Aminopeptidase A Effect on Angiotensin Peptides and Their Blood Pressure Action
Abstract
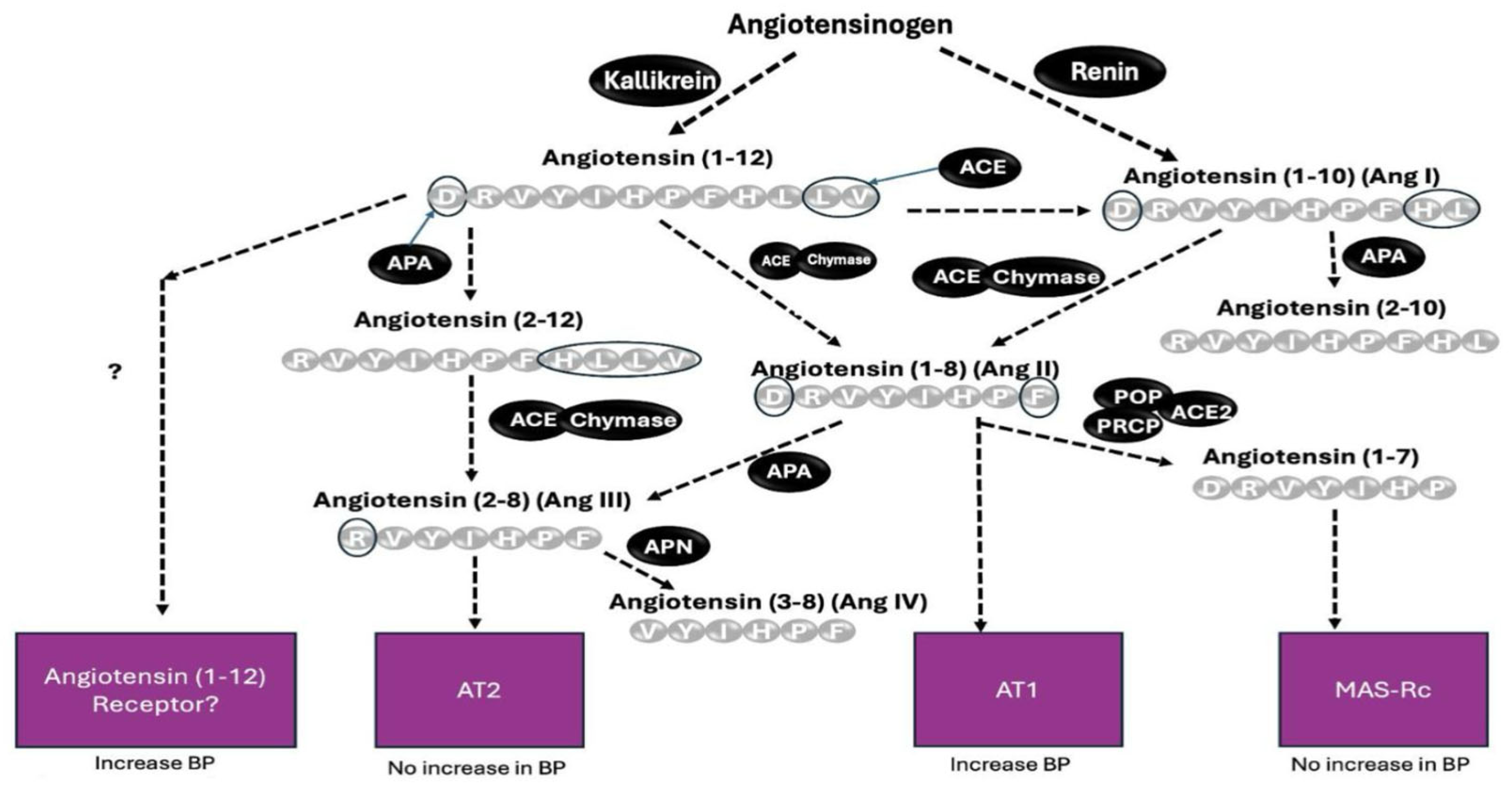
1. Introduction
2. Results
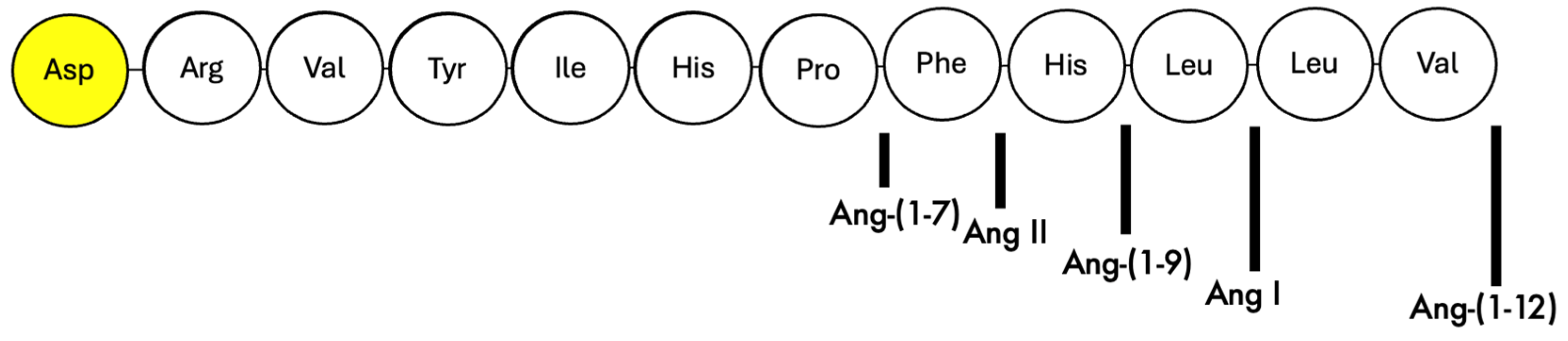
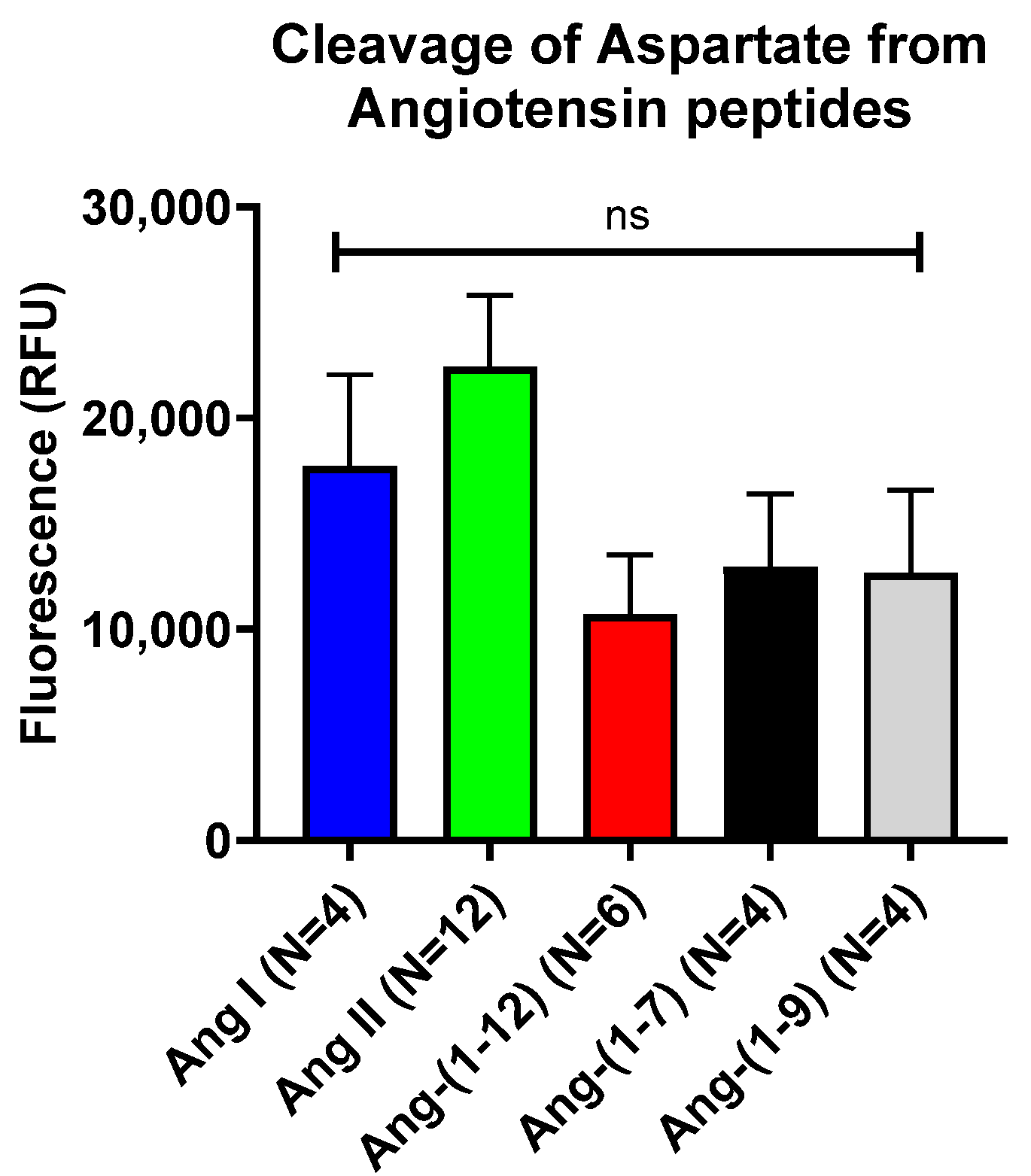
2.1. In Vitro Assessment of Cleavage of N-Terminal Aspartate from Various Angiotensin Peptides by Recombinant APA
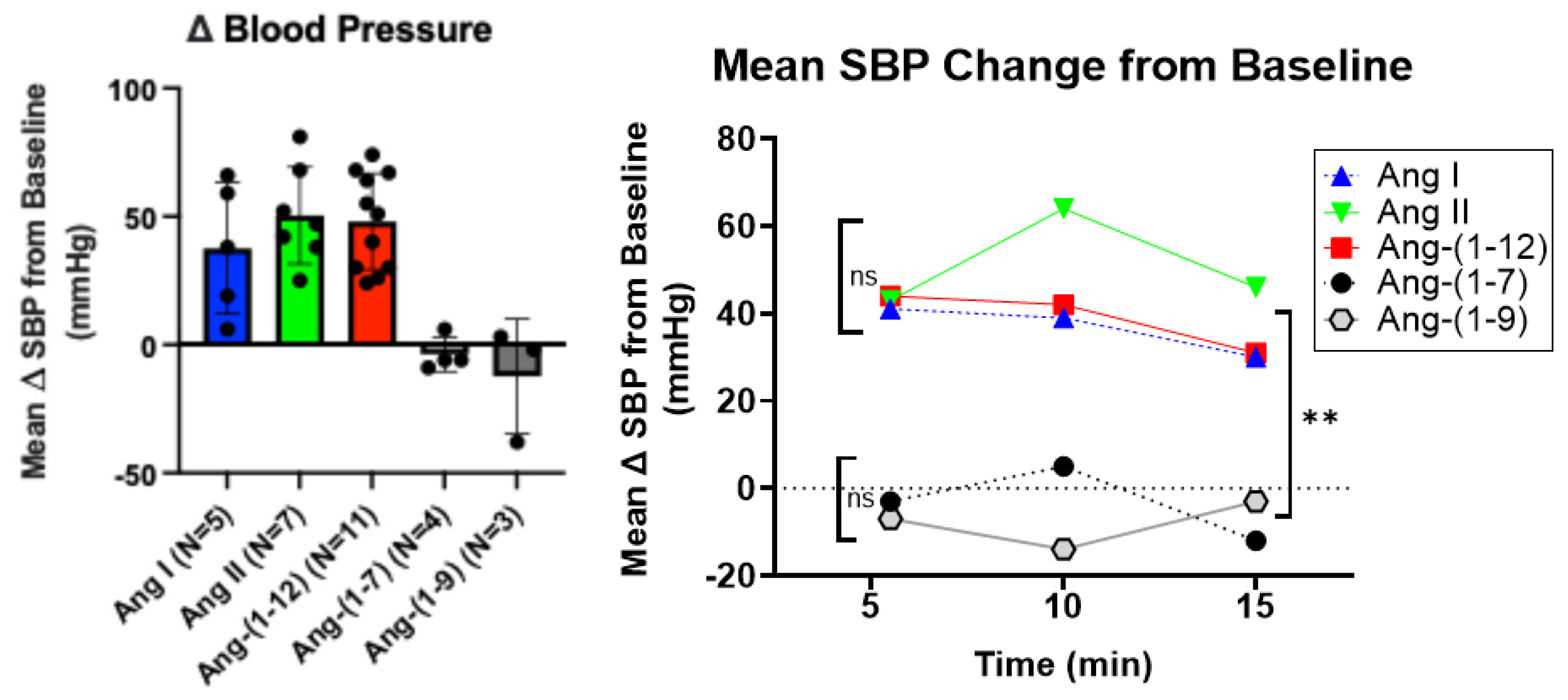
2.2. Effect of APA-Cleavable Ang Peptides on Systolic Blood Pressure
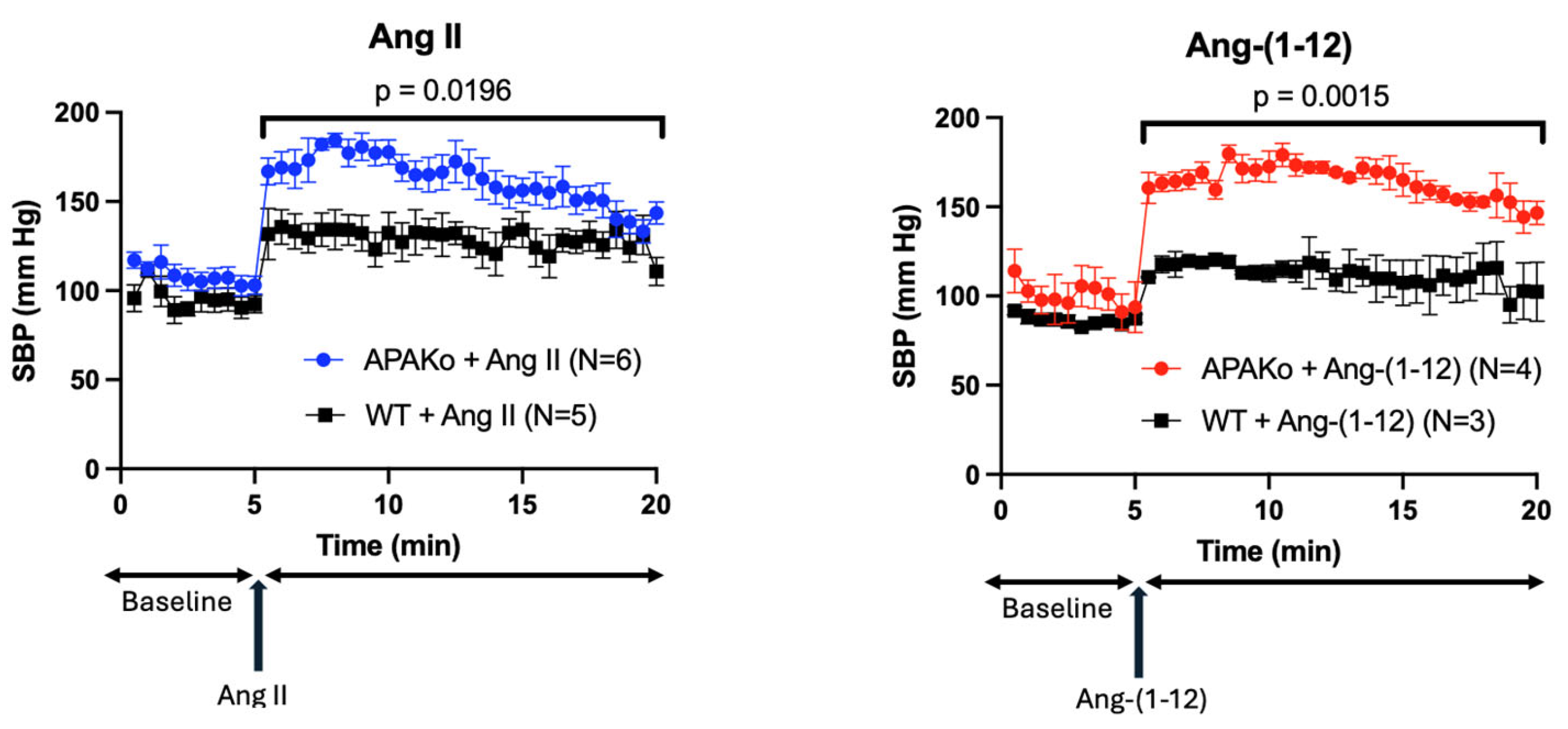
2.3. Murine Recombinant Aminopeptidase a Reduces Acute Hypertension Induced by Ang I, Ang II, and Ang-(1-12)
2.4. Effect of Acute Ang II and Ang-(1-12) Infusion on Systolic Blood Pressure in a Model of Global APA Deficiency
2.5. Effect of ACE Inhibitor and AT1 Receptor Blocker on Ang-(1-12) Infusion
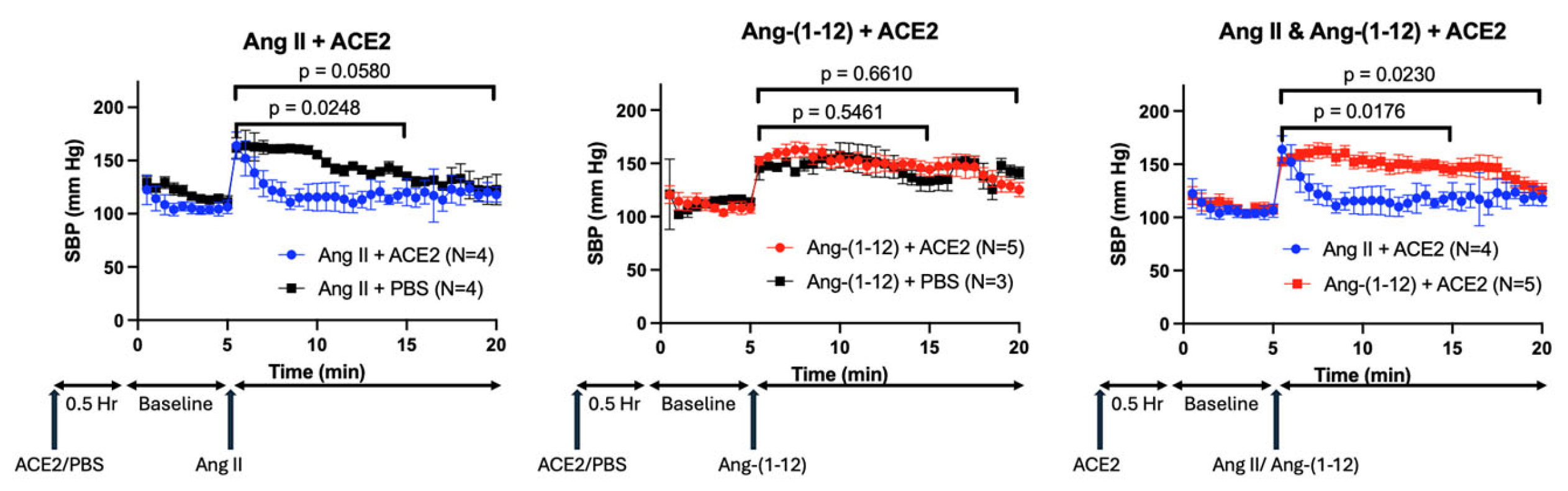
2.6. Effect of rACE2 on Ang-(1-12) Infusion
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Vitro Assessment of Cleavage of N-Terminal Aspartate from Various Angiotensin Peptides by Recombinant APA
4.2. In Vivo Studies
4.3. Blood Pressure Measurement
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, W.J. Systemic hypertension. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2007, 32, 201–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, S.S.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; Wang, T.J. The Framingham Heart Study and the epidemiology of cardiovascular disease: A historical perspective. Lancet 2014, 383, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Rauf, A.; Khan, H.; Abu-Izneid, T. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAAS): The ubiquitous system for homeostasis and pathologies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Riet, L.; van Esch, J.H.; Roks, A.J.; van den Meiracker, A.H.; Danser, A.H. Hypertension: Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system alterations. