Design of a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Based on Fasciola gigantica Cathepsin B and Evaluation of Immunological Responses in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Primary Analysis of Amino Acid Sequence Retrieval
2.2. BCL Epitopes Prediction
2.3. HTL Epitopes Prediction
2.4. The Novel BCL and HTL Epitopes’ Selection and Construction
2.5. Design of the MeFgCatB Peptide
2.6. Predicting Solubility, Toxicity, Antigenicity, Allergenicity, and Physicochemical Characteristics
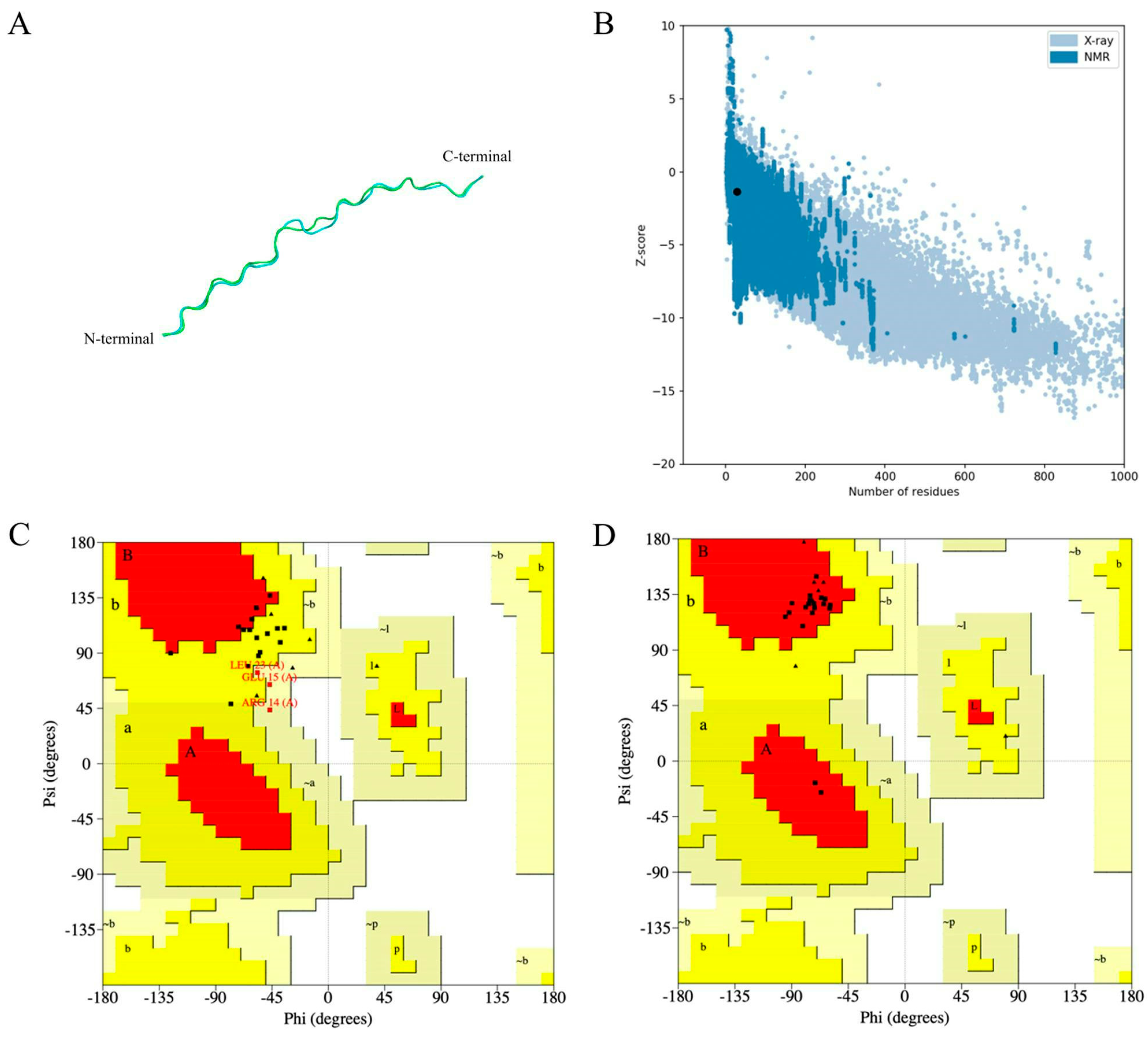
2.7. Prediction, Refinement, and Validation of the MeFgCatB Peptide Tertiary Structure
2.8. Predicting Discontinuous and Continuous B-Cell Epitopes
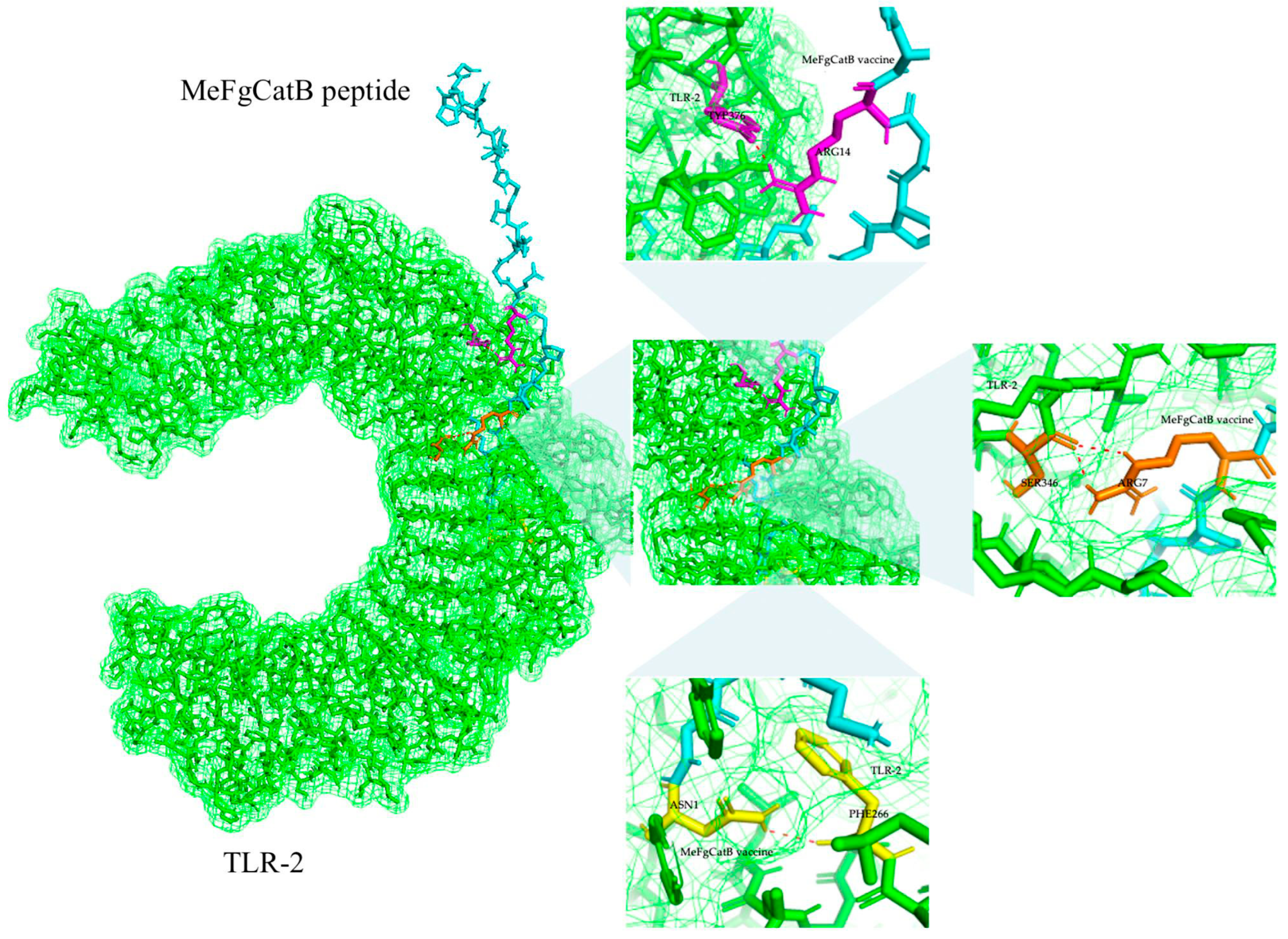
2.9. MeFgCatB Peptide with TLR-2 Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamic (MD) Simulation
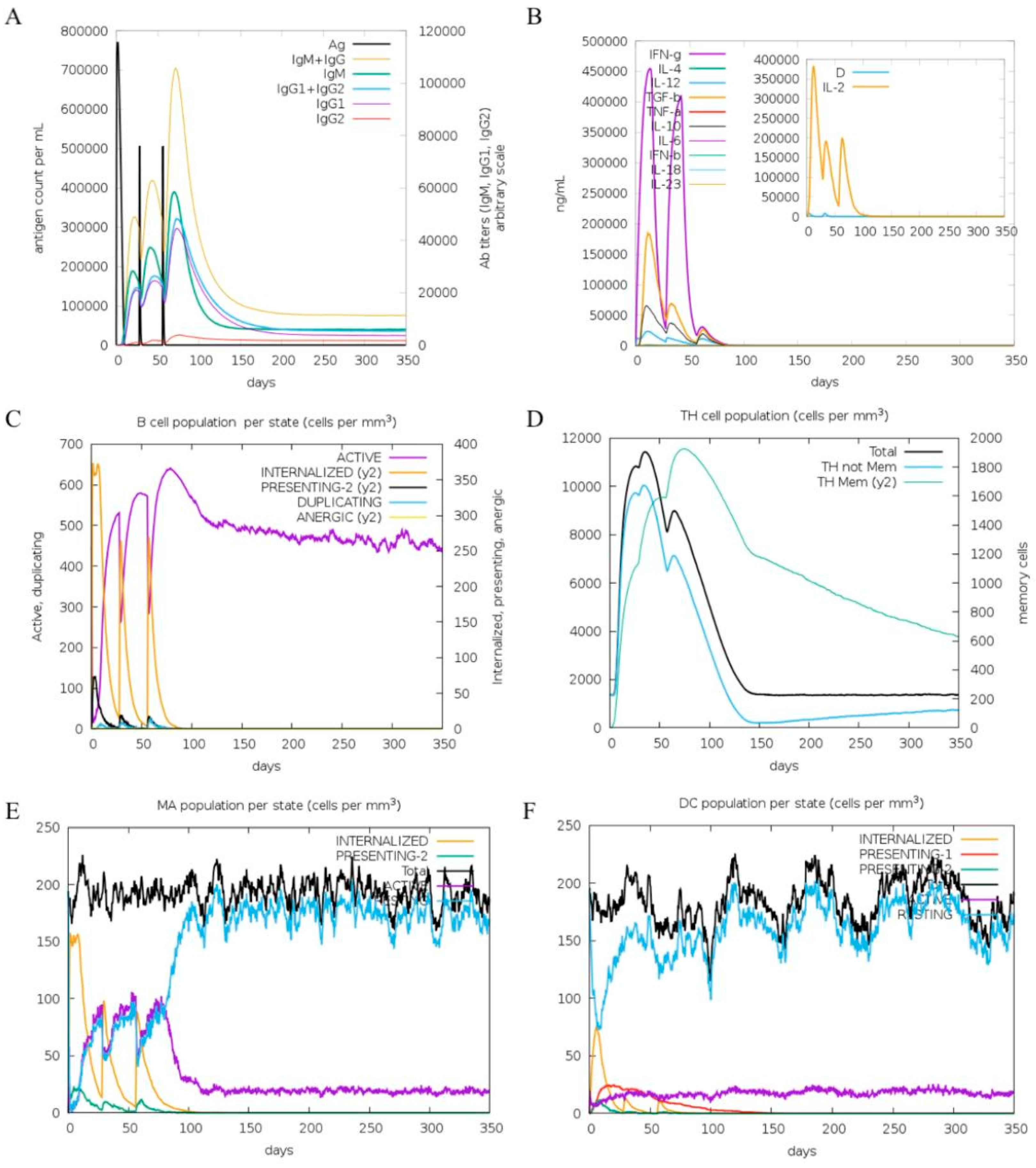
2.10. In Silico Immune Response Simulation
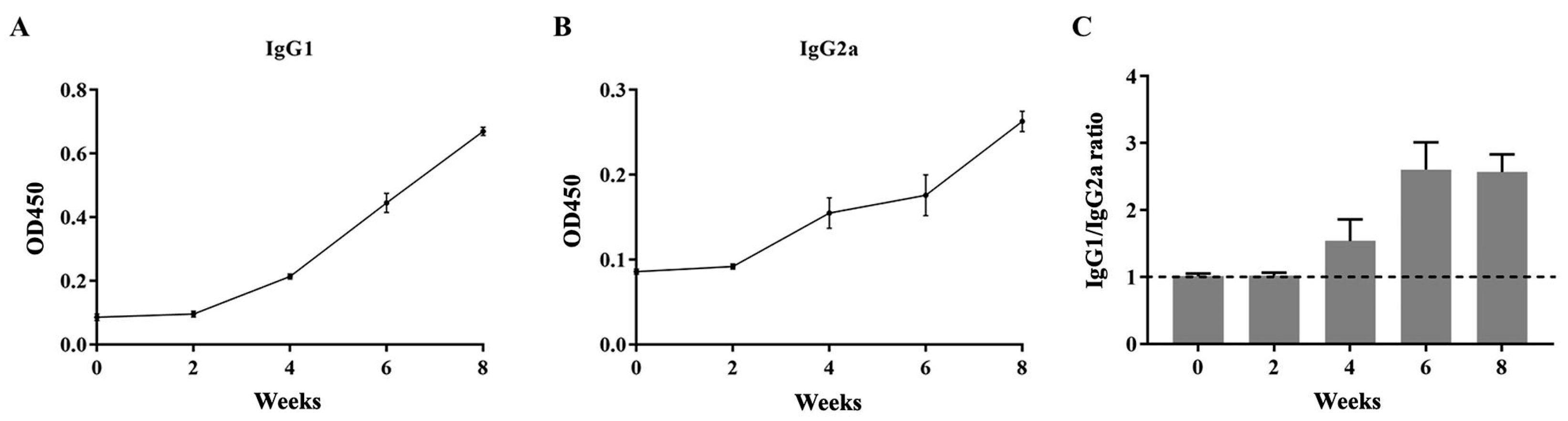
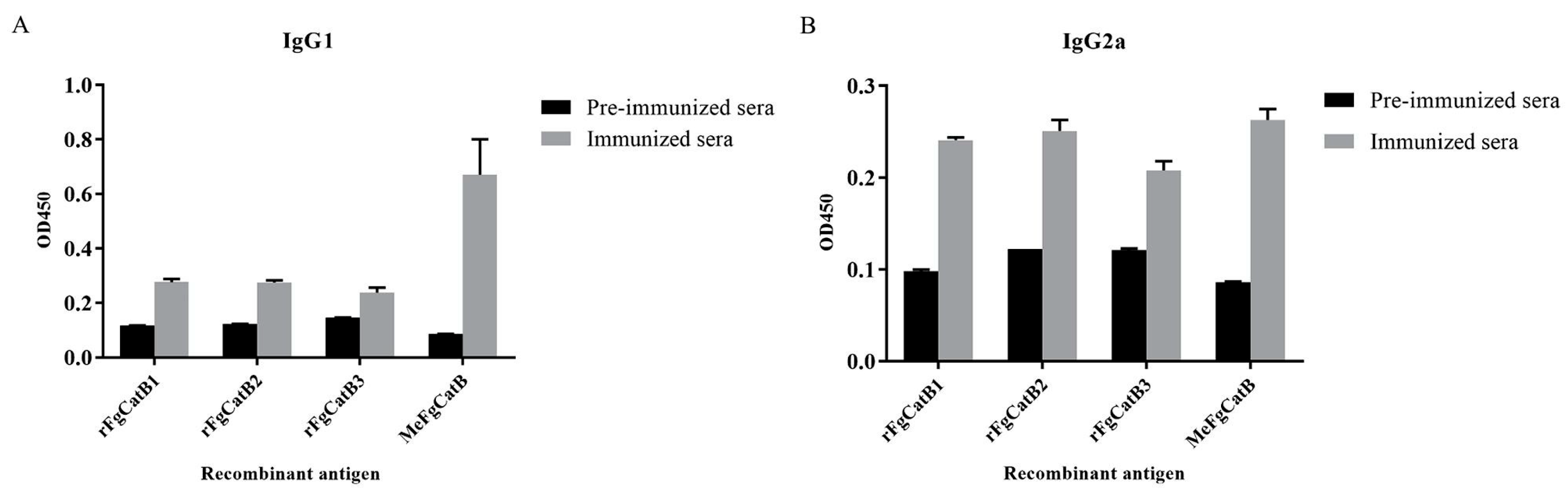
2.11. The Levels of IgG1 and IgG2a
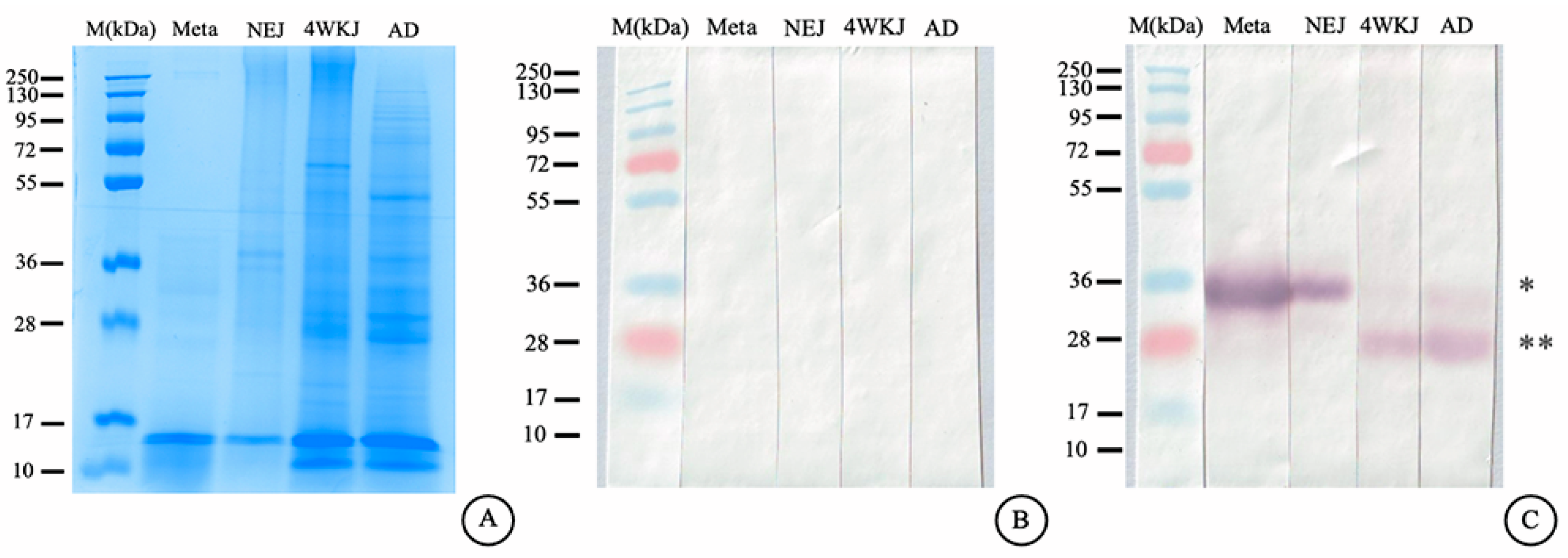
2.12. Immunoblotting Analysis
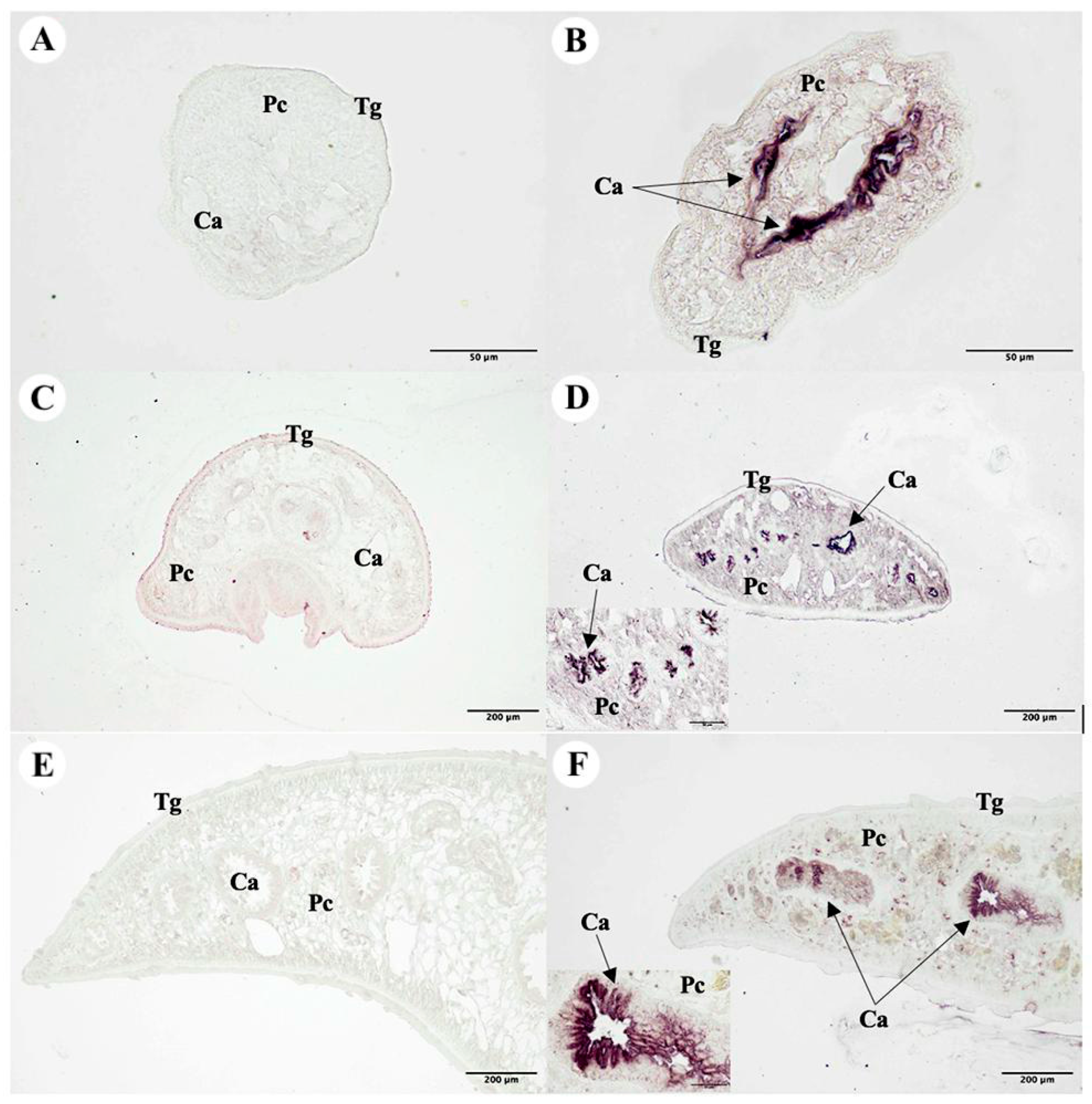
2.13. Immunolocalization of the F. gigantica Tissue
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sequence Retrieval of Amino Acids
4.2. Prediction of the BCL Epitopes
4.3. Prediction of the HTL Epitopes
4.4. The Novel BCL and HTL Epitopes’ Selection and Construction
4.5. Design of the MeFgCatB Peptide
4.6. Predicting Solubility, Toxicity, Antigenicity, Allergenicity, and Physicochemical Characteristics
4.7. Prediction, Refinement, and Validation of the MeFgCatB Peptide Tertiary Structure
4.8. Predicting Discontinuous and Continuous B-Cell Epitopes
4.9. MeFgCatB Peptide with TLR-2 Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamic (MD) Simulation
4.10. In Silico Immune Response Simulation
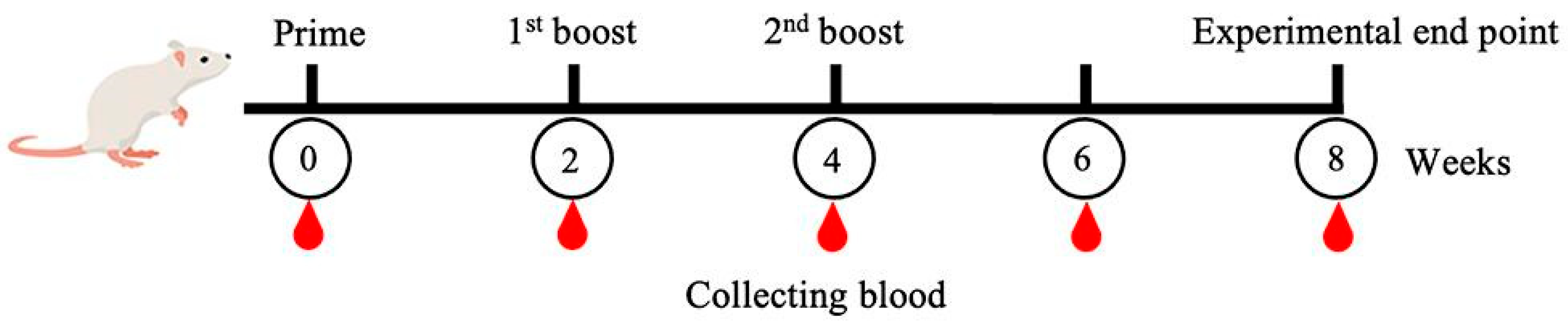
4.11. The MeFgCatB Peptide Synthesis and Mice Immunization
4.12. Parasite Collection
4.13. Recombinant Protein Expression
4.14. Determination of IgG1 and IgG2a Levels by Indirect ELISA
4.15. Immunoblotting Analysis
4.16. Localization of the F. gigantica Tissue
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nyindo, M.; Lukambagire, A.H. Fascioliasis: An Ongoing Zoonotic Trematode Infection. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, W.; Abdel-Rady, A.; El-Dakroury, M.F.; Felefel, W. Field Trials to Evaluate Five Fasciolicides against Natural Liver Fluke Infection in Cattle and Sheep in Egypt. Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 12, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolan, R.W. Fascioliasis Due to Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica Infection: An Update on This “neglected” Neglected Tropical Disease. Lab. Med. 2011, 42, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Hostos Infantes, L.R.; Paredes Yataco, G.A.; Ortiz-Martínez, Y.; Mayer, T.; Terashima, A.; Franco-Paredes, C.; Gonzalez-Diaz, E.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Vargas Barahona, L.; et al. The Global Prevalence of Human Fascioliasis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, 20499361231185413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winaya, I.B.O.; Oka, I.B.M.; Adnyana, I.B.W.; Sudipa, P.H. Fibrosis and Collagen-I Accumulation in Bali Cattle Liver Tissue Infected with Fasciola gigantica. Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 12, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Report of the WHO Informal Meeting on Use of Triclabendazole in Fascioliasis Control; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fairweather, I. Triclabendazole: New Skills to Unravel an Old(Ish) Enigma. J. Helminthol. 2005, 79, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cwiklinski, K.; Jewhurst, H.; McVeigh, P.; Barbour, T.; Maule, A.G.; Tort, J.; O’Neill, S.M.; Robinson, M.W.; Donnelly, S.; Dalton, J.P. Infection by the Helminth Parasite Fasciola Hepatica Requires Rapid Regulation of Metabolic, Virulence, and Invasive Factors to Adjust to Its Mammalian Host. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2018, 17, 792–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beesley, N.J.; Cwiklinski, K.; Allen, K.; Hoyle, R.C.; Spithill, T.W.; James La Course, E.; Williams, D.J.L.; Paterson, S.; Hodgkinson, J.E. A Major Locus Confers Triclabendazole Resistance in Fasciola Hepatica and Shows Dominant Inheritance. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Moreno, A.; Jiménez, V.; Martínez-Cruz, M.S.; Martínez-Moreno, F.J.; Becerra, C.; Hernández, S. Triclabendazole Treatment in Experimental Goat Fasciolosis: Anthelmintic Efficacy and Influence in Antibody Response and Pathophysiology of the Disease. Vet. Parasitol. 1997, 68, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, J.M.; Elliott, T.P.; Beddoe, T.; Anderson, G.; Skuce, P.; Spithill, T.W. Current Threat of Triclabendazole Resistance in Fasciola Hepatica. Trends. Parasitol. 2016, 32, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabada, M.M.; Lopez, M.; Cruz, M.; Delgado, J.R.; Hill, V.; White, A.C. Treatment Failure after Multiple Courses of Triclabendazole among Patients with Fascioliasis in Cusco, Peru: A Case Series. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, M.L.; Tanabe, M.B.; White, A.C.; Lopez, M.; Bascope, R.; Cabada, M.M. Triclabendazole Treatment Failure for Fasciola Hepatica Infection among Preschool and School-Age Children, Cusco, Peru. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1850–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, J.P.; Neill, S.O.; Stack, C.; Collins, P.; Walshe, A.; Sekiya, M.; Doyle, S.; Mulcahy, G.; Hoyle, D.; Khaznadji, E.; et al. Fasciola Hepatica Cathepsin L-like Proteases: Biology, Function, and Potential in the Development of First Generation Liver Fluke Vaccines. Int. J. Parasitology 2003, 33, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Velázquez, L.M.; Ruiz-Campillo, M.T.; Herrera-Torres, G.; Martínez-Moreno, Á.; Martínez-Moreno, F.J.; Zafra, R.; Buffoni, L.; Rufino-Moya, P.J.; Molina-Hernández, V.; Pérez, J. Fasciolosis: Pathogenesis, Host-Parasite Interactions, and Implication in Vaccine Development. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1270064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ur Rehman, T.; Elsaid, F.G.; Toledo, M.M.G.; Gentile, A.; Gul, R.A.; Rashid, M.; Aleem, M.T.; Zaman, M.A. Fasciolosis: Recent Update in Vaccines Development and Their Efficacy. Pak. Vet. J. 2023, 43, 2074–7764. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, M.W.; Dalton, J.P. Zoonotic Helminth Infections with Particular Emphasis on Fasciolosis and Other Trematodiases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Bio. Sci. 2009, 364, 2763–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangpairoj, K.; Apisawetakan, S.; Changklungmoa, N.; Kueakhai, P.; Chaichanasak, P.; Sobhon, P.; Chaithirayanon, K. Potential of Recombinant 2-Cys Peroxiredoxin Protein as a Vaccine for Fasciola gigantica Infection. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 194, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, J.P.; McGonigle, S.; Rolph, T.P.; Andrews, S.J. Induction of Protective Immunity in Cattle against Infection with Fasciola hepatica by Vaccination with Cathepsin L Proteinases and with Hemoglobin. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 5066–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kueakhai, P.; Changklungmoa, N.; Waseewiwat, P.; Thanasinpaiboon, T.; Cheukamud, W.; Chaichanasak, P.; Sobhon, P. Characterization and Vaccine Potential of Fasciola gigantica Saposin-like Protein 1 (SAP-1). Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 233, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kueakhai, P.; Changklungmoa, N.; Riengrojpitak, S.; Chaichanasak, P.; Meemon, K.; Chaithirayanon, K.; Chantree, P.; Sansri, V.; Itagaki, T.; Sobhon, P. Vaccine Potential of Recombinant Saposin-like Protein 2 against Fasciolosis gigantica in Mice. Vaccine 2013, 31, 5518–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaikua, W.; Kueakhai, P.; Chaithirayanon, K.; Tanomrat, R.; Wongwairot, S.; Riengrojpitak, S.; Sobhon, P.; Changklungmoa, N. Cytosolic Superoxide Dismutase Can Provide Protection against Fasciola gigantica. Acta Trop. 2016, 162, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preyavichyapugdee, N.; Sahaphong, S.; Riengrojpitak, S.; Grams, R.; Viyanant, V.; Sobhon, P. Fasciola gigantica and Schistosoma mansoni: Vaccine Potential of Recombinant Glutathione S-Transferase (RFgGST26) against Infections in Mice. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 119, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Anju, V.; Gaurav, N.; Chandra, D.; Samanta, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Adeppa, J.; Raina, O.K. Vaccination of Buffaloes with Fasciola gigantica Recombinant Glutathione S-Transferase and Fatty Acid Binding Protein. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Abán, J.; Esteban, A.; Vicente, B.; Rojas-Caraballo, J.; del Olmo, E.; Martínez-Fernández, A.R.; Hillyer, G.V.; Muro, A. Adaptive Immune Stimulation Is Required to Obtain High Protection with Fatty Acid Binding Protein Vaccine Candidate against Fasciola hepatica in Balb/C Mice. J. Parasitol. 2012, 98, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changklungmoa, N.; Kueakhai, P.; Riengrojpitak, S.; Chaithirayanon, K.; Chaichanasak, P.; Preyavichyapugdee, N.; Chantree, P.; Sansri, V.; Itagaki, T.; Sobhon, P. Immunization with Recombinant Leucine Aminopeptidase Showed Protection against Fasciola gigantica in Mice. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3653–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raina, O.K.; Nagar, G.; Varghese, A.; Prajitha, G.; Alex, A.; Maharana, B.R.; Joshi, P. Lack of Protective Efficacy in Buffaloes Vaccinated with Fasciola gigantica Leucine Aminopeptidase and Peroxiredoxin Recombinant Proteins. Acta Trop. 2011, 118, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piacenza, L.; Acosta, D.; Basmadjian, I.; Dalton, J.P.; Carmona, C. Vaccination with Cathepsin L Proteinases and with Leucine Aminopeptidase Induces High Levels of Protection against Fascioliasis in Sheep. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, O.; Flynn, R.J.; Read, C.; Sekiya, M.; Donnelly, S.M.; Stack, C.; Dalton, J.P.; Mulcahy, G. Protection of Cattle against a Natural Infection of Fasciola Hepatica by Vaccination with Recombinant Cathepsin L1 (RFhCL1). Vaccine 2010, 28, 5551–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa-Mancera, A.; Reynoso-Palomar, A.; Utrera-Quintana, F.; Carreón-Luna, L. Cathepsin L1 Mimotopes with Adjuvant Quil A Induces a Th1/Th2 Immune Response and Confers Significant Protection against Fasciola hepatica Infection in Goats. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansri, V.; Meemon, K.; Changklungmoa, N.; Kueakhai, P.; Chantree, P.; Chaichanasak, P.; Lorsuwannarat, N.; Itagaki, T.; Sobhon, P. Protection against Fasciola gigantica Infection in Mice by Vaccination with Recombinant Juvenile-Specific Cathepsin L. Vaccine 2015, 33, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kueakhai, P.; Changklungmoa, N.; Cheukamud, W.; Osotprasit, S.; Chantree, P.; Preyavichyapugdee, N.; Sobhon, P.; Meemon, K. The Combined Recombinant Cathepsin L1H and Cathepsin B3 Vaccine against Fasciola gigantica Infection. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 83, 102353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changklungmoa, N.; Phoinok, N.; Yencham, C.; Sobhon, P.; Kueakhai, P. Vaccine Potential of Recombinant CathepsinL1G against Fasciola gigantica in Mice. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 226, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kueakhai, P.; Changklungmoa, N.; Chaichanasak, P.; Jaikua, W.; Itagaki, T.; Sobhon, P. Vaccine Potential of Recombinant Pro- and Mature CathepsinL1 against Fasciolosis gigantica in Mice. Acta Trop. 2015, 150, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantree, P.; Phatsara, M.; Meemon, K.; Chaichanasak, P.; Changklungmoa, N.; Kueakhai, P.; Lorsuwannarat, N.; Sangpairoj, K.; Songkoomkrong, S.; Wanichanon, C.; et al. Vaccine Potential of Recombinant Cathepsin B against Fasciola gigantica. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 135, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tort, J.; Brindley, P.J.; Knox, D.; Wolfe, K.H.; Dalton, J.P. Proteinases and Associated Genes of Parasitic Helminths. Adv. Parasitol. 1999, 43, 161–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meemon, K.; Grams, R.; Vichasri-Grams, S.; Hofmann, A.; Korge, G.; Viyanant, V.; Upatham, E.S.; Habe, S.; Sobhon, P. Molecular Cloning and Analysis of Stage and Tissue-Specific Expression of Cathepsin B Encoding Genes from Fasciola gigantica. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2004, 136, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethadavit, M.; Meemon, K.; Jardim, A.; Spithill, T.W.; Sobhon, P. Identification, Expression and Immunolocalization of Cathepsin B3, a Stage-Specific Antigen Expressed by Juvenile Fasciola gigantica. Acta Trop. 2009, 112, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantree, P.; Wanichanon, C.; Phatsara, M.; Meemon, K.; Sobhon, P. Characterization and Expression of Cathepsin B2 in Fasciola gigantica. Exp. Parasitol. 