Identification of Drug Repurposing Candidates for Coxsackievirus B3 Infection in iPSC-Derived Brain-like Endothelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
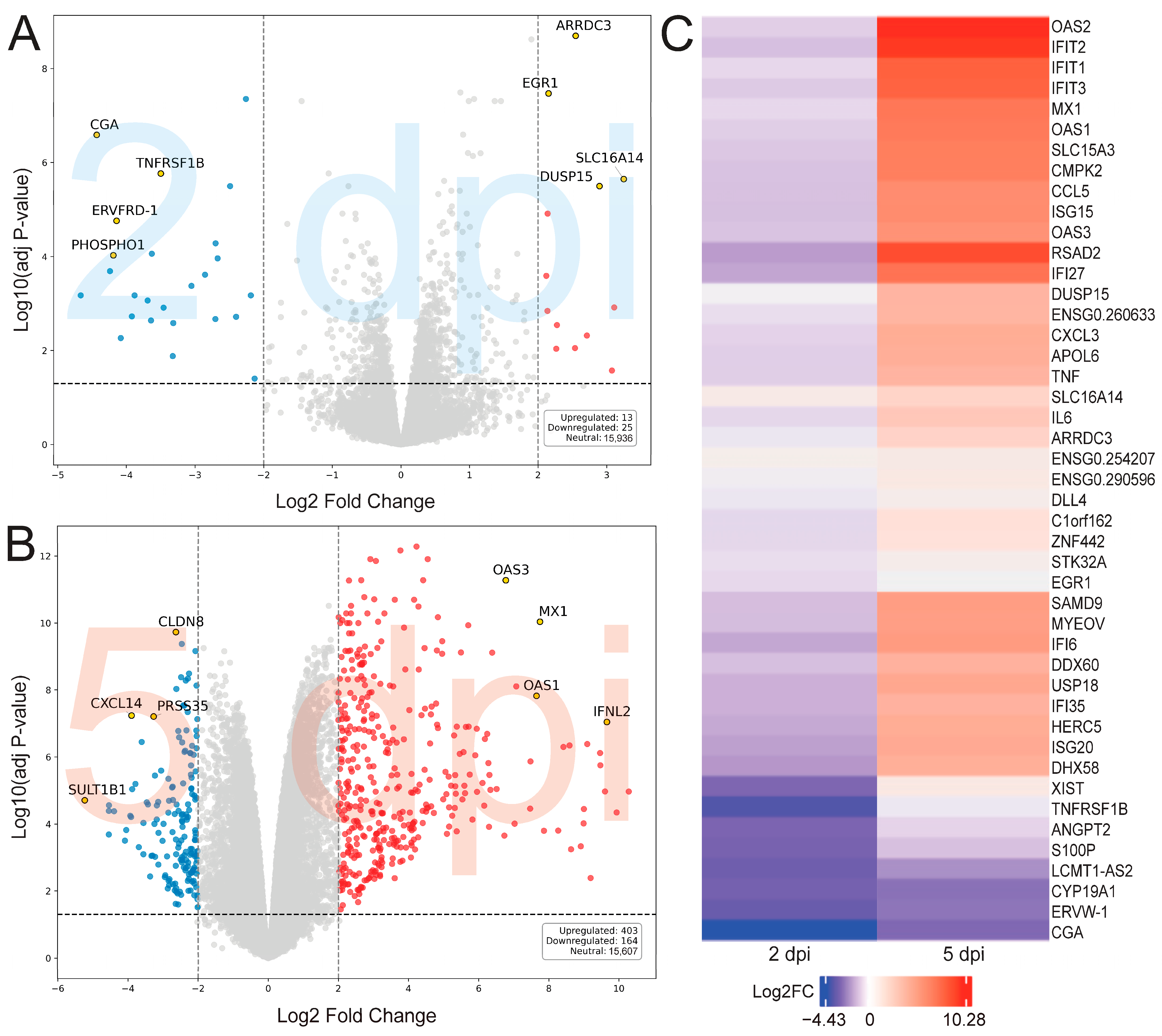
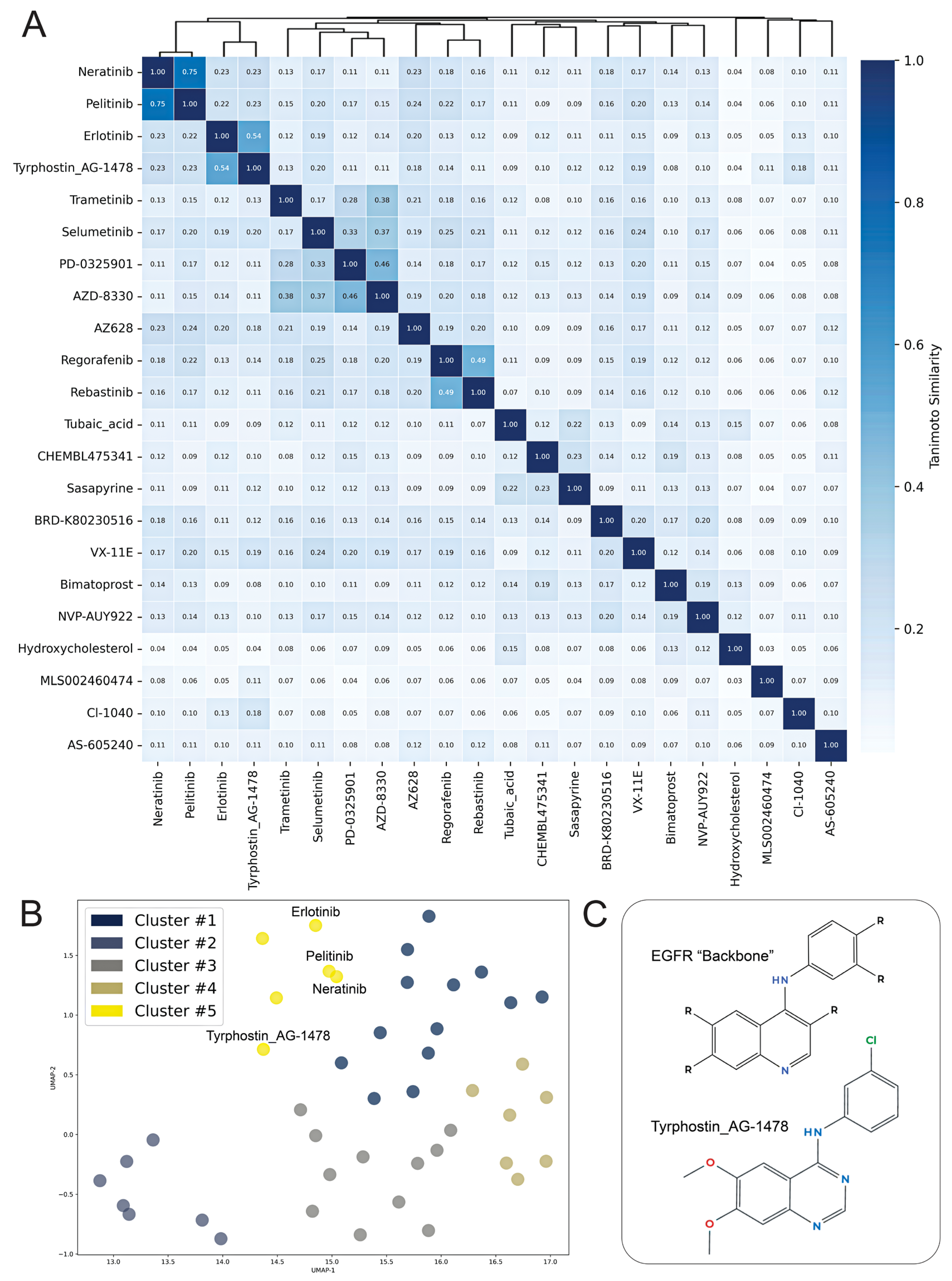
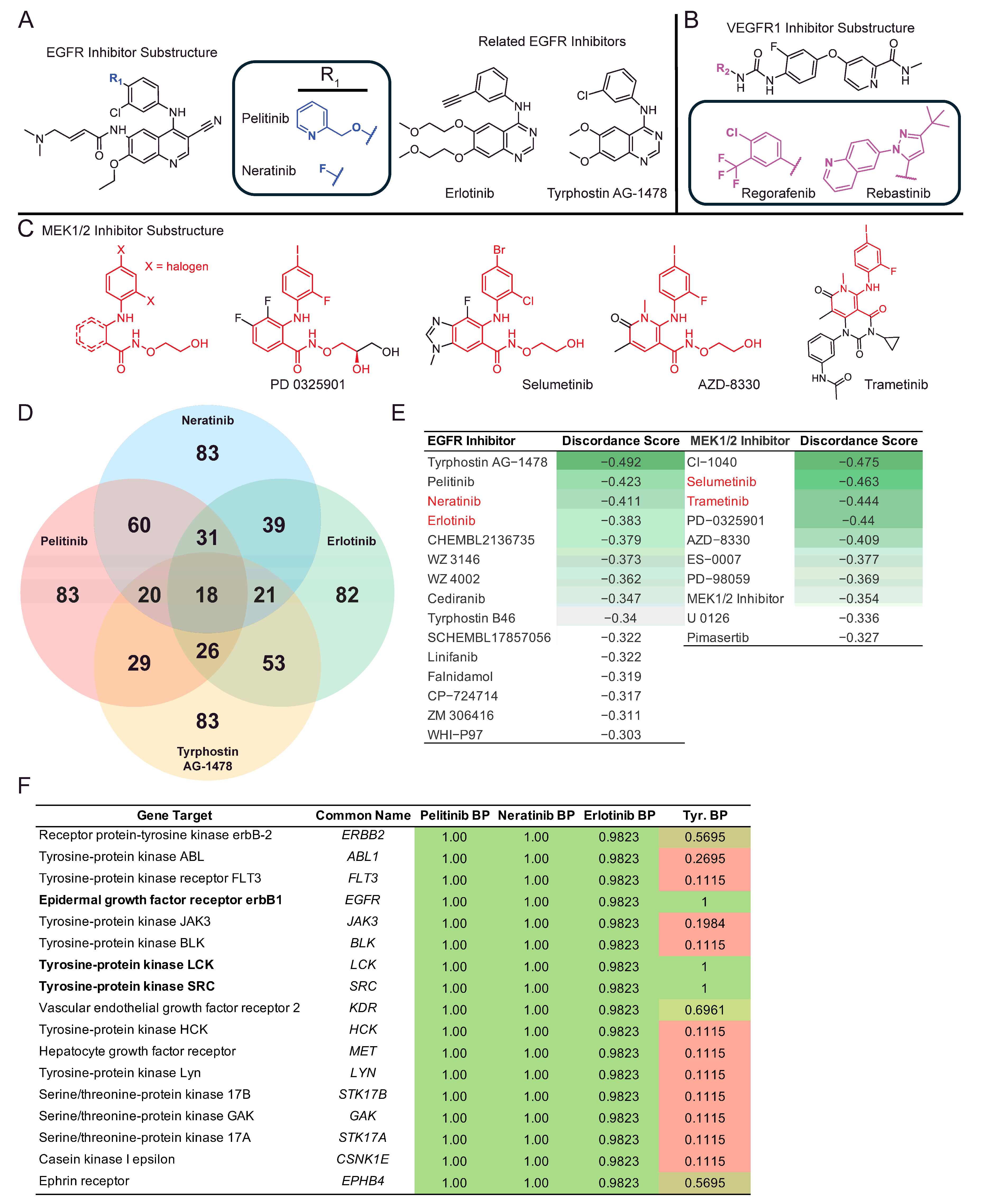
2. Results
3. Discussion
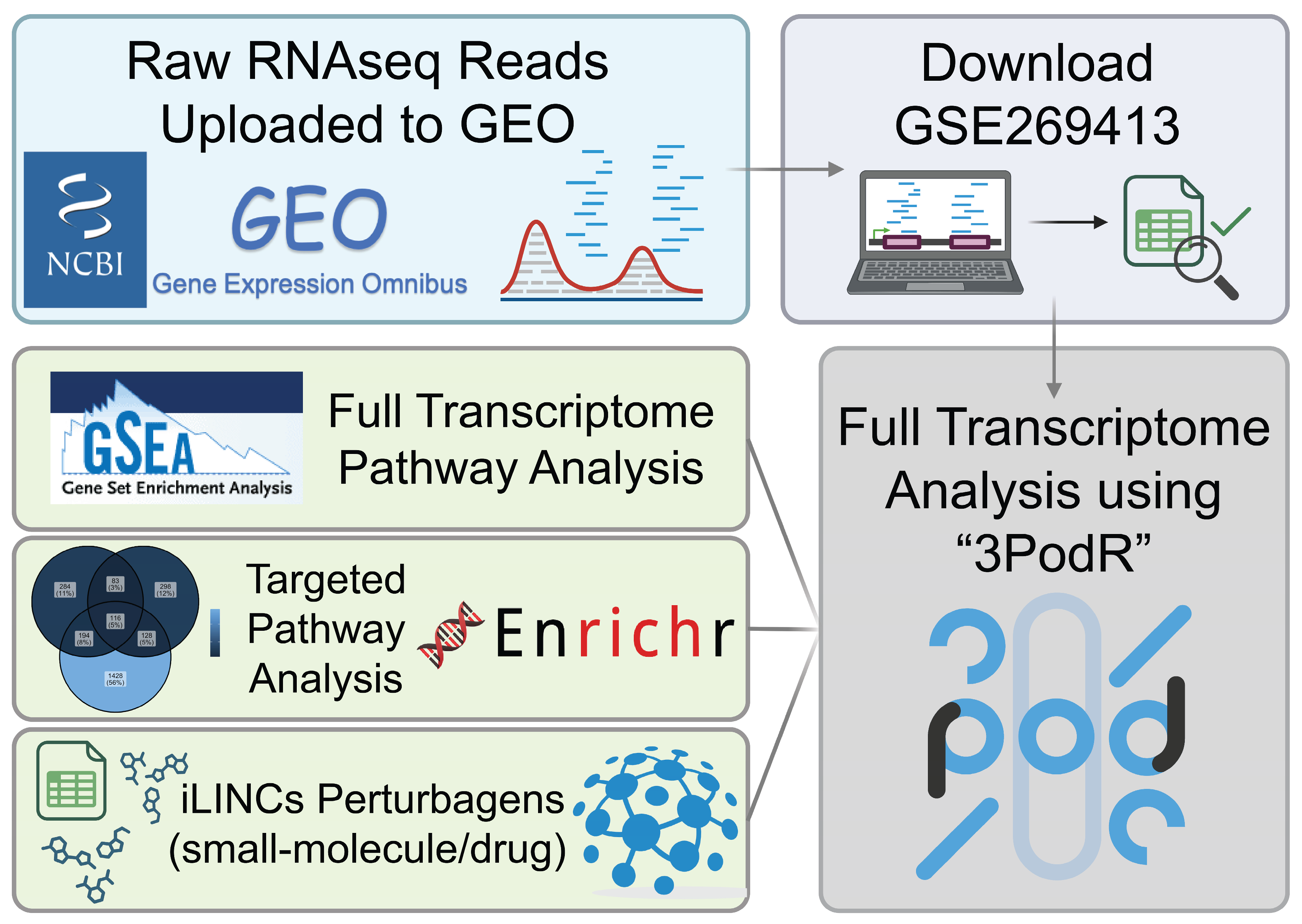
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CVB3 | Coxsackievirus B3 |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| iPSCs | Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells |
| iBECs | iPSC Brain Endothelial Cells |
| BECs | Brain Endothelial Cells |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| dpi | Days post infection |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| DEG | Differential Gene Expression |
| LE | Leading Edge |
| GSEA | Gene Set Enrichment Analysis |
| LINCS | Library of Integrated Network-Based Signatures |
| NES | Normalized Enrichment Score |
| UMAP | Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection |
References
- Garmaroudi, F.S.; Marchant, D.; Hendry, R.; Luo, H.; Yang, D.; Ye, X.; Shi, J.; McManus, B.M. Coxsackievirus B3 replication and pathogenesis. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 629–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotbart, H.A. Viral meningitis. Semin. Neurol. 2000, 20, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, J.R. Pediatric group B coxsackievirus infections. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 323, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sin, J.; Mangale, V.; Thienphrapa, W.; Gottlieb, R.A.; Feuer, R. Recent progress in understanding coxsackievirus replication, dissemination, and pathogenesis. Virology 2015, 484, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khetsuriani, N.; Lamonte-Fowlkes, A.; Oberst, S.; Pallansch, M.A. Enterovirus surveillance--United States, 1970–2005. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2006, 55, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Non-Polio Enterovirus: About Enteroviruses; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022.