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 960–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocki, J.; Ye, M.; Rodriguez, E.; González-Pacheco, F.R.; Barrios, C.; Evora, K.; Schuster, M.; Loibner, H.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Ferrario, C.M.; et al. Targeting the degradation of angiotensin II with recombinant angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Prevention of angiotensin II-dependent hypertension. Hypertension 2010, 55, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Wysocki, J.; Gonzalez-Pacheco, F.R.; Salem, M.; Evora, K.; Garcia-Halpin, L.; Poglitsch, M.; Schuster, M.; Batlle, D. Murine recombinant angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Effect on angiotensin II-dependent hypertension and distinctive angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 inhibitor characteristics on rodent and human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Hypertension 2012, 60, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, P.K.; Ye, M.; Wysocki, J.; Maier, C.; Haque, S.K.; Batlle, D. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-independent action of presumed angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activators: Studies in vivo, ex vivo, and in vitro. Hypertension 2014, 63, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocki, J.; Schulze, A.; Batlle, D. Novel Variants of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 of Shorter Molecular Size to Target the Kidney Renin Angiotensin System. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, A.; Wysocki, J.; Pandit, J.; Batlle, D. An update on ACE2 amplification and its therapeutic potential. Acta. Physiol. 2021, 231, e13513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marahrens, B.; Schulze, A.; Wysocki, J.; Lin, M.H.; Ye, M.; Kanwar, Y.S.; Bader, M.; Velez, J.C.Q.; Miner, J.H.; Batlle, D. Knockout of aminopeptidase A in mice causes functional alterations and morphological glomerular basement membrane changes in the kidneys. