Prognostic Potential of Apoptosis-Related Biomarker Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers
Abstract
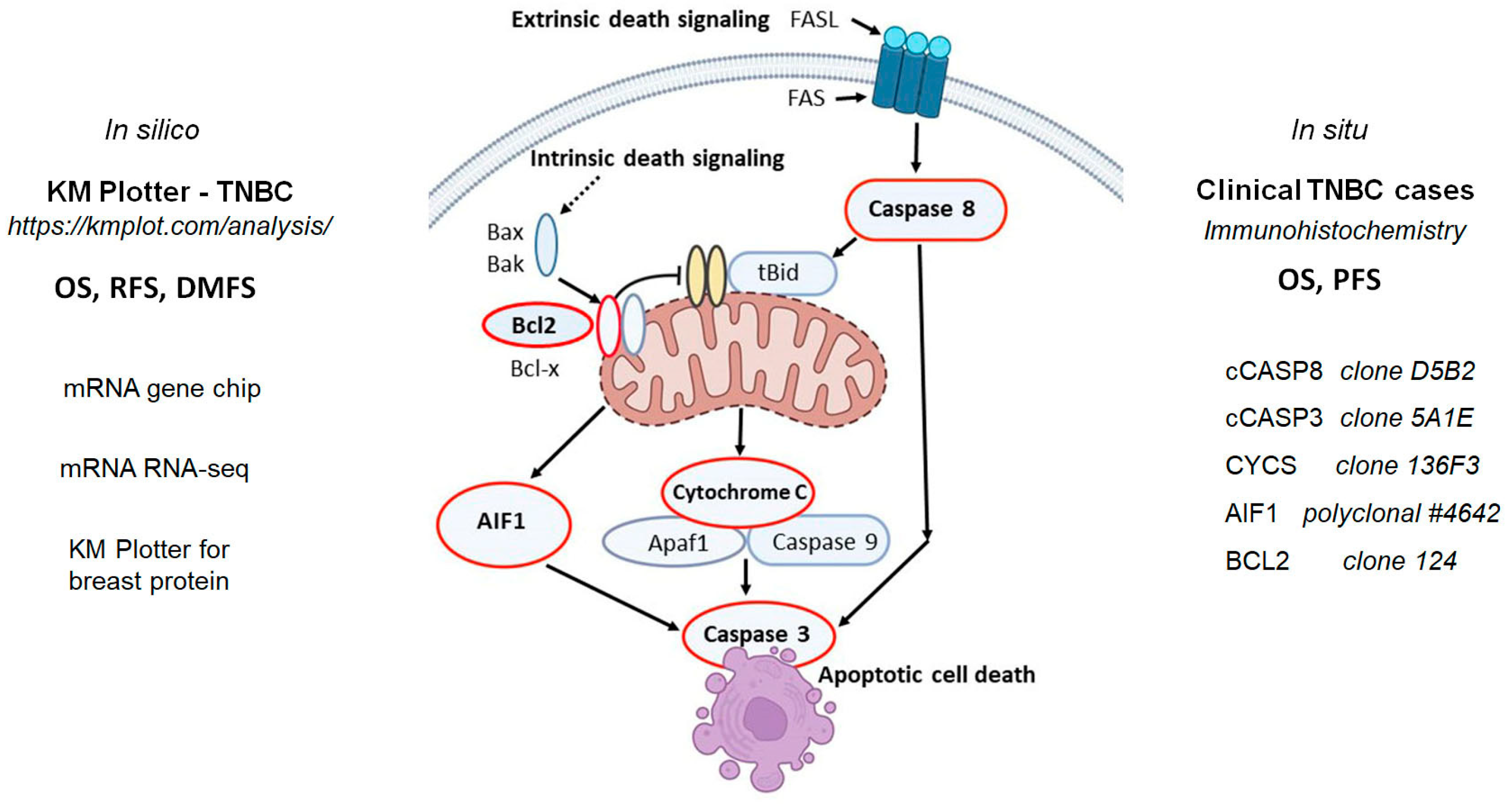
1. Introduction
2. Results
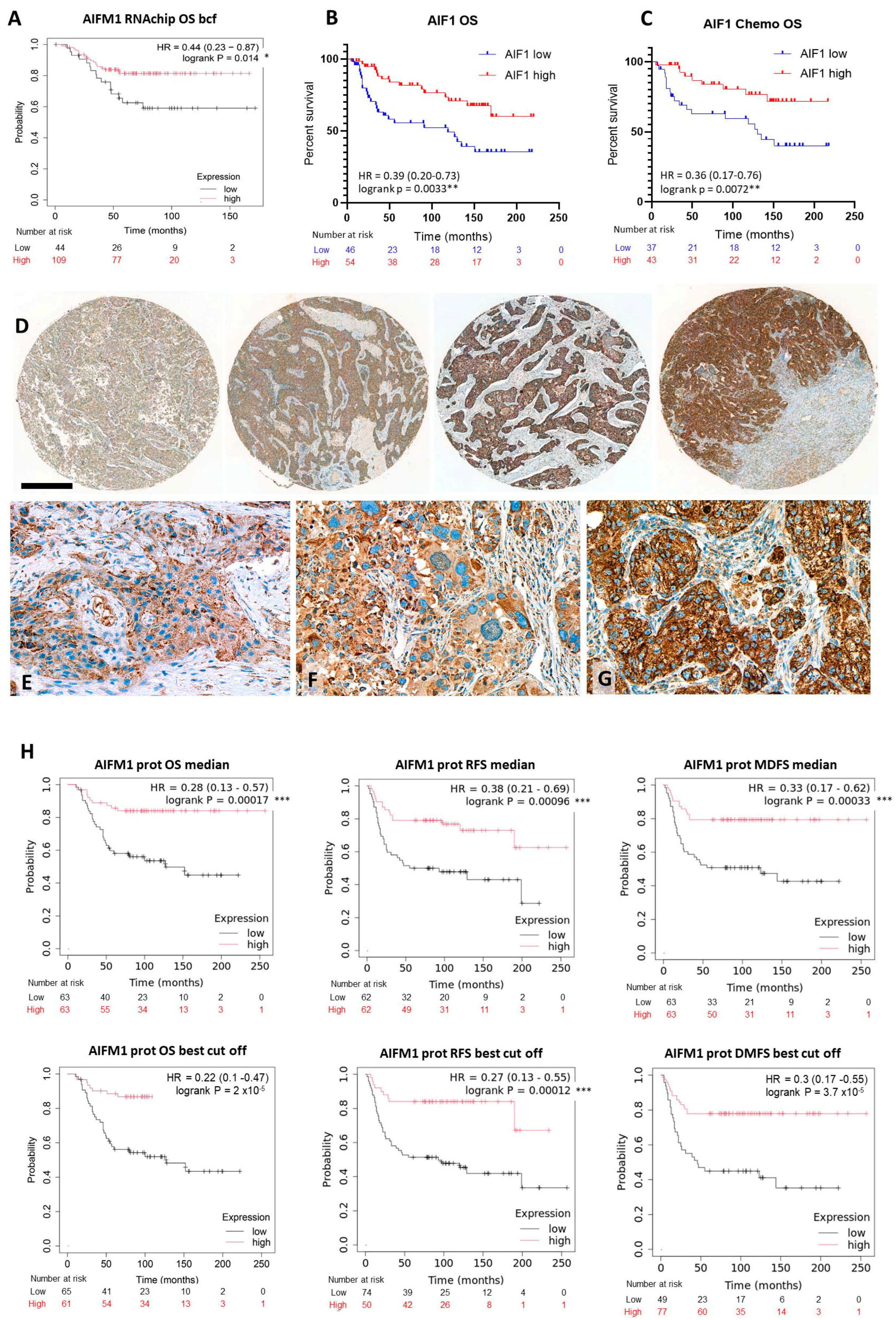
2.1. Apoptosis-Inducing Factor-1 Expression and TNBC Prognosis
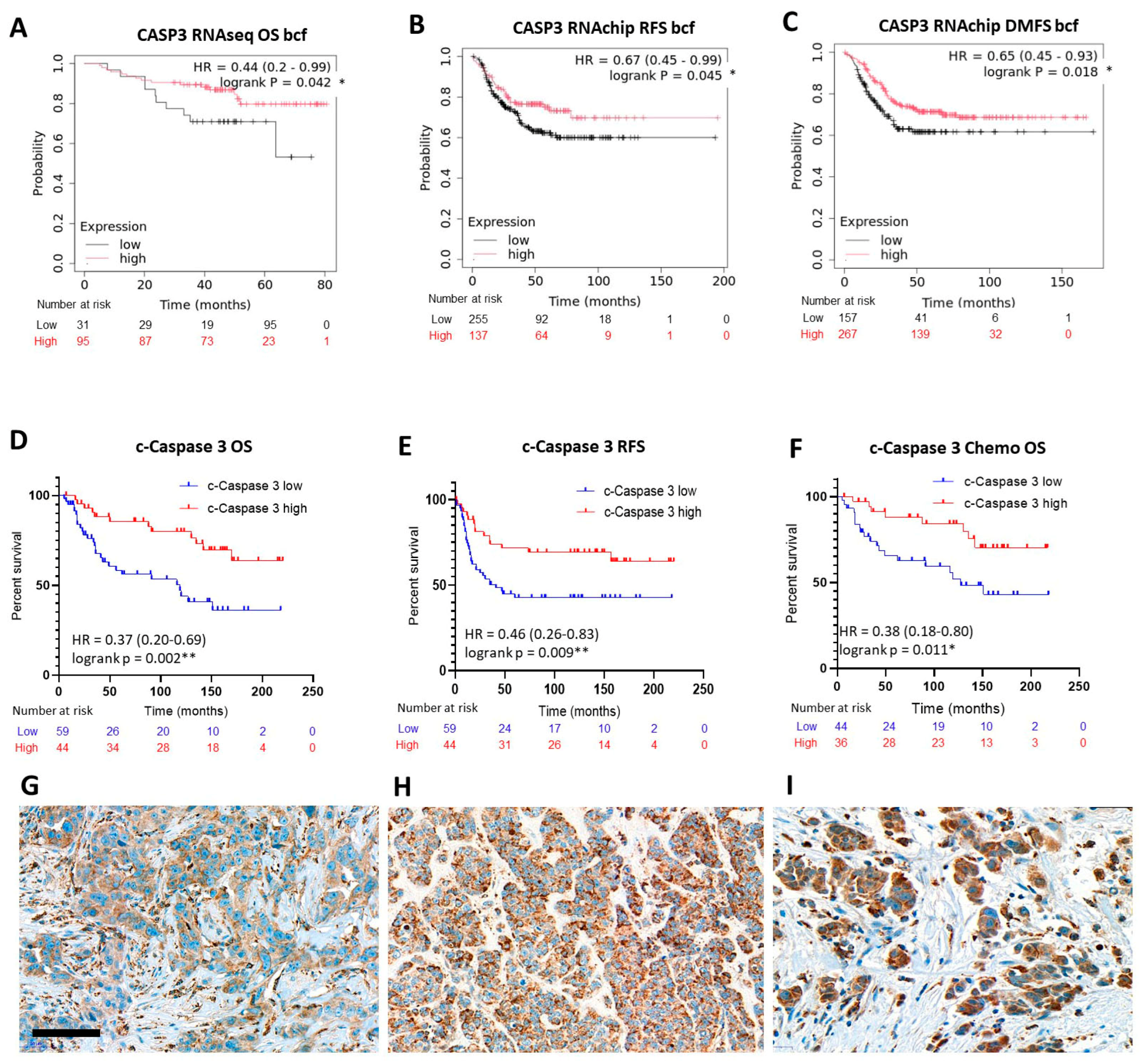
2.2. Expression of the Executioner Caspase, Caspase 3 in Relation with TNBC Prognosis
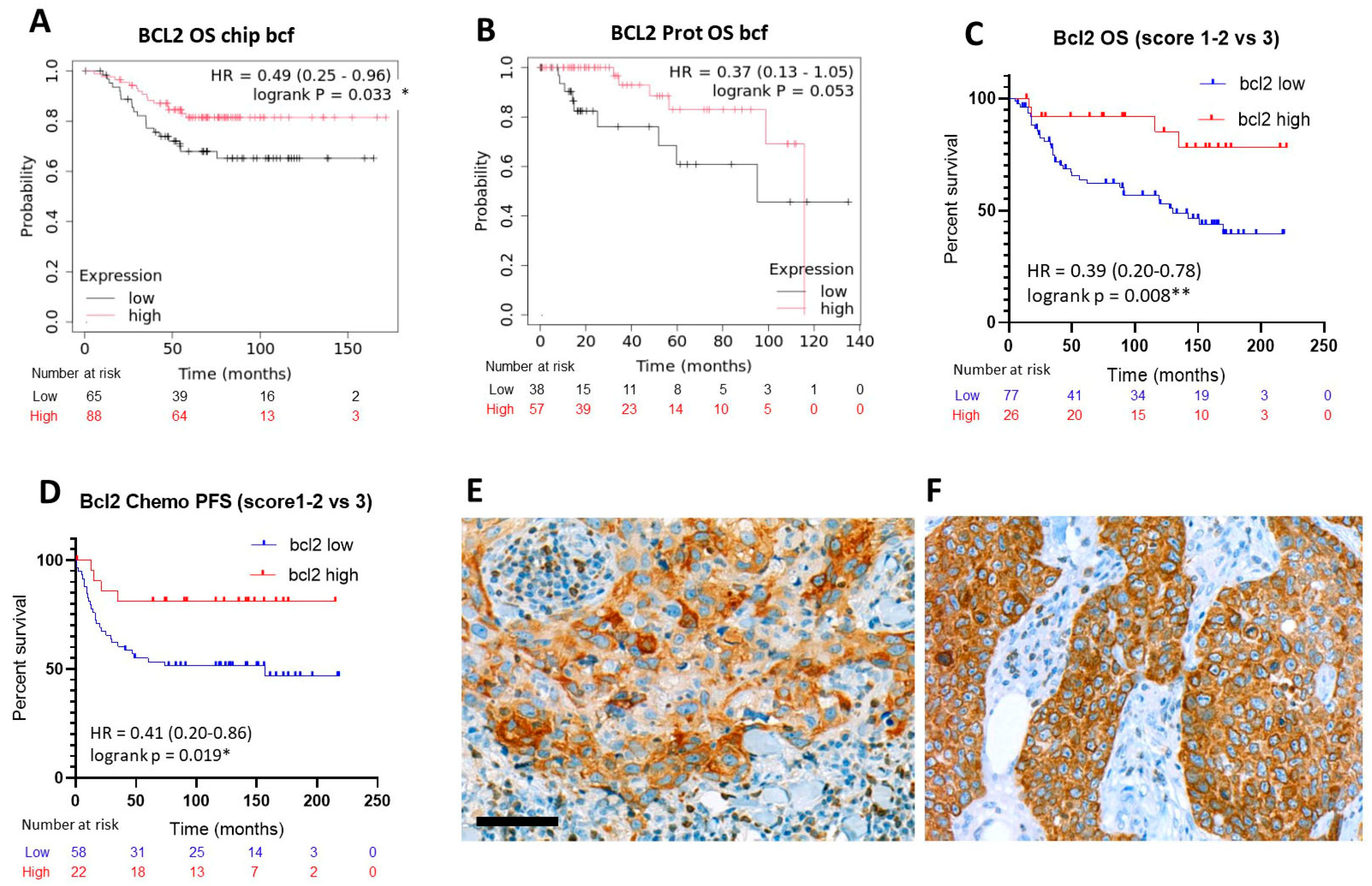
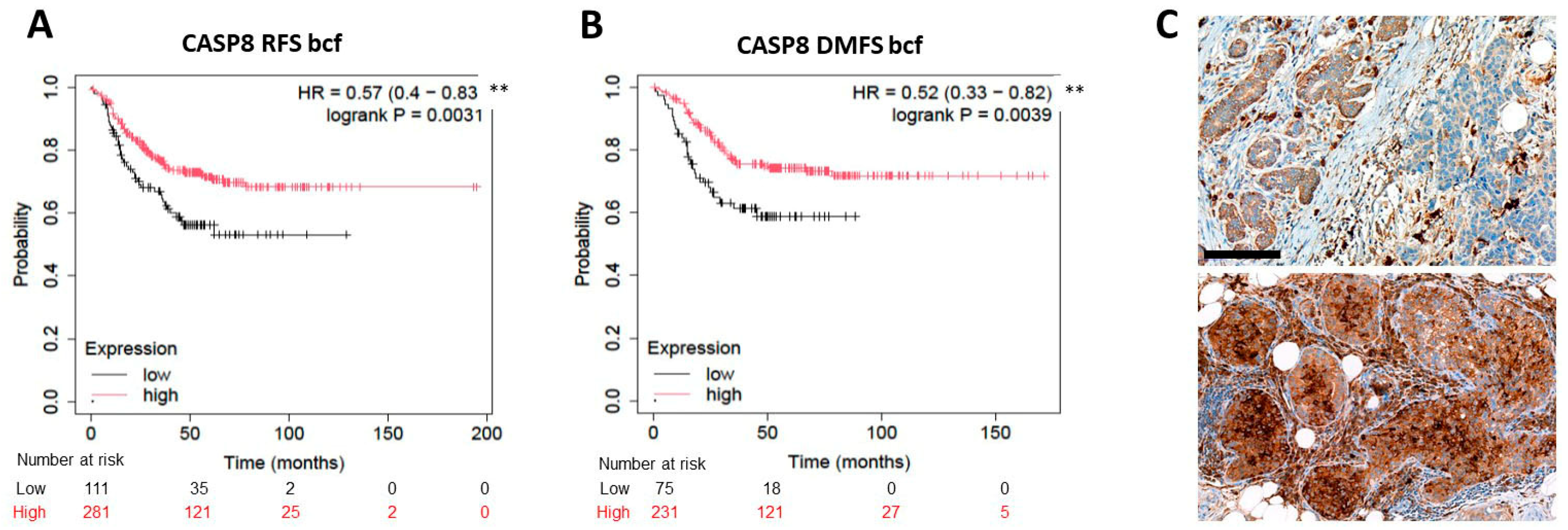
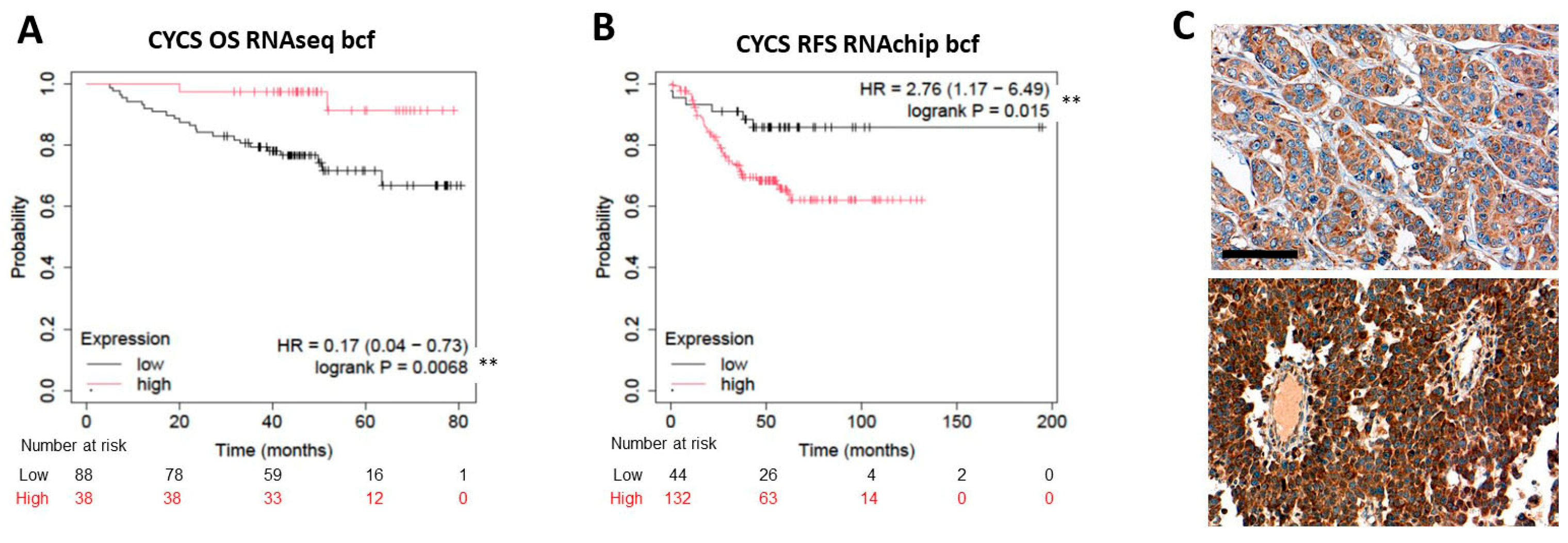
2.3. Expression of the Rest of Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis Biomarkers Tested and TNBC Prognosis
2.4. Reproducibility of Immunoscoring and Correlations Between the Tested Biomarker Levels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Silico mRNA and Protein Expression Analysis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
4.2. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cohort Used for Testing In Situ Protein Expression
4.3. Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Scoring of Immunoreactions
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Laversanne, M.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Sotiriou, C.; Pusztai, L. Gene-expression signatures in breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Duan, J.J.; Bian, X.W.; Yu, S.C. Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, F.M.; Olopade, O.I. Epidemiology of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Review. Cancer J. 2021, 27, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asleh, K.; Riaz, N.; Nielsen, T.O. Heterogeneity of triple negative breast cancer: Current advances in subtyping and treatment implications. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeichner, S.B.; Terawaki, H.; Gogineni, K. A Review of Systemic Treatment in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer 2016, 10, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareja, F.; Geyer, F.C.; Marchiò, C.; Burke, K.A.; Weigelt, B.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Triple-negative breast cancer: The importance of molecular and histologic subtyping, and recognition of low-grade variants. NPJ Breast Cancer 2016, 2, 16036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, E.T.; Jo, V.Y.; Schnitt, S.J. Salivary Gland-like Tumors of the Breast. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2023, 147, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.Y.; Zhang, W.W.; Sun, J.Y.; Li, F.Y.; He, Z.Y.; Wu, S.G. The Clinicopathological Features and Survival Outcomes of Different Histological Subtypes in Triple-negative Breast Cancer. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Jovanović, B.; Chen, X.; Estrada, M.V.; Johnson, K.N.; Shyr, Y.; Moses, H.L.; Sanders, M.E.; Pietenpol, J.A. Refinement of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes: Implications for Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Selection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, M.D.; Tsimelzon, A.; Poage, G.M.; Covington, K.R.; Contreras, A.; Fuqua, S.A.; Savage, M.I.; Osborne, C.K.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Chang, J.C.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis identifies novel subtypes and targets of triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, S.; Tian, Y.; Liu, C. New Perspectives for Resistance to PARP Inhibitors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 578095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, G.; De Angelis, C.; Licata, L.; Gianni, L. Treatment landscape of triple-negative breast cancer—Expanded options, evolving needs. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Jin, J.; Ji, W.; Guan, X. Therapeutic landscape in mutational triple negative breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoni, M.; Romagnoli, E.; Saladino, T.; Foghini, L.; Guarino, S.; Capponi, M.; Giannini, M.; Cognigni, P.D.; Ferrara, G.; Battelli, N. Triple negative breast cancer: Key role of Tumor-Associated Macrophages in regulating the activity of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 agents. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2018, 1869, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anestis, A.; Sarantis, P.; Theocharis, S.; Zoi, I.; Tryfonopoulos, D.; Korogiannos, A.; Koumarianou, A.; Xingi, E.; Thomaidou, D.; Kontos, M.; et al. Estrogen receptor beta increases sensitivity to enzalutamide in androgen receptor-positive triple-negative breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, I.; Pietrocola, F.; Guilbaud, E.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Agostini, M.; Agostinis, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; et al. Apoptotic cell death in disease-Current understanding of the NCCD 2023. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 1097–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Letai, A.; Sarosiek, K. Regulation of apoptosis in health and disease: The balancing act of BCL-2 family proteins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, B.A.; El-Deiry, W.S. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.S. Apoptosis in cancer: From pathogenesis to treatment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Han, Z.; Luo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zuo, H. Radiotherapy modulates tumor cell fate decisions: A review. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue-Yamauchi, A.; Jeng, P.S.; Kim, K.; Chen, H.C.; Han, S.; Ganesan, Y.T.; Ishizawa, K.; Jebiwott, S.; Dong, Y.; Pietanza, M.C.; et al. Targeting the differential addiction to anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family for cancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowinsky, E.K. Targeted induction of apoptosis in cancer management: The emerging role of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor activating agents. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 9394–9407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Arguello, O.A.; Haisma, H.J. Apoptosis-Inducing TNF Superfamily Ligands for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocquet, L.; Roul, J.; Lefebvre, C.C.; Duarte, L.; Campone, M.; Juin, P.P.; Souazé, F. Low BCL-xL expression in triple-negative breast cancer cells favors chemotherapy efficacy, and this effect is limited by cancer-associated fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhoshani, A.; Alatawi, F.O.; Al-Anazi, F.E.; Attafi, I.M.; Zeidan, A.; Agouni, A.; El Gamal, H.M.; Shamoon, L.S.; Khalaf, S.; Korashy, H.M. BCL-2 Inhibitor Venetoclax Induces Autophagy-Associated Cell Death, Cell Cycle Arrest, and Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 13357–13370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Wong, C.N.; Hsu, F.T.; Chen, J.H.; Yang, C.C.; Liu, H.H.; Chen, W.L.; Weng, Y.S. Accessing Apoptosis Induction and Metastasis Inhibition Effect of Magnolol on Triple Negative Breast Cancer In Vitro. In Vivo 2023, 37, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Lee, J.; Liu, H.; Pearson, T.; Lu, A.Y.; Tripathy, D.; Devi, G.R.; Bartholomeusz, C.; Ueno, N.T. Birinapant Enhances Gemcitabine’s Antitumor Efficacy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Inducing Intrinsic Pathway-Dependent Apoptosis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susin, S.A.; Lorenzo, H.K.; Zamzami, N.; Marzo, I.; Snow, B.E.; Brothers, G.M.; Mangion, J.; Jacotot, E.; Costantini, P.; Loeffler, M.; et al. Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature 1999, 397, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L.; Liang, Z. Apoptosis-inducing factor: A mitochondrial protein associated with metabolic diseases-a narrative review. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2023, 13, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melloul, O.; Zabit, S.; Lichtenstein, M.; Duran, D.; Grunewald, M.; Lorberboum-Galski, H. Inducing Targeted, Caspase-Independent Apoptosis with New Chimeric Proteins for Treatment of Solid Cancers. Cancers 2025, 17, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cande, C.; Cohen, I.; Daugas, E.; Ravagnan, L.; Larochette, N.; Zamzami, N.; Kroemer, G. Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): A novel caspase-independent death effector released from mitochondria. Biochimie 2002, 84, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.Q.; Stingl, C.; Look, M.P.; Smid, M.; Braakman, R.B.; De Marchi, T.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Span, P.N.; Sweep, F.C.; Linderholm, B.K.; et al. Comparative proteome analysis revealing an 11-protein signature for aggressive triple-negative breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, djt376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.M.; Guo, M.; Xiong, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, F.F.; Chen, G.Q. AIF inhibits tumor metastasis by protecting PTEN from oxidation. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 1563–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Chu, C.; Xue, S.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Xia, W.; Lin, H. Identification and validation of a prognostic signature of drug resistance and mitochondrial energy metabolism-related differentially expressed genes for breast cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956, 123, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, I.; Carrillo-Bosch, L.; Seoane, J. Targeting the Warburg Effect in Cancer: Where Do We Stand? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Qin, H.Z.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhu, H.; Long, L.; Xu, L.B. Gallic acid suppresses the progression of triple-negative breast cancer HCC1806 cells via modulating PI3K/AKT/EGFR and MAPK signaling pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1049117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, H.; Heo, J.S.; Kim, P.; Lian, Z.; Lee, S.; Park, J.; Hong, E.; Pang, K.; Park, Y.; Ooshima, A.; et al. Tetraarsenic hexoxide enhances generation of mitochondrial ROS to promote pyroptosis by inducing the activation of caspase-3/GSDME in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, S.; Tian, X.; Jiang, Y. Expression of cleaved caspase-3 predicts good chemotherapy response but poor survival for patients with advanced primary triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 4363–4373. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhong, D.N.; Qin, H.; Wu, P.R.; Wei, K.L.; Chen, G.; He, R.Q.; Zhong, J.C. Caspase-3 over-expression is associated with poor overall survival and clinicopathological parameters in breast cancer: A meta-analysis of 3091 cases. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 8629–8641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contadini, C.; Ferri, A.; Cirotti, C.; Stupack, D.; Barilà, D. Caspase-8 and Tyrosine Kinases: A Dangerous Liaison in Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blasio, A.; Di Fiore, R.; Morreale, M.; Carlisi, D.; Drago-Ferrante, R.; Montalbano, M.; Scerri, C.; Tesoriere, G.; Vento, R. Unusual roles of caspase-8 in triple-negative breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 2339–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. The Bcl-2 protein family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science 1998, 281, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Garcia-Saez, A.J. Mechanisms of BCL-2 family proteins in mitochondrial apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 732–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callagy, G.M.; Webber, M.J.; Pharoah, P.D.; Caldas, C. Meta-analysis confirms BCL2 is an independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, K.T.; Kim, Y.A.; Kim, J.; Oh, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Choi, I.S.; Park, J.H.; Oh, S.; Chu, A.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. Prognostic influences of BCL1 and BCL2 expression on disease-free survival in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, Y.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, A.; Song, B.J.; Chae, B.J. BCL2 as a Subtype-Specific Prognostic Marker for Breast Cancer. J. Breast Cancer 2016, 19, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fatah, T.M.; Perry, C.; Dickinson, P.; Ball, G.; Moseley, P.; Madhusudan, S.; Ellis, I.O.; Chan, S.Y. Bcl2 is an independent prognostic marker of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) and predicts response to anthracycline combination (ATC) chemotherapy (CT) in adjuvant and neoadjuvant settings. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2801–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchalova, K.; Svoboda, M.; Kharaishvili, G.; Vrbkova, J.; Bouchal, J.; Trojanec, R.; Koudelakova, V.; Radova, L.; Cwiertka, K.; Hajduch, M.; et al. BCL2 is an independent predictor of outcome in basal-like triple-negative breast cancers treated with adjuvant anthracycline-based chemotherapy. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 4243–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroppi, P.; Sinibaldi, F.; Fiorucci, L.; Santucci, R. Apoptosis and human diseases: Mitochondrion damage and lethal role of released cytochrome C as proapoptotic protein. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 4058–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Shen, W.; Du, R.; Luo, X.; Yu, J.; Zhou, W.; Dong, X.; Gao, R.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.; et al. Three inflammation-related genes could predict risk in prognosis and metastasis of patients with breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yin, S.; Luo, B.; Wu, X.; Yan, H.; Yan, D.; Chen, C.; Guan, F.; Yuan, J. VDAC1 Conversely Correlates with Cytc Expression and Predicts Poor Prognosis in Human Breast Cancer Patients. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 7647139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramczyk, H.; Brozek-Pluska, B.; Kopeć, M. Double face of cytochrome c in cancers by Raman imaging. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.C.; Borutaite, V. Regulation of apoptosis by the redox state of cytochrome c. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1777, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, T.; Guell, M.; Serrano, L. Correlation of mRNA and protein in complex biological samples. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 3966–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Beyer, A.; Aebersold, R. On the Dependency of Cellular Protein Levels on mRNA Abundance. Cell 2016, 165, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefke, B.; Sun, W.; Li, Y.S.; Fang, L.; Chen, W. The evolution of posttranscriptional regulation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2018, 9, e1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Xiao, X.