- Mone, K.; Lasrado, N.; Sur, M.; Reddy, J. Vaccines against Group B Coxsackieviruses and Their Importance. Vaccines 2023, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, A.M.; Orille, E.; Waseem, M. Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Yang, Q.; Han, J. Transcriptomic analysis reveals that coxsackievirus B3 Woodruff and GD strains use similar key genes to induce FoxO signaling pathway activation in HeLa cells. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassmann, A.; Martin, U.; Saluz, H.P.; Peter, S.; Munder, T.; Henke, A. Identification of gene expression profiles in HeLa cells and HepG2 cells infected with Coxsackievirus B3. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 187, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, L.A.; Carthy, C.M.; Yang, D.; Saad, K.; Wong, D.; Schreiner, G.; Stanton, L.W.; McManus, B.M. Host gene regulation during coxsackievirus B3 infection in mice: Assessment by microarrays. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.J.; Gim, J.A.; Lee, J.K.; Park, H.; Shin, O.S. Coxsackievirus B3 Infection of Human Neural Progenitor Cells Results in Distinct Expression Patterns of Innate Immune Genes. Viruses 2020, 12, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Huang, C. Coxsackieviruses B3 infection of myocardial microvascular endothelial cells activates fractalkine via the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 7548–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathcock, S.F.; Mamana, J.; Keyzer, T.E.; Vollmuth, N.; Shokri, M.R.; Mauser, H.D.; Correll, R.N.; Lam, D.W.; Kim, B.J.; Sin, J. Transcriptomic analysis of coxsackievirus B3 infection in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived brain-like endothelial cells. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e0182424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franks, I. Brain endothelial cells support HCV entry and replication. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura-Ohba, S.; Kitamura, M.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Kogaki, S.; Sakai, S.; Fushimi, H.; Matsuoka, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Itoh, K.; Ueda, K.; et al. Viral entry and translation in brain endothelia provoke influenza-associated encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 2024, 147, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, I.A.; Prevost, M.-C.; Perret, E.; Adamson, P.; Greenwood, J.; Couraud, P.-O.; Ozden, S. Interactions between Brain Endothelial Cells and Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1-Infected Lymphocytes: Mechanisms of Viral Entry into the Central Nervous System. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6021–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilarczyk, M.; Fazel-Najafabadi, M.; Kouril, M.; Shamsaei, B.; Vasiliauskas, J.; Niu, W.; Mahi, N.; Zhang, L.; Clark, N.A.; Ren, Y.; et al. Connecting omics signatures and revealing biological mechanisms with iLINCS. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, W. 3PodR Bookdown. Available online: https://github.com/willgryan/3PodR_bookdown.git (accessed on 8 August 2024).
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, F.; Carturan, E.; Chimenti, C.; Pieroni, M.; Agostini, C.; Angelini, A.; Crosato, M.; Valente, M.; Boffa, G.M.; Frustaci, A.; et al. Overexpression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)alpha and TNFalpha receptor I in human viral myocarditis: Clinicopathologic correlations. Mod. Pathol. 2004, 17, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Rao, B. The expression of TNF-alpha mRNA and its significance in murine viral myocarditis. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2002, 31, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dalskov, L.; Gad, H.H.; Hartmann, R. Viral recognition and the antiviral interferon response. EMBO J. 2023, 42, e112907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huai, W.; Yang, K.; Xing, C.; Song, K.; Lyu, H.; Williams, N.S.; Wu, J.; Yan, N. OAS cross-activates RNase L intercellularly through cell-to-cell transfer of 2-5A to spread innate immunity. Immunity 2025, 58, 797–810.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.X.; Wang, H.; Lv, H.; Liu, P.P.; Xia, S.G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.D.; Yang, C.Q.; et al. Polymorphism of OAS2 rs739901 C/A Involves the Susceptibility to EV71 Infection in Chinese Children. Curr. Med. Sci. 2018, 38, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, D.; Liu, G. Ribosomal control in RNA virus-infected cells. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1026887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, A.; Shuwei, P.; Xu, S.; Yuanfeng, Z.; Lixia, L.; Renyong, J.; Zhongqiong, Y. Chlorogenic acid is a positive regulator of MDA5, TLR7 and NF-κB signaling pathways mediated antiviral responses against Gammacoronavirus infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Fu, X.X.; Duan, R.; Wei, B.; Cao, H.M.; Yan, E.