2012, 132, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaner, S.; Galiano, A.; Trelis, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; del Portillo, H.A.; Bernal, D.; Marcilla, A. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Modulating the Host Immune Response during Parasitic Infections. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capron, A.; Dessaint, J.P.; Haque, A.; Capron, M. Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity against Parasites. Prog. Allergy 1982, 31, 234–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, M.; Nazari, M. New Generation Vaccines for COVID-19 Based on Peptide, Viral Vector, Artificial Antigen Presenting Cell, DNA or MRNA. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2022, 14, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malonis, R.J.; Lai, J.R.; Vergnolle, O. Peptide-Based Vaccines: Current Progress and Future Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 3210–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Peptide-Based Synthetic Vaccines. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, B.L.; Pellicane, A.J.; Tyring, S.K. Vaccine Immunology. Dermatol. Ther. 2009, 22, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, I.; Jeon, D.; Moseman, J.E.; Muralidhar, A.; Potluri, H.K.; McNeel, D.G. Role of B Cells as Antigen Presenting Cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 954936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawan, M.M.A.K.; Sharma, A.R.; Halder, S.K.; Al Arian, T.; Shuvo, M.N.; Sarker, S.R.; Hasan, M.A. Advances in Computational and Bioinformatics Tools and Databases for Designing and Developing a Multi-Epitope-Based Peptide Vaccine. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2023, 29, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Melo, T.T.; Mendes, M.M.; Alves, C.C.; Carvalho, G.B.; Fernandes, V.C.; Pimenta, D.L.F.; de Moraes Mourão, M.; Gai, F.; Kalli, M.; Coelho, A.; et al. The Schistosoma mansoni Cyclophilin A Epitope 107-121 Induces a Protective Immune Response against Schistosomiasis. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 111, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzinelli-Guimarães, A.C.; Nogueira, D.S.; Amorim, C.C.O.; Oliveira, F.M.S.; Coqueiro-Dos-Santos, A.; Carvalho, S.A.P.; Kraemer, L.; Barbosa, F.S.; Fraga, V.G.; Santos, F.V.; et al. ASCVac-1, a Multi-Peptide Chimeric Vaccine, Protects Mice Against Ascaris suum Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 788185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawawi, A.; Forman, R.; Smith, H.; Mair, I.; Jibril, M.; Albaqshi, M.H.; Brass, A.; Derrick, J.P.; Else, K.J. In Silico Design of a T-Cell Epitope Vaccine Candidate for Parasitic Helminth Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Sun, X.; Huang, J.; Zhan, B.; Zhu, X. A Multiple Antigen Peptide Vaccine Containing CD4+ T Cell Epitopes Enhances Humoral Immunity against Trichinella spiralis Infection in Mice. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 2074803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chansap, S.; Cheukamud, W.; Suthisintong, T.; Kueakhai, P.; Changklungmoa, N. Development of Multi-Epitope Cathepsin L Driven Short Peptide Vaccine against Fasciola gigantica. Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1547937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Caraballo, J.; López-Abán, J.; Pérez Del Villar, L.; Vizcaíno, C.; Vicente, B.; Fernández-Soto, P.; Del Olmo, E.; Patarroyo, M.A.; Muro, A. In Vitro and in Vivo Studies for Assessing the Immune Response and Protection-Inducing Ability Conferred by Fasciola Hepatica-Derived Synthetic Peptides Containing B- and T-Cell Epitopes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakili, B.; Nezafat, N.; Zare, B.; Erfani, N.; Akbari, M.; Ghasemi, Y.; Rahbar, M.R.; Hatam, G.R. A New Multi-Epitope Peptide Vaccine Induces Immune Responses and Protection against Leishmania infantum in BALB/c Mice. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 209, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Yang, H.; Tang, F.; Yin, R.; Liu, H.; Gong, X.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Liu, K. Oral Immunization with a Multivalent Epitope-Based Vaccine, Based on NAP, Urease, HSP60, and HpaA, Provides Therapeutic Effect on H. pylori Infection in Mongolian Gerbils. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.Z.; Wang, X.; Yuan, S.; Li, W.; Dou, Y.; Poon, V.K.M.; Chan, C.C.S.; Cai, J.P.; Chik, K.K.H.; Tang, K.; et al. A Novel Linker-Immunodominant Site (LIS) Vaccine Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Protects against Severe COVID-19 in Syrian hamsters. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, R.; Kim, W.; Lv, H.; Mou, Z.; Scherm, M.J.; Schmitz, A.J.; Turner, J.S.; Tan, T.J.C.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, W.O.; et al. Leveraging Vaccination-Induced Protective Antibodies to Define Conserved Epitopes on Influenza N2 Neuraminidase. Immunity 2023, 56, 2621–2634.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapin, N.; Lund, O.; Bernaschi, M.; Castiglione, F. Computational Immunology Meets Bioinformatics: The Use of Prediction Tools for Molecular Binding in the Simulation of the Immune System. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotkin, S.; Robinson, J.M.; Cunningham, G.; Iqbal, R.; Larsen, S. The Complexity and Cost of Vaccine Manufacturing—An Overview. Vaccine 2017, 35, 4064–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoufi, E.; Hemmati, M.; Eftekhari, S.; Khaksaran, K.; Mahmodi, Z.; Farajollahi, M.M.; Mohsenzadegan, M. Epitope Prediction by Novel Immunoinformatics Approach: A State-of-the-Art Review. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamley, I.W. Peptides for Vaccine Development. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2022, 5, 905–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, H.; Sun, L.; Yu, J. Fast Batch Searching for Protein Homology Based on Compression and Clustering. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vojtek, I.; Buchy, P.; Doherty, T.M.; Hoet, B. Would Immunization Be the Same without Cross-Reactivity? Vaccine 2019, 37, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trier, N.H.; Houen, G. Antibody Cross-Reactivity in Auto-Immune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaap-Johansen, A.L.; Vujović, M.; Borch, A.; Hadrup, S.R.; Marcatili, P. T Cell Epitope Prediction and Its Application to Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 712488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy Chichili, V.P.; Kumar, V.; Sivaraman, J. Linkers in the Structural Biology of Protein-Protein Interactions. Protein Sci. 2013, 22, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Khan, S.; Ali, A.; Akbar, H.; Sayaf, A.M.; Khan, A.; Wei, D.Q. Immunoinformatics Approaches to Explore Helicobacter Pylori Proteome (Virulence Factors) to Design B and T Cell Multi-Epitope Subunit Vaccine. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurina, V.; Adianingsih, O.R. Predicting Epitopes for Vaccine Development Using Bioinformatics Tools. Ther. Adv. Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 10, 25151355221100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zaro, J.L.; Shen, W.C. Fusion Protein Linkers: Property, Design and Functionality. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyagari, V.S.; Venkateswarulu, T.C.; Abraham Peele, K.; Srirama, K. Design of a Multi-Epitope-Based Vaccine Targeting M-Protein of SARS-CoV2: An Immunoinformatics Approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 2963–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, Y.; Shoenfeld, Y. Vaccine-Induced Autoimmunity: The Role of Molecular Mimicry and Immune Crossreaction. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamage, D.G.; Gunaratne, A.; Periyannan, G.R.; Russell, T.G. Applicability of Instability Index for In Vitro Protein Stability Prediction. Protein Pept. Lett. 2019, 26, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplin, D.D. Overview of the Immune Response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S3–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiltgen, M. Algorithms for Structure Comparison and Analysis: Homology Modelling of Proteins. In Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology: ABC of Bioinformatics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Wiederstein, M.; Sippl, M.J. ProSA-Web: Interactive Web Service for the Recognition of Errors in Three-Dimensional Structures of Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W407–W410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.W.; Lee, B.H.; Song, S.H.; Kim, M.K. Revisiting the Ramachandran Plot Based on Statistical Analysis of Static and Dynamic Characteristics of Protein Structures. J. Struct. Biol. 2023, 215, 107939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdous, S.; Kelm, S.; Baker, T.S.; Shi, J.; Martin, A.C.R. B-Cell Epitopes: Discontinuity and Conformational Analysis. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 114, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanmohammadi, S.; Rezaei, N. Role of Toll-like Receptors in the Pathogenesis of COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2735–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalita, P.; Lyngdoh, D.L.; Padhi, A.K.; Shukla, H.; Tripathi, T. Development of Multi-Epitope Driven Subunit Vaccine against Fasciola gigantica Using Immunoinformatics Approach. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basto, A.P.; Leitão, A. Targeting TLR2 for Vaccine Development. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 619410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Nascimento, L.; Massari, P.; Wetzler, L.M. The Role of TLR2 Ininfection and Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.C.; Konhar, R.; Biswal, D.K. Fasciola gigantica Vaccine Construct: An in Silico Approach towards Identification and Design of a Multi-Epitope Subunit Vaccine Using Calcium Binding EF-Hand Proteins. BMC Immunol. 2023, 24, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalita, J.; Padhi, A.K.; Tripathi, T. Designing a Vaccine for Fascioliasis Using Immunogenic 24 KDa Mu-Class Glutathione s-Transferase. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 83, 104352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akıl, M.; Aykur, M.; Karakavuk, M.; Can, H.; Döşkaya, M. Construction of a Multiepitope Vaccine Candidate against Fasciola Hepatica: An in Silico Design Using Various Immunogenic Excretory/Secretory Antigens. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2022, 21, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Blanco, J.R.; Aliaga, J.I.; Quintana-Ortí, E.S.; Chacón, P. IMODS: Internal Coordinates Normal Mode Analysis Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W271–W276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanches, R.C.O.; Tiwari, S.; Ferreira, L.C.G.; Oliveira, F.M.; Lopes, M.D.; Passos, M.J.F.; Maia, E.H.B.; Taranto, A.G.; Kato, R.; Azevedo, V.A.C.; et al. Immunoinformatics Design of Multi-Epitope Peptide-Based Vaccine Against Schistosoma mansoni Using Transmembrane Proteins as a Target. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 621706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, D.; Al Rimon, R.; Chowdhury, U.F.; Islam, M.R. A Multi-Epitope Based Vaccine against the Surface Proteins Expressed in Cyst and Trophozoite Stages of Parasite Entamoeba histolytica. J. Immunol. Methods 2023, 517, 113475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyotisha; Qureshi, R.; Qureshi, I.A. Development of a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Candidate for Leishmanial Parasites Applying Immunoinformatics and in Vitro Approaches. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1269774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Vashishtha, S.; Kundu, B.; Ghosh, M. In-Silico Design of an Immunoinformatics Based Multi-Epitope Vaccine against Leishmania donovani. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfraz, A.; Wara, T.U.; Sheheryar; Chen, K.; Ansari, S.H.; Zaman, A.; Nishan, U.; Iqbal, A.; Ullah, R.; Ali, E.A.; et al. Structural Informatics Approach for Designing an Epitope-Based Vaccine against the Brain-Eating Naegleria fowleri. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1284621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.; Waqas, M.; Halim, S.A.; Ali, A.; Iqbal, A.; Iqbal, M.; Khan, A.; Al-Harrasi, A. Exploring Whole Proteome to Contrive Multi-Epitope-Based Vaccine for NeoCoV: An Immunoinformtics and in-Silico Approach. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 956776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, J.P.; Robinson, M.W.; Mulcahy, G.; O’Neill, S.M.; Donnelly, S. Immunomodulatory Molecules of Fasciola hepatica: Candidates for Both Vaccine and Immunotherapeutic Development. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 195, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meira, C.d.S.; Gedamu, L. Protective or Detrimental? Understanding the Role of Host Immunity in Leishmaniasis. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Zhang, S.