In-Depth Characterization of L1CAM+ Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Biomarkers for Anti-CD20 Therapy Response in Relapsing–Remitting Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
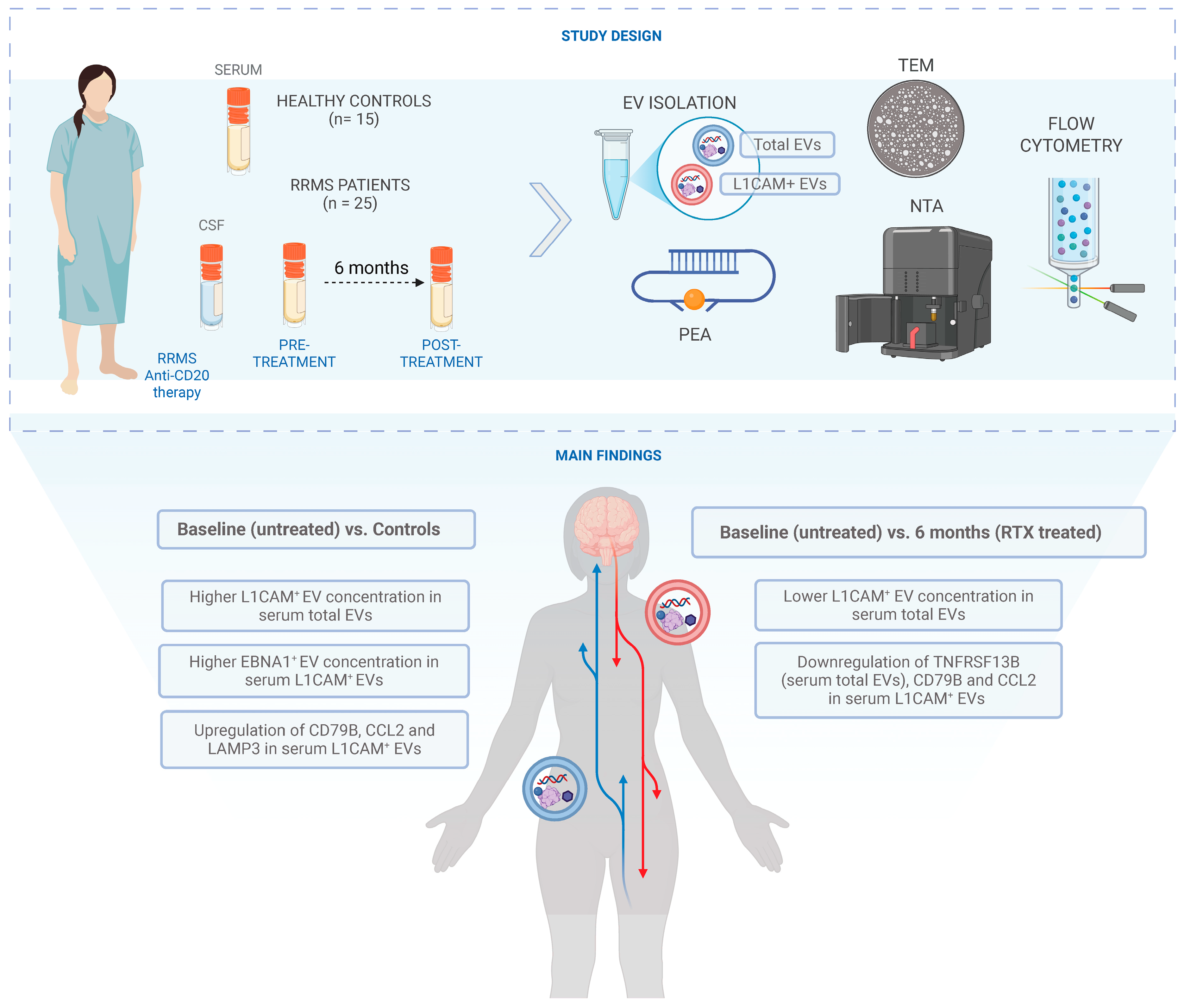
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics and EV Characterization: Size, Morphology, and Tetraspanin Profiling
2.2. Significant Changes in L1CAM+ EV Concentrations Before and After Rituximab-CD20 Treatment in Serum Total EVs
2.3. Significantly Elevated EBNA1+ EV Concentration in Serum L1CAM+ EVs at Baseline Before Rituximab Treatment Compared to HC
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Cohorts and Control Samples
4.2. Isolation of EVs from CSF and Serum Samples
4.3. Characterization of EVs
4.3.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Imaging
4.3.2. Nanoparticle Tracking (NTA) Analysis
4.3.3. Flow Cytometry
4.3.4. Proximity Extension Assay (PEA)
4.4. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walton, C.; King, R.; Rechtman, L.; Kaye, W.; Leray, E.; Marrie, R.A.; Robertson, N.; La Rocca, N.; Uitdehaag, B.; van der Mei, I.; et al. Rising prevalence of multiple sclerosis worldwide: Insights from the Atlas of MS, third edition. Mult. Scler. 2020, 26, 1816–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.J.; Baranzini, S.E.; Geurts, J.; Hemmer, B.; Ciccarelli, O. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2018, 391, 1622–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Fournier, M.; López-Molina, M.; Torres Iglesias, G.; Botella, L.; Chamorro, B.; Laso-García, F.; Puertas, I.; Tallón Barranco, A.; Otero-Ortega, L.; Frank-García, A.; et al. Antibody Content against Epstein–Barr Virus in Blood Extracellular Vesicles Correlates with Disease Activity and Brain Volume in Patients with Relapsing–Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrad, M.F.; Saba, E.S.; Nakib, L.; Khoury, S.J. Exosomes From Subjects With Multiple Sclerosis Express EBV-Derived Proteins and Activate Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Amp Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornevik, K.; Cortese, M.; Healy, B.C.; Kuhle, J.; Mina, M.J.; Leng, Y.; Elledge, S.J.; Niebuhr, D.W.; Scher, A.I.; Munger, K.L.; et al. Longitudinal analysis reveals high prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus associated with multiple sclerosis. Science 2022, 375, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkildsen, Ø.; Myhr, K.M.; Bø, L. Disease-modifying treatments for multiple sclerosis—A review of approved medications. Eur. J. Neurol. 2016, 23 (Suppl. 1), 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhr, K.M.; Torkildsen, Ø.; Lossius, A.; Bø, L.; Holmøy, T. B cell depletion in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 19, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, A.L.; Hauser, S.L. B-cell Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis: Entering an era. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann-Horn, K.; Kinzel, S.; Weber, M.S. Deciphering the Role of B Cells in Multiple Sclerosis—Towards Specific Targeting of Pathogenic Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, L.; Fox, E.; Hartung, H.P.; Alvarez, E.; Qian, P.; Wray, S.; Robertson, D.; Huang, D.; Selmaj, K.; Wynn, D.; et al. Ublituximab versus Teriflunomide in Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanichamy, A.; Jahn, S.; Nickles, D.; Derstine, M.; Abounasr, A.; Hauser, S.L.; Baranzini, S.E.; Leppert, D.; von Büdingen, H.C. Rituximab efficiently depletes increased CD20-expressing T cells in multiple sclerosis patients. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holley, J.E.; Bremer, E.; Kendall, A.C.; de Bruyn, M.; Helfrich, W.; Tarr, J.M.; Newcombe, J.; Gutowski, N.J.; Eggleton, P. CD20+inflammatory T-cells are present in blood and brain of multiple sclerosis patients and can be selectively targeted for apoptotic elimination. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2014, 3, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, J.; Vinayagasundaram, U.; Mowry, E.M.; Matthews, I.R.; Marino, J.A.; Cheng, J.; Waubant, E. Effects of rituximab on lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2014, 3, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatino, J.J.; Wilson, M.R.; Calabresi, P.A.; Hauser, S.L.; Schneck, J.P.; Zamvil, S.S. Anti-CD20 therapy depletes activated myelin-specific CD8+ T cells in multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25800–25807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novi, G.; Bovis, F.; Fabbri, S.; Tazza, F.; Gazzola, P.; Maietta, I.; Currò, D.; Bruschi, N.; Roccatagliata, L.; Boffa, G.; et al. Tailoring B cell depletion therapy in MS according to memory B cell monitoring. Neurol.—Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kempen, Z.L.; Toorop, A.A.; Sellebjerg, F.; Giovannoni, G.; Killestein, J. Extended dosing of monoclonal antibodies in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2021, 28, 13524585211065711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lötvall, J.; Hill, A.F.; Hochberg, F.; Buzás, E.I.; Di Vizio, D.; Gardiner, C.; Gho, Y.S.; Kurochkin, I.V.; Mathivanan, S.; Quesenberry, P.; et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 26913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Jeyaraj, M.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.H. Review of the Isolation, Characterization, Biological Function, and Multifarious Therapeutic Approaches of Exosomes. Cells 2019, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Du, X.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Xu, Y. The Emerging Role of Neural Cell-Derived Exosomes in Intercellular Communication in Health and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 738442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mycko, M.P.; Baranzini, S.E. microRNA and exosome profiling in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2020, 26, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, S.; Dutta, S.; Bitan, G. CNS-Derived Blood Exosomes as a Promising Source of Biomarkers: Opportunities and Challenges. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres Iglesias, G.; Fernández-Fournier, M.; Botella, L.; Piniella, D.; Laso-García, F.; Carmen Gómez-de Frutos, M.; Chamorro, B.; Puertas, I.; Tallón Barranco, A.; Fuentes, B.; et al. Brain and immune system-derived extracellular vesicles mediate regulation of complement system, extracellular matrix remodeling, brain repair and antigen tolerance in Multiple sclerosis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 113, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres Iglesias, G.; Fernández-Fournier, M.; López-Molina, M.; Piniella, D.; Laso-García, F.; Gómez-de Frutos, M.C.; Alonso-López, E.; Botella, L.; Chamorro, B.; Sánchez-Velasco, S.; et al. Dual role of peripheral B cells in multiple sclerosis: Emerging remote players in demyelination and novel diagnostic biomarkers. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1224217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucco, M.; Mannheim, W.; Shetty, S.V.; Linden, J.R. CNS endothelial derived extracellular vesicles are biomarkers of active disease in multiple sclerosis. Fluids Barriers CNS 2022, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Miana, R.D.C.; Arizaga-Echebarria, J.K.; Sabas-Ortega, V.; Crespillo-Velasco, H.; Prada, A.; Castillo-Triviño, T.; Otaegui, D. Tetraspanins, GLAST and L1CAM Quantification in Single Extracellular Vesicles from Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum of People with Multiple Sclerosis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres Iglesias, G.; López-Molina, M.; Botella, L.; Laso-García, F.; Chamorro, B.; Fernández-Fournier, M.; Puertas, I.; Bravo, S.B.; Alonso-López, E.; Díez-Tejedor, E.; et al. Differential Protein Expression in Extracellular Vesicles Defines Treatment Responders and Non-Responders in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim Falk, V.; Mueller-Wirth, N.; Karathanasis, D.; Evangelopoulos, M.E.; Maleska Maceski, A.; Zadic, A.; Kuhle, J.; Schlup, C.; Marti, S.; Guse, K.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle Marker Changes Associated With Disease Activity in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2025, 12, e200404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, C.D. NeuroEVs: Characterizing Extracellular Vesicles Generated in the Neural Domain. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 9262–9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, D.E.; Witwer, K.W. L1CAM-associated extracellular vesicles: A systematic review of nomenclature, sources, separation, and characterization. J. Extracell. Biol. 2022, 1, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.F. Extracellular Vesicles and Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 9269–9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, M.; Ter-Ovanesyan, D.; Trieu, W.; Lazarovits, R.; Kowal, E.J.K.; Lee, J.H.; Chen-Plotkin, A.S.; Regev, A.; Church, G.M.; Walt, D.R. L1CAM is not associated with extracellular vesicles in human cerebrospinal fluid or plasma. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueras-Ortiz, C.J.; Eren, E.; Yao, P.; Calzada, E.; Dunn, C.; Volpert, O.; Delgado-Peraza, F.; Mustapic, M.; Lyashkov, A.; Rubio, F.J.; et al. Single-extracellular vesicle (EV) analyses validate the use of L1 Cell Adhesion Molecule (L1CAM) as a reliable biomarker of neuron-derived EVs. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marostica, G.; Gelibter, S.; Gironi, M.; Nigro, A.; Furlan, R. Extracellular Vesicles in Neuroinflammation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 623039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapic, M.; Eitan, E.; Werner, J.K., Jr.; Berkowitz, S.T.; Lazaropoulos, M.P.; Tran, J.; Goetzl, E.J.; Kapogiannis, D. Plasma Extracellular Vesicles Enriched for Neuronal Origin: A Potential Window into Brain Pathologic Processes. