira, A.; Neves, D.; et al. Impact of Obesity and Ageing on the Expression of Key Mediators of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Human Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157313
Salazar M, Ferreira M, Oliveira SM, Saraiva F, Pinho C, Jarnalo M, Correia-Sá I, Falcão-Pires I, Leite-Moreira A, Neves D, et al. Impact of Obesity and Ageing on the Expression of Key Mediators of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Human Adipose Tissue. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157313
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalazar, Maria, Mariana Ferreira, Sandra Marisa Oliveira, Francisca Saraiva, Carlos Pinho, Mariana Jarnalo, Inês Correia-Sá, Inês Falcão-Pires, Adelino Leite-Moreira, Delminda Neves, and et al. 2025. "Impact of Obesity and Ageing on the Expression of Key Mediators of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Human Adipose Tissue" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157313
APA StyleSalazar, M., Ferreira, M., Oliveira, S. M., Saraiva, F., Pinho, C., Jarnalo, M., Correia-Sá, I., Falcão-Pires, I., Leite-Moreira, A., Neves, D., Almeida, H., Rodrigues, A. R., & Gouveia, A. M. (2025). Impact of Obesity and Ageing on the Expression of Key Mediators of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Human Adipose Tissue. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157313