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yao, H.; Liu, G. Combined Immunoinformatics to Design and Evaluate a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Candidate against Streptococcus suis Infection. Vaccines 2024, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, A.; Haque, A.; Alghamdi, Y.S.; Mashraqi, M.M.; Rehman, A.; Shahid, F.; Khurshid, M.; Ashfaq, U.A. Development of a Candidate Multi-Epitope Subunit Vaccine against Klebsiella aerogenes: Subtractive Proteomics and Immuno-Informatics Approach. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovsky, N.; Aguilar, J.C. Vaccine Adjuvants: Current State and Future Trends. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2004, 82, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; O’Hagan, D.T. Recent Advances in Veterinary Vaccine Adjuvants. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, S.G.; Orr, M.T.; Fox, C.B. Key Roles of Adjuvants in Modern Vaccines. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, L.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, D.; Zhou, J.; Jing, L.; Chen, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, C.; et al. Intramuscular Inoculation of AS02-Adjuvanted Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) F Subunit Vaccine Shows Better Efficiency and Safety Than Subcutaneous Inoculation in BALB/c Mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 938598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelallah, N.H.; Abdeltawab, N.F.; Boseila, A.A.; Amin, M.A. Chitosan and Sodium Alginate Combinations Are Alternative, Efficient, and Safe Natural Adjuvant Systems for Hepatitis B Vaccine in Mouse Model. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 7659684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, F.; Espino, A.M. Adjuvant-Enhanced Antibody and Cellular Responses to Inclusion Bodies Expressing FhSAP2 Correlates with Protection of Mice to Fasciola hepatica. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 160, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielke, D.; Bandawe, G.; Pollara, J.; Abrahams, M.R.; Nyanhete, T.; Moore, P.L.; Thebus, R.; Yates, N.L.; Kappes, J.C.; Ochsenbauer, C.; et al. Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC)-Mediating Antibodies Constrain Neutralizing Antibody Escape Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arts, E.J.; Hazuda, D.J. HIV-1 Antiretroviral Drug Therapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a007161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groß, A.; Hashimoto, C.; Sticht, H.; Eichler, J. Synthetic Peptides as Protein Mimics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 3, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jespersen, M.C.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M.; Marcatili, P. BepiPred-2.0: Improving Sequence-Based B-Cell Epitope Prediction Using Conformational Epitopes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W24–W29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doytchinova, I.A.; Flower, D.R. VaxiJen: A Server for Prediction of Protective Antigens, Tumour Antigens and Subunit Vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, I.; Naneva, L.; Doytchinova, I.; Bangov, I. AllergenFP: Allergenicity Prediction by Descriptor Fingerprints. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynisson, B.; Alvarez, B.; Paul, S.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M. NetMHCpan-4.1 and NetMHCIIpan-4.0: Improved Predictions of MHC Antigen Presentation by Concurrent Motif Deconvolution and Integration of MS MHC Eluted Ligand Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 48, W449–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Kapoor, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Gautam, A.; Kumar, R.; Raghava, G.P.S. Peptide Toxicity Prediction. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1268, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, P.; Pozzati, G.; Elofsson, A. Improved Prediction of Protein-Protein Interactions Using AlphaFold2. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, L.; Park, H.; Seok, C. GalaxyRefine: Protein Structure Refinement Driven by Side-Chain Repacking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W384–W388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponomarenko, J.; Bui, H.H.; Li, W.; Fusseder, N.; Bourne, P.E.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. ElliPro: A New Structure-Based Tool for the Prediction of Antibody Epitopes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vajda, S.; Yueh, C.; Beglov, D.; Bohnuud, T.; Mottarella, S.E.; Xia, B.; Hall, D.R.; Kozakov, D. New Additions to the ClusPro Server Motivated by CAPRI. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2017, 85, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein Measurement with the Folin Phenol Reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