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandendriessche, C.; Bruggeman, A.; Van Cauwenberghe, C.; Vandenbroucke, R.E. Extracellular Vesicles in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease: Small Entities with Large Consequences. Cells 2020, 9, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolcetti, E.; Bruno, A.; Guadalupi, L.; Rizzo, F.R.; Musella, A.; Gentile, A.; De Vito, F.; Caioli, S.; Bullitta, S.; Fresegna, D.; et al. Emerging Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathophysiology of Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghav, A.; Singh, M.; Jeong, G.B.; Giri, R.; Agarwal, S.; Kala, S.; Gautam, K.A. Extracellular vesicles in neurodegenerative diseases: A systematic review. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1061076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barro, C.; Healy, B.C.; Liu, Y.; Saxena, S.; Paul, A.; Polgar-Turcsanyi, M.; Guttmann, C.R.G.; Bakshi, R.; Kropshofer, H.; Weiner, H.L.; et al. Serum GFAP and NfL Levels Differentiate Subsequent Progression and Disease Activity in Patients With Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Fernández, M.; de la Cuesta, F.; Tallón, A.; Cuesta, I.; Fernández-Fournier, M.; Laso-García, F.; Gómez-de Frutos, M.C.; Díez-Tejedor, E.; Otero-Ortega, L. Potential Roles of Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers and a Novel Treatment Approach in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahad, D.; Callahan, M.K.; Williams, K.A.; Ubogu, E.E.; Kivisäkk, P.; Tucky, B.; Kidd, G.; Kingsbury, G.A.; Chang, A.; Fox, R.J.; et al. Modulating CCR2 and CCL2 at the blood-brain barrier: Relevance for multiple sclerosis pathogenesis. Brain 2006, 129 Pt 1, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anandan, S.; Maciak, K.; Breinbauer, R.; Otero-Ortega, L.; Feliciello, G.; Stojanović Gužvić, N.; Torkildsen, O.; Myhr, K.-M. In-Depth Characterization of L1CAM+ Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Biomarkers for Anti-CD20 Therapy Response in Relapsing–Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157213
Anandan S, Maciak K, Breinbauer R, Otero-Ortega L, Feliciello G, Stojanović Gužvić N, Torkildsen O, Myhr K-M. In-Depth Characterization of L1CAM+ Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Biomarkers for Anti-CD20 Therapy Response in Relapsing–Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157213
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnandan, Shamundeeswari, Karina Maciak, Regina Breinbauer, Laura Otero-Ortega, Giancarlo Feliciello, Nataša Stojanović Gužvić, Oivind Torkildsen, and Kjell-Morten Myhr. 2025. "In-Depth Characterization of L1CAM+ Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Biomarkers for Anti-CD20 Therapy Response in Relapsing–Remitting Multiple Sclerosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157213
APA StyleAnandan, S., Maciak, K., Breinbauer, R., Otero-Ortega, L., Feliciello, G., Stojanović Gužvić, N., Torkildsen, O., & Myhr, K.-M. (2025). In-Depth Characterization of L1CAM+ Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Biomarkers for Anti-CD20 Therapy Response in Relapsing–Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7213. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157213