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 900–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez, J.C.; Bland, A.M.; Arthur, J.M.; Raymond, J.R.; Janech, M.G. Characterization of renin-angiotensin system enzyme activities in cultured mouse podocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2007, 293, F398–F407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velez, J.C.Q.; Arif, E.; Rodgers, J.; Hicks, M.P.; Arthur, J.M.; Nihalani, D.; Bruner, E.T.; Budisavljevic, M.N.; Atkinson, C.; Fitzgibbon, W.R.; et al. Deficiency of the Angiotensinase Aminopeptidase A Increases Susceptibility to Glomerular Injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2119–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysocki, J.; Ye, M.; Batlle, D. Plasma and Kidney Angiotensin Peptides: Importance of the Aminopeptidase A/Angiotensin III Axis. Am. J. Hypertens 2015, 28, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsui, T.; Nomura, S.; Okada, M.; Ohno, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Nakashima, Y.; Murata, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Kuno, N.; Nagasaka, T.; et al. Hypertension and angiotensin II hypersensitivity in aminopeptidase A-deficient mice. Mol. Med. 2003, 9, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomar, S.A.; Alghabban, S.A.; Alharbi, H.A.; Almoqati, M.F.; Alduraibi, Y.; Abu-Zaid, A. Firibastat, the first-in-class brain aminopeptidase a inhibitor, in the management of hypertension: A review of clinical trials. Avicenna J. Med. 2021, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Taniuchi, I.; Kitamura, D.; Wang, J.; Kearney, J.F.; Watanabe, T.; Cooper, M.D. T and B cell development in BP-1/6C3/aminopeptidase A-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 