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chen, C.; Chong, B.; Zhao, X.; Hai, S.; Li, S.; An, Z.; et al. Protein posttranslational modifications in health and diseases: Functions, regulatory mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. MedComm 2023, 4, e261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveto, S.; Mancino, M.; Manfrini, N.; Biffo, S. Role of microRNAs in translation regulation and cancer. World J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 8, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Shi, J. Standardization of Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry. In Handbook of Practical Immunohistochemistry; Lin, F., Prichard, J.W., Liu, H., Wilkerson, M.L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lánczky, A.; Győrffy, B. Web-Based Survival Analysis Tool Tailored for Medical Research (KMplot): Development and Implementation. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e27633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene Expression Omnibus. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/ (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- European Genome-Phenome Archive. Available online: https://ega-archive.org/ (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Chen, M.M.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Akbani, R.; Lu, Y.; Mills, G.B.; Liang, H. TCPA v3.0: An Integrative Platform to Explore the Pan-Cancer Analysis of Functional Proteomic Data. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2019, 18, S15–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyorffy, B. Survival analysis across the entire transcriptome identifies biomarkers with the highest prognostic power in breast cancer. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 4101–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Marker | Kappa (κ) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| AIF1 | 0.949 | <0.001 |
| BCL2-2 | 0.856 | <0.001 |
| cCASP3 | 0.846 | <0.001 |
| cCASP8 | 0.796 | <0.001 |
| CYCS | 0.852 | <0.001 |
| Marker Pair | Pearson Correlation | Pearson p-Value | Spearman’s Correlation | Spearman’s p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cCASP3-AIF1 | 0.260 | 0.008 * | 0.277 | 0.005 * |
| cCASP8-AIF1 | 0.143 | 0.150 | 0.126 | 0.206 |
| BCL2-AIF1 | 0.088 | 0.375 | 0.0940 | 0.345 |
| CYCS-AIF1 | 0.438 | <0.001 * | 0.459 | <0.001 * |
| cCASP3-cCASP8 | 0.126 | 0.203 | 0.089 | 0.371 |
| cCASP3-BCL2 | 0.250 | 0.011 * | 0.255 | 0.009 * |
| cCASP3-CYCS | 0.077 | 0.438 | 0.039 | 0.697 |
| cCASP8-BCL2 | −0.002 | 0.980 | 0.029 | 0.768 |
| cCASP8-CYCS | −0.019 | 0.847 | 0.021 | 0.827 |
| BCL2-CYCS | 0.021 | 0.831 | 0.017 | 0.863 |