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.D.; Jiang, T. The Alzheimer’s disease-associated gene TREML2 modulates inflammation by regulating microglia polarization and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.; Zhang, P.; Chen, S.; Shi, W.; Ye, J.; Chen, S.; Ju, R.; Liu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y. Immune Cell Landscape of Patients With Diabetic Macular Edema by Single-Cell RNA Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 754933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zheng, M.; Feng, Z.; Lin, Q. CCL4L2 participates in tendinopathy progression by promoting macrophage inflammatory responses: A single-cell analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2024, 19, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen-Rou, W.; Yu-Yun, C.; Shun-Min, Y.; Yin-Li, C.; Jim-Tong, H. Phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK in an early entry step of enterovirus 71. Life Sci. 2005, 78, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qiao, R.; Hao, M.; Xu, L.; Wang, D.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Cheng, T.; et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 as a potential host target for the inhibition of enterovirus replication. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0112924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, W.-H.; Lee, I.T.; Hsieh, H.-L.; Yang, C.-M. EV71 induces COX-2 expression via c-Src/PDGFR/PI3K/Akt/p42/p44 MAPK/AP-1 and NF-κB in rat brain astrocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 224, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: Updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opavsky, M.A.; Martino, T.; Rabinovitch, M.; Penninger, J.; Richardson, C.; Petric, M.; Trinidad, C.; Butcher, L.; Chan, J.; Liu, P.P. Enhanced ERK-1/2 activation in mice susceptible to coxsackievirus-induced myocarditis. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grün, K.; Markova, B.; Böhmer, F.-D.; Berndt, A.; Kosmehl, H.; Leipner, C. Elevated expression of PDGF-C in coxsackievirus B3-induced chronic myocarditis. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minghetti, L. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in Inflammatory and Degenerative Brain Diseases. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 63, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delsing, L.; Herland, A.; Falk, A.; Hicks, R.; Synnergren, J.; Zetterberg, H. Models of the blood-brain barrier using iPSC-derived cells. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2020, 107, 103533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risau, W. Development and differentiation of endothelium. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, S3–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioni, C.; Turlizzi, E.; Zanelli, U.; Oliveri, G.; Annunziata, P. Expression of Tight Junction and Drug Efflux Transporter Proteins in an in vitro Model of Human Blood-Brain Barrier. Front. Psychiatry 2012, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czupalla, C.J.; Liebner, S.; Devraj, K. In vitro models of the blood-brain barrier. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1135, 415–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippmann, E.S.; Azarin, S.M.; Kay, J.E.; Nessler, R.A.; Wilson, H.K.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Palecek, S.P.; Shusta, E.V. Derivation of blood-brain barrier endothelial cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolet, B.P.; Wolkers, M.C. The relationship of mRNA with protein expression in CD8+ T cells associates with gene class and gene characteristics. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, C.W.; Chen, Y.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. voom: Precision weights unlock linear model analysis tools for RNA-seq read counts. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Bailey, A.; Kuleshov, M.V.; Clarke, D.J.B.; Evangelista, J.E.; Jenkins, S.L.; Lachmann, A.; Wojciechowicz, M.L.; Kropiwnicki, E.; Jagodnik, K.M.; et al. Gene Set Knowledge Discovery with Enrichr. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donovan, S.M.; Imami, A.; Eby, H.; Henkel, N.D.; Creeden, J.F.; Asah, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Alnafisah, R.; Taylor, R.T.; et al. Identification of candidate repurposable drugs to combat COVID-19 using a signature-based approach. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Xue, X.; Au, E.; McIntyre, W.B.; Asgariroozbehani, R.; Panganiban, K.; Tseng, G.C.; Papoulias, M.; Smith, E.; Monteiro, J.; et al. Glucose dysregulation in antipsychotic-naive first-episode psychosis: In silico exploration of gene expression signatures. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolde, R. Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps (R Version 1.0.13). 2018. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pheatmap/index.html (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Wilke, C.O. Ggridges: Ridgeline Plots in ‘Ggplot2’ (R Version 0.5.6). 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggridges/index.html (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Landrum, G.; Tosco, P.; Kelley, B.; Rodriguez, R.; Cosgrove, D.; Vianello, R.; Sriniker; Gedeck, P.; Jones, G.; Kawashima, E.; et al. RDKit: Open-Source Cheminformatics (Version 2025.3.2). 2025. Available online: https://github.com/rdkit/rdkit (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Waskom, M.L. seaborn: Statistical data visualization. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Cell Line | Significant Genes | Significant Pathways | Methods | Authorship |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVB3 | HeLa | CCNG2, GADD45B, PIM1, RBM15, KLF10 | FoxO | DESeq2, PPI network, KEGG | Liu et al. [9] |
| CVB3 | HeLa/HepG2 | IL3RA, CASP3, ATF1, TPM1, MMP9, CCL27, TNFa | IFN and IL | DNA Microarray | Rassmann et al. [10] |
| CVB3 | A/J (H-2) | PABP, UBP41, inorganic pyrophosphatase genes | B-Ox. And CAC/ETC pathways | DNA Microarray | Taylor et al. [11] |
| CVB3 | nHPC’s | RIG-I, MDA5, IFN-, IP-10, ISG15, OAS1, OAS2 | Innate Immune response/IFN | Quantseq, KEGG | Oh et al. [12] |
| CVB3 | CMEC | ERK1/2, FKN, CX3C | MAPK, ERK1/2 | Western blotting, RNAi | Wen et al. [13] |
| 2 Day GSEA Pathways | 5 Day GSEA Pathways | padj | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulation of viral genome replication | Response to virus | <0.01 | 1 |
| Negative regulation of viral genome replication | Defense response to symbiont | <0.01 | 2 |
| Negative regulation of viral process | Defense response to virus | <0.01 | 3 |
| Defense response to symbiont | Defense response to other organism | <0.01 | 4 |
| Defense response to virus | Innate immune response | <0.01 | 5 |
| Regulation of viral life cycle | Response to external biotic stimulus | <0.01 | 6 |
| Positive regulation of IFN-beta production | Response to other organism | <0.01 | 7 |
| Response to virus | Response to biotic stimulus | <0.01 | 8 |
| Positive regulation of mirna process | Negative regulation of viral process | <0.01 | 9 |
| Regulation of viral process | Immune response | <0.01 | 10 |
| Perturbagen | Discordance Score | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| N6022 | −0.5 | Unknown |
| Tyrphostin AG-1478 | −0.49 | EGFR inhibitor |
| CI-1040 | −0.47 | MEK inhibitor |
| BRD-K80230516 | −0.47 | Unknown |
| Selumetinib | −0.46 | MEK inhibitor |
| Tubaic acid | −0.45 | Mitochondrial complex I inhibitor |
| AZ628 | −0.44 | RAF inhibitor |
| Trametinib | −0.44 | MEK inhibitor |
| PD-0325901 | −0.44 | MAP kinase, MEK inhibitor |
| Bimatoprost | −0.42 | Unknown |
| Perturbagen | Discordance Score | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Hydroquinidine | −0.46 | Antiarrhythmic |
| AZD-8055 | −0.45 | MTOR inhibitor |
| BMS-536924 | −0.42 | IGF-1 inhibitor |
| TSU-68 | −0.42 | FGFR, PDGFR, VEGFR inhibitor |
| CAY-10594 | −0.41 | Phospholipase inhibitor |
| Pilocarpine | −0.40 | Acetylcholine receptor agonist |
| Ampalex | −0.40 | Unknown |
| BRD-K42573370-001-01-1 | −0.40 | Nucleophosmin inhibitor |
| Betahistine | −0.40 | Histamine receptor agonist/antagonist |
| Naftifine | −0.4 | Squalene monooxygenase inhibitor |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wood, J.F.; Vergis, J.M.; Imami, A.S.; Ryan, W.G., V; Sin, J.J.; Kim, B.J.; Schiefer, I.T.; McCullumsmith, R.E. Identification of Drug Repurposing Candidates for Coxsackievirus B3 Infection in iPSC-Derived Brain-like Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157041
Wood JF, Vergis JM, Imami AS, Ryan WG V, Sin JJ, Kim BJ, Schiefer IT, McCullumsmith RE. Identification of Drug Repurposing Candidates for Coxsackievirus B3 Infection in iPSC-Derived Brain-like Endothelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157041
Chicago/Turabian StyleWood, Jacob F., John M. Vergis, Ali S. Imami, William G. Ryan, V, Jon J. Sin, Brandon J. Kim, Isaac T. Schiefer, and Robert E. McCullumsmith. 2025. "Identification of Drug Repurposing Candidates for Coxsackievirus B3 Infection in iPSC-Derived Brain-like Endothelial Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157041
APA StyleWood, J. F., Vergis, J. M., Imami, A. S., Ryan, W. G., V, Sin, J. J., Kim, B. J., Schiefer, I. T., & McCullumsmith, R. E. (2025). Identification of Drug Repurposing Candidates for Coxsackievirus B3 Infection in iPSC-Derived Brain-like Endothelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7041. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157041