4681–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, V.; Vanholder, R.; van der Giet, M.; Tolle, M.; Karadogan, S.; Gobom, J.; Furkert, J.; Oksche, A.; Krause, E.; Tran, T.N.; et al. Mass-spectrometric identification of a novel angiotensin peptide in human plasma. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautner, R.Q.; Villela, D.C.; Fraga-Silva, R.A.; Silva, N.; Verano-Braga, T.; Costa-Fraga, F.; Jankowski, J.; Jankowski, V.; Sousa, F.; Alzamora, A.; et al. Discovery and characterization of alamandine: A novel component of the renin-angiotensin system. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poglitsch, M.; Domenig, O.; Schwager, C.; Stranner, S.; Peball, B.; Janzek, E.; Wagner, B.; Jungwirth, H.; Loibner, H.; Schuster, M. Recombinant Expression and Characterization of Human and Murine ACE2: Species-Specific Activation of the Alternative Renin-Angiotensin-System. Int. J. Hypertens. 2012, 2012, 428950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, M.; Steckelings, U.M.; Alenina, N.; Santos, R.A.S.; Ferrario, C.M. Alternative Renin-Angiotensin System. Hypertension 2024, 81, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, C.; Hales, P.; Kaushik, V.; Dick, L.; Gavin, J.; Tang, J.; Godbout, K.; Parsons, T.; Baronas, E.; Hsieh, F.; et al. Hydrolysis of biological peptides by human angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14838–14843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, J.; Berthold, H.; Schaefer, F.; Ehmke, H.; Parekh, N. Quantification of conversion and degradation of circulating angiotensin in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, R412–R418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrand, D.; Merkel, P.; Eggers, L.F.; Schluter, H. Proteolytic processing of angiotensin-I in human blood plasma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zini, S.