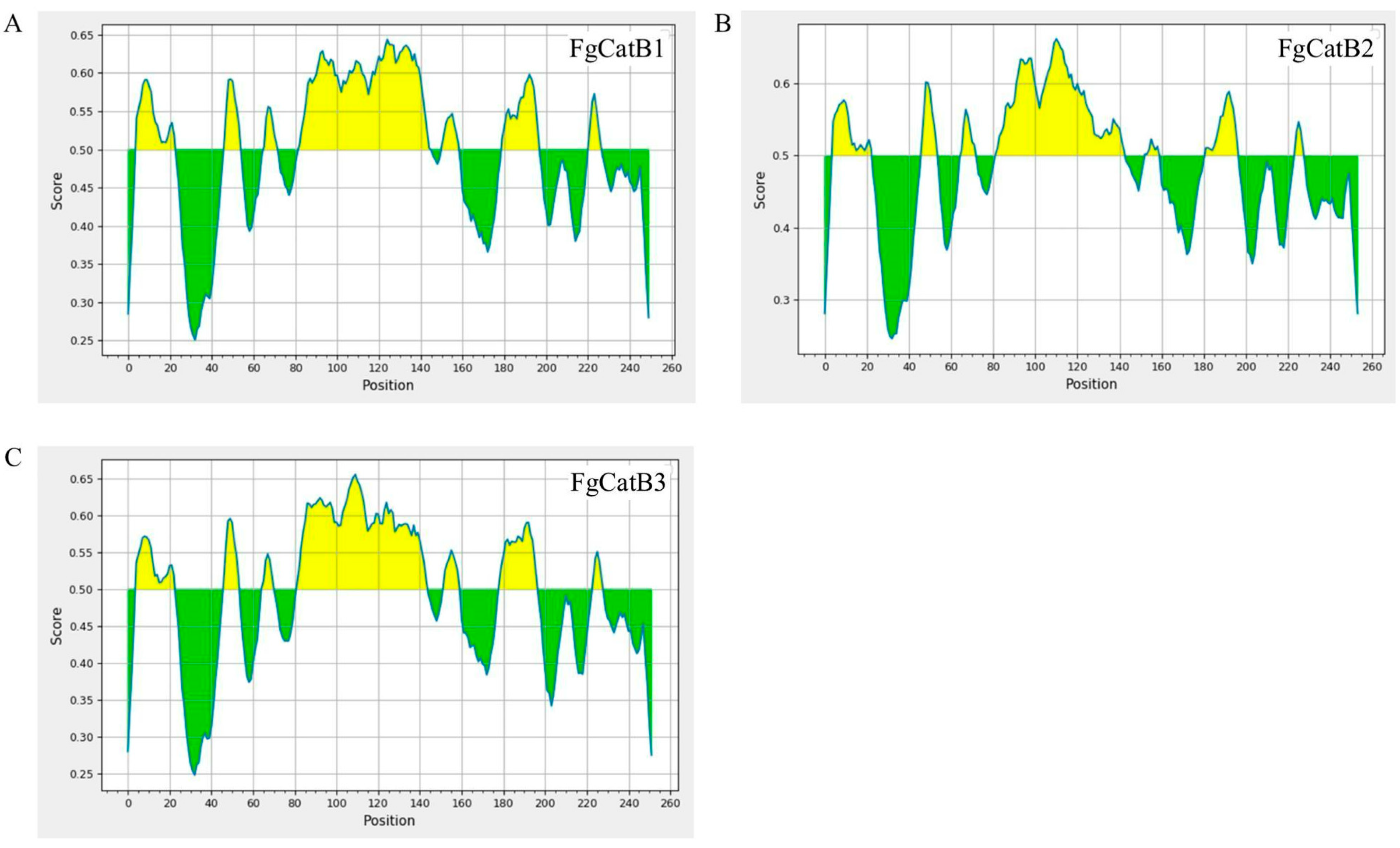
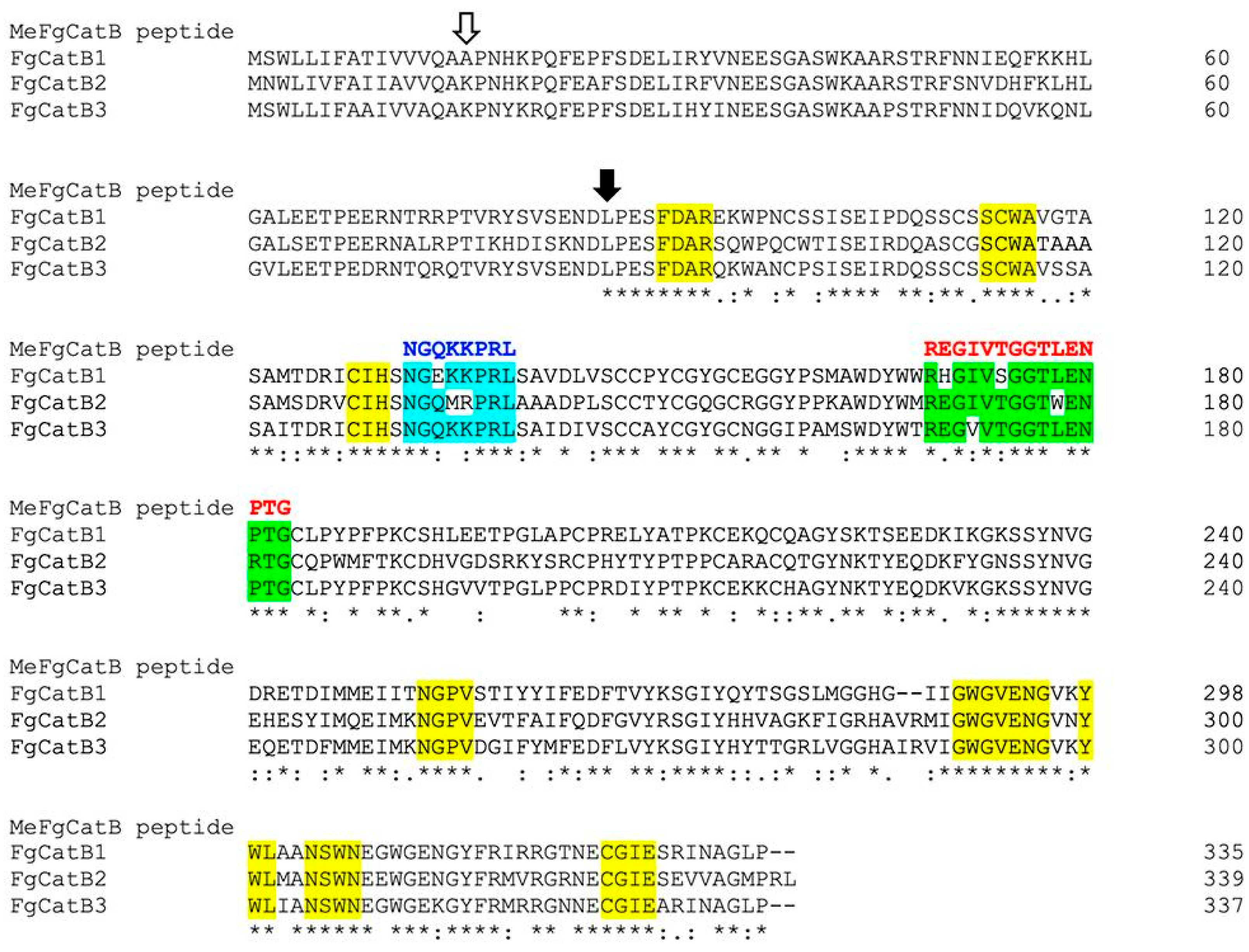
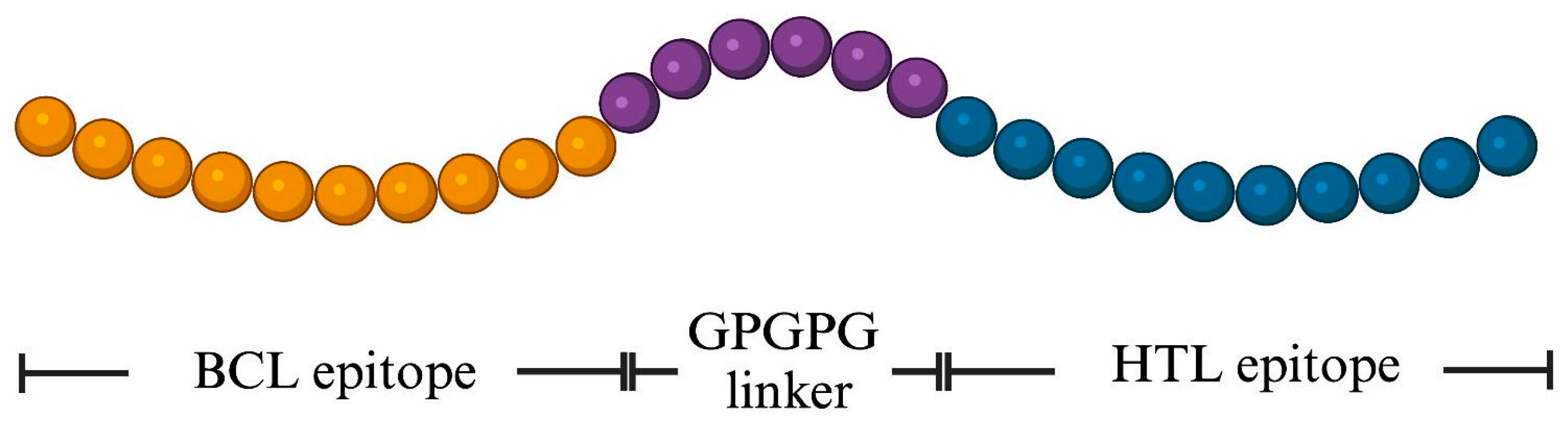
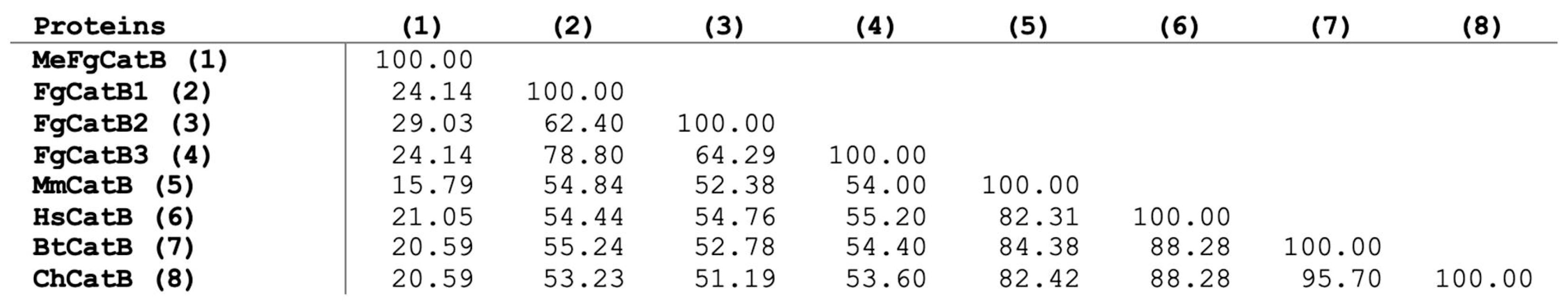


| Proteins | Accession ID | Antigenicity | Allergen | Solubility | MW (kDa) | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FgCatB1 | AAO73002 | 0.4738 | Yes | Good | 27.977 | −0.419 |
| FgCatB2 | AAO73003 | 0.5909 | No | Poor | 28.842 | −0.559 |
| FgCatB3 | AAO73004 | 0.4678 | No | Good | 27.625 | −0.465 |
| No. | Start | End | Peptide Sequences | Lengths (aa) | Antigenicity | Allergenicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FgCatB1 | ||||||
| 1 | 47 | 54 | NGEKKPRL | 8 | 0.9741 | No |
| 2 | 66 | 72 | CGYGCEG | 7 | 3.3484 | No |
| 3 | 221 | 227 | NEGWGEN | 7 | 1.4453 | No |
| FgCatB2 | ||||||
| 1 | 47 | 54 | NGQMRPRL | 8 | 1.7296 | No |
| 2 | 66 | 72 | CGQGCRG | 7 | 2.0161 | No |
| FgCatB3 | ||||||
| 1 | 47 | 54 | NGQKKPRL | 8 | 0.8798 | No |
| 2 | 82 | 144 | WTREGVVTGGTLENPTGCLPYPFPKCSHGVVTPGLPPCPRDIYPTPKCEKKCHAGYNKTYEQD | 63 | 0.7660 | No |
| No. | Allele | Start | End | Peptide Sequence | Antigenicity | Allergenicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FgCatB1 | ||||||
| 1 | H2-IAb | 80 | 94 | DYWWRHGIVSGGTLE | 1.2868 | No |
| 2 | H2-IAb | 82 | 96 | WWRHGIVSGGTLENP | 1.6390 | No |
| 3 | H2-IAb | 83 | 97 | WRHGIVSGGTLENPT | 1.4469 | No |
| 4 | H2-IAb | 84 | 98 | RHGIVSGGTLENPTG | 1.0879 | No |
| 5 | H2-IAb | 123 | 137 | LYATPKCEKQCQAGY | 0.9071 | No |
| 6 | H2-IAb | 184 | 198 | YKSGIYQYTSGSLMG | 0.5161 | No |
| 7 | H2-IAb | 187 | 201 | GIYQYTSGSLMGGHG | 0.6313 | No |
| FgCatB2 | ||||||
| 1 | H2-IAb | 28 | 42 | SCWATAAASAMSDRV | 0.7423 | No |
| 2 | H2-IAb | 84 | 98 | REGIVTGGTWENRTG | 1.6318 | No |
| 3 | H2-IAb | 116 | 130 | YSRCPHYTYPTPPCA | 0.7205 | No |
| 4 | H2-IAb | 117 | 131 | SRCPHYTYPTPPCAR | 0.9486 | No |
| 5 | H2-IAb | 118 | 132 | RCPHYTYPTPPCARA | 0.9528 | No |
| 6 | H2-IAb | 142 | 156 | EQDKFYGNSSYNVGE | 0.7000 | No |
| 7 | H2-IAb | 144 | 158 | DKFYGNSSYNVGEHE | 0.6180 | No |
| FgCatB3 | ||||||
| 1 | H2-IAb | 84 | 98 | REGVVTGGTLENPTG | 1.4574 | No |
| 2 | H2-IAb | 107 | 121 | CSHGVVTPGLPPCPR | 1.0781 | No |
| 3 | H2-IAb | 108 | 122 | SHGVVTPGLPPCPRD | 1.1865 | No |
| 4 | H2-IAb | 192 | 206 | TTGRLVGGHAIRVIG | 0.6327 | No |
| 5 | H2-IAb | 193 | 207 | TGRLVGGHAIRVIGW | 0.9272 | No |
| Group | Conserved Residues (aa) | Total Residue (aa) | Percentage of Conserved Residues |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCL epitope | |||
| B1 | 5 | 8 | 62.50 |
| HTL epitope | |||
| T1 | 11 | 15 | 73.33 |
| No. | Residues | Residue Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| Discontinuous epitopes | ||
| 1 | A:N25, A:P26, A: T27, A:G28 | 4 |
| 2 | A:N1, A:G2, A:Q3, A:K4 | 4 |
| Continuous epitopes | ||
| 1 | A:L23, A:E24, A:N25, A:P26, A:T27, A:G28 | 6 |
| 2 | A:N1, A:G2, A:Q3, A:K4, A:K5, A:P6, A:R7, A:L8 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chansap, S.; Cheukamud, W.; Suthisintong, T.; Kueakhai, P.; Changklungmoa, N. Design of a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Based on Fasciola gigantica Cathepsin B and Evaluation of Immunological Responses in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146971
Chansap S, Cheukamud W, Suthisintong T, Kueakhai P, Changklungmoa N. Design of a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Based on Fasciola gigantica Cathepsin B and Evaluation of Immunological Responses in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146971
Chicago/Turabian StyleChansap, Supanan, Werachon Cheukamud, Thitikul Suthisintong, Pornanan Kueakhai, and Narin Changklungmoa. 2025. "Design of a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Based on Fasciola gigantica Cathepsin B and Evaluation of Immunological Responses in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146971
APA StyleChansap, S., Cheukamud, W., Suthisintong, T., Kueakhai, P., & Changklungmoa, N. (2025). Design of a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Based on Fasciola gigantica Cathepsin B and Evaluation of Immunological Responses in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146971