| Correlations | Cases | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cCASP3-low | cCASP3-high | |||
| AIF-low | 33 | 13 | Kappa = 0.254 SE = 0.092 95% CI: 0.074–0.434 | 46 |
| AIF-high | 26 | 31 | 57 | |
| Total | 59 | 44 | 64 vs. 39 correlate | 103 |
| CYCS3-low | CYCS-high | |||
| AIF-low | 31 | 15 | Kappa = 0.338 SE = 0.093 95% CI: 0.156–0.519 | 46 |
| AIF-high | 19 | 38 | 57 | |
| Total | 50 | 53 | 67 vs. 36 correlate | 103 |
| cCASP3-low | cCASP3-high | |||
| BCL2-low | 49 | 10 | Kappa = 0.205 SE = 0.092 95% CI: 0.025–0.385 | 59 |
| BCL2-high | 28 | 16 | 44 | |
| Total | 77 | 26 | 65 vs. 38 correlate | 103 |
| Number of patients | 103 |
| Histology | invasive ductal carcinoma |
| Median age (at case diagnosis) | 69 years (range: 29–91 years) |
| Median follow-up | 98 months (range: 5–220 months) |
| Endpoint category | LFU-AWD: 13, LFU-NED: 13, AWD: 2, AWOD: 2 DOD: 13, DOOC: 14, DWD: 3, NED: 28 |
| Median mortality | 65 months (range: 5–170 months) |
| Median progression | 26 months (range: 1–157 months) |
| Tumor size | 22.1 mm (range: 7–55 mm) |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | 9 |
| pT Category | pT1: 51, pT2: 43, pT3: 4, pT4: 5 |
| pN Category | pN0: 54, pN1: 35, pN2: 10, pN3: 2, pNx: 1 |
| Grade | G1: 0, G2: 4, G3: 99 |
| Surgery type | Breast conservative: 77, Mastectomy: 26, SNB: 52, SNB + ABD: 23, ABD: 26, No axillary surgery: 2 |
| Chemo and Radiotherapy | Only chemotherapy: 9, Chemo- and radiotherapy: 72, Only radiotherapy: 9, Neither chemo- nor radiotherapy: 13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Török, M.; Nagy, Á.; Cserni, G.; Karancsi, Z.; Gregus, B.; Nagy, D.H.; Árkosy, P.; Kovács, I.; Méhes, G.; Krenács, T. Prognostic Potential of Apoptosis-Related Biomarker Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157227
Török M, Nagy Á, Cserni G, Karancsi Z, Gregus B, Nagy DH, Árkosy P, Kovács I, Méhes G, Krenács T. Prognostic Potential of Apoptosis-Related Biomarker Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157227
Chicago/Turabian StyleTörök, Miklós, Ágnes Nagy, Gábor Cserni, Zsófia Karancsi, Barbara Gregus, Dóra Hanna Nagy, Péter Árkosy, Ilona Kovács, Gabor Méhes, and Tibor Krenács. 2025. "Prognostic Potential of Apoptosis-Related Biomarker Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157227
APA StyleTörök, M., Nagy, Á., Cserni, G., Karancsi, Z., Gregus, B., Nagy, D. H., Árkosy, P., Kovács, I., Méhes, G., & Krenács, T. (2025). Prognostic Potential of Apoptosis-Related Biomarker Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157227