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; Chauvel, E.; Roques, B.P.; Corvol, P.; Llorens-Cortes, C. Identification of metabolic pathways of brain angiotensin II and III using specific aminopeptidase inhibitors: Predominant role of angiotensin III in the control of vasopressin release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 11968–11973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugler, P. Aminopeptidase A is angiotensinase A. II. Biochemical studies on aminopeptidase A and M in rat kidney homogenate. Histochemistry 1982, 74, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Ward, P.E. Role of aminopeptidase activity in the regulation of the pressor activity of circulating angiotensins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1990, 252, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Chappell, M.C.; Tallant, E.A.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Diz, D.I. Counterregulatory actions of angiotensin-(1-7). Hypertension 1997, 30, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Munoz, M.; Work, L.M.; Douglas, K.; Denby, L.; Dominiczak, A.F.; Graham, D.; Nicklin, S.A. Angiotensin-(1-9) attenuates cardiac fibrosis in the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat via the angiotensin type 2 receptor. Hypertension 2012, 59, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, J.M.; Neusy, A.J.; Lowenstein, J. The effects of des-Asp1-angiotensin II on blood pressure, plasma aldosterone concentration, and plasma renin activity in the rabbit. Circ. Res. 1976, 38, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.W.; Roberts, K.A.; Cook, V.I.; Murray, C.E.; Sardinia, M.F.; Harding, J.W. Intracerebroventricularly infused [D-Arg1]angiotensin III, is superior to [D-Asp1]angiotensin II, as a pressor agent in rats. Brain Res. 1990, 514, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simington, S.W.; Moniwa, N.; Ahmad, S.; VonCannon, J.L.; Dell’Italia, L.J.; Varagic, J.; Ferrario, C.M. Abstract 628: Renin Does not Participate in the Production of Plasma Ang-(1-12) from Angiotensinogen. Hypertension 2012, 60, A628-A628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Iyer, S.R.; Burnett, J.C., Jr.; Ahmad, S.; Wright, K.N.; VonCannon, J.L.; Saha, A.; Groban, L. Angiotensin (1-12) in Humans With Normal Blood Pressure and Primary Hypertension. Hypertension 2021, 77, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Simmons, T.; Varagic, J.; Moniwa, N.; Chappell, M.C.; Ferrario, C.M. Chymase-dependent generation of angiotensin II from angiotensin-(1-12) in human atrial tissue. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, S.; Kato, J.; Sasaki, K.; Minamino, N.; Eto, T.; Kitamura, K. Isolation and identification of proangiotensin-12, a possible component of the renin-angiotensin system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 350, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Ahmad, S.; Nagata, S.; Simington, S.W.; Varagic, J.; Kon, N.; Dell’italia, L.J. An evolving story of angiotensin-II-forming pathways in rodents and humans. Clin. Sci. 2014, 126, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Wong, Y.H.; Dun, N.J. Angiotensin-[1-12] interacts with angiotensin type I receptors. Neuropharmacology 2014, 81, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez, J.C.; Janech, M.G.; Hicks, M.P.; Morinelli, T.A.; Rodgers, J.; Self, S.E.; Arthur, J.M.; Fitzgibbon, W.R. Lack of renoprotective effect of chronic intravenous angiotensin-(1-7) or angiotensin-(2-10) in a rat model of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, H.J.; Souza, L.L.; Costa-Neto, C.M.; Salgado, M.C.; Oliveira, E.B. Carboxypeptidases A1 and A2 from the perfusate of rat mesenteric arterial bed differentially process angiotensin peptides. Peptides 2012, 33, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, Y.; Kida, N.; Nozaki, N.; Kuwasako, K.; Nagata, S.; Kitamura, K.; Kato, J. Effects of proangiotensin-12 infused continuously over 14 days in conscious rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 683, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitravanshi, V.C.; Sapru, H.N. Cardiovascular responses elicited by a new endogenous angiotensin in the nucleus tractus solitarius of the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H230–H240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, H.; Chitravanshi, V.C.; Sapru, H.N. The hypothalamic arcuate nucleus: A new site of cardiovascular action of angiotensin-(1-12) and angiotensin II. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H951–H960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, H.; Kawabe, K.; Sapru, H.N. Angiotensin-(1-12) in the rostral ventrolateral medullary pressor area of the rat elicits sympathoexcitatory responses. Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, A.C.; Isa, K.; Shaltout, H.A.; Nautiyal, M.; Ferrario, C.M.; Chappell, M.C.; Diz, D.I. Angiotensin-(1-12) requires angiotensin converting enzyme and AT1 receptors for cardiovascular actions within the solitary tract nucleus. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 299, H763–H771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Punzi, H.A.; Wright, K.N.; Groban, L.; Ferrario, C.M. Newly developed radioimmunoassay for Human Angiotensin-(1-12) measurements in plasma and urine. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2021, 529, 111256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.F.; Domenig, O.; Poglitsch, M.; Bader, M.; Danser, A.H.J. Angiotensin-(1-12): Does It Exist? A Critical Evaluation in Humans, Rats, and Mice. Hypertension 2024, 81, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Whitesall, S.; Zhang, Y.; Beibel, M.; D’Alecy, L.; DiPetrillo, K. Validation of volume-pressure recording tail-cuff blood pressure measurements. Am. J. Hypertens. 2008, 21, 1288–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Pamidimukkala, J.; Hay, M. Sex differences in the development of angiotensin II-induced hypertension in conscious mice. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 288, H2177–H2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Zheng, W.; Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Ecelbarger, C.M.; Watkins, R.; Arnold, A.P.; Sandberg, K. Sex chromosome effects unmasked in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Hypertension 2010, 55, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forster, P.; Wysocki, J.; Abedini, Y.; Müller, T.; Ye, M.; Ferrario, C.M.; Batlle, D. Aminopeptidase A Effect on Angiotensin Peptides and Their Blood Pressure Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6990. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146990
Forster P, Wysocki J, Abedini Y, Müller T, Ye M, Ferrario CM, Batlle D. Aminopeptidase A Effect on Angiotensin Peptides and Their Blood Pressure Action. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6990. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146990
Chicago/Turabian StyleForster, Peter, Jan Wysocki, Yasemin Abedini, Tilman Müller, Minghao Ye, Carlos M. Ferrario, and Daniel Batlle. 2025. "Aminopeptidase A Effect on Angiotensin Peptides and Their Blood Pressure Action" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6990. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146990
APA StyleForster, P., Wysocki, J., Abedini, Y., Müller, T., Ye, M., Ferrario, C. M., & Batlle, D. (2025). Aminopeptidase A Effect on Angiotensin Peptides and Their Blood Pressure Action. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6990. